- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Clinical anatomy of the head презентация
Содержание
- 1. Clinical anatomy of the head
- 2. Topographic anatomy & operative surgery TOPOGRAPHIC ANATOMY
- 3. Cranial bones The cranial bones enclose and
- 4. SKULL The human skull, consisting of 8
- 5. The eight bones of the cranium articulate
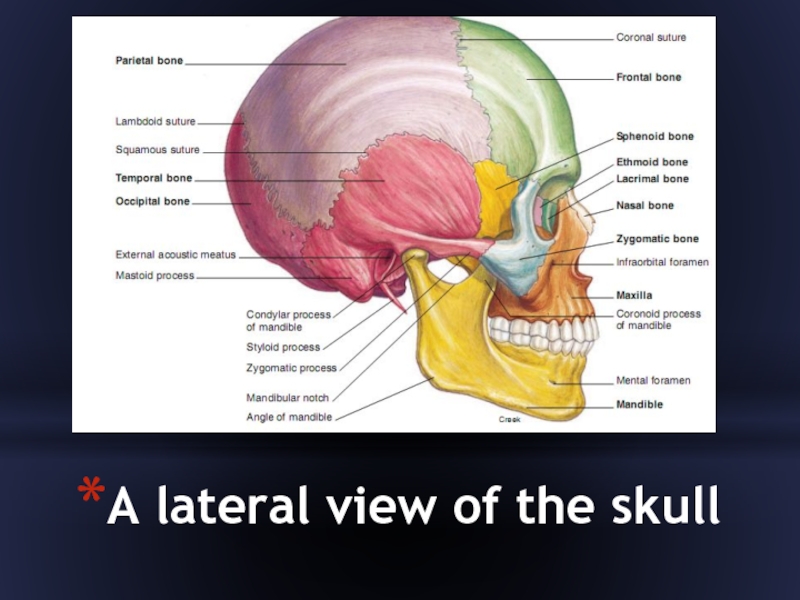
- 6. A lateral view of the skull
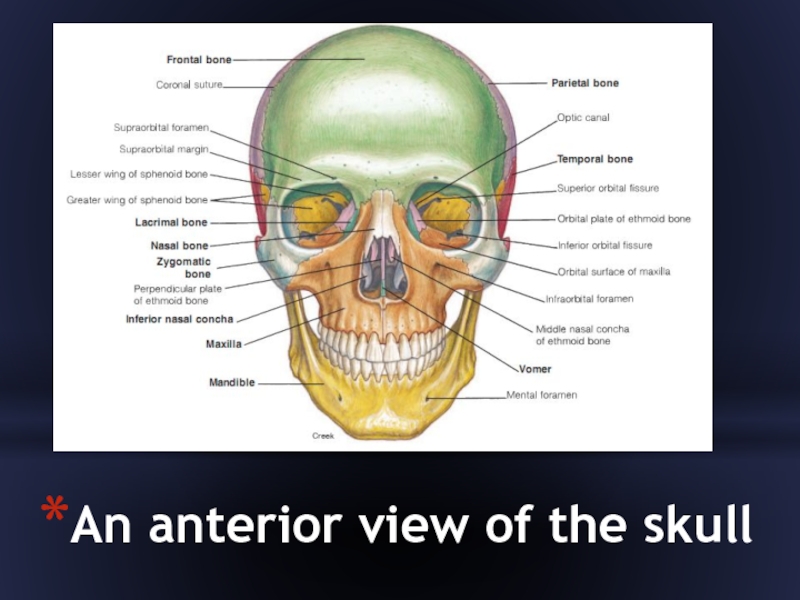
- 7. An anterior view of the skull
- 8. Regio fronto-parieto-occipitalis 1 - кожа; 2
- 9. Sinuses of dura mater encephali 1 -
- 10. Regio temporalis
- 11. Regio temporalis 1 - r. parietalis a.
- 12. ) 1 — a. meningea media; 2
- 13. Bony-plastic trpanation I — выкраивание кожно-апоневротического
- 14. Regio mastoidea 1 - linea temporalis;
