- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Main parts of ships презентация
Содержание
- 1. Main parts of ships
- 2. HULL There are two main parts of
- 3. The keel is the backbone of the hull
- 4. The hull is divided into three areas: fore end, after end and amidships.
- 5. The fore end is bow, the after
- 7. BOW
- 8. KEEL
- 9. The depth of ship’s bottom or keel
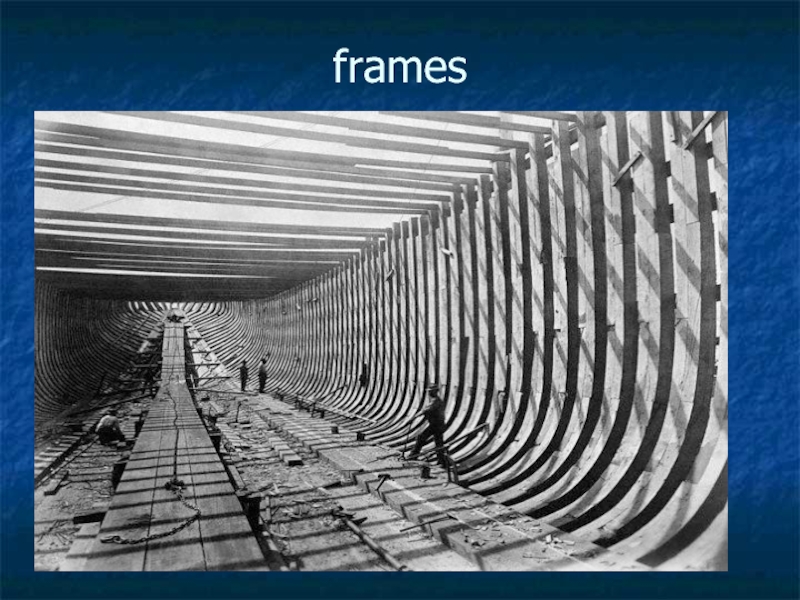
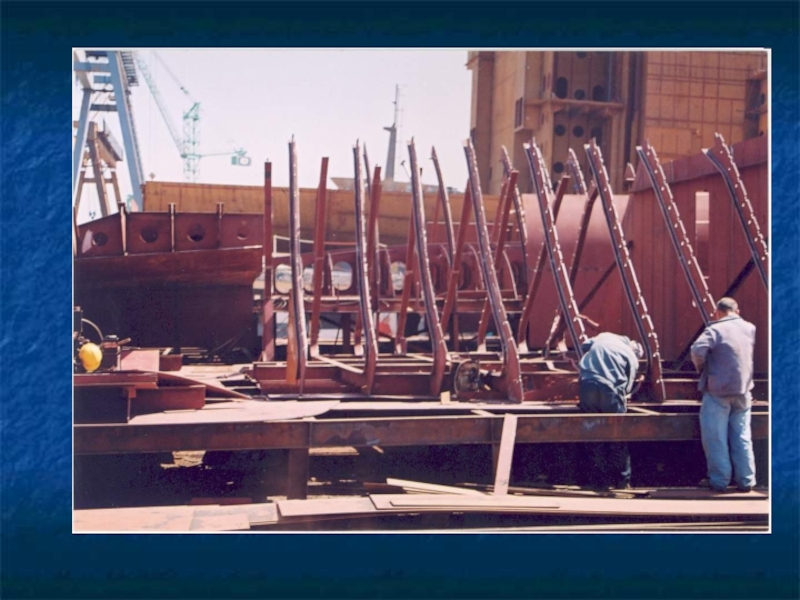
- 10. The frames, bulkheads, floors and beams complete
- 11. frames
- 19. DECK The upper deck covers the holds
- 20. The cargo is loaded or unloaded through hatches by cranes or by derricks.
