- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Segmental Stability of The Cervical Spine презентация
Содержание
- 1. Segmental Stability of The Cervical Spine
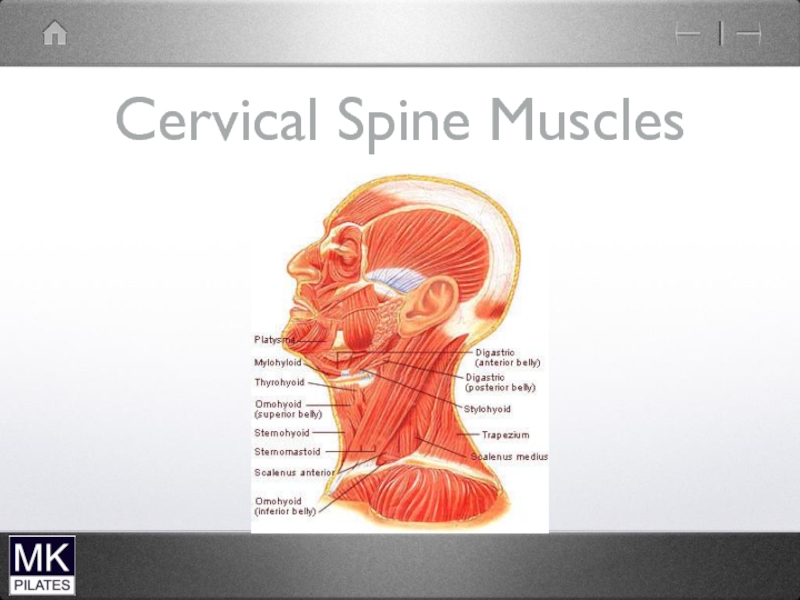
- 2. Cervical Spine Muscles
- 3. Neck Flexors Superficial Sternocleidomastoid Scalenes Supra-hyoid muscles
- 4. Deep neck flexors Deep Attach directly to
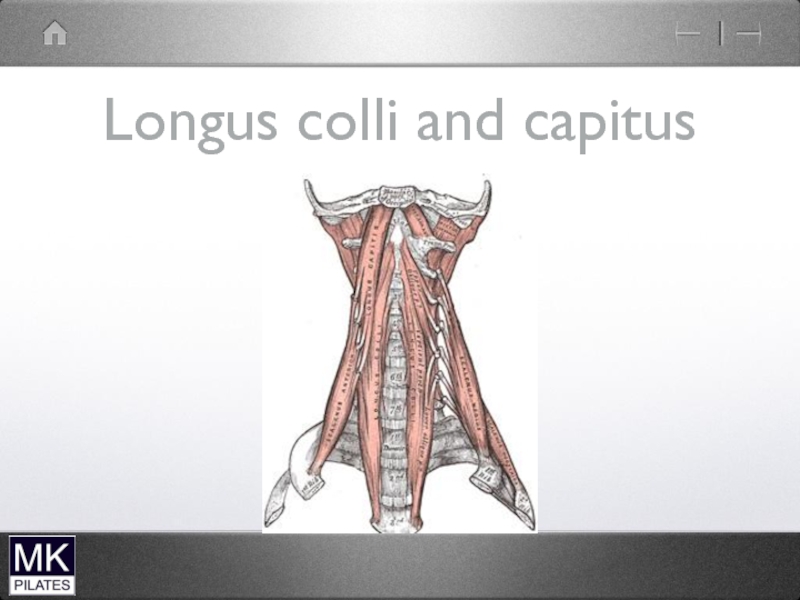
- 5. Longus colli and capitus
- 6. Longus colli and capitus
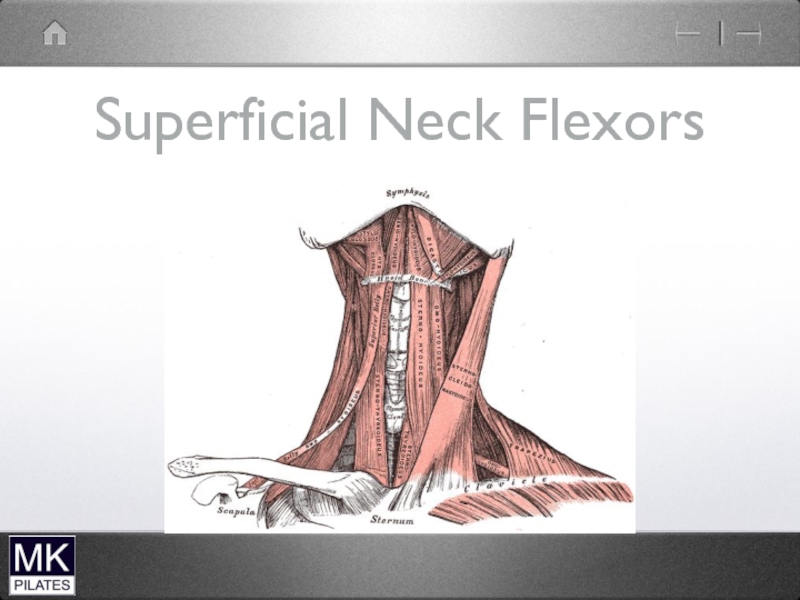
- 7. Superficial Neck Flexors Predominantly Mobilisers Also lateral
- 8. Superficial Neck Flexors
- 9. Scalenes
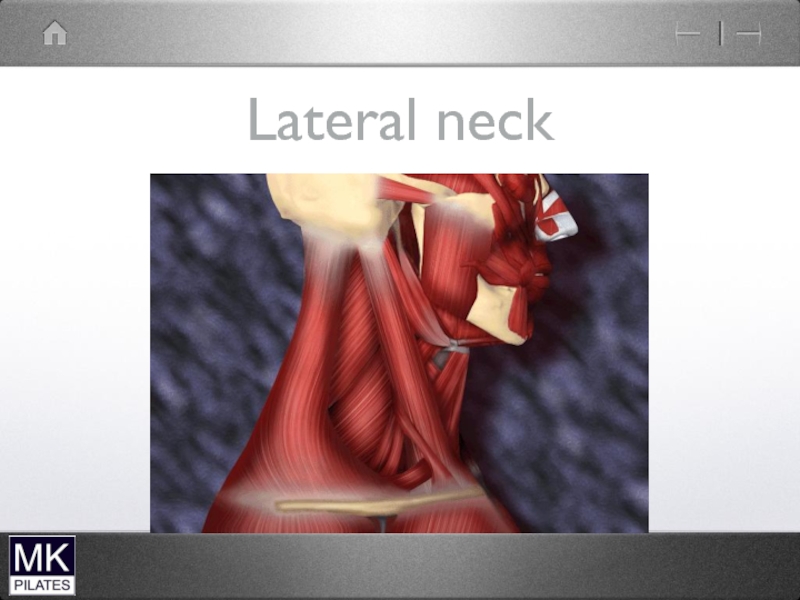
- 10. Lateral neck
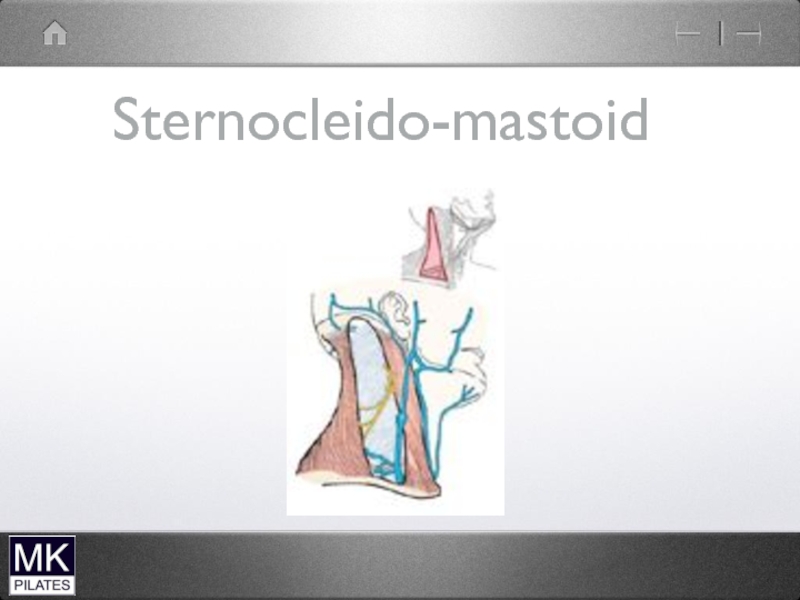
