- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Hypoxia. (Subject 7) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Hypoxia. (Subject 7)
- 2. Hypoxia classification
- 3. Hypoxia classification Due to time of development
- 4. Hypoxia classification Due to prevalence of clinical
- 5. Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia hypobaric type ? atmospheric
- 6. Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia normobaric type Normal atmospheric
- 7. Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia Low oxygen in
- 8. Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia Low oxygen
- 9. Respiratory hypoxia Causes Disturbances of lungs
- 10. Respiratory hypoxia Alveolar hypoventilation reasons: Obstructive violations
- 11. Respiratory hypoxia Disturbances of lungs blood supply
- 12. Circulatory hypoxia Causes vascular disorders Decreased heart activity Hypovolaemia
- 13. Circulatory hypoxia - systemic Decrease of heart
- 14. Circulatory hypoxia Local type of circulatory hypoxia
- 15. Hemic hypoxia Anemic type – accompanying different
- 16. Hemic hypoxia The reasons of anemia: chronic
- 17. Hemic hypoxia Carbon monoxide poisoning: CO has
- 18. Histotoxic hypoxia The inability of cells to
- 19. Histotoxic hypoxia Cyanide poisoning Cyanide ions bind
- 20. Histotoxic hypoxia Disturbance of respiratory enzymes synthesis
- 21. Histotoxic hypoxia Dissociation of oxidation and phosphorylation
- 22. Overload hypoxia Occur during physical overload of
- 23. Substrate hypoxia Deficiency of the substrate to
- 24. Combined hypoxia It is a
- 25. Combined hypoxia Respiratory failure Respiratory hypoxia Disturbed
- 26. Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems
- 27. Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems
- 28. Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems
- 29. Adaptation to hypoxia The reactions of urgent
- 30. Urgent adaptation The reason of adaptation -
- 31. Urgent adaptation Heart – tachycardia, ? heart
- 32. Urgent adaptation Blood - activation of RBC
- 33. Adaptation to hypoxia Urgent reactions -
- 34. Permanent adaptation Lungs - increased surface of
- 35. Permanent adaptation Number of the vessels in
- 36. Clinical application of hypoxia Intermittent hypoxia -
- 37. Clinical application of hypoxia Interval Hypoxic Training
- 38. Clinical application of hypoxia Adaptation to hypoxia
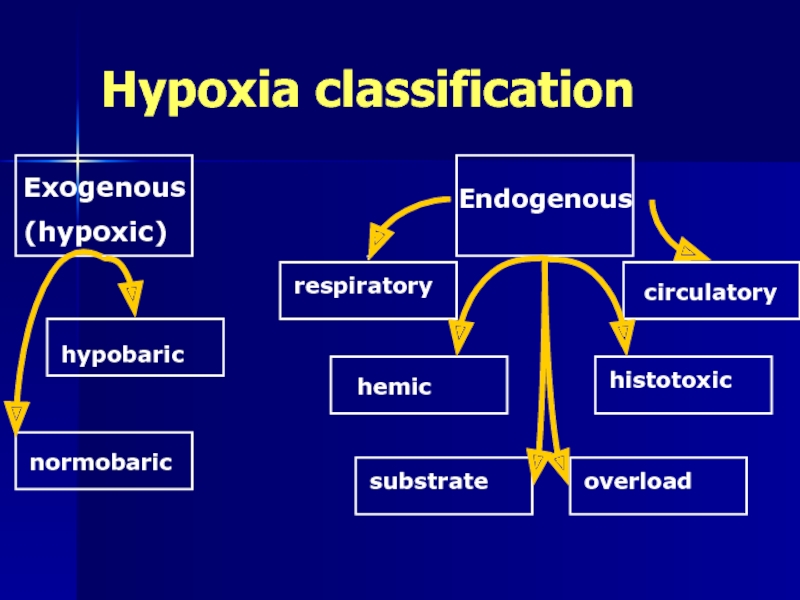
Слайд 2Hypoxia classification
Exogenous
(hypoxic)
Endogenous
hypobaric
normobaric
respiratory
hemic
circulatory
histotoxic
substrate
overload
Слайд 3Hypoxia classification
Due to time of development
Fulminant (immediate) –several seconds (cyanide poisoning).
