© American College of Cardiology Foundation and American Heart Association, Inc.
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults презентация
Содержание
- 1. Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults
- 2. Publication Information This slide set is adapted
- 3. 2017 High Blood Pressure Guideline Writing Committee
- 4. Applying Class of Recommendation and Level of
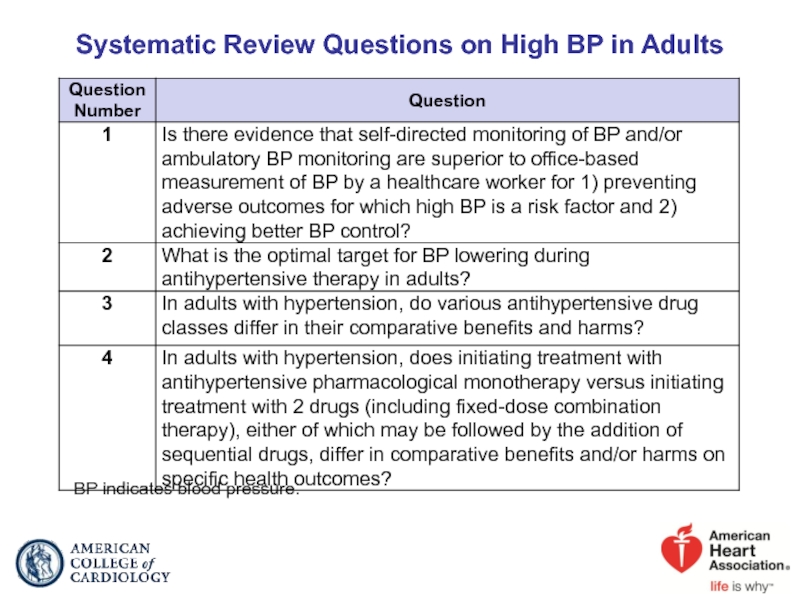
- 5. Systematic Review Questions on High BP in Adults BP indicates blood pressure.
- 6. BP Measurement Definitions *See Section 4
- 7. BP and CVD Risk 2017 Hypertension Clinical Practice Guidelines
- 8. Coexistence of Hypertension and Related Chronic Conditions
- 9. CVD Risk Factors Common in Patients With
- 10. Classification of BP 2017 Hypertension Guideline
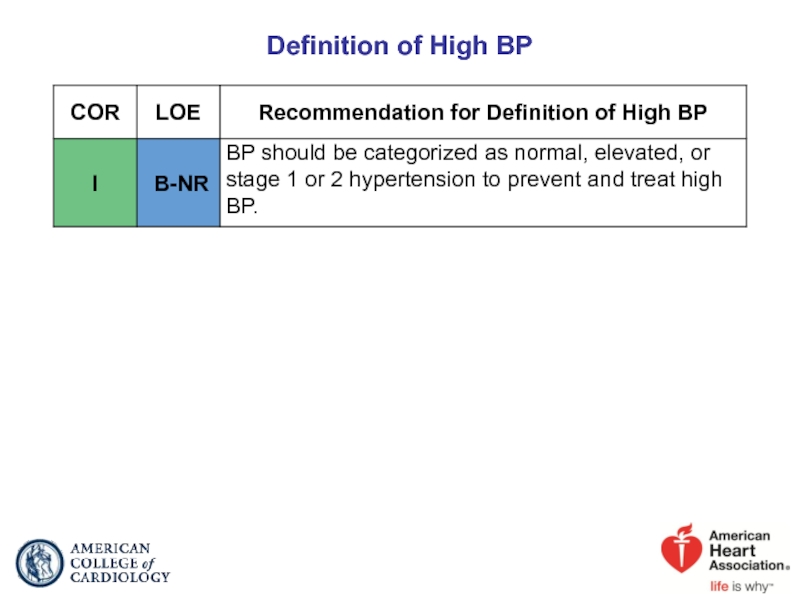
- 11. Definition of High BP
- 12. Categories of BP in Adults* *Individuals
- 13. Prevalence of Hypertension Based on 2 SBP/DBP
- 14. Measurement of BP 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 15. Accurate Measurement of BP in the Office
- 16. Checklist for Accurate Measurement of BP
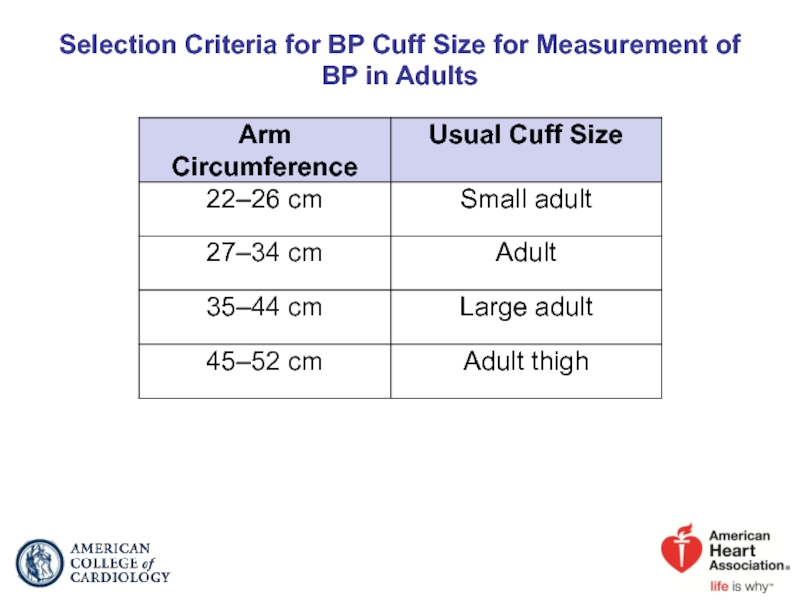
- 17. Selection Criteria for BP Cuff Size for Measurement of BP in Adults
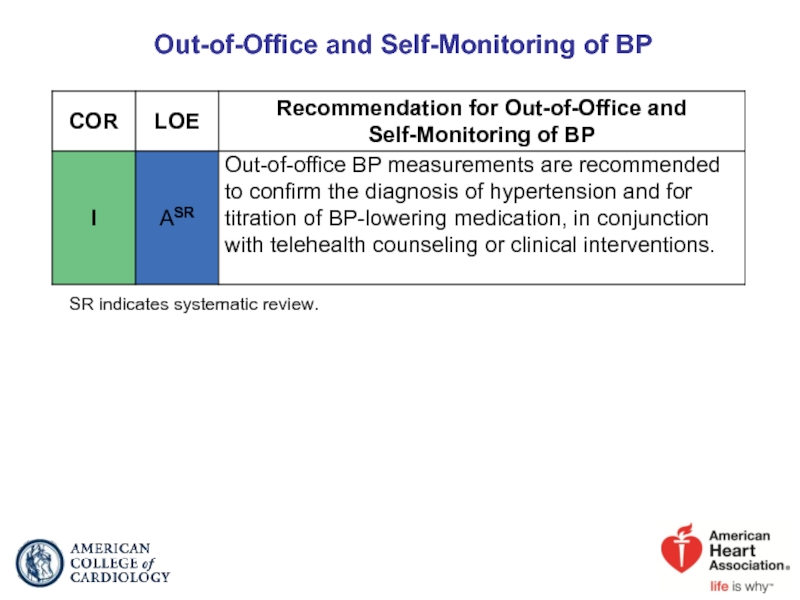
- 18. Out-of-Office and Self-Monitoring of BP SR indicates systematic review.
- 19. Corresponding Values of SBP/DBP for Clinic, HBPM,
- 20. Masked and White Coat Hypertension
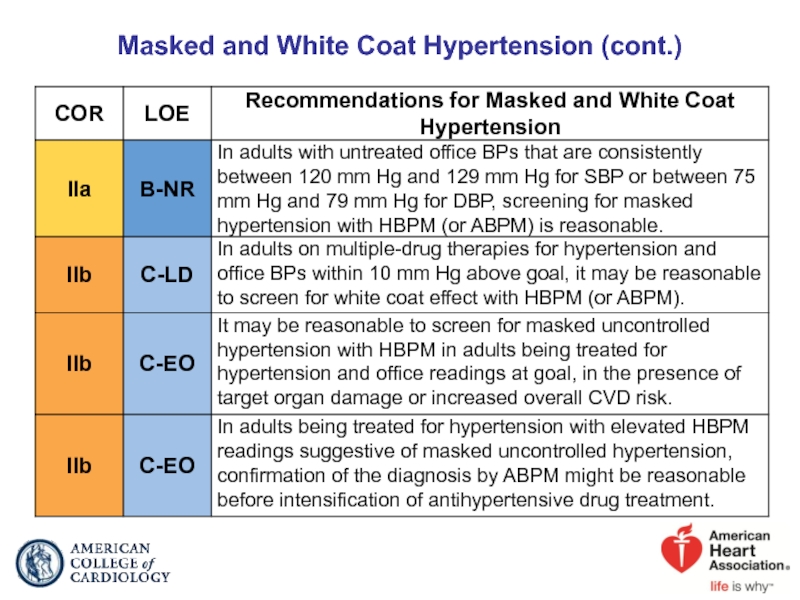
- 21. Masked and White Coat Hypertension (cont.)
