- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Designing & Deploying Network Solutions for Small and Medium Busines презентация
Содержание
- 1. Designing & Deploying Network Solutions for Small and Medium Busines
- 45. CSMA/CD Shared media Ethernet uses a network
- 46. When a collision occurs: All involved
- 47. Collision Domain As a network grows larger
- 48. VLAN In the early days of networking,
- 49. VLAN The simplest type of VLAN is
- 50. VLAN and Ethernet When using VLANs
- 51. Defined by 802.11 standards. Standards in the
- 52. Current Wireless Standards 802.11g is downward compatible
- 53. CSMA/CA The network access method used by
- 54. Authentication and resource access Data and communication security Security Basics
- 55. What you know Password or PIN
- 56. Prevent data from being exposed Prevent data
- 57. The OSI model describes network functions as
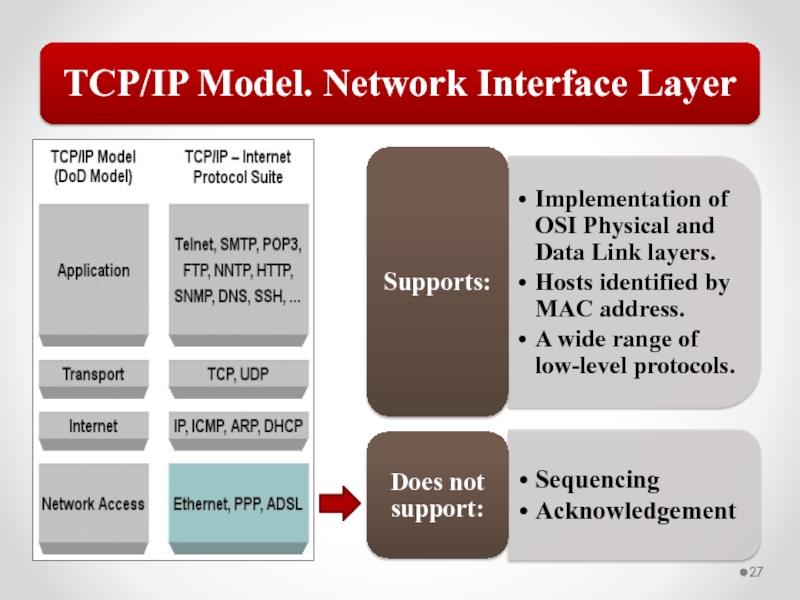
- 58. The MAC address is implemented at Layer
- 59. Network traffic can be a mix of
- 60. Thank you for your attention!
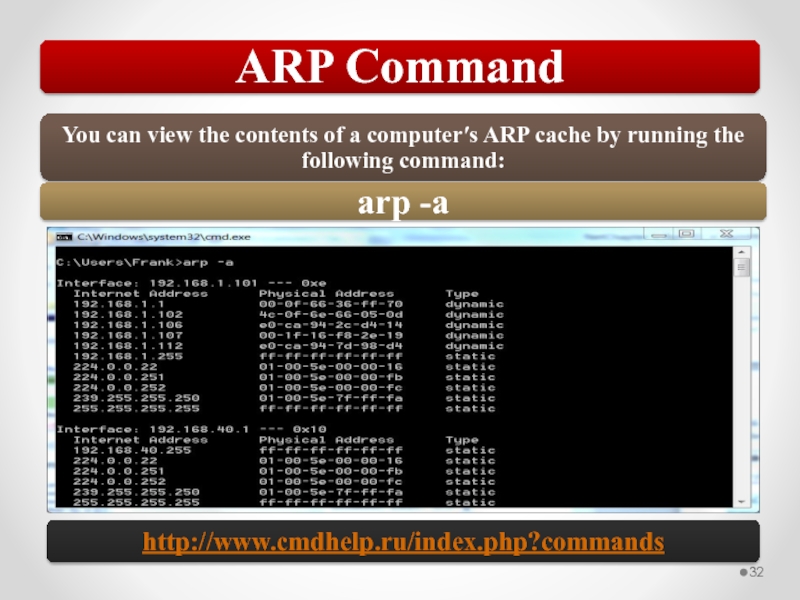
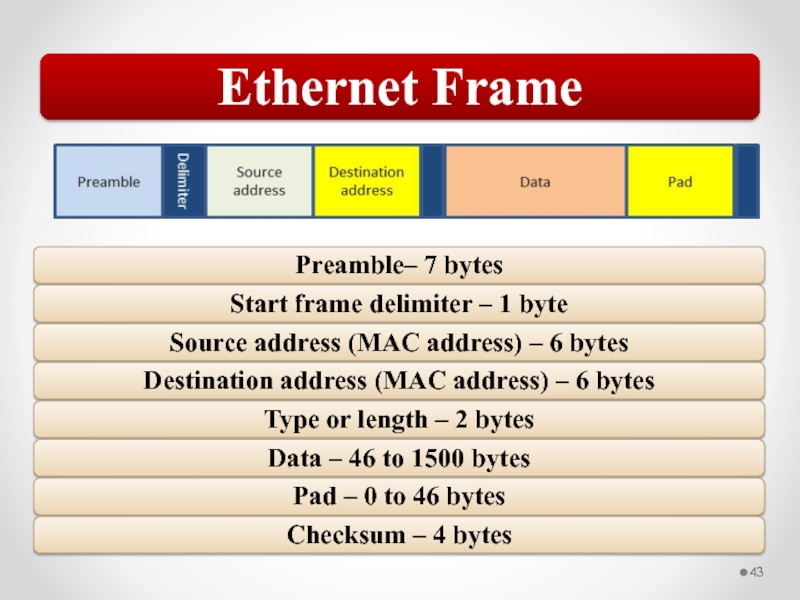
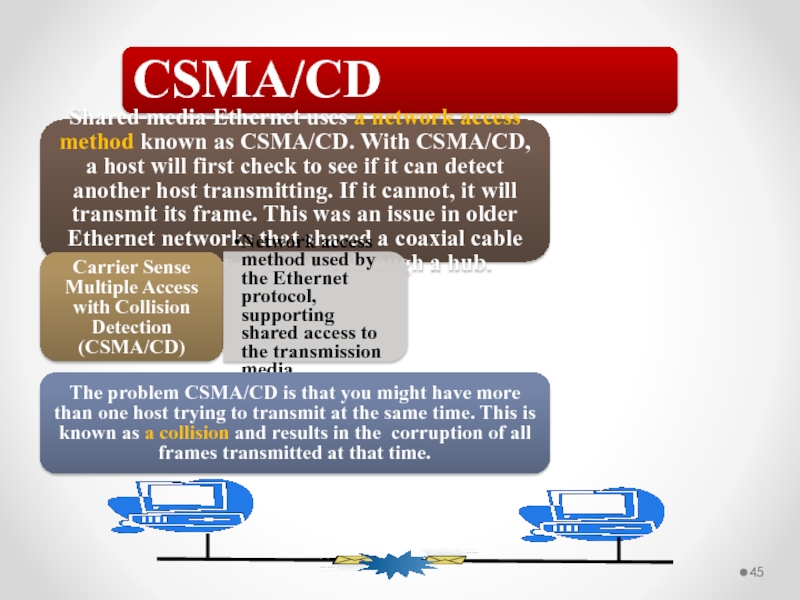
Слайд 45CSMA/CD
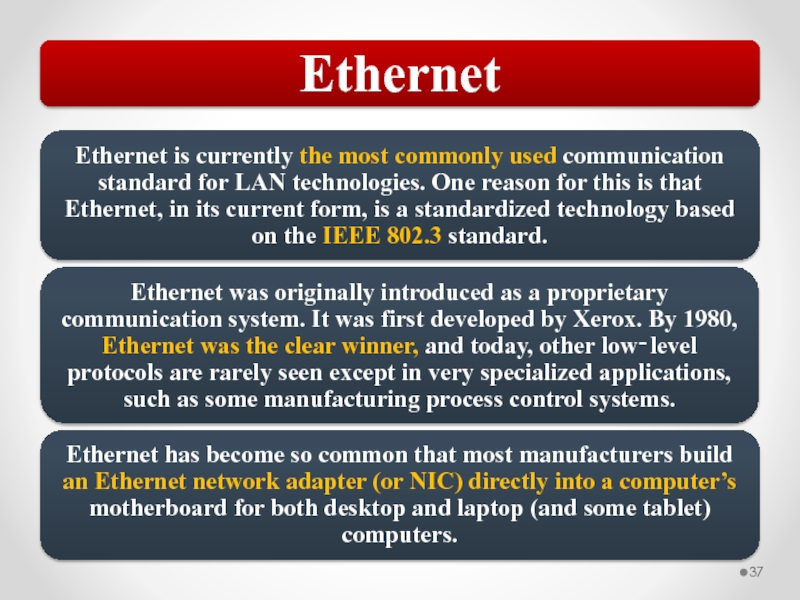
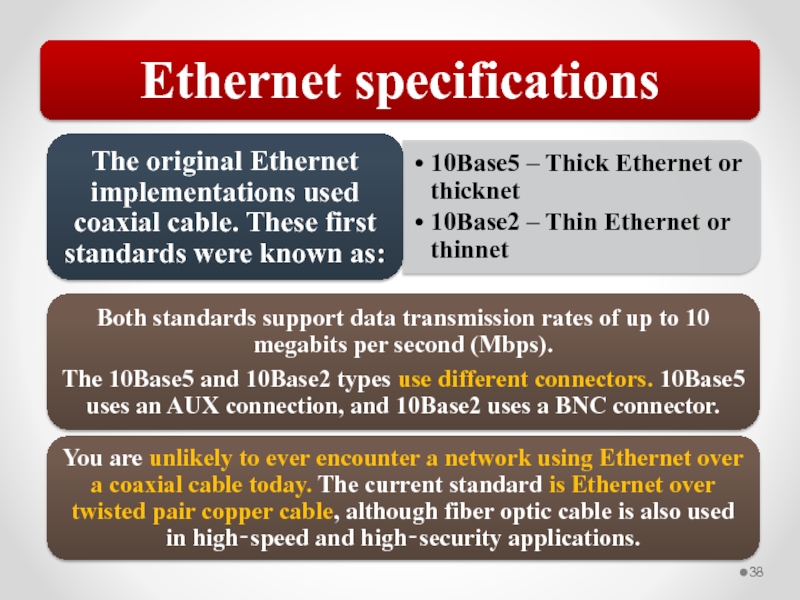
Shared media Ethernet uses a network access method known as CSMA/CD.
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
