- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Contemporary HRM. Training and Development презентация
Содержание
- 1. Contemporary HRM. Training and Development
- 2. Session plan… Definitions and differentiations Knowledge
- 3. Session objectives… By the end of this
- 4. Definitions… Learning Training Development What do these terms mean to you?
- 5. Definitions… Learning: ‘a qualitative change in a
- 6. Human resource development… ‘The procedures and processes
- 7. Discussion questions: For what reasons is
- 8. Three levels of learning needs… Organisational General
- 9. Context.. Increase in ICT and AI –
- 10. Skills and jobs… The ability to work
- 11. However… Who has responsibility? Many organisations
- 12. UK skills situation… The World Economic Forum’s
- 13. The organisational level… Successful employers view investing
- 14. The individual level… Those getting on Those
- 15. Changing emphasis – personal qualities and generic
- 16. Discussion question: What organisational risks are there of identifying generic lists of skills/competencies?
- 17. Training and learning… Training as a
- 18. The learning process… Learning theories: Behaviourism Cognitivism Constructivism Experiential learning
- 19. Behaviourism… Key Figures: Pavlov (1927); Skinner (1953)
- 20. Cognitivism… Knowledge is organised into structures –
- 21. Constructivism… Knowledge is internal to the individual
- 22. Think about an excellent personal learning experience…
- 23. Experiential learning… Honey and Mumford’s learning styles
- 24. Experiential learning… Key Figure: Kolb (1984) Learning
- 25. Group discussion: Which is your preferred learning
- 26. Systematic Training Cycle (Foot and Hook, 2005:209)…
- 27. Assessing training needs… A training need exists
- 28. Identifying a training gap…
- 29. Designing training programmes… Establish overall aims
- 30. Writing learning objectives… Objectives should be SMART(ER): S………… M………… A………… R………… T………… E………… R…………
- 31. Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Objectives (1956)…
- 32. % of what we remember when we…
- 33. Learning/training methods…
- 34. The (new) global classroom…
- 35. Pause for thought Google – 1998 Wikipedia
- 36. Purpose of learning technology? Communication Instruction Training Learning Development Learning how to learn?
- 37. Example virtual environments… Simulations Serious Games
- 38. Game created to give students a more interactive experience in developing disaster victim identification
- 42. Group discussion, ‘virtual learning’... What does
- 43. Key considerations Clarity on organization and
- 44. Instruction Programmed Scripted Directive (Source:
- 45. Evaluating training… ‘A process to identify
- 46. Kirkpatrick (1956), cited in Foot and Hook
- 47. Evaluation methods… Feedback form One-to-one discussions Focus
- 48. Trends in learning and development… Linking learning
- 49. Group activity: Design a short
- 50. Some conclusions… Training is important for the
Слайд 1Contemporary HRM
Training and Development
Dr Kirsteen Grant
K.Grant@napier.ac.uk
Room 2.38, Craiglockhart
Слайд 2Session plan…
Definitions and differentiations
Knowledge and skill (national, organisational and individual levels)
Learning
theories and learning styles
Systematic training cycle
Trends in learning and development
Practical exercise
Systematic training cycle
Trends in learning and development
Practical exercise
Слайд 3Session objectives…
By the end of this session you will be able
to:
Critically examine the importance of and different approaches to learning, training and development
Analyse and apply the stages in the systematic training cycle
Discuss current trends, issues and controversies within learning and development
Critically examine the importance of and different approaches to learning, training and development
Analyse and apply the stages in the systematic training cycle
Discuss current trends, issues and controversies within learning and development
Слайд 5Definitions…
Learning: ‘a qualitative change in a person’s way of seeing, experiencing,
understanding and conceptualising something in the real world (Marton and Ramsden, 1988; in Harrison, 2005:xx)
Training: ‘a narrower concept and usually involves planned instructional activities, or other developmental activities and processes’ (Foot and Hook, 2005:228)
Development: ‘a process of becoming increasingly complex, more elaborate by virtue of learning and maturation’ (Beardwell and Claydon, 2007:266). ‘Changes in the whole person and what they can do’ (Banfield and Kay, 2007:240)
Training: ‘a narrower concept and usually involves planned instructional activities, or other developmental activities and processes’ (Foot and Hook, 2005:228)
Development: ‘a process of becoming increasingly complex, more elaborate by virtue of learning and maturation’ (Beardwell and Claydon, 2007:266). ‘Changes in the whole person and what they can do’ (Banfield and Kay, 2007:240)
Слайд 6Human resource development…
‘The procedures and processes that purposely seek to provide
learning activities to enhance the skills, knowledge and capabilities of people, teams and the organisation so that there is a change in action to achieve the desired outcomes’
(Bratton and Gold, 2007:306).
