- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Review for midterm exam II презентация
Содержание
- 1. Review for midterm exam II
- 2. The Line Balancing Problem The problem is
- 3. Line Balancing The actual cycle time which
- 4. If the demand is 12 cases per
- 5. Question 2: Chapter 9, Problem 16, Line Balancing
- 6. Question 2: Chapter 9, Problem 16, Line
- 7. Inventory Management EOQ Model
- 8. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as
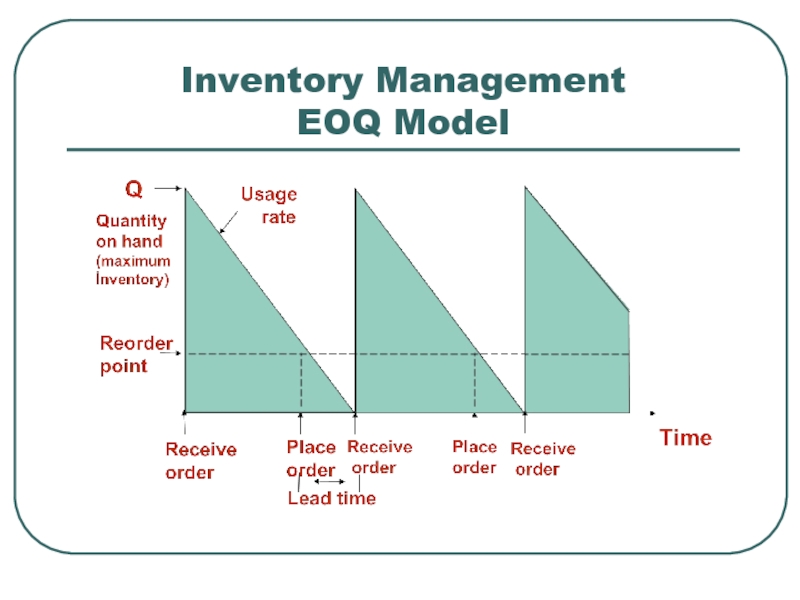
- 9. Inventory Management EOQ Model
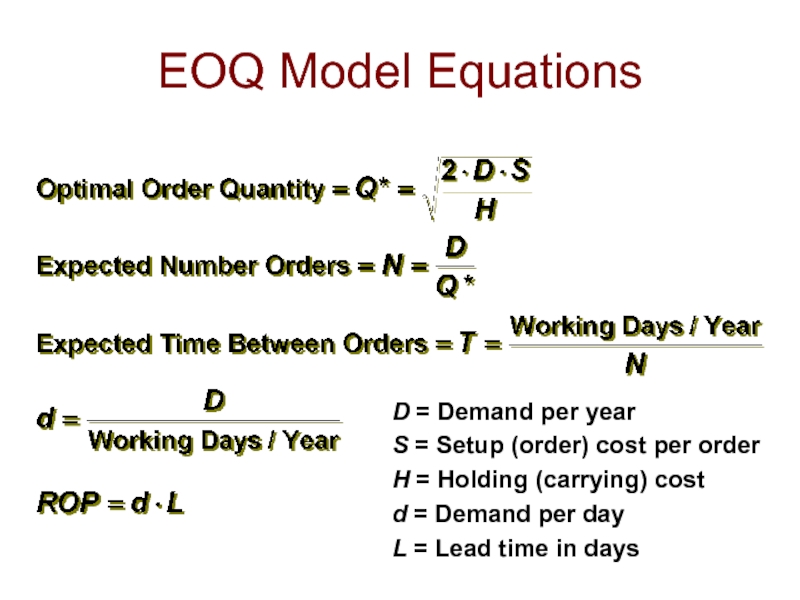
- 10. EOQ Model Equations D = Demand per
- 11. Question 3, EOQ The ABC store needs
- 12. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as
- 13. EOQ and POQ Models In the EOQ
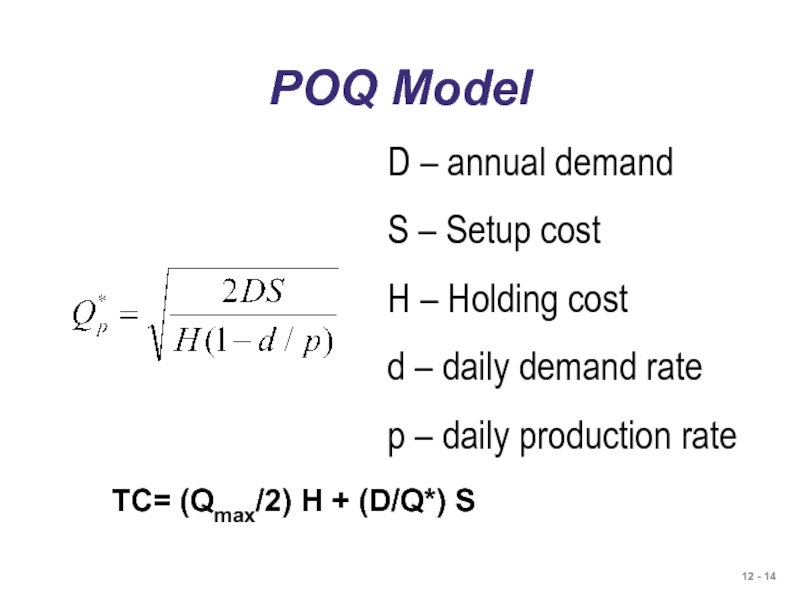
- 14. POQ Model D – annual demand S
- 15. Question 4, POQ A plant manager of
- 16. Question 5:Chapter 12, Problem 20, POQ
- 17. © Wiley 2010 Quantity Discount Model