- 21. The derricks are fitted to the masts
- 22. HOLD
- 23. CARGO HOLD
- 24. HATCHES
- 25. HATCH
- 26. MAST
- 27. CRANE
- 28. DERRICKS
- 29. ANCHOR
- 30. ANCHOR
- 31. MOORING
- 32. The anchoring arrangement is the windlass used
- 33. WINDLASS
- 35. BOLLARD
- 36. BITTS
- 37. FAIRLEAD
- 38. PADEYE
- 39. CLEAT
- 40. SHACKLE
- 41. ANCHOR CHAIN
- 42. ROPE
- 44. Lifeboats are arranged on the port and
- 45. LIFERAFT
- 47. LIFEBOAT
- 48. LIFERING
- 49. STERN The purpose of the steering gear
- 50. The rudder is turned by steering engine
- 51. STERN
- 52. STEERING GEAR COMPARTMENT
- 53. STEERING GEAR
- 54. RUDDER
- 56. PROPULSION The ship is moved through
- 57. PROPULSION SYSTEM
- 58. PROPELLER
- 59. BRIDGE The ship is controlled from the
- 60. BRIDGE
- 62. FUNNEL
- 63. The captain, officers and the crew are accommodated in cabins.
- 64. The meals are prepared in galleys and laundry is done in the laundry room.
- 65. Officers usually eat in the officers' mess
- 66. CABIN(STATEROOM)
- 67. GALLEY
- 68. LAUNDRY
- 70. ANSWER THE QUESTIONS 1-What are mooring arrangements?
- 71. 2-How is cargo loaded?
- 72. 3-What is the rear part of the ship called?
- 73. 4-Where is the laundry done?
- 74. 5-What is a galley?
- 75. ETYMOLOGY Deck < German, decken, to cover
- 76. Galley < The galley is the kitchen
- 77. Mast
- 78. SOME TERMS Accommodate (v)- To provide a
- 79. ‘The depth of the ship’s keel from
- 80. ‘The depth of the ship’s keel from waterline’ is; c. draught
- 81. Derricks are fitted to the ship’s;
- 82. Derricks are fitted to the ship’s; c. masts
- 83. Which is not an enclosed space?
- 84. Which is not an enclosed space? e. forecastle
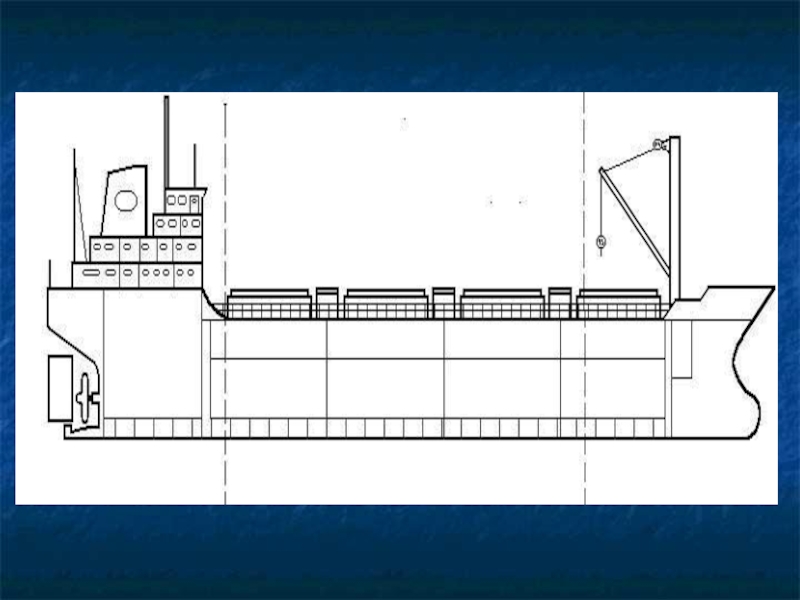
Слайд 2HULL
There are two main parts of a ship: the hull and
the machinery.
The main structure of a ship is hull.
The main structure of a ship is hull.
Слайд 5The fore end is bow, the after end is stern. The
right side of ship is called the starboard and the other side is port
Слайд 9 The depth of ship’s bottom or keel below the waterline is
draught. The beam of the ship is the distance between the two sides.
