- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
WORKSHOP 4MID-SURFACE EXTRACTION EXAMPLE презентация
Содержание
- 1. WORKSHOP 4MID-SURFACE EXTRACTION EXAMPLE
- 3. Problem Description Instead of meshing with solid
- 4. Suggested Exercise Steps Create a database midsurface.db,
- 5. Step 1. Create new database and import
- 6. Step 1. Create new database and import
- 7. Step 1. Create new database and import
- 8. Step 2. Create group for midsurfaces Create
- 9. Step 3. Create Midsurfaces from Parasolid Solid
- 10. Step 4. Post Midsurfaces Group only Post
- 11. Step 5. Edit Gussets Edit the Gussets
- 12. Step 6. Associate Gusset Edges to Midsurface
- 13. Step 6. Associate Gusset Edges to Midsurface
- 14. Step 7. Paver Mesh All Midsurface Surfaces
- 15. Step 8. Equivalence Nodes to Connect 2D
- 16. Step 8. Equivalence Nodes to Connect 2D
- 17. Step 9. Create Distributed Loads Create the
- 18. Step 9. Create Distributed Loads (Cont.) Continue
- 19. Step 9. Create Distributed Loads (Cont.) This
- 20. Step 10. Constrain the Base of the
- 21. Step 10. Constrain the Base of the
- 22. Step 11. Add Material and Element Properties
- 23. Step 11. Add Material and Element Properties
- 24. Step 12. Check Load Case Check the
- 25. Step 13. Run the analysis Run the
- 26. Step 14. Look at the Results Observe
- 27. Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
- 28. Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
- 29. Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
- 30. Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
- 31. Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
- 32. Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
Слайд 3Problem Description
Instead of meshing with solid elements the parasolid solid that
Слайд 4Suggested Exercise Steps
Create a database midsurface.db, and import a parasolid solid
Create a group that the midsurfaces will be placed in, midsurfaces. Use Group/Create.
Create midsurfaces for the junction box. They will be in group midsurfaces.
Post only the group with midsurfaces.
Edit the gussets created by the midsurface operation. This involves eliminating the long thin tops of the gussets.
Associate the edges of the gussets with the midsurfaces that represent the junction box.
Paver mesh the midsurfaces.
Equivalence the nodes to connect the 2D quad4 elements.
Apply distributed loads to midsurface surfaces.
Constrain select points of midsurface surfaces.
Create material and element properties.
Check the load case.
Submit the finite element model to MSC.Nastran for analysis.
Post process the results from MSC.Nastran
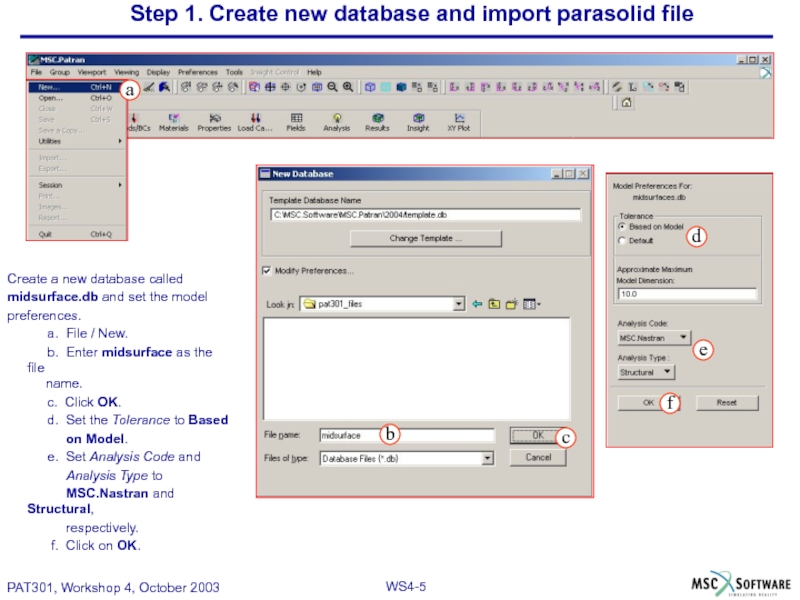
Слайд 5Step 1. Create new database and import parasolid file
Create a new
midsurface.db and set the model
preferences.
a. File / New.
b. Enter midsurface as the file name.
c. Click OK.
d. Set the Tolerance to Based
on Model.
e. Set Analysis Code and
Analysis Type to
MSC.Nastran and Structural,
respectively.
f. Click on OK.
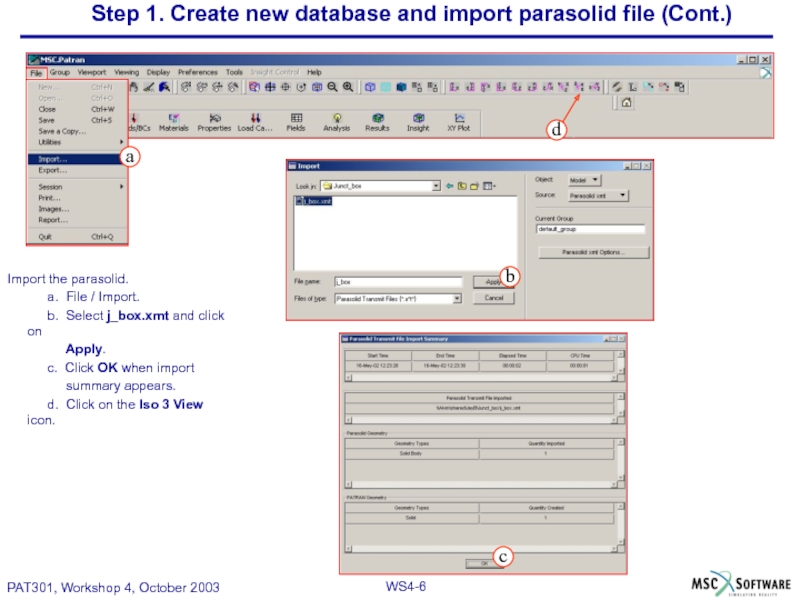
Слайд 6Step 1. Create new database and import parasolid file (Cont.)
Import the
a. File / Import.
b. Select j_box.xmt and click on
Apply.
c. Click OK when import
summary appears.
d. Click on the Iso 3 View icon.