Network access method used by the Ethernet protocol, supporting shared access to the transmission media.
The problem CSMA/CD is that you might have more than one host trying to transmit at the same time. This is known as a collision and results in the corruption of all frames transmitted at that time.
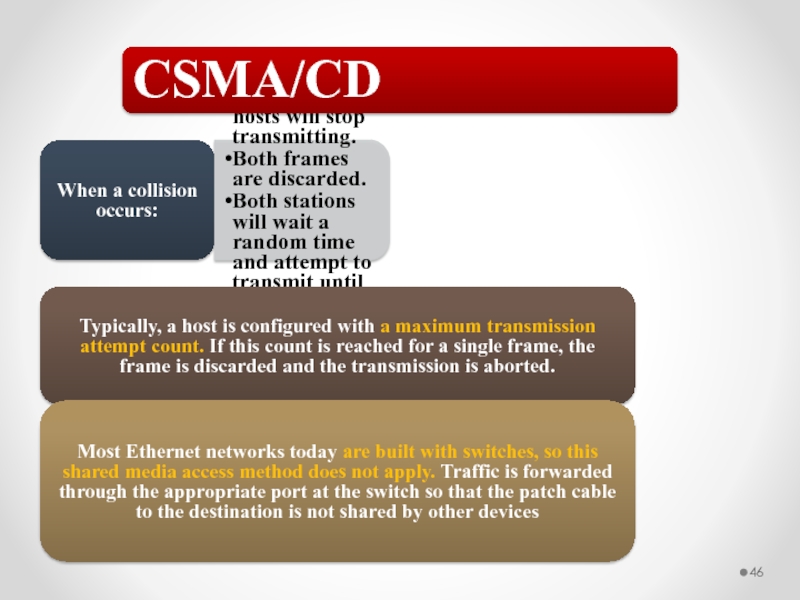
Слайд 46When a collision occurs:
All involved hosts will stop transmitting.
Both frames are
Both stations will wait a random time and attempt to transmit until successful.
CSMA/CD
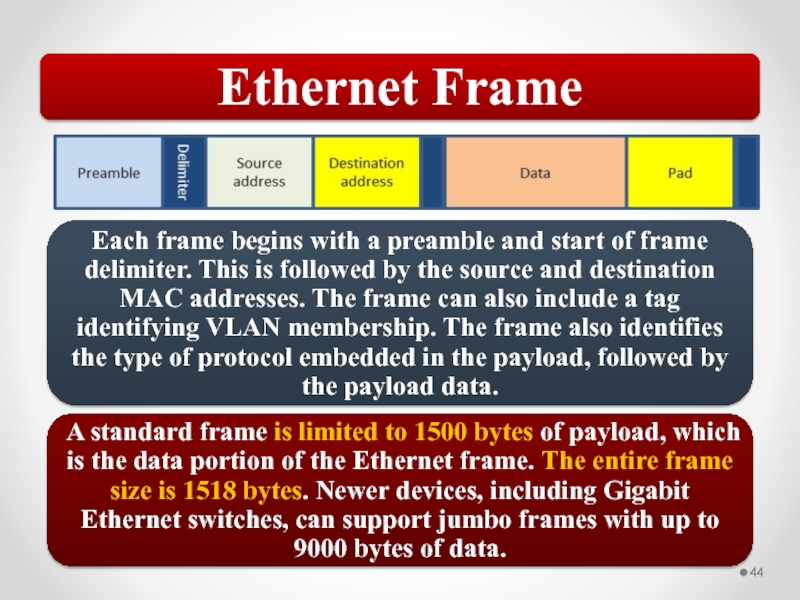
Typically, a host is configured with a maximum transmission attempt count. If this count is reached for a single frame, the frame is discarded and the transmission is aborted.
Most Ethernet networks today are built with switches, so this shared media access method does not apply. Traffic is forwarded through the appropriate port at the switch so that the patch cable to the destination is not shared by other devices
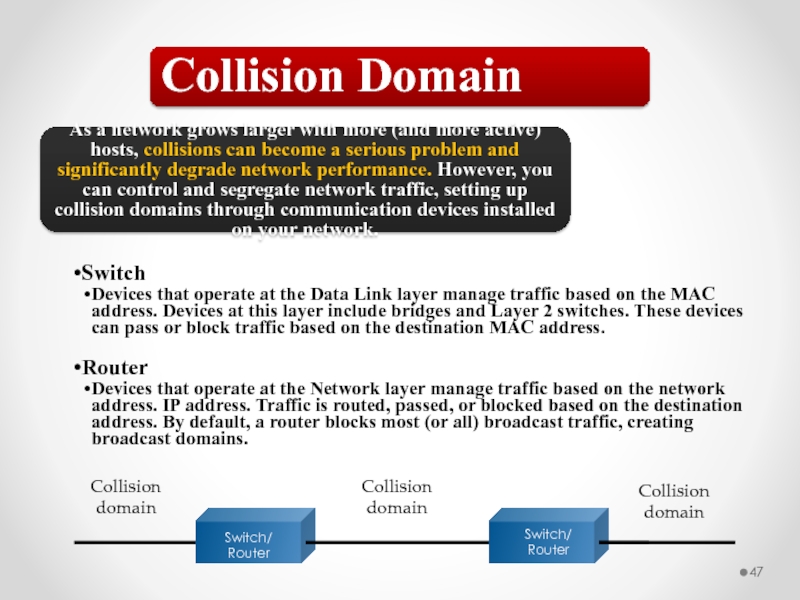
Слайд 47Collision Domain
As a network grows larger with more (and more active)
Switch
Devices that operate at the Data Link layer manage traffic based on the MAC address. Devices at this layer include bridges and Layer 2 switches. These devices can pass or block traffic based on the destination MAC address.