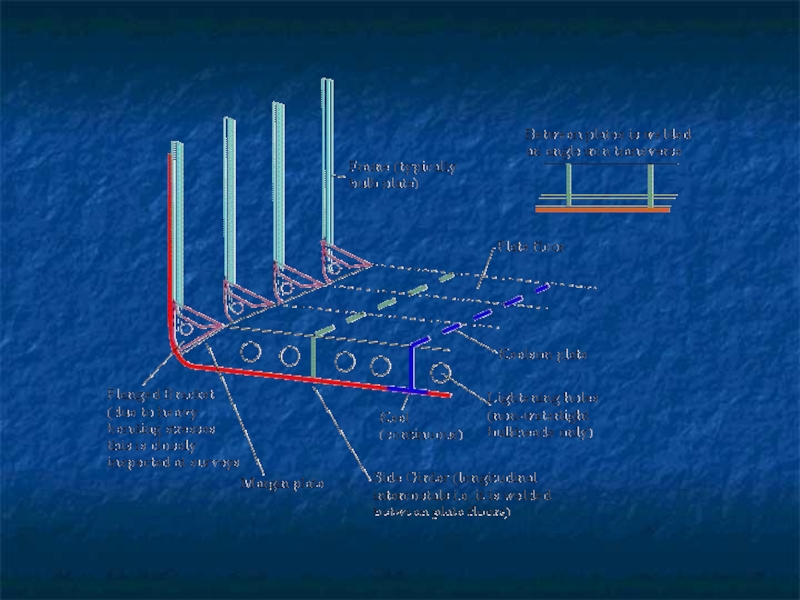
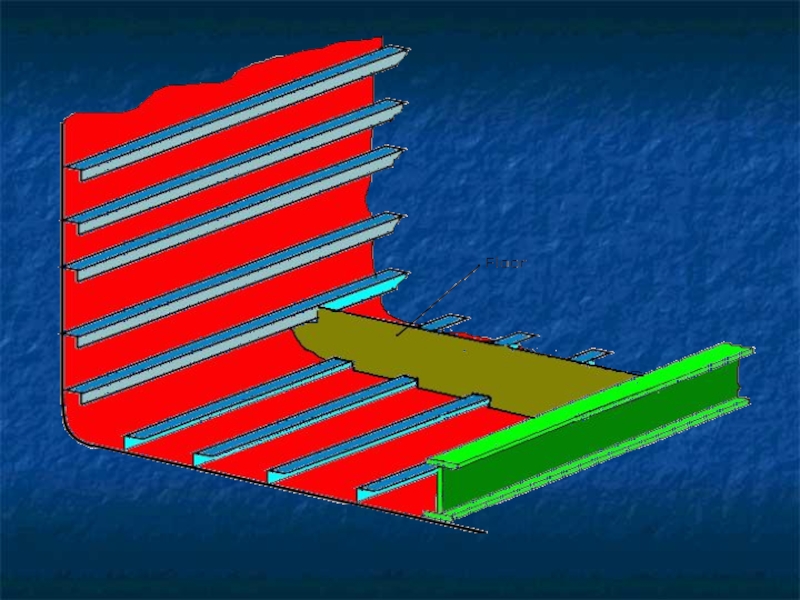
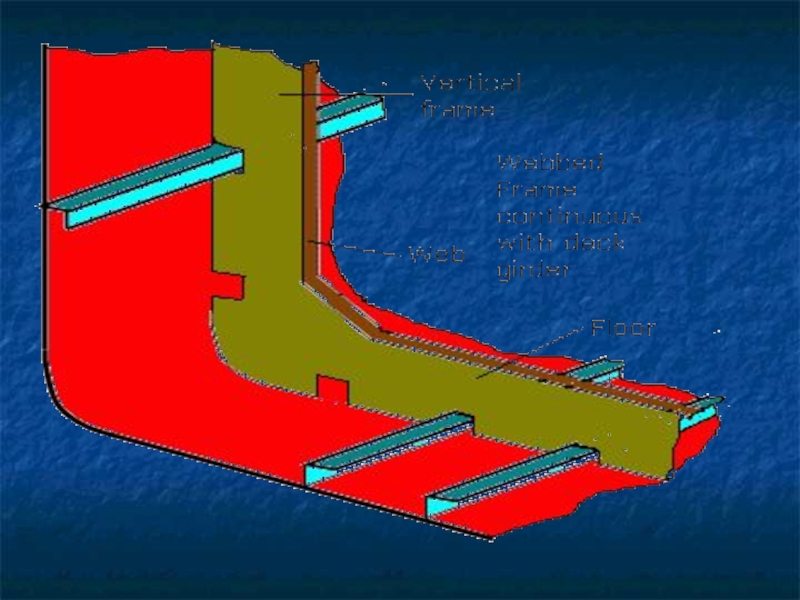
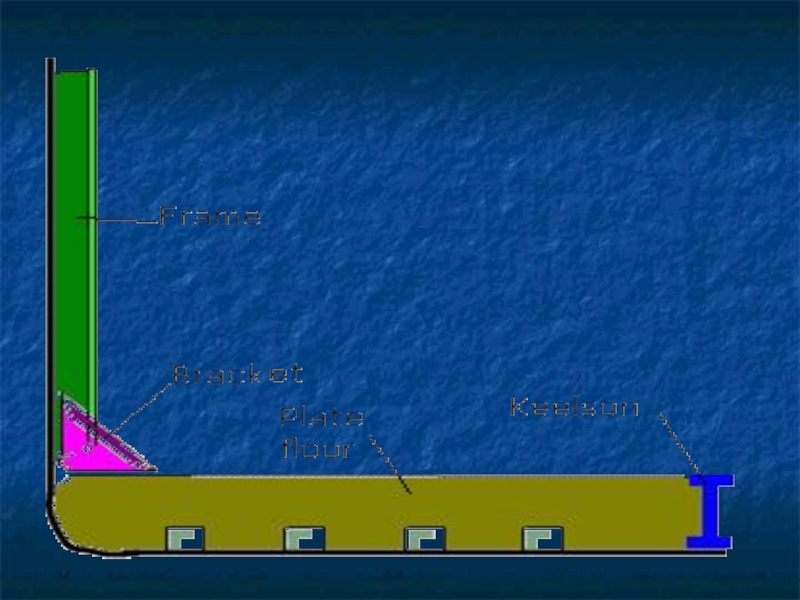