- 18. Question 6: Quantity Discount Model ABC Sport
- 19. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as
- 20. Question 7: Quantity Discount Model
- 21. Total Cost with Constant Holding Costs
- 22. Question 8: Reorder Point for Variable Demand
- 23. Demand per day is variable
- 24. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
- 25. Question 9: Aggregate Production Planning © 2011
- 26. Question 9: Aggregate Production Planning Which of
- 27. a) Chase Demand © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
- 28. b) Level Production © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Слайд 2The Line Balancing Problem
The problem is to arrange the individual tasks
Note that it is nearly impossible to reach perfect balance
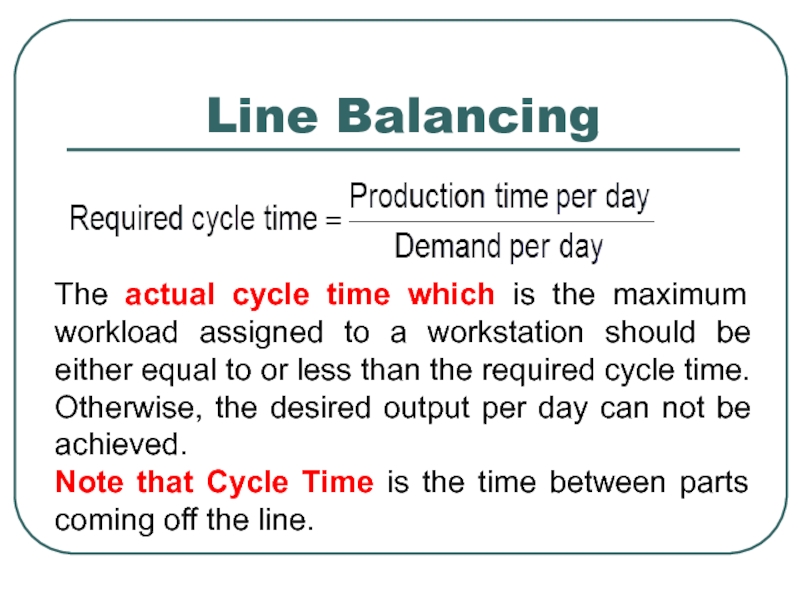
Слайд 3Line Balancing
The actual cycle time which is the maximum workload assigned
Note that Cycle Time is the time between parts coming off the line.