- 22. BP Patterns Based on Office and Out-of-Office
- 23. Detection of White Coat Hypertension or Masked
- 24. Detection of White Coat Effect or Masked
- 25. Causes of Hypertension 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 26. Secondary Forms of Hypertension
- 27. Screening for Secondary Hypertension Colors correspond
- 28. Causes of Secondary Hypertension With Clinical Indications
- 29. Primary Aldosteronism
- 30. Renal Artery Stenosis
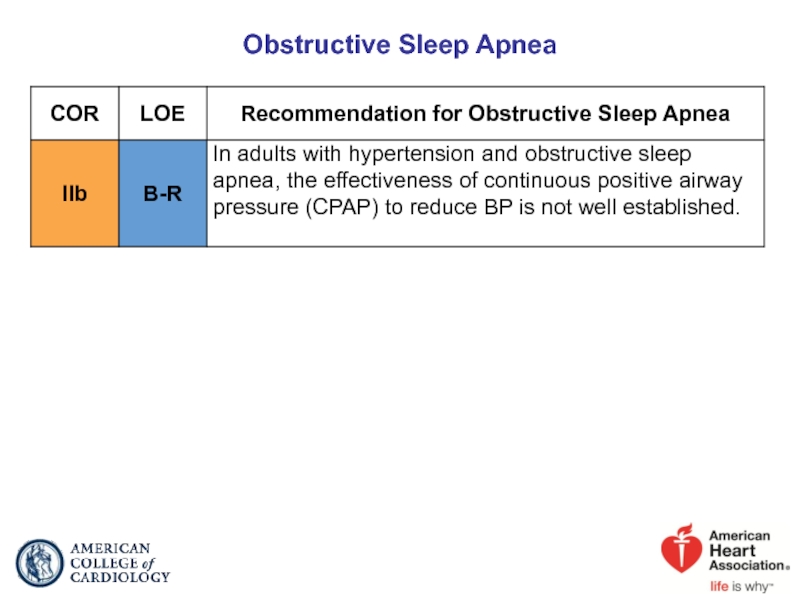
- 31. Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- 32. Nonpharmacological Interventions 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 33. Nonpharmacological Interventions
- 34. Nonpharmacological Interventions (cont.) *In the United
- 35. Best Proven Nonpharmacological Interventions for Prevention and
- 36. Best Proven Nonpharmacological Interventions for Prevention and
- 37. Patient Evaluation 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 38. Basic and Optional Laboratory Tests for Primary
- 39. Treatment of High BP 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 40. BP Treatment Threshold and the Use of
- 41. Blood Pressure (BP) Thresholds and Recommendations for
- 42. Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation
- 43. Follow-Up After Initial BP Evaluation
- 44. Follow-Up After Initial BP Evaluation (cont.)
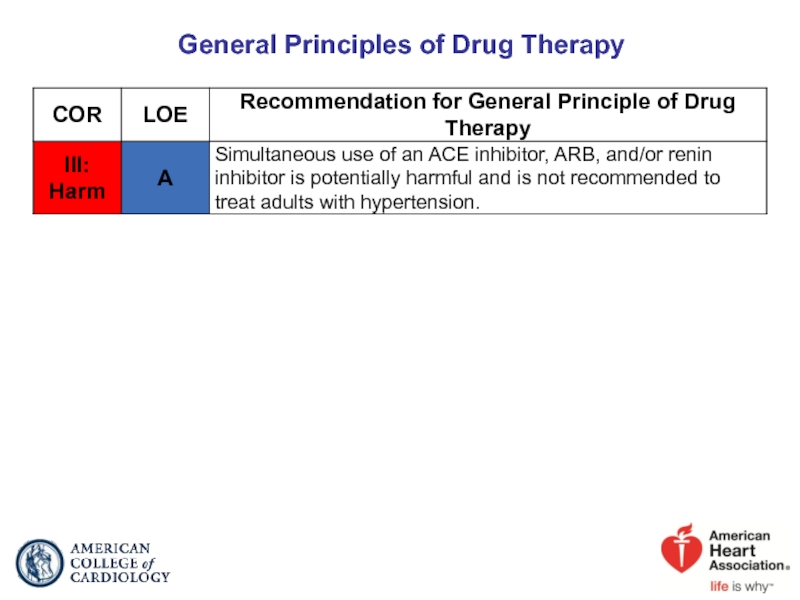
- 45. General Principles of Drug Therapy
- 46. BP Goal for Patients With Hypertension SR indicates systematic review.
- 47. Choice of Initial Medication SR indicates systematic review.
- 48. Choice of Initial Monotherapy Versus Initial Combination Drug Therapy
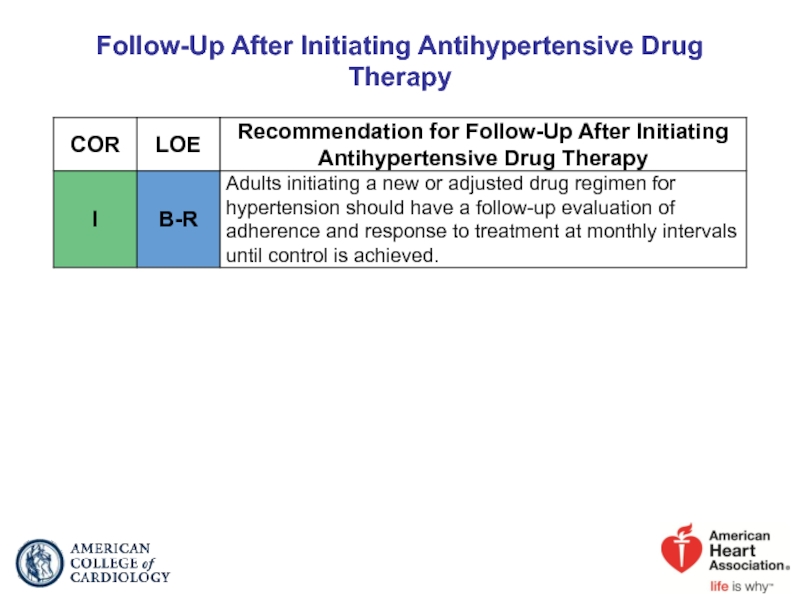
- 49. Follow-Up After Initiating Antihypertensive Drug Therapy
- 50. Monitoring Strategies to Improve Control of BP in Patients on Drug Therapy for High BP
- 51. Hypertension in Patients With Comorbidities 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 52. Stable Ischemic Heart Disease
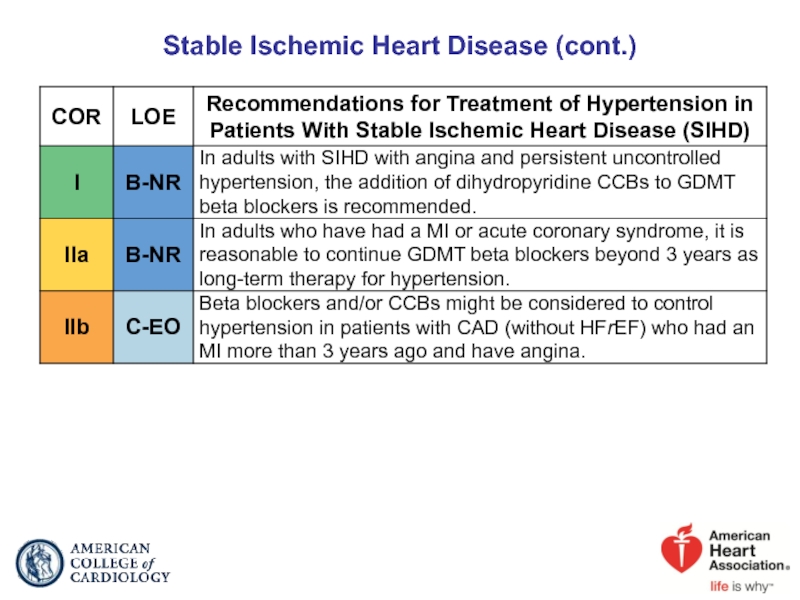
- 53. Stable Ischemic Heart Disease (cont.)