Acute
Subacute – several hours or days (respiratory failure).
Chronic – months and years.
Слайд 4Hypoxia classification
Due to prevalence of clinical symptoms:
local and general.
Due to
light;
moderate;
severe;
critical (lethal) hypoxia.
Слайд 5Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia
hypobaric type
? atmospheric pressure+? partial oxygen pressure in the
Mountain sickness factors: low partial pressure of oxygen, low barometric pressure, physical loading, cooling, increased exposure to UV rays.
Altitude sickness factors: low barometric pressure and low partial pressure of oxygen
Слайд 6Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia
normobaric type
Normal atmospheric pressure + ?oxygen % in the
- in small rooms with bad ventilation (elevators, mines, mineshafts);
- in divers, when there are problems with aqualung function;
- incorrect conduction of artificial lungs ventilation during surgical operations.
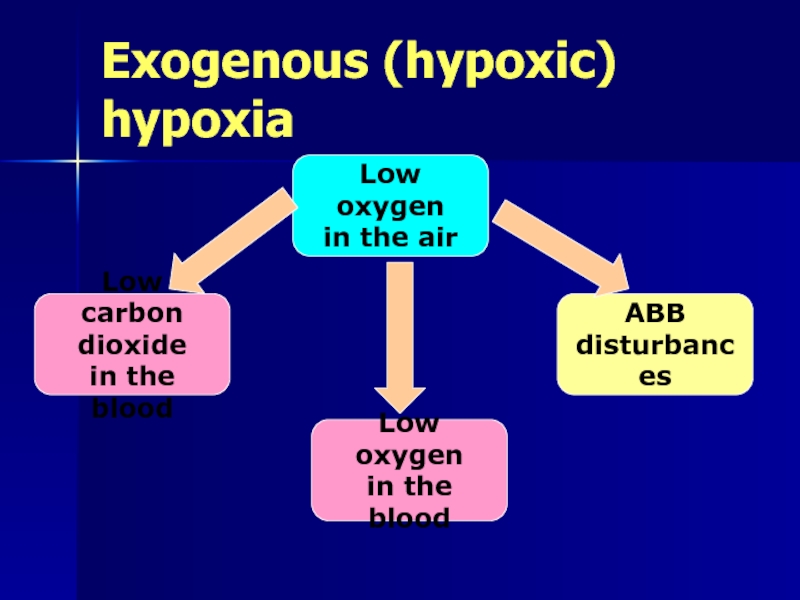
Слайд 7Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia
Low oxygen
in the air
Low oxygen
in the blood
Low
dioxide
in the blood
ABB
disturbances
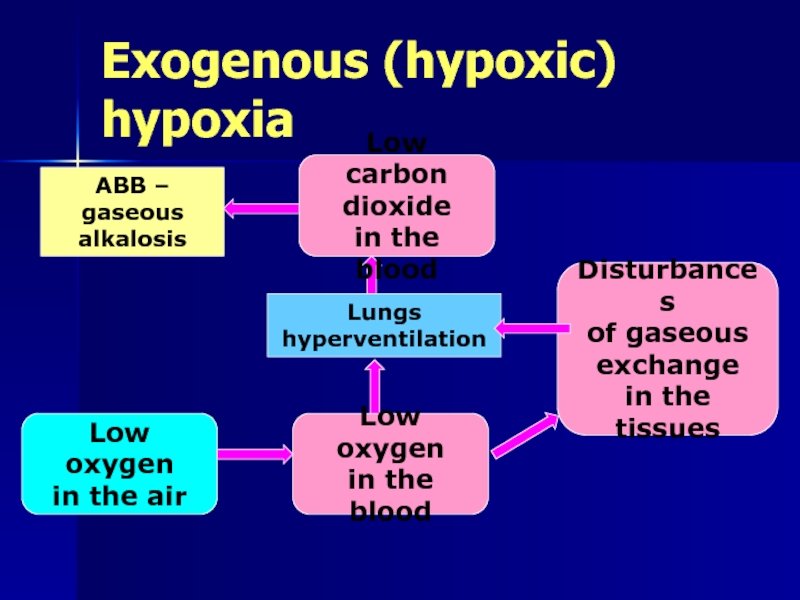
Слайд 8
Exogenous (hypoxic) hypoxia
Low oxygen
in the air
Low oxygen
in the blood
Disturbances
of gaseous
exchange
in the tissues
Low carbon
dioxide
in the blood
Lungs
hyperventilation
ABB –
gaseous
alkalosis
