- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Antihistamine agents. Immunopharmacology презентация
Содержание
- 1. Antihistamine agents. Immunopharmacology
- 2. Allergic Reactions on Drugs include 4
- 3. ANTIALLERGIC DRUGS 1. Drugs Stabilizing Mast Cell
- 4. Drugs used to treat Delayed Type
- 5. H1- and H2- Receptors exert their effects
- 7. H1-Receptor Antagonists I GENERATION (SEDATIVE): Dimedrol
- 8. Pharmacodynamics of antihistamine H1 blockers ▶
- 9. Dimedrol (Diphenhydramine)-Tab 0.05 g, amp 1%-1 ml
- 10. Suprastine (Chloropyramine)-Tab. 0.025 g, amp. 2% -
- 11. Terfenadine (Claritin)-. ● blocks cardiac K+
- 12. Telfast (Fexofenadine) and Zirtek (Cetirizine) non-toxic
- 13. Drugs used to treat Delayed Type Hypersensitivity
- 14. Clinical uses of immunosupressants: ▶ to suppress
- 15. Cyclosporine amp.5% - 1 ml, caps. 50
- 16. 2.Glucocorticoids Prednisolone Beclomethasone Hydrocortisone Betamethasone Triamcinolone Fluocinolone
- 17. 3. Antitumor Cytotoxic Drugs Cyclophosphan (Cyclophosphamide)
- 19. Methotrexate – the folate analogue –
- 20. Azathioprine – Tab. 50 mg - interferes
- 21. Basiliximab (Simulect) and Daclizumab - Monoclonal
- 23. IMMUNOMODULATING AGENTS I. Biogenic substances: 1. Preparations
- 24. 4. Interferons: Interferon –
- 25. Cycloferon (amp 12.5%-2 ml, Tab 0.15 )
- 26. Inerferon-α (Laferon) – amp. 1 and 3
- 27. Clinical uses: Neoplasms Chronic Myelogenous
- 28. BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guerin) vaccine viable strain
- 29. Thank you for Attention !
Слайд 2
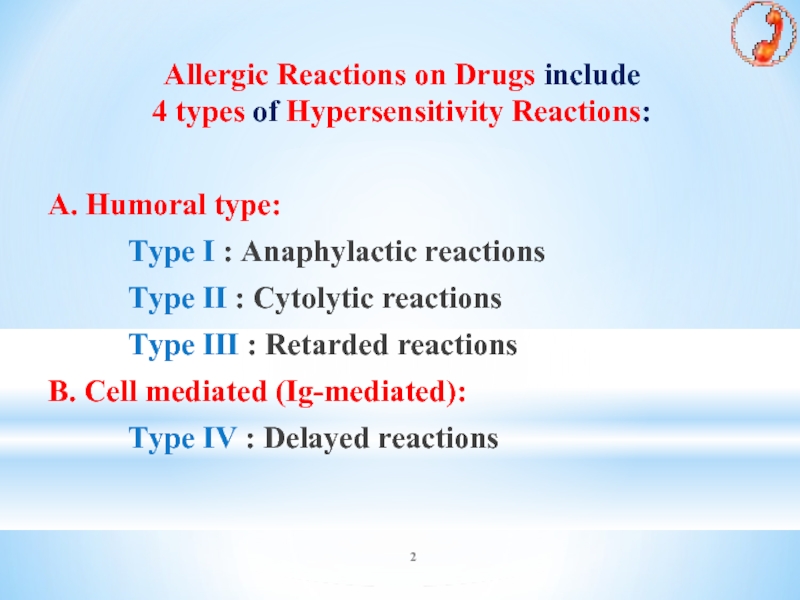
Allergic Reactions on Drugs include
4 types of Hypersensitivity Reactions:
A. Humoral
type:
Type I : Anaphylactic reactions
Type II : Cytolytic reactions
Type III : Retarded reactions
B. Cell mediated (Ig-mediated):
Type IV : Delayed reactions