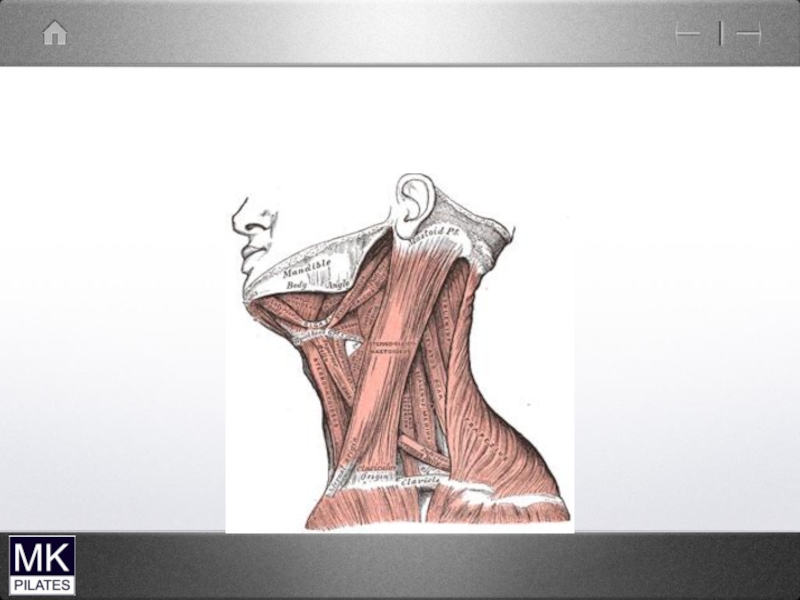
- 11. Sternocleido-mastoid
- 12. Sternocleido-mastoid
- 14. Neck Extensors Deep Extensors Spinales Semispinalis Rotators
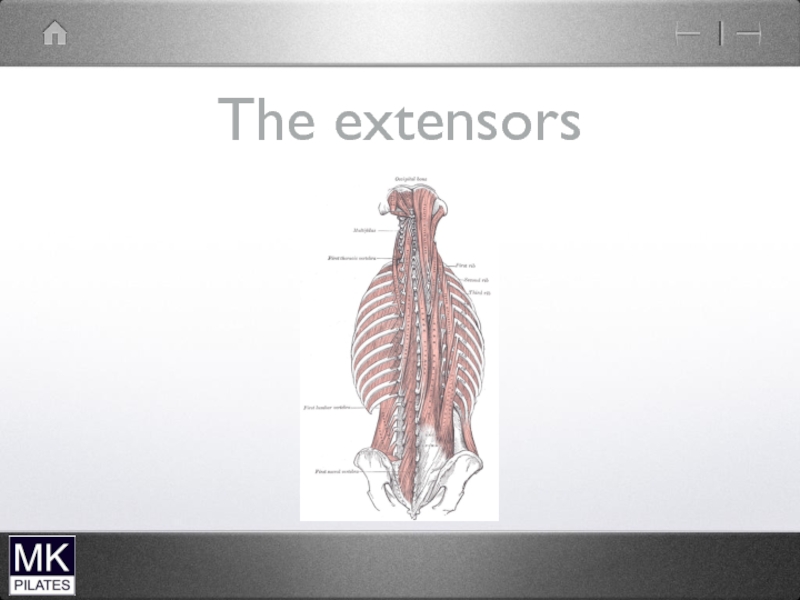
- 15. The extensors
- 16. Sub-Occipital Extensors ( upper cervical spine) Rectus
- 17. Upper cervical extensors Bilaterally upper cervical extension
- 18. Deep neck extensors ( mid to low
- 19. Deep neck extensors Segmental control of extension
- 20. Mobility Muscles Splenius mastoid to C4-T3 Slenius
- 21. Superficial Extensors Upper and lower cervical extension
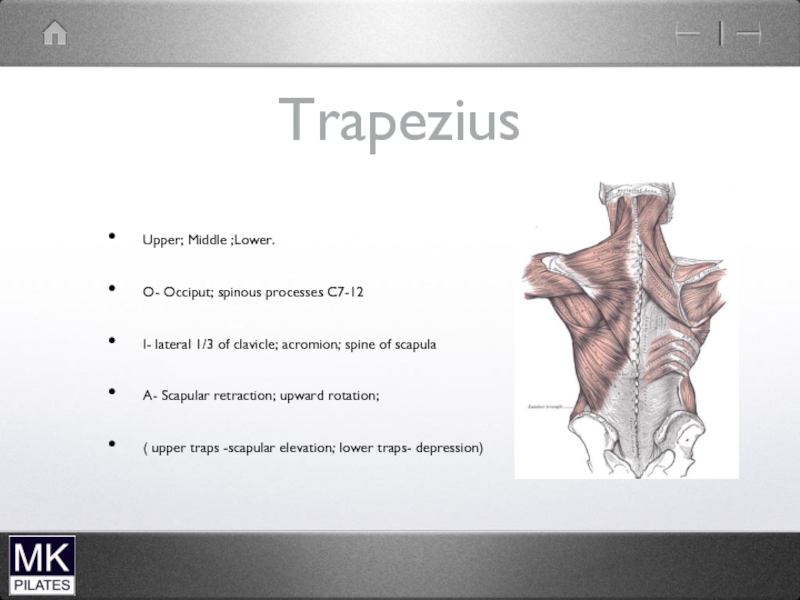
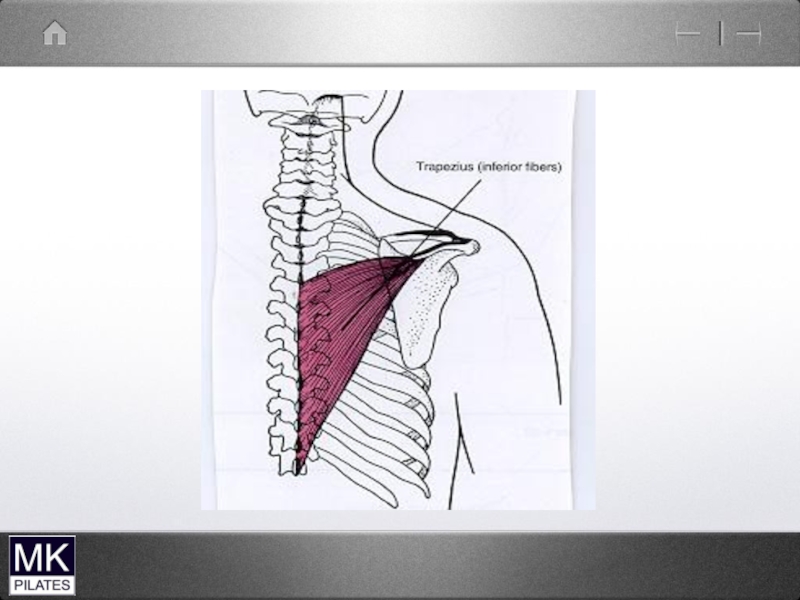
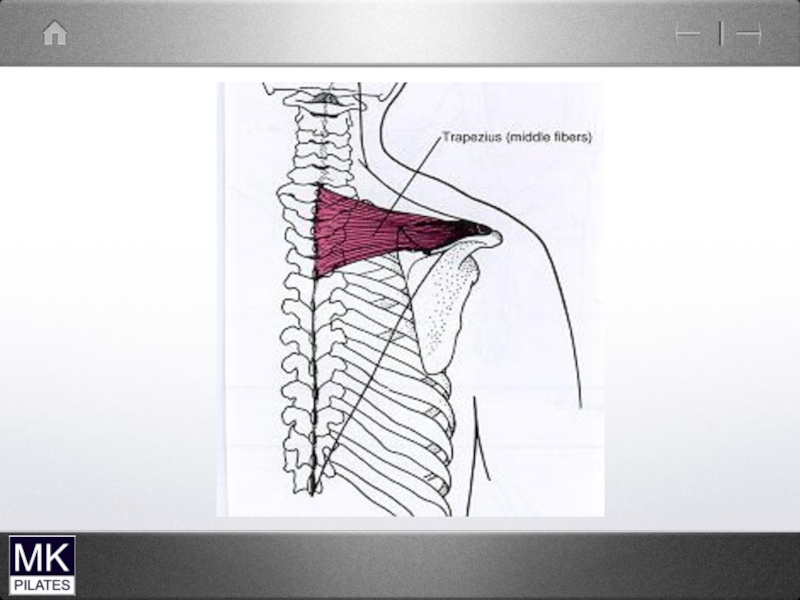
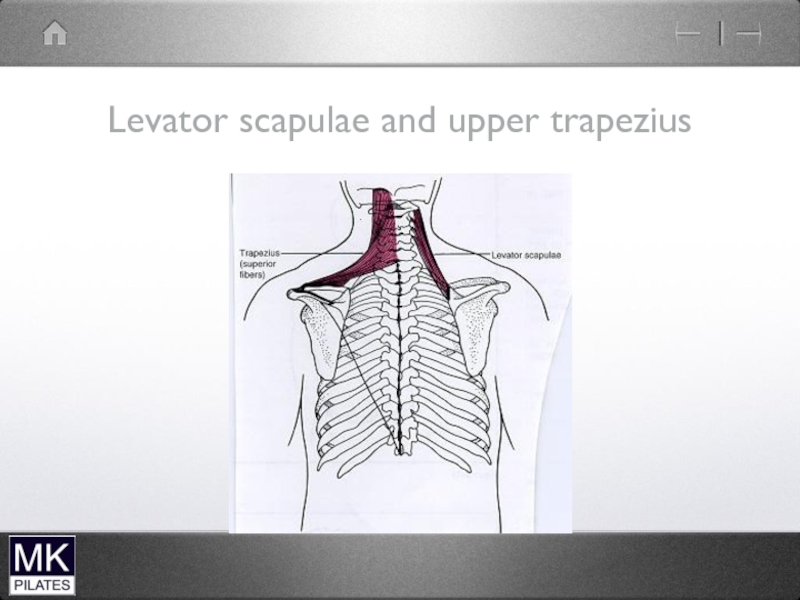