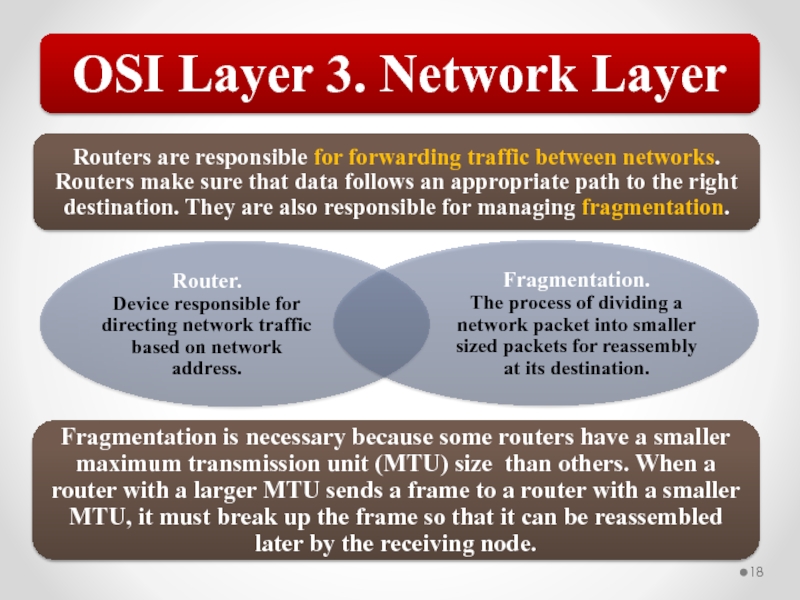
Router
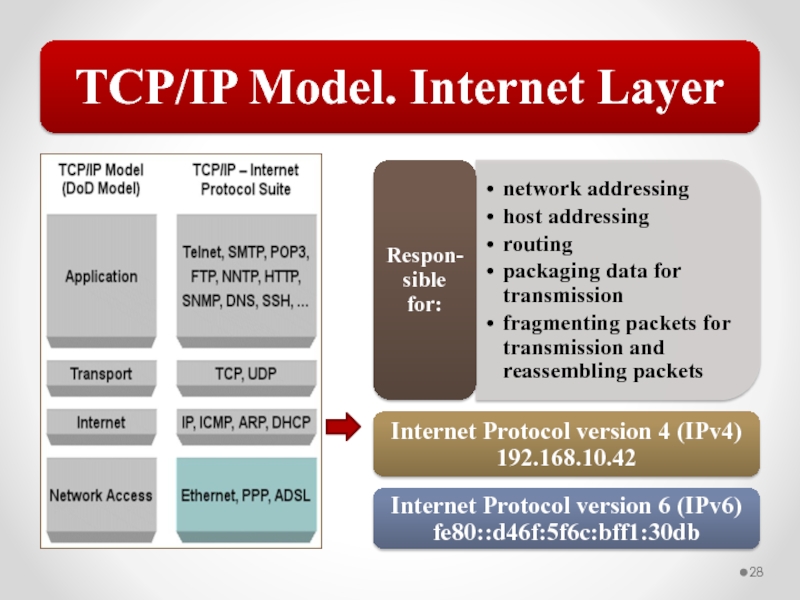
Devices that operate at the Network layer manage traffic based on the network address. IP address. Traffic is routed, passed, or blocked based on the destination address. By default, a router blocks most (or all) broadcast traffic, creating broadcast domains.
Слайд 48VLAN
In the early days of networking, network hosts could be organized
Modern switches provide segmentation through VLANs. A VLAN looks like a routed subnet, also referred to as a Layer 3 subnetwork, to the rest of the network. Each VLAN has its own network IP address for routing purposes.
Слайд 49VLAN
The simplest type of VLAN is a static VLAN. In this
A VLAN can also be created and managed dynamically. You can assign ports to a VLAN based on factors such as a connected computer’s MAC address or the username used when logging onto the computer.
Static VLAN - are also known as Port-based VLANs are created by allocating ports to a VLAN manually.
Dynamic VLAN – are made by allocating the host to a VLAN when host is plugged in a switch by the use of hardware addresses from database.
Слайд 50VLAN and Ethernet
When using VLANs on an Ethernet network, each
Слайд 51Defined by 802.11 standards. Standards in the 802.11 family define a
Wireless adapters (NIC) include radio frequency transmitter and receiver operating in a specific frequency range, depending on the standard or standards that the wireless NIC supports.
Access points (APs) provide a common connection point for devices. Most 802.11 wireless network configurations are based around one or more access points (APs). The AP acts as a central point of access for wireless hosts.
Wireless Networking
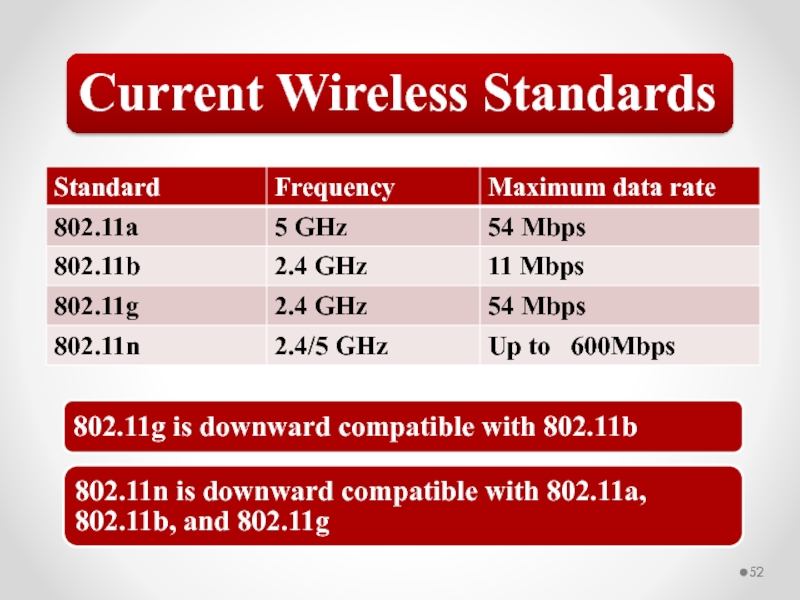
Слайд 52Current Wireless Standards
802.11g is downward compatible with 802.11b
802.11n is downward compatible
Слайд 53CSMA/CA
The network access method used by 802.11 wireless is CSMA/CA
With CSMA/CA, a host listens for a predetermined amount of time to ensure the availability of the channel it is going to use for transmission.
A request to send (RTS) signal is sent, informing the other hosts of its intent to transmit.
The sending host waits for a clear-to‐send (CTS) signal before starting transmission.
Слайд 55What you know
Password or PIN
What you have
Smart card, ID badge, etc.
Who
Biometric information
Authentication Forms
If you have ever logged onto a computer, when connecting to a network, running management utilities, or attempting to access resources, such as files, you have taken part in an authentication process. For users, authentication is usually based on one or more of the following:
Слайд 56Prevent data from being exposed
Prevent data from being corrupted
Data Security
The use
Encryption - the process of using an algorithm to render the data unreadable without the technology and knowledge necessary to reverse the process.