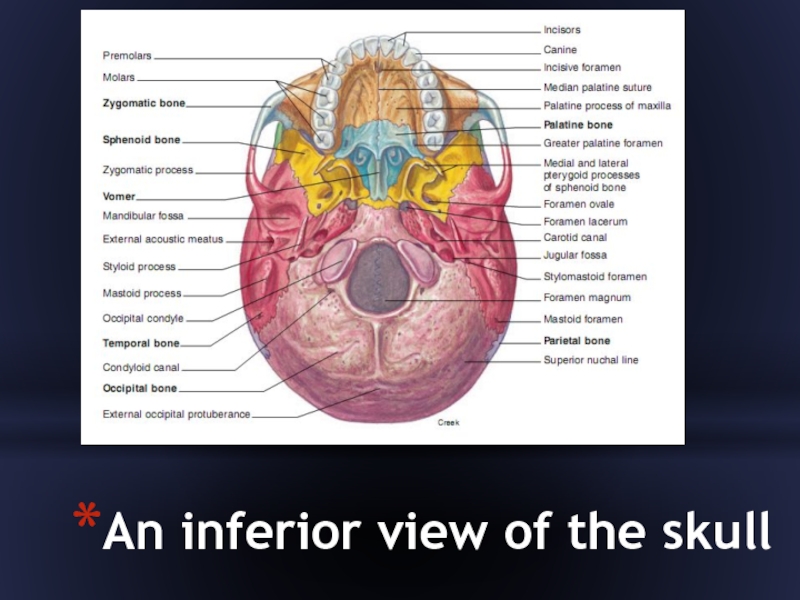
- 15. An inferior view of the skull
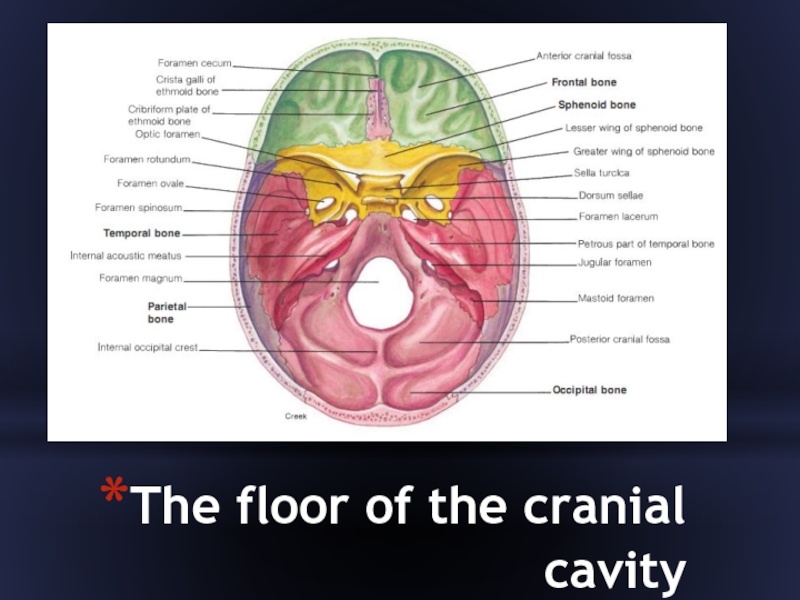
- 16. The floor of the cranial cavity
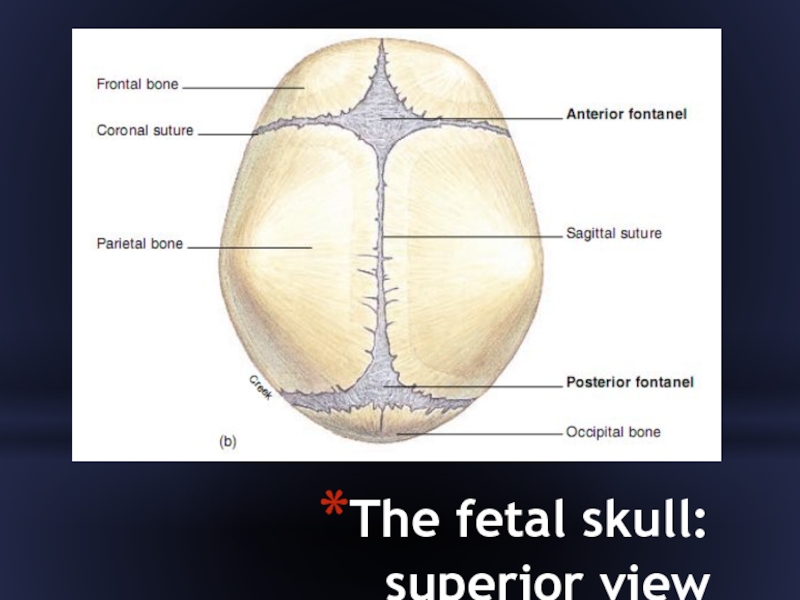
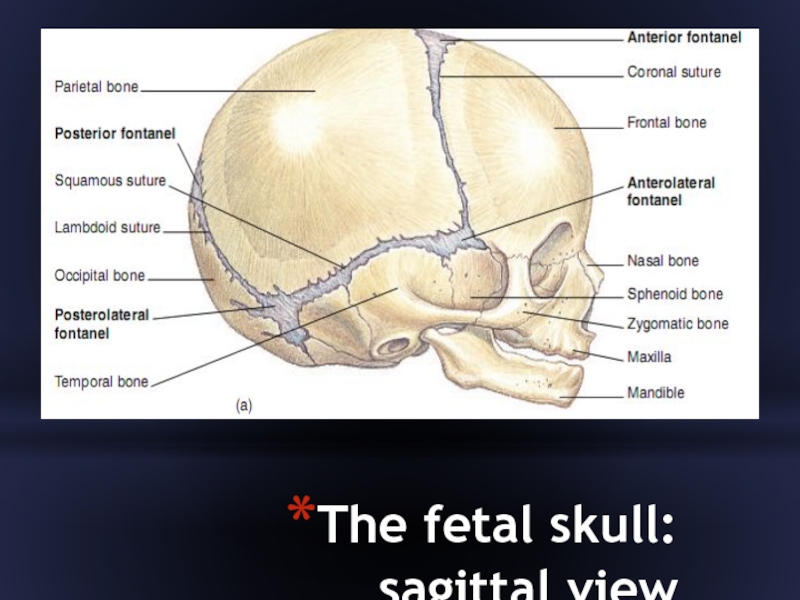
- 17. Fontanels
- 18. The fetal skull: superior view
- 19. The fetal skull: sagittal view
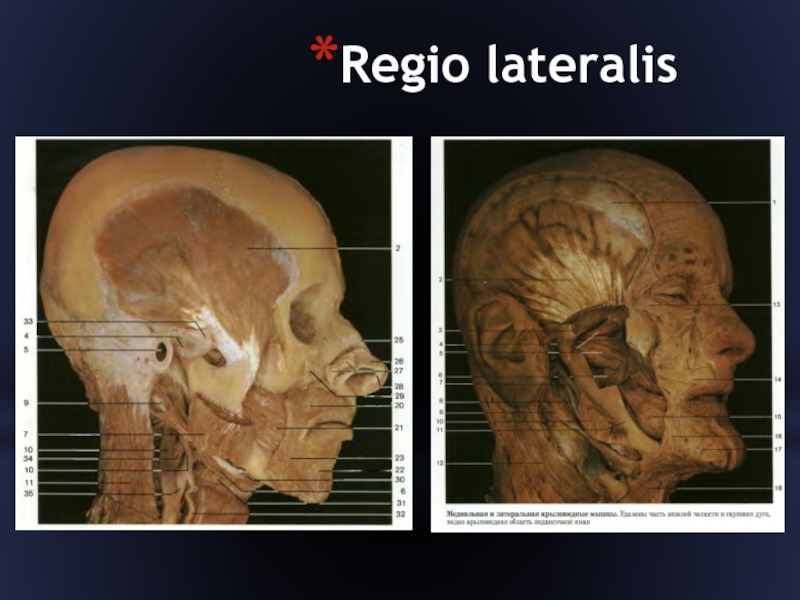
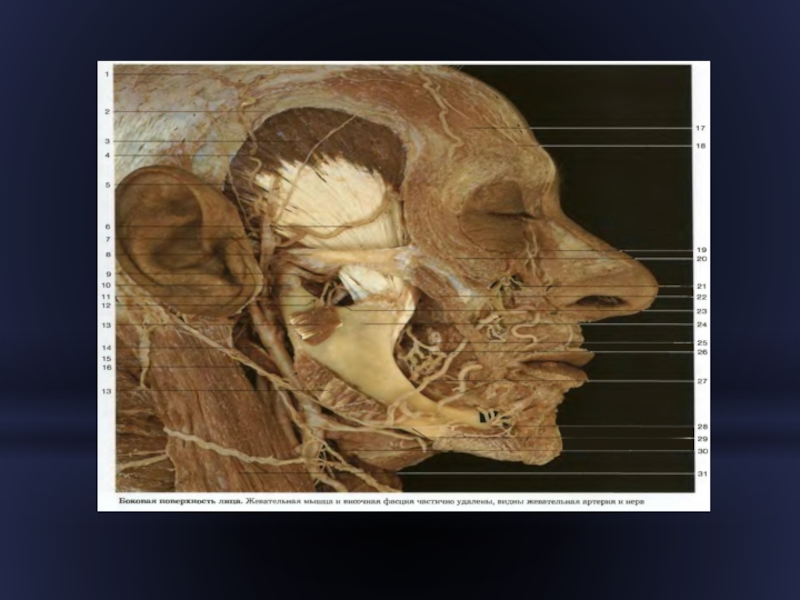
- 20. Regio lateralis
- 22. Parapharyngeal space 1 — mandibula; 2 —
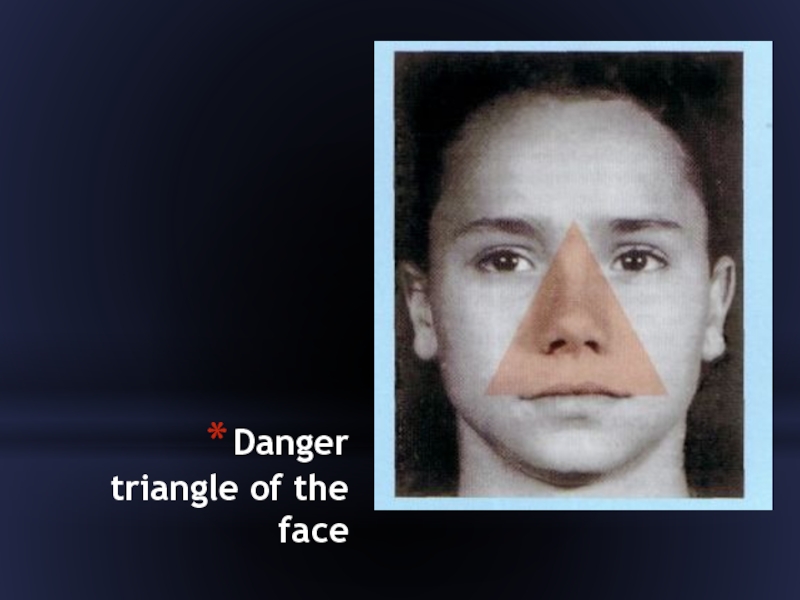
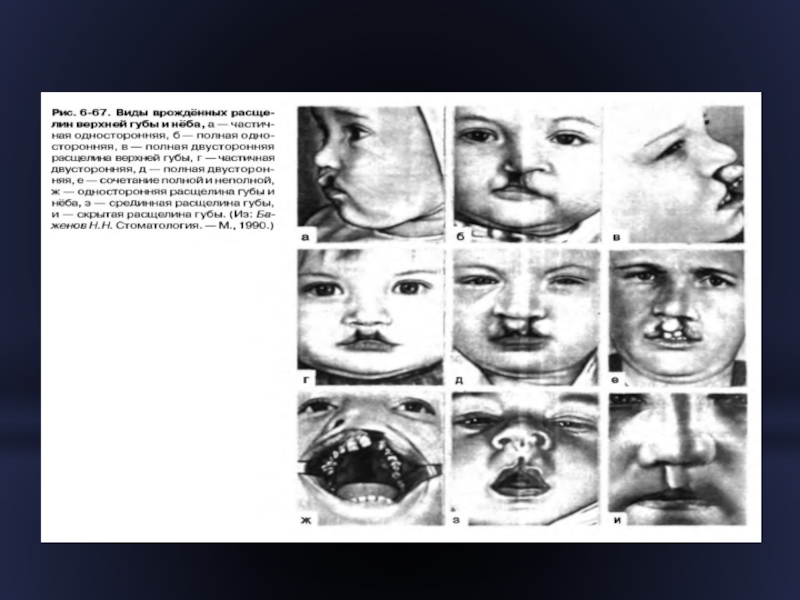
- 24. Danger triangle of the face
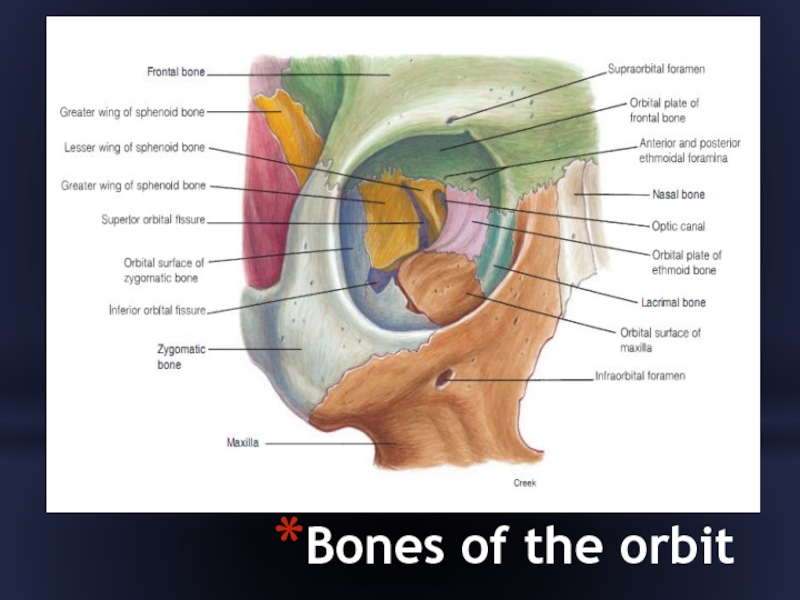
- 29. Bones of the orbit
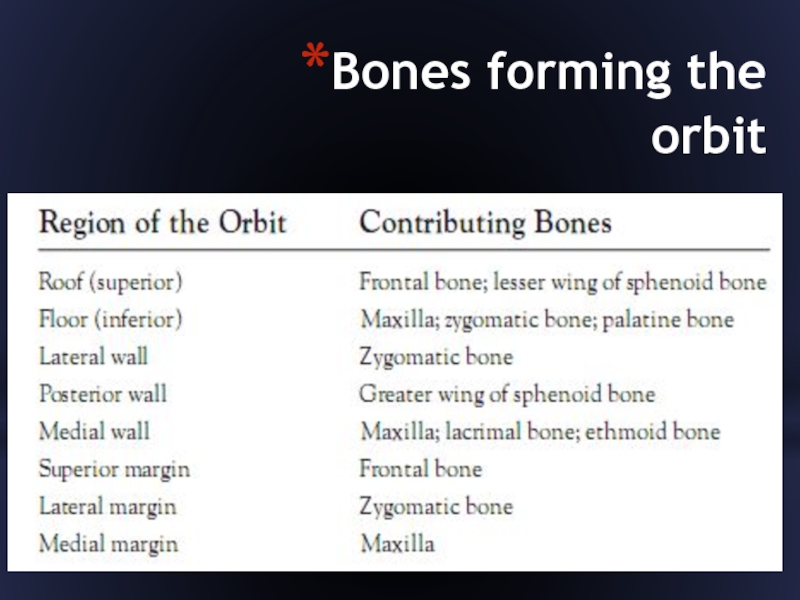
- 30. Bones forming the orbit
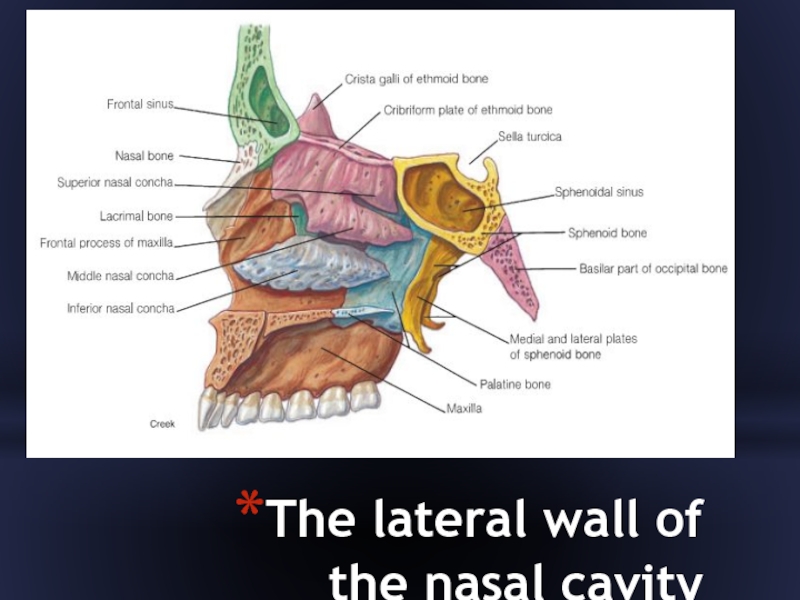
