- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
IPV6 Addressing презентация
Содержание
- 1. IPV6 Addressing
- 2. Outline Review IPv4 addressing . Basic IPv6 address concepts. IPv6 address space. Subnetting IPv6 space.
- 3. IPv4 Address 32bit address space. Subnet defined
- 4. IPv4 Address 32 bits address space. 11010010
- 5. IPv4 Address Multicast address. 1110xxxx +
- 6. IPv4 Addresses and IPv6 Equivalents IPv4 Address IPv6
- 7. IPV6 Address syntax. 128bits space. (split by
- 8. IPv6 Address concept IPv6 address syntax: Compressing Zeros FE80:0:0:0:2AA:FF:FE9A:4CA2 becomes FE80::2AA:FF:FE9A:4CA2 FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:2 FF02::2
- 9. IPv6 Address concept Prefix is part of
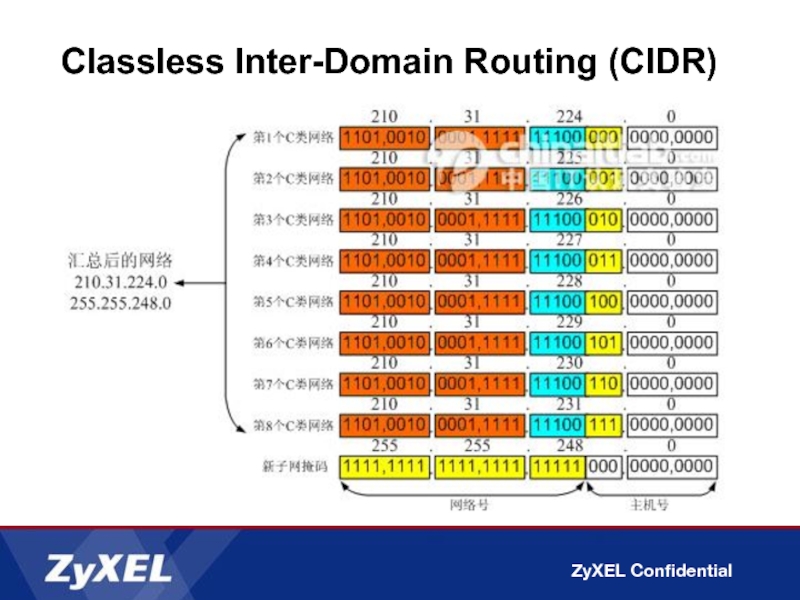
- 10. Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
- 11. IPv6 Addresses Application Router 1 Subnet 2
- 12. IPv6 Address concept Subnet Mask: not required
- 13. IPv6 Address concept Unicast address Aggregatable global
- 14. IPv6 Address concept IPv6 Address space 64bits
- 15. Unicast address Aggregatable global unicast addresses Top-Level
- 16. Unicast address Topologies Within Global Addresses Public
- 17. Unicast address Link-local addresses Used between
- 18. Unicast address Link-local addresses 1111 1110 10
- 19. Unicast address Site-local addresses Used between
- 20. Unicast address Site-local addresses 1111 1110 11
- 21. Unicast address Special addresses Unspecified address 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 or :: Loopback address 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 or ::1
- 22. Unicast address Compatibility Addresses IPv4-compatible address 0:0:0:0:0:0:w.x.y.z
- 23. Multicast IPv6 Address Defined multicast addresses All-Nodes
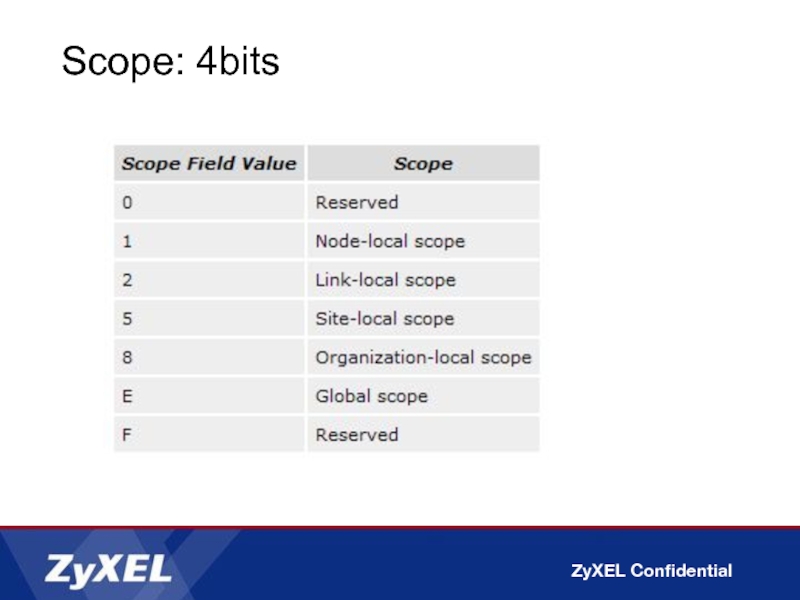
- 24. Scope: 4bits
- 25. Multicast IPv6 Address Recommended Multicast IPv6 Addresses
- 26. Multicast IPv6 Address Solicited-Node Address Acts as
- 27. Multicast IPv6 Address Solicited-Node Address Interface ID
- 28. Anycast IPv6 Address An anycast address is
- 29. IPv6 Addresses Application IPv6 Addresses for a
- 30. IPv6 Addresses Application IPv6 Addresses for a
- 31. IPv6 Addresses Application Router 1 Subnet 2
- 32. IPv6 Interface Identifiers Interface identifier based on:
- 33. IEEE EUI-64 Addresses Extended Unique Identifier Company ID Extension ID
- 34. IPv6 Interface Identifiers Extended Unique Identifier (EUI)-64 address Extended Unique Identifier Company ID Extension ID
- 35. Conversion of an IEEE 802 Address to
- 36. 00000000 00001101 01100000 11001011 1100010 1010101 11111111
- 37. Temporary Address Interface Identifiers Random IPv6 interface
- 38. IPv6 Multicast Address 33-33- 8
- 39. IPv6 Addresses Application Router 1 Subnet 2
- 40. Subnetting the IPv6 Address Space Subnetting for
- 41. Subnetting the IPv6 Address Space Subnetting for
- 42. Expression Based on s (the number of
- 43. Example To perform a 3-bit subnetting of
- 44. Q&A
- 45. Date Subject Lecturer Introduction to IPv6
- 46. Date Subject Lecturer Setting Up an
Слайд 2Outline
Review IPv4 addressing .
Basic IPv6 address concepts.
IPv6 address space.
Subnetting IPv6 space.
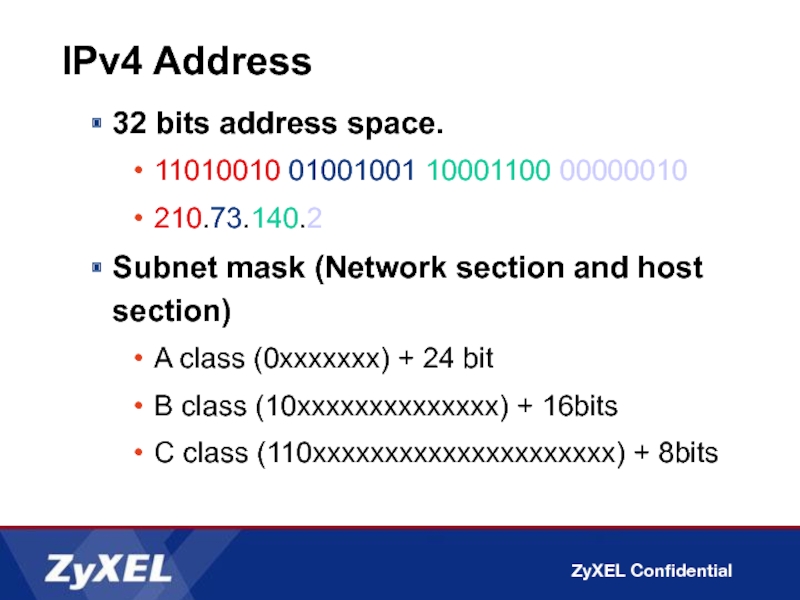
Слайд 3IPv4 Address
32bit address space.
Subnet defined by a mask.
Unicast host address.
Multicast
Broadcast address.
Special address.
Слайд 4IPv4 Address
32 bits address space.