- 22. Upper Trapezius and levator Scapulae
- 23. Trapezius
- 24. Levator Scapulae and Upper Trapezius Mainly mobility
- 25. Ideal Neck Posture Plane of neck and
- 26. Common Posture types Chin Poke ( upper
- 27. Work posture
- 28. Chin Poke upper cervical spine Short/overactive muscles
- 29. Chin Poke
- 30. Forward Head lower cervical spine Short overactive
- 32. Forward Head Posture
- 35. Make best use of office space
- 36. Occupational therapy for patients can be used creatively to ease the A&C shortages
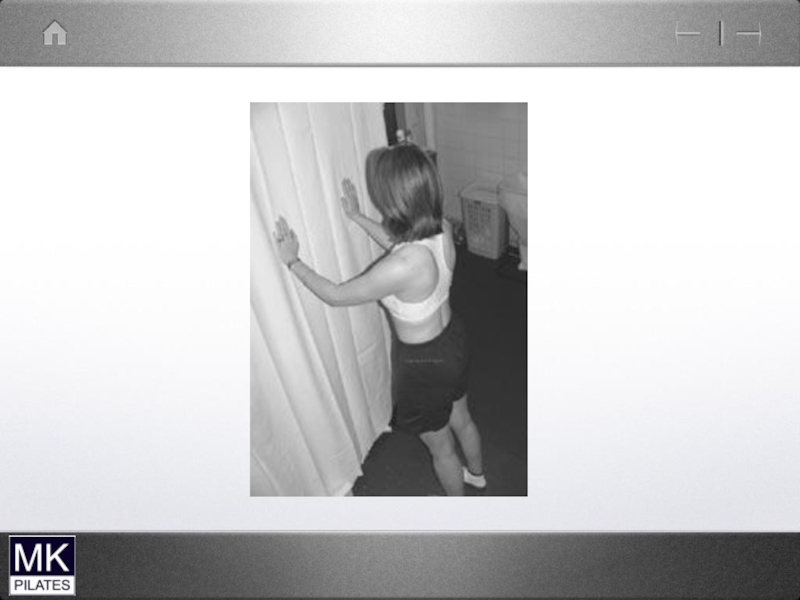
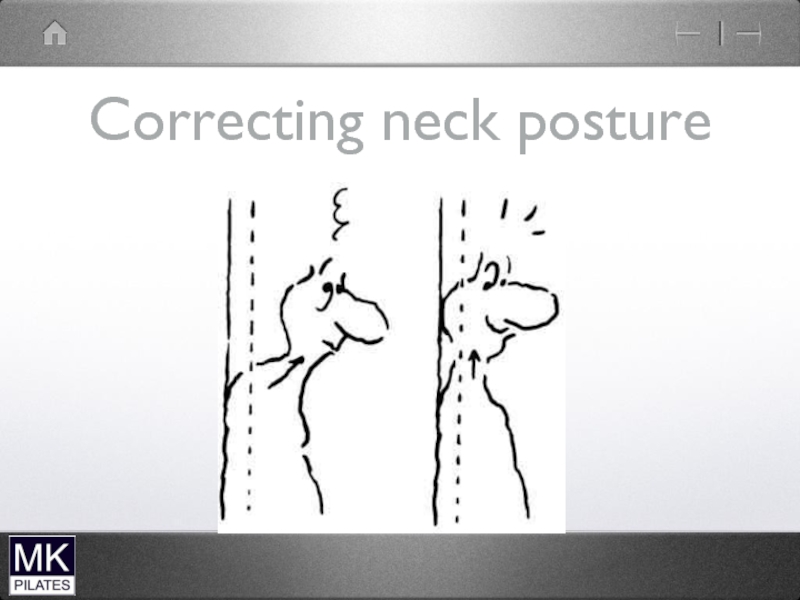
- 37. Correcting neck posture
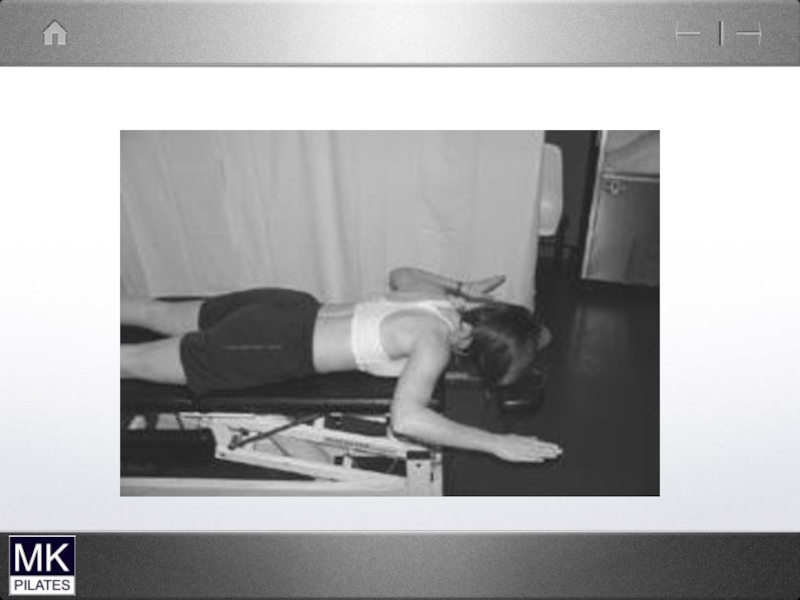
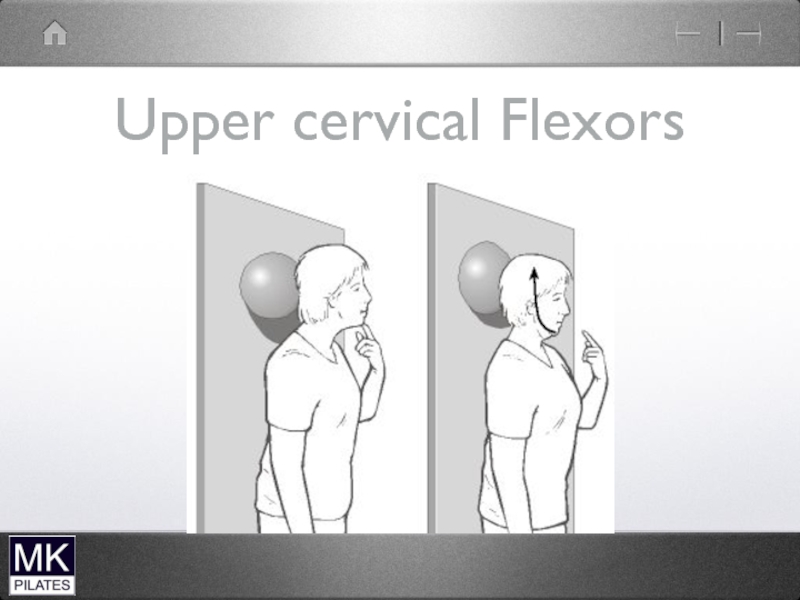