(Bratton and Gold, 2007:306).
Слайд 7Discussion questions:
For what reasons is learning important to individuals and organisations?
How can individuals’ learning can be turned into organisational learning?
How does learning thence impact on organisational performance?
What are the individual and organisational barriers to learning, training and development?
Слайд 8Three levels of learning needs…
Organisational
General weakness, issue or gap in the
organisation where learning is required; often generated by change.
Occupational
Skills, knowledge or attitudes required for different specialisms and/or professional institutes.
Individual
Gaps in skills, knowledge and/or attitude.
Occupational
Skills, knowledge or attitudes required for different specialisms and/or professional institutes.
Individual
Gaps in skills, knowledge and/or attitude.
Слайд 9Context..
Increase in ICT and AI – less knowledge required?
Employers in industry
concerned about lack of basic and soft skills; not lack of ‘smart knowledge’
Universities focusing on skills development as well as knowledge development (employability)
Knowing how to does not = being able to do it (knowledge v competence)
Universities focusing on skills development as well as knowledge development (employability)
Knowing how to does not = being able to do it (knowledge v competence)
Слайд 10Skills and jobs…
The ability to work to the required standard in
employment and practice
Low skill v high skill jobs
Economic implications
Low skill jobs = low skill economy = few driving forces to develop human potential
High skill jobs = substantial and sustained development
(Grant et al., 2014)
Low skill v high skill jobs
Economic implications
Low skill jobs = low skill economy = few driving forces to develop human potential
High skill jobs = substantial and sustained development
(Grant et al., 2014)
Слайд 11However…
Who has responsibility?
Many organisations are not interested in up-skilling beyond what
the job requires/ for other organisations/ or for society in general.
Слайд 12UK skills situation…
The World Economic Forum’s Global Competitiveness Index (2016/17) ranks
the UK as 7th
There is regularly updated data on the UK’s relative performance in investment, innovation, skills, enterprise and competition (the five drivers of productivity)
Leitch Report 2006:
Gaps due to relatively poor skills in UK
Skills for Scotland (2007; 2010) – UK productivity gap
There is regularly updated data on the UK’s relative performance in investment, innovation, skills, enterprise and competition (the five drivers of productivity)
Leitch Report 2006:
Gaps due to relatively poor skills in UK
Skills for Scotland (2007; 2010) – UK productivity gap
Слайд 13The organisational level…
Successful employers view investing in skills as one of
the most powerful things to do to gain competitive advantage
But:
There is a need to create a culture in which employees consider improving their skills to be one of the most important things they can do to realise their career aspirations
Employees need to take ownership of their skills and development
But:
There is a need to create a culture in which employees consider improving their skills to be one of the most important things they can do to realise their career aspirations
Employees need to take ownership of their skills and development
Слайд 14The individual level…
Those getting on
Those getting by
Those getting nowhere
Depends on:
Education
Motivation levels
Participation
levels
Opportunities and resources
Opportunities and resources
Слайд 15Changing emphasis – personal qualities and generic skills…
Skills are increasingly being
defined in attitudinal, even emotional, terms.