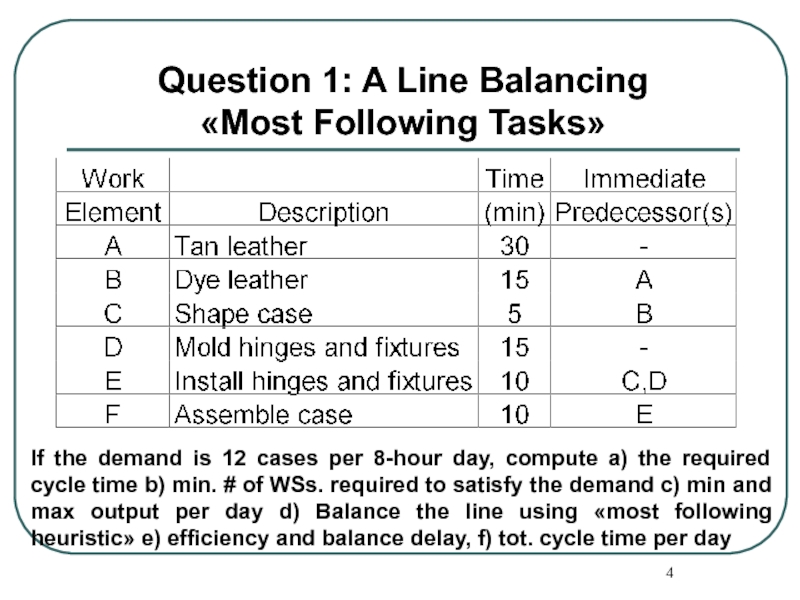
Слайд 4If the demand is 12 cases per 8-hour day, compute a)
Question 1: A Line Balancing
«Most Following Tasks»
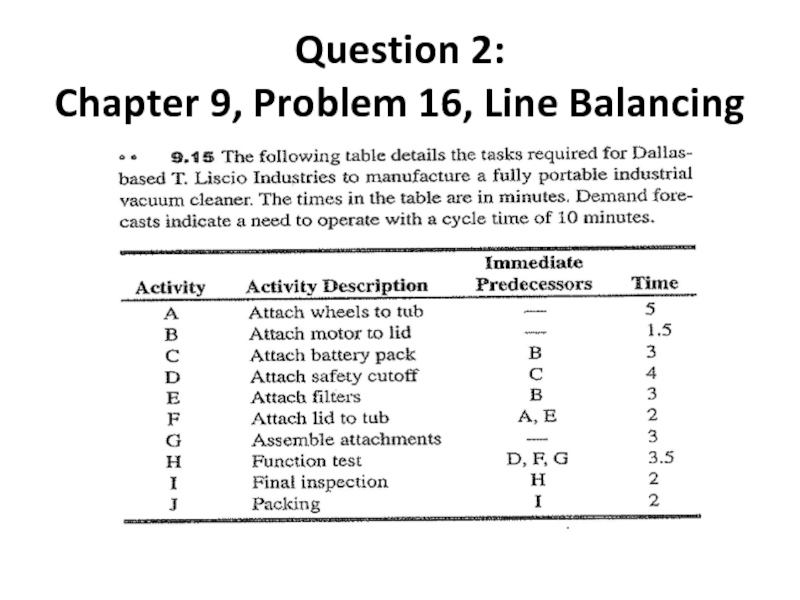
Слайд 6Question 2:
Chapter 9, Problem 16, Line Balancing
a) Draw the precedence diagram
b)
c) Calculate min. # of WSs. required to satisfy the demand
d) Balance the line using «most following heuristic» to satisfy the demand
e) Calculate efficiency and balance delay
f) Calculate total idle time per day
Слайд 8© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
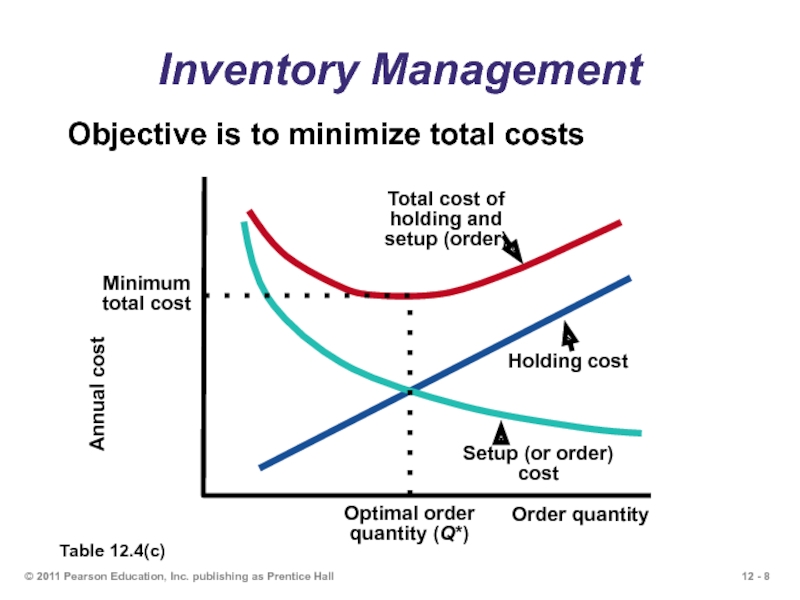
Inventory Management
Objective is
Table 12.4(c)
Слайд 10EOQ Model Equations
D = Demand per year
S = Setup (order) cost
H = Holding (carrying) cost
d = Demand per day
L = Lead time in days
Слайд 11Question 3, EOQ
The ABC store needs 1000 coffee makers per year.