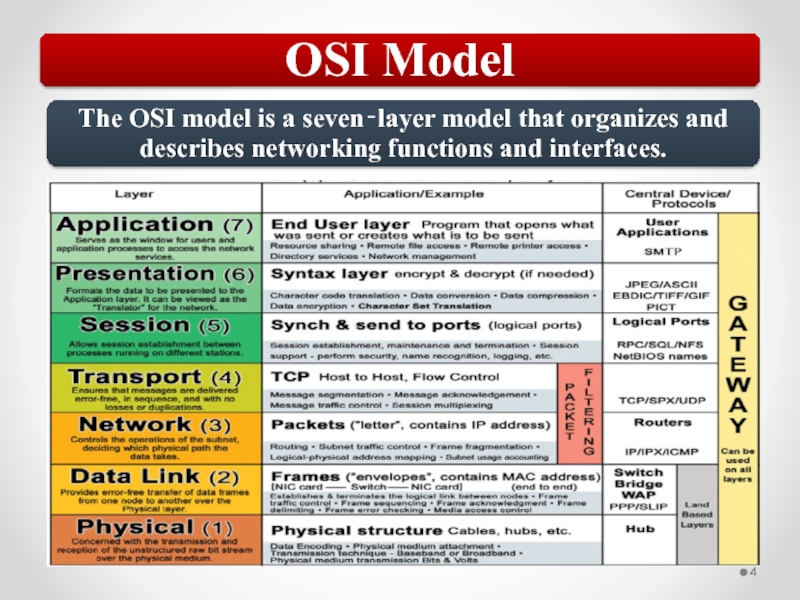
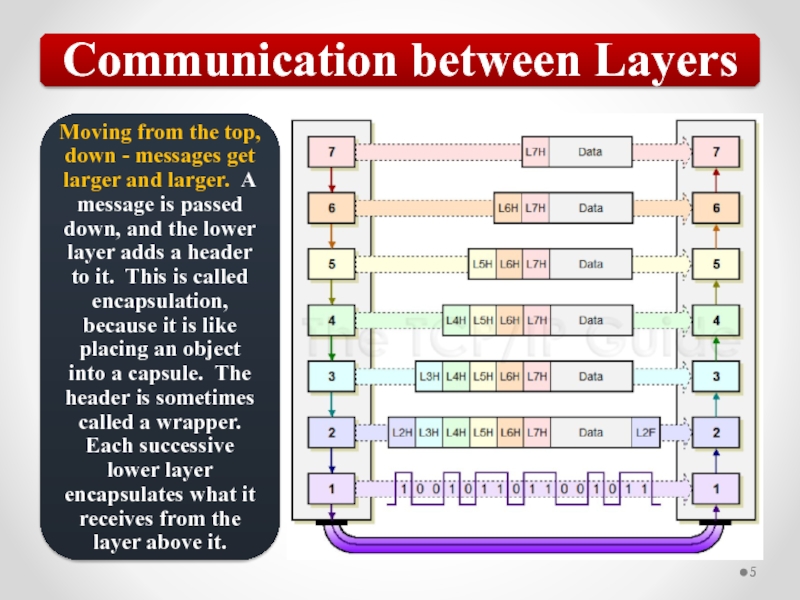
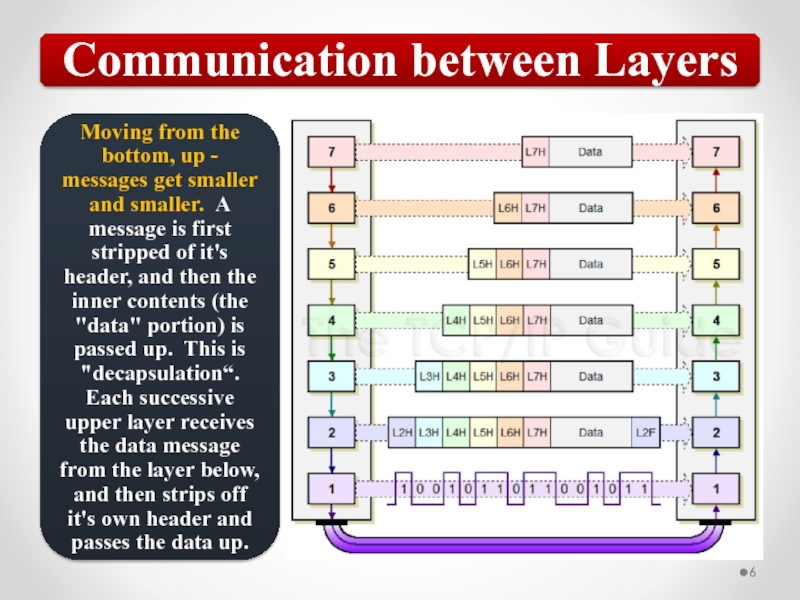
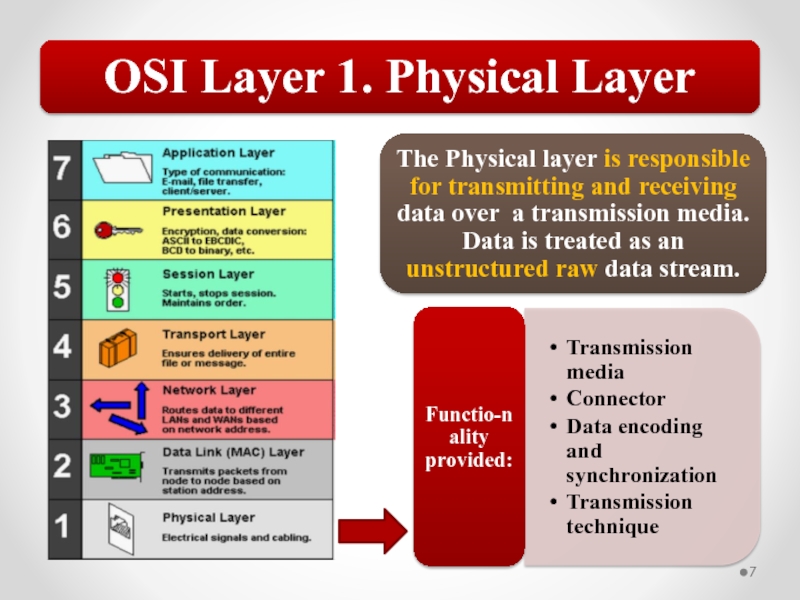
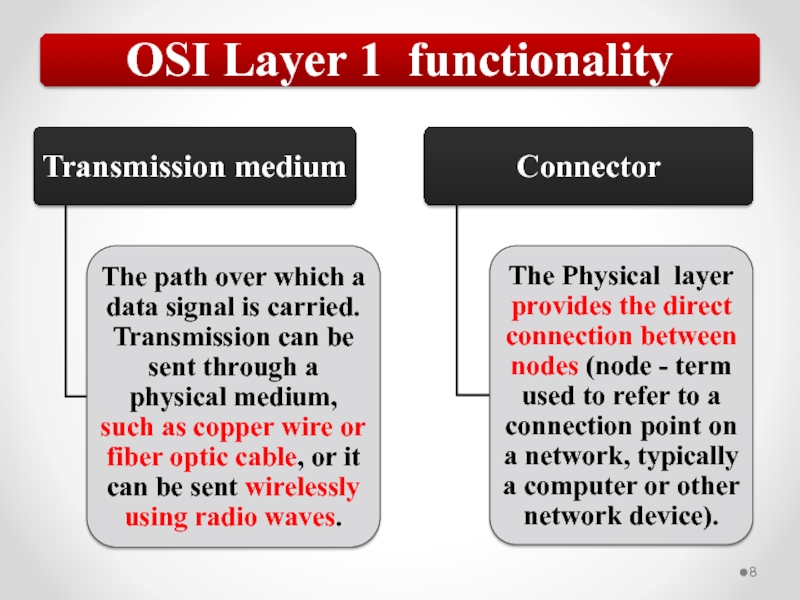