11010010 01001001 10001100 00000010
210.73.140.2
Subnet mask
A class (0xxxxxxx) + 24 bit
B class (10xxxxxxxxxxxxxx) + 16bits
C class (110xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx) + 8bits
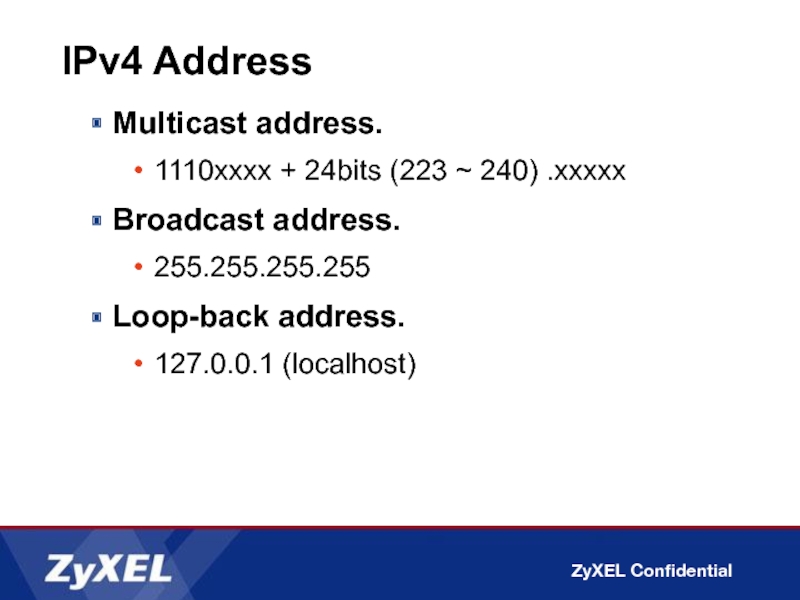
Слайд 5IPv4 Address
Multicast address.
1110xxxx + 24bits (223 ~ 240) .xxxxx
Broadcast address.
255.255.255.255
Loop-back address.
127.0.0.1 (localhost)
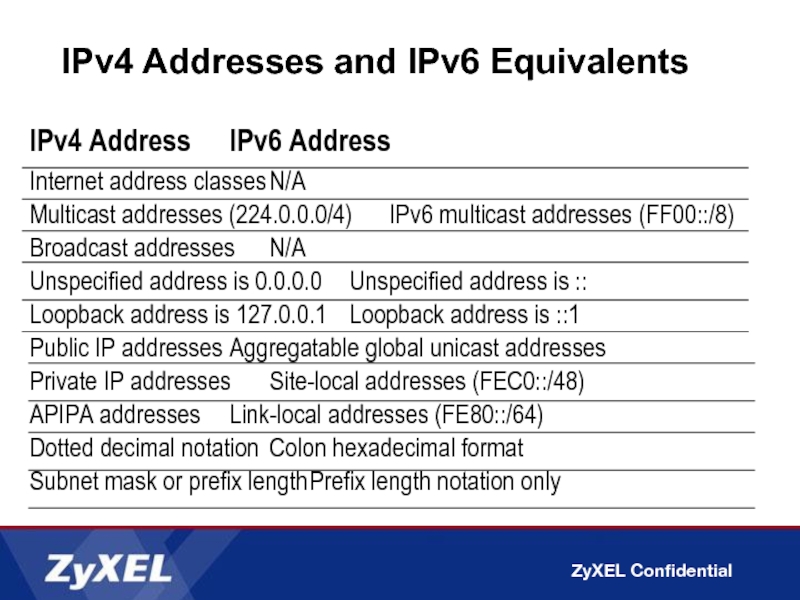
Слайд 6IPv4 Addresses and IPv6 Equivalents
IPv4 Address IPv6 Address
Internet address classes N/A
Multicast addresses (224.0.0.0/4) IPv6
Broadcast addresses N/A
Unspecified address is 0.0.0.0 Unspecified address is ::
Loopback address is 127.0.0.1 Loopback address is ::1
Public IP addresses Aggregatable global unicast addresses
Private IP addresses Site-local addresses (FEC0::/48)
APIPA addresses Link-local addresses (FE80::/64)
Dotted decimal notation Colon hexadecimal format
Subnet mask or prefix length Prefix length notation only
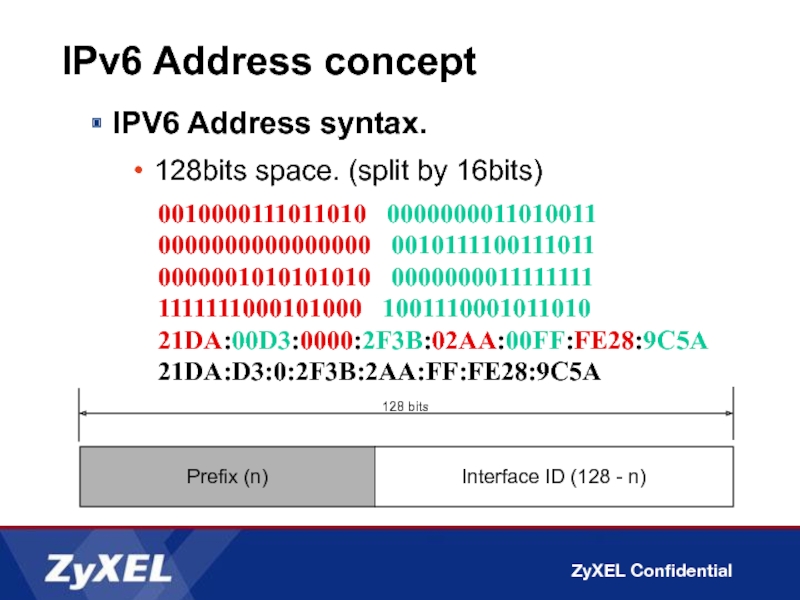
Слайд 7IPV6 Address syntax.
128bits space. (split by 16bits)
IPv6 Address concept
0010000111011010 0000000011010011
0000001010101010 0000000011111111 1111111000101000 1001110001011010
21DA:00D3:0000:2F3B:02AA:00FF:FE28:9C5A
21DA:D3:0:2F3B:2AA:FF:FE28:9C5A
Prefix (n)
Interface ID (128 - n)
128 bits
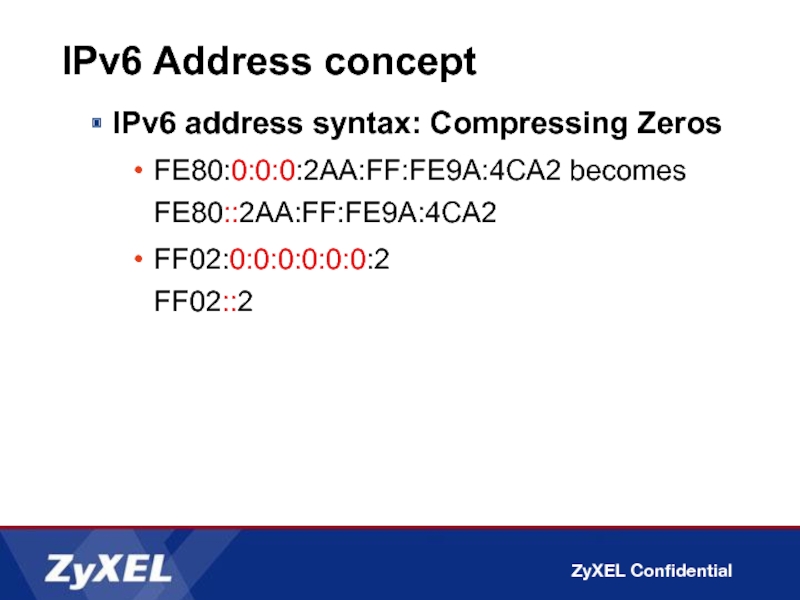
Слайд 8IPv6 Address concept
IPv6 address syntax: Compressing Zeros