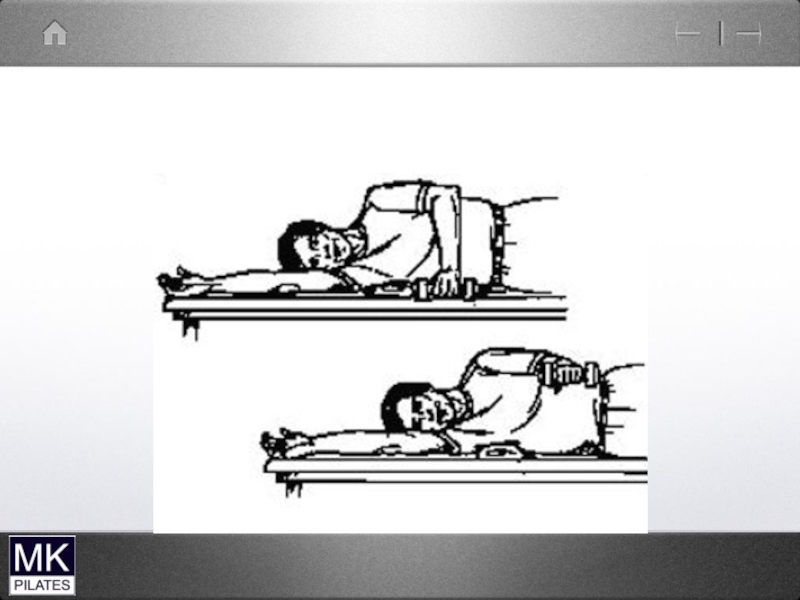
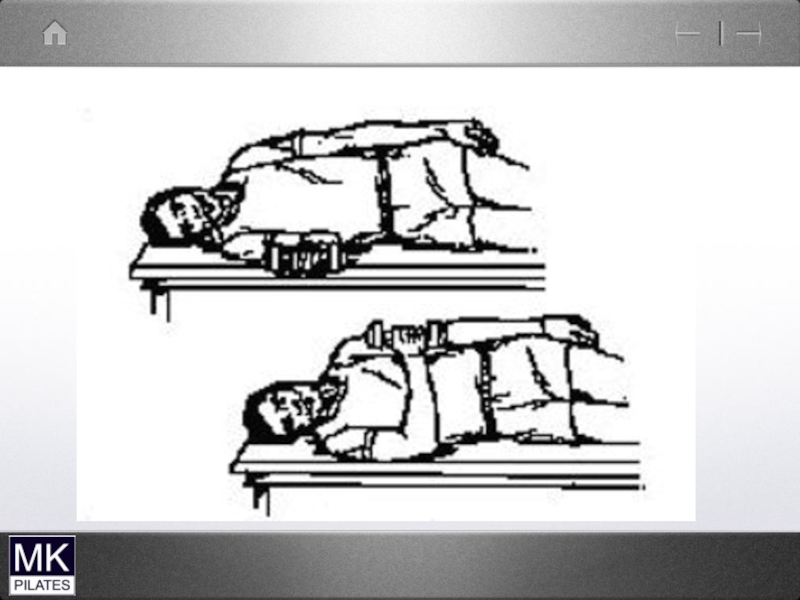
- 38. Upper cervical Flexors
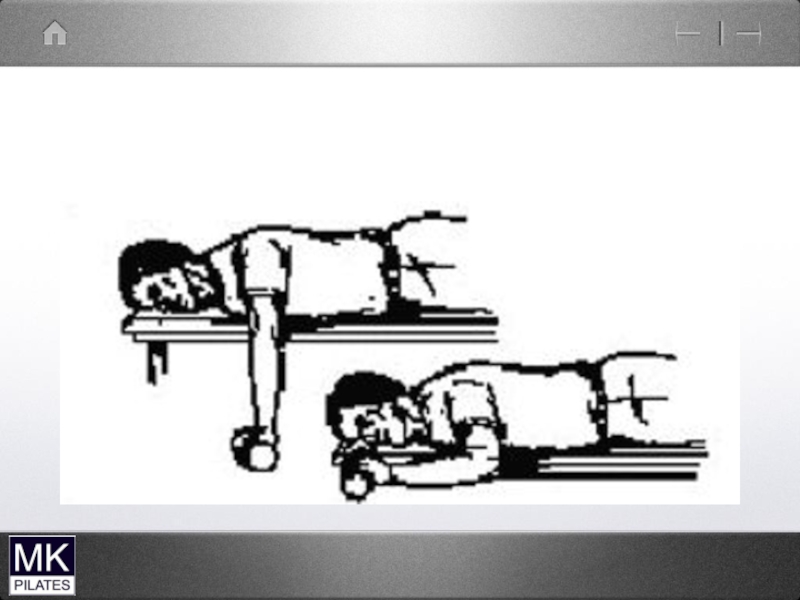
- 40. Cervical flexion test-supine Lead with chin…..dominant sterno-cleidomastoid
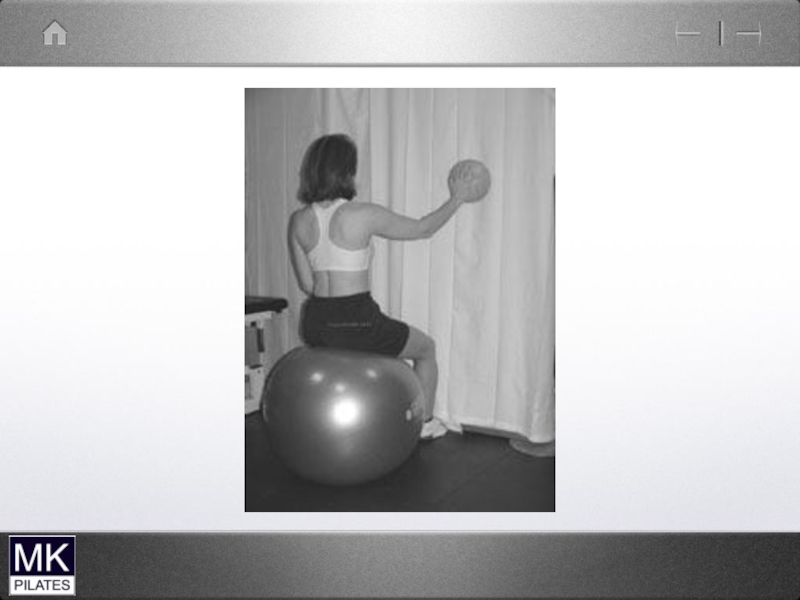
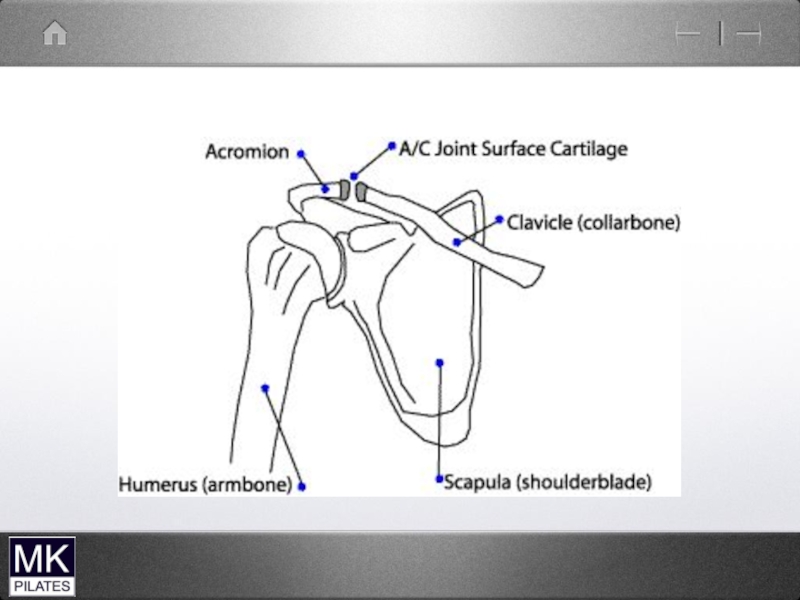
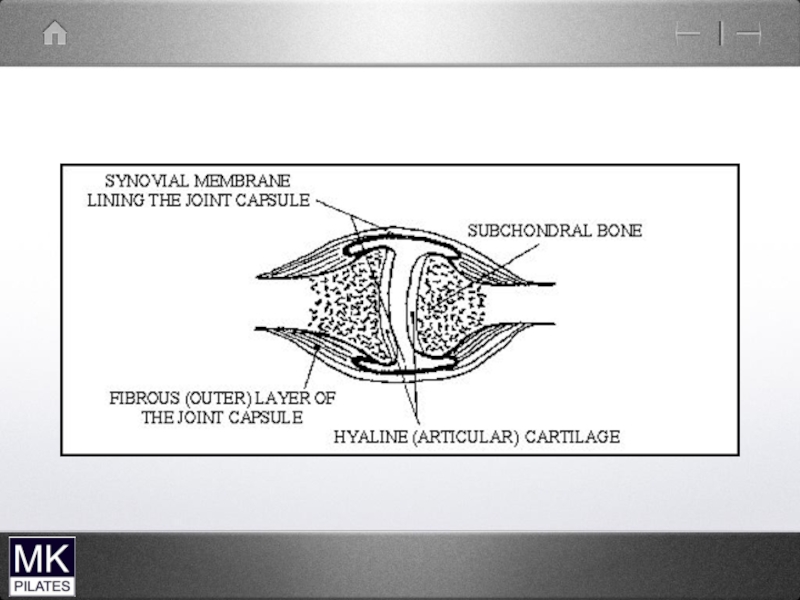
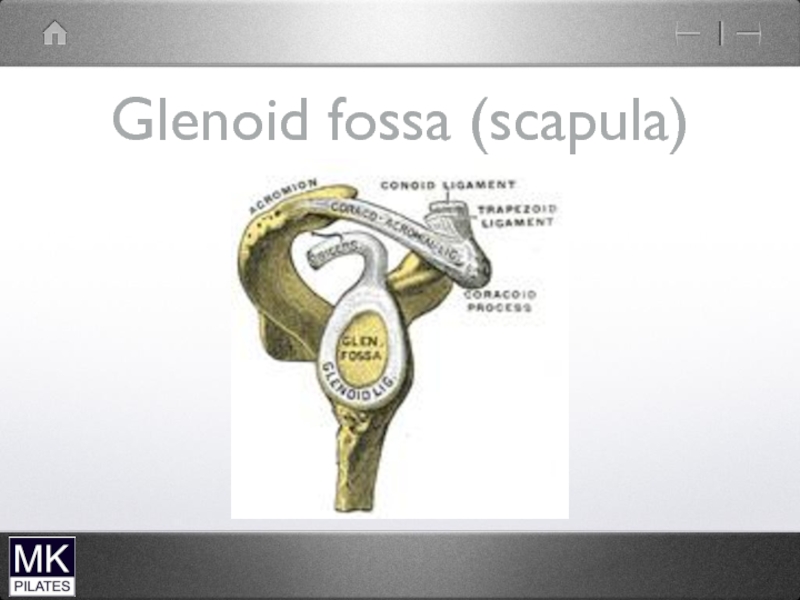
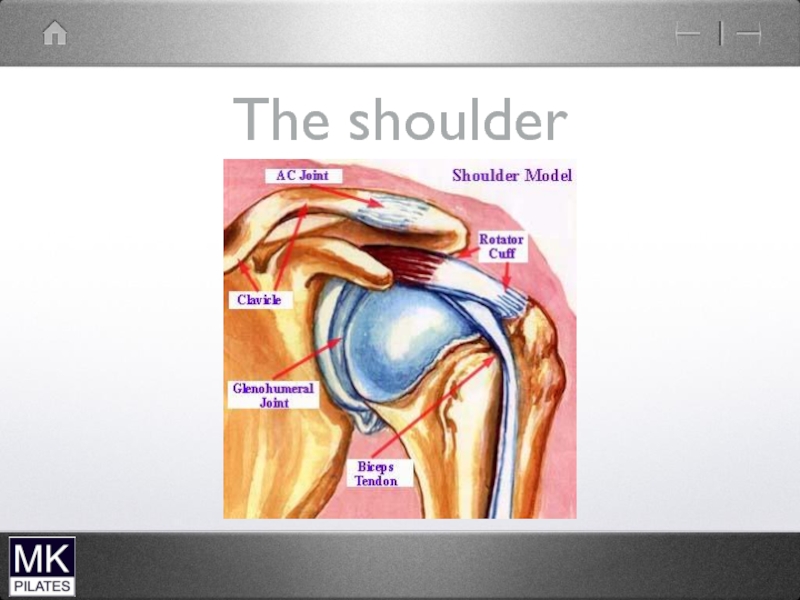
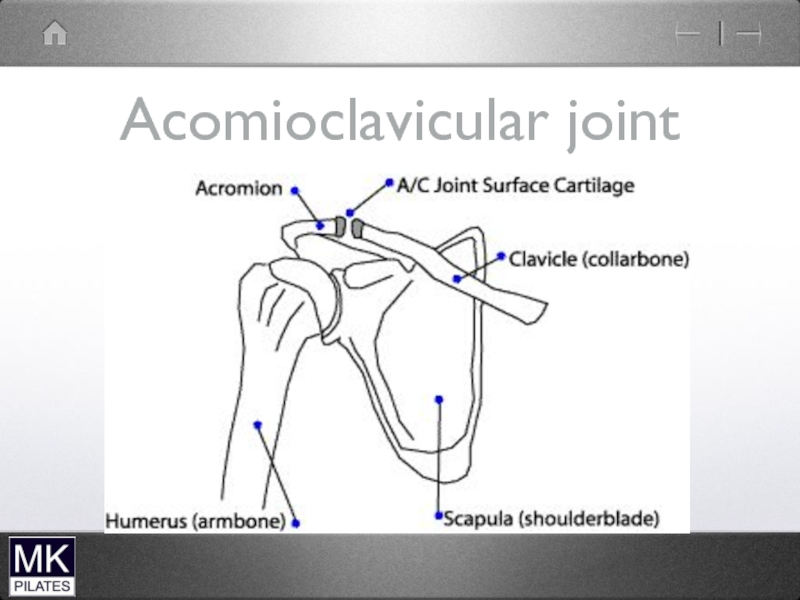
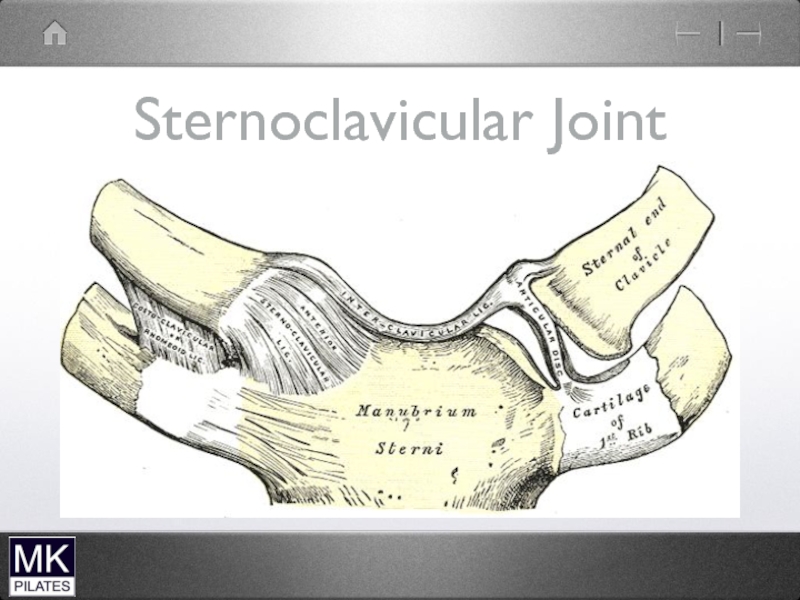
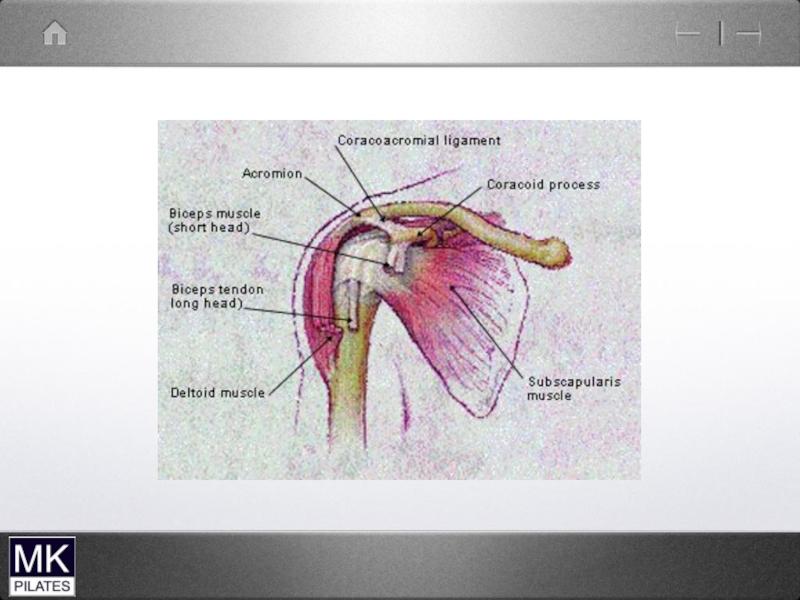
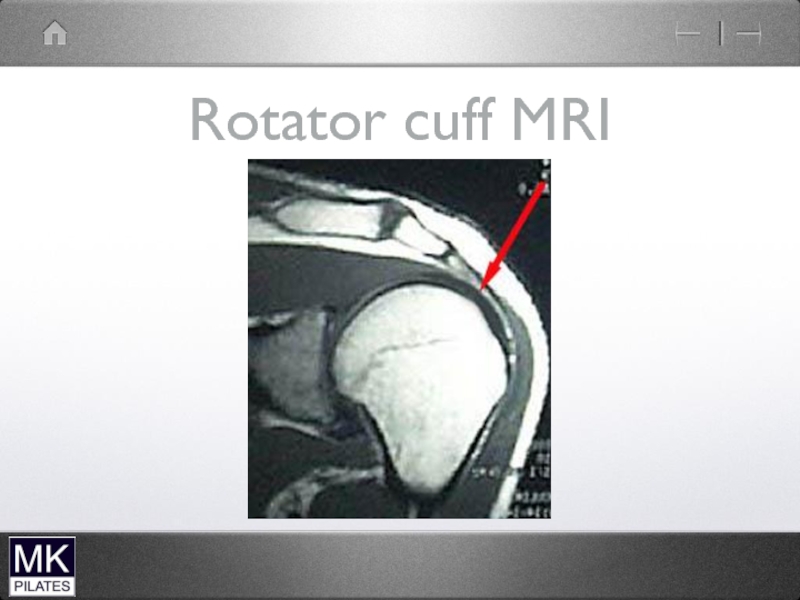
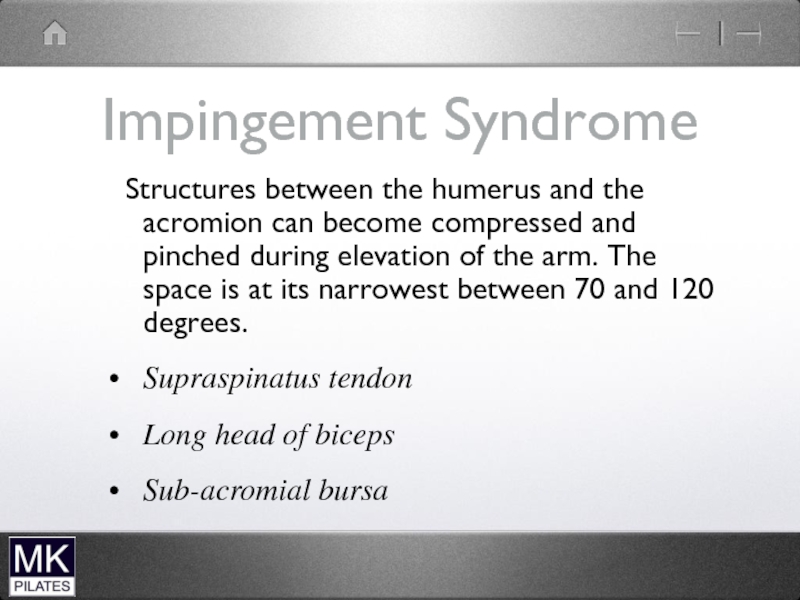
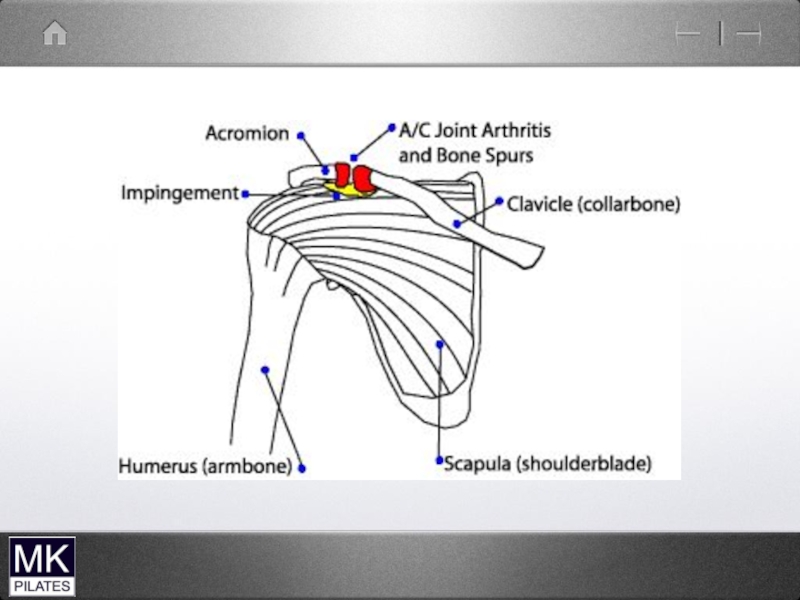