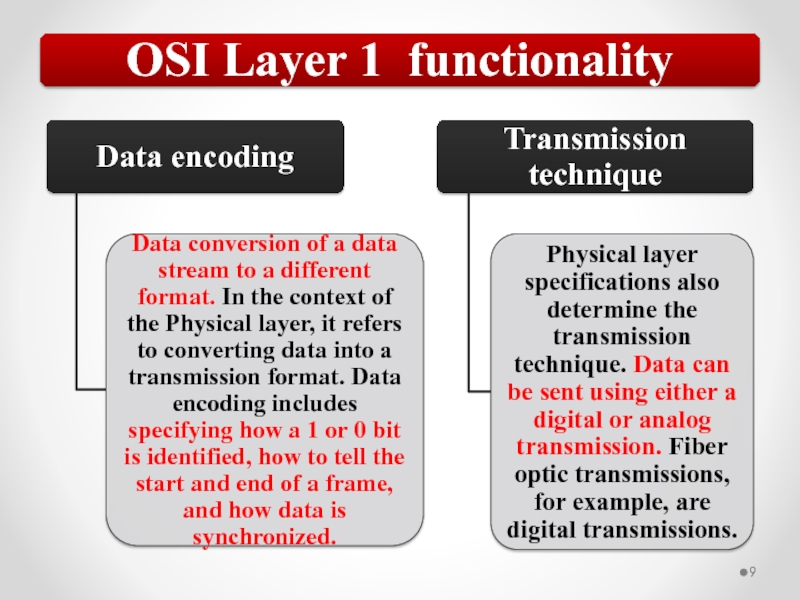
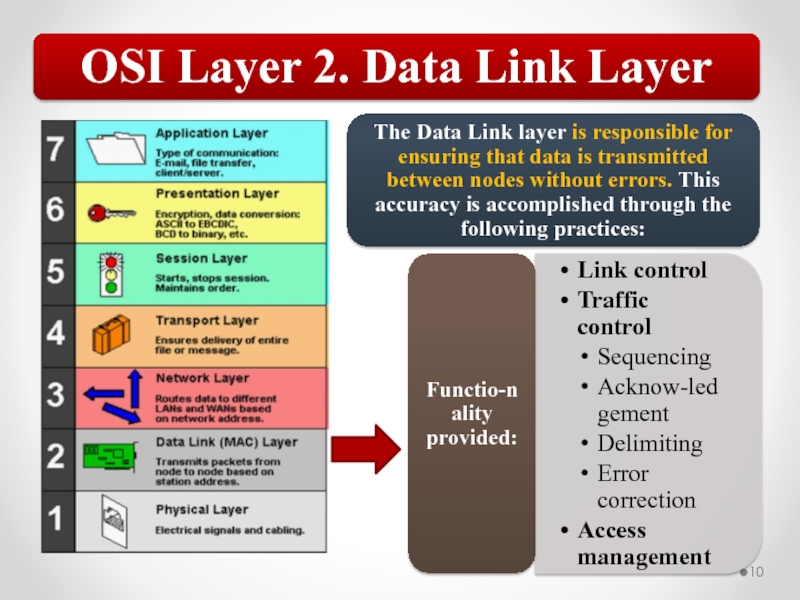
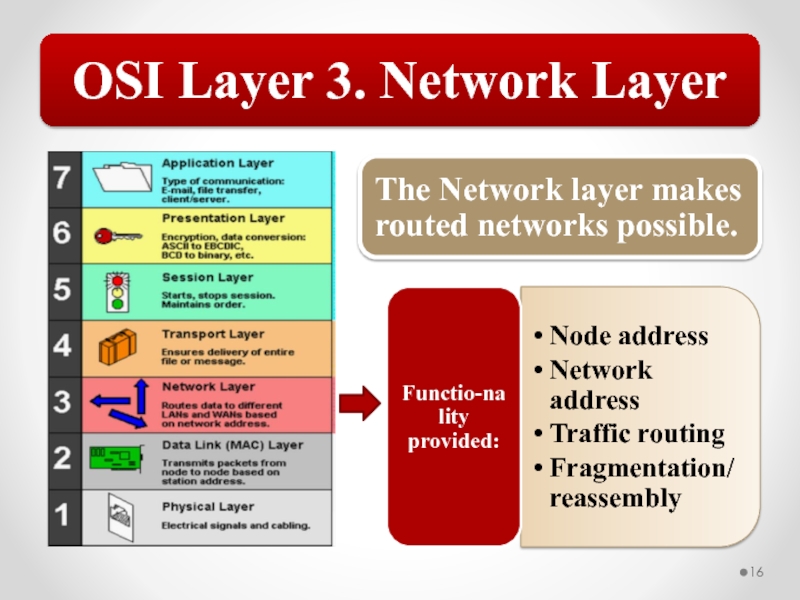
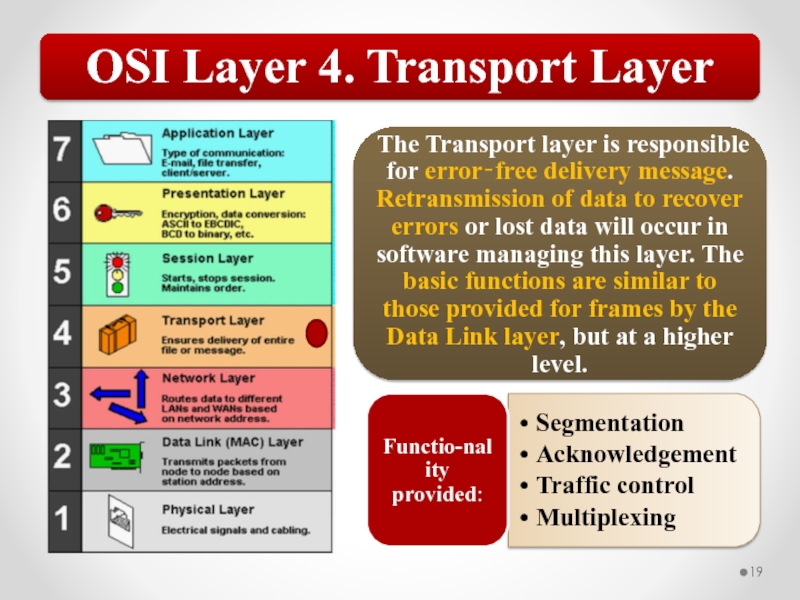
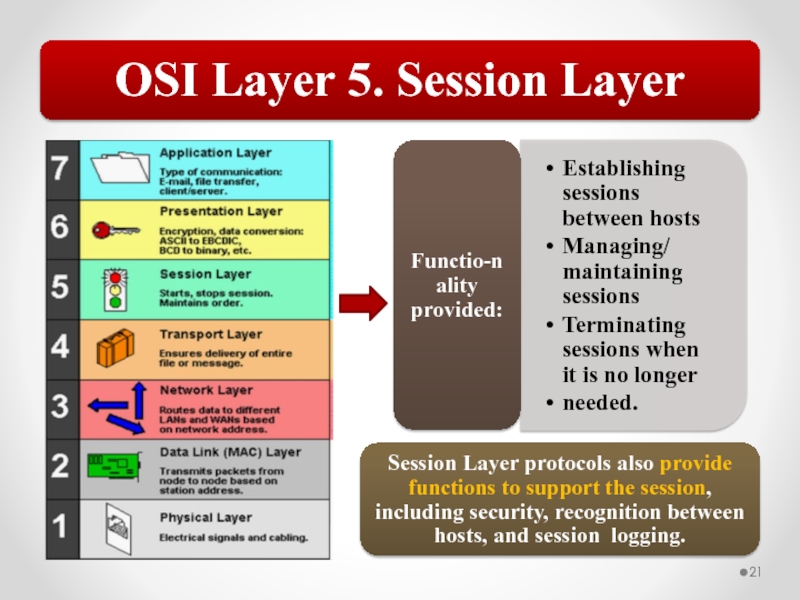
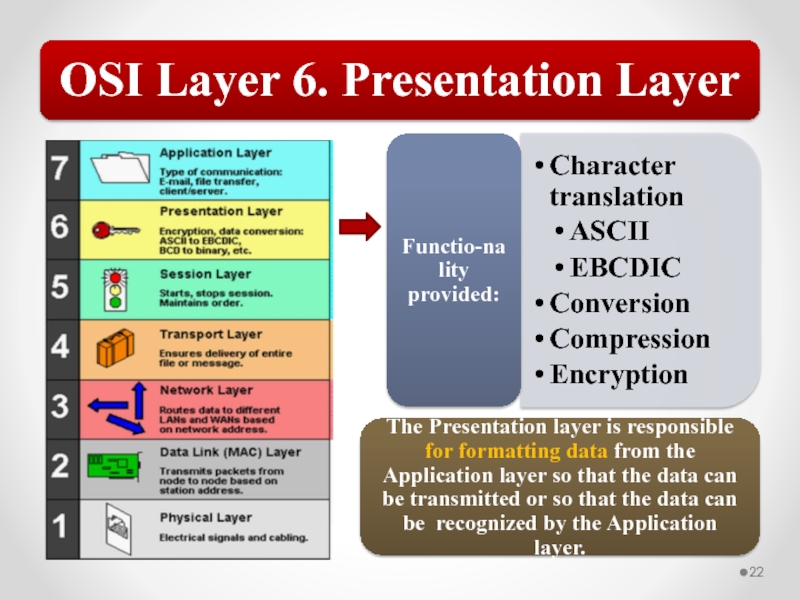