FE80:0:0:0:2AA:FF:FE9A:4CA2 becomes FE80::2AA:FF:FE9A:4CA2
FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:2
FF02::2
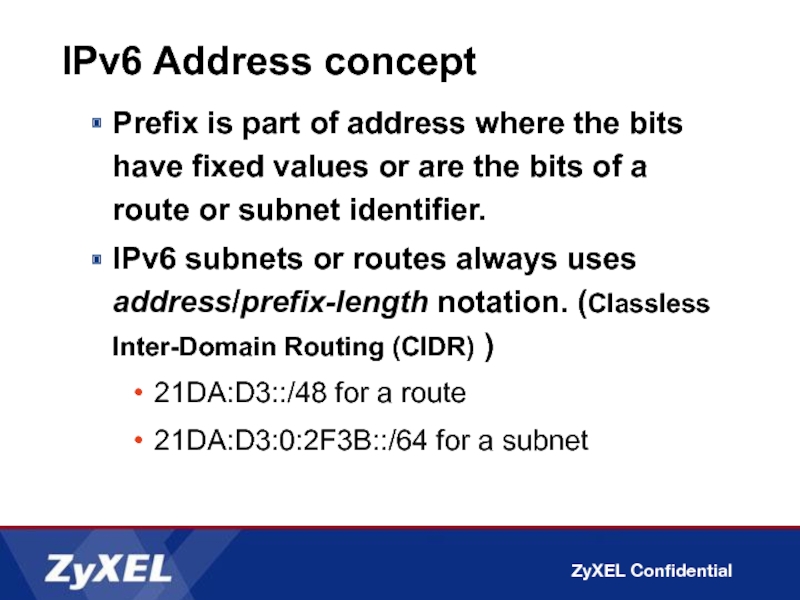
Слайд 9IPv6 Address concept
Prefix is part of address where the bits have
IPv6 subnets or routes always uses address/prefix-length notation. (Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) )
21DA:D3::/48 for a route
21DA:D3:0:2F3B::/64 for a subnet
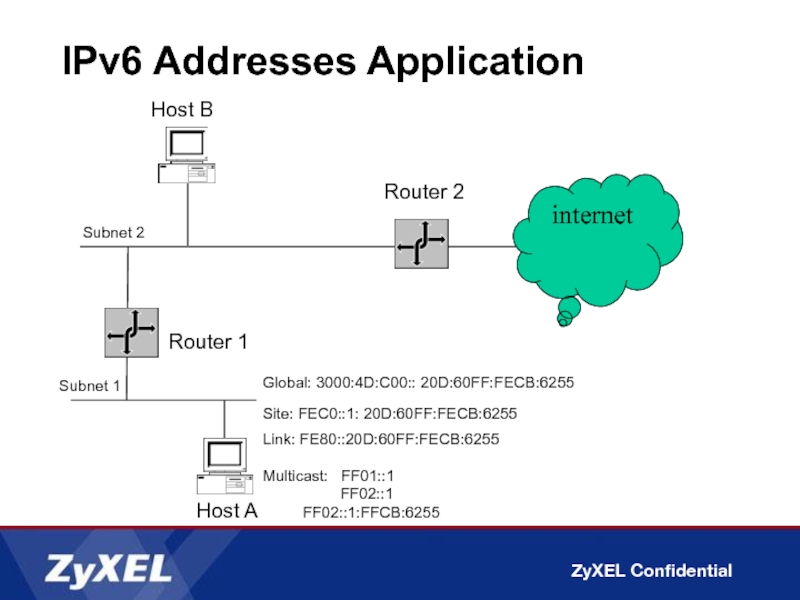
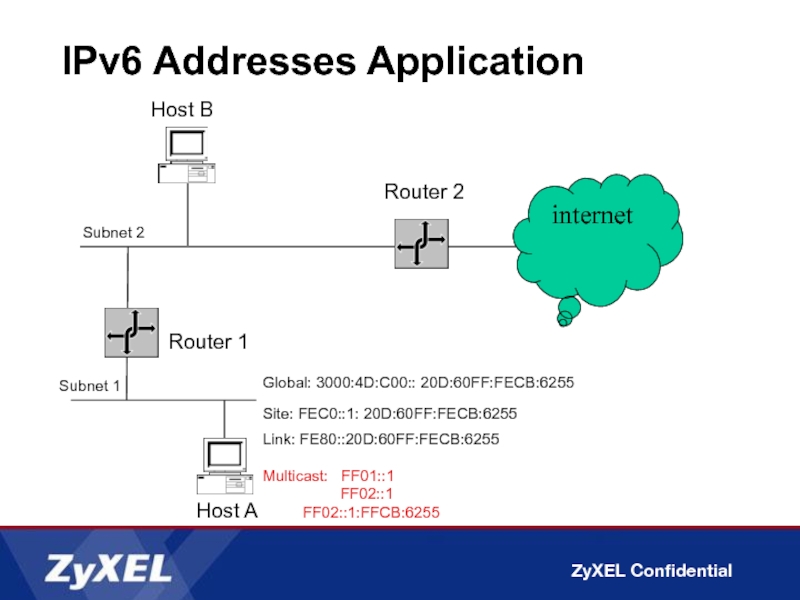
Слайд 11IPv6 Addresses Application
Router 1
Subnet 2
Subnet 1
Router 2
Host A
Host B
Site: FEC0::1: 20D:60FF:FECB:6255
Link:
Multicast: FF01::1
FF02::1
FF02::1:FFCB:6255
internet
Global: 3000:4D:C00:: 20D:60FF:FECB:6255
Слайд 12IPv6 Address concept
Subnet Mask: not required and as prefix of IPv6
Type of address
Unicast
Address of a single interface
One-to-one delivery to single interface
Multicast
Address of a set of interfaces
One-to-many delivery to all interfaces in the set
Anycast
Address of a set of interfaces
One-to-one-of-many delivery to a single interface in the set that is closest
No broadcast addresses
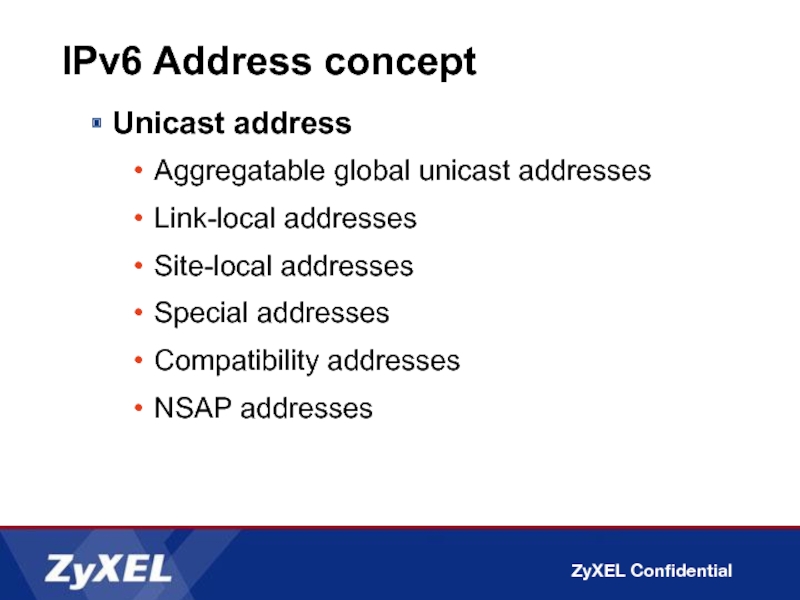
Слайд 13IPv6 Address concept
Unicast address
Aggregatable global unicast addresses
Link-local addresses
Site-local addresses
Special addresses
Compatibility addresses
NSAP
Слайд 14IPv6 Address concept
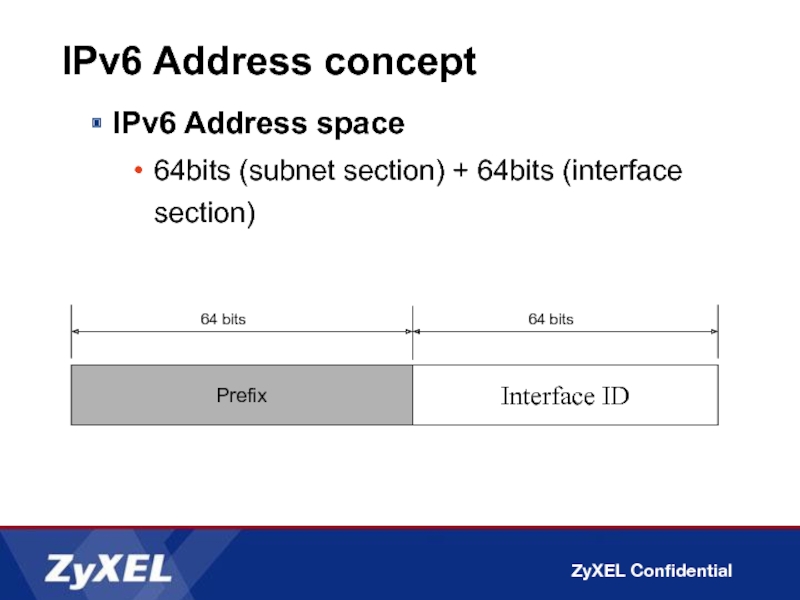
IPv6 Address space