Economic Order Quantity(EOQ),
Total annual cost
Reorder Point
Expected time between orders
Слайд 12© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
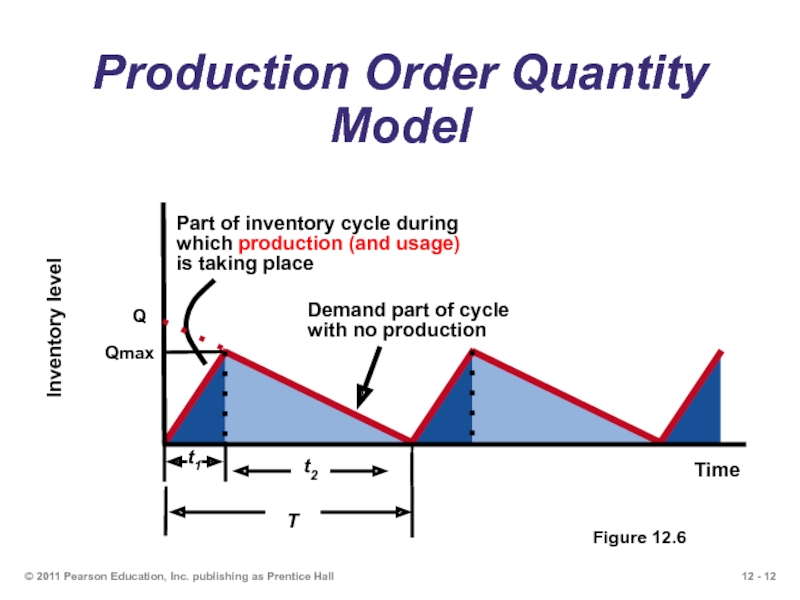
Production Order Quantity
Figure 12.6
Слайд 13EOQ and POQ Models
In the EOQ model, maximum inventory is equal
Average Inventory = Q/2
In the POQ model, maximum inventory is less than the Order Size.
Why? Because we produce the item and use it while it is being produced.
Average Inventory = Qmax / 2
where Qmax= (p-d)Q/p
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Слайд 14POQ Model
D – annual demand
S – Setup cost
H – Holding cost
d
p – daily production rate
TC= (Qmax/2) H + (D/Q*) S
Слайд 15Question 4, POQ
A plant manager of XYZ chemical plant must determine
What is the optimal production quantity?
What is the optimal number of production runs per year?
What is the time between production runs?
What is the total annual cost?
What is the percent of time spent for production.