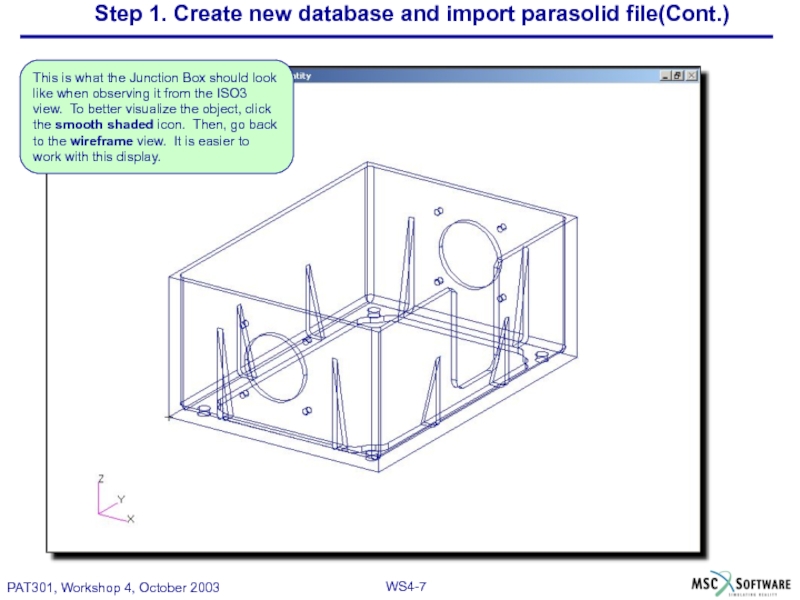
Слайд 7Step 1. Create new database and import parasolid file(Cont.)
This is what
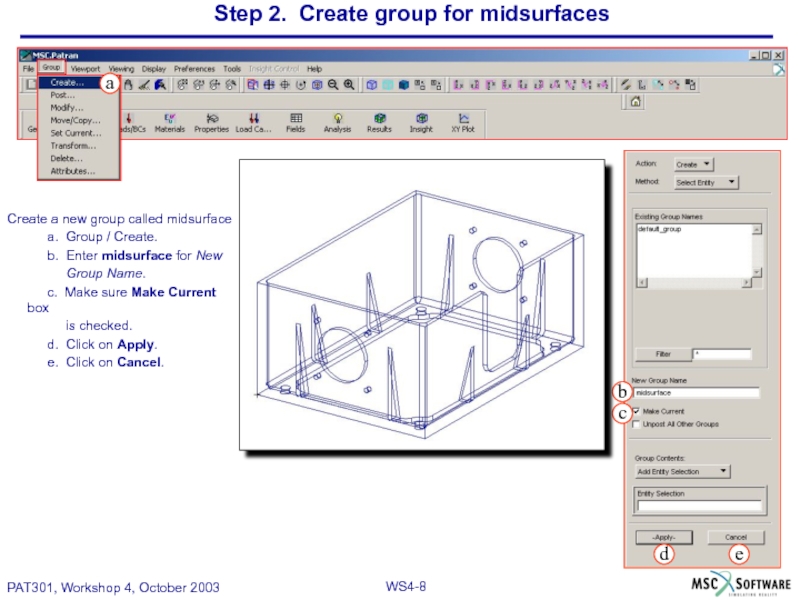
Слайд 8Step 2. Create group for midsurfaces
Create a new group called midsurface
a.
b. Enter midsurface for New
Group Name.
c. Make sure Make Current box
is checked.
d. Click on Apply.
e. Click on Cancel.
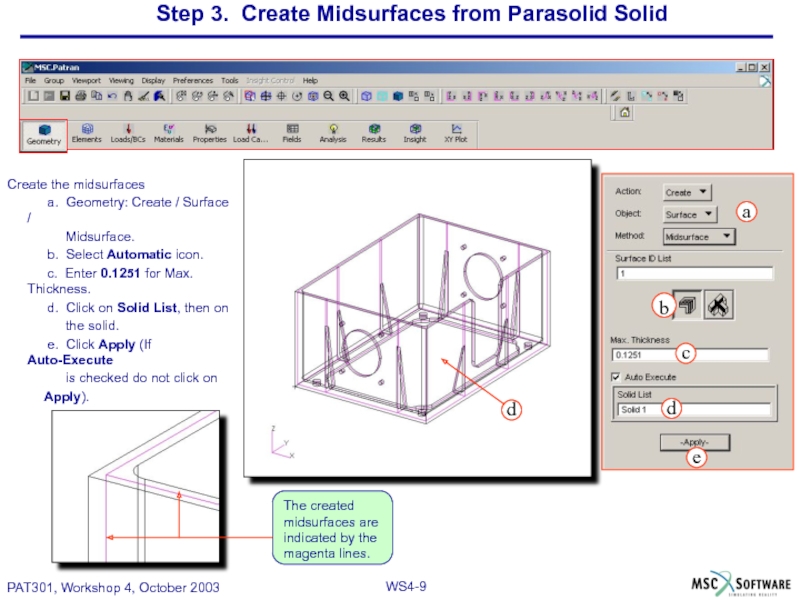
Слайд 9Step 3. Create Midsurfaces from Parasolid Solid
Create the midsurfaces
a. Geometry: Create
Midsurface.
b. Select Automatic icon.
c. Enter 0.1251 for Max. Thickness.
d. Click on Solid List, then on
the solid.
e. Click Apply (If Auto-Execute
is checked do not click on
Apply).
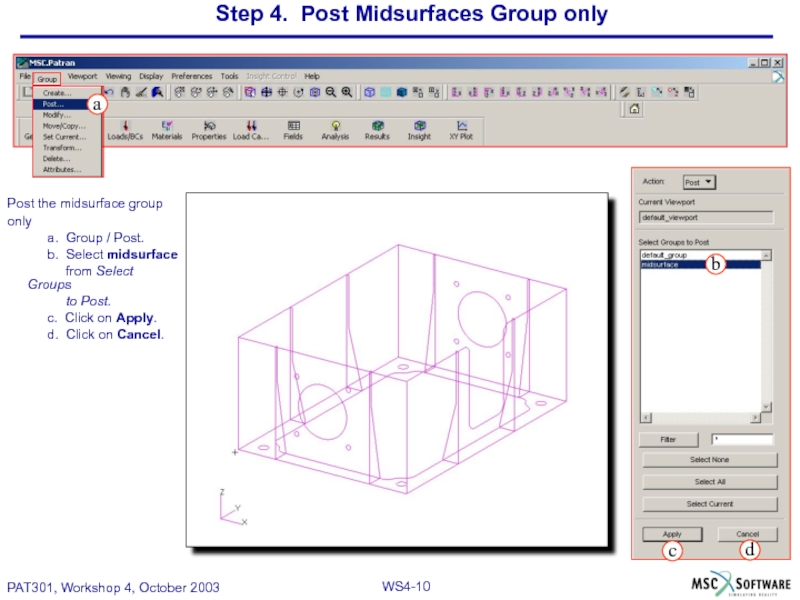
Слайд 10Step 4. Post Midsurfaces Group only
Post the midsurface group
only
a. Group
b. Select midsurface
from Select Groups
to Post.
c. Click on Apply.
d. Click on Cancel.