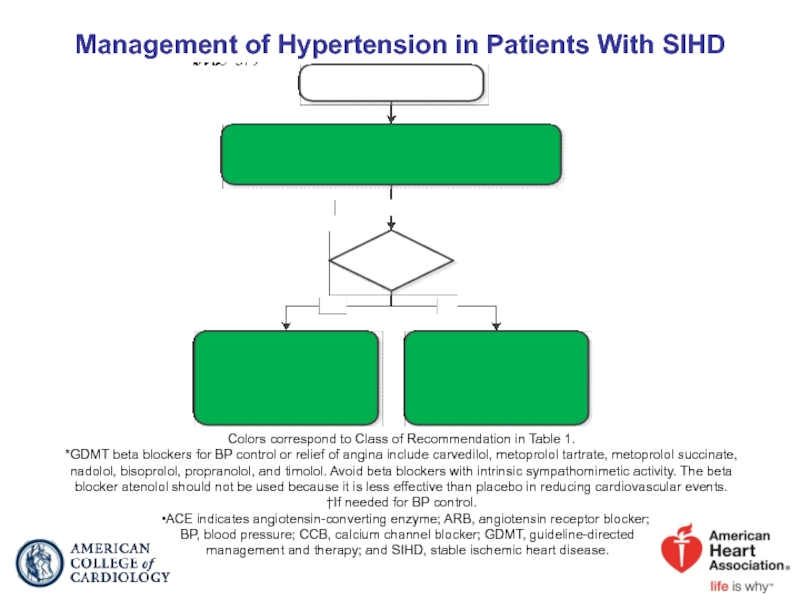
- 54. Management of Hypertension in Patients With SIHD
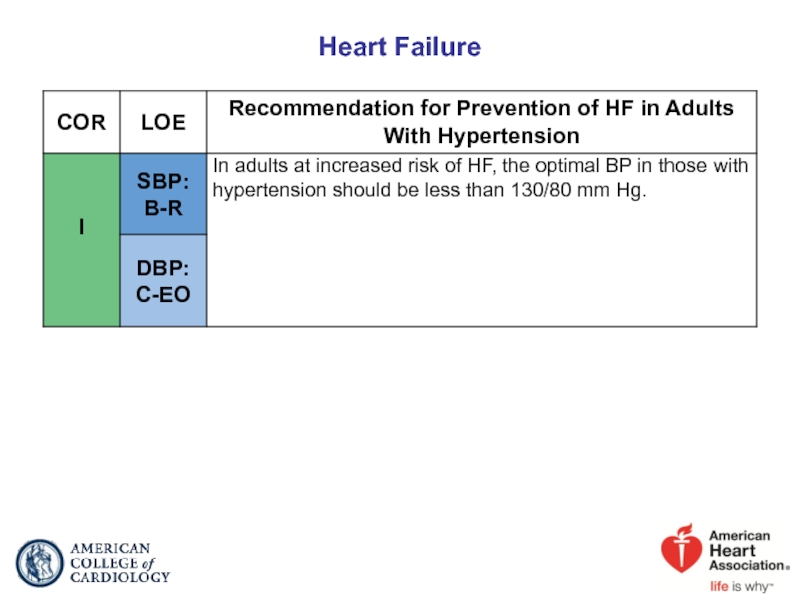
- 55. Heart Failure
- 56. Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction
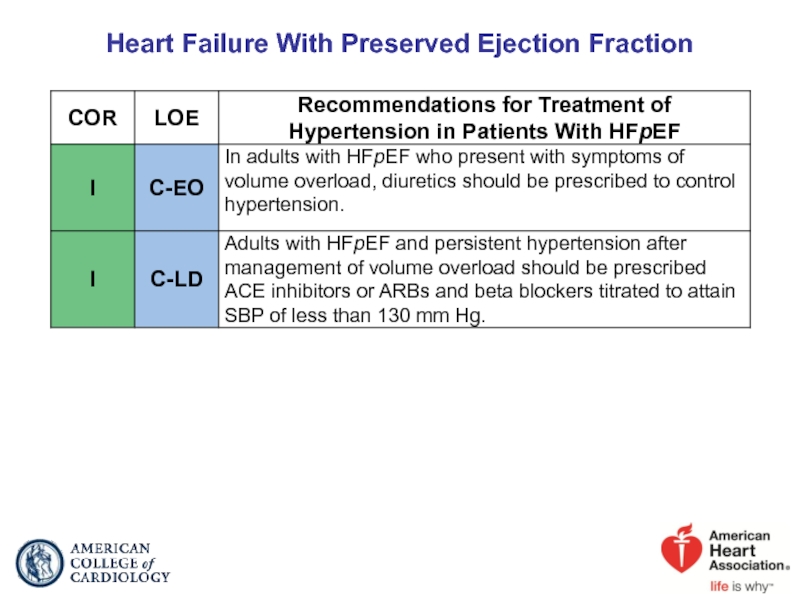
- 57. Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
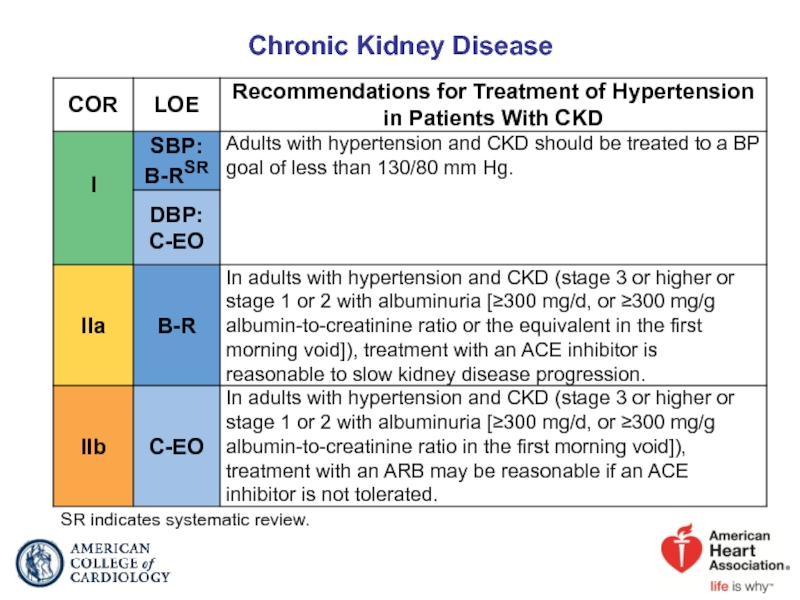
- 58. Chronic Kidney Disease SR indicates systematic review.
- 59. Management of Hypertension in Patients With CKD
- 60. Hypertension After Renal Transplantation
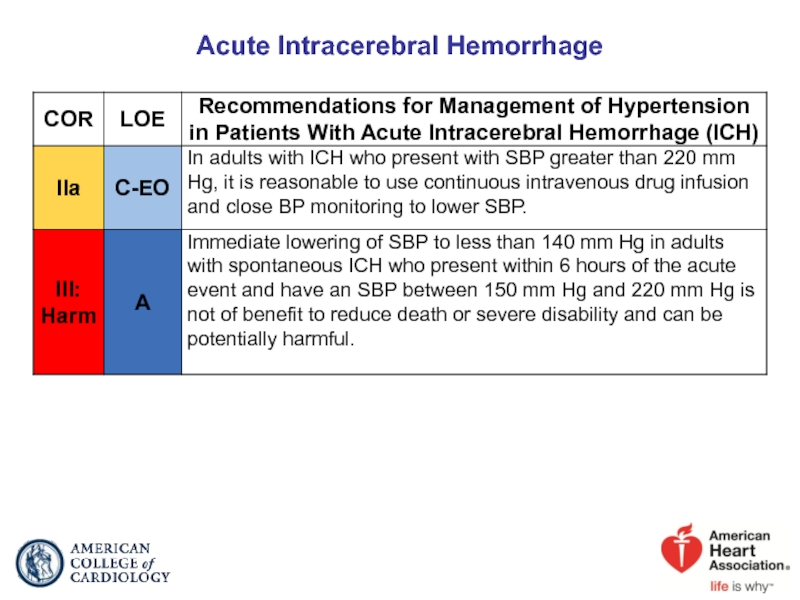
- 61. Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- 62. Management of Hypertension in Patients With Acute
- 63. Acute Ischemic Stroke
- 64. Acute Ischemic Stroke (cont.)
- 65. Management of Hypertension in Patients With Acute
- 66. Secondary Stroke Prevention
- 67. Secondary Stroke Prevention (cont.)
