- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Cloud 101: The Basics of Cloud Computing презентация
Содержание
- 1. Cloud 101: The Basics of Cloud Computing
- 2. This webinar is being recorded and an
- 3. Cloud Overview Cloud Infrastructure Migration Strategies &
- 4. CLOUD COMPUTING OVERVIEW
- 5. IMPORTANCE OF THE CLOUD
- 6. IMPORTANCE OF THE CLOUD
- 7. SURVEYING THE CLOUD ENVIRONMENT
- 8. HOW DID WE GET HERE?
- 9. DEFINING THE CLOUD Cloud computing is Internet-based
- 10. KEY ELEMENTS OF CLOUD SERVICES
- 11. EXAMPLE: GMAIL
- 12. AS IT TURNS OUT…GOOGLE DATA CENTERS
- 13. APPROACHING THE CLOUD Cost to Business
- 14. CLOUD IN ACTION – A CRM SOLUTION
- 15. Speed to Implement Affordability Continuous Improvement Availability
- 16. WHY SHOULD YOU CARE? Managing
- 17. Security among top 5 reasons mid-size firms
- 18. CLOUD COMPUTING INFRASTRUCTURE
- 19. DELIVERY MODELS Public Cloud Services
- 20. DELIVERY MODELS, CONT’D HOSTING OR COLO What
- 21. DELIVERY MODELS, CONT’D IaaS - SERVER What
- 22. DELIVERY MODELS, CONT’D CLOUD DESKTOP (DaaS) What
- 23. DELIVERY MODELS, CONT’D SOFTWARE aaS What is
- 24. MIGRATION STRATEGIES & BEST PRACTICES
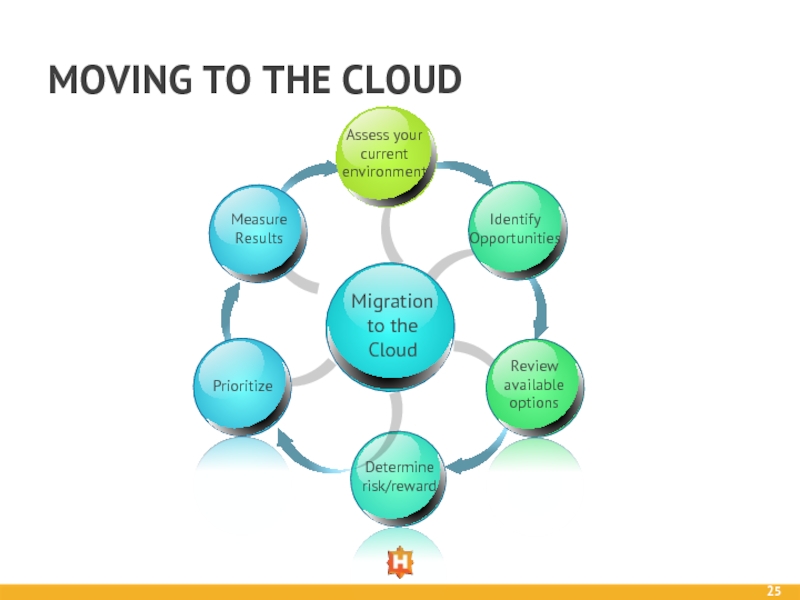
- 25. MOVING TO THE CLOUD
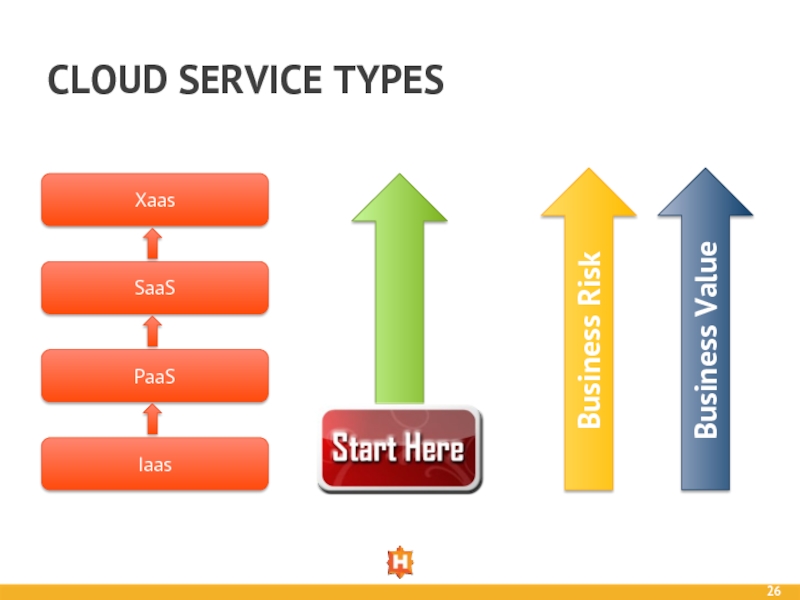
- 26. CLOUD SERVICE TYPES Business Value Business Risk
- 27. HOSTING – YOUR PARTNER TO THE CLOUD
- 28. HOSTING builds and operates high-performance clouds for business-critical operations. HOSTING’S APPROACH
- 29. When moving to a cloud-based infrastructure, consider:
- 30. The worldwide cloud computing industry is rapidly
- 31. THANK YOU! View on-demand webinar here.