64bits (subnet section) + 64bits (interface section)
Prefix
Interface
64 bits
64 bits
Слайд 15Unicast address
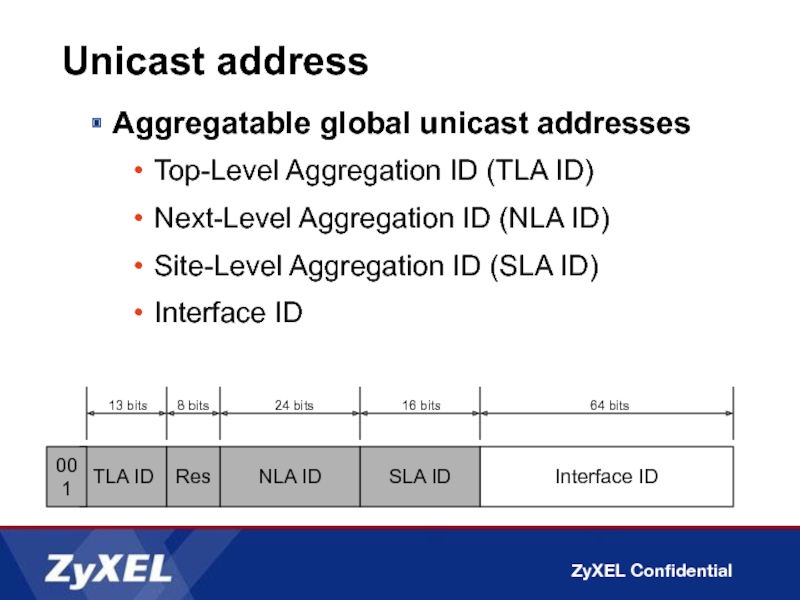
Aggregatable global unicast addresses
Top-Level Aggregation ID (TLA ID)
Next-Level Aggregation ID
Site-Level Aggregation ID (SLA ID)
Interface ID
TLA ID
Interface ID
13 bits
64 bits
SLA ID
24 bits
001
NLA ID
16 bits
Res
8 bits
Слайд 16Unicast address
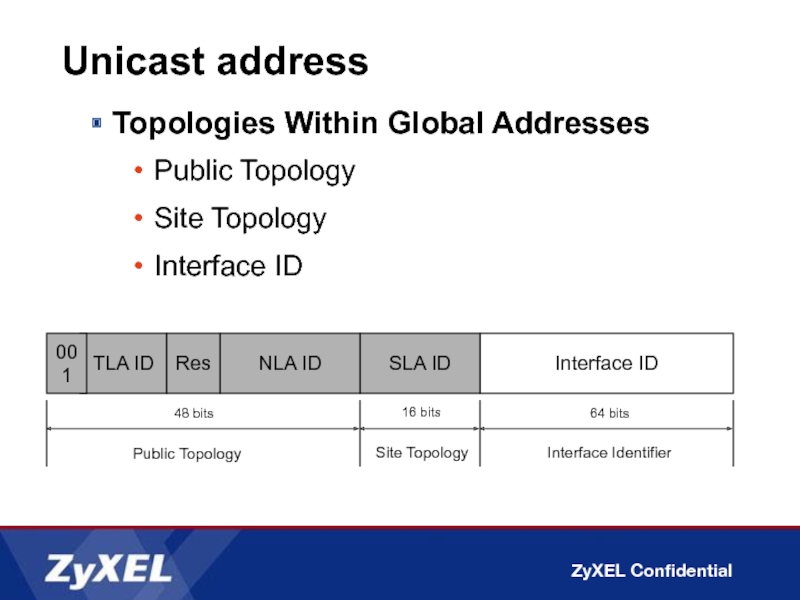
Topologies Within Global Addresses
Public Topology
Site Topology
Interface ID
TLA ID
Interface ID
64 bits
SLA
001
NLA ID
16 bits
Res
48 bits
Public Topology
Site Topology
Interface Identifier
Слайд 17Unicast address
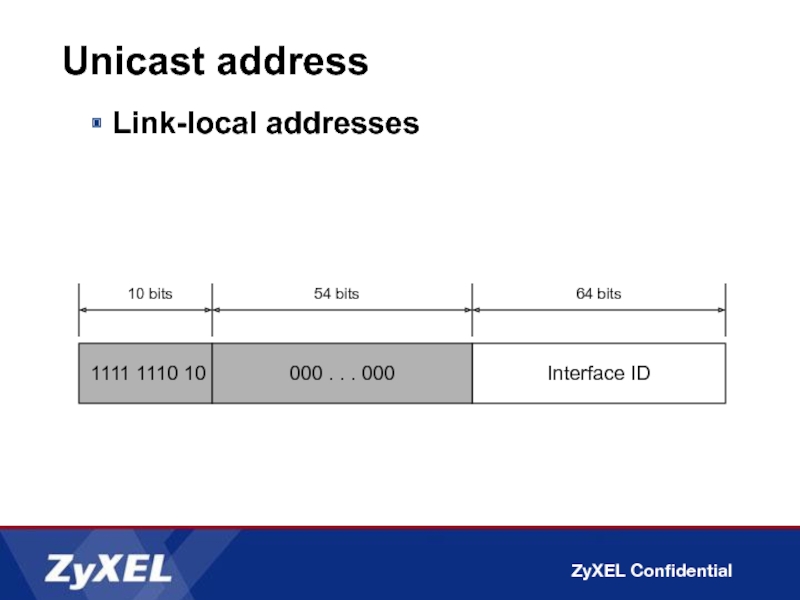
Link-local addresses
Used between on-link neighbors and for Neighbor Discovery
Format
FE80::/64 prefix
Used for local link only
Single subnet, no router
Address autoconfiguration
Neighbor Discovery
Слайд 18Unicast address
Link-local addresses
1111 1110 10
Interface ID
10 bits
64 bits
000 . . .
54 bits
Слайд 19Unicast address
Site-local addresses
Used between nodes in the same site
Format Prefix
FEC0::/48 prefix for site
Used for local site only
Replacement for IPv4 private addresses
Intranets not connected to the Internet
Routers do not forward site-local traffic outside the site
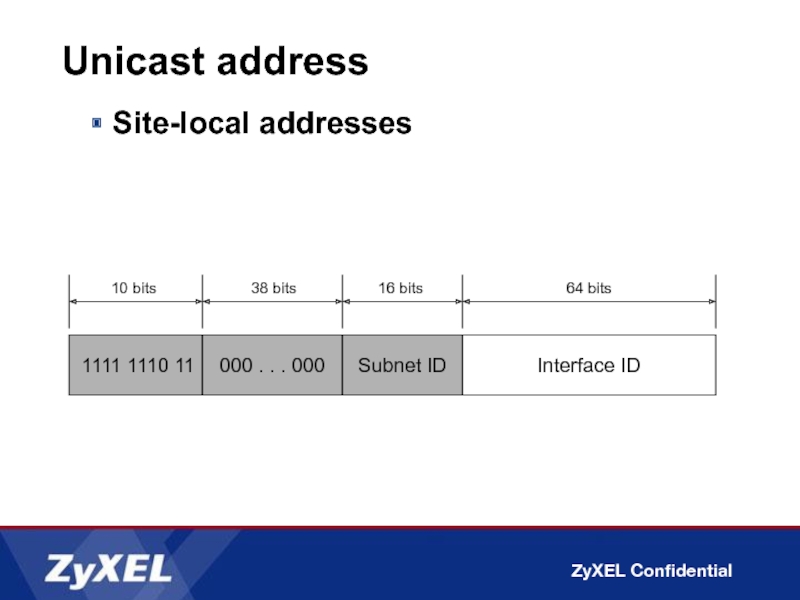
Слайд 20Unicast address
Site-local addresses
1111 1110 11
Interface ID
10 bits
64 bits
000 . . .
