- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
HUMANITY DIVIDED Confronting inequality in Developing Countries презентация
Содержание
- 1. HUMANITY DIVIDED Confronting inequality in Developing Countries
- 2. 1 OUTLINE 1 Conceptual Framework 2 Inequality
- 3. TAKING THE DEBATE FORWARD
- 4. 1/21/2015 Footer Text ? INEQUALITY: WHAT HAS HAPPENED AND WHY
- 5. INCOME INEQUALITY CHANGES IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES Income
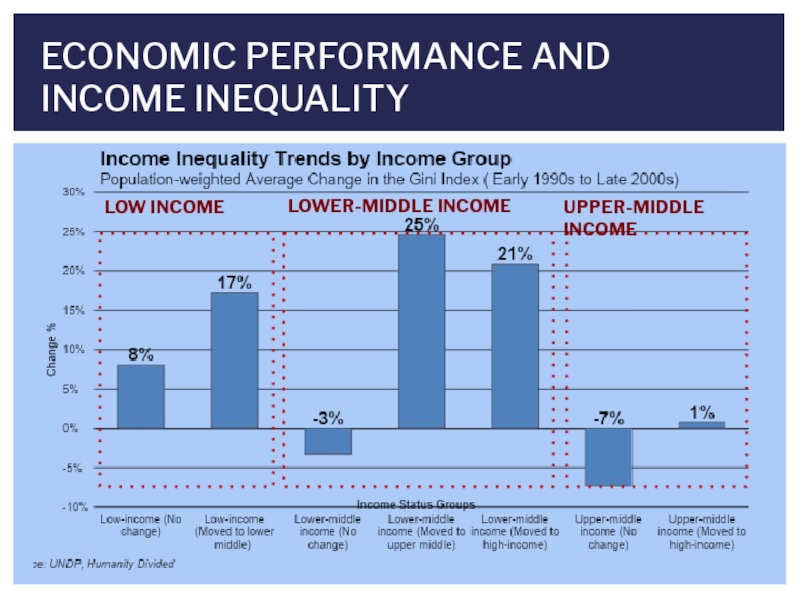
- 6. ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE AND INCOME INEQUALITY LOW INCOME LOWER-MIDDLE INCOME UPPER-MIDDLE INCOME
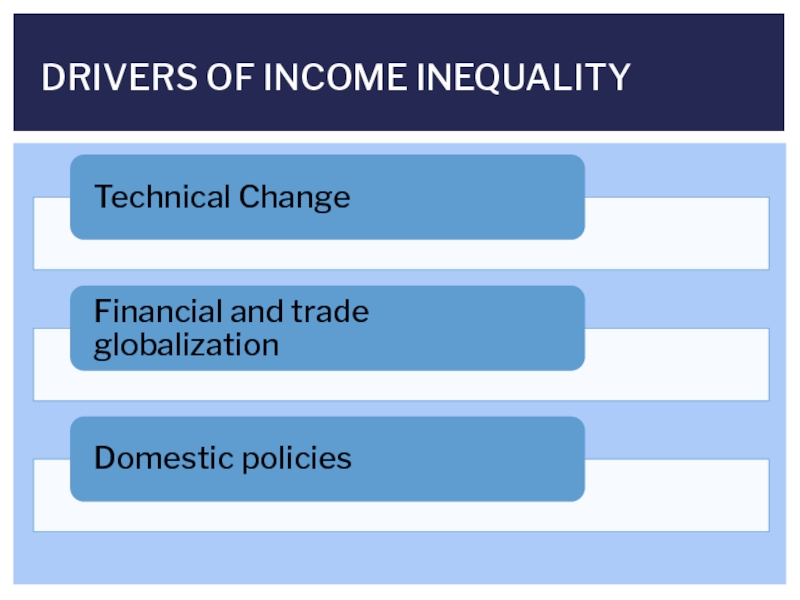
- 7. DRIVERS OF INCOME INEQUALITY
- 8. Not every country that had above
- 9. THE REDISTRIBUTIVE IMPACT OF FISCAL POLICY IN
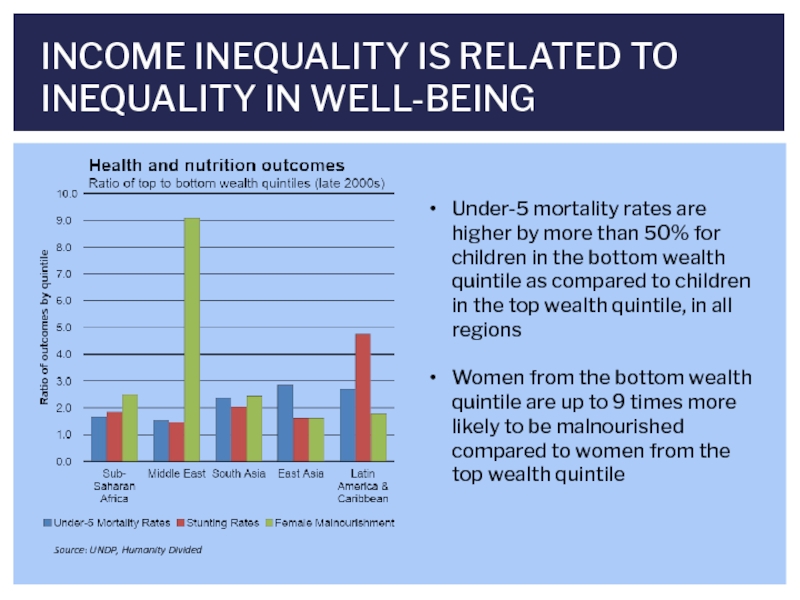
- 10. INCOME INEQUALITY IS RELATED TO INEQUALITY IN
- 11. Gender inequality has declined for some indicators.
- 12. Reasons to be concerned about trends.
- 13. 1/21/2015 Footer Text ? HOW TO ADDRESS INEQUALITY
- 14. A COMPREHENSIVE POLICY FRAMEWORK
- 15. You can download the report
Слайд 1
HUMANITY DIVIDED
Confronting inequality in Developing Countries
Almudena Fernandez, Bureau for Policy and
Dialogue on Inequality, Istanbul
21 January 2015
Слайд 21
OUTLINE
1
Conceptual Framework
2
Inequality in developing countries: what has happened and why
3
Policy framework
Слайд 5INCOME INEQUALITY CHANGES IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES
Income Inequality rose by 35% in
Meanwhile, it fell in both Sub-Saharan Africa by 7% and in the Latin America and Caribbean region by 5%.
Source: UNDP, Humanity Divided
Слайд 8
Not every country that had above average growth during this period
In the last 20 years, of 24 developing countries with above average growth (3% or more), 11 countries experienced an increase in inequality but 13 countries were able to maintain or lower inequality.
DO WE HAVE TO SACRIFICE FASTER GROWTH FOR GREATER EQUITY?
Слайд 9THE REDISTRIBUTIVE IMPACT OF FISCAL POLICY IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES
In the majority
The average redistributive impact of taxes and transfers was 11% in Upper-Middle Income countries, 4% in Lower-Middle and 3% in Low-Income countries.
Yet, country experiences vary widely. Even among low and lower middle income countries there are cases where taxes and transfer reduce inequality by more than 30%
Source: UNDP, Humanity Divided
Слайд 10INCOME INEQUALITY IS RELATED TO INEQUALITY IN WELL-BEING
Under-5 mortality rates are
Women from the bottom wealth quintile are up to 9 times more likely to be malnourished compared to women from the top wealth quintile
Source: UNDP, Humanity Divided
Слайд 11Gender inequality has declined for some indicators.
The F/M ratio of total
The global ratio of F/M employment rates rose from 62% in 1990 to 70% in 2010.
Exception:
Worsening job segregation in industrial sector.
Wage gaps remain large and widening in many countries.
1/21/2015
Footer Text
GENDER INEQUALITY
Слайд 12Reasons to be concerned about trends.
Employment equality substantially lags educational
Closing educational gaps not sufficient in order to achieve gender equality.
Gaps in political representation remain wide. Public policy does not reflect women’s life conditions and perspective in allocation of resources.
1/21/2015
Footer Text
GENDER INEQUALITY