- 32. Bill
Слайд 2This webinar is being recorded and an on-demand version will be
Please submit questions via the button on your screen.
On Twitter? Join the conversation: #HOSTINGspeaks, #Cloud101, @HOSTINGdotcom
HOUSEKEEPING
Слайд 3Cloud Overview
Cloud Infrastructure
Migration Strategies & Best Practices
HOSTING – Your Partner to
CLOUD 101 AGENDA
Слайд 5IMPORTANCE OF THE CLOUD
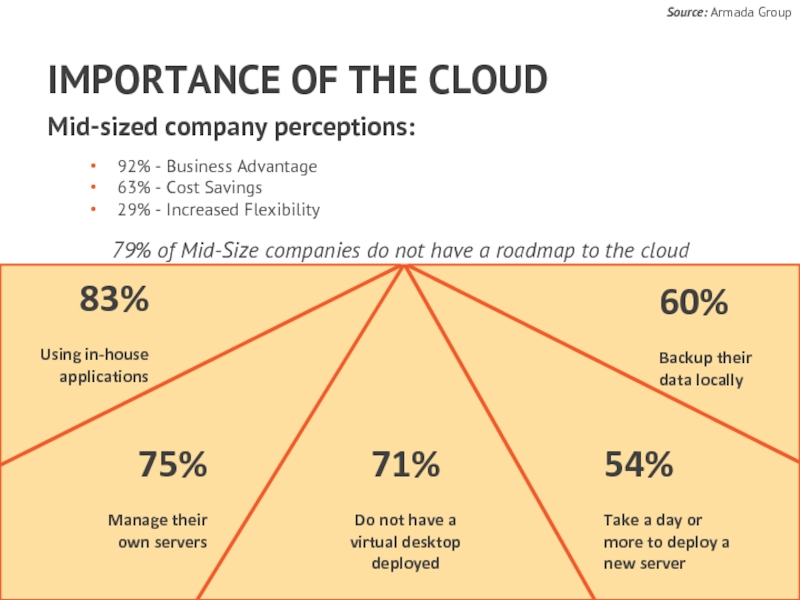
71%
Do not have a virtual desktop deployed
75%
Manage their
83%
Using in-house applications
54%
Take a day or more to deploy a new server
60%
Backup their data locally
79% of Mid-Size companies do not have a roadmap to the cloud
Mid-sized company perceptions:
92% - Business Advantage
63% - Cost Savings
29% - Increased Flexibility
Source: Armada Group
Слайд 6IMPORTANCE OF THE CLOUD
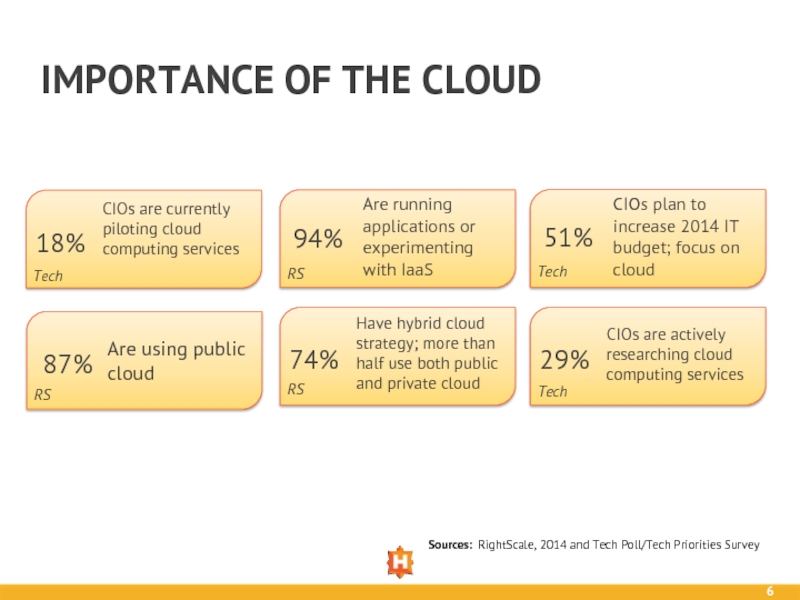
87%
94%
74%
Are using public cloud
Are running applications or experimenting
Have hybrid cloud strategy; more than half use both public and private cloud
Sources: RightScale, 2014 and Tech Poll/Tech Priorities Survey
51%
29%
CIOs plan to increase 2014 IT budget; focus on cloud
CIOs are actively researching cloud computing services
18%
CIOs are currently piloting cloud computing services
RS
RS
RS
Tech
Tech
Tech
Слайд 7SURVEYING THE CLOUD ENVIRONMENT
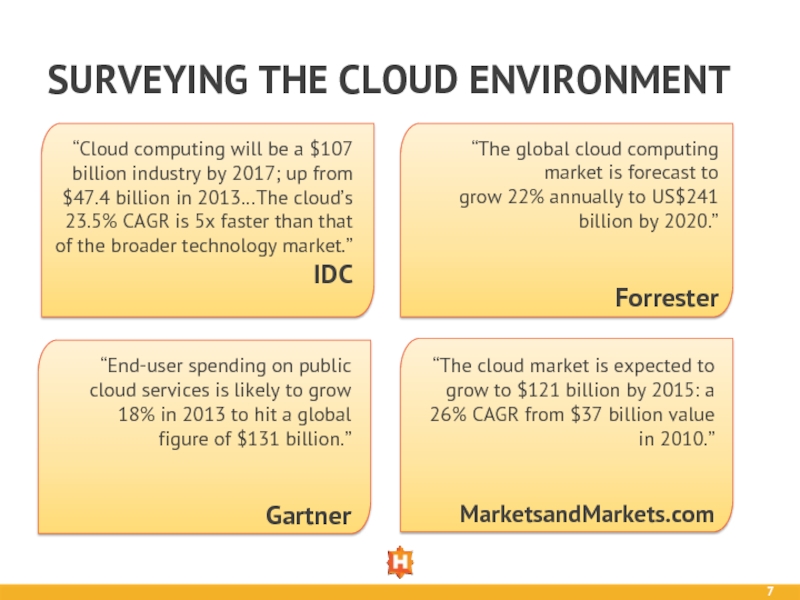
“Cloud computing will be a $107 billion industry
IDC
“The global cloud computing market is forecast to
grow 22% annually to US$241 billion by 2020.”
Forrester
“End-user spending on public cloud services is likely to grow 18% in 2013 to hit a global figure of $131 billion.”
Gartner
“The cloud market is expected to grow to $121 billion by 2015: a 26% CAGR from $37 billion value in 2010.”
MarketsandMarkets.com
Слайд 8HOW DID WE GET HERE?
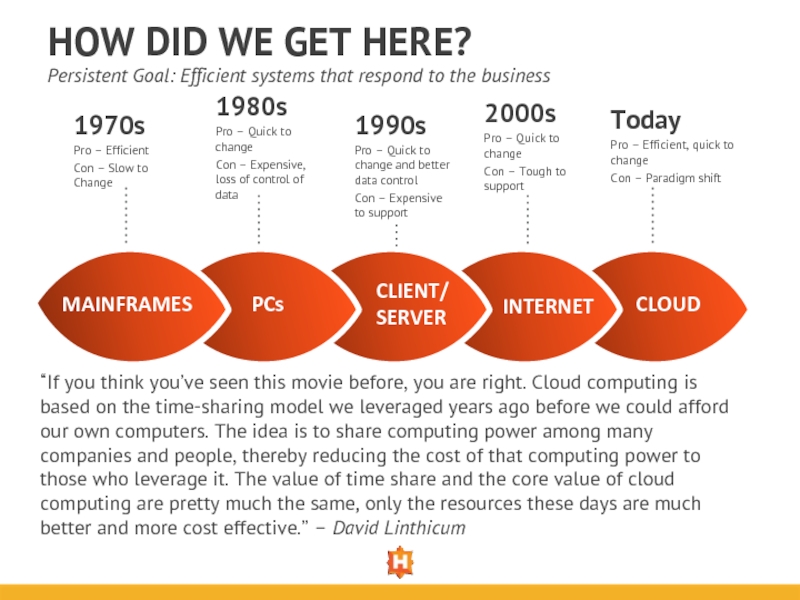