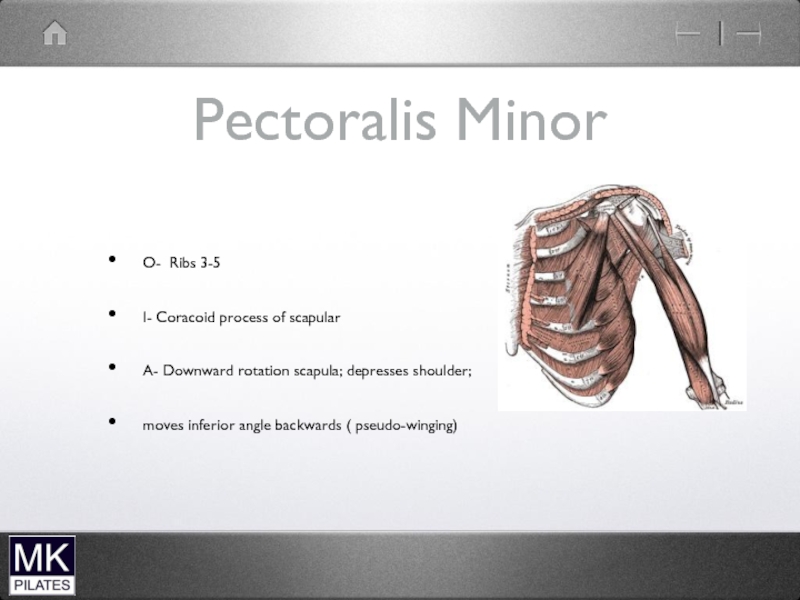
- 42. The Shoulder Complex
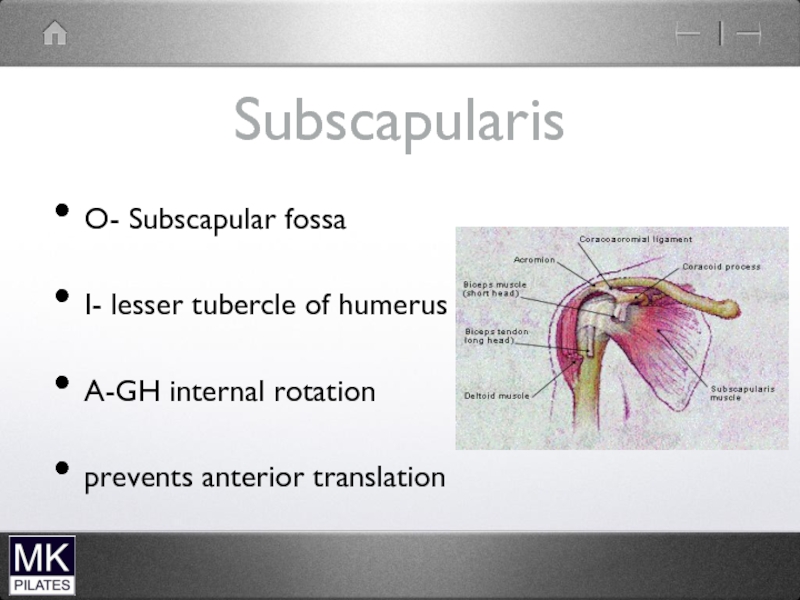
Слайд 3Neck Flexors
Superficial
Sternocleidomastoid
Scalenes
Supra-hyoid muscles
Infrahyoid musles
Deep
Longus Colli
Longus Capitus
Rectus Capitus
Anterior
Rectus Capitus Lateralis
Rectus Capitus Lateralis
Слайд 4Deep neck flexors
Deep
Attach directly to the vertebrae
Single segments
Close to axis of
rotation
Tonic activity
Support the spinal curve
Tonic activity
Support the spinal curve
Слайд 7Superficial Neck Flexors
Predominantly Mobilisers
Also lateral flexion and rotation
Hyoid muscles also control
hyoid movement (for speech and swallowing)
therefore only secondary cervical spine mobilisers