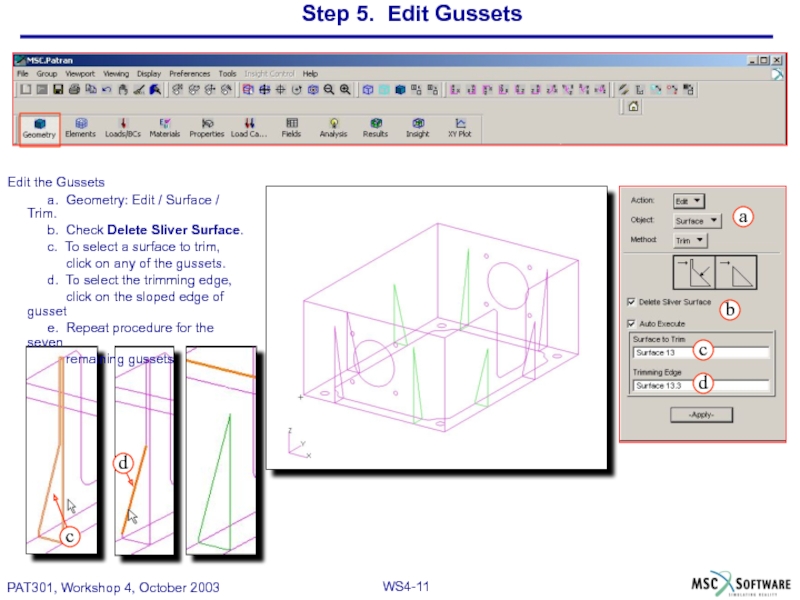
Слайд 11Step 5. Edit Gussets
Edit the Gussets
a. Geometry: Edit / Surface /
b. Check Delete Sliver Surface.
c. To select a surface to trim,
click on any of the gussets.
d. To select the trimming edge,
click on the sloped edge of gusset
e. Repeat procedure for the seven
remaining gussets
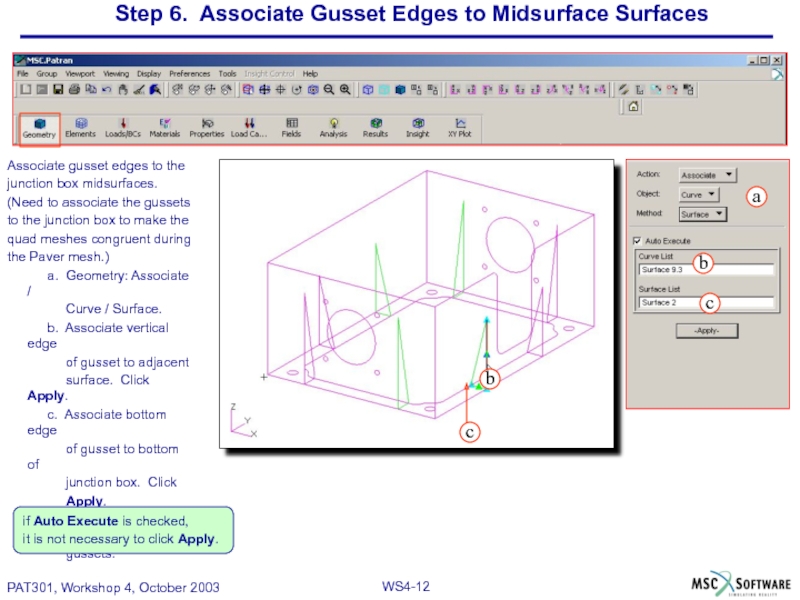
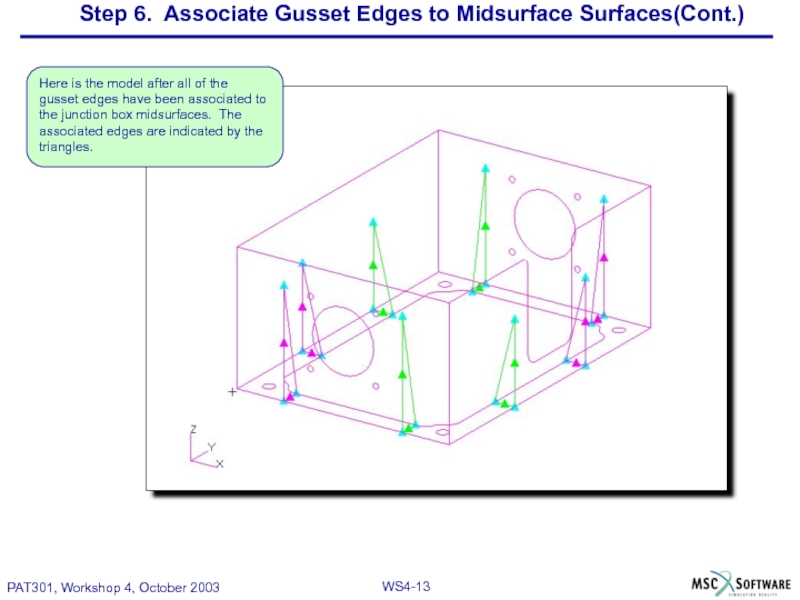
Слайд 12Step 6. Associate Gusset Edges to Midsurface Surfaces
Associate gusset edges to
junction box midsurfaces.
(Need to associate the gussets
to the junction box to make the
quad meshes congruent during
the Paver mesh.)
a. Geometry: Associate /
Curve / Surface.
b. Associate vertical edge
of gusset to adjacent
surface. Click Apply.
c. Associate bottom edge
of gusset to bottom of
junction box. Click
Apply.
d. Repeat for all remaining
gussets.
if Auto Execute is checked,
it is not necessary to click Apply.
Слайд 13Step 6. Associate Gusset Edges to Midsurface Surfaces(Cont.)