MAINFRAMES
PCs
CLIENT/
SERVER
INTERNET
CLOUD
1970s
Pro – Efficient
Con – Slow to Change
1980s
Pro – Quick to change
Con – Expensive, loss of control of data
1990s
Pro – Quick to change and better data control
Con – Expensive to support
2000s
Pro – Quick to change
Con – Tough to support
Today
Pro – Efficient, quick to change
Con – Paradigm shift
Persistent Goal: Efficient systems that respond to the business
“If you think you’ve seen this movie before, you are right. Cloud computing is based on the time-sharing model we leveraged years ago before we could afford our own computers. The idea is to share computing power among many companies and people, thereby reducing the cost of that computing power to those who leverage it. The value of time share and the core value of cloud computing are pretty much the same, only the resources these days are much better and more cost effective.” – David Linthicum
Слайд 9DEFINING THE CLOUD
Cloud computing is Internet-based computing, whereby shared resources, software
Computing in which services and storage are provided over the Internet (or "cloud")…en.wiktionary.org/wiki/cloud_computing
A technology used to access services offered on the Internet cloud. Everything an informatics system has to offer is provided as a service, so users can access these services available on the “Internet cloud” without having any previous know-how (or at least not as an expert) on managing the...www.en.masterbase.com/support/glossary.asp
On-demand self-service Internet infrastructure where you pay-as-you-go and use only what you need, all managed by a browser, application or API. Cloud computing is broken up into multiple segments including: Cloud Infrastructure, Cloud Platforms and Cloud Applications. (see "Cloud Pyramid")...www.servepath.com/support/definitions.php