- 31. The lateral wall of the nasal cavity
- 32. Bones that enclose the nasal cavity
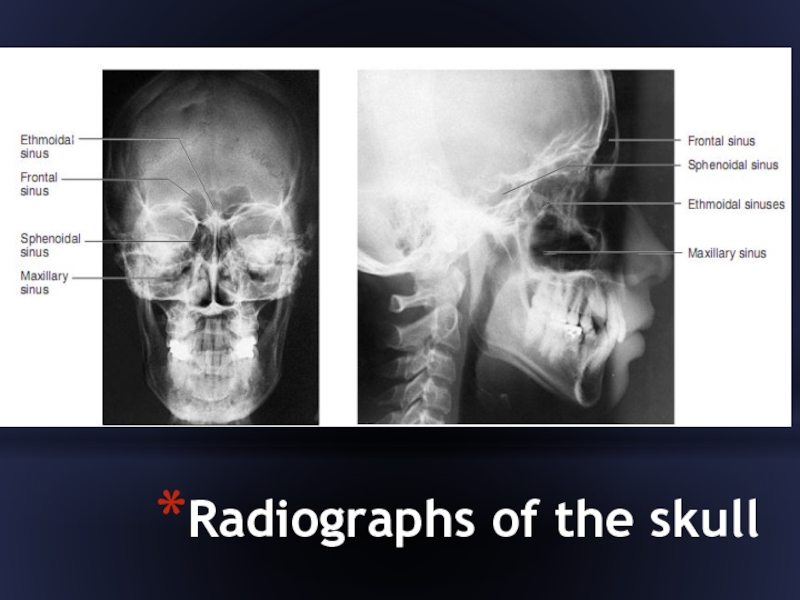
- 33. Radiographs of the skull
- 34. Cavities of the scull The skull has
- 35. Cavities of the scull Middle and inner-ear
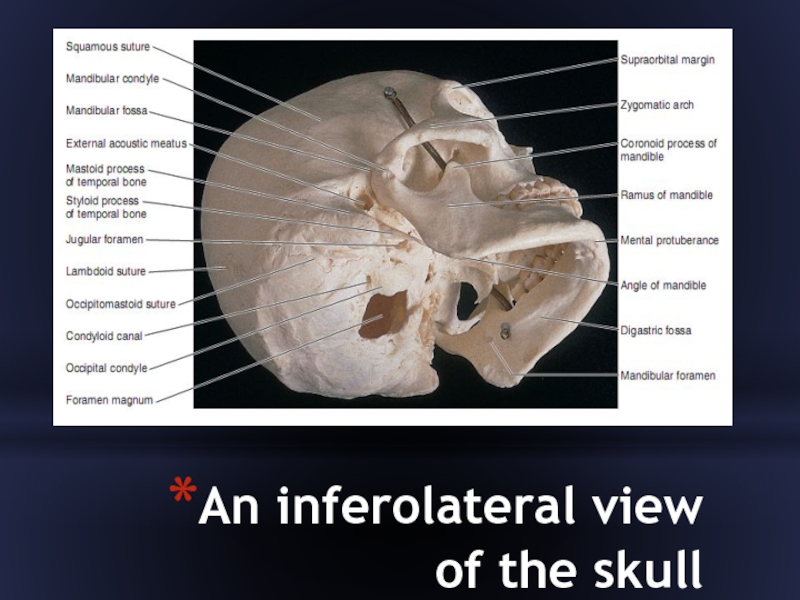
- 36. An inferolateral view of the skull
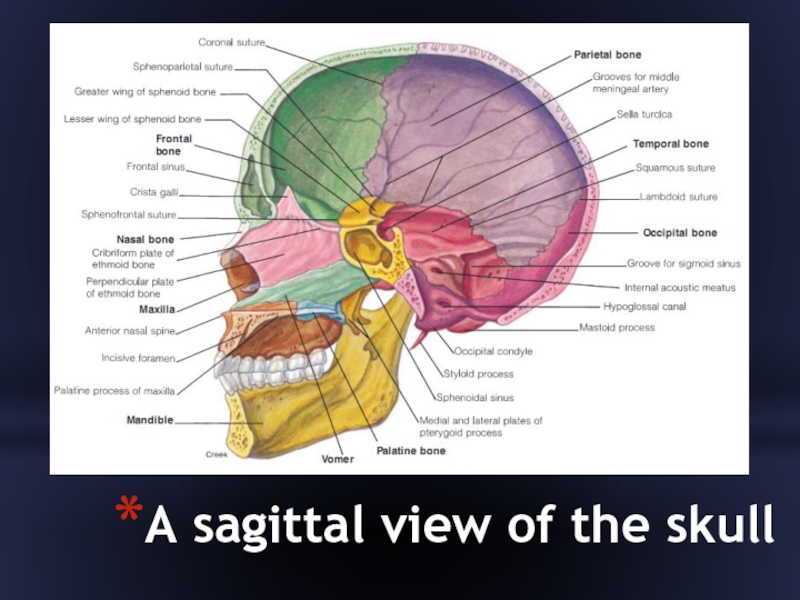
- 37. A sagittal view of the skull
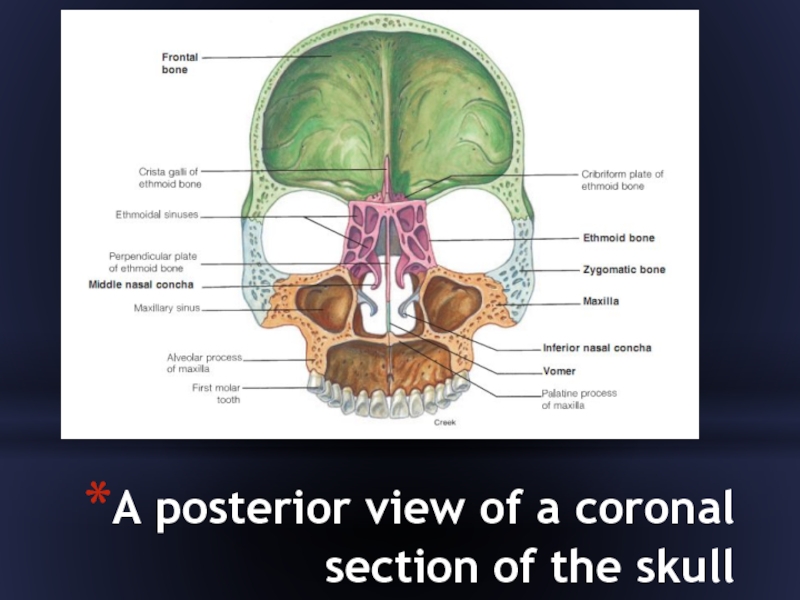
- 38. A posterior view of a coronal section of the skull
Слайд 2Topographic anatomy & operative surgery
TOPOGRAPHIC ANATOMY is a science which studies
relations between organs and tissues in various regions of the human body
Operative surgery is a subject about techniques, ways of surgical operations