Type I : Anaphylactic reactions
Type II : Cytolytic reactions
Type III : Retarded reactions
B. Cell mediated (Ig-mediated):
Type IV : Delayed reactions
Слайд 3ANTIALLERGIC DRUGS
1. Drugs Stabilizing Mast Cell Membrane:
Glucocorticoids: Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone
Antihistamine H1
: Ketotifen
Mast cell stabilizers: Cromolyn, Nedocromil
β-adrenomimetics: Adrenaline, Ephedrine
Methylxanthines: Euphylline (Aminophylline)
2. Antihistamine H1 agents: Dimedrol, Diprazine, Loratadine
3. Agents eliminating generalized symptoms of immediate allergic reactions:
Adrenomimetics: Adrenaline
Methylxanthines: Euphylline, Theophylline
Ca2+ preparations: Calcium chloride, Calcium gluconate
4. Agents decreasing tissue damage: Glucocorticoids
Mast cell stabilizers: Cromolyn, Nedocromil
β-adrenomimetics: Adrenaline, Ephedrine
Methylxanthines: Euphylline (Aminophylline)
2. Antihistamine H1 agents: Dimedrol, Diprazine, Loratadine
3. Agents eliminating generalized symptoms of immediate allergic reactions:
Adrenomimetics: Adrenaline
Methylxanthines: Euphylline, Theophylline
Ca2+ preparations: Calcium chloride, Calcium gluconate
4. Agents decreasing tissue damage: Glucocorticoids
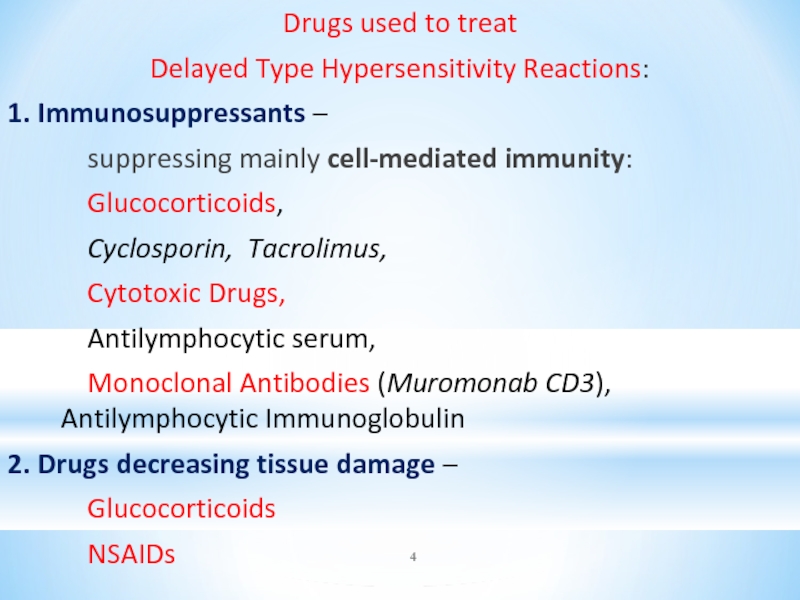
Слайд 4Drugs used to treat
Delayed Type Hypersensitivity Reactions:
1. Immunosuppressants –
suppressing mainly cell-mediated immunity:
Glucocorticoids,
Cyclosporin, Tacrolimus,
Cytotoxic Drugs,
Antilymphocytic serum,
Monoclonal Antibodies (Muromonab CD3), Antilymphocytic Immunoglobulin
2. Drugs decreasing tissue damage –
Glucocorticoids
NSAIDs
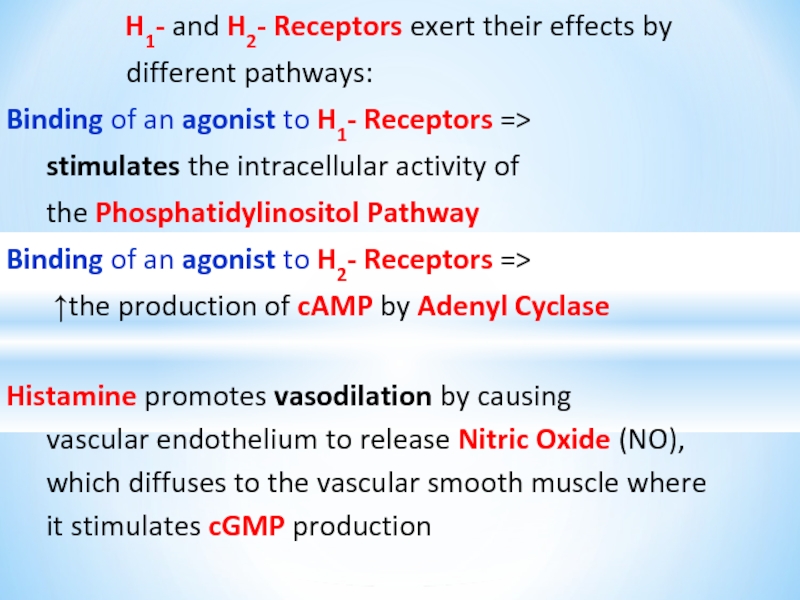
Слайд 5H1- and H2- Receptors exert their effects by
different pathways:
Binding of
an agonist to H1- Receptors =>
stimulates the intracellular activity of
the Phosphatidylinositol Pathway