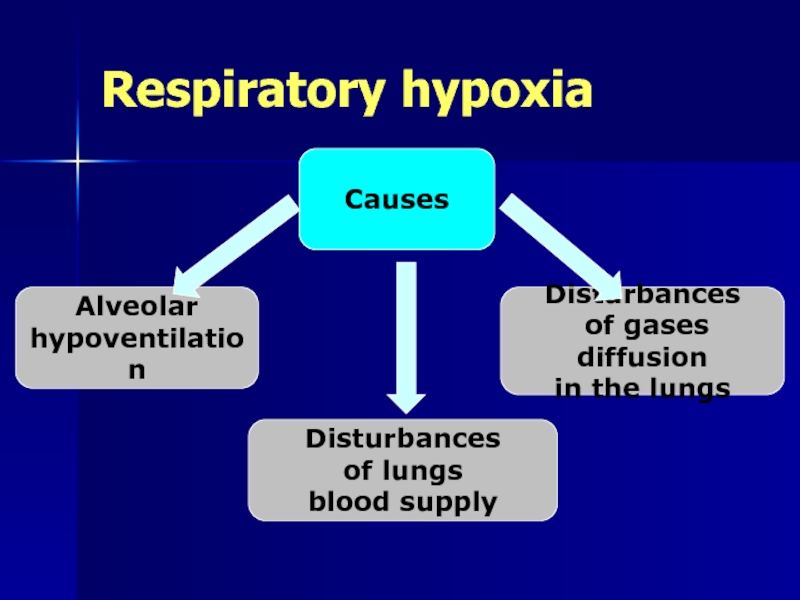
Слайд 9Respiratory hypoxia
Causes
Disturbances
of lungs
blood supply
Alveolar
hypoventilation
Disturbances
of gases diffusion
in the lungs
Слайд 10Respiratory hypoxia
Alveolar hypoventilation reasons:
Obstructive violations (lung edema, tumors or foreign bodies
Restrictive violations (chronic inflammatory or sclerotic processes in the lungs and in the chest).
Disturbances of respiratory regulation (toxic substances poisoning, brain trauma).
Слайд 11Respiratory hypoxia
Disturbances of lungs blood supply - heart failure, decreased circulating
Disturbances of gases diffusion in lungs chronic inflammatory diseases of the lungs, lungs edema.
Blood indices: low oxygen, high CO2, low pH (acidosis)
Слайд 13Circulatory hypoxia - systemic
Decrease of heart activity - myocardial infarction, myocarditis.
Hypovolaemia - severe blood loss, dehydration of the organism after burns, cholera, vomiting.
Vascular disorders (low vascular tone) - shock, collapse, aldosterone deficiency.
Слайд 14Circulatory hypoxia
Local type of circulatory hypoxia -insufficient blood supply of the
Blood indices: normal oxygen in arterial blood, low oxygen in venous blood, low pH (acidosis).
Слайд 15Hemic hypoxia
Anemic type – accompanying different anemias.
Inactivation type - poisoning with
Blood indices: low O2 in arterial and venous blood, non-gaseous acidosis.