Here is the model
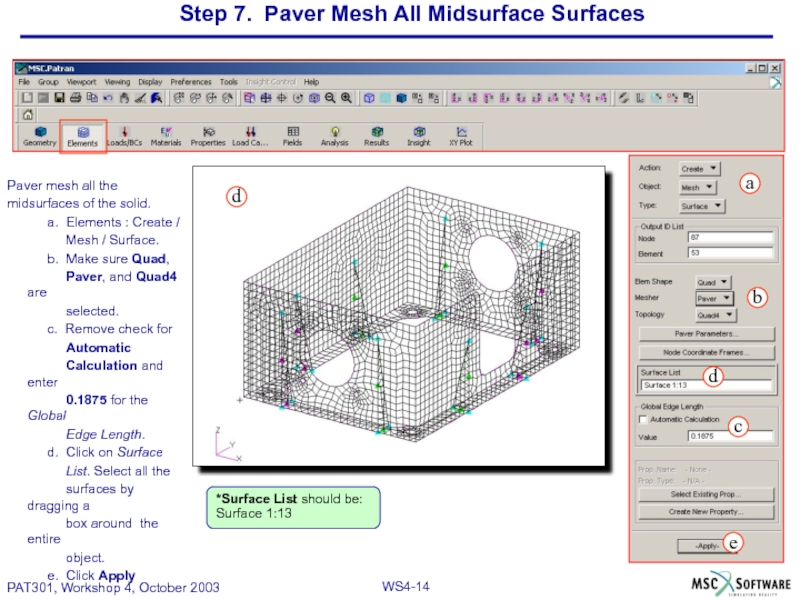
Слайд 14Step 7. Paver Mesh All Midsurface Surfaces
Paver mesh all the
midsurfaces
a. Elements : Create /
Mesh / Surface.
b. Make sure Quad,
Paver, and Quad4 are
selected.
c. Remove check for
Automatic
Calculation and enter
0.1875 for the Global
Edge Length.
d. Click on Surface
List. Select all the
surfaces by dragging a
box around the entire
object.
e. Click Apply
*Surface List should be: Surface 1:13
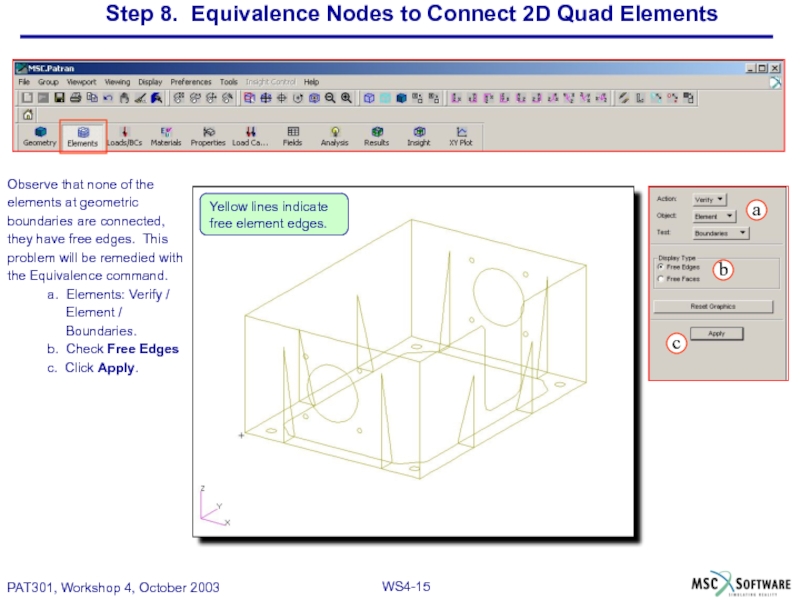
Слайд 15Step 8. Equivalence Nodes to Connect 2D Quad Elements
Observe that none
elements at geometric
boundaries are connected,
they have free edges. This
problem will be remedied with
the Equivalence command.
a. Elements: Verify /
Element /
Boundaries.
b. Check Free Edges
c. Click Apply.
Yellow lines indicate free element edges.
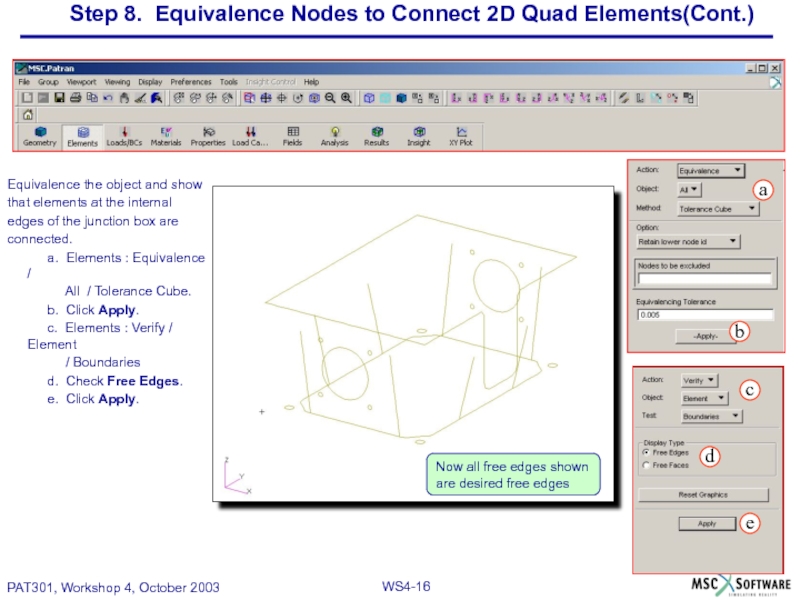
Слайд 16Step 8. Equivalence Nodes to Connect 2D Quad Elements(Cont.)
Equivalence the object
that elements at the internal
edges of the junction box are
connected.
a. Elements : Equivalence /
All / Tolerance Cube.
b. Click Apply.
c. Elements : Verify / Element
/ Boundaries
d. Check Free Edges.
e. Click Apply.
Now all free edges shown are desired free edges
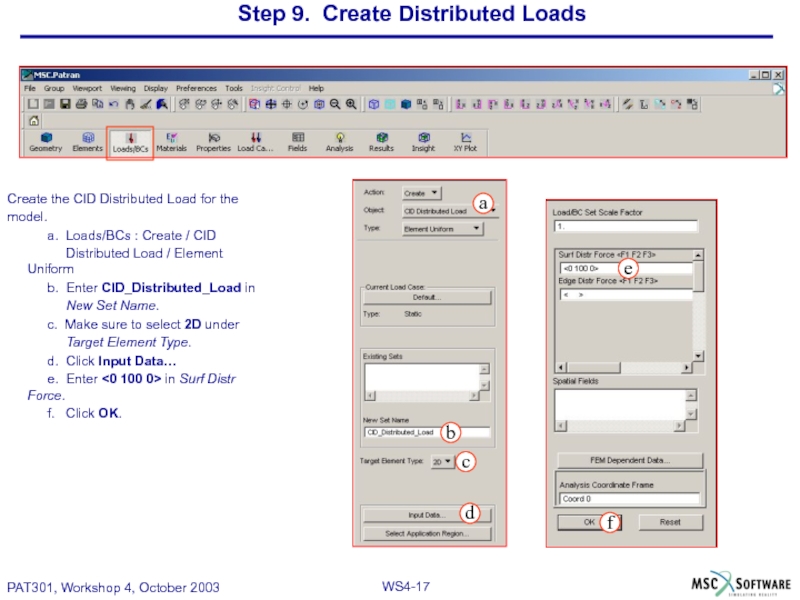
Слайд 17Step 9. Create Distributed Loads
Create the CID Distributed Load for the
model.
a. Loads/BCs : Create / CID
Distributed Load / Element Uniform
b. Enter CID_Distributed_Load in
New Set Name.
c. Make sure to select 2D under
Target Element Type.
d. Click Input Data…
e. Enter <0 100 0> in Surf Distr Force.
f. Click OK.