- 68. Management of Hypertension in Patients With a
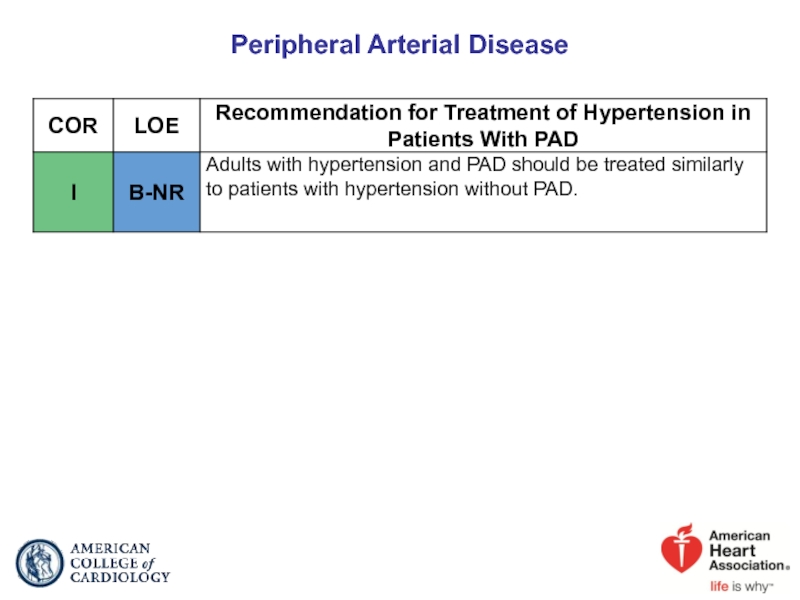
- 69. Peripheral Arterial Disease
- 70. Diabetes Mellitus SR indicates systematic review.
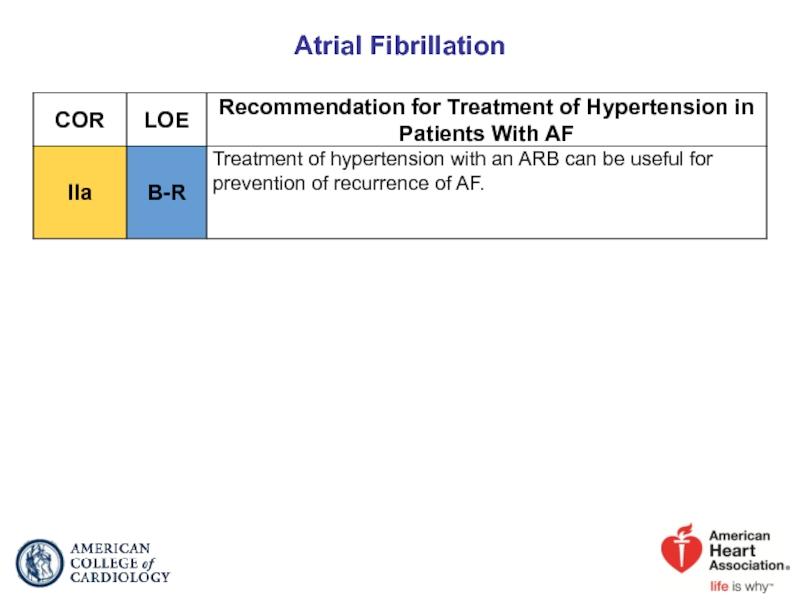
- 71. Atrial Fibrillation
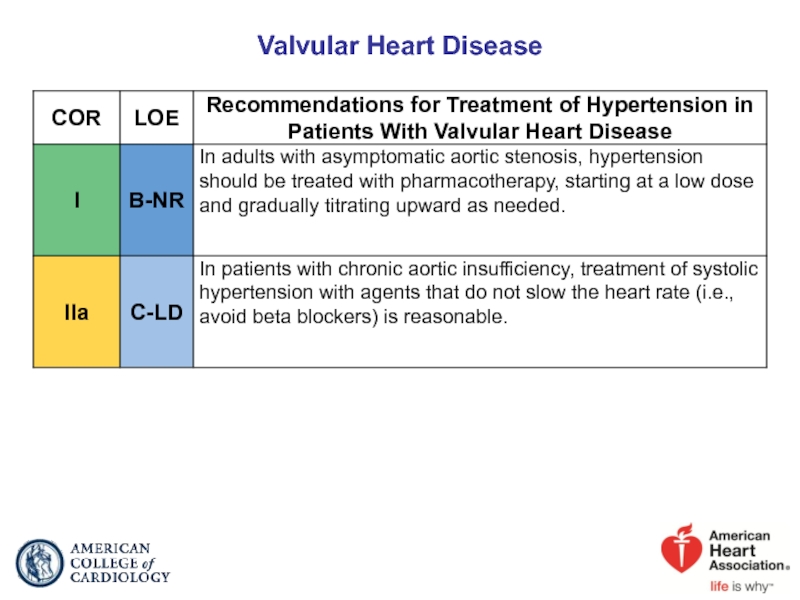
- 72. Valvular Heart Disease
- 73. Aortic Disease
- 74. Special Patient Groups 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 75. Racial and Ethnic Differences in Treatment
- 76. Pregnancy
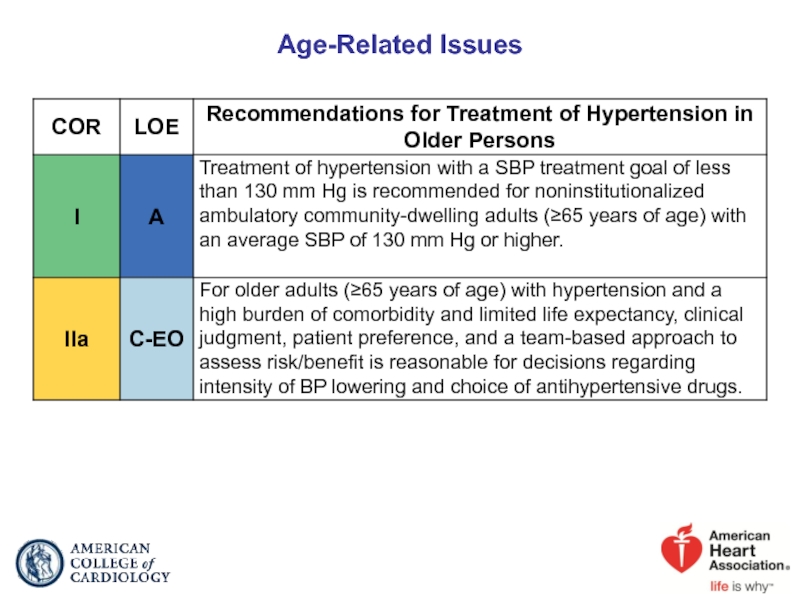
- 77. Age-Related Issues
- 78. Other Considerations 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 79. Resistant Hypertension: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment
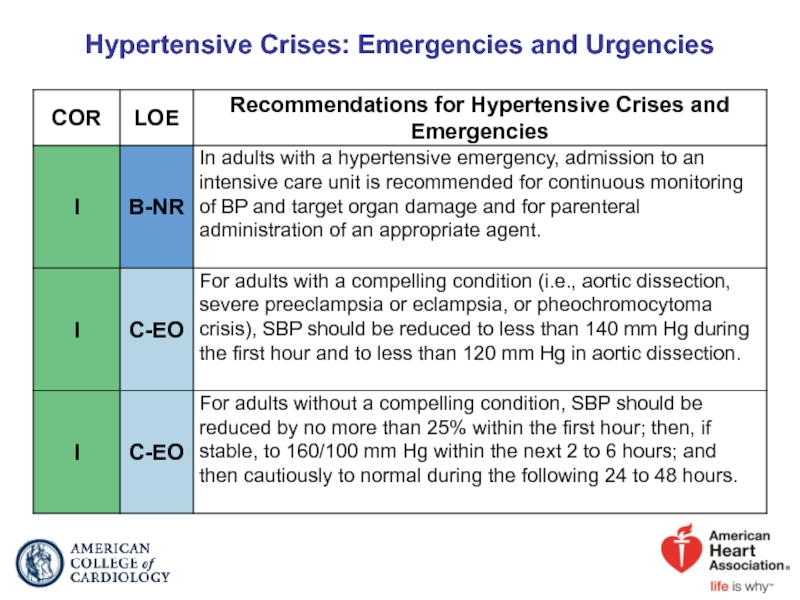
- 80. Hypertensive Crises: Emergencies and Urgencies
- 81. Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation
- 82. Cognitive Decline and Dementia
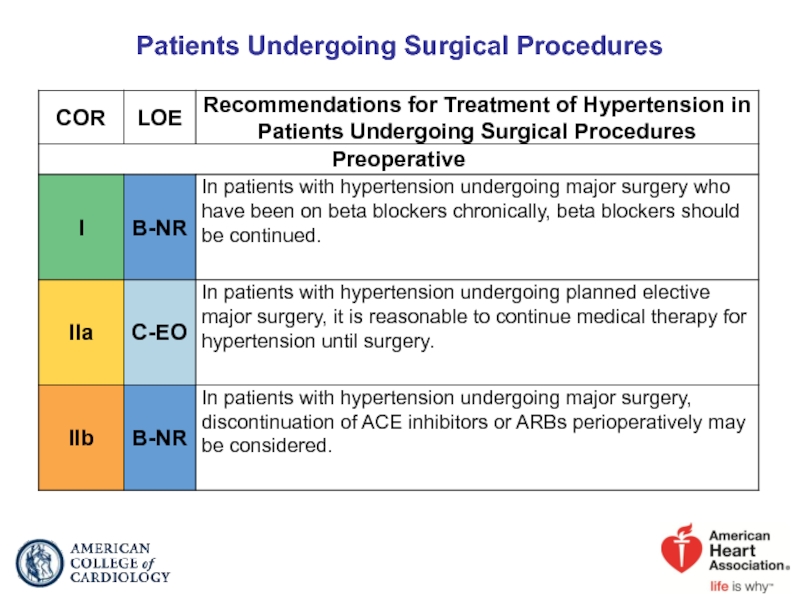
- 83. Patients Undergoing Surgical Procedures
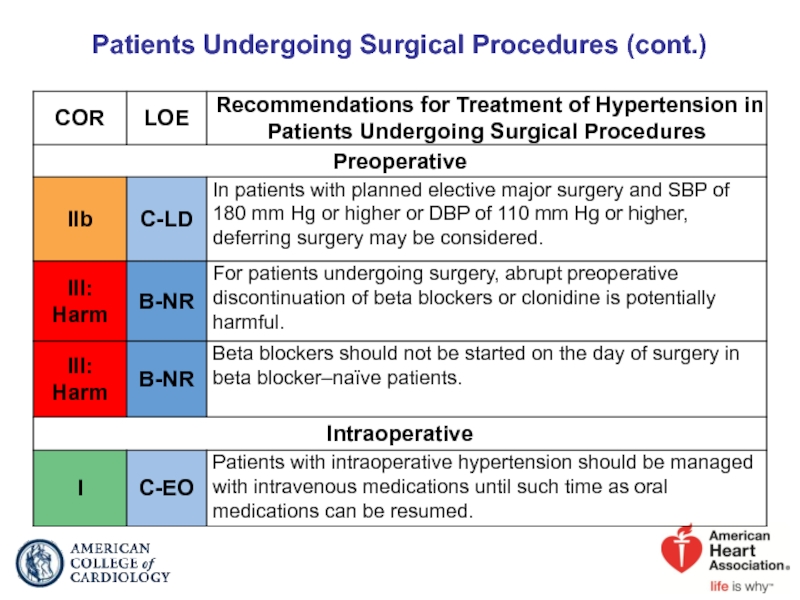
- 84. Patients Undergoing Surgical Procedures (cont.)