38 bits
Subnet ID
16 bits
Слайд 21Unicast address
Special addresses
Unspecified address
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 or ::
Loopback address
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 or ::1
Слайд 22Unicast address
Compatibility Addresses
IPv4-compatible address
0:0:0:0:0:0:w.x.y.z or ::w.x.y.z
IPv4-mapped address
0:0:0:0:0:FFFF:w.x.y.z or ::FFFF:w.x.y.z
6over4 address
[64-bit prefix]:0:0:WWXX:YYZZ
6to4 address
2002:WWXX:YYZZ:[SLA ID]:[Interface ID]
ISATAP address
Interface ID of ::0:5EFE:w.x.y.z
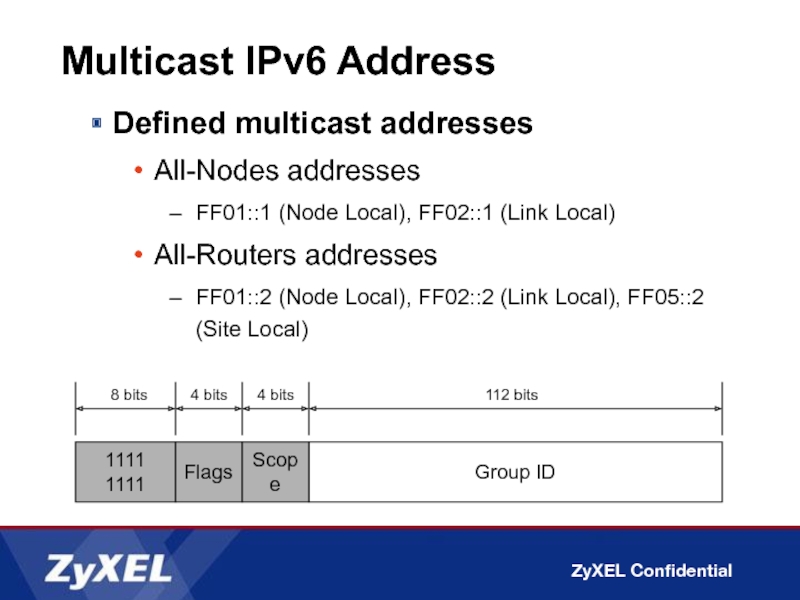
Слайд 23Multicast IPv6 Address
Defined multicast addresses
All-Nodes addresses
FF01::1 (Node Local), FF02::1 (Link Local)
All-Routers
FF01::2 (Node Local), FF02::2 (Link Local), FF05::2 (Site Local)
1111 1111
Group ID
8 bits
112 bits
Flags
4 bits
Scope
4 bits
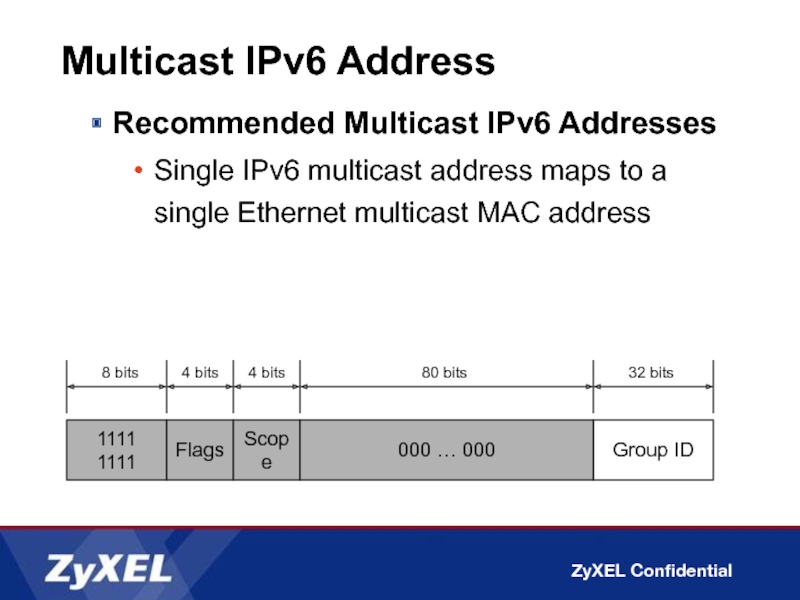
Слайд 25Multicast IPv6 Address
Recommended Multicast IPv6 Addresses
Single IPv6 multicast address maps to
1111 1111
Group ID
8 bits
32 bits
Flags
4 bits
Scope
4 bits
80 bits
000 … 000
Слайд 26Multicast IPv6 Address
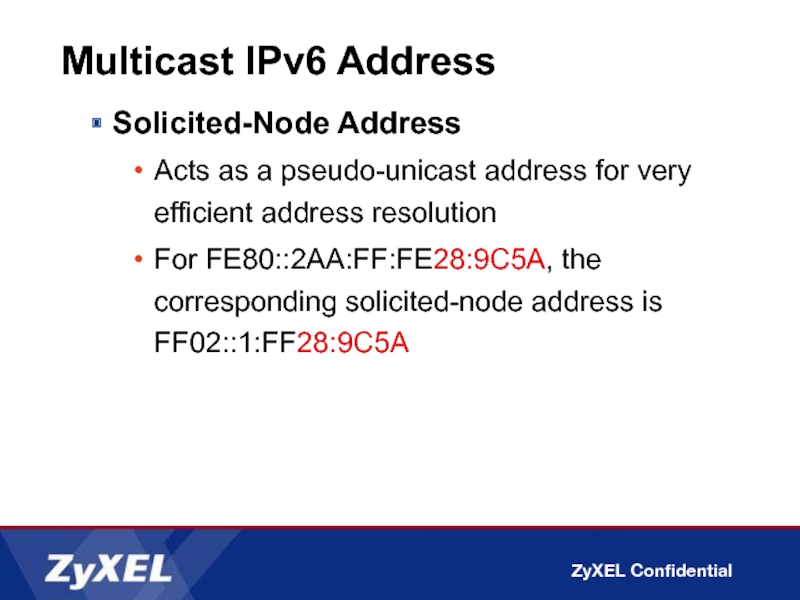
Solicited-Node Address
Acts as a pseudo-unicast address for very efficient
For FE80::2AA:FF:FE28:9C5A, the corresponding solicited-node address is FF02::1:FF28:9C5A
Слайд 27Multicast IPv6 Address
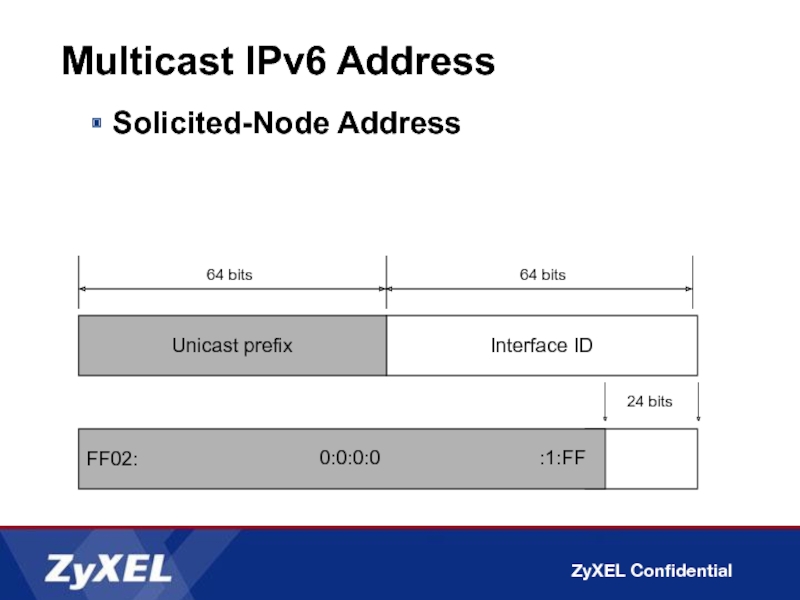
Solicited-Node Address
Interface ID
64 bits
Unicast prefix
64 bits
FF02:
24 bits
:1:FF
0:0:0:0
Слайд 28Anycast IPv6 Address
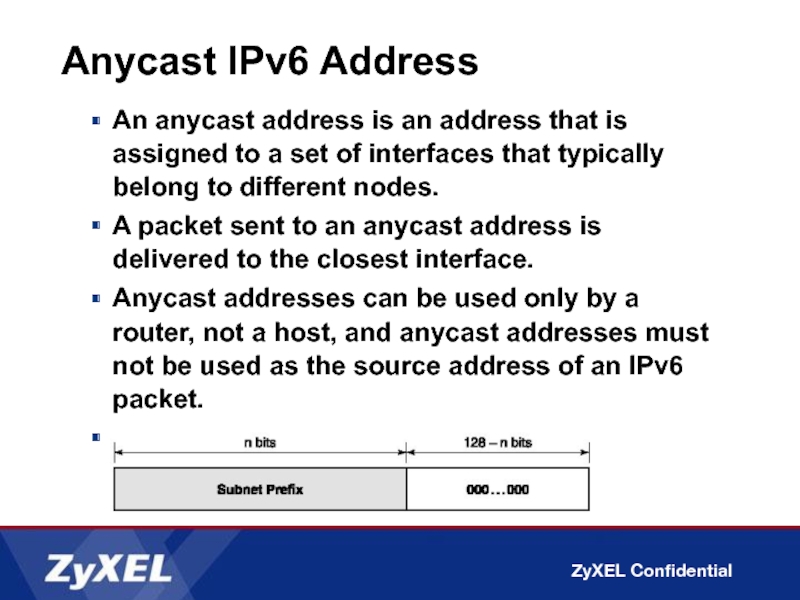
An anycast address is an address that is assigned
A packet sent to an anycast address is delivered to the closest interface.