Binding of an agonist to H2- Receptors =>
↑the production of cAMP by Adenyl Cyclase
Histamine promotes vasodilation by causing
vascular endothelium to release Nitric Oxide (NO),
which diffuses to the vascular smooth muscle where
it stimulates cGMP production
stimulates the intracellular activity of
the Phosphatidylinositol Pathway
Binding of an agonist to H2- Receptors =>
↑the production of cAMP by Adenyl Cyclase
Histamine promotes vasodilation by causing
vascular endothelium to release Nitric Oxide (NO),
which diffuses to the vascular smooth muscle where
it stimulates cGMP production
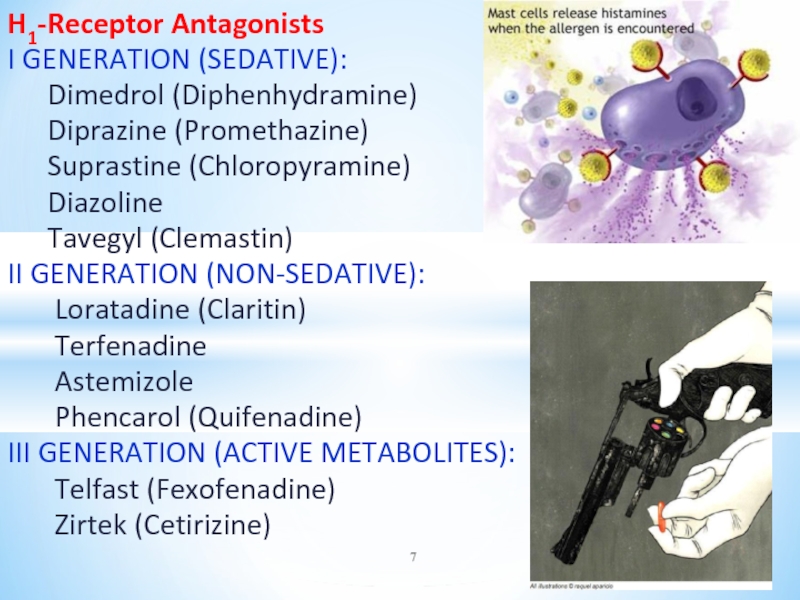
Слайд 7H1-Receptor Antagonists
I GENERATION (SEDATIVE):
Dimedrol (Diphenhydramine)
Diprazine (Promethazine)
Suprastine (Chloropyramine)
Diazoline
Tavegyl (Clemastin)
II GENERATION
(NON-SEDATIVE):
Loratadine (Claritin)
Terfenadine
Astemizole
Phencarol (Quifenadine)
III GENERATION (ACTIVE METABOLITES):
Telfast (Fexofenadine)
Zirtek (Cetirizine)
Loratadine (Claritin)
Terfenadine
Astemizole
Phencarol (Quifenadine)
III GENERATION (ACTIVE METABOLITES):
Telfast (Fexofenadine)
Zirtek (Cetirizine)
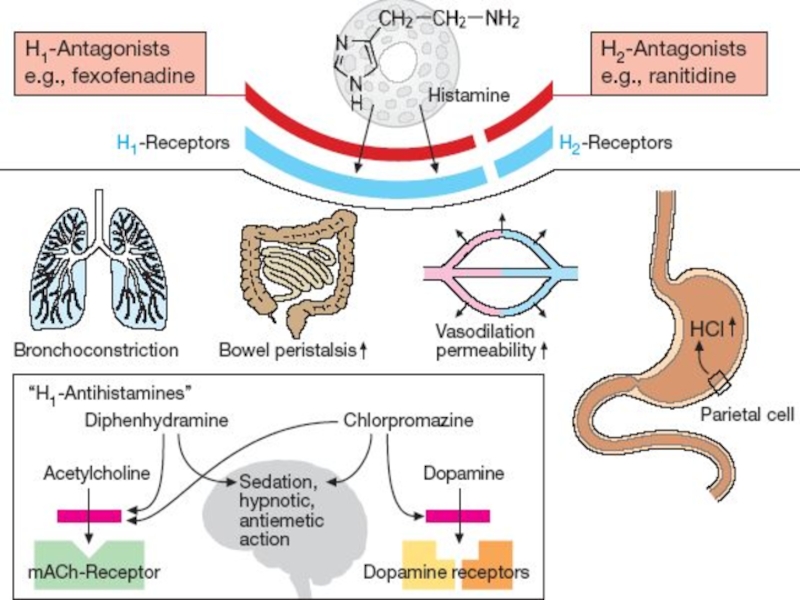
Слайд 8Pharmacodynamics of antihistamine H1 blockers
▶ Block the actions of histamine
by reversible competitive
antagonism at the H1-receptor
▶ Antagonist effects at other receptors:
▶ M - Cholinoceptors
▶ α1 - Adrenoreceptors
▶ 5-Hydrohytryptamine (5-HT) receptors
Diprazin ▶ Dimedrol ▶ Suprastin ▶ Diazolin
antagonism at the H1-receptor
▶ Antagonist effects at other receptors:
▶ M - Cholinoceptors
▶ α1 - Adrenoreceptors
▶ 5-Hydrohytryptamine (5-HT) receptors
Diprazin ▶ Dimedrol ▶ Suprastin ▶ Diazolin
Слайд 9Dimedrol (Diphenhydramine)-Tab 0.05 g, amp 1%-1 ml
competes to H1 receptors
on the smooth muscle of
the bronchi, GIT, uterus, and large blood vessels.