- 85. Strategies to Improve Hypertension Treatment and Control 2017 Hypertension Guideline
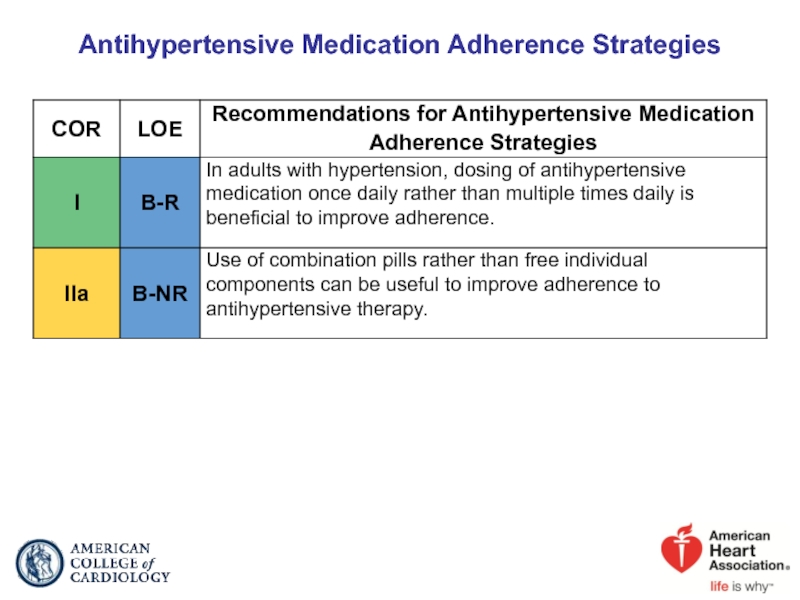
- 86. Antihypertensive Medication Adherence Strategies
- 87. Strategies to Promote Lifestyle Modification
- 88. Structured, Team-Based Care Interventions for Hypertension Control
- 89. EHR and Patient Registries
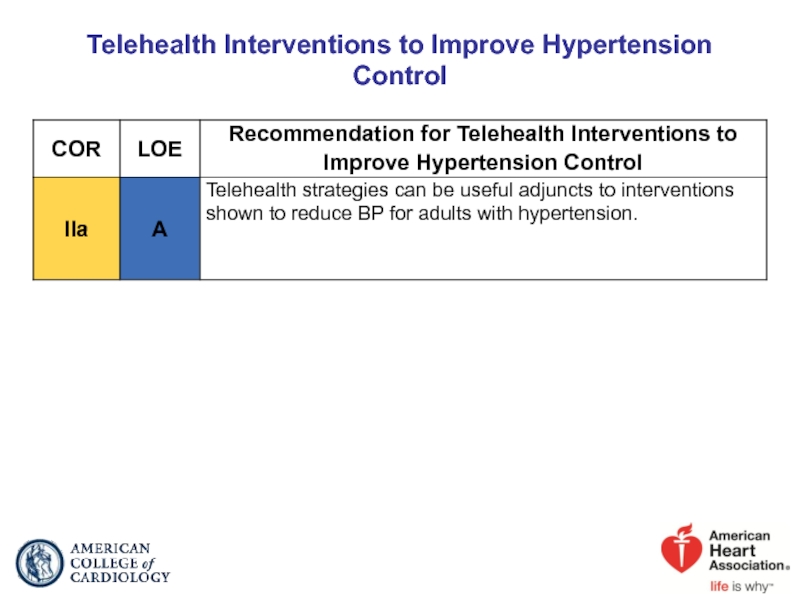
- 90. Telehealth Interventions to Improve Hypertension Control
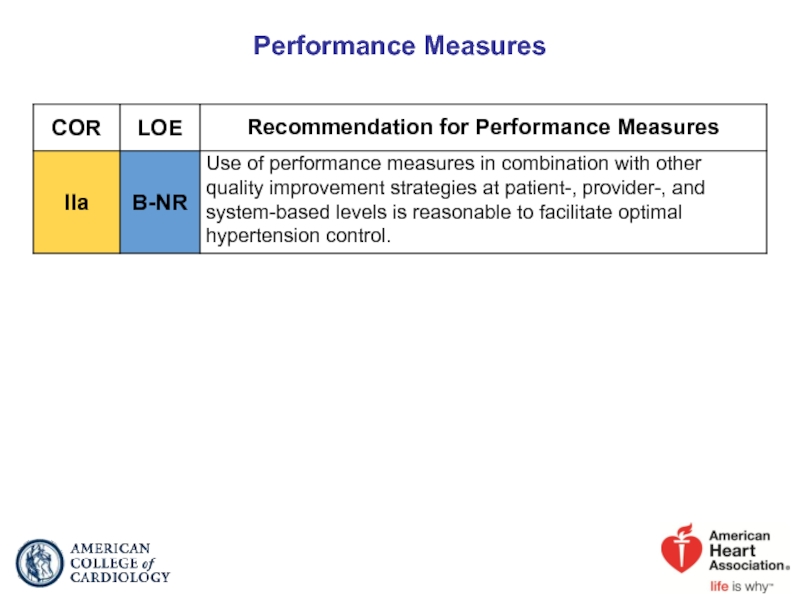
- 91. Performance Measures
- 92. Quality Improvement Strategies
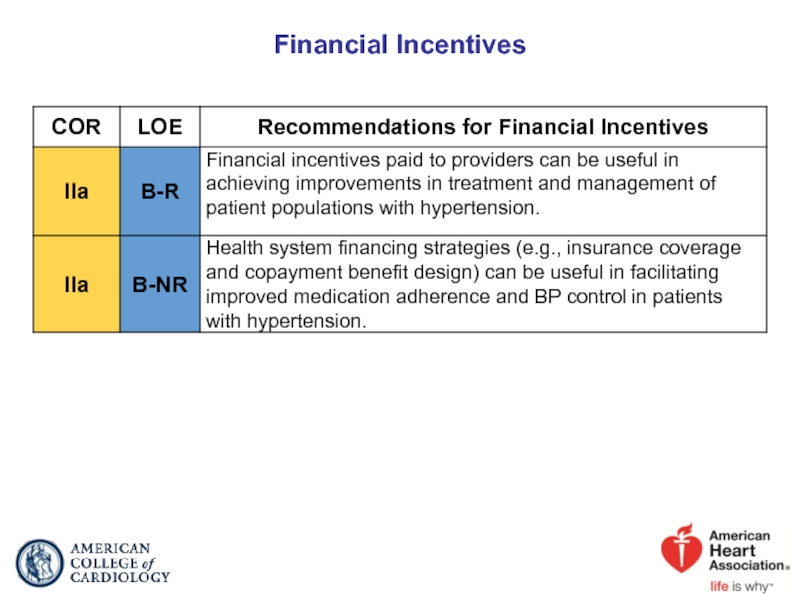
- 93. Financial Incentives
- 94. The Plan of Care for Hypertension 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 95. The Plan of Care for Hypertension
- 96. Clinician’s Sequential Flow Chart for the Management
- 97. Summary of BP Thresholds and Goals for
- 98. BP Thresholds for and Goals of Pharmacological
Слайд 12017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/ APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management
Слайд 2Publication Information
This slide set is adapted from the 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/ NMA/PCNA
Published on November 13, 2017, available at: Hypertension and Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The full-text guidelines are also available on the following websites: AHA (professional.heart.orgThe full-text guidelines are also available on the following websites: AHA (professional.heart.org) and ACC (www.acc.org)
Слайд 32017 High Blood Pressure Guideline Writing Committee
*American Society for Preventive Cardiology
Слайд 4Applying Class of Recommendation and Level of Evidence to Clinical Strategies,
in Patient Care*
(Updated August 2015)
Слайд 6BP Measurement Definitions
*See Section 4 for a description of Korotkoff sounds.