Competency-based approaches:
Communication
Problem solving
Team working
Improving personal learning
Judgement
Leadership
Initiative
Emotional Intelligence (Goleman, 1999)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YQqyeWBZrLQ
Competency-based approaches:
Communication
Problem solving
Team working
Improving personal learning
Judgement
Leadership
Initiative
Emotional Intelligence (Goleman, 1999)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YQqyeWBZrLQ
Слайд 16Discussion question:
What organisational risks are there of identifying generic lists of
skills/competencies?
Слайд 17Training and learning…
Training as a product
We all learn differently
We learn every
day
Learning affects our behaviour
Reflective practice is important
Learning affects our behaviour
Reflective practice is important
Learning as a process, rather than a product
Слайд 18The learning process…
Learning theories:
Behaviourism
Cognitivism
Constructivism
Experiential learning
Слайд 19Behaviourism…
Key Figures: Pavlov (1927); Skinner (1953)
Related to objective, observed behaviour
We
learn by conditioning
Use of reinforcement to indicate a correct behavioural response (reward and punishment)
Use of reinforcement to indicate a correct behavioural response (reward and punishment)
Слайд 20Cognitivism…
Knowledge is organised into structures – new experience and prior experience
must overlap
Learning as information processing
Learning as information processing
Слайд 21Constructivism…
Knowledge is internal to the individual and is created by personally
constructing meaning out of experience within social/ work environments
Learning occurs in a dynamic interaction between the individual and their environment
Learning occurs in a dynamic interaction between the individual and their environment
Слайд 22Think about an excellent personal learning experience…
What did you learn?
How did
you learn it?
Why and how was the learning effective for you?
Why and how was the learning effective for you?
Слайд 23Experiential learning…
Honey and Mumford’s learning styles questionnaire:
Activists: ‘Doing’ people: Enthusiastic –
tend to be involved in generating new ideas – action oriented – act first, consider consequences later
Reflectors: ‘Reflective’ people: Stand back and observe experiences, avoid reaching conclusions for as long as possible. Sometimes take back seat
Theorists: ‘Theory’ people: Try to understand and predict behaviour – produce step-by-step analysis. Value rationality and logic
Pragmatists: ‘Move on’ people: Always planning next step, keen to try out new ideas, eager to try out new things. Act quickly and confidently on ideas. Hate long discussions
Reflectors: ‘Reflective’ people: Stand back and observe experiences, avoid reaching conclusions for as long as possible. Sometimes take back seat
Theorists: ‘Theory’ people: Try to understand and predict behaviour – produce step-by-step analysis. Value rationality and logic
Pragmatists: ‘Move on’ people: Always planning next step, keen to try out new ideas, eager to try out new things. Act quickly and confidently on ideas. Hate long discussions
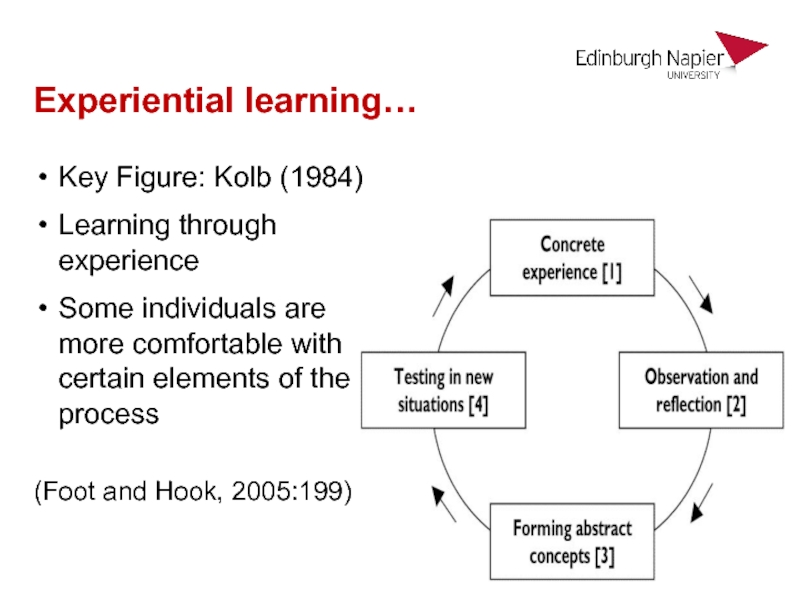
Слайд 24Experiential learning…
Key Figure: Kolb (1984)
Learning through experience
Some individuals are more comfortable
with certain elements of the process
(Foot and Hook, 2005:199)
(Foot and Hook, 2005:199)
Слайд 25Group discussion:
Which is your preferred learning style?