The use of a Web services such as Flickr, Google Docs, Jing (video screencapture service) to perform the functions that were traditionally done with software installed on an individual computer…ets.tlt.psu.edu/learningdesign/web20glossary
A new generation of computing that utilizes distant servers for data storage and management, allowing the device to use smaller and more efficient chips that consume less energy than standard computers...www.financenewmexico.org/glossary.html
Refers to accessing computing resources that are typically owned and operated by a third-party provider on a consolidated basis in data center locations....en.citizendium.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
Computing in “the cloud” may refer to a company's own network, but it typically refers to the Internet and the use of Web browser-based or rich client applications. In these applications, the software comes from the Web Servers, and the data may be saved on the servers as well....www7.hp.com/enewsletter/cache/611914-0-0-225-121.html
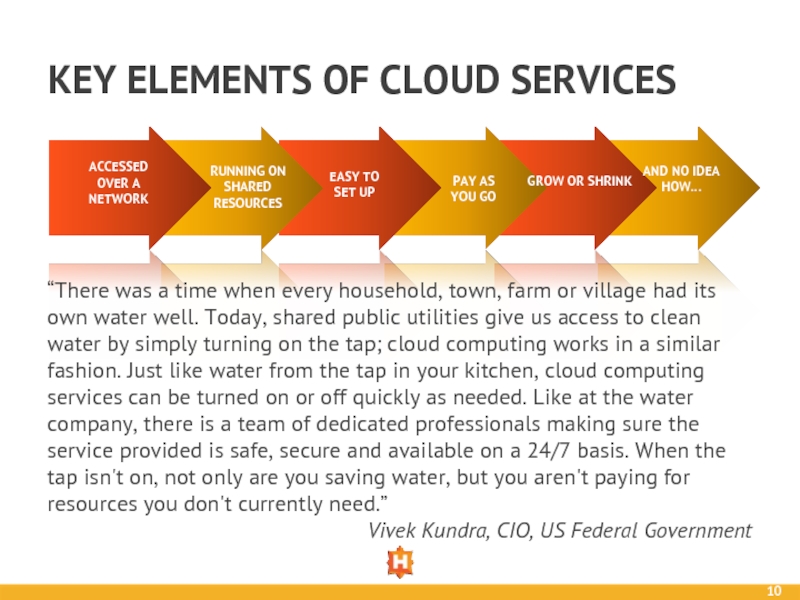
Слайд 10KEY ELEMENTS OF CLOUD SERVICES
ACCESSED OVER A NETWORK
RUNNING ON SHARED RESOURCES
EASY
SET UP
PAY AS
YOU GO
GROW OR SHRINK
AND NO IDEA HOW…
“There was a time when every household, town, farm or village had its own water well. Today, shared public utilities give us access to clean water by simply turning on the tap; cloud computing works in a similar fashion. Just like water from the tap in your kitchen, cloud computing services can be turned on or off quickly as needed. Like at the water company, there is a team of dedicated professionals making sure the service provided is safe, secure and available on a 24/7 basis. When the tap isn't on, not only are you saving water, but you aren't paying for resources you don't currently need.”
Vivek Kundra, CIO, US Federal Government
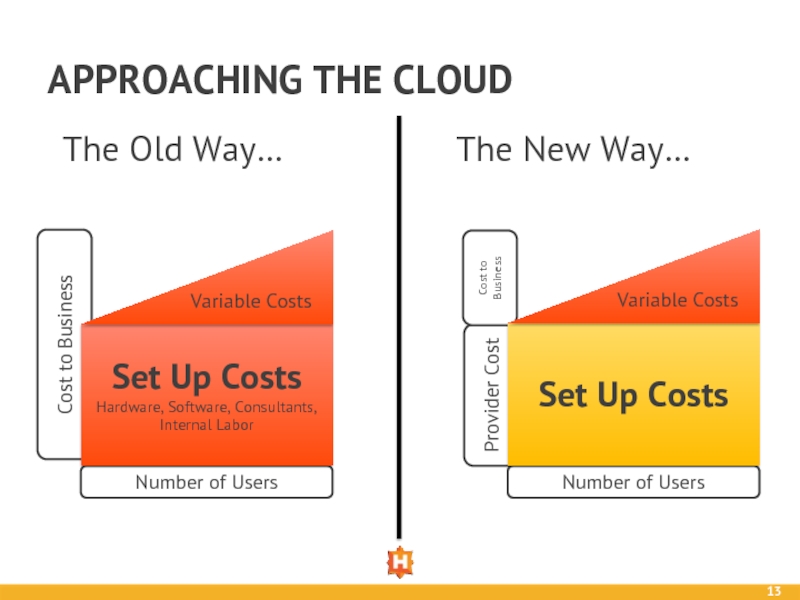
Слайд 13APPROACHING THE CLOUD
Cost to Business
Number of Users
Set Up Costs
Hardware, Software, Consultants,
Variable Costs
The Old Way…
Provider Cost
Cost to Business
Number of Users
Set Up Costs
Variable Costs
The New Way…
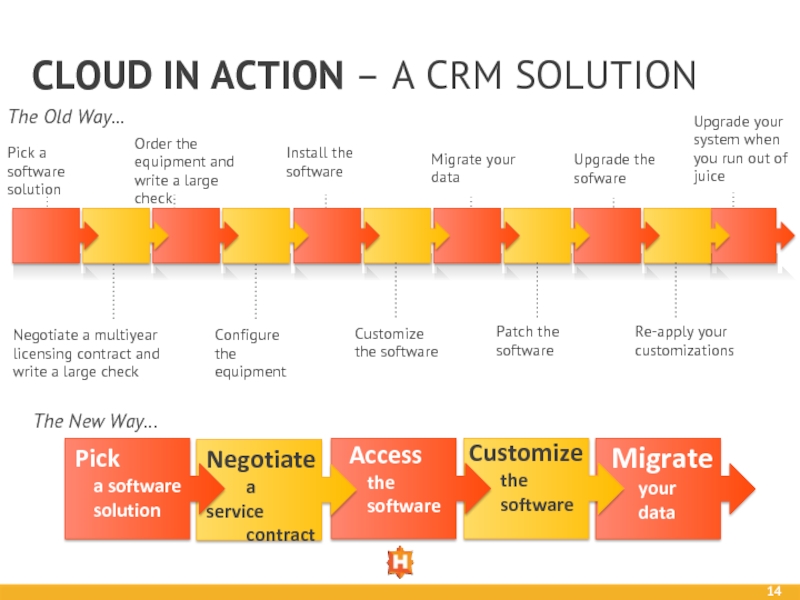
Слайд 14CLOUD IN ACTION – A CRM SOLUTION
The Old Way…
Pick a
Order the equipment and write a large check
Install the software
Migrate your data
Upgrade the sofware
Upgrade your system when you run out of juice
Negotiate a multiyear licensing contract and write a large check
Configure the equipment
Customize the software
Patch the software
Re-apply your customizations
The New Way…
Pick
a software
solution
Negotiate
a service
contract
Access
the
software
Migrate
your
data
Customize
the
software
Слайд 15Speed to Implement
Affordability
Continuous Improvement
Availability
Fewer Technical Resources
Customization
Integration
BUSINESS VALUE OF CLOUD OFFERINGS
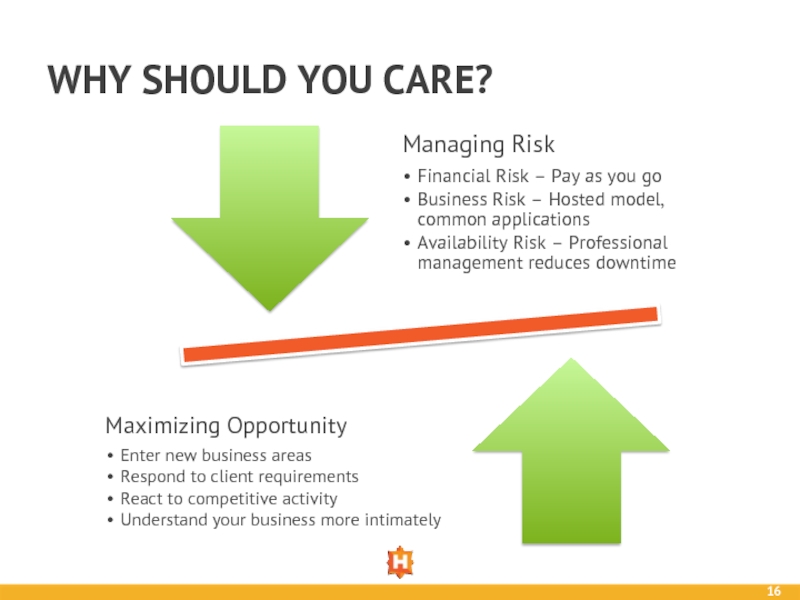
Слайд 16WHY SHOULD YOU CARE?
Managing Risk
Financial Risk – Pay as you go
Business
Availability Risk – Professional management reduces downtime
Maximizing Opportunity
Enter new business areas
Respond to client requirements
React to competitive activity
Understand your business more intimately
Слайд 17Security among top 5 reasons mid-size firms choose the cloud
Most cloud
HTTPs, password protection, encryption help to keep data secure
Audits and reviews still necessary
KEEPING DATA SAFE
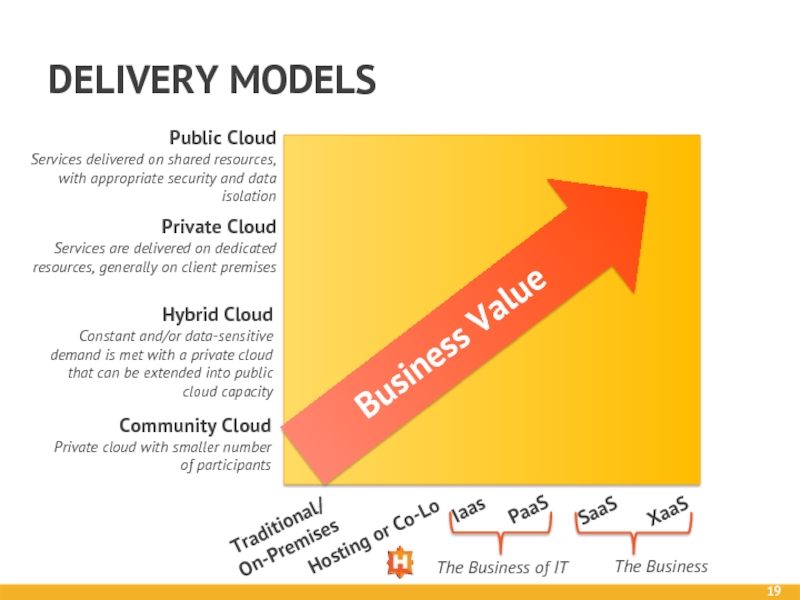
Слайд 19DELIVERY MODELS
Public Cloud
Services delivered on shared resources, with appropriate security and
Private Cloud
Services are delivered on dedicated resources, generally on client premises
Hybrid Cloud
Constant and/or data-sensitive demand is met with a private cloud that can be extended into public cloud capacity
Community Cloud
Private cloud with smaller number of participants
Traditional/
On-Premises
Hosting or Co-Lo
Iaas
PaaS
SaaS
XaaS
Business Value
The Business of IT
The Business
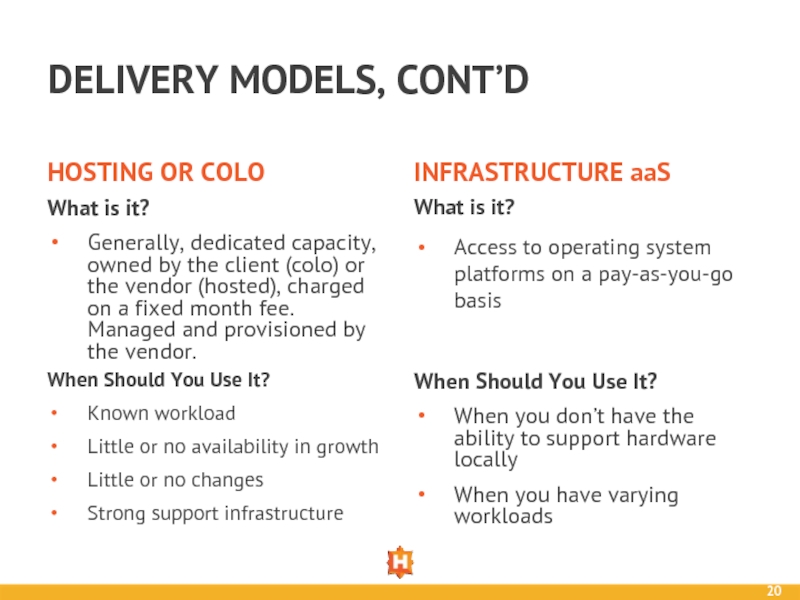
Слайд 20DELIVERY MODELS, CONT’D
HOSTING OR COLO
What is it?
Generally, dedicated capacity, owned by
INFRASTRUCTURE aaS
When Should You Use It?
Known workload
Little or no availability in growth
Little or no changes
Strong support infrastructure
What is it?
Access to operating system platforms on a pay-as-you-go basis
When Should You Use It?
When you don’t have the ability to support hardware locally
When you have varying workloads
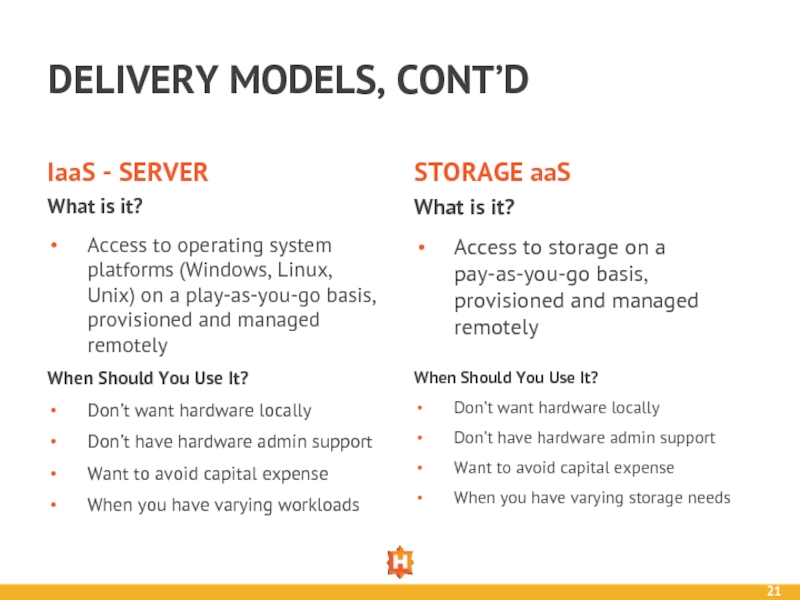
Слайд 21DELIVERY MODELS, CONT’D
IaaS - SERVER
What is it?
Access to operating system platforms
STORAGE aaS
When Should You Use It?
Don’t want hardware locally
Don’t have hardware admin support
Want to avoid capital expense
When you have varying workloads
What is it?
Access to storage on a pay-as-you-go basis, provisioned and managed remotely
When Should You Use It?
Don’t want hardware locally
Don’t have hardware admin support
Want to avoid capital expense
When you have varying storage needs
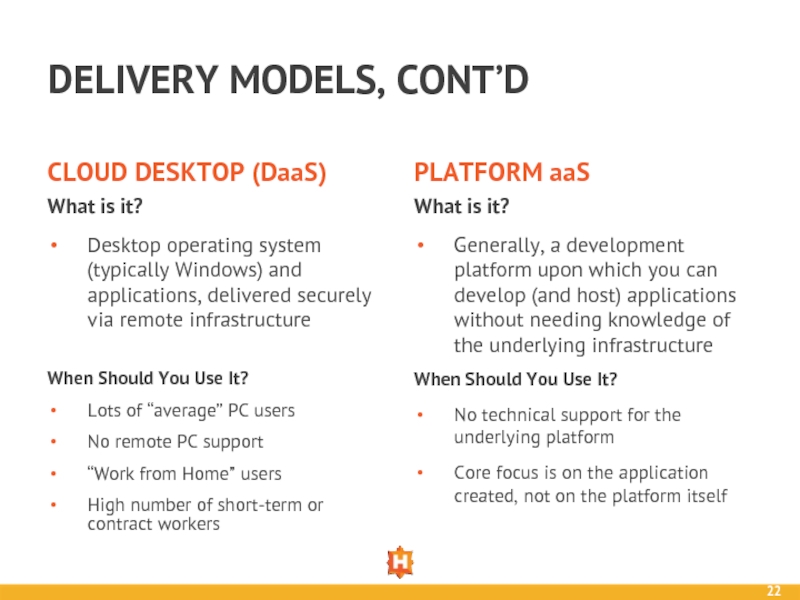
Слайд 22DELIVERY MODELS, CONT’D
CLOUD DESKTOP (DaaS)
What is it?