Слайд 16Hemic hypoxia
The reasons of anemia:
chronic bleedings,
erythrocytes hemolysis,
depression of erythropoiesis.
Слайд 17Hemic hypoxia
Carbon monoxide poisoning:
CO has the affinity to Hb 300 times
Carboxy-Hb (HbCO) is formed (stable substance)
Symptoms: drowsiness and headache, unconsciousness, respiratory failure, and death.
Слайд 18Histotoxic hypoxia
The inability of cells to utilize oxygen
Causes:
tissue poisoning (alcohol,
biological oxidation enzymes inhibition and the disturbance of their synthesis;
the damage of membrane structures of the cell.
Слайд 19Histotoxic hypoxia
Cyanide poisoning
Cyanide ions bind to the Fe atom of cytochrome
The ATP synthesis stops.
Nervous system and the heart are particularly affected.
Слайд 20Histotoxic hypoxia
Disturbance of respiratory enzymes synthesis results from vitamins deficiency (B
Damage of mitochondrial membranes and other cellular elements (radiation injury, over-heating, intoxication, infection, cachexia, uremia).
Blood indices: the pressure, saturation and content of O 2 in blood are near normal.
Слайд 21Histotoxic hypoxia
Dissociation of oxidation and phosphorylation processes in respiratory chain:
energy
ATP synthesis is low.
The factors: hormones of thyroid gland, excess of Ca, toxins.
Слайд 22Overload hypoxia
Occur during physical overload of certain organ or tissue.
It
Blood indices: arterial and venous hypoxemia and hypercapnia.
Local heart hypoxia may transform to secondary general circulatory hypoxia
In the excessive muscular work - bloodflow in the muscles is increased ischemia of other tissues.
Слайд 23Substrate hypoxia
Deficiency of the substrate to be oxidized - glucose
Carbohydrate
Слайд 24
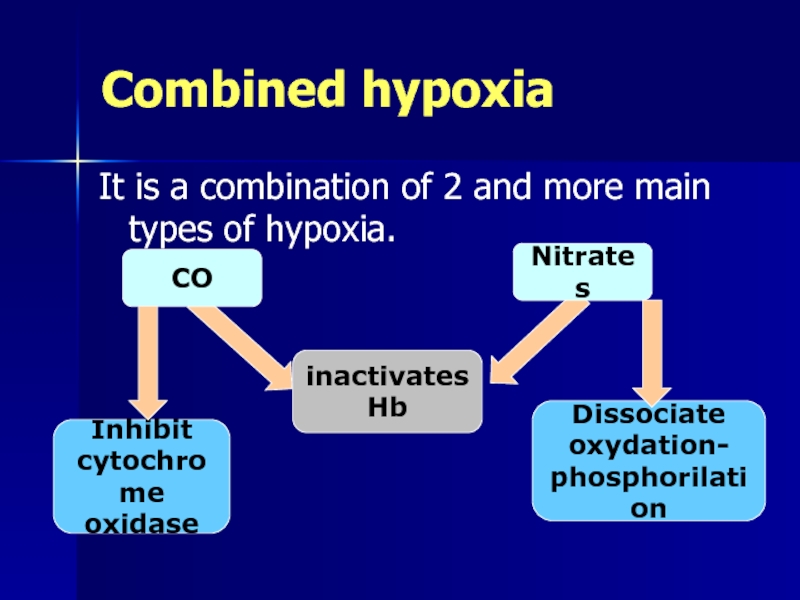
Combined hypoxia
It is a combination of 2 and more main types
CO
Inhibit
cytochrome
oxidase
Nitrates
Dissociate
oxydation-
phosphorilation
inactivates
Hb
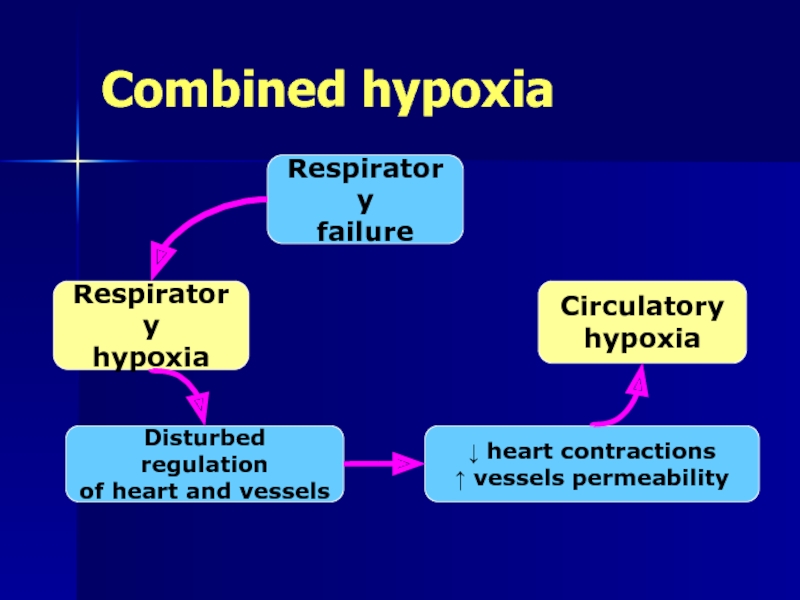
Слайд 25Combined hypoxia
Respiratory
failure