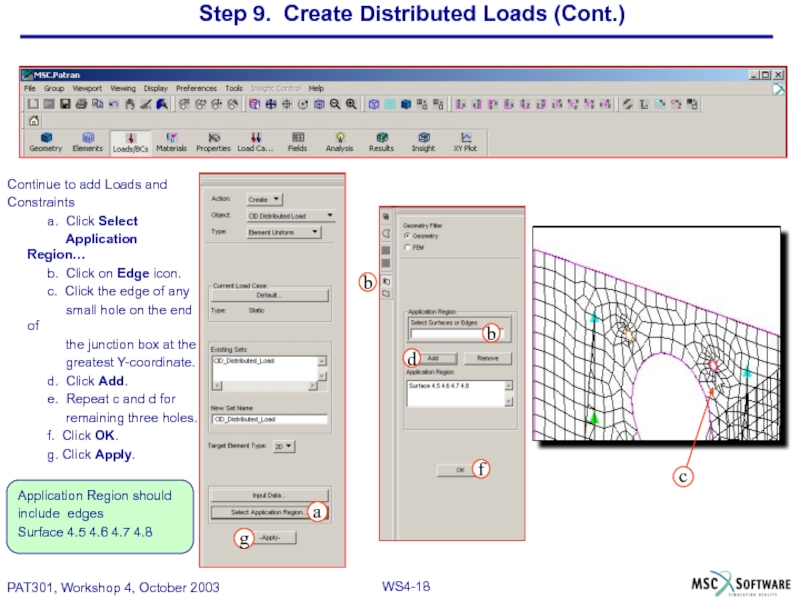
Слайд 18Step 9. Create Distributed Loads (Cont.)
Continue to add Loads and
Constraints
a.
Application Region…
b. Click on Edge icon.
c. Click the edge of any
small hole on the end of
the junction box at the
greatest Y-coordinate.
d. Click Add.
e. Repeat c and d for
remaining three holes.
f. Click OK.
g. Click Apply.
Application Region should
include edges
Surface 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8
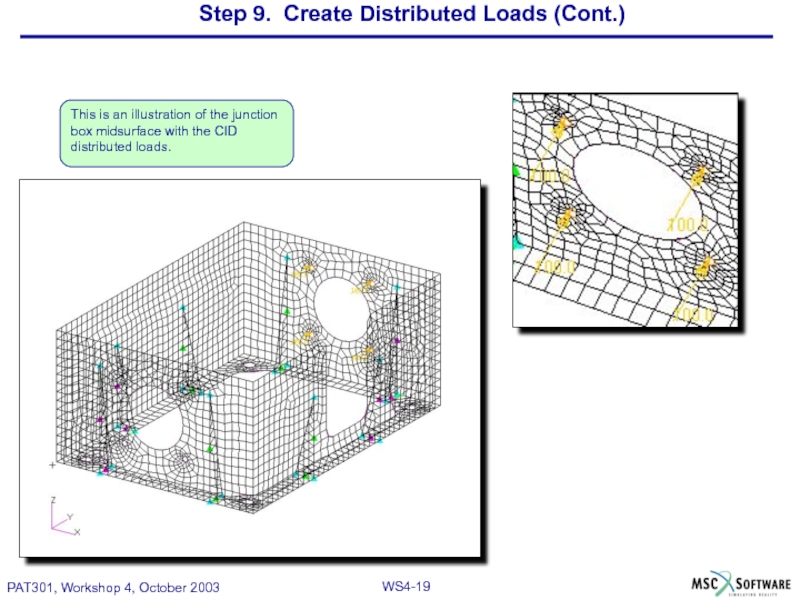
Слайд 19Step 9. Create Distributed Loads (Cont.)
This is an illustration of the
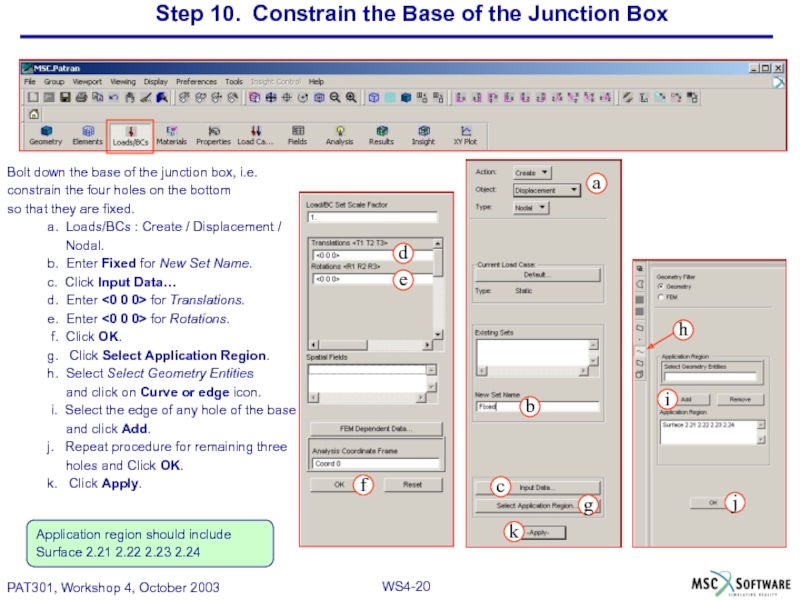
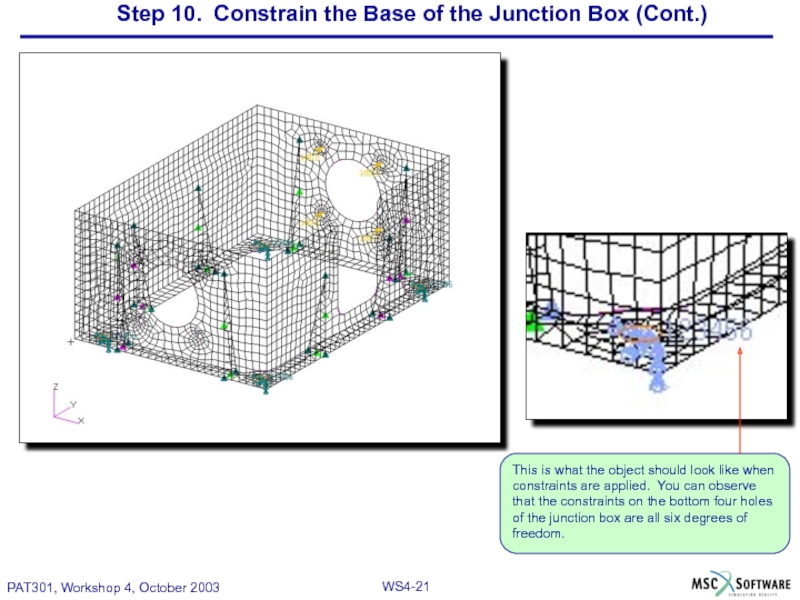
Слайд 20Step 10. Constrain the Base of the Junction Box
Bolt down the
constrain the four holes on the bottom
so that they are fixed.