By binding to receptors, suppresses histamine-induced allergic symptoms, even though it does not prevent its release.
Central antimuscarinic actions is responsible for antivertigo, antiemetic, and antidyskinetic action.
Clinical uses:
▶ Allergy symptoms
▶ Motion sickness
▶ Parkinson’s disease
▶ Nonproductive cough
▶ Insomnia
the bronchi, GIT, uterus, and large blood vessels.
By binding to receptors, suppresses histamine-induced allergic symptoms, even though it does not prevent its release.
Central antimuscarinic actions is responsible for antivertigo, antiemetic, and antidyskinetic action.
Clinical uses:
▶ Allergy symptoms
▶ Motion sickness
▶ Parkinson’s disease
▶ Nonproductive cough
▶ Insomnia
Слайд 10Suprastine (Chloropyramine)-Tab. 0.025 g, amp. 2% - 2 ml -
H1 receptor
antagonist of I generation.
It competes to histamine H1 receptor sites on the smooth muscle of the bronchi, GIT, uterus, and large blood vessels.
It has less expressed antihistamine, M-cholinoblocker and sedative effects than Dimedrol.
Clinical uses:
▶ Allergic dermatosis
▶ Allergic rhinitis
▶ Conjunctivitis
▶ Quincke’s edema
▶ Medicamental allergy
▶ Hay (pollen) fever
It competes to histamine H1 receptor sites on the smooth muscle of the bronchi, GIT, uterus, and large blood vessels.
It has less expressed antihistamine, M-cholinoblocker and sedative effects than Dimedrol.
Clinical uses:
▶ Allergic dermatosis
▶ Allergic rhinitis
▶ Conjunctivitis
▶ Quincke’s edema
▶ Medicamental allergy
▶ Hay (pollen) fever
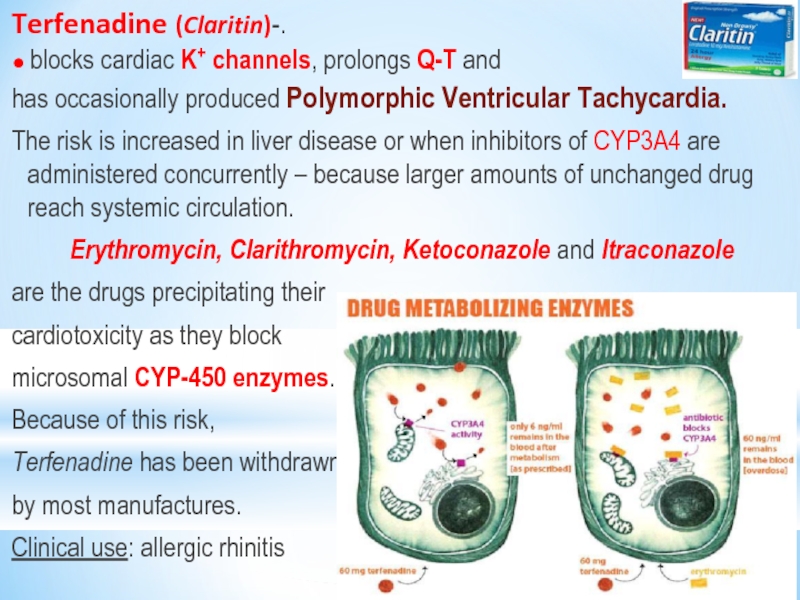
Слайд 11Terfenadine (Claritin)-.
● blocks cardiac K+ channels, prolongs Q-T and
has
occasionally produced Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia.