†Calculation
BP indicates blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Слайд 9CVD Risk Factors Common in Patients With Hypertension
*Factors that can be
†Factors that are difficult to change (CKD, low socioeconomic/educational status, obstructive sleep apnea, cannot be changed (family history, increased age, male sex), or, if changed through the use of current intervention techniques, may not reduce CVD risk (psychosocial stress).
CKD indicates chronic kidney disease; and CVD, cardiovascular disease.
Слайд 12Categories of BP in Adults*
*Individuals with SBP and DBP in 2
BP indicates blood pressure (based on an average of ≥2 careful readings obtained on ≥2 occasions, as detailed in DBP, diastolic blood pressure; and SBP systolic blood pressure.
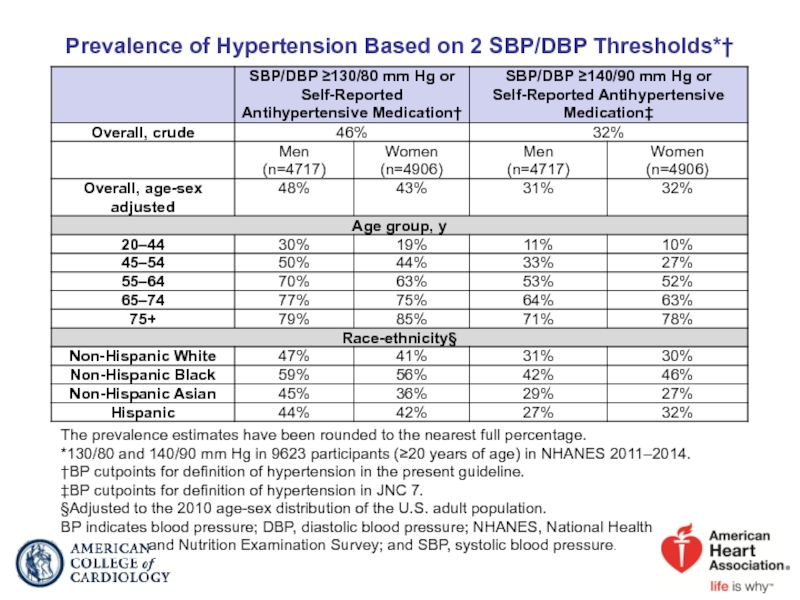
Слайд 13Prevalence of Hypertension Based on 2 SBP/DBP Thresholds*†
The prevalence estimates
*130/80 and 140/90 mm Hg in 9623 participants (≥20 years of age) in NHANES 2011–2014.
†BP cutpoints for definition of hypertension in the present guideline.
‡BP cutpoints for definition of hypertension in JNC 7.
§Adjusted to the 2010 age-sex distribution of the U.S. adult population.
BP indicates blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; NHANES, National Health
and Nutrition Examination Survey; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Слайд 19Corresponding Values of SBP/DBP for Clinic, HBPM, Daytime, Nighttime, and 24-Hour
ABPM indicates ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; BP, blood pressure; DBP diastolic blood pressure; HBPM, home blood pressure monitoring; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.
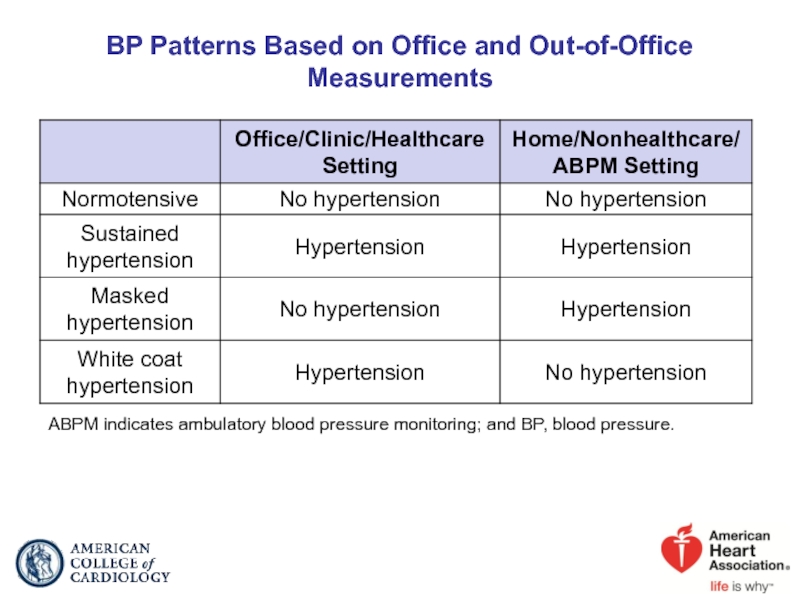
Слайд 22BP Patterns Based on Office and Out-of-Office Measurements
ABPM indicates ambulatory blood
Слайд 23Detection of White Coat Hypertension or Masked Hypertension in Patients Not
Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1.
ABPM indicates ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; BP, blood pressure; and HBPM, home blood pressure monitoring.
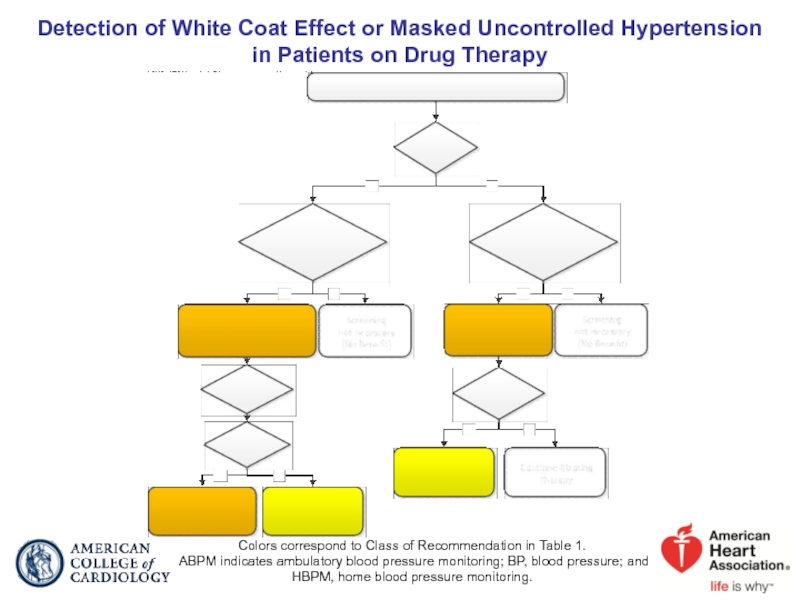
Слайд 24Detection of White Coat Effect or Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension in Patients
Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1.
ABPM indicates ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; BP, blood pressure; and HBPM, home blood pressure monitoring.