Operative surgery is a subject about techniques, ways of surgical operations
Слайд 3Cranial bones
The cranial bones enclose and protect the brain and associated
sensory organs.
They consist of one frontal, two parietals, two temporals, one occipital, one sphenoid and one ethmoid bone.
They consist of one frontal, two parietals, two temporals, one occipital, one sphenoid and one ethmoid bone.
Слайд 4SKULL
The human skull, consisting of 8 cranial and 14 facial bones,
contains several cavities that house the brain and sensory organs.
Each bone of the skull articulates with the adjacent bones and has diagnostic and functional processes, surface features and foramina.
Each bone of the skull articulates with the adjacent bones and has diagnostic and functional processes, surface features and foramina.
Слайд 5The eight bones of the cranium articulate firmly with one another
to enclose and protect the brain and sensory organs.
The 14 fascial bones form the framework for the facial region and support the teeth.
Variation in size, shape and density of the facial bones is a major contributor to the individuality of each human face.
The facial bones, with the exeption of the mandible, are also firmly interlocked with one another and the cranial bones.
The 14 fascial bones form the framework for the facial region and support the teeth.
Variation in size, shape and density of the facial bones is a major contributor to the individuality of each human face.
The facial bones, with the exeption of the mandible, are also firmly interlocked with one another and the cranial bones.