therefore only secondary cervical spine mobilisers
Слайд 14Neck Extensors
Deep Extensors
Spinales
Semispinalis
Rotators
Intertransversarii
Interspinales
Suboccipital extensors
Multifidus
Superficial Extensors
Upper trapezius
Levator scapulae
Splenius
Longisimus
Слайд 16Sub-Occipital Extensors
( upper cervical spine)
Rectus Capitus posterior major and minor
Occiput to C1 and C2
Obliquus capitus superior and inferior
Occiput to C1 and C1 to C2
Head on Neck Stabilisers
Obliquus capitus superior and inferior
Occiput to C1 and C1 to C2
Head on Neck Stabilisers
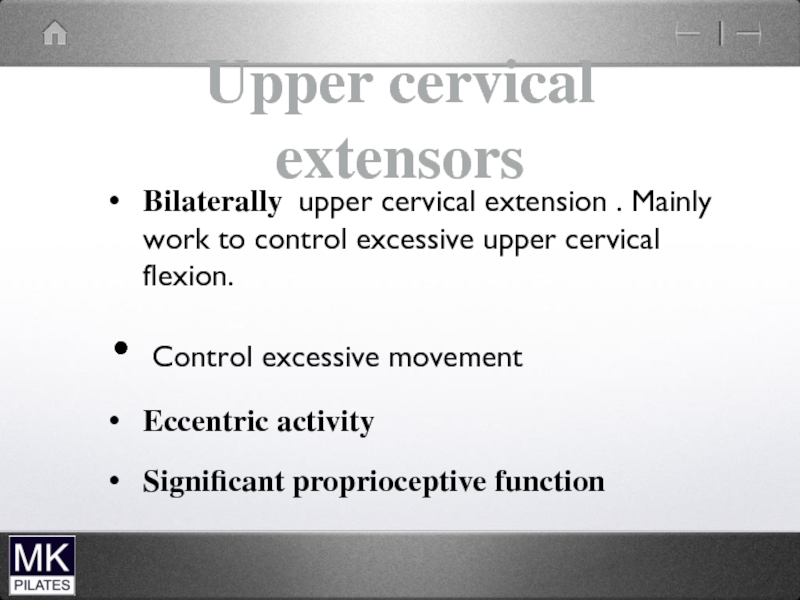
Слайд 17Upper cervical extensors
Bilaterally upper cervical extension . Mainly work to control
excessive upper cervical flexion.