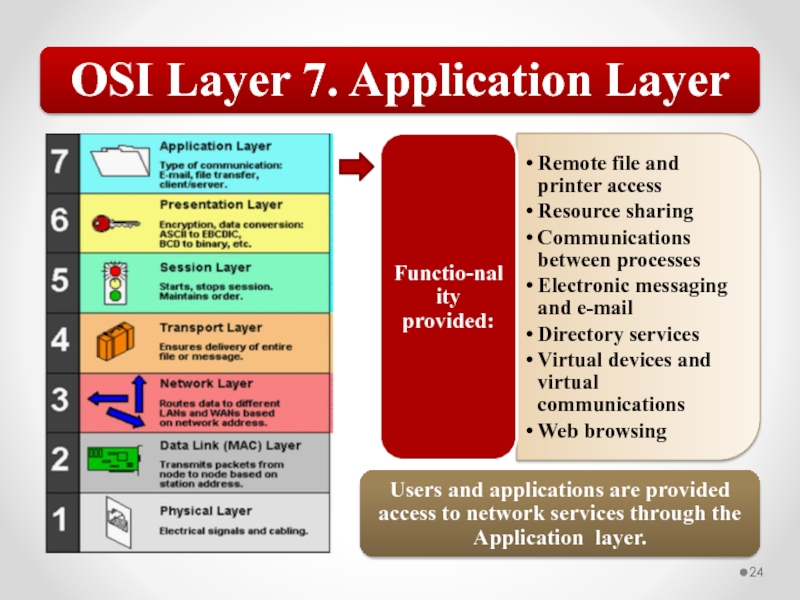
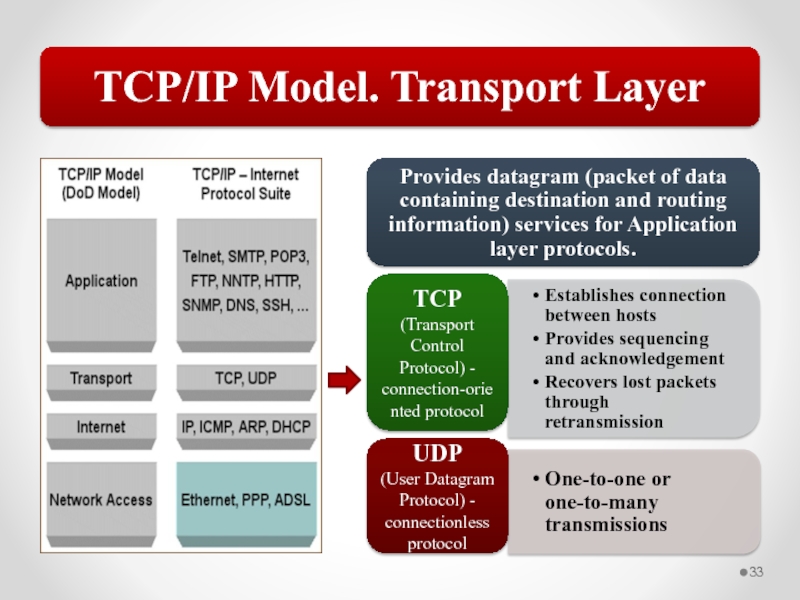
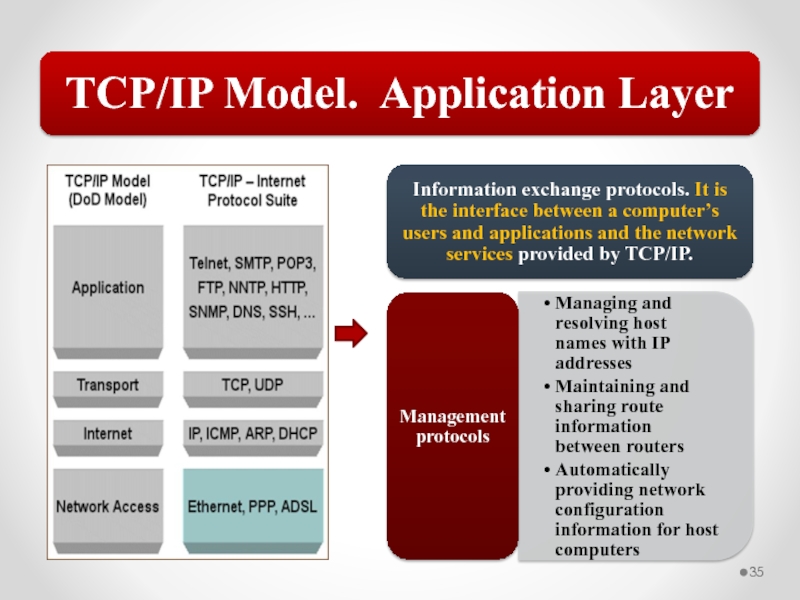
Слайд 57The OSI model describes network functions as seven distinct layers.
