- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Packaging Materials презентация
Содержание
- 1. Packaging Materials
- 2. Packaging Materials Cans Glass Containers Rigid plastic
- 3. Cans Advantages: Cheap & widely used in
- 4. Cans Aluminium Cans
- 5. Cans Steel Cans
- 6. Cans Cans that have bulges or dents
- 7. Glass Containers Characteristics: Chemically inert - wont
- 8. Glass Containers Uses: Semi-liquid, liquid & solid
- 9. Paper & Cardboard Paper: Used for a
- 10. Paper & Cardboard
- 11. Paper & Cardboard
- 12. Paper & cardboard
- 13. Rigid Plastic Packaging Advantages: Lightweight & strong
- 14. Rigid Plastic Packaging
- 15. Rigid Plastic Packaging Types of plastic used:
- 16. Rigid Plastic Packaging
- 17. Flexible Plastic Packaging Any plastic that is
- 18. Flexible Plastic Packaging Plastics are made by
- 19. Extrusion
- 20. Flexible Plastic Packaging
- 21. Flexible Plastic Packaging Laminations (composite plastics): Combining
- 22. Flexible Plastic Packaging
- 23. Flexible Plastic packaging
- 24. Aluminium Foils Most foils made from aluminium
- 25. Laminations Aluminium foil joined with other materials
- 26. Tetra Pak
- 27. Others Combination Packages: 2 or more separate
Packaging Materials Cans Glass Containers Rigid plastic containers Flexible plastic packaging Paper & board Aluminium foil & laminates Styrofoam
Слайд 2Packaging Materials
Cans
Glass Containers
Rigid plastic containers
Flexible plastic packaging
Paper & board
Aluminium foil
& laminates
Styrofoam
Styrofoam
Слайд 3Cans
Advantages:
Cheap & widely used in Australia
Provides good protection of the contents
Easy
to handle during manufacture (filling stacking & packing)
Stack easily on supermarket shelves
Store for long periods of time
Steel cans:
coated in tin which acts as a barrier and prevents the food reacting with the steel.
Cans containing acidic ingredients are coated with a plastic lacquer to prevent a reaction with the metal
Used for solid & semi-solid foods.
Aluminium cans:
used for soft drinks & beer
Stack easily on supermarket shelves
Store for long periods of time
Steel cans:
coated in tin which acts as a barrier and prevents the food reacting with the steel.
Cans containing acidic ingredients are coated with a plastic lacquer to prevent a reaction with the metal
Used for solid & semi-solid foods.
Aluminium cans:
used for soft drinks & beer
Слайд 6Cans
Cans that have bulges or dents
Air may have entered so there
is a risk of microbial contamination
Lacquer may be damaged & food may have reacted with the metal Canned food do not have a use-by date as they are required only on foods with a shelf life less than 2 years
Canned food do not have a use-by date as they are only required on foods that have a shelf life of less than 2 years
Lacquer may be damaged & food may have reacted with the metal Canned food do not have a use-by date as they are required only on foods with a shelf life less than 2 years
Canned food do not have a use-by date as they are only required on foods that have a shelf life of less than 2 years
Слайд 7Glass Containers
Characteristics:
Chemically inert - wont react with its contents
Non porous
Odourless &
hygienic
Contents can be seen as glass is transparent
Great strength (continually getting stronger & lighter)
Easy open & re-sealable
Variety of shapes & sizes
Long-term storage & extended shelf-life
Sustainable - can be recycled or re-used
Contents can be seen as glass is transparent
Great strength (continually getting stronger & lighter)
Easy open & re-sealable
Variety of shapes & sizes
Long-term storage & extended shelf-life
Sustainable - can be recycled or re-used
Слайд 8Glass Containers
Uses:
Semi-liquid, liquid & solid foods
Examples:
Preparation:
Air blowing, rinsing with warm water,
washing in detergent, sterilising (aseptic)
Слайд 9Paper & Cardboard
Paper:
Used for a wide variety of products
Versatile & cost
effective
Variety of shapes, textures & thickness' available
Greaseproof paper can be used when packaging products such as confectionary & butter. They act as a barrier to odours & moisture
Paperboard (thicker paper-based packaging)
Can be laminated with other materials to create strength & moisture resistance E.g. Tetra packs
Pulped Fibreboard
Offers protection for products such as eggs because of the airsplace between the particles
Refer to table 11.2 Pg 218
Variety of shapes, textures & thickness' available
Greaseproof paper can be used when packaging products such as confectionary & butter. They act as a barrier to odours & moisture
Paperboard (thicker paper-based packaging)