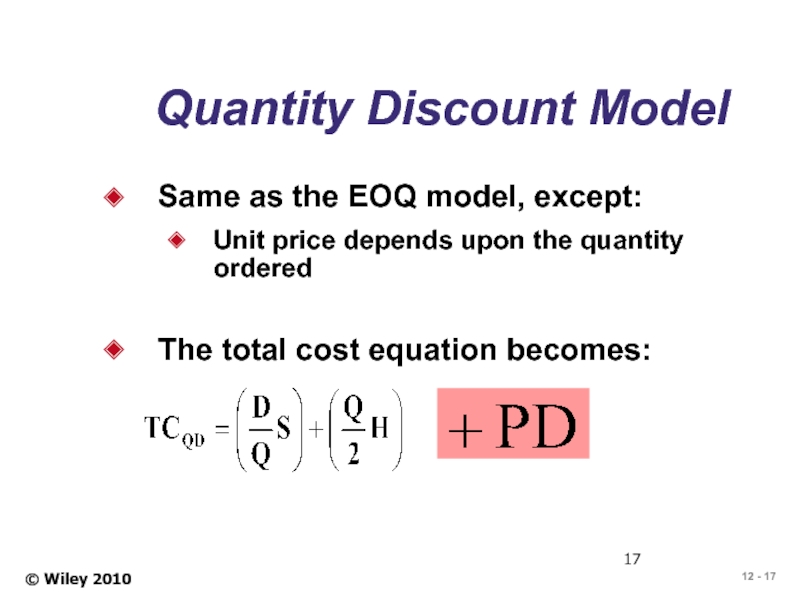
Слайд 17© Wiley 2010
Quantity Discount Model
Same as the EOQ model, except:
Unit price
The total cost equation becomes:
Слайд 18Question 6: Quantity Discount Model
ABC Sport store is considering going to
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
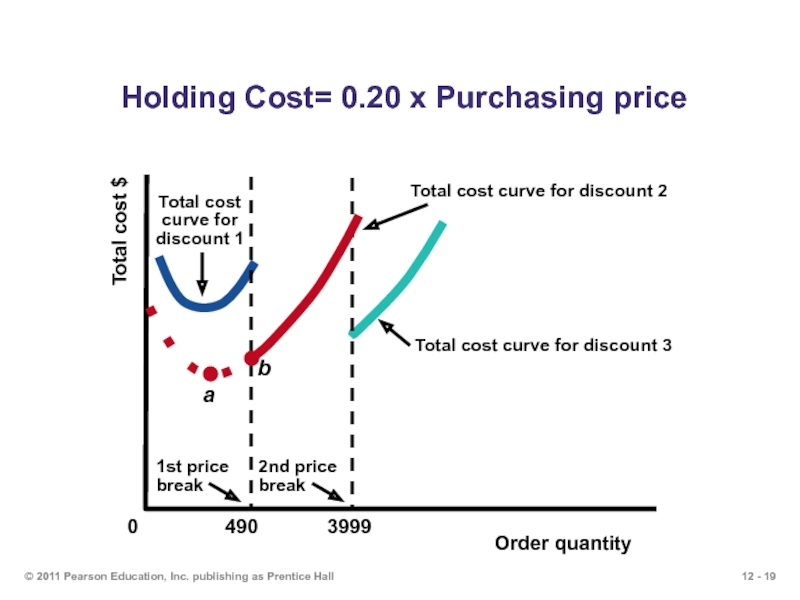
Слайд 19© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Holding Cost=
Слайд 20
Question 7: Quantity Discount Model
A company has a chance to reduce
Order Quantity(units) Price/unit($)