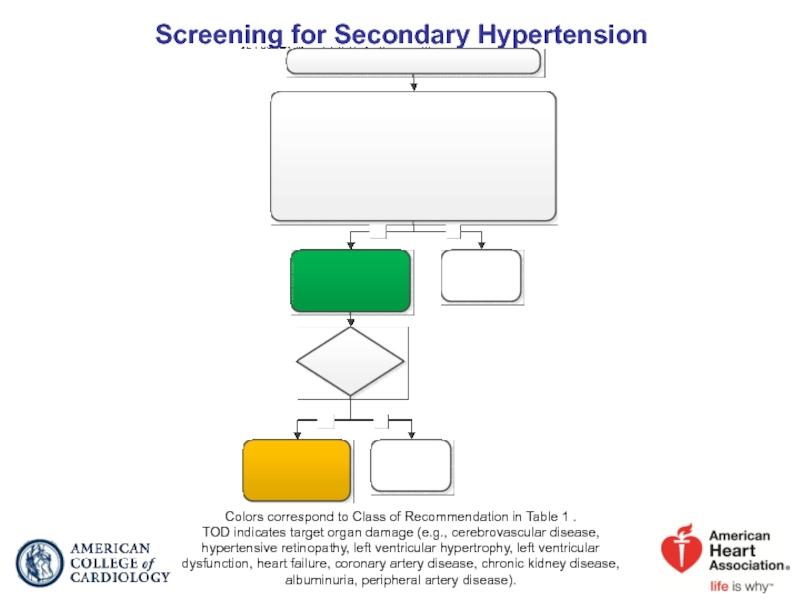
Слайд 27Screening for Secondary Hypertension
Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table
TOD indicates target organ damage (e.g., cerebrovascular disease, hypertensive retinopathy, left ventricular hypertrophy, left ventricular dysfunction, heart failure, coronary artery disease, chronic kidney disease, albuminuria, peripheral artery disease).
Слайд 34Nonpharmacological Interventions (cont.)
*In the United States, 1 “standard” drink contains
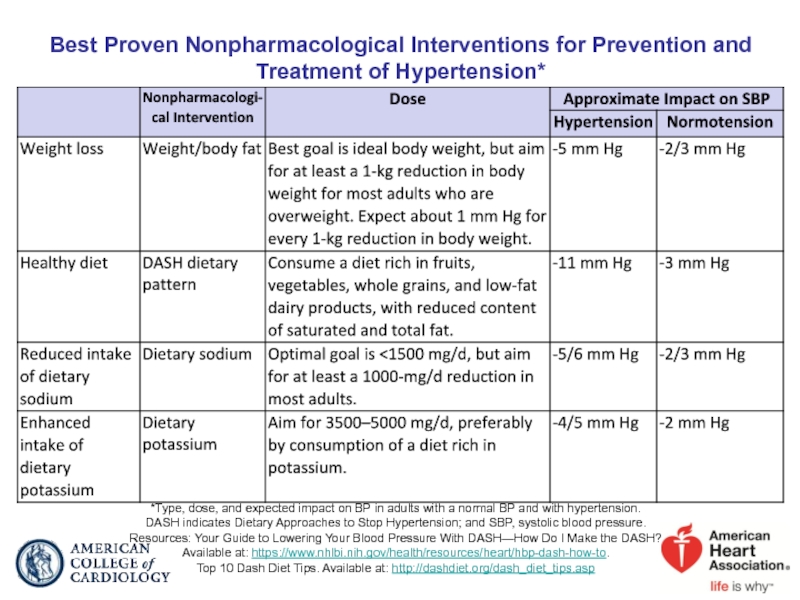
Слайд 35Best Proven Nonpharmacological Interventions for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension*
*Type, dose,
DASH indicates Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Resources: Your Guide to Lowering Your Blood Pressure With DASH—How Do I Make the DASH?
Available at: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/resources/heart/hbp-dash-how-to.
Top 10 Dash Diet Tips. Available at: http://dashdiet.org/dash_diet_tips.asp
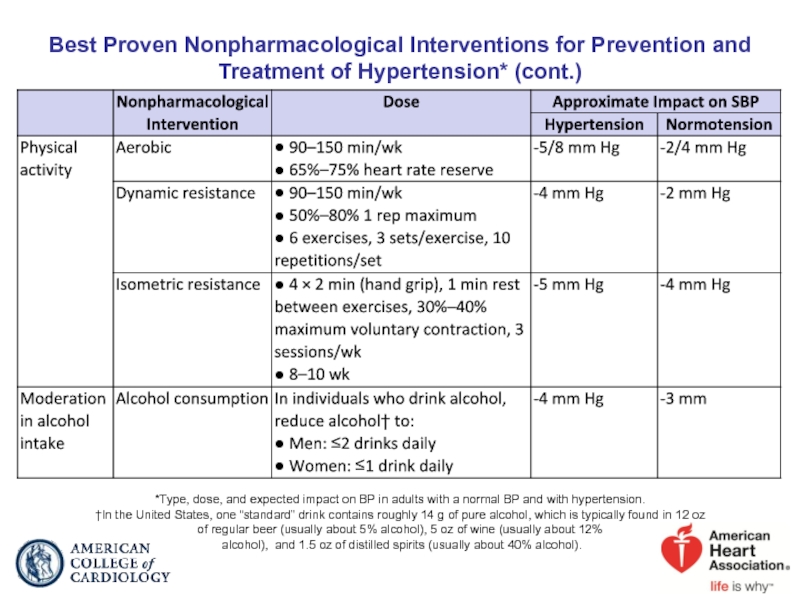
Слайд 36Best Proven Nonpharmacological Interventions for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension* (cont.)
*Type, dose, and expected impact on BP in adults with a normal BP and with hypertension.
†In the United States, one “standard” drink contains roughly 14 g of pure alcohol, which is typically found in 12 oz of regular beer (usually about 5% alcohol), 5 oz of wine (usually about 12%
alcohol), and 1.5 oz of distilled spirits (usually about 40% alcohol).
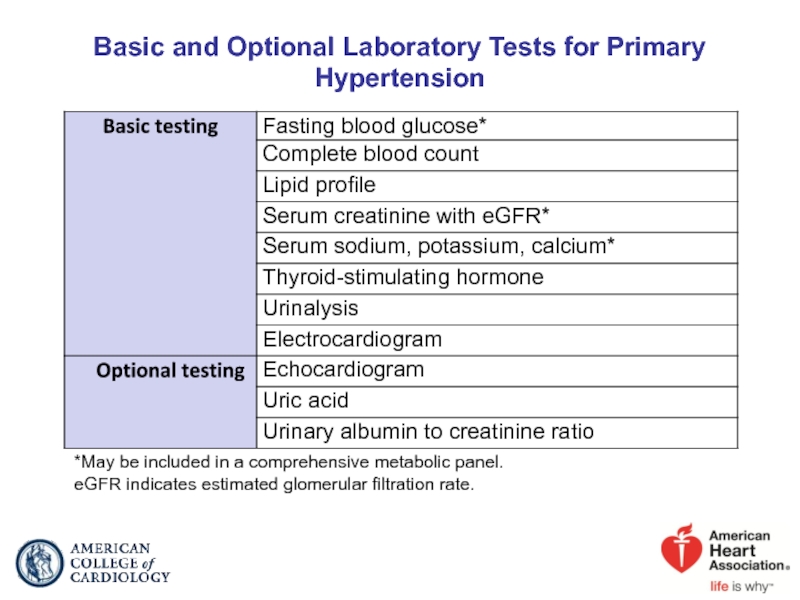
Слайд 38Basic and Optional Laboratory Tests for Primary Hypertension
*May be included in
eGFR indicates estimated glomerular filtration rate.
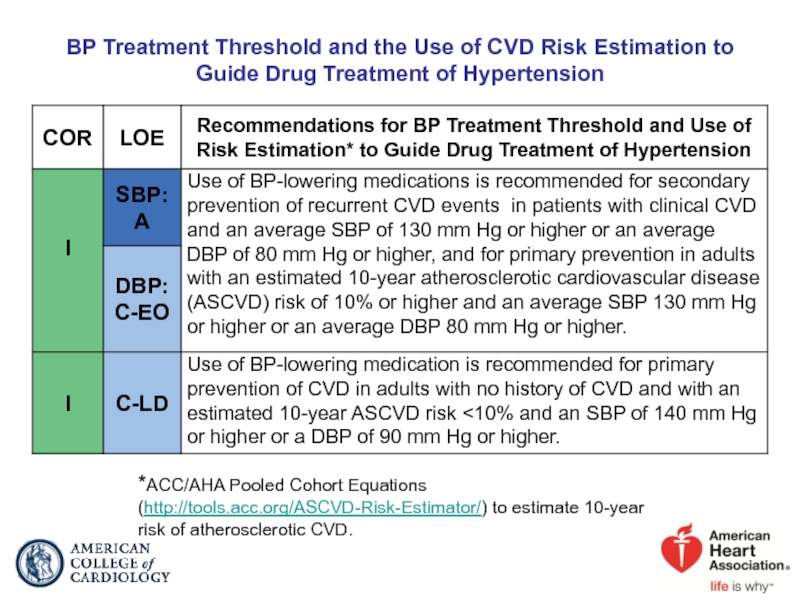
Слайд 40BP Treatment Threshold and the Use of CVD Risk Estimation to
*ACC/AHA Pooled Cohort Equations (http://tools.acc.org/ASCVD-Risk-Estimator/) to estimate 10-year risk of atherosclerotic CVD.