How can this help you
to understand the learning activities that are more effective for you?
Can you identify any barriers to learning?
Can you identify any barriers to learning?
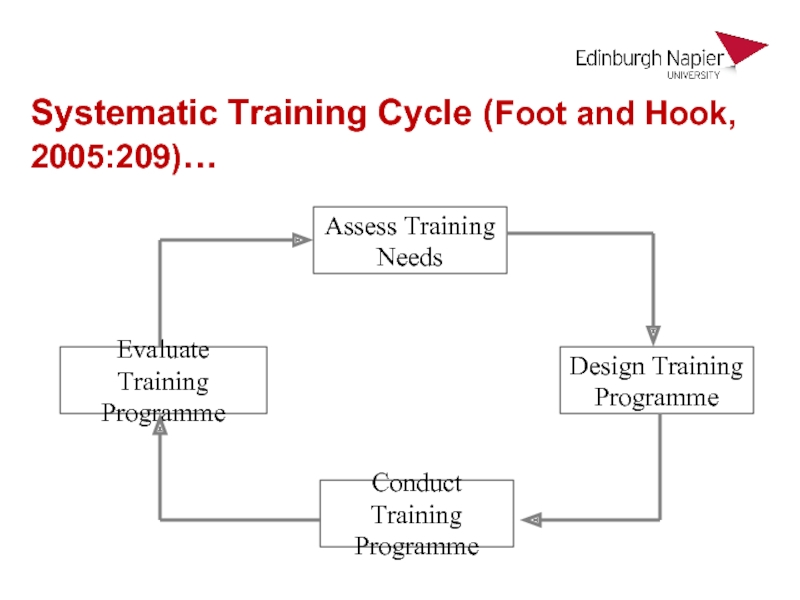
Слайд 26Systematic Training Cycle (Foot and Hook, 2005:209)…
Assess Training
Needs
Design Training
Programme
Conduct Training
Programme
Evaluate
Training
Programme
Programme
Слайд 27Assessing training needs…
A training need exists when there is a gap
between present skills and knowledge of employees and skills and knowledge they require for effective performance
Training needs arise for three reasons:
Job changes
Person changes
Performance deficiencies
Training needs arise for three reasons:
Job changes
Person changes
Performance deficiencies
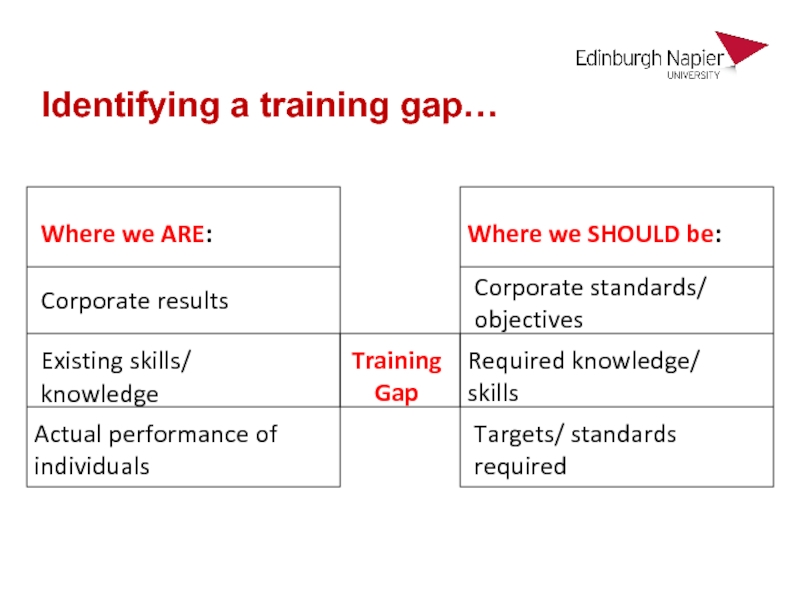
Слайд 28Identifying a training gap…
Where we ARE:
Where we SHOULD be:
Corporate results
Existing skills/
knowledge
Corporate
standards/ objectives
Targets/ standards required
Required knowledge/ skills
Actual performance of individuals
Training Gap
Слайд 29Designing training programmes…
Establish overall aims and learning outcomes for the programme
Entry
behaviours and learner analysis – learning styles
Design appropriate assessment instruments
Choose an training strategy and method(s)
Consider learning transfer
Design evaluation strategy (positioning)?