Respiratory
hypoxia
Disturbed regulation
of heart and vessels
↓ heart contractions
↑ vessels permeability
Circulatory
hypoxia
Слайд 26Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems
Nervous system –
emotional
disturbances of reflex activity and regulation of breathing and blood circulation;
loss of consciousness and convulsions.
Heart and vessels – tachycardia, arrhythmia, low BP.
Слайд 27Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems
Lungs - irregular breathing; decreased
Liver (chronic hypoxia) - disturbance of all kinds of metabolism, inhibition of detoxication, decreased synthesis of substances.
Слайд 28Disturbances in the Organs and Physiological Systems
GIT organs (chronic hypoxia) -
Immune system (chronic hypoxia) - low functional activity of the immune cells and innate immunity factors.
Слайд 29Adaptation to hypoxia
The reactions of urgent adaptation (protective-adaptive) manifest in acute
Permanent -adaptive (compensatory) - during long-term or repeating hypoxic effects.
Слайд 30Urgent adaptation
The reason of adaptation - lack of energy supply due
Respiratory system - ? blood oxygen and ? CO2 irritate chemoreceptors. This result in the increase of the alveolar ventilation.
Слайд 31Urgent adaptation
Heart – tachycardia, ? heart stroke volume and minute blood
Vessels - centralization of bloodflow (dilation of the brain and heart arterioles with simultaneous constriction of the arterioles in others tissues and organs).
Слайд 32Urgent adaptation
Blood - activation of RBC outflow from the bone marrow
Increased affinity of Hb to oxygen and the degree of oxyHb dissociation in the tissues.
Tissues systems of biological oxidation - ? anaerobic glycolysis, the activation of respiratory enzymes.
Слайд 33Adaptation to hypoxia
Urgent reactions - activation of the oxygen transport
Permanent compensation - activation of biological oxidation and structural changes of organs and systems that are transporting oxygen.