The risk is increased in liver disease or when inhibitors of CYP3A4 are administered concurrently – because larger amounts of unchanged drug reach systemic circulation.
Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Ketoconazole and Itraconazole
are the drugs precipitating their
cardiotoxicity as they block
microsomal CYP-450 enzymes.
Because of this risk,
Terfenadine has been withdrawn
by most manufactures.
Clinical use: allergic rhinitis
The risk is increased in liver disease or when inhibitors of CYP3A4 are administered concurrently – because larger amounts of unchanged drug reach systemic circulation.
Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Ketoconazole and Itraconazole
are the drugs precipitating their
cardiotoxicity as they block
microsomal CYP-450 enzymes.
Because of this risk,
Terfenadine has been withdrawn
by most manufactures.
Clinical use: allergic rhinitis
Слайд 12Telfast (Fexofenadine) and Zirtek (Cetirizine)
non-toxic metabolites of Terfenadine
that do
not block K+ channels in the heart –
does not prolong Q-T interval.
Telfast has plasma T1/2 11-16 hours and duration of action 24 hours.
does not prolong Q-T interval.
Telfast has plasma T1/2 11-16 hours and duration of action 24 hours.
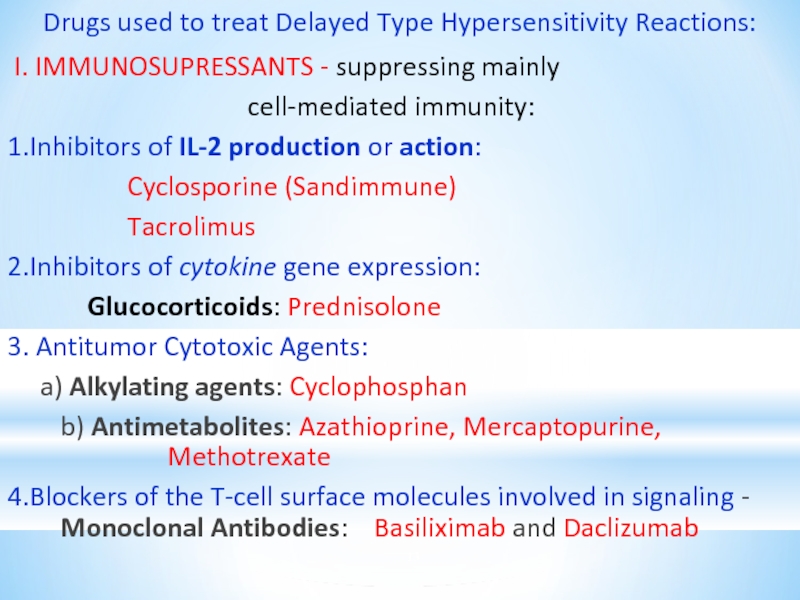
Слайд 13Drugs used to treat Delayed Type Hypersensitivity Reactions:
I. IMMUNOSUPRESSANTS
- suppressing mainly
cell-mediated immunity:
1.Inhibitors of IL-2 production or action:
Cyclosporine (Sandimmune)
Tacrolimus
2.Inhibitors of cytokine gene expression:
Glucocorticoids: Prednisolone
3. Antitumor Cytotoxic Agents:
a) Alkylating agents: Cyclophosphan
b) Antimetabolites: Azathioprine, Mercaptopurine, Methotrexate
4.Blockers of the T-cell surface molecules involved in signaling - Monoclonal Antibodies: Basiliximab and Daclizumab
cell-mediated immunity:
1.Inhibitors of IL-2 production or action:
Cyclosporine (Sandimmune)
Tacrolimus
2.Inhibitors of cytokine gene expression:
Glucocorticoids: Prednisolone
3. Antitumor Cytotoxic Agents:
a) Alkylating agents: Cyclophosphan
b) Antimetabolites: Azathioprine, Mercaptopurine, Methotrexate
4.Blockers of the T-cell surface molecules involved in signaling - Monoclonal Antibodies: Basiliximab and Daclizumab
Слайд 14Clinical uses of immunosupressants:
▶ to suppress rejection of transplanted organs
▶
to suppress graft-versus-host disease
▶ to treat diseases that are believed to have autoimmune component in their pathogenesis:
● Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
● Hemolytic anemia
● Glomerulonephritis
● Myasthenia gravis
● Systemic lupus erythematosus
● Rheumatoid arthritis
● Psoriasis
▶ to treat diseases that are believed to have autoimmune component in their pathogenesis:
● Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
● Hemolytic anemia
● Glomerulonephritis
● Myasthenia gravis
● Systemic lupus erythematosus
● Rheumatoid arthritis
● Psoriasis
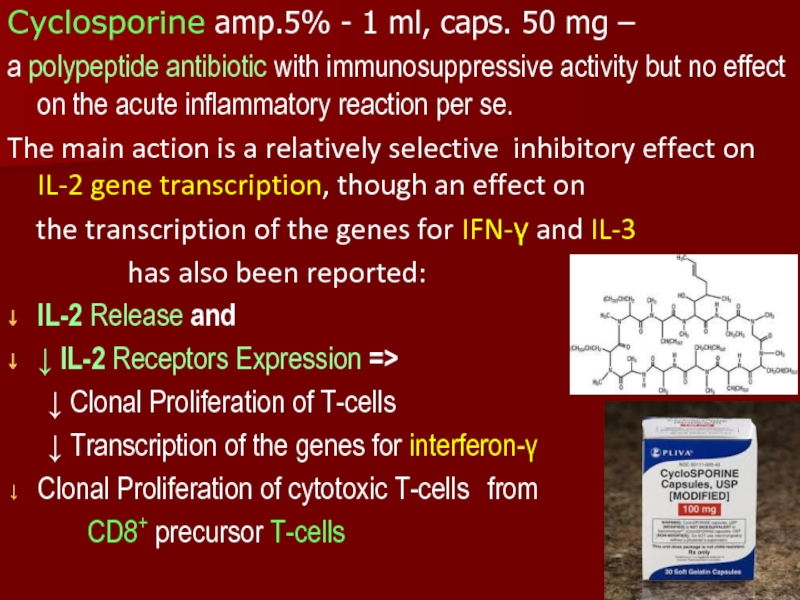
Слайд 15Cyclosporine amp.5% - 1 ml, caps. 50 mg –
a polypeptide
antibiotic with immunosuppressive activity but no effect on the acute inflammatory reaction per se.
The main action is a relatively selective inhibitory effect on IL-2 gene transcription, though an effect on
the transcription of the genes for IFN-γ and IL-3
has also been reported:
IL-2 Release and
↓ IL-2 Receptors Expression =>
↓ Clonal Proliferation of T-cells
↓ Transcription of the genes for interferon-γ
Clonal Proliferation of cytotoxic T-cells from
CD8+ precursor T-cells
The main action is a relatively selective inhibitory effect on IL-2 gene transcription, though an effect on
the transcription of the genes for IFN-γ and IL-3
has also been reported:
IL-2 Release and
↓ IL-2 Receptors Expression =>
↓ Clonal Proliferation of T-cells
↓ Transcription of the genes for interferon-γ
Clonal Proliferation of cytotoxic T-cells from
CD8+ precursor T-cells
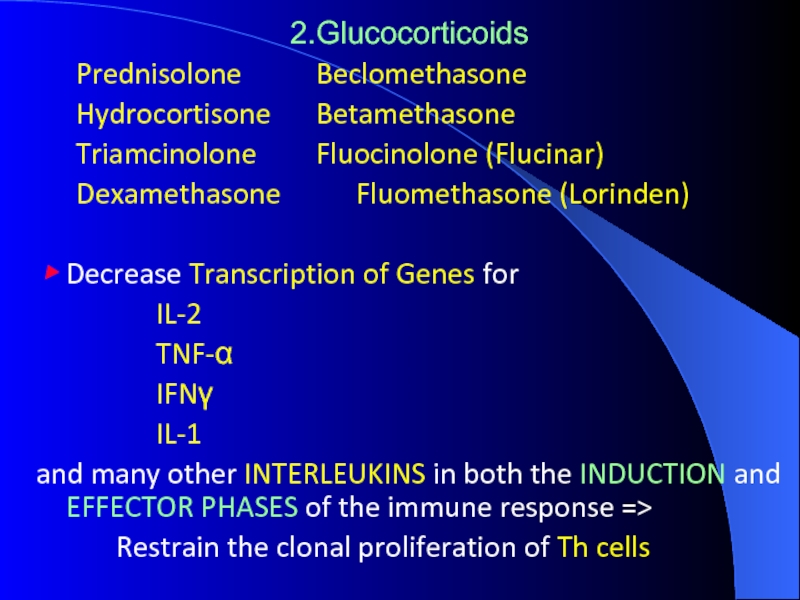
Слайд 162.Glucocorticoids
Prednisolone Beclomethasone
Hydrocortisone Betamethasone
Triamcinolone Fluocinolone (Flucinar)
Dexamethasone Fluomethasone (Lorinden)
▶ Decrease Transcription of
Genes for
IL-2
TNF-α
IFNγ
IL-1
and many other INTERLEUKINS in both the INDUCTION and EFFECTOR PHASES of the immune response =>
Restrain the clonal proliferation of Th cells
IL-2
TNF-α
IFNγ
IL-1
and many other INTERLEUKINS in both the INDUCTION and EFFECTOR PHASES of the immune response =>
Restrain the clonal proliferation of Th cells
Слайд 173. Antitumor Cytotoxic Drugs
Cyclophosphan (Cyclophosphamide)
Tab. 0.05 g, amp. 0.2 and
0.5 g
● is cytotoxic only after generation of
its alkylating species, following
their hydroxylation by CYP-450.
▶ Exerts its cytotoxic effects by
covalently binding to nucleophylic groups
on various cell constituents
▶ Destroys proliferating lymphoid cells
but also appears to alkylate
some resting cells.
● is cytotoxic only after generation of
its alkylating species, following
their hydroxylation by CYP-450.
▶ Exerts its cytotoxic effects by
covalently binding to nucleophylic groups
on various cell constituents
▶ Destroys proliferating lymphoid cells
but also appears to alkylate
some resting cells.
Слайд 19 Methotrexate – the folate analogue –
acts as a false substrate,
inhibits enzyme activity of dihydrofolate reductase =>
↓Tetrahydrofolic acid required for the synthesis of
Purine Bases and Thymidine =>
=> Synthesis of DNA and RNA building blocks ceases.
The effect of these antimetabolites can be reversed by administration of Folic acid.
inhibits enzyme activity of dihydrofolate reductase =>
↓Tetrahydrofolic acid required for the synthesis of
Purine Bases and Thymidine =>
=> Synthesis of DNA and RNA building blocks ceases.
The effect of these antimetabolites can be reversed by administration of Folic acid.
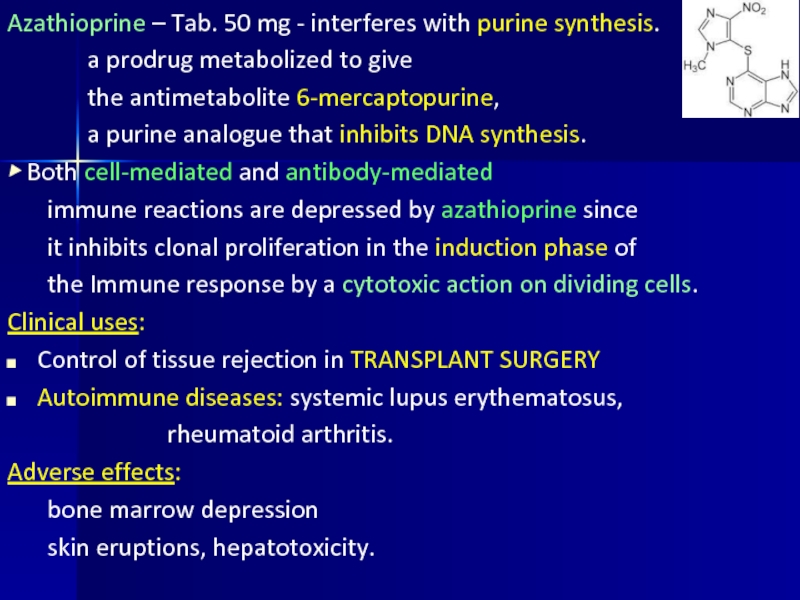
Слайд 20Azathioprine – Tab. 50 mg - interferes with purine synthesis.
a prodrug
metabolized to give
the antimetabolite 6-mercaptopurine,
a purine analogue that inhibits DNA synthesis.
▶ Both cell-mediated and antibody-mediated
immune reactions are depressed by azathioprine since
it inhibits clonal proliferation in the induction phase of
the Immune response by a cytotoxic action on dividing cells.
Clinical uses:
Control of tissue rejection in TRANSPLANT SURGERY
Autoimmune diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus,
rheumatoid arthritis.
Adverse effects:
bone marrow depression
skin eruptions, hepatotoxicity.
the antimetabolite 6-mercaptopurine,
a purine analogue that inhibits DNA synthesis.
▶ Both cell-mediated and antibody-mediated
immune reactions are depressed by azathioprine since
it inhibits clonal proliferation in the induction phase of
the Immune response by a cytotoxic action on dividing cells.
Clinical uses:
Control of tissue rejection in TRANSPLANT SURGERY
Autoimmune diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus,
rheumatoid arthritis.
Adverse effects:
bone marrow depression
skin eruptions, hepatotoxicity.
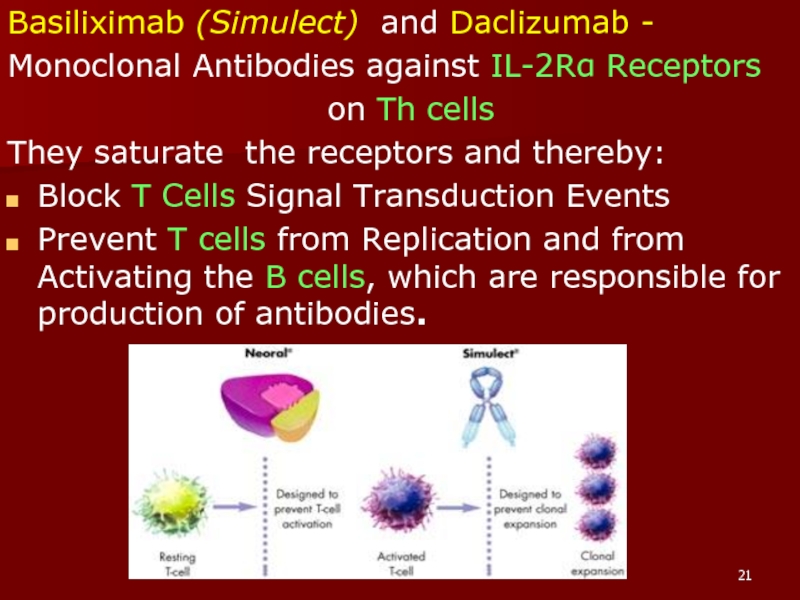
Слайд 21Basiliximab (Simulect) and Daclizumab -
Monoclonal Antibodies against IL-2Rα Receptors
on
Th cells
They saturate the receptors and thereby:
Block T Cells Signal Transduction Events
Prevent T cells from Replication and from Activating the B cells, which are responsible for production of antibodies.
They saturate the receptors and thereby:
Block T Cells Signal Transduction Events
Prevent T cells from Replication and from Activating the B cells, which are responsible for production of antibodies.
Слайд 23IMMUNOMODULATING AGENTS
I. Biogenic substances:
1. Preparations of the Thymus:
Thymosin
Thymalin
Tactivine
2. Peptides:
Thymogen
3. Inductor of Interferon:
Cycloferon
Слайд 244. Interferons:
Interferon – α: amp. 1 and
3 million IU, SC
amp. 100,000 IU – intranasally
Interferon - β: IFN β-1a, IFN β-1b
Interferon - γ 1b
5. Inerleukin-2
6. BCG
II. Synthetic compounds:
Levamisol (Decaris) – Tab. 50 mg and 150 mg
amp. 100,000 IU – intranasally
Interferon - β: IFN β-1a, IFN β-1b
Interferon - γ 1b
5. Inerleukin-2
6. BCG
II. Synthetic compounds:
Levamisol (Decaris) – Tab. 50 mg and 150 mg
Слайд 25Cycloferon (amp 12.5%-2 ml, Tab 0.15 )
- low-molecular inductor of interferon
(Acridone-Acetic Acid)
▶ Immunomodulating
▶ Antiviral
▶ Antinflammatory effects
Clinical uses:
Viral Hepatitis
Herpetic and Cytomegalovirus Infections
Chlamidiosis
HIV-infection (AIDS, stage IIA-IIIB)
Immunodeficiency conditions
Слайд 26Inerferon-α (Laferon) – amp. 1 and 3 million IU or SC,
amp. 100,000 IU – intranasally
Mechanism of action:
direct antiproliferative action against tumor cells or
viral cells to inhibit replication and modulation of
host immune response by:
■ enhancing phagocytic activity of macrophages
■ augmenting specific cytotoxicity of
lymphocytes for target cells.
Mechanism of action:
direct antiproliferative action against tumor cells or
viral cells to inhibit replication and modulation of
host immune response by:
■ enhancing phagocytic activity of macrophages
■ augmenting specific cytotoxicity of
lymphocytes for target cells.
Слайд 27Clinical uses:
Neoplasms
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Malignant Melanoma and Kaposi’s Sarcoma
Renal Cell Carcinoma
T-cell Leukemia
Hepatitis B and C
Multiplied Sclerosis
Acute Respiratory Virus Infection
T-cell Leukemia
Hepatitis B and C
Multiplied Sclerosis
Acute Respiratory Virus Infection
Слайд 28BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guerin) vaccine
viable strain of Mycobacterium bovis
nonspecific immunostimulant
has been successful only in intravesical therapy for Superficial Bladder Cancer.
BCG appears to act via activation of macrophages
to make them more effective killer cells