Design appropriate assessment instruments
Choose an training strategy and method(s)
Consider learning transfer
Design evaluation strategy (positioning)?
Слайд 30Writing learning objectives…
Objectives should be SMART(ER):
S…………
M…………
A…………
R…………
T…………
E…………
R…………
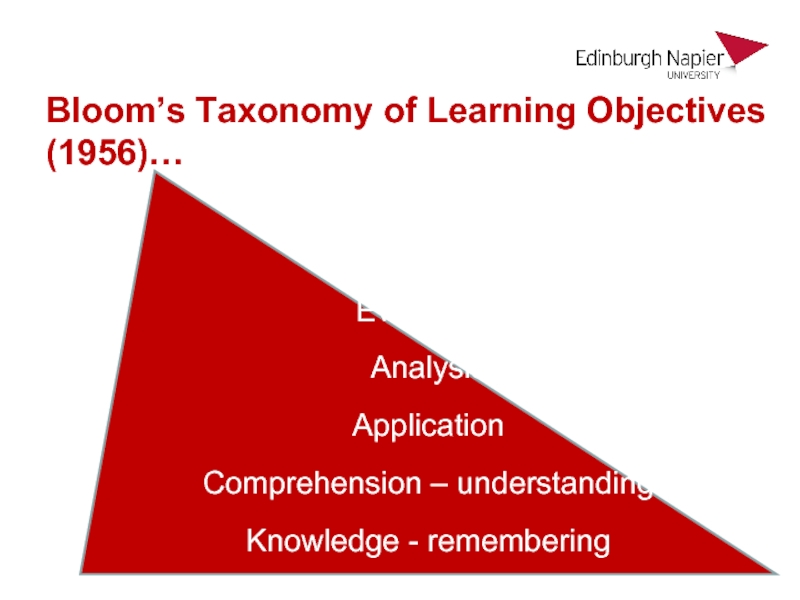
Слайд 31Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Objectives (1956)…
Creating
Evaluation
Analysis
Application
Comprehension – understanding
Knowledge - remembering
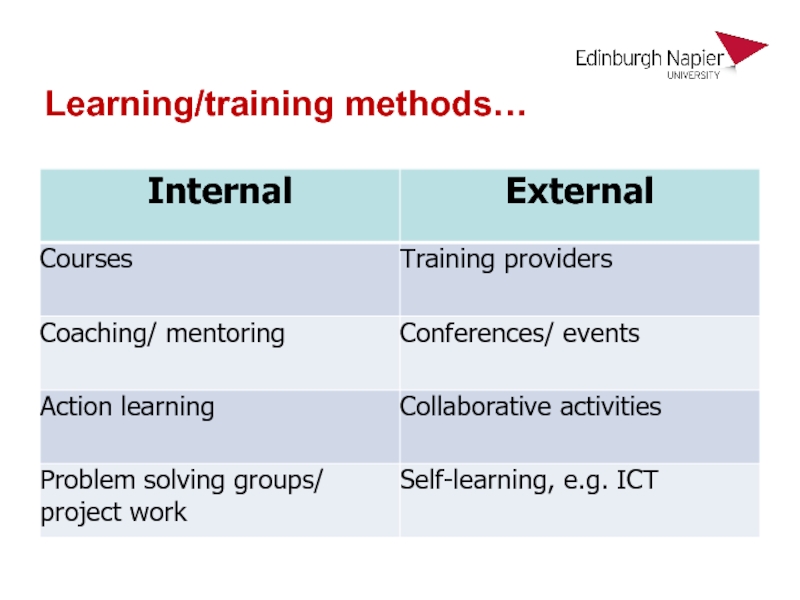
Слайд 32% of what we remember when we…
Based on Dr Vernon Magnesen,University
of Texas, cited in Colin Rose, Master it Faster (The Industrial Society, 2000).