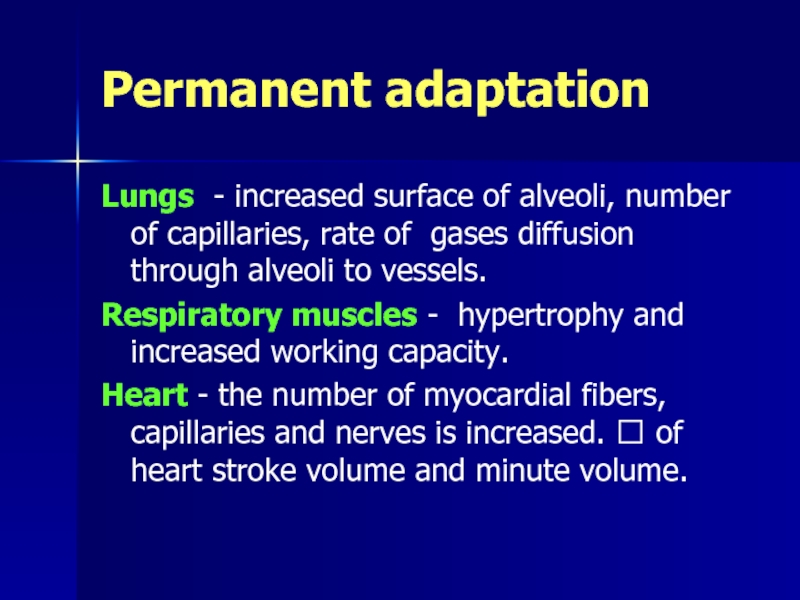
Слайд 34Permanent adaptation
Lungs - increased surface of alveoli, number of capillaries, rate
Respiratory muscles - hypertrophy and increased working capacity.
Heart - the number of myocardial fibers, capillaries and nerves is increased. ? of heart stroke volume and minute volume.
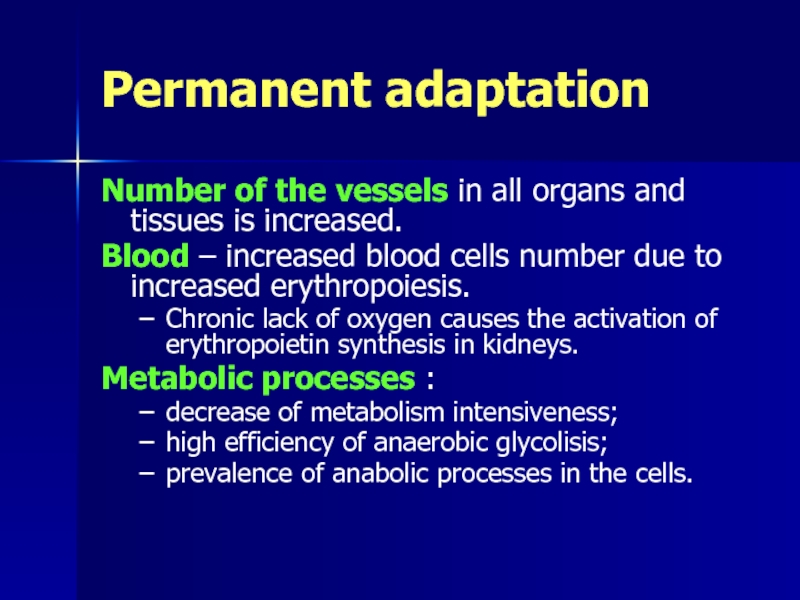
Слайд 35Permanent adaptation
Number of the vessels in all organs and tissues is
Blood – increased blood cells number due to increased erythropoiesis.
Chronic lack of oxygen causes the activation of erythropoietin synthesis in kidneys.
Metabolic processes :
decrease of metabolism intensiveness;
high efficiency of anaerobic glycolisis;
prevalence of anabolic processes in the cells.
Слайд 36Clinical application of hypoxia
Intermittent hypoxia - repeated episodes of hypoxia interspersed
Hypoxic episodes are created by exposure to natural high altitude, sojourns in hypobaric chambers or by breathing hypoxic gas mixtures in normobaric conditions.
Слайд 37Clinical application of hypoxia
Interval Hypoxic Training is used for the treatment
The method is effective to increase physical and mental working capacity.
The counter-indications are: all acute somatic and infectious diseases.
Слайд 38Clinical application of hypoxia
Adaptation to hypoxia provides resistance to other stress
Adaptation to hypoxia is characterized with structural and functional changes in many organs and tissues.
Body resistance is increased to hypothermia, overheating, physical overstrain, infections