Can be laminated with other materials to create strength & moisture resistance E.g. Tetra packs
Pulped Fibreboard
Offers protection for products such as eggs because of the airsplace between the particles
Refer to table 11.2 Pg 218
Слайд 13Rigid Plastic Packaging
Advantages:
Lightweight & strong
High resistance to breakage
Available in a wide
variety of colours, shapes, sizes & textures
Can add to the sale appeal of the product
Cheap and easy to produce compared to other packaging materials
Can add to the sale appeal of the product
Cheap and easy to produce compared to other packaging materials
Слайд 15Rigid Plastic Packaging
Types of plastic used:
polyethylene terephalate (PET) - used clear
as colouring has an impact on the strength. E.g. soft drink, water & oil
high density polyethylene (HDPE) - stronger when colour is added. Used for products with a shorter shelf life E.g. milk
Polypropylene (PP) - high melting point so is useful for hot fill products such as soups & fruits in syrup. Can be moulded easily E.g. yoghurt & ice cream
Polystyrene (PS) - Aerated texture allows package to protect the product from physical damage. Also provide thermal retention E.g. trays & cups
high density polyethylene (HDPE) - stronger when colour is added. Used for products with a shorter shelf life E.g. milk
Polypropylene (PP) - high melting point so is useful for hot fill products such as soups & fruits in syrup. Can be moulded easily E.g. yoghurt & ice cream
Polystyrene (PS) - Aerated texture allows package to protect the product from physical damage. Also provide thermal retention E.g. trays & cups
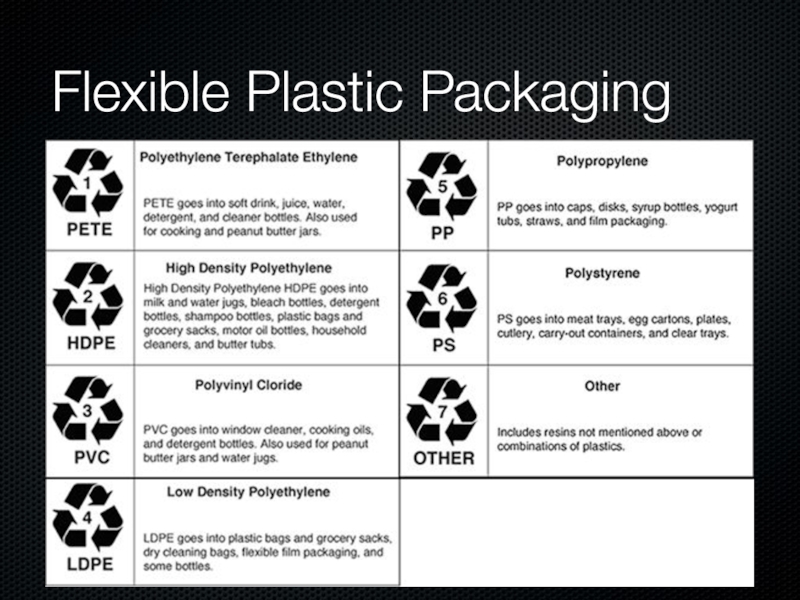
Слайд 17Flexible Plastic Packaging
Any plastic that is formed into a sheet or
reel with a thickness os up to 0.375mm
Plastic films & Bags:
Polyethylene (PET) E.g. cling wrap
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) E.g. Cereal bags
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) E.g. Kraft singles wrappers
Polypropylene (PP) E.g. chip, biscuit, 2 minute noodle wrappers
Plastic films & Bags:
Polyethylene (PET) E.g. cling wrap
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) E.g. Cereal bags
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) E.g. Kraft singles wrappers
Polypropylene (PP) E.g. chip, biscuit, 2 minute noodle wrappers
Слайд 18Flexible Plastic Packaging
Plastics are made by melting a pellet and forcing
it out into the desired shape. This process is known as EXTRUSION
Слайд 21Flexible Plastic Packaging
Laminations (composite plastics):
Combining 2 or more plastic materials from
separate reels that are glued together with adhesive
Plastics are extruded and glued together at the same time
MAP packaged and vacuum packages can use 3-11 layers
Plastics are extruded and glued together at the same time
MAP packaged and vacuum packages can use 3-11 layers
Слайд 24Aluminium Foils
Most foils made from aluminium
Advantages:
light
flexible
strong
Able to withstand moderate heat
Examples:
Tubes -
condensed milk
Trays - frozen foods
Product seals - sour cream, butter & yoghurt
Wrappers - Cadbury chocolate block
Trays - frozen foods
Product seals - sour cream, butter & yoghurt
Wrappers - Cadbury chocolate block
Слайд 25Laminations
Aluminium foil joined with other materials such as plastic and paper
to create a stronger packaging material.
Example:
Muesli bar wrapper (paper, foil & plastic)
Tetra Packs:
Multi-layered laminations known as composite packages
Each layer provides a different purpose
Metallising:
Plastic coated in a fine layer of metal. E.g. Twisties chip packets
Example:
Muesli bar wrapper (paper, foil & plastic)
Tetra Packs:
Multi-layered laminations known as composite packages
Each layer provides a different purpose
Metallising:
Plastic coated in a fine layer of metal. E.g. Twisties chip packets
Слайд 27Others
Combination Packages:
2 or more separate packaging materials that function independently of
one another
E.g. Breakfast Cereal
Primary, Secondary & Tertiary Packaging:
Primary - Package in which the food is sold to the consumer
Secondary - Food sold with a secondary level of packaging. E.g. 6 pack of poppers
Tertiary - Used to secure multiple secondary packages to make bulk handling & transportation easier. E.g. shrink wrapped pallets
E.g. Breakfast Cereal
Primary, Secondary & Tertiary Packaging:
Primary - Package in which the food is sold to the consumer
Secondary - Food sold with a secondary level of packaging. E.g. 6 pack of poppers
Tertiary - Used to secure multiple secondary packages to make bulk handling & transportation easier. E.g. shrink wrapped pallets