Слайд 35Pause for thought
Google – 1998
Wikipedia – 2001
LinkedIn – 2003
Facebook – 2004
Youtube
– 2005
Twitter – 2006
Pinterest and Instagram – 2010
Snapchat – 2011
Tinder – 2012
Periscope – 2015
Twitter – 2006
Pinterest and Instagram – 2010
Snapchat – 2011
Tinder – 2012
Periscope – 2015
Слайд 36Purpose of learning technology?
Communication
Instruction
Training
Learning
Development
Learning how to learn?
Слайд 37Example virtual environments…
Simulations
Serious Games
Virtual Operational Meetings
Virtual Conferences and Exhibitions
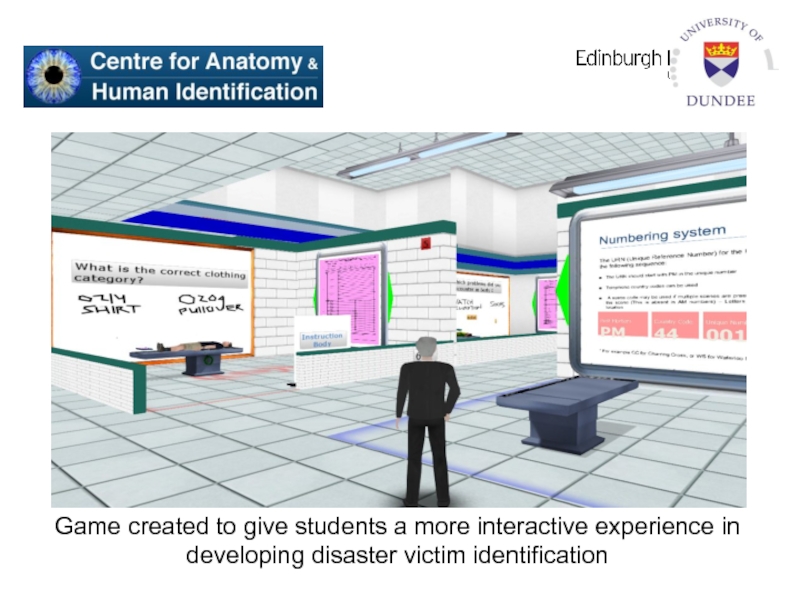
Слайд 38Game created to give students a more interactive experience in developing
disaster victim identification
Слайд 42Group discussion, ‘virtual learning’...
What does the future virtual landscape look
like?
Implications for learning and training?
Mobile learning
Social media
Opportunities and barriers
Implications for learning and training?
Mobile learning
Social media
Opportunities and barriers
Слайд 43Key considerations
Clarity on organization and learner needs and expectations?
Organization culture
Resource
implications
Facilitator and learner competency
Training or learning? Formal or informal?
Equality and inclusion
How to monitor (control?)
How to evaluate – and why!
Technological capability
Facilitator and learner competency
Training or learning? Formal or informal?
Equality and inclusion
How to monitor (control?)
How to evaluate – and why!