a. Loads/BCs : Create / Displacement /
Nodal.
b. Enter Fixed for New Set Name.
c. Click Input Data…
d. Enter <0 0 0> for Translations.
e. Enter <0 0 0> for Rotations.
f. Click OK.
g. Click Select Application Region.
h. Select Select Geometry Entities
and click on Curve or edge icon.
i. Select the edge of any hole of the base
and click Add.
j. Repeat procedure for remaining three
holes and Click OK.
k. Click Apply.
Application region should include
Surface 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24
Слайд 21Step 10. Constrain the Base of the Junction Box (Cont.)
This is
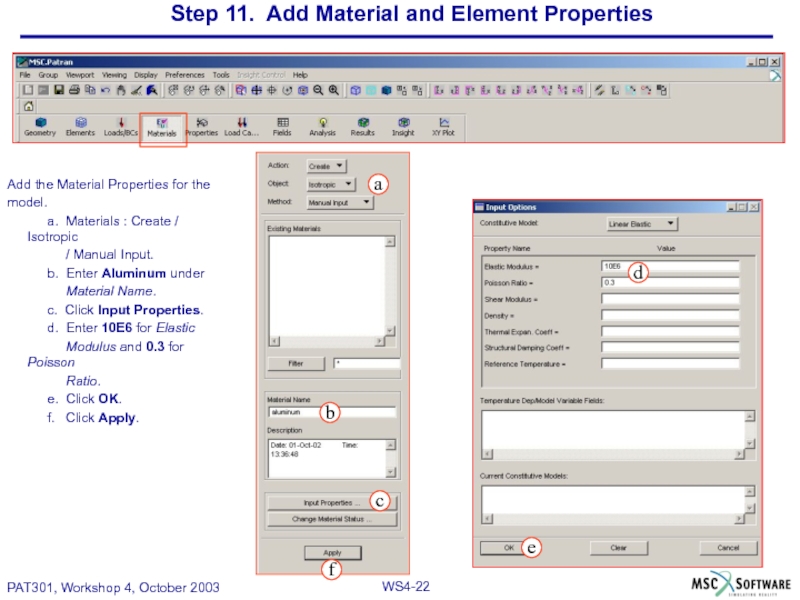
Слайд 22Step 11. Add Material and Element Properties
Add the Material Properties for
model.
a. Materials : Create / Isotropic
/ Manual Input.
b. Enter Aluminum under
Material Name.
c. Click Input Properties.
d. Enter 10E6 for Elastic
Modulus and 0.3 for Poisson
Ratio.
e. Click OK.
f. Click Apply.
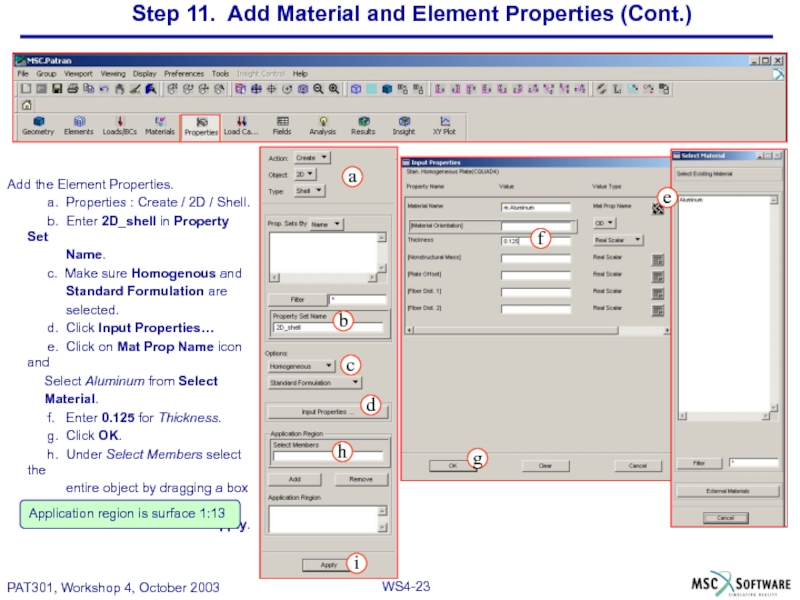
Слайд 23Step 11. Add Material and Element Properties (Cont.)
Add the Element Properties.
a.
b. Enter 2D_shell in Property Set
Name.
c. Make sure Homogenous and
Standard Formulation are
selected.
d. Click Input Properties…
e. Click on Mat Prop Name icon and
Select Aluminum from Select
Material.
f. Enter 0.125 for Thickness.
g. Click OK.
h. Under Select Members select the
entire object by dragging a box
around the junction box.
I. Click Add and then click Apply.
Application region is surface 1:13
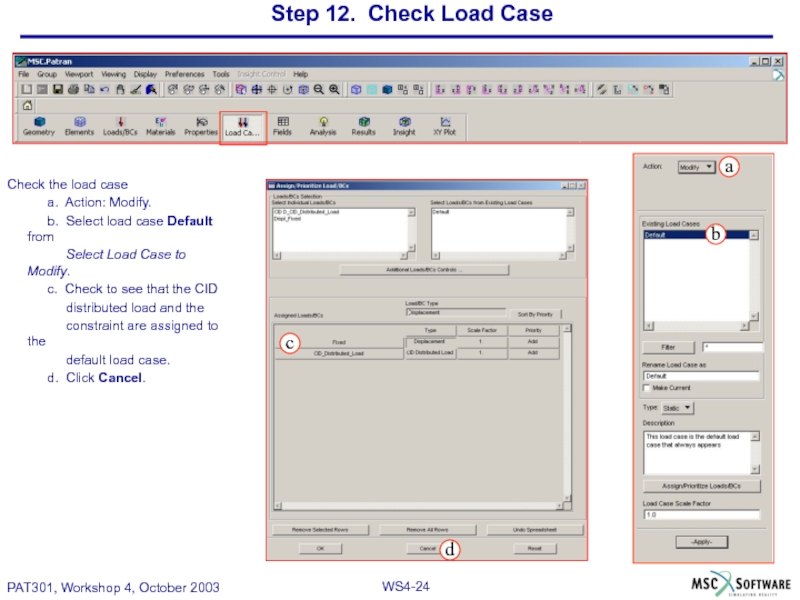
Слайд 24Step 12. Check Load Case
Check the load case
a. Action: Modify.
b. Select
Select Load Case to Modify.
c. Check to see that the CID
distributed load and the
constraint are assigned to the
default load case.
d. Click Cancel.
