- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Index of Refraction презентация
Содержание
- 1. Index of Refraction
- 2. In uniform isotropic linear media, the wave
- 3. We can define the index of refraction
- 4. Let the electric field of optical wave
- 5. The solution is The induced dipole moment
- 6. If the second term is small enough
- 7. The complex refractive index is Normalized plot
- 8. For more than one resonance frequencies for
- 9. By definition, We can easily get: Relation Between Dielectric Constant and Refractive Index
- 10. Real and imaginary part of the index
- 11. The real part and imaginary part of
- 12. Typical experimental setup ( 1) halogen lamp;
- 13. Snell Law become: Reflection of p-polarized light
- 14. Results Based on Reflection Measurement FIG. 2.
- 15. Use AFM to Determine the Refractive Index
- 16. The optical lever operates by reflecting a
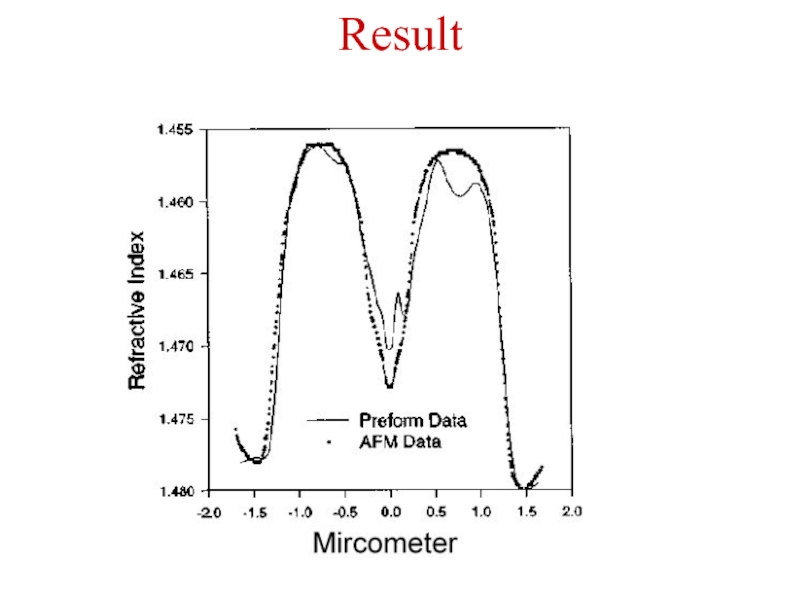
- 17. Result
- 18. For θ=0, input wave function a e