Anycast addresses can be used only by a router, not a host, and anycast addresses must not be used as the source address of an IPv6 packet.
Subnet router anycast address
Слайд 29IPv6 Addresses Application
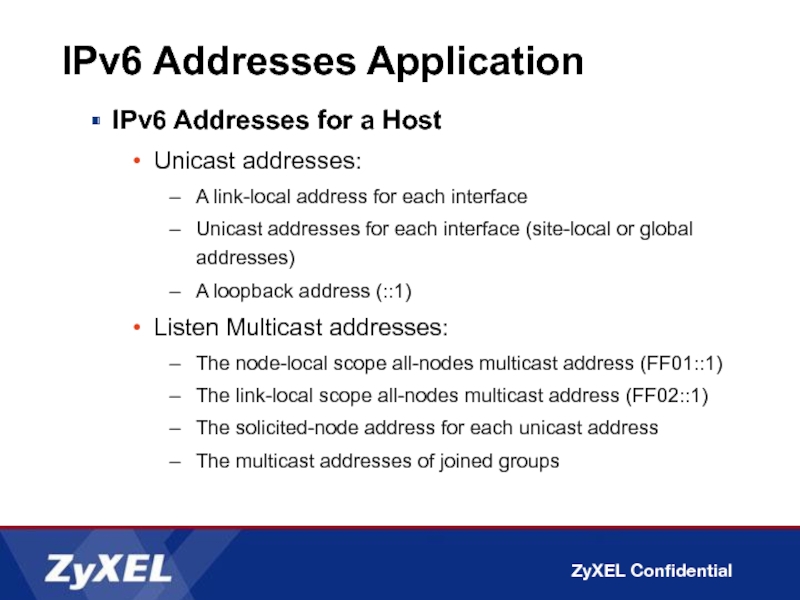
IPv6 Addresses for a Host
Unicast addresses:
A link-local address for
Unicast addresses for each interface (site-local or global addresses)
A loopback address (::1)
Listen Multicast addresses:
The node-local scope all-nodes multicast address (FF01::1)
The link-local scope all-nodes multicast address (FF02::1)
The solicited-node address for each unicast address
The multicast addresses of joined groups
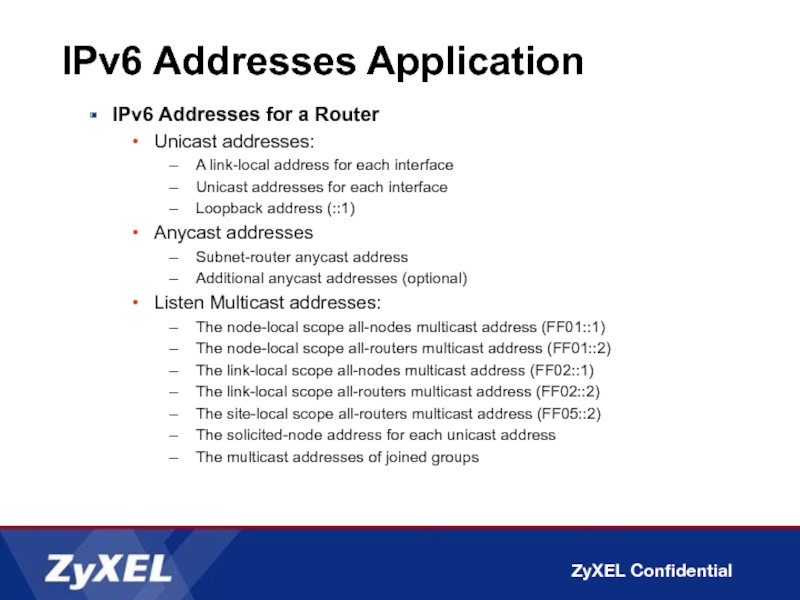
Слайд 30IPv6 Addresses Application
IPv6 Addresses for a Router
Unicast addresses:
A link-local address for
Unicast addresses for each interface
Loopback address (::1)
Anycast addresses
Subnet-router anycast address
Additional anycast addresses (optional)
Listen Multicast addresses:
The node-local scope all-nodes multicast address (FF01::1)
The node-local scope all-routers multicast address (FF01::2)
The link-local scope all-nodes multicast address (FF02::1)
The link-local scope all-routers multicast address (FF02::2)
The site-local scope all-routers multicast address (FF05::2)
The solicited-node address for each unicast address
The multicast addresses of joined groups
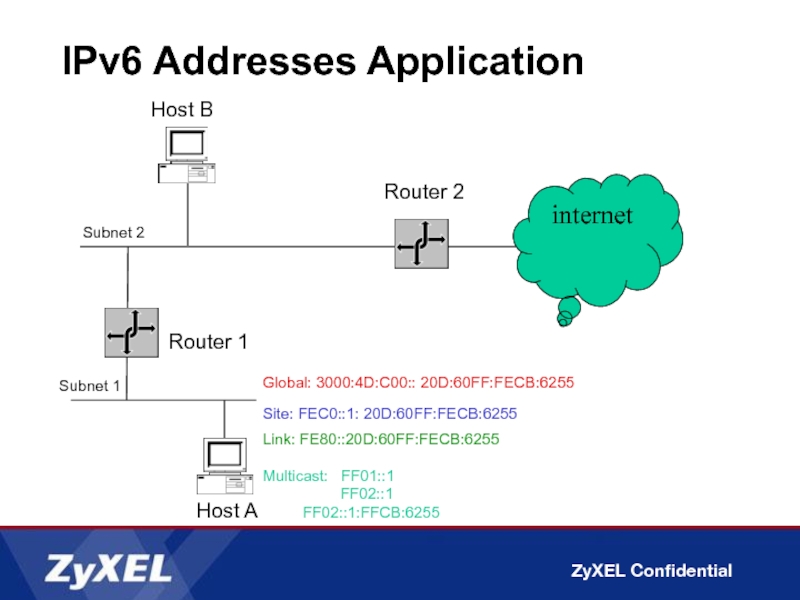
Слайд 31IPv6 Addresses Application
Router 1
Subnet 2
Subnet 1
Router 2
Host A
Host B
Site: FEC0::1: 20D:60FF:FECB:6255
Link:
Multicast: FF01::1
FF02::1
FF02::1:FFCB:6255
internet
Global: 3000:4D:C00:: 20D:60FF:FECB:6255
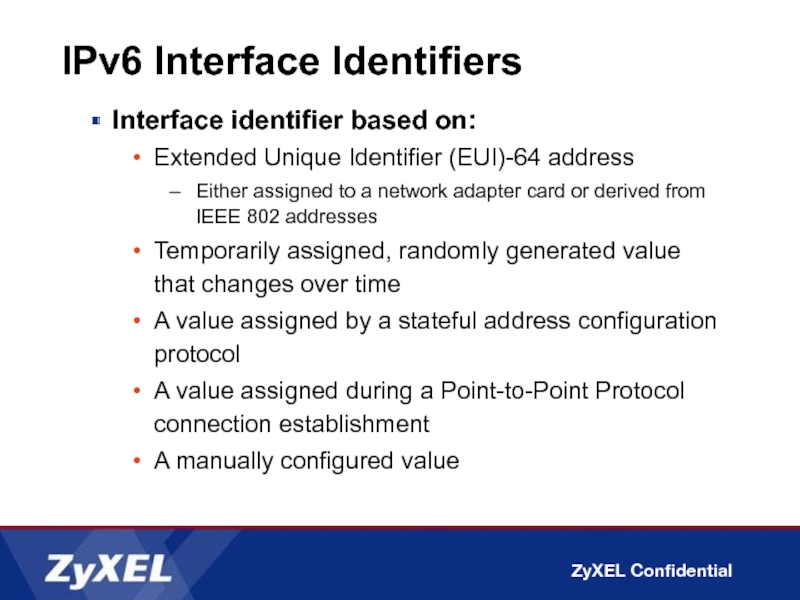
Слайд 32IPv6 Interface Identifiers
Interface identifier based on:
Extended Unique Identifier (EUI)-64 address
Either assigned