0 to 2,499 $1.20
2,500 to 3,999 1.00
4,000 or more .98
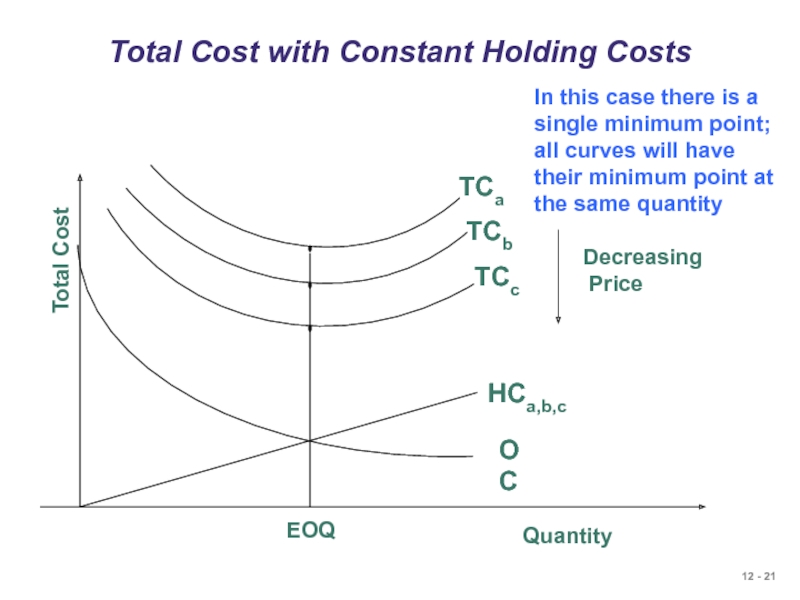
Слайд 21Total Cost with Constant Holding Costs
In this case there is
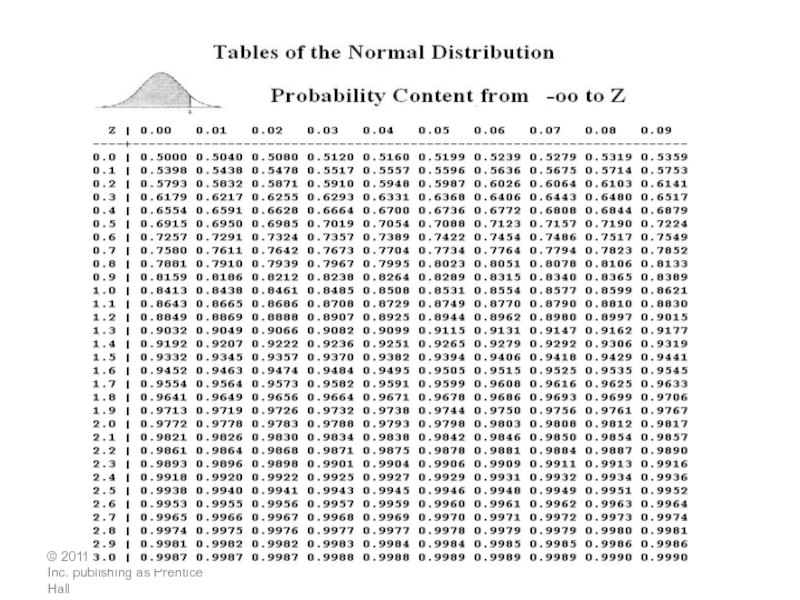
Слайд 22Question 8: Reorder Point for Variable Demand
The manager of a
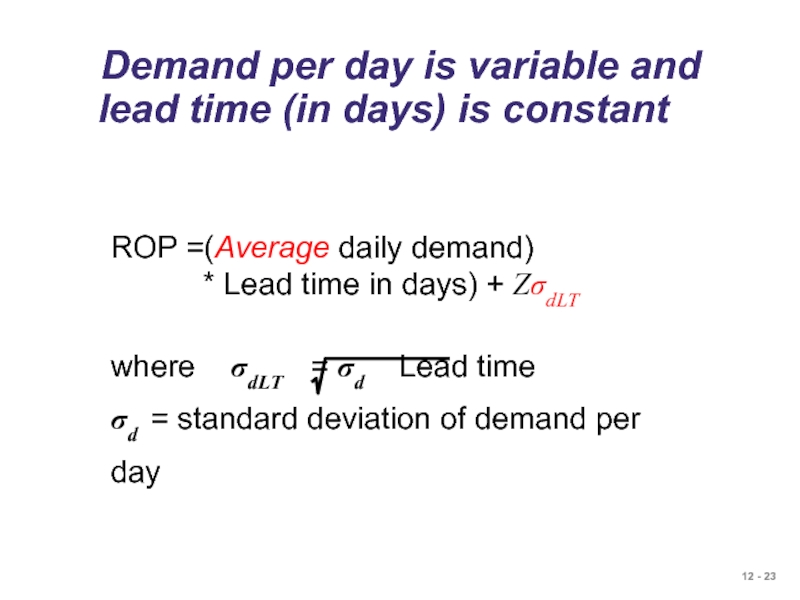
Слайд 23 Demand per day is variable and lead time (in
ROP =(Average daily demand)
* Lead time in days) + ZσdLT
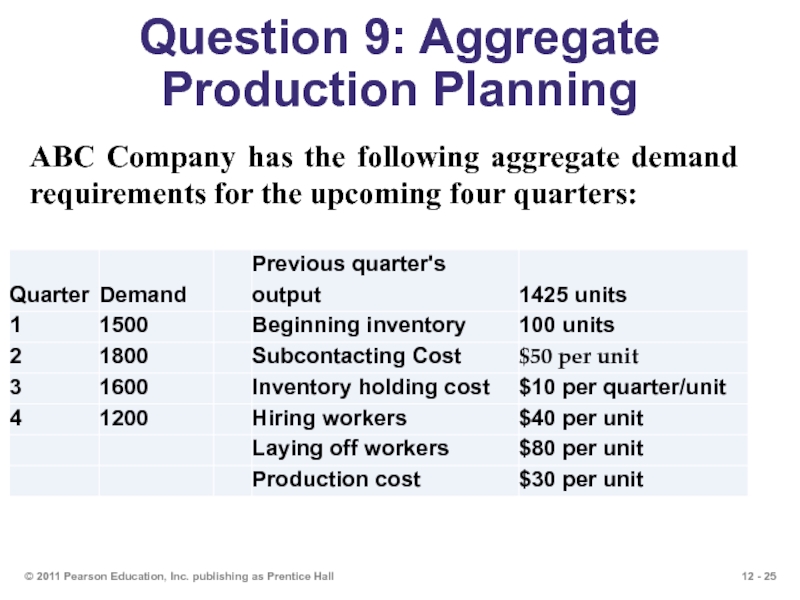
Слайд 25Question 9: Aggregate Production Planning