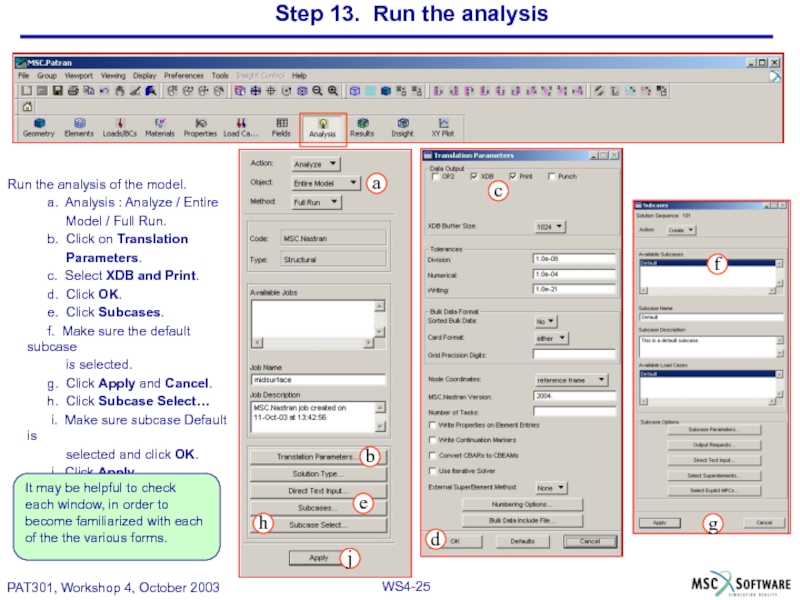
Слайд 25Step 13. Run the analysis
Run the analysis of the model.
a. Analysis
Model / Full Run.
b. Click on Translation
Parameters.
c. Select XDB and Print.
d. Click OK.
e. Click Subcases.
f. Make sure the default subcase
is selected.
g. Click Apply and Cancel.
h. Click Subcase Select…
i. Make sure subcase Default is
selected and click OK.
j. Click Apply.
It may be helpful to check
each window, in order to
become familiarized with each
of the the various forms.
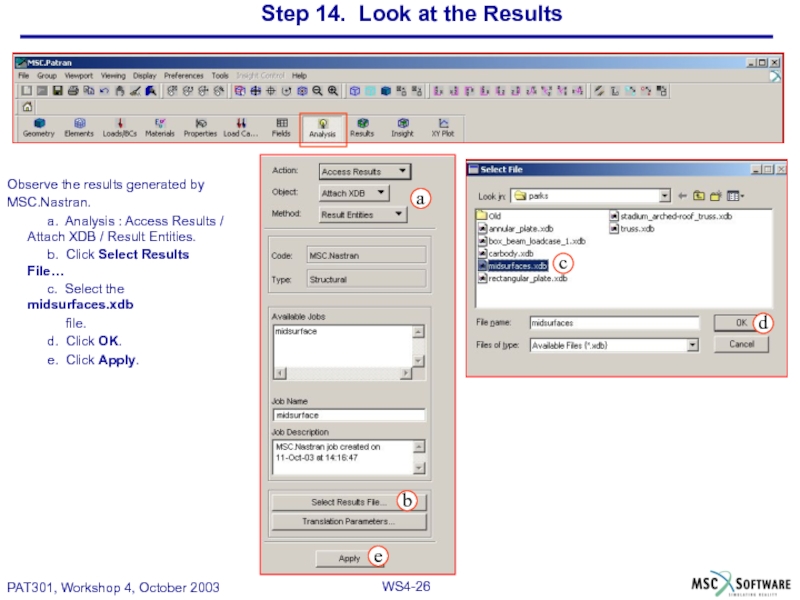
Слайд 26Step 14. Look at the Results
Observe the results generated by
MSC.Nastran.
a. Analysis
b. Click Select Results File…
c. Select the midsurfaces.xdb
file.
d. Click OK.
e. Click Apply.
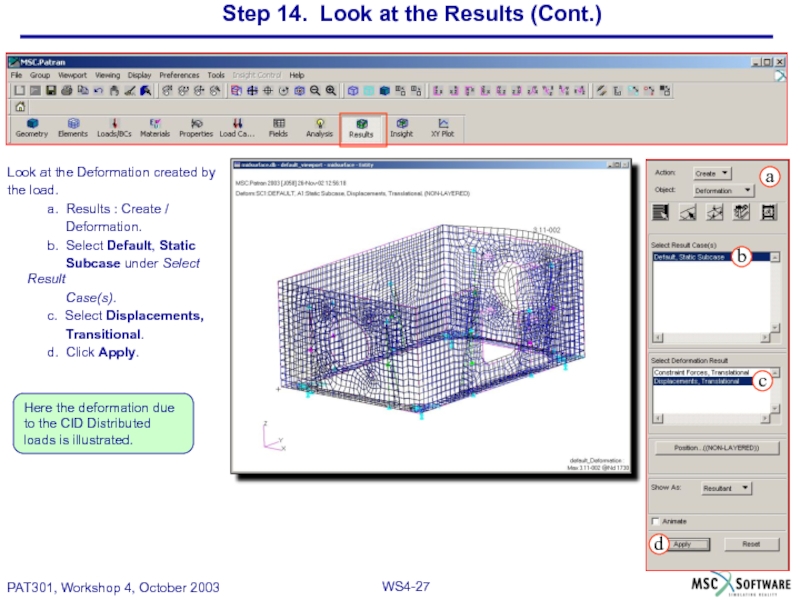
Слайд 27Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
Look at the Deformation created
the load.
a. Results : Create /
Deformation.
b. Select Default, Static
Subcase under Select Result
Case(s).
c. Select Displacements,
Transitional.
d. Click Apply.
Here the deformation due to the CID Distributed loads is illustrated.