Слайд 8Regio fronto-parieto-occipitalis
1 - кожа;
2 - подкожная клетчатка;
3 - сухожильный
шлем;
4 - диплоическая вена;
5 - подапоневротическая клетчатка;
6 - надкостница;
7 - поднадкостничная клетчатка:
8 - пахионовы грануляции;
11 - твердая мозговая оболочка:
12 - паутинная оболочка;
13 - спинномозговая жидкость подпаутинного пространства;
14 - мягкая мозговая оболочка;
15 - кора полушарий большого мозга;
16 - серповидный отросток твердой мозговой оболочки; 19 - верхняя сагиттальная пазуха твердой мозговой оболочки;
4 - диплоическая вена;
5 - подапоневротическая клетчатка;
6 - надкостница;
7 - поднадкостничная клетчатка:
8 - пахионовы грануляции;
11 - твердая мозговая оболочка:
12 - паутинная оболочка;
13 - спинномозговая жидкость подпаутинного пространства;
14 - мягкая мозговая оболочка;
15 - кора полушарий большого мозга;
16 - серповидный отросток твердой мозговой оболочки; 19 - верхняя сагиттальная пазуха твердой мозговой оболочки;
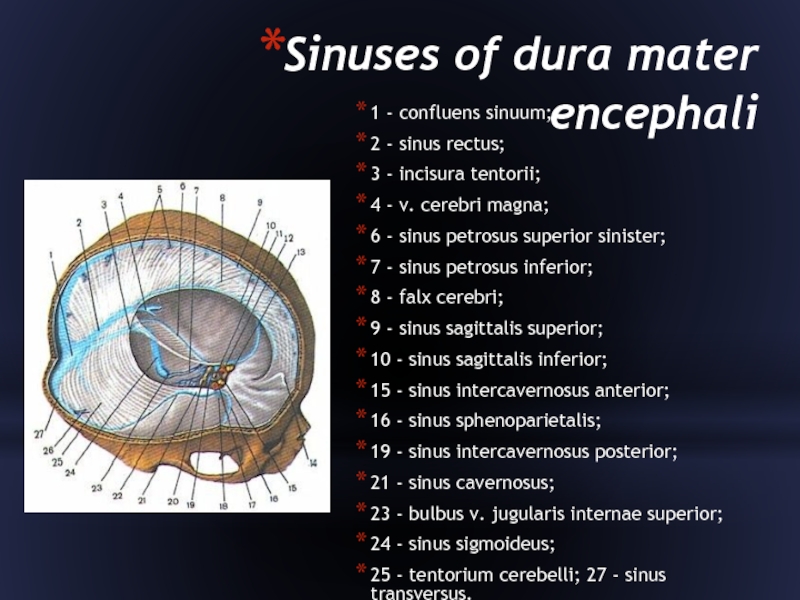
Слайд 9Sinuses of dura mater encephali
1 - confluens sinuum;
2 - sinus
rectus;
3 - incisura tentorii;
4 - v. cerebri magna;
6 - sinus petrosus superior sinister;
7 - sinus petrosus inferior;
8 - falx cerebri;
9 - sinus sagittalis superior;
10 - sinus sagittalis inferior;
15 - sinus intercavernosus anterior;
16 - sinus sphenoparietalis;
19 - sinus intercavernosus posterior;
21 - sinus cavernosus;
23 - bulbus v. jugularis internae superior;
24 - sinus sigmoideus;
25 - tentorium cerebelli; 27 - sinus transversus.
3 - incisura tentorii;
4 - v. cerebri magna;
6 - sinus petrosus superior sinister;
7 - sinus petrosus inferior;
8 - falx cerebri;
9 - sinus sagittalis superior;
10 - sinus sagittalis inferior;
15 - sinus intercavernosus anterior;
16 - sinus sphenoparietalis;
19 - sinus intercavernosus posterior;
21 - sinus cavernosus;
23 - bulbus v. jugularis internae superior;
24 - sinus sigmoideus;
25 - tentorium cerebelli; 27 - sinus transversus.
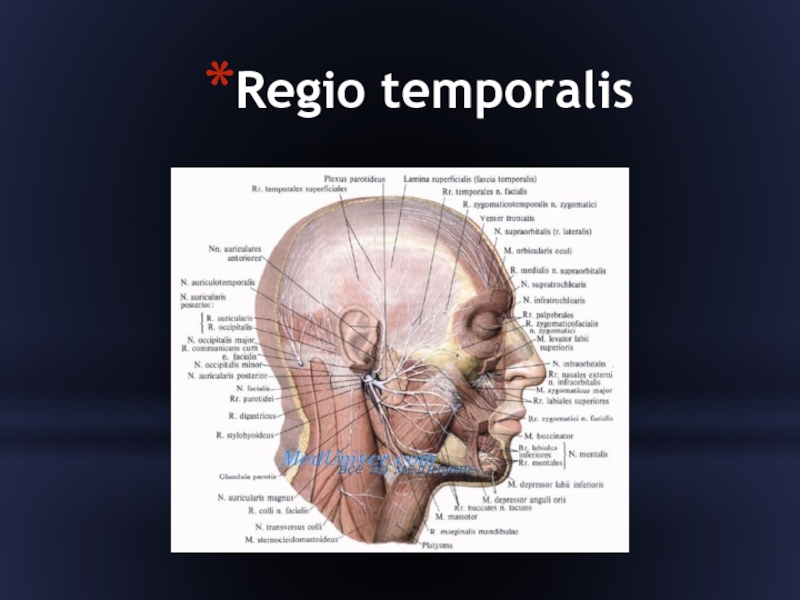
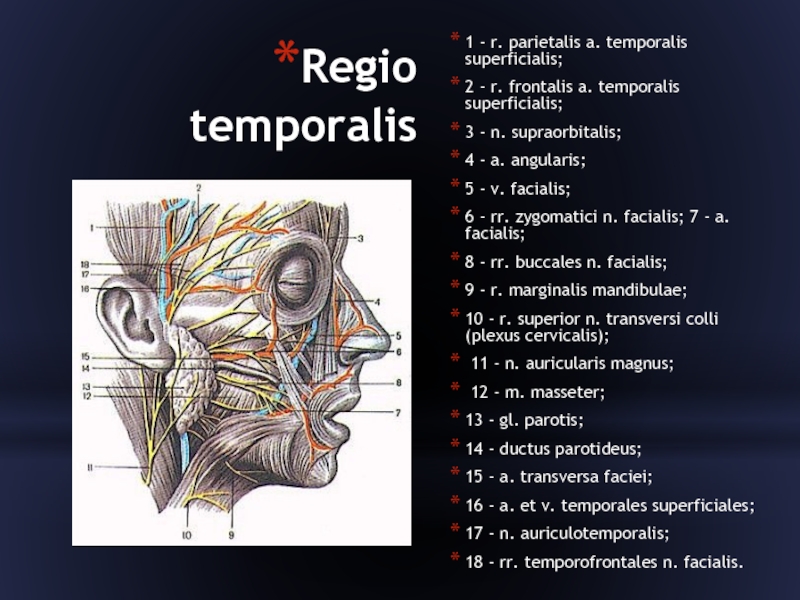
Слайд 11Regio temporalis
1 - r. parietalis a. temporalis superficialis;
2 - r.
frontalis a. temporalis superficialis;
3 - n. supraorbitalis;
4 - a. angularis;
5 - v. facialis;
6 - rr. zygomatici n. facialis; 7 - a. facialis;
8 - rr. buccales n. facialis;
9 - r. marginalis mandibulae;
10 - r. superior n. transversi colli (plexus cervicalis);
11 - n. auricularis magnus;
12 - m. masseter;
13 - gl. parotis;
14 - ductus parotideus;
15 - a. transversa faciei;
16 - a. et v. temporales superficiales;
17 - n. auriculotemporalis;
18 - rr. temporofrontales n. facialis.