Temporarily assigned, randomly generated value that changes over time
A value assigned by a stateful address configuration protocol
A value assigned during a Point-to-Point Protocol connection establishment
A manually configured value
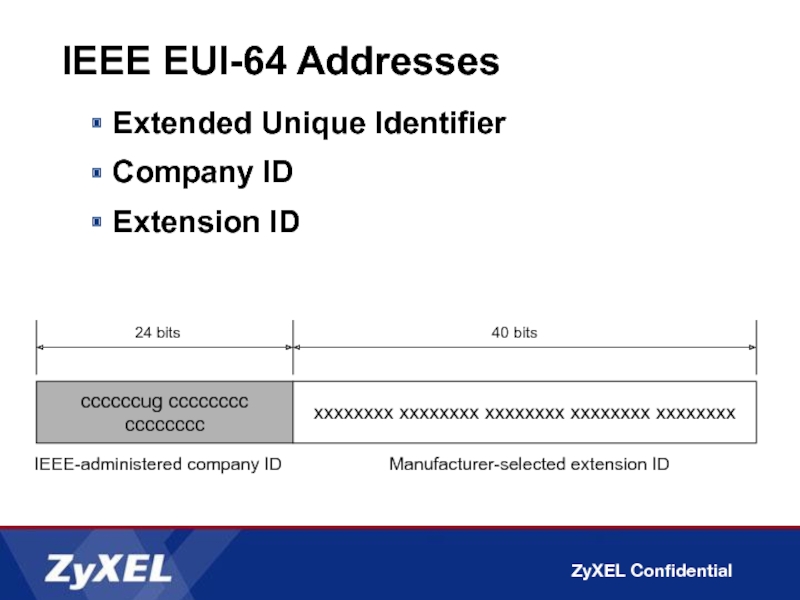
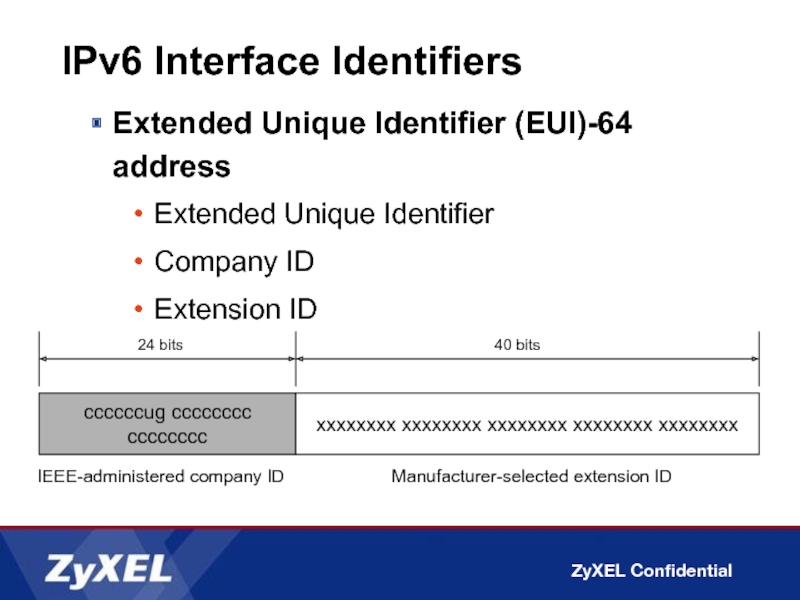
Слайд 34IPv6 Interface Identifiers
Extended Unique Identifier (EUI)-64 address
Extended Unique Identifier
Company ID
Extension ID
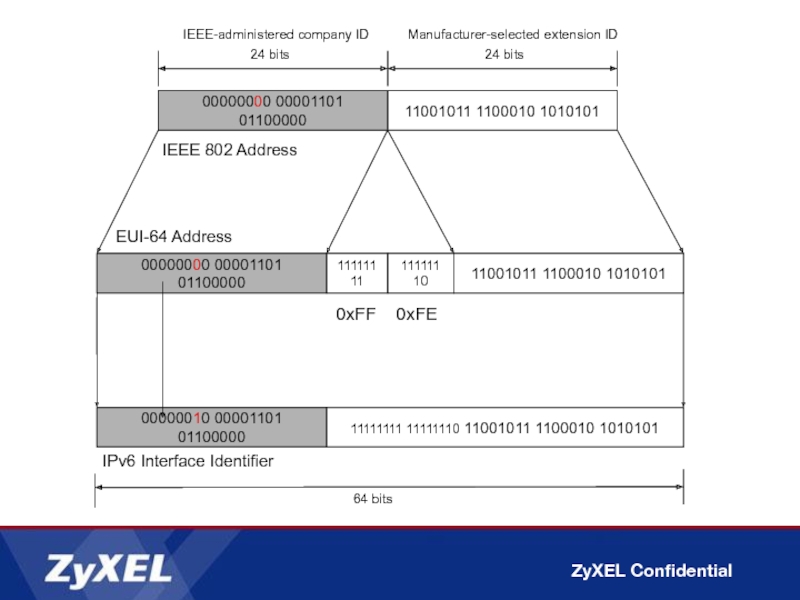
Слайд 35Conversion of an IEEE 802 Address to an EUI-64 Address
Host A
1. Convert to EUI-64 format
00-0D-60-FF-FE-CB-62-55
2. Complement the U/L bit
The first byte in binary form is 00000000. When the seventh bit is complemented, it becomes 00000010 (0x02).
Result is 02-0D-60-FF-FE-CB-62-55
3. Convert to colon hexadecimal notation
20D:60FF:FECB:6255
Link-local address for node with the MAC address of 00-0D-60-CB-62-55 is FE80:: 20D:60FF:FECB:6255.
Слайд 3600000000 00001101 01100000
11001011 1100010 1010101
11111111
11111110
0xFF
0xFE
EUI-64 Address
00000000 00001101 01100000
24 bits
24 bits
11001011 1100010
IEEE-administered company ID
Manufacturer-selected extension ID
IEEE 802 Address
00000010 00001101 01100000
64 bits
11111111 11111110 11001011 1100010 1010101
IPv6 Interface Identifier
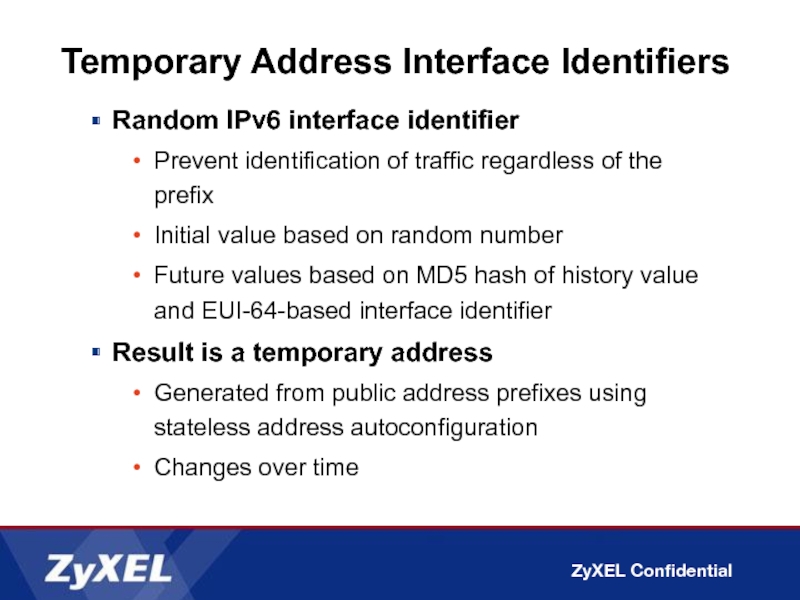
Слайд 37Temporary Address Interface Identifiers
Random IPv6 interface identifier
Prevent identification of traffic regardless
Initial value based on random number
Future values based on MD5 hash of history value and EUI-64-based interface identifier
Result is a temporary address
Generated from public address prefixes using stateless address autoconfiguration
Changes over time
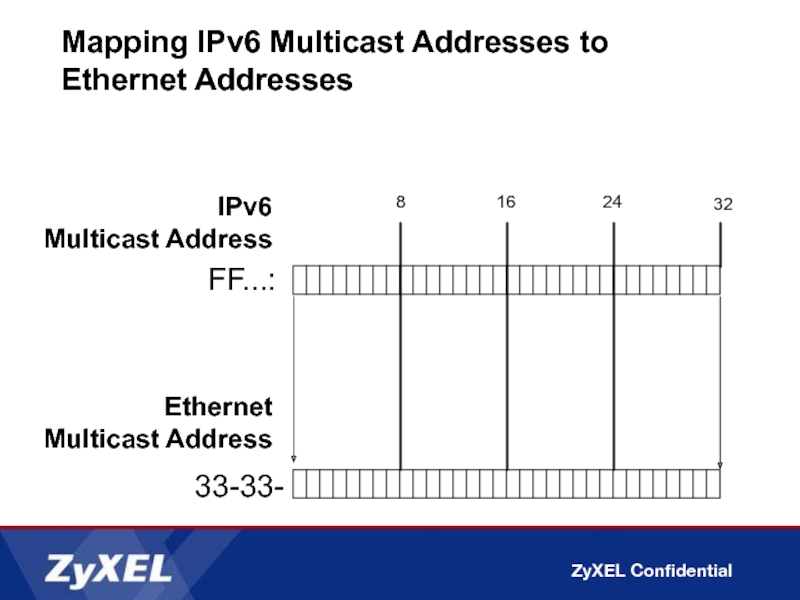
Слайд 38IPv6
Multicast Address
33-33-
8
16
24
32
FF...:
Ethernet
Multicast Address