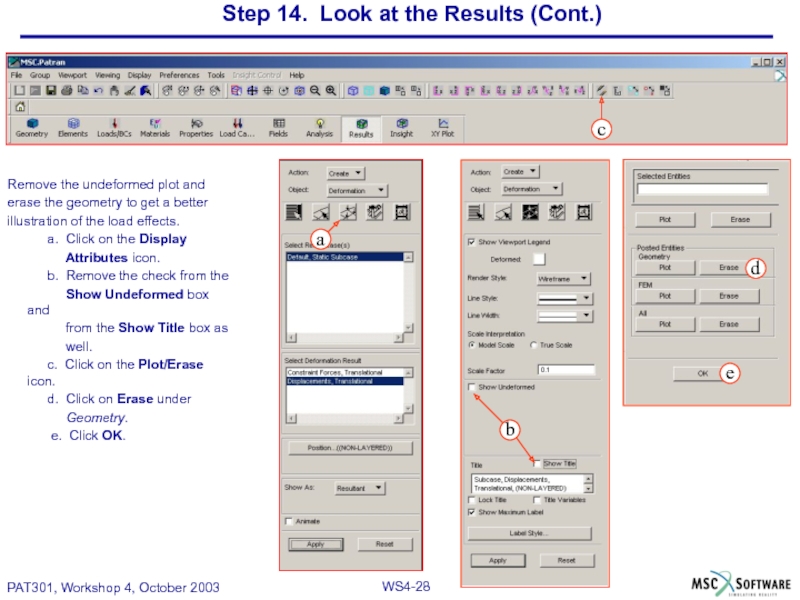
Слайд 28Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
Remove the undeformed plot and
erase the geometry to get a better
illustration of the load effects.
a. Click on the Display
Attributes icon.
b. Remove the check from the
Show Undeformed box and
from the Show Title box as
well.
c. Click on the Plot/Erase icon.
d. Click on Erase under
Geometry.
e. Click OK.
Слайд 30Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
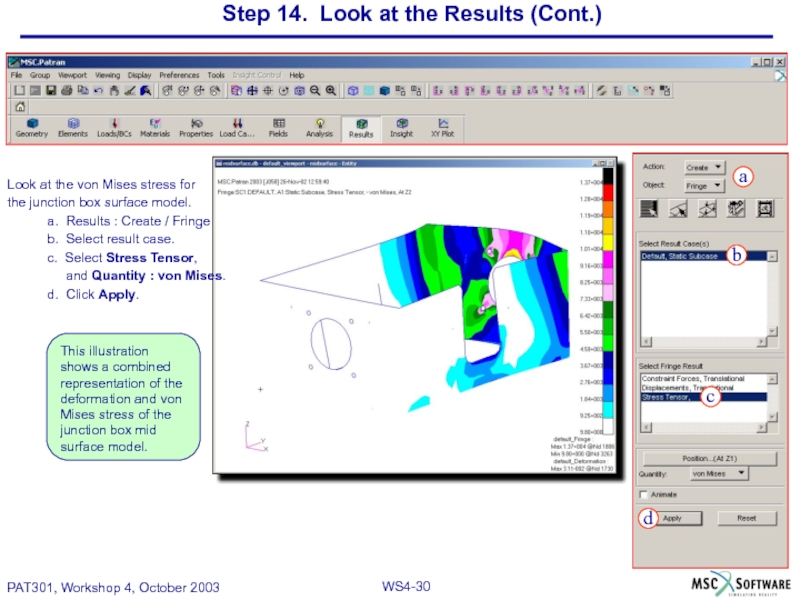
Look at the von Mises
the junction box surface model.
a. Results : Create / Fringe
b. Select result case.
c. Select Stress Tensor,
and Quantity : von Mises.
d. Click Apply.
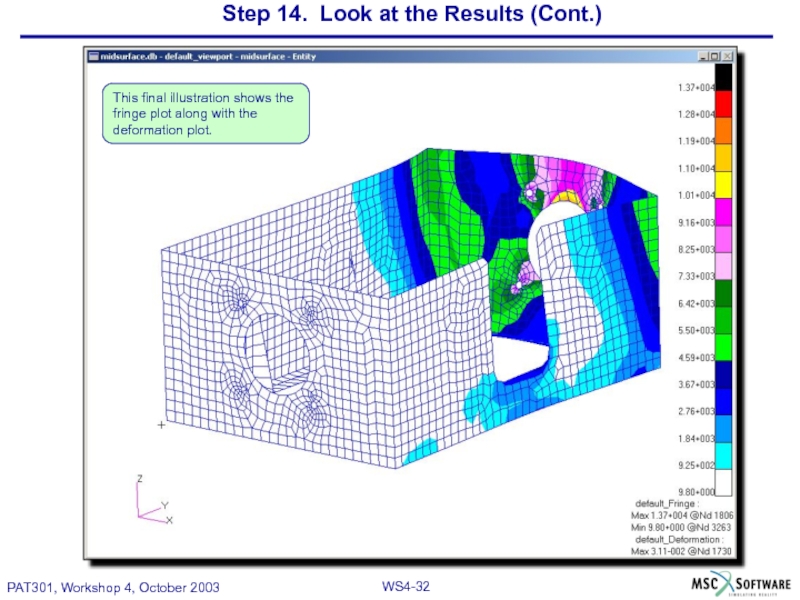
This illustration shows a combined representation of the deformation and von Mises stress of the junction box mid surface model.
Слайд 31Step 14. Look at the Results (Cont.)
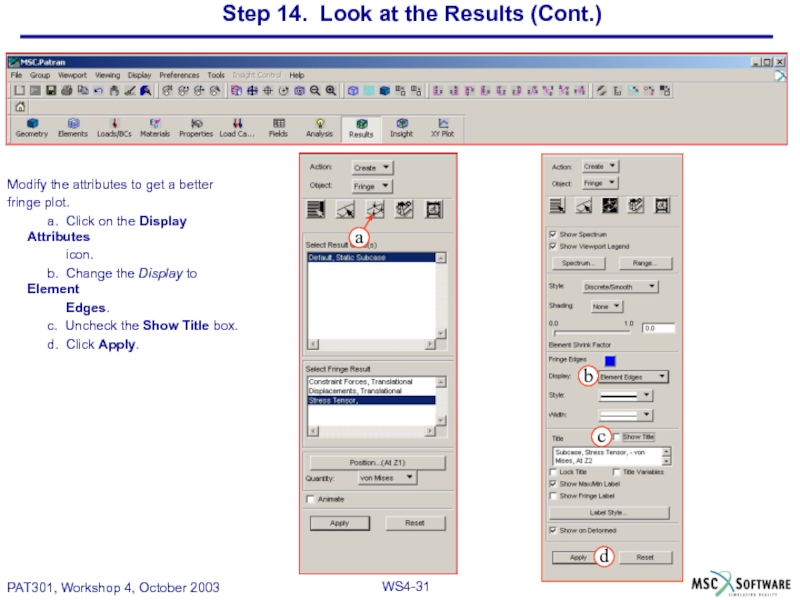
Modify the attributes to get
fringe plot.
a. Click on the Display Attributes
icon.
b. Change the Display to Element
Edges.
c. Uncheck the Show Title box.
d. Click Apply.