Layer 1,
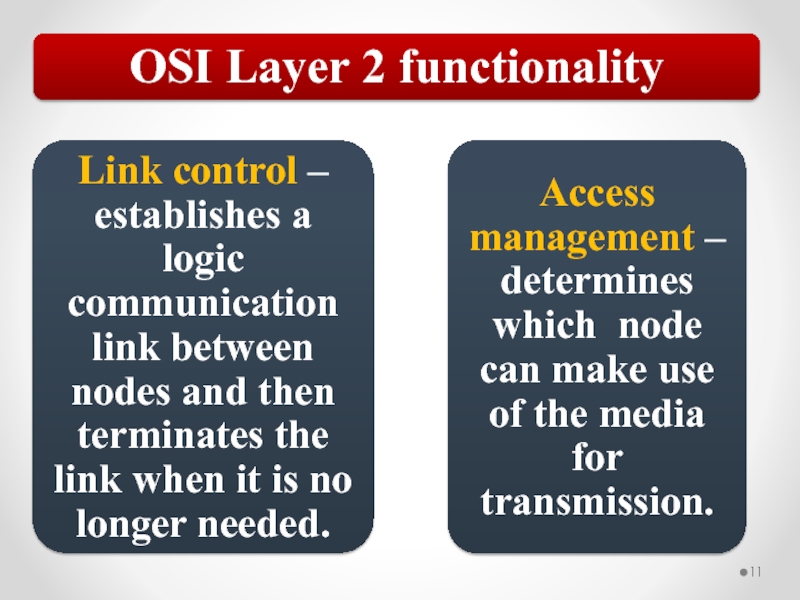
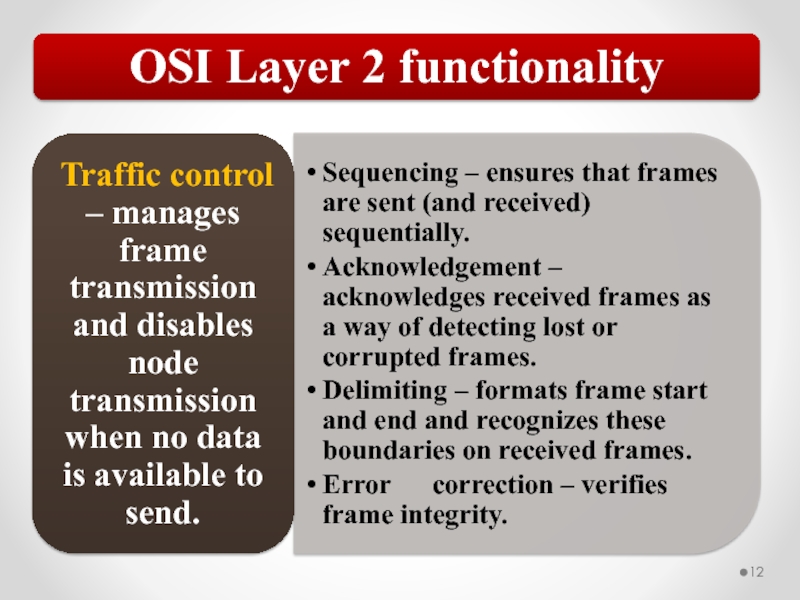
Layer 2, the Data Link layer, is responsible for low-level link control and traffic control.
Layer 3, the Network layer, is responsible for network addressing and routing traffic through a network.
Layer 4, the Transport layer, is responsible for ensuring error-free message delivery.
Layer 5, the Session layer, establishes and manages communication sessions between hosts.
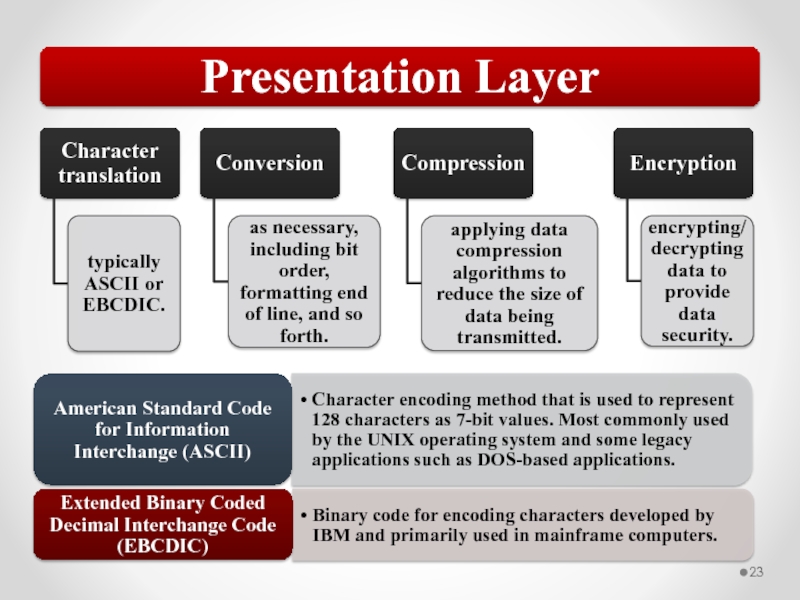
Layer 6, the Presentation layer, is responsible for data translation and formatting.
Layer 7, the Application layer, provides users and applications with access to networking functionality and network services.
Summary
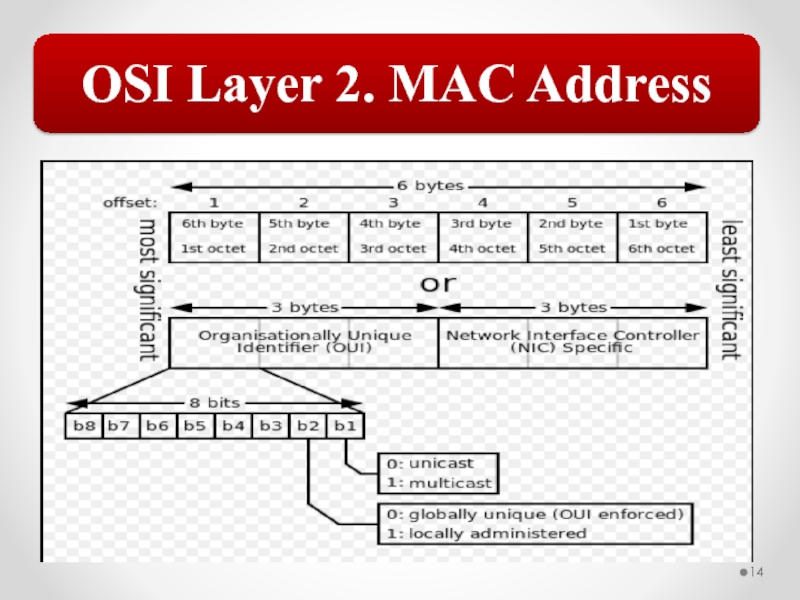
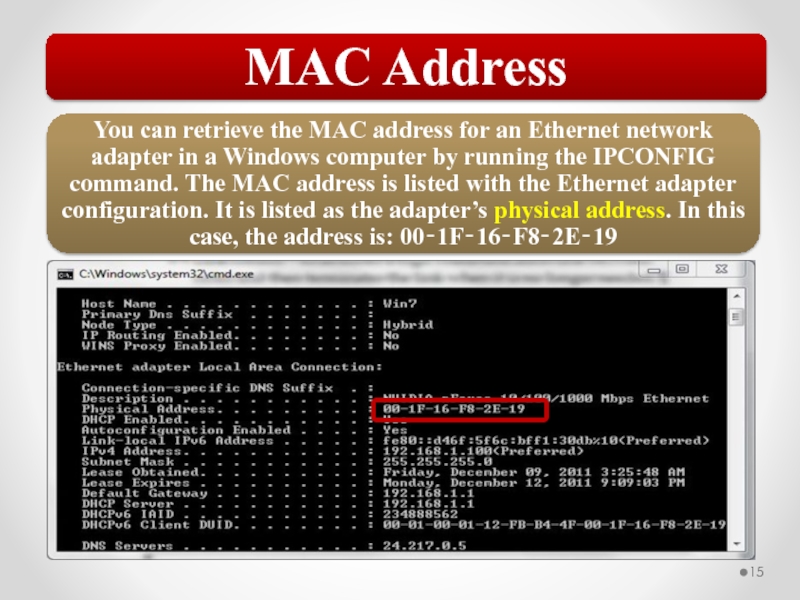
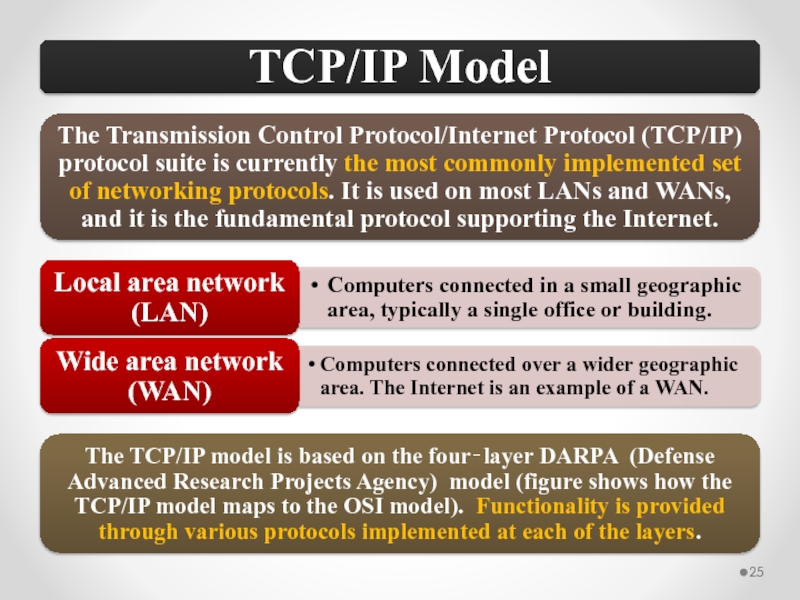
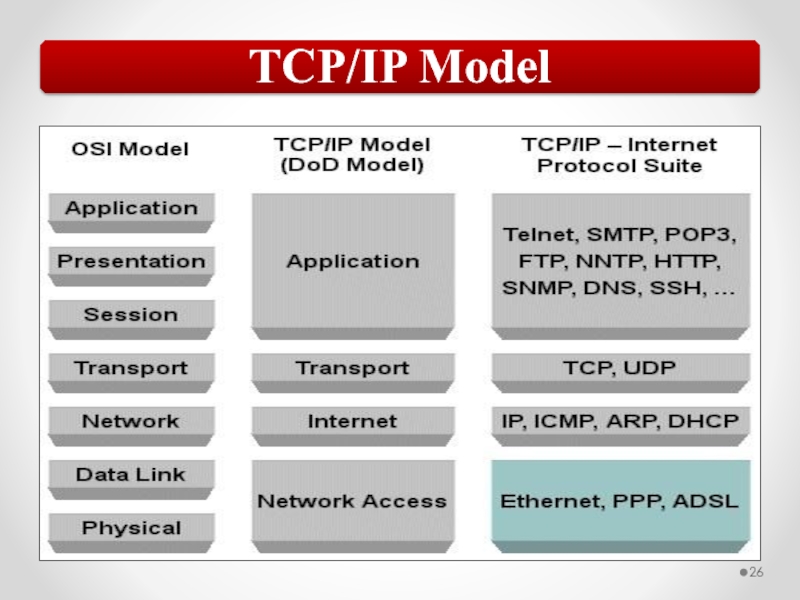
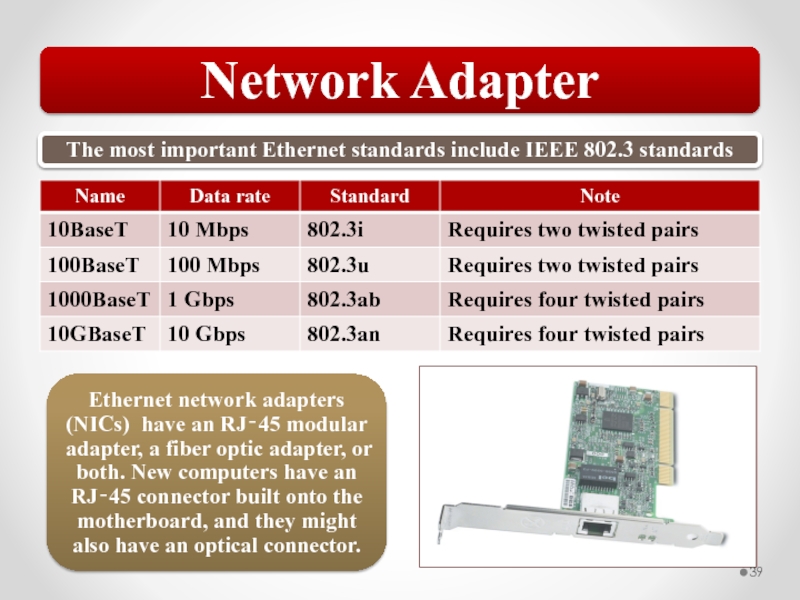
Слайд 58The MAC address is implemented at Layer 2 and uniquely identifies
The TCP/IP Network Interface layer implements functionality from the OSI model Physical and Data Link layers.