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as
ABC Company has the following aggregate demand requirements for the upcoming four quarters:
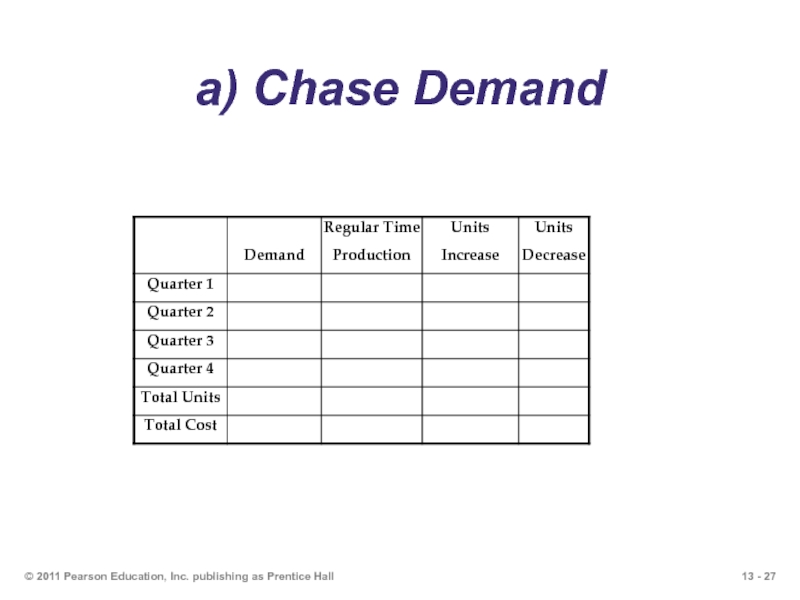
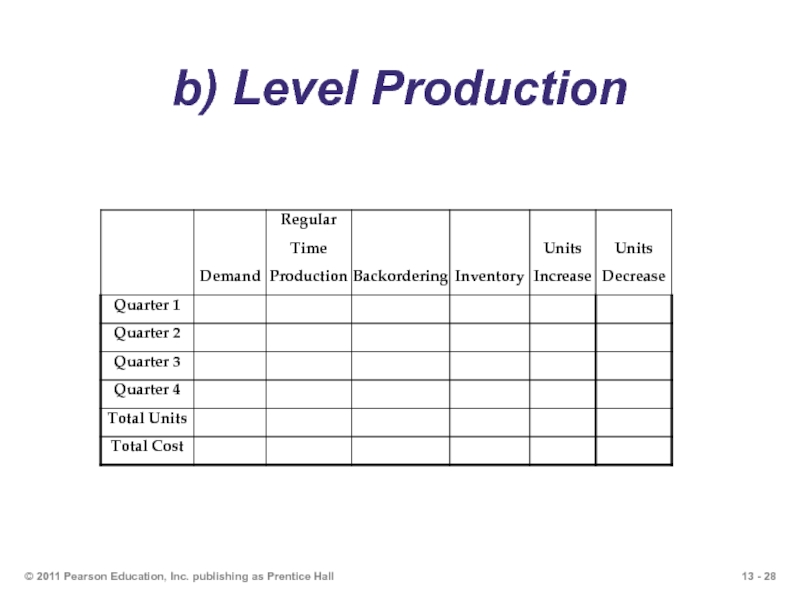
Слайд 26Question 9: Aggregate Production Planning
Which of the following production plans is
Plan A–chase demand by hiring and layoffs
Plan B–level strategy and subcontracting
Calculate the total cost of each production plan.
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall