- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Intro to Urban Geography презентация
Содержание
- 1. Intro to Urban Geography
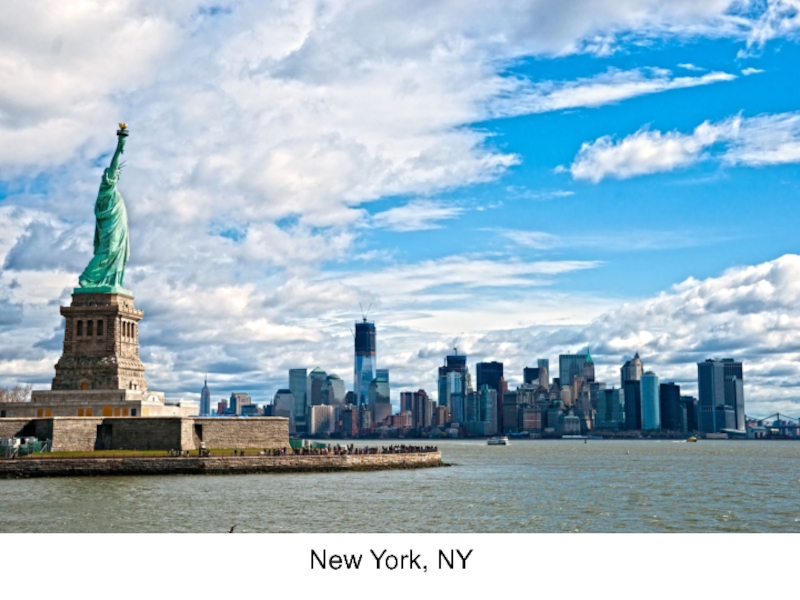
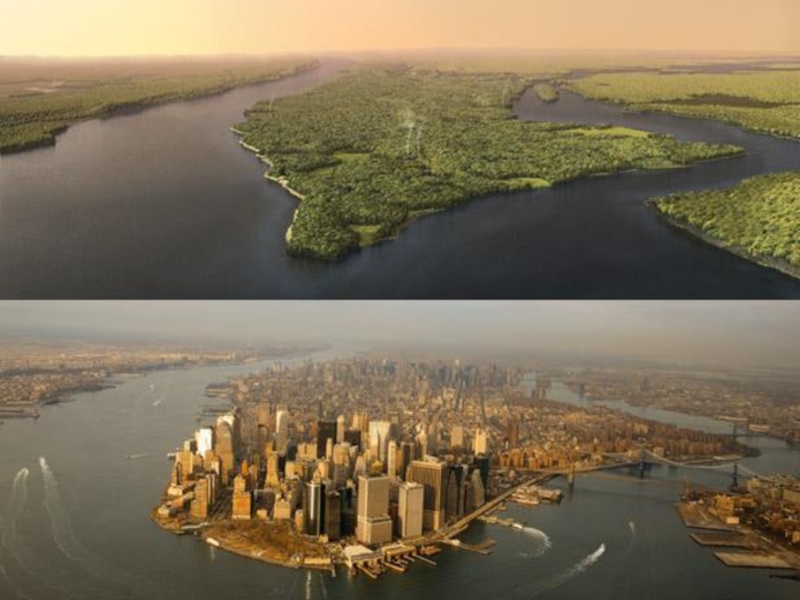
- 2. New York, NY
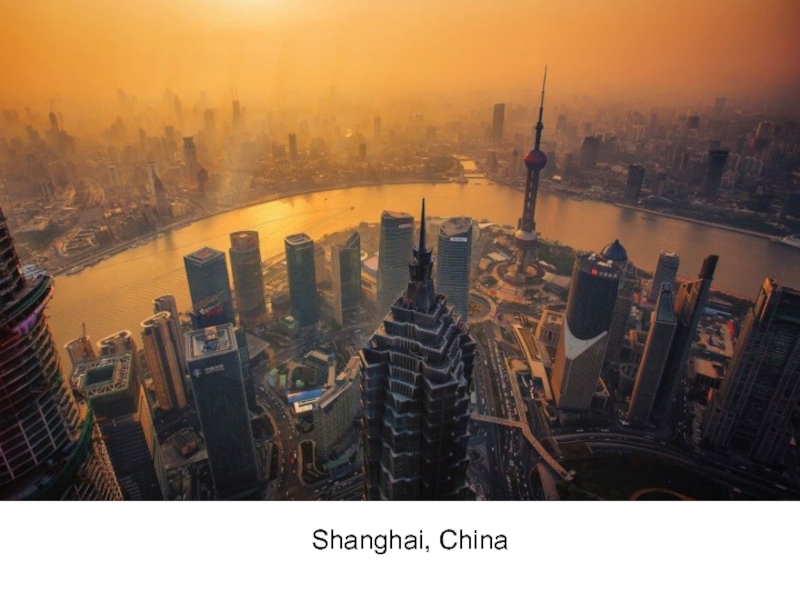
- 3. Shanghai, China
- 4. Hong Kong, SAR China
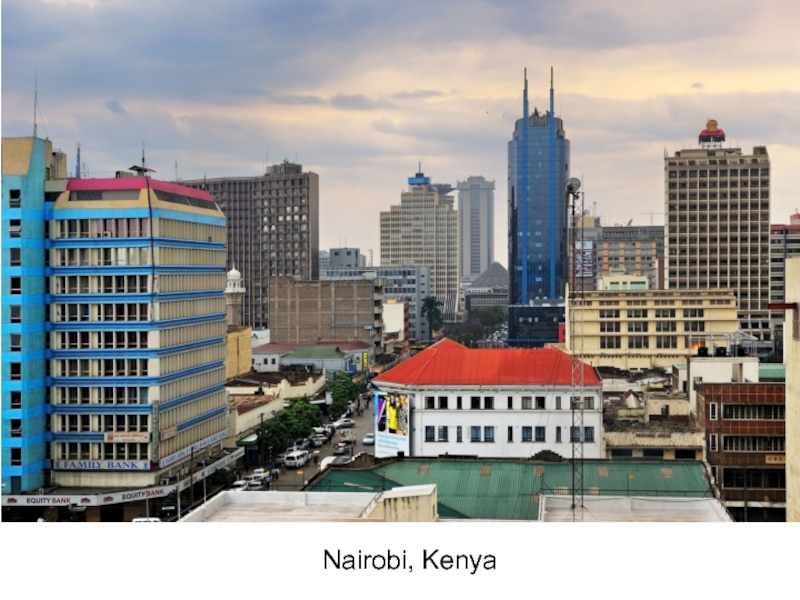
- 5. Nairobi, Kenya
- 6. Paris, France
- 7. Cairo, Egypt
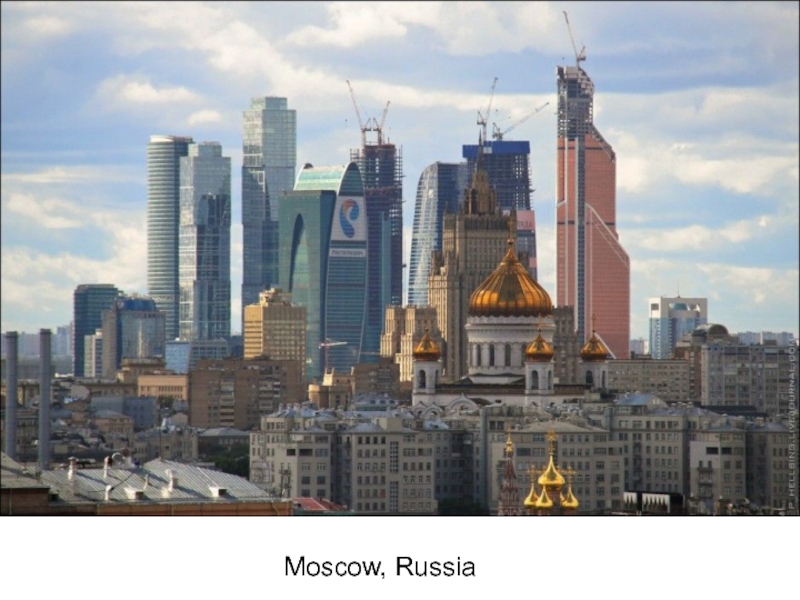
- 8. Moscow, Russia