3 - n. supraorbitalis;
4 - a. angularis;
5 - v. facialis;
6 - rr. zygomatici n. facialis; 7 - a. facialis;
8 - rr. buccales n. facialis;
9 - r. marginalis mandibulae;
10 - r. superior n. transversi colli (plexus cervicalis);
11 - n. auricularis magnus;
12 - m. masseter;
13 - gl. parotis;
14 - ductus parotideus;
15 - a. transversa faciei;
16 - a. et v. temporales superficiales;
17 - n. auriculotemporalis;
18 - rr. temporofrontales n. facialis.
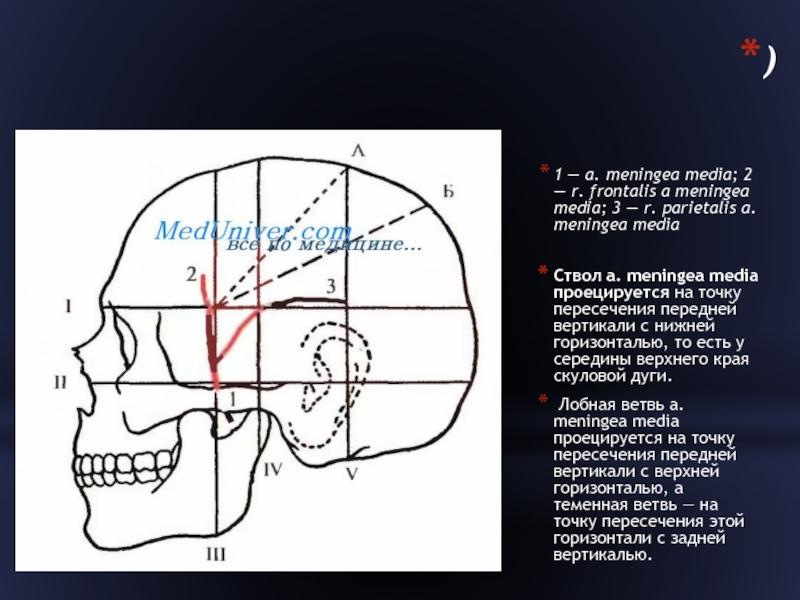
Слайд 12)
1 — a. meningea media; 2 — r. frontalis a meningea
media; 3 — r. parietalis a. meningea media
Ствол a. meningea media проецируется на точку пересечения передней вертикали с нижней горизонталью, то есть у середины верхнего края скуловой дуги.
Лобная ветвь a. meningea media проецируется на точку пересечения передней вертикали с верхней горизонталью, а теменная ветвь — на точку пересечения этой горизонтали с задней вертикалью.
Ствол a. meningea media проецируется на точку пересечения передней вертикали с нижней горизонталью, то есть у середины верхнего края скуловой дуги.
Лобная ветвь a. meningea media проецируется на точку пересечения передней вертикали с верхней горизонталью, а теменная ветвь — на точку пересечения этой горизонтали с задней вертикалью.
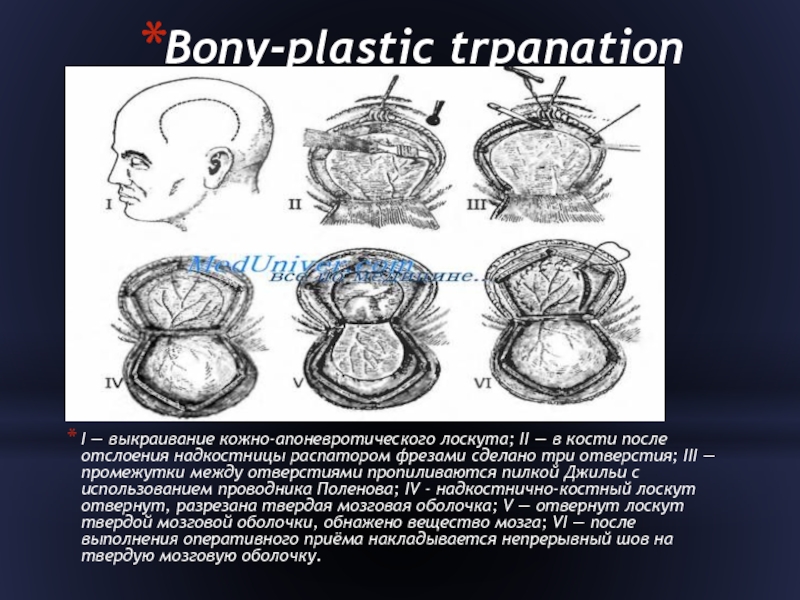
Слайд 13Bony-plastic trpanation
I — выкраивание кожно-апоневротического лоскута; II — в кости
после отслоения надкостницы распатором фрезами сделано три отверстия; III — промежутки между отверстиями пропиливаются пилкой Джильи с использованием проводника Поленова; IV - надкостнично-костный лоскут отвернут, разрезана твердая мозговая оболочка; V — отвернут лоскут твердой мозговой оболочки, обнажено вещество мозга; VI — после выполнения оперативного приёма накладывается непрерывный шов на твердую мозговую оболочку.