Desktop operating system (typically Windows)
PLATFORM aaS
When Should You Use It?
Lots of “average” PC users
No remote PC support
“Work from Home” users
High number of short-term or contract workers
What is it?
Generally, a development platform upon which you can develop (and host) applications without needing knowledge of the underlying infrastructure
When Should You Use It?
No technical support for the underlying platform
Core focus is on the application created, not on the platform itself
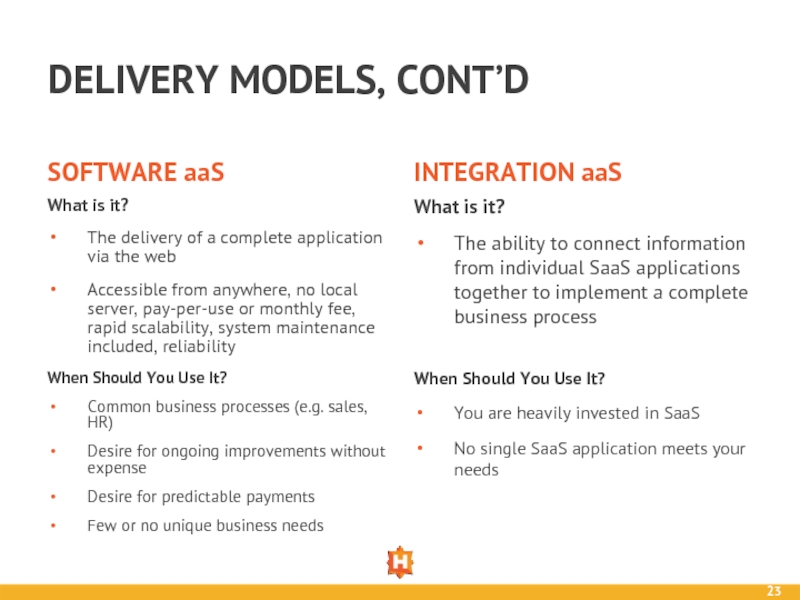
Слайд 23DELIVERY MODELS, CONT’D
SOFTWARE aaS
What is it?
The delivery of a complete application
Accessible from anywhere, no local server, pay-per-use or monthly fee, rapid scalability, system maintenance included, reliability
INTEGRATION aaS
When Should You Use It?
Common business processes (e.g. sales, HR)
Desire for ongoing improvements without expense
Desire for predictable payments
Few or no unique business needs
What is it?
The ability to connect information from individual SaaS applications together to implement a complete business process
When Should You Use It?
You are heavily invested in SaaS
No single SaaS application meets your needs
Слайд 28HOSTING builds and operates high-performance clouds for business-critical operations.
HOSTING’S APPROACH
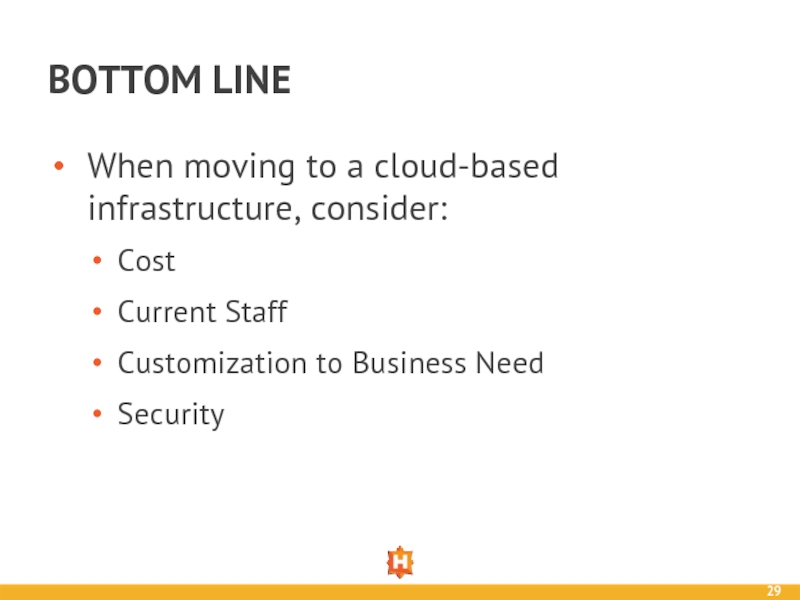
Слайд 29When moving to a cloud-based infrastructure, consider:
Cost
Current Staff
Customization to Business Need
Security
BOTTOM
Слайд 30The worldwide cloud computing industry is rapidly gaining value
Cloud computing represents
Moving to the cloud affords many benefits to business-critical applications
HOSTING offers custom managed cloud solutions to meet your unique business needs
IN SUMMARY