Mapping IPv6 Multicast Addresses to Ethernet
Слайд 39IPv6 Addresses Application
Router 1
Subnet 2
Subnet 1
Router 2
Host A
Host B
Site: FEC0::1: 20D:60FF:FECB:6255
Link:
Multicast: FF01::1
FF02::1
FF02::1:FFCB:6255
internet
Global: 3000:4D:C00:: 20D:60FF:FECB:6255
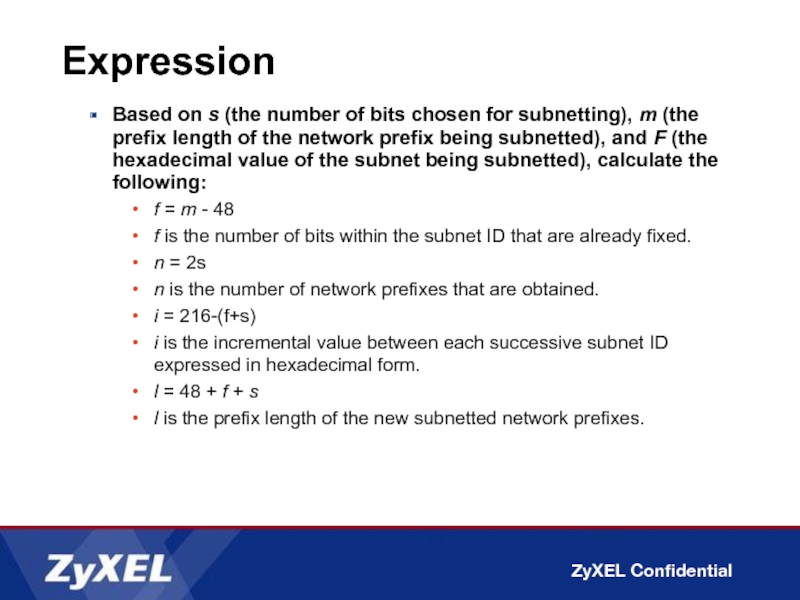
Слайд 42Expression
Based on s (the number of bits chosen for subnetting), m
f = m - 48
f is the number of bits within the subnet ID that are already fixed.
n = 2s
n is the number of network prefixes that are obtained.
i = 216-(f+s)
i is the incremental value between each successive subnet ID expressed in hexadecimal form.
l = 48 + f + s
l is the prefix length of the new subnetted network prefixes.
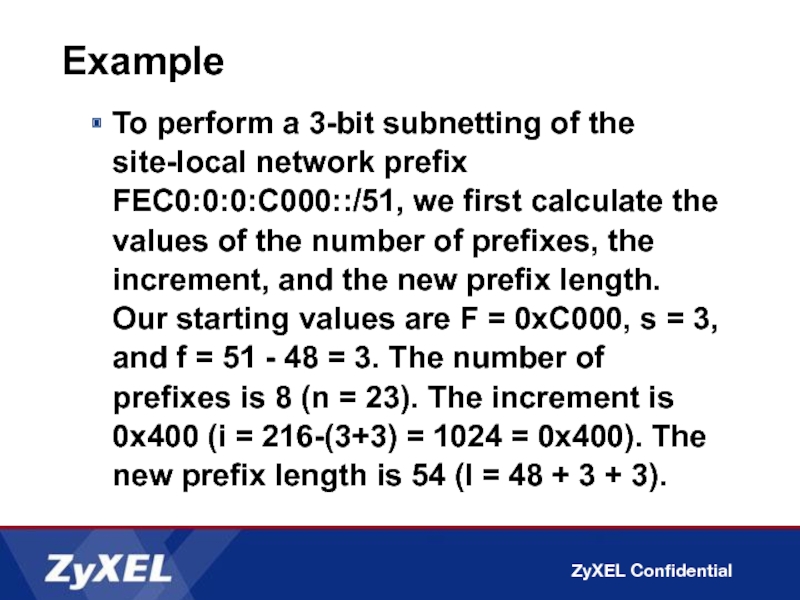
Слайд 43Example
To perform a 3-bit subnetting of the site-local network prefix FEC0:0:0:C000::/51,
Слайд 45
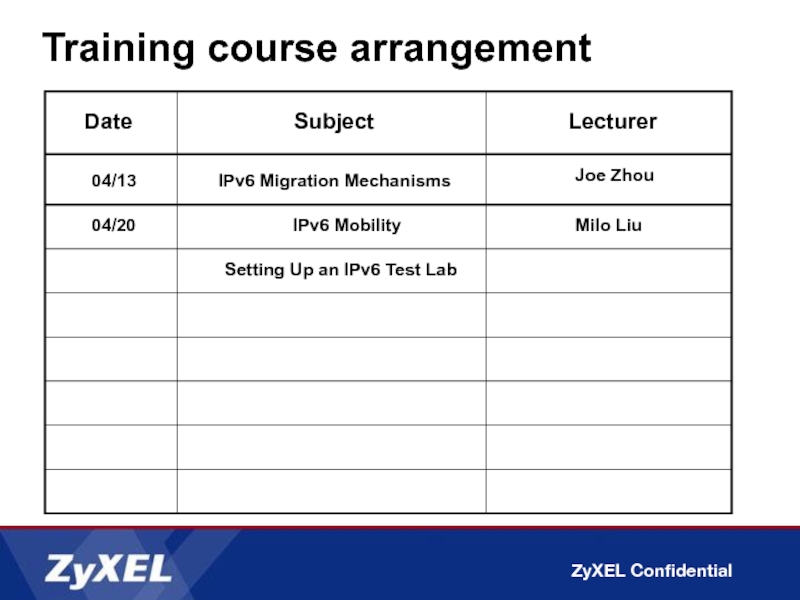
Date
Subject
Lecturer
Introduction to IPv6
IPv6 Addressing
IPv6 Header & Extensions
Neighbor Discovery Protocol
Multicast Listener Discovery
IPv6
ICMPv6
Address Autoconfigurator
Joe Zhao
Milo Liu
Joe Zhao
Feng Zhou
Billy Bian
Jeffrey Zhou
Feng Zhou
Milo Liu
03/10
03/16
03/23
03/23
03/30
03/30
04/06
04/06
Training course arrangement







![Unicast addressCompatibility AddressesIPv4-compatible address0:0:0:0:0:0:w.x.y.z or ::w.x.y.zIPv4-mapped address0:0:0:0:0:FFFF:w.x.y.z or ::FFFF:w.x.y.z6over4 address[64-bit prefix]:0:0:WWXX:YYZZ 6to4 address2002:WWXX:YYZZ:[SLA ID]:[Interface ID]ISATAP](/img/tmb/6/511089/b6122a597101442594d542a30d7df80a-800x.jpg)

![Subnetting the IPv6 Address SpaceSubnetting for NLA IDs[16-bit prefix]:00frs](/img/tmb/6/511089/d8a88814e28cbabf794c6e8454130fb8-800x.jpg)
![Subnetting the IPv6 Address SpaceSubnetting for SLA IDs[48-bit prefix]:::fsr](/img/tmb/6/511089/f6f88cdc7d47a5331e10f56807b052cb-800x.jpg)