Слайд 14Regio mastoidea
1 - linea temporalis;
2 - cellulae mastoideae (проекция);
3
- spina suprameatica;
4 - проекция лицевого нерва;
5 - crista mastoidea;
6 - foramen mastoideum;
7 - проекция sinus sigmoideus
4 - проекция лицевого нерва;
5 - crista mastoidea;
6 - foramen mastoideum;
7 - проекция sinus sigmoideus
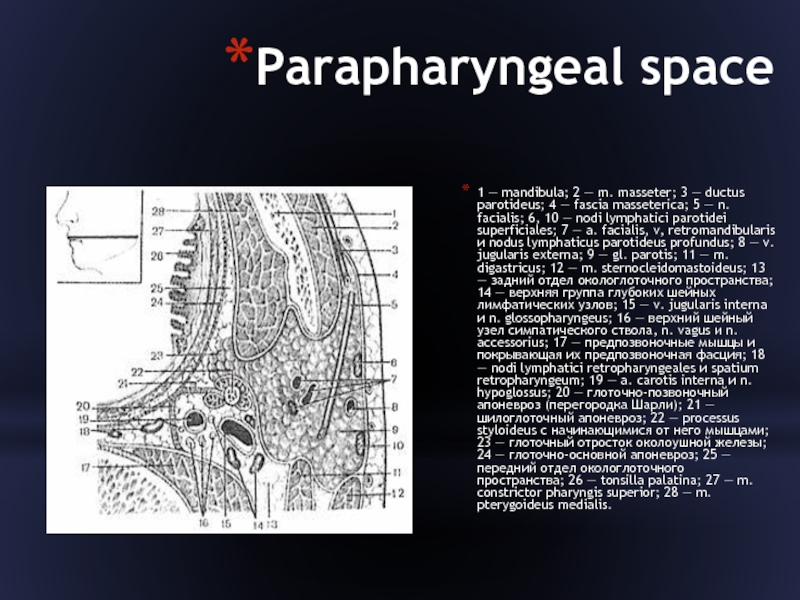
Слайд 22Parapharyngeal space
1 — mandibula; 2 — m. masseter; 3 — ductus
parotideus; 4 — fascia masseterica; 5 — n. facialis; 6, 10 — nodi lymphatici parotidei superficiales; 7 — a. facialis, v, retromandibularis и nodus lymphaticus parotideus profundus; 8 — v. jugularis externa; 9 — gl. parotis; 11 — m. digastricus; 12 — m. sternocleidomastoideus; 13 — задний отдел окологлоточного пространства; 14 — верхняя группа глубоких шейных лимфатических узлов; 15 — v. jugularis interna и n. glossopharyngeus; 16 — верхний шейный узел симпатического ствола, n. vagus и n. accessorius; 17 — предпозвоночные мышцы и покрывающая их предпозвоночная фасция; 18 — nodi lymphatici retropharyngeales и spatium retropharyngeum; 19 — a. carotis interna и n. hypoglossus; 20 — глоточно-позвоночный апоневроз (перегородка Шарли); 21 — шилоглоточный апоневроз; 22 — processus styloideus с начинающимися от него мышцами; 23 — глоточный отросток околоушной железы; 24 — глоточно-основной апоневроз; 25 — передний отдел окологлоточного пространства; 26 — tonsilla palatina; 27 — m. constrictor pharyngis superior; 28 — m. pterygoideus medialis.
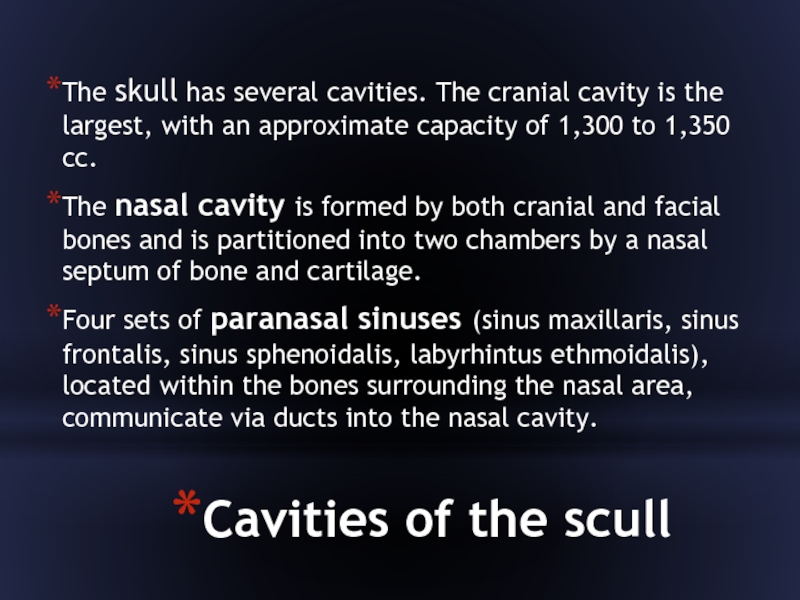
Слайд 34Cavities of the scull
The skull has several cavities. The cranial cavity
is the largest, with an approximate capacity of 1,300 to 1,350 cc.
The nasal cavity is formed by both cranial and facial bones and is partitioned into two chambers by a nasal septum of bone and cartilage.
Four sets of paranasal sinuses (sinus maxillaris, sinus frontalis, sinus sphenoidalis, labyrhintus ethmoidalis), located within the bones surrounding the nasal area, communicate via ducts into the nasal cavity.
The nasal cavity is formed by both cranial and facial bones and is partitioned into two chambers by a nasal septum of bone and cartilage.
Four sets of paranasal sinuses (sinus maxillaris, sinus frontalis, sinus sphenoidalis, labyrhintus ethmoidalis), located within the bones surrounding the nasal area, communicate via ducts into the nasal cavity.
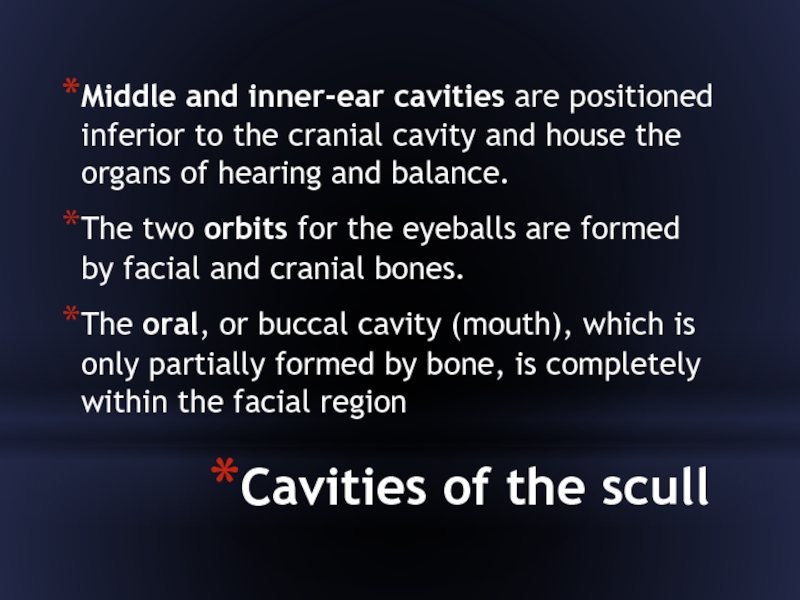
Слайд 35Cavities of the scull
Middle and inner-ear cavities are positioned inferior to
the cranial cavity and house the organs of hearing and balance.
The two orbits for the eyeballs are formed by facial and cranial bones.
The oral, or buccal cavity (mouth), which is only partially formed by bone, is completely within the facial region
The two orbits for the eyeballs are formed by facial and cranial bones.
The oral, or buccal cavity (mouth), which is only partially formed by bone, is completely within the facial region