Control excessive movement
Eccentric activity
Significant proprioceptive function
Control excessive movement
Eccentric activity
Significant proprioceptive function
Слайд 18Deep neck extensors
( mid to low cervical spine)
Eccentric action to control
movement
Proprioceptive role
Proprioceptive role
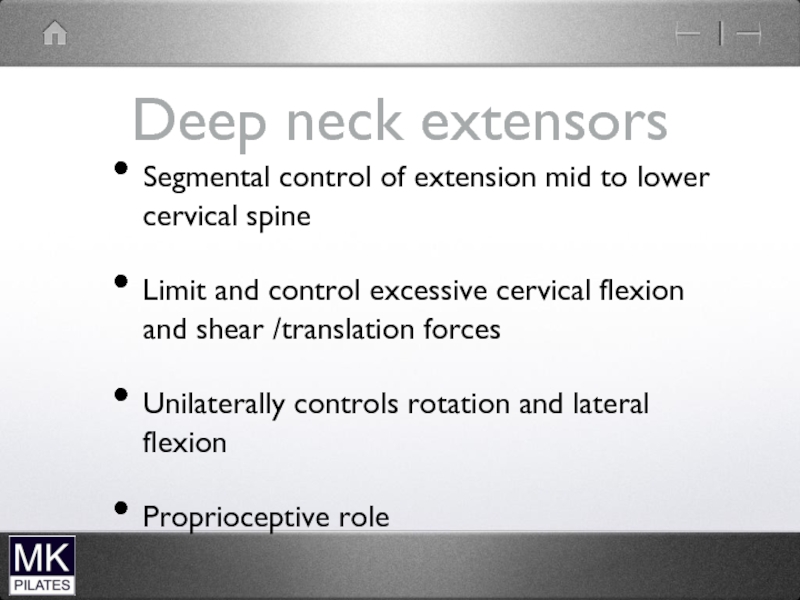
Слайд 19Deep neck extensors
Segmental control of extension mid to lower cervical spine
Limit
and control excessive cervical flexion and shear /translation forces
Unilaterally controls rotation and lateral flexion
Proprioceptive role
Unilaterally controls rotation and lateral flexion
Proprioceptive role
Слайд 20Mobility Muscles
Splenius mastoid to C4-T3
Slenius cervicus TP C1-2 to Sp T4-6
Longissimus
capitus Mastoid to TPC5-6
Iliocostalis cervicus TP C4-6 to ribs 3-6
Levator scapulae TP C1-4 to superiormedial border of scapula
Lets just call them superficial extensors!!!
Iliocostalis cervicus TP C4-6 to ribs 3-6
Levator scapulae TP C1-4 to superiormedial border of scapula
Lets just call them superficial extensors!!!
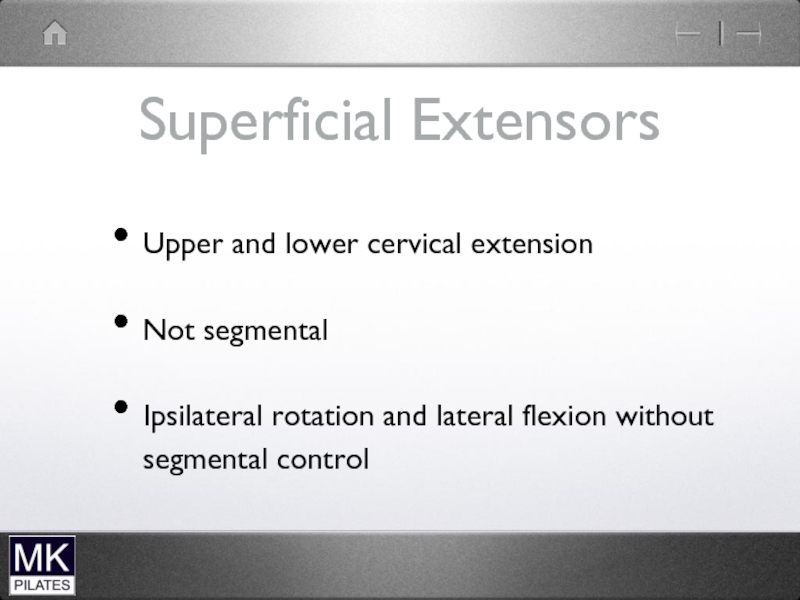
Слайд 21Superficial Extensors
Upper and lower cervical extension
Not segmental
Ipsilateral rotation and lateral
flexion without segmental control
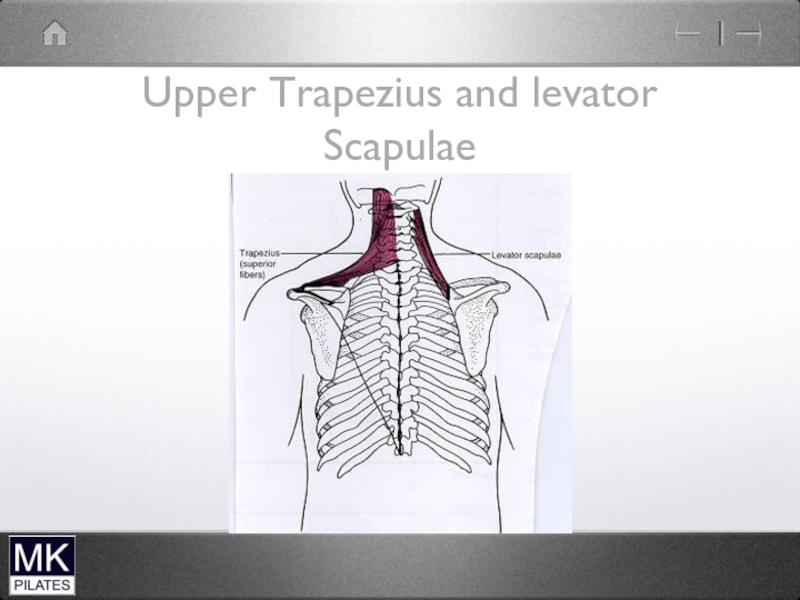
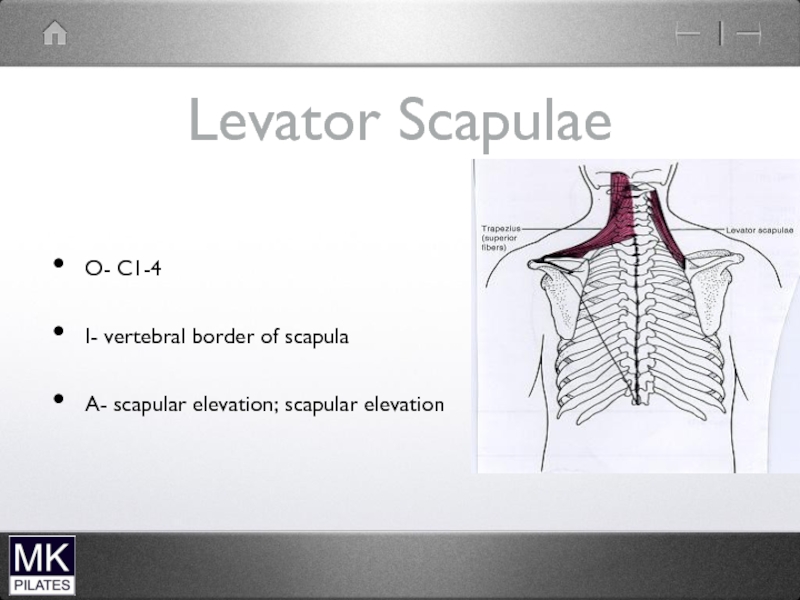
Слайд 24Levator Scapulae and Upper Trapezius
Mainly mobility of scapula
Can also produce Neck
extension and lateral flexion but not their prime role
No segmental control
problematic if become short and stiff