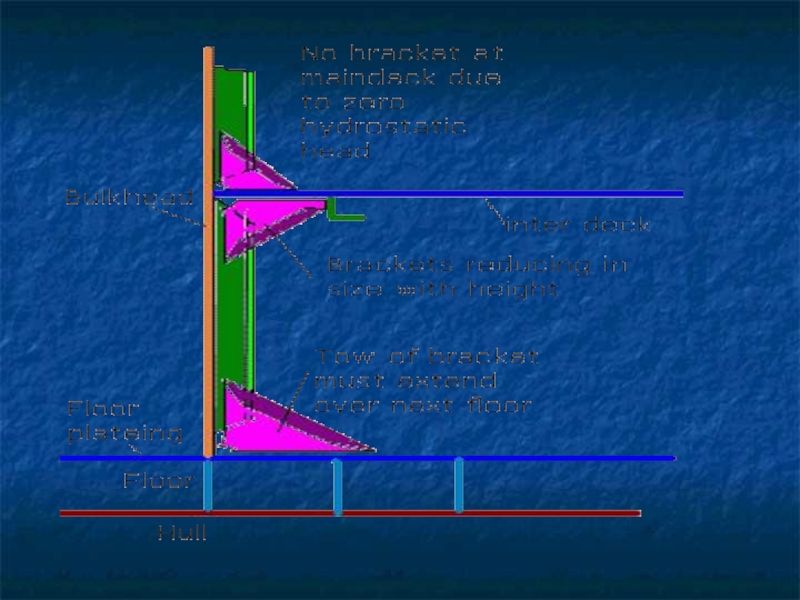
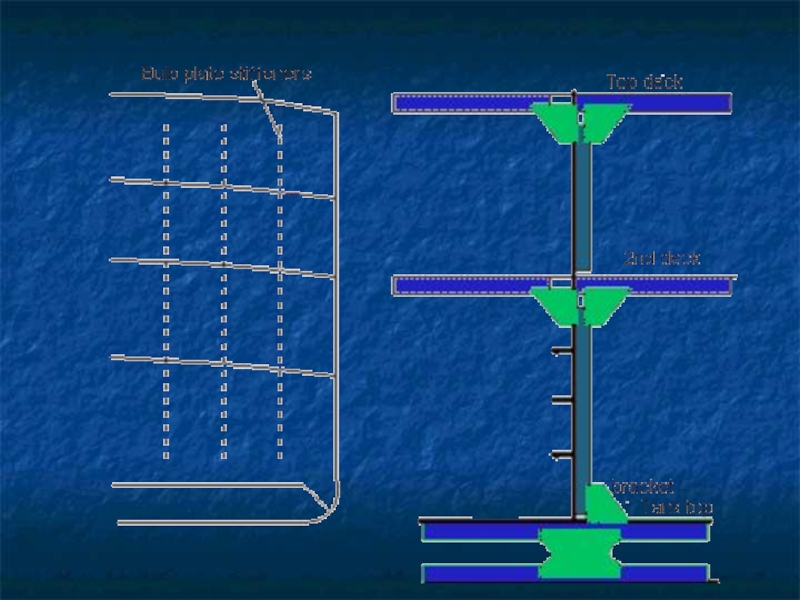
Слайд 10The frames, bulkheads, floors and beams complete the skeleton of hull.
The frames which are ribs of the ship are covered by plating.
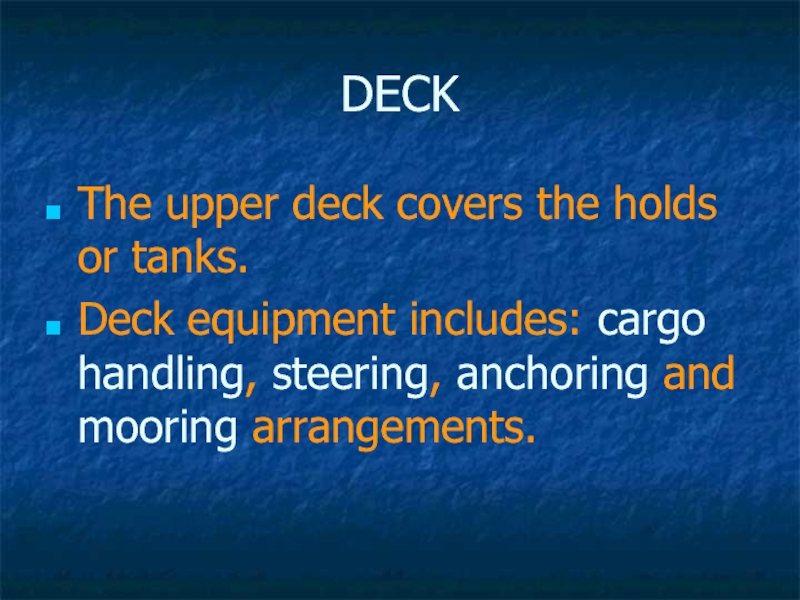
Слайд 19DECK
The upper deck covers the holds or tanks.
Deck equipment includes:
cargo handling, steering, anchoring and mooring arrangements.
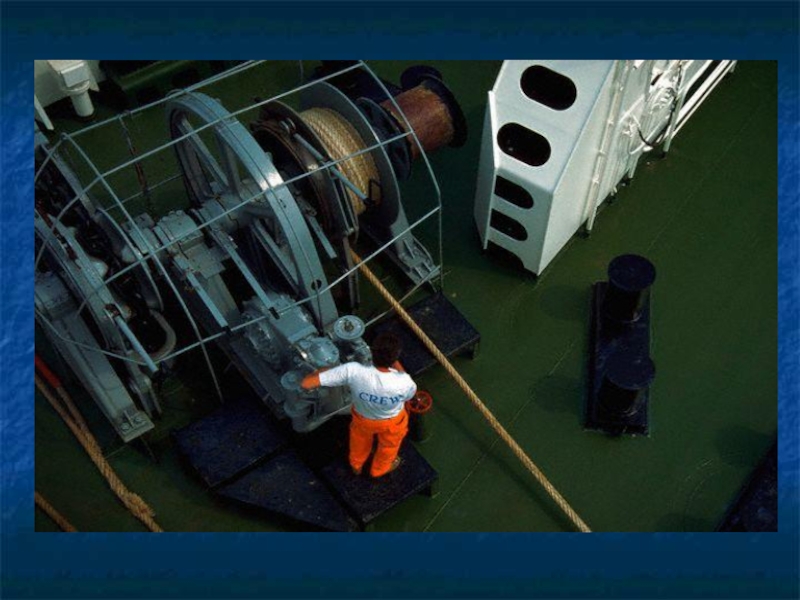
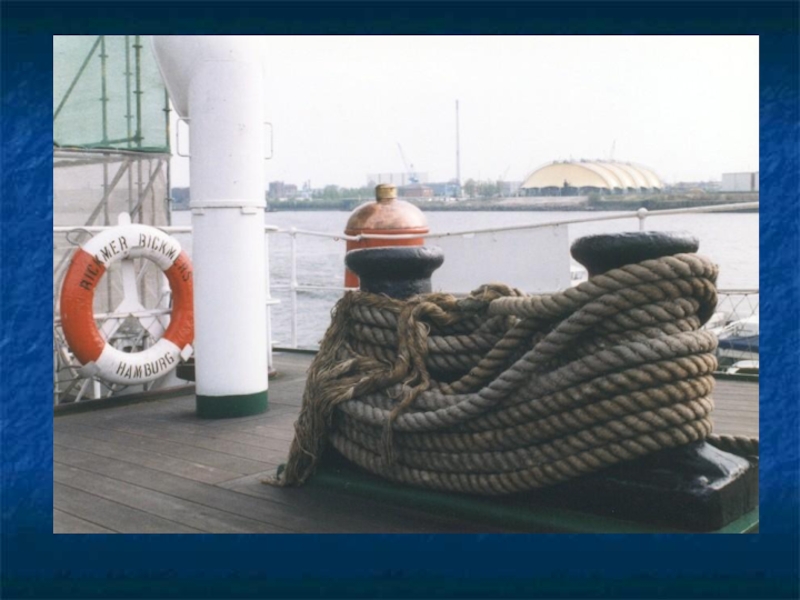
Слайд 32The anchoring arrangement is the windlass used for lowering and raising
the anchor an anchor chain. The mooring arrangement consists of a winch, bitts and fairleads .
Слайд 44Lifeboats are arranged on the port and starboard side. They are
carried in davits and are used for life-saving purposes.
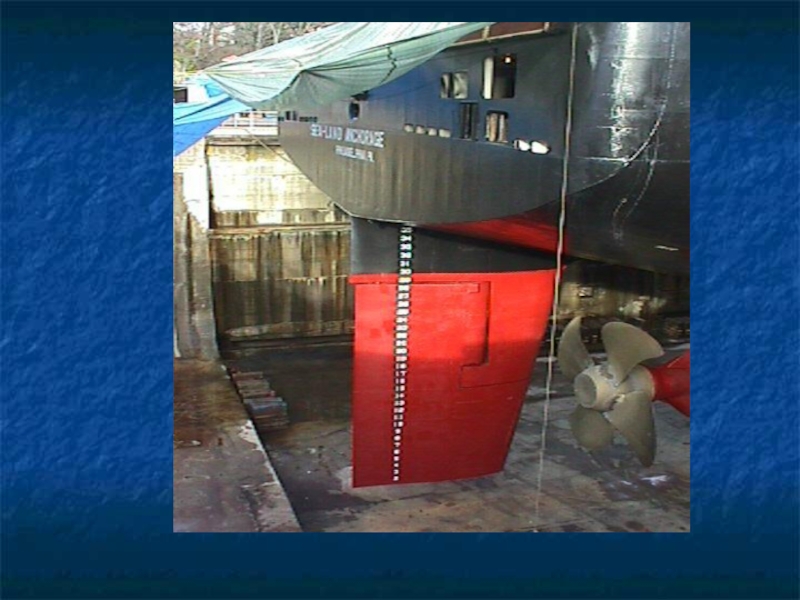
Слайд 49STERN
The purpose of the steering gear is to keep the vessel
on a steady course.
A ship is steered by its rudder which is a flat plate at the ship's stern.
A ship is steered by its rudder which is a flat plate at the ship's stern.
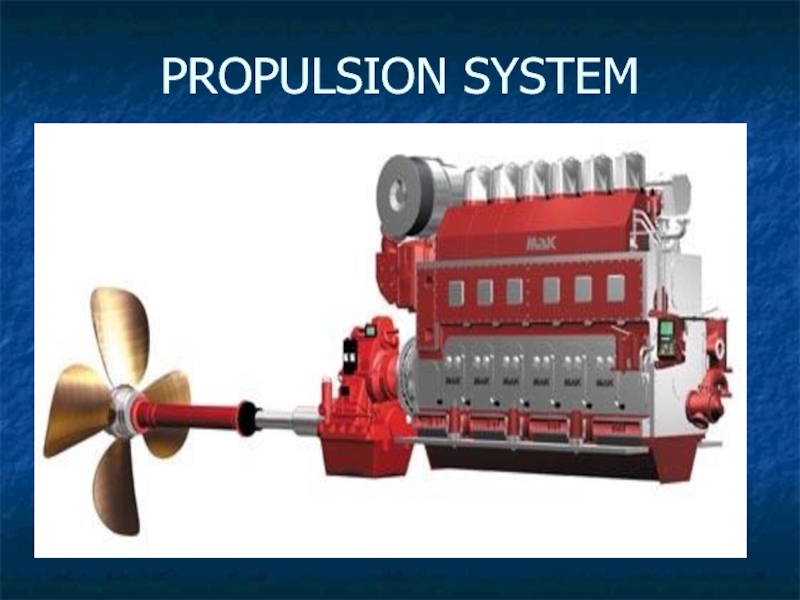
Слайд 56PROPULSION
The ship is moved through the water by one or more
propellers.
Shafts transmit the rotary motion of a ship's engines to its propellers.
The engine is fitted in the engine room .
Shafts transmit the rotary motion of a ship's engines to its propellers.
The engine is fitted in the engine room .
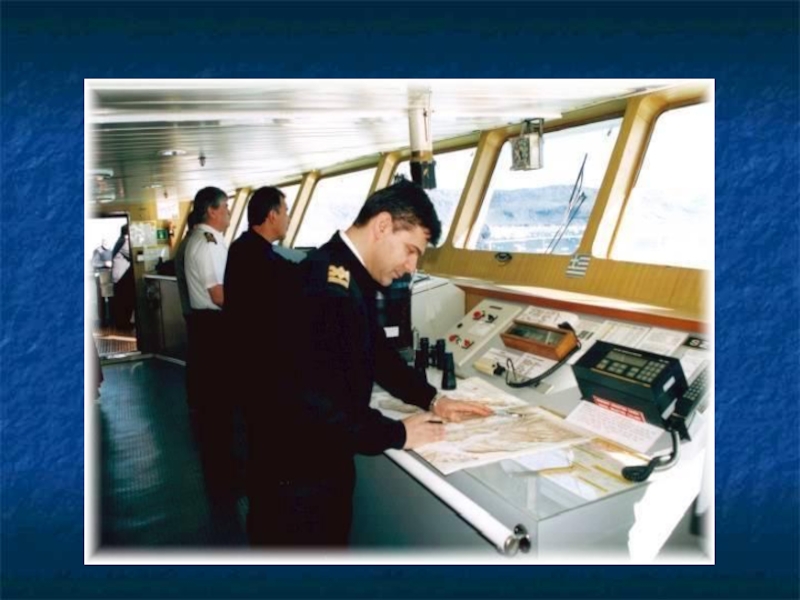
Слайд 59BRIDGE
The ship is controlled from the bridge by the captain or
navigating officers.
Near the bridge there is funnel.
Near the bridge there is funnel.
Слайд 65Officers usually eat in the officers' mess with waiter service.
Crew
members dine in the self-service or waiter service crew mess.
Слайд 75ETYMOLOGY
Deck < German, decken, to cover
Derrick < after Thomas Derrick, London
hangman of the early 17th century, applied to a gallows
Слайд 76Galley < The galley is the kitchen of the ship. It
is a corruption of "gallery". Ancient sailors cooked their meals on a brick or stone gallery laid amidships.
Слайд 78SOME TERMS
Accommodate (v)- To provide a place to stay, live or
work.
Propel (v)- To drive and move forward.
Rotary (adj.) - Moving in circles round a central point
Propel (v)- To drive and move forward.
Rotary (adj.) - Moving in circles round a central point
Слайд 79‘The depth of the ship’s keel from waterline’ is;
a. freeboard
b. bottom
c.
draught
d. water line
e. deck
d. water line
e. deck
Слайд 83Which is not an enclosed space?
a. galley
b. engine room
c. steering gear
compartment
d. hold
e. forecastle
d. hold
e. forecastle