The TCP/IP Internet layer implements functionality from the OSI model Network layer (IPv4 and IPv6 are implemented at the Internet layer).
The TCP/IP Transport layer implements functionality from the OSI model Transport and Session layers.
The TCP/IP Application layer implements functionality from the OSI model Session, Presentation, and Application layers.
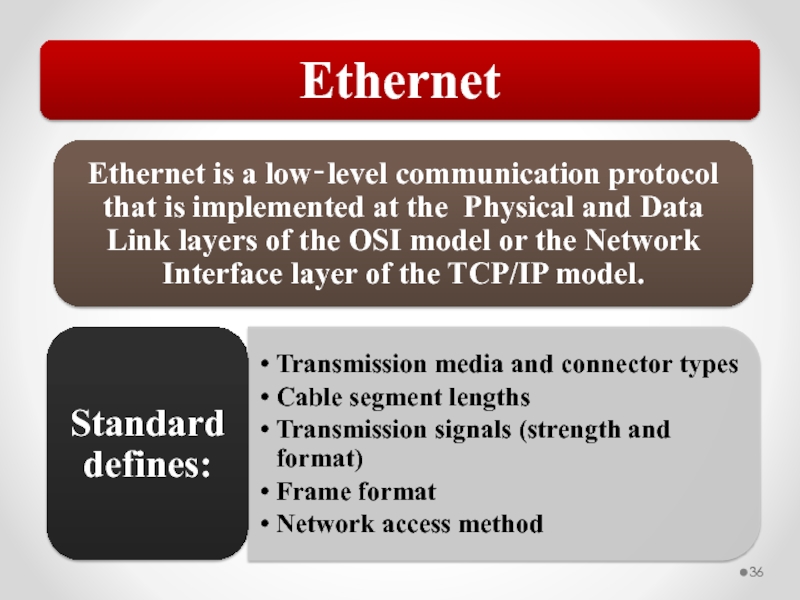
802.3 Ethernet and 802.11 Wi-Fi are implemented at the OSI model Physical and Data Link layers.
Summary (cont’d)
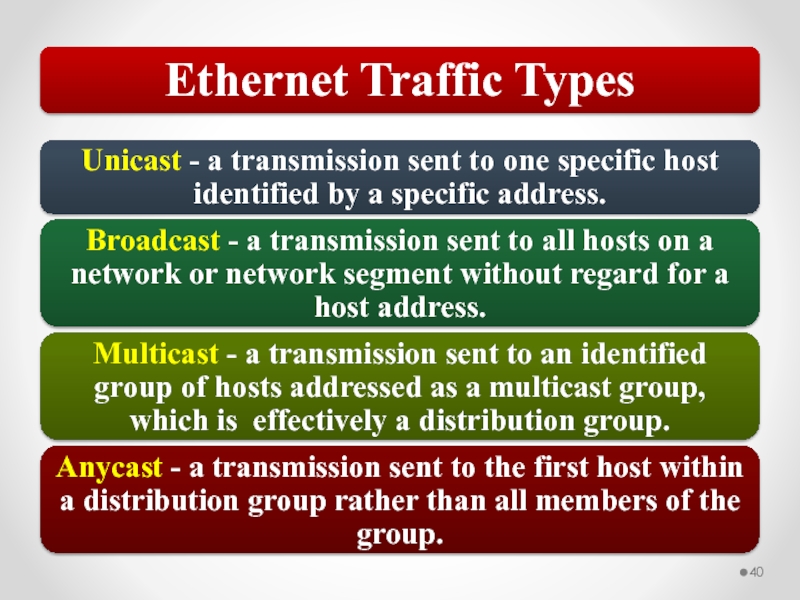
Слайд 59Network traffic can be a mix of unicast, broadcast, multicast, and
802.3 uses CSMA/CD for network access.
802.11 uses CSMA/CA for network access.
Authentication factors include what you know, what you have, and who you are.
Data security helps to prevent data from being improperly disclosed or corrupted.
VLANs provide a way to segment network devices based on port connection or other characteristics rather than physical location.
Summary (cont’d)