- 9. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
- 10. What is Urbanization? The growth of a
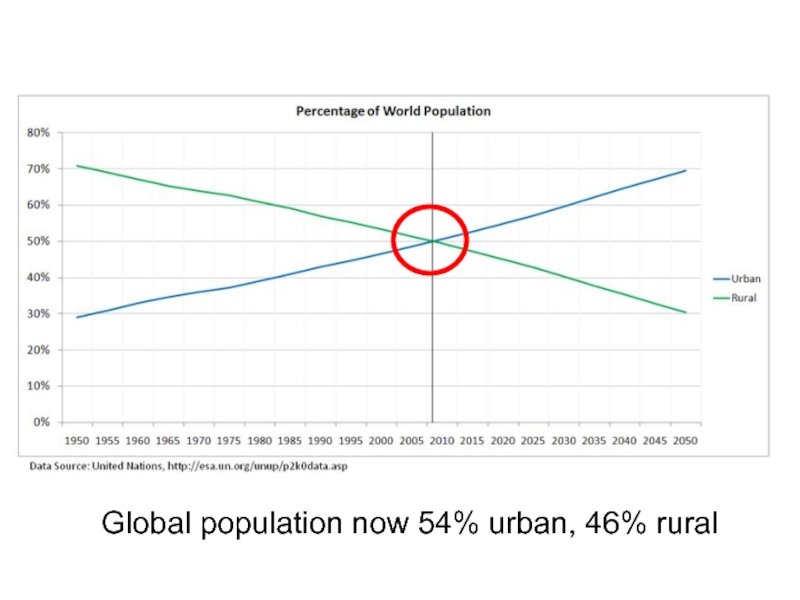
- 12. Global population now 54% urban, 46% rural
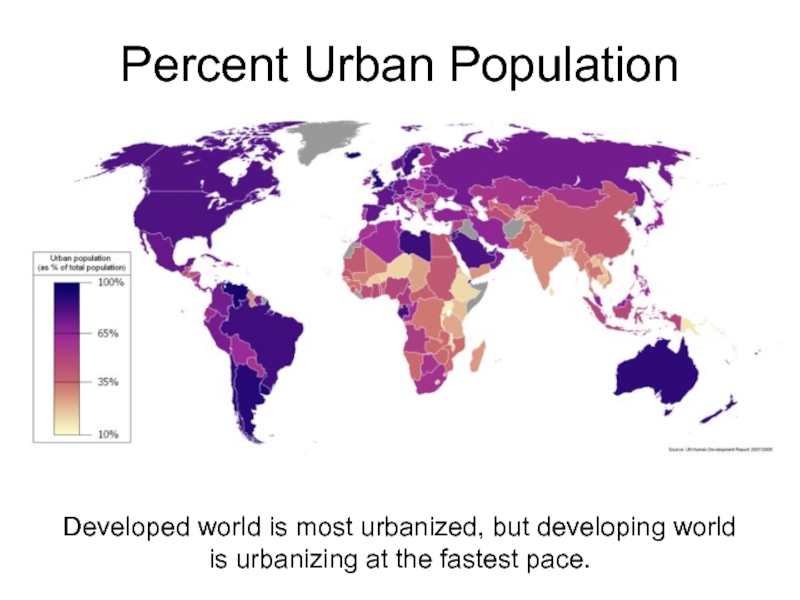
- 13. Percent Urban Population Developed world is most
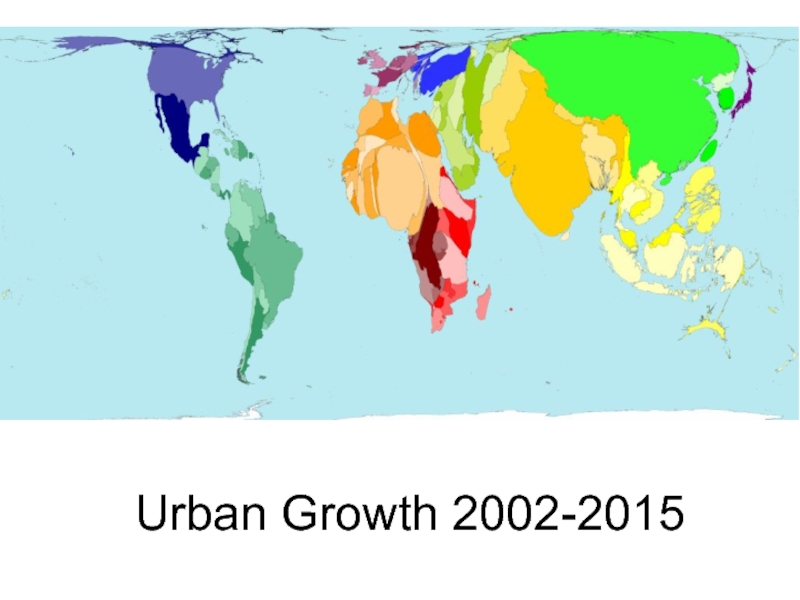
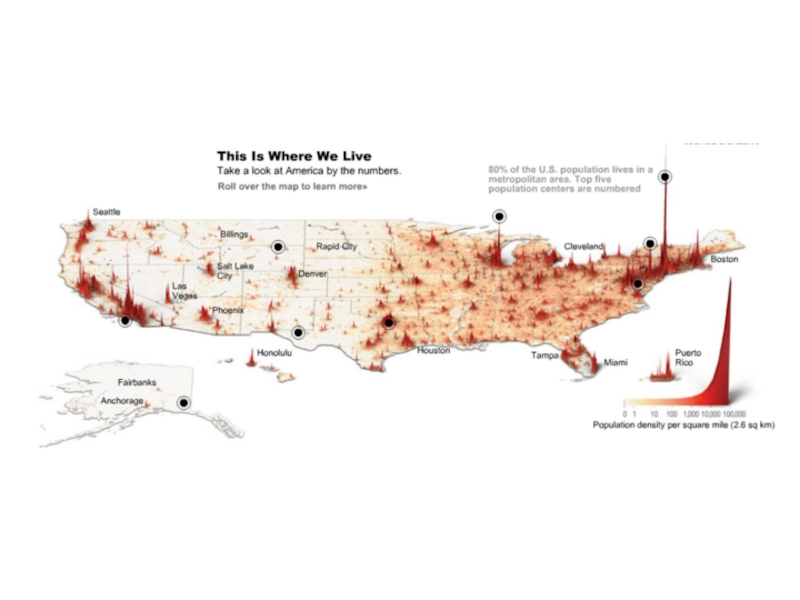
- 14. Urban Growth 2002-2015
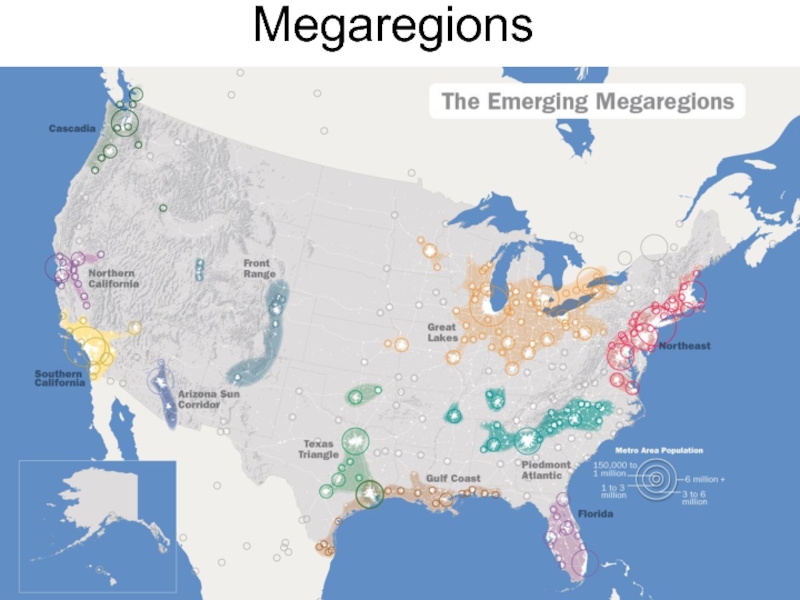
- 16. Megaregions
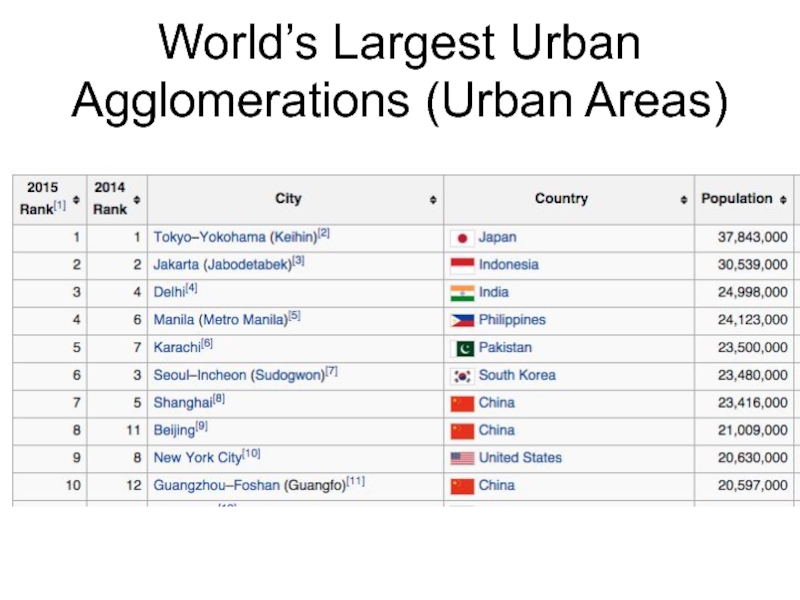
- 17. World’s Largest Urban Agglomerations (Urban Areas)
- 18. What Is A City? A node in
- 19. Terms Urban: town or city, high density
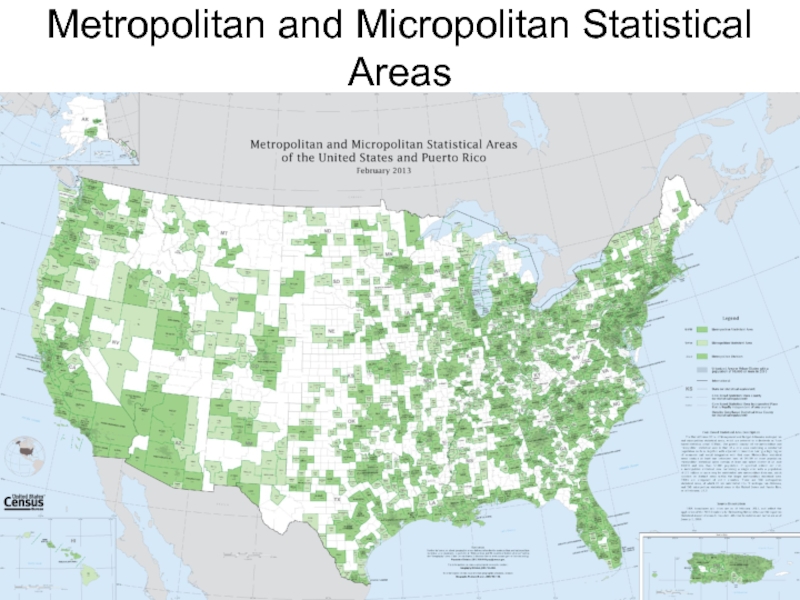
- 20. Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas
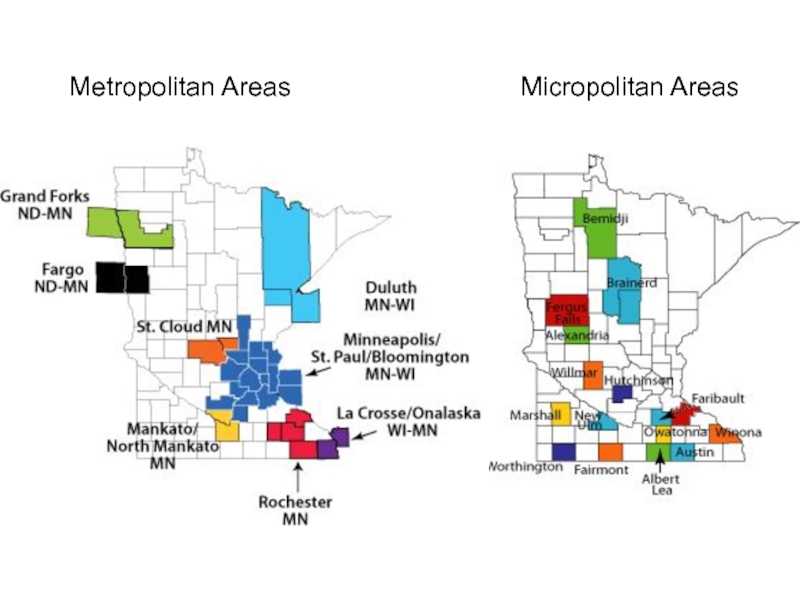
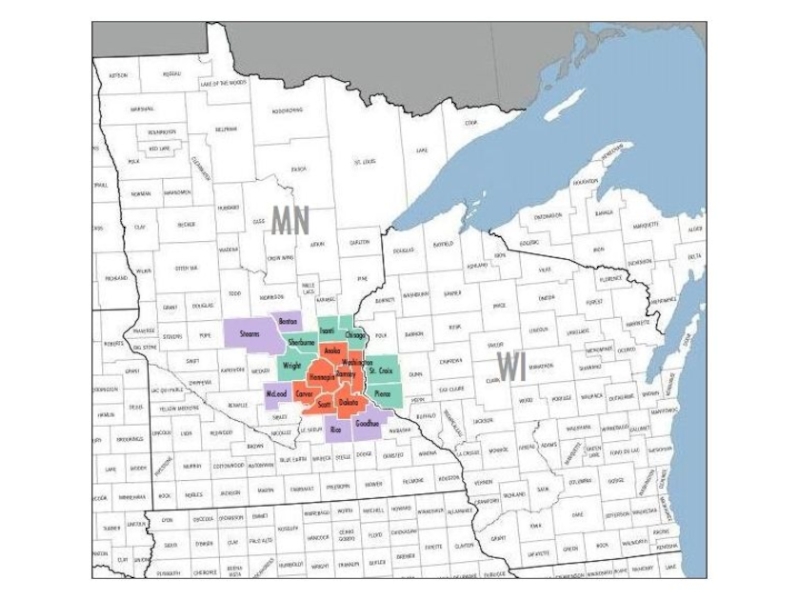
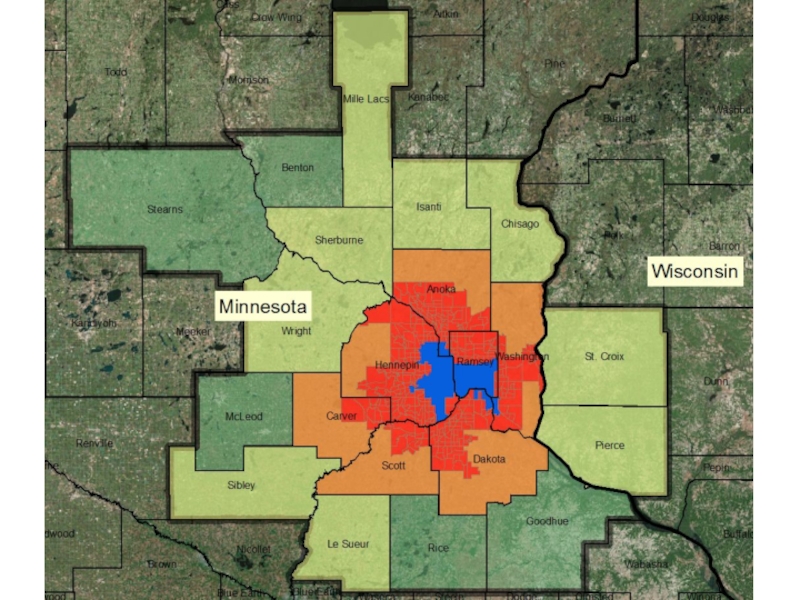
- 21. Metropolitan Areas Micropolitan Areas
- 27. 1st Urban Revolution Corresponds to 1st
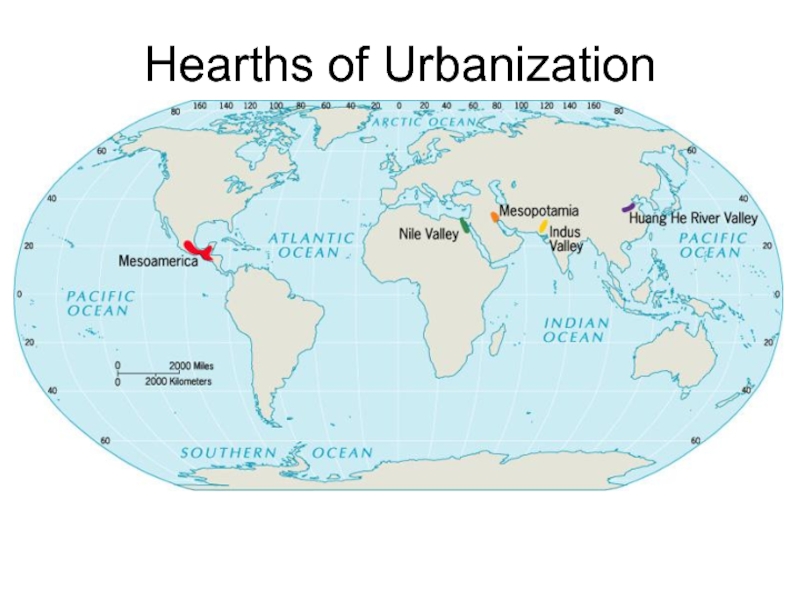
- 28. Hearths of Urbanization
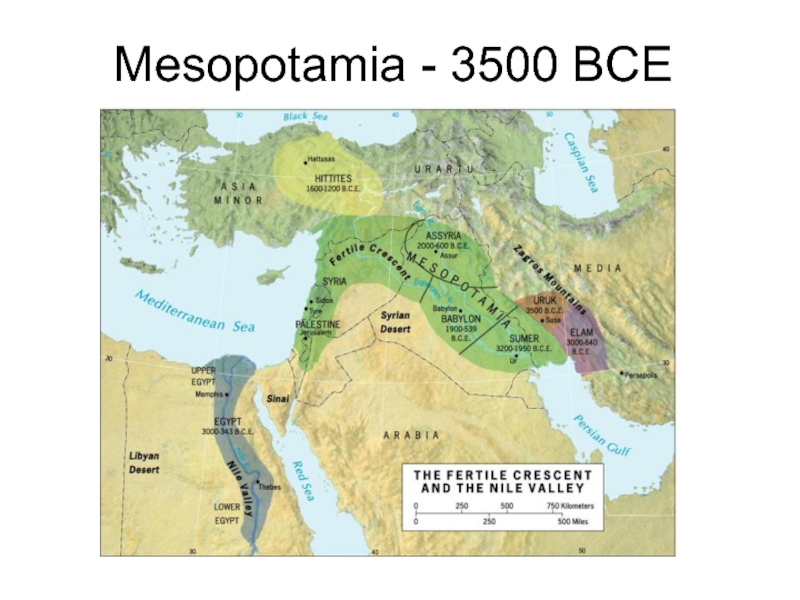
- 29. Mesopotamia - 3500 BCE
- 30. 2nd Urban Revolution Corresponds to Industrial
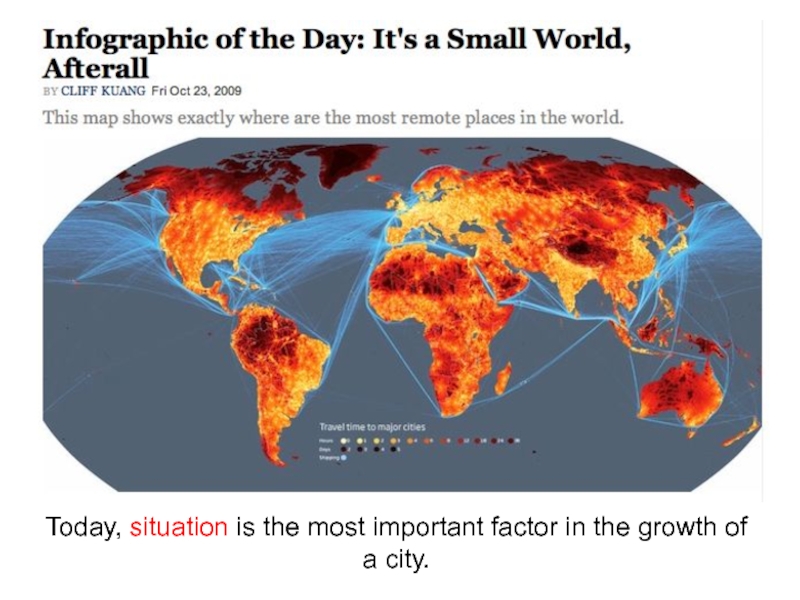
- 31. Site and Situation Affect Whether Or Not
- 33. Today, situation is the most important factor in the growth of a city.
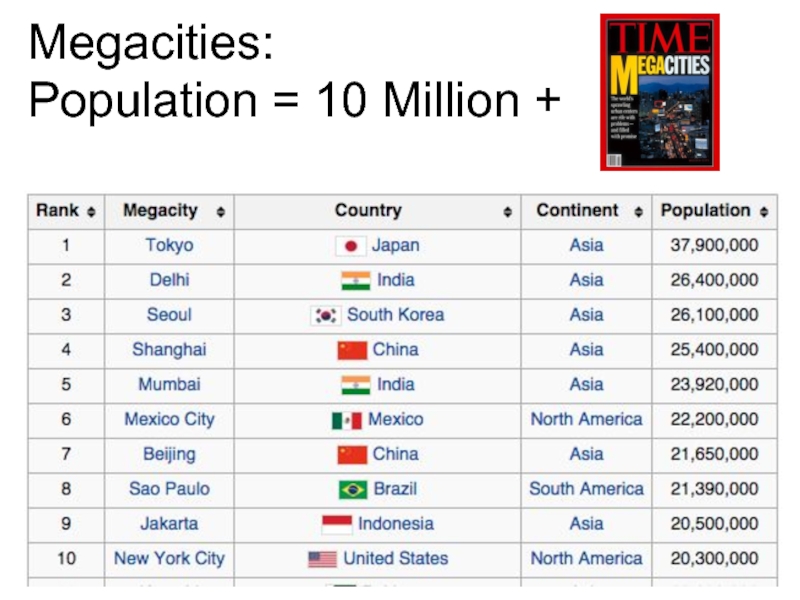
- 34. Megacities: Population = 10 Million +
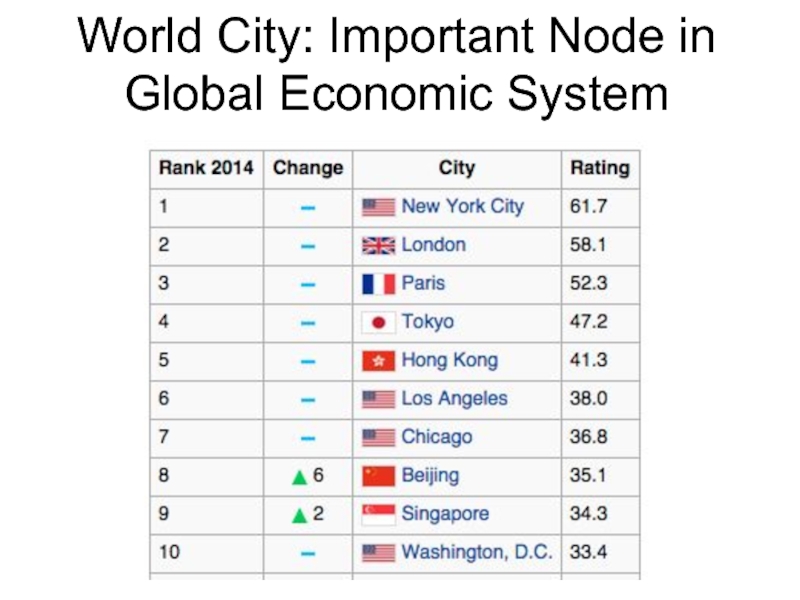
- 35. World City: Important Node in Global Economic System
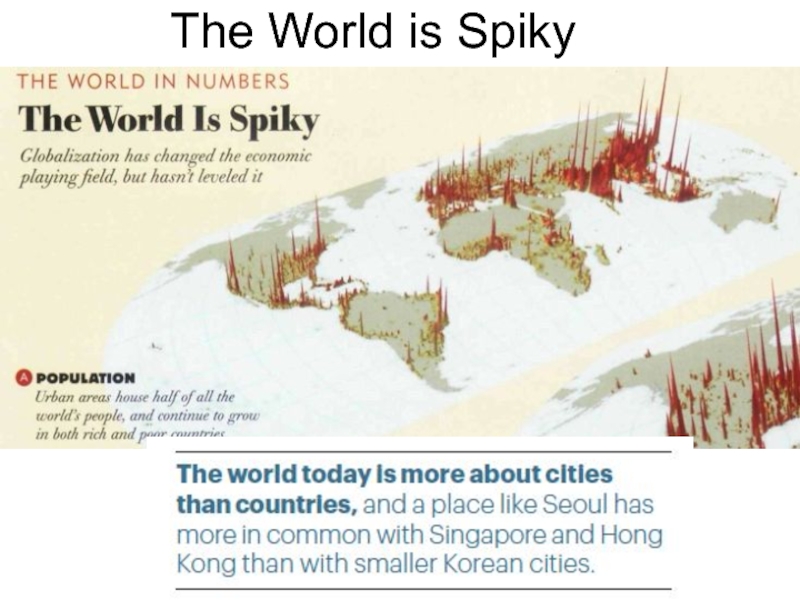
- 36. The World is Spiky
- 38. A leading city that is disproportionately larger
- 39. Rank-Size Rule Population of city is
- 40. Largest Cities in U.S. Does Rank-Size Rule Work?
Слайд 10What is Urbanization?
The growth of a central city and its suburbs
The
Слайд 13Percent Urban Population
Developed world is most urbanized, but developing world is
Слайд 18What Is A City?
A node in a circulation system of people,
There is no set size for a city - definitions vary from country to country and state to state.
Слайд 19Terms
Urban: town or city, high density of human-made structures
Micropolitan: urban area
Metropolitan: densely populated urban core & its surrounding areas sharing industry, infrastructure & housing
Exurban: prosperous communities beyond the suburbs that are commuter towns for an urban area
Слайд 271st Urban Revolution
Corresponds to 1st Ag Revolution
Dates?
Crops, domesticated animals
Food surpluses -
People no longer have to move in search of food
Rise of specialization & social classes
Populations grow - cities emerge
Слайд 302nd Urban Revolution
Corresponds to Industrial Revolution & 2nd Ag Revolution
Dates?
Mechanization -
Industrialization
Large scale movement of people to cities to work in factories
Слайд 31Site and Situation Affect Whether Or Not Cities Grow and Prosper
Situation:
Accessibility
Connectivity
Proximity to resources
Site: characteristics of the absolute location of a city
Landforms
Climate
Vegetation
Water supply
Soil quality
Minerals
Wildlife
Слайд 38A leading city that is disproportionately larger than the other cities
London, UK
Mexico City, Mexico
Paris, France
Primate City
Слайд 39Rank-Size Rule
Population of city is inversely proportional to its rank in
For example:
Largest city = Population 12 million
2nd largest = Population 6 million
3rd largest = Population 4 million
4th largest = Population 3 million
Does not work in regions with primate cities