Technological capability
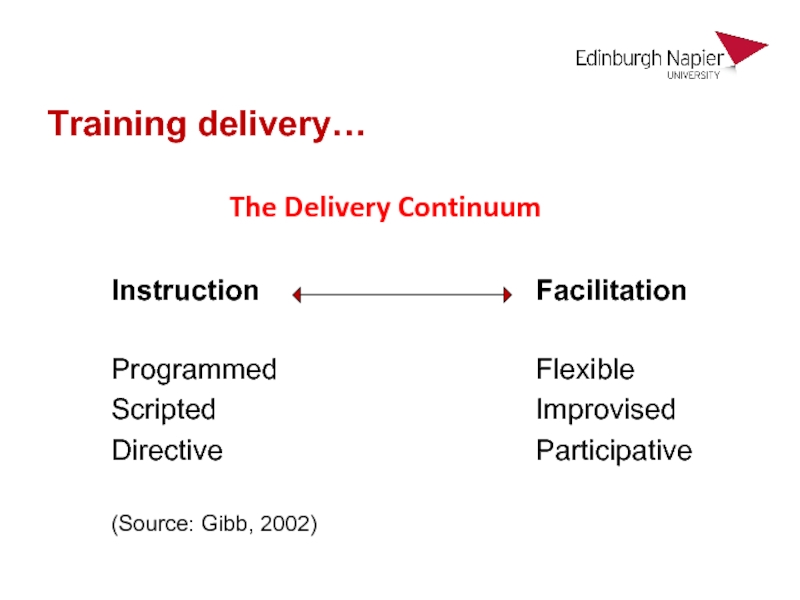
Слайд 44Instruction
Programmed
Scripted
Directive
(Source: Gibb, 2002)
Facilitation
Flexible
Improvised
Participative
Training delivery…
The Delivery Continuum
Слайд 45Evaluating training…
‘A process to identify the total value of a learning
event or process, thereby placing it into its organisational context and aiding future planning’ (Harrison, 2005:143).
Слайд 46Kirkpatrick (1956), cited in Foot and Hook (2005:218)…
Reaction – immediate impressions
– ‘happy sheet’
Learning – have training objectives been met? Assessment
Behaviour – has the trainee’s performance improved? (Performance appraisal)
Results – has the ‘new’ performance produced improved results overall? (RoI)
Learning – have training objectives been met? Assessment
Behaviour – has the trainee’s performance improved? (Performance appraisal)
Results – has the ‘new’ performance produced improved results overall? (RoI)
Слайд 47Evaluation methods…
Feedback form
One-to-one discussions
Focus groups
Individual performance review meetings
Table on agenda at
team meetings
Improvement in individual, team or organisational performance
360 degree feedback
Improvement in individual, team or organisational performance
360 degree feedback
Слайд 48Trends in learning and development…
Linking learning to strategy (strategic HRD) –
organisational learning?
Focus on learning, not training
Action learning, social learning
e-Learning and blended learning
Work-based learning – formal-informal methods
Continuing professional development (CPD)
Lifelong learning – “we need to create a culture…in which individuals see improving their skills as one of the greatest things they can do to realise their career aspirations” (Kevin Brennan, Minster for Further Education and Skills, 2009).
Focus on learning, not training
Action learning, social learning
e-Learning and blended learning
Work-based learning – formal-informal methods
Continuing professional development (CPD)
Lifelong learning – “we need to create a culture…in which individuals see improving their skills as one of the greatest things they can do to realise their career aspirations” (Kevin Brennan, Minster for Further Education and Skills, 2009).
Слайд 49
Group activity:
Design a short training intervention:
Purpose
Learning objectives
Delivery plan
Delivery methods
Evaluation method(s)
Слайд 50Some conclusions…
Training is important for the development of individual and organisational
capabilities – depends on skill levels required for jobs
Training and development is not straightforwardly a ‘good thing’ – not all training is developmental and not all development is integrated into work (Redman and Wilkinson, 2009)
Organisational (learning) culture plays a role
Studies show decline in workers’ discretion (learning transfer) (Felstead et al., 2007)
Training and development is not straightforwardly a ‘good thing’ – not all training is developmental and not all development is integrated into work (Redman and Wilkinson, 2009)
Organisational (learning) culture plays a role
Studies show decline in workers’ discretion (learning transfer) (Felstead et al., 2007)