No segmental control
problematic if become short and stiff
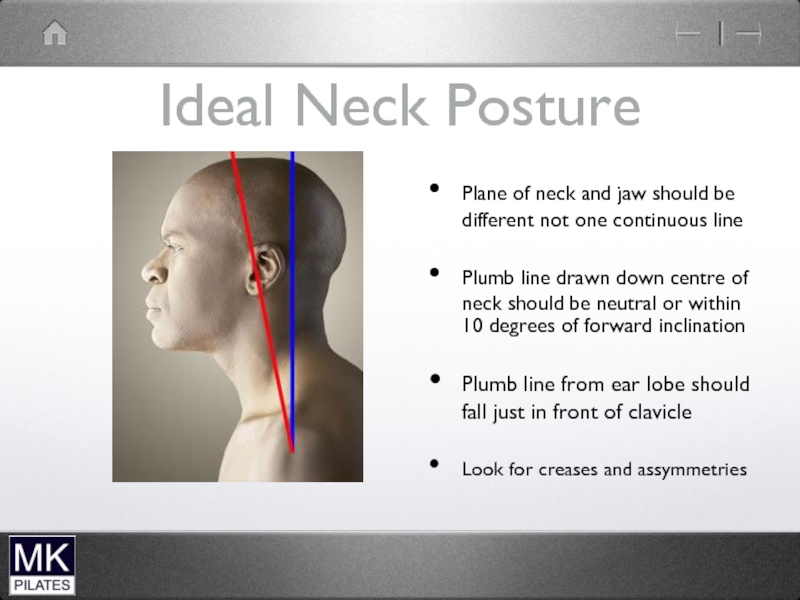
Слайд 25Ideal Neck Posture
Plane of neck and jaw should be different not
one continuous line
Plumb line drawn down centre of neck should be neutral or within 10 degrees of forward inclination
Plumb line from ear lobe should fall just in front of clavicle
Look for creases and assymmetries
Plumb line drawn down centre of neck should be neutral or within 10 degrees of forward inclination
Plumb line from ear lobe should fall just in front of clavicle
Look for creases and assymmetries
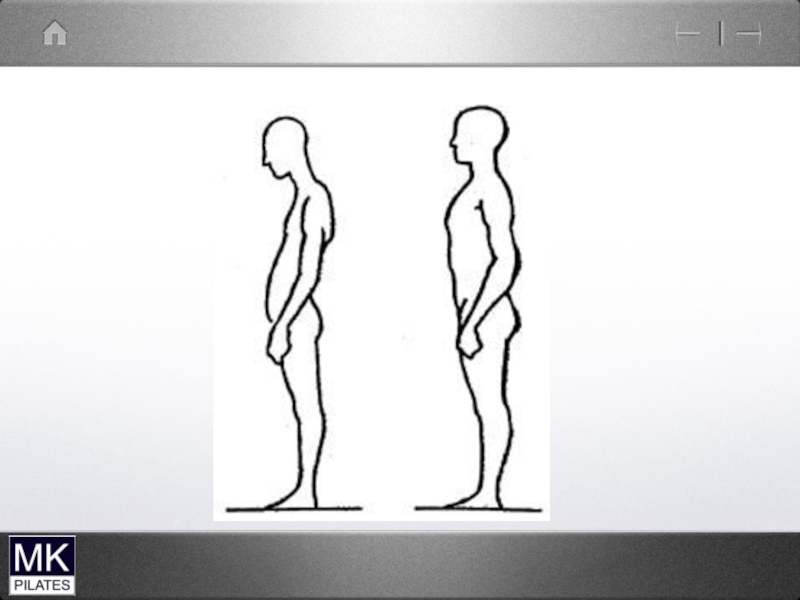
Слайд 26Common Posture types
Chin Poke ( upper cervical spine)
Forward head ( lower
cervical spine)
Forward head with chin poke
Can also get a hinge or mid cervical collapse
Forward head with chin poke
Can also get a hinge or mid cervical collapse
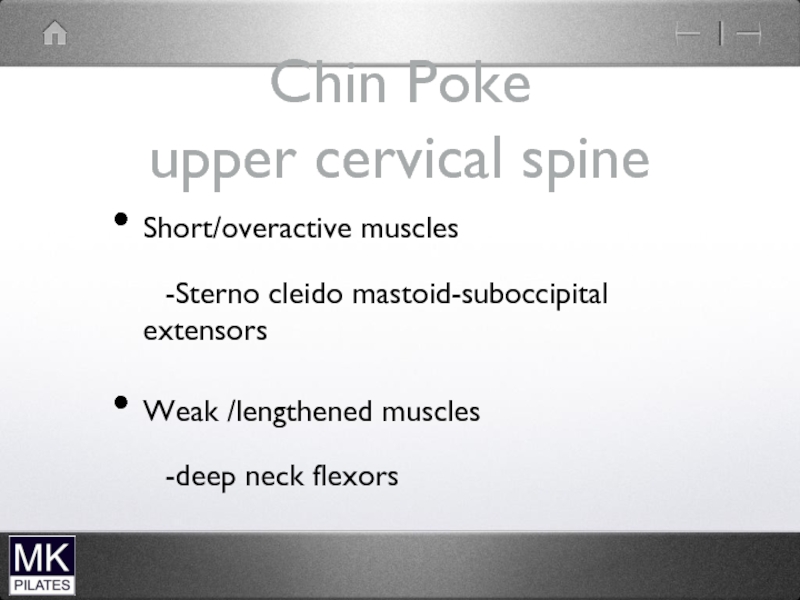
Слайд 28Chin Poke
upper cervical spine
Short/overactive muscles
-Sterno cleido mastoid-suboccipital extensors
Weak /lengthened muscles
-deep neck
flexors
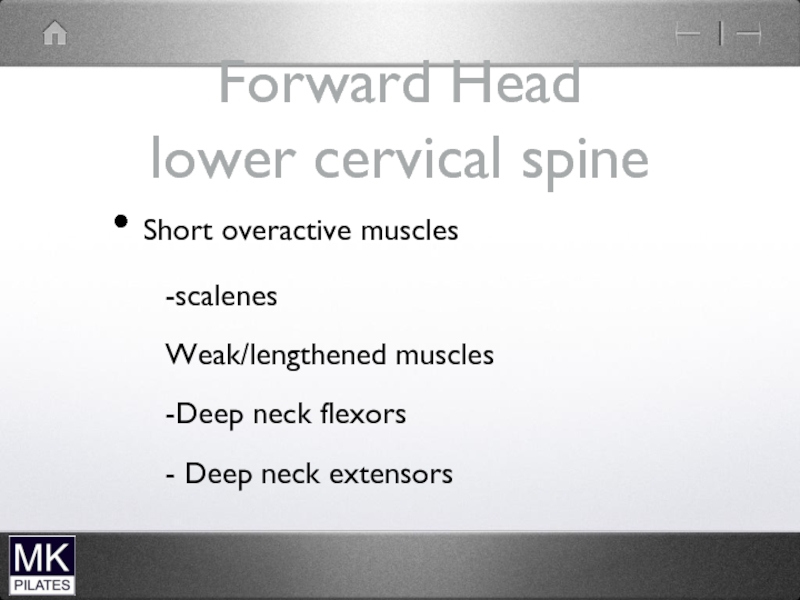
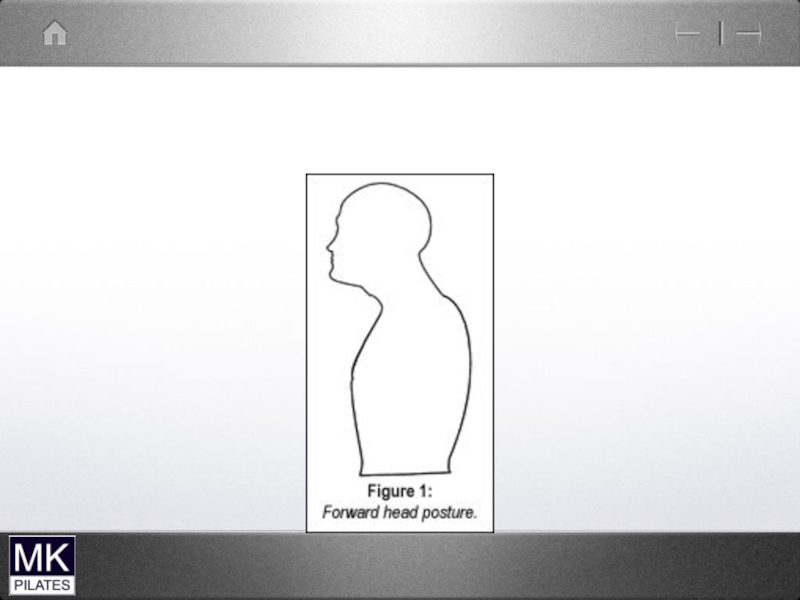
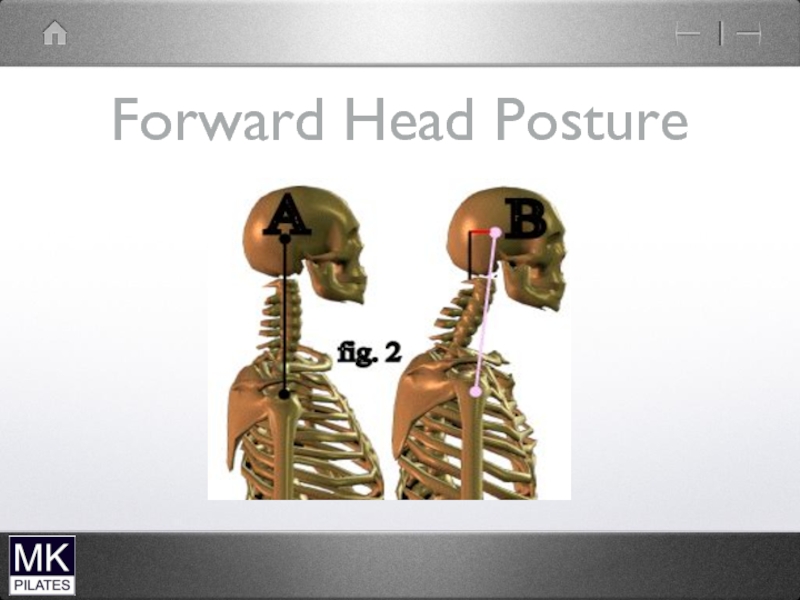
Слайд 30Forward Head
lower cervical spine
Short overactive muscles
-scalenes
Weak/lengthened muscles
-Deep neck flexors
- Deep neck
extensors
Слайд 40Cervical flexion test-supine
Lead with chin…..dominant sterno-cleidomastoid
Over flexion upper cervical spine …overactive
scalenes
Clenching of teeth…hyoid muscles
Clenching of teeth…hyoid muscles