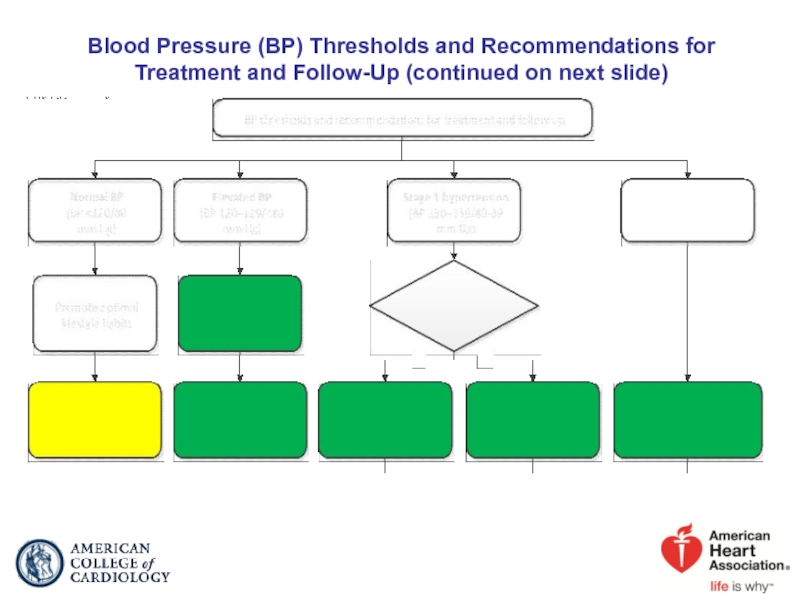
Слайд 41Blood Pressure (BP) Thresholds and Recommendations for Treatment and Follow-Up (continued
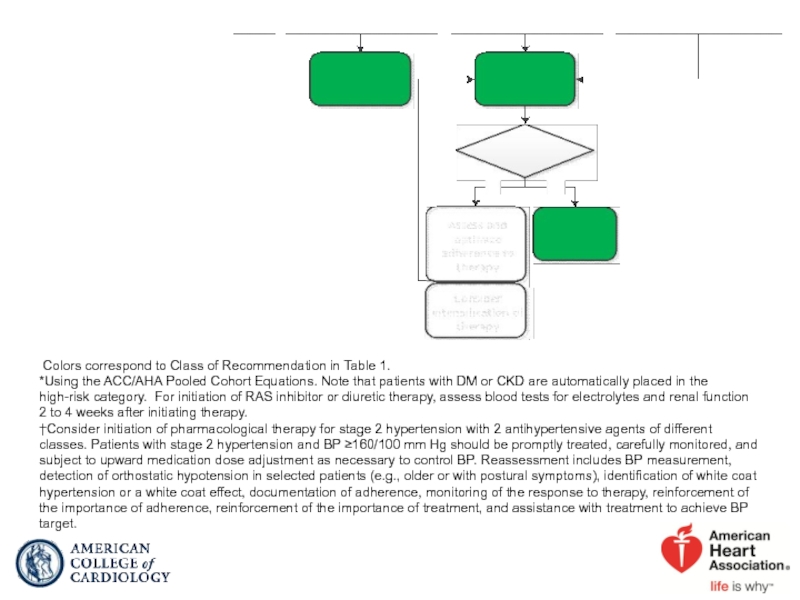
Слайд 42
Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1.
*Using the ACC/AHA
†Consider initiation of pharmacological therapy for stage 2 hypertension with 2 antihypertensive agents of different classes. Patients with stage 2 hypertension and BP ≥160/100 mm Hg should be promptly treated, carefully monitored, and subject to upward medication dose adjustment as necessary to control BP. Reassessment includes BP measurement, detection of orthostatic hypotension in selected patients (e.g., older or with postural symptoms), identification of white coat hypertension or a white coat effect, documentation of adherence, monitoring of the response to therapy, reinforcement of the importance of adherence, reinforcement of the importance of treatment, and assistance with treatment to achieve BP target.
Слайд 54Management of Hypertension in Patients With SIHD
ACE indicates angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB,
Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1.
*GDMT beta blockers for BP control or relief of angina include carvedilol, metoprolol tartrate, metoprolol succinate, nadolol, bisoprolol, propranolol, and timolol. Avoid beta blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. The beta blocker atenolol should not be used because it is less effective than placebo in reducing cardiovascular events.
†If needed for BP control.
Слайд 59Management of Hypertension in Patients With CKD
Colors correspond to Class of
*CKD stage 3 or higher or stage 1 or 2 with albuminuria ≥300 mg/d or ≥300 mg/g creatinine.
ACE indicates angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BP blood pressure; and CKD, chronic kidney disease.
.
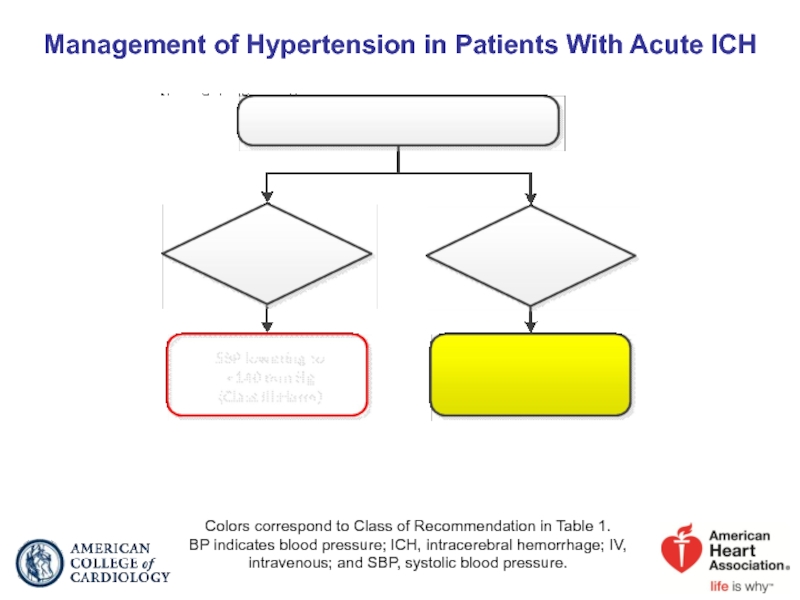
Слайд 62Management of Hypertension in Patients With Acute ICH
Colors correspond to Class
BP indicates blood pressure; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; IV, intravenous; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Слайд 65Management of Hypertension in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke
Colors correspond
BP indicates blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; IV, intravenous; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.
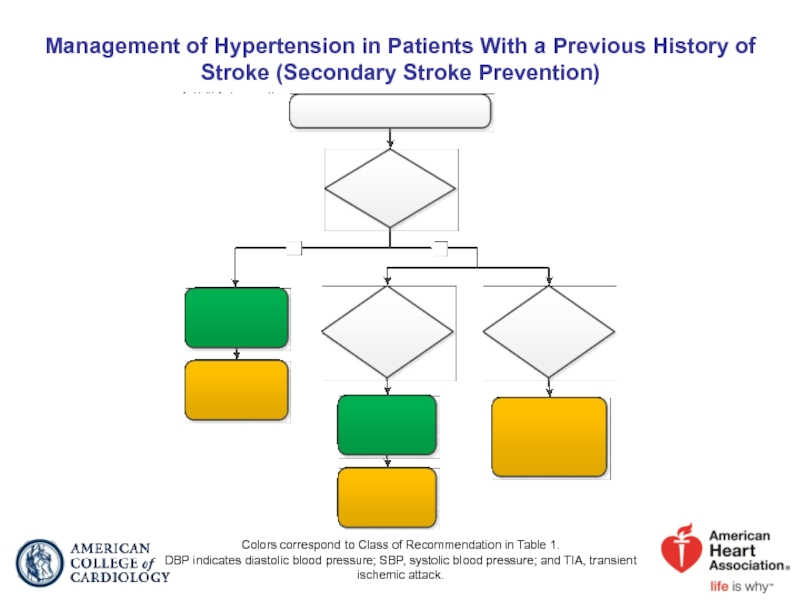
Слайд 68Management of Hypertension in Patients With a Previous History of Stroke
Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1.
DBP indicates diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; and TIA, transient ischemic attack.
Слайд 79Resistant Hypertension: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment
.
BP indicates blood pressure;
Adapted with permission from Calhoun et al.
Слайд 81
Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1.
*Use drug(s) specified
†If other comorbidities are present, select a drug specified in Table 20.
BP indicates blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; ICU, intensive care unit; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Diagnosis and Management of a Hypertensive Crisis
Слайд 96Clinician’s Sequential Flow Chart for the Management of Hypertension
ASCVD indicates atherosclerotic
Слайд 97Summary of BP Thresholds and Goals for Pharmacological Therapy Plan of
2017 Hypertension Guideline
Слайд 98BP Thresholds for and Goals of Pharmacological Therapy in Patients With
ASCVD indicates atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BP, blood pressure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; and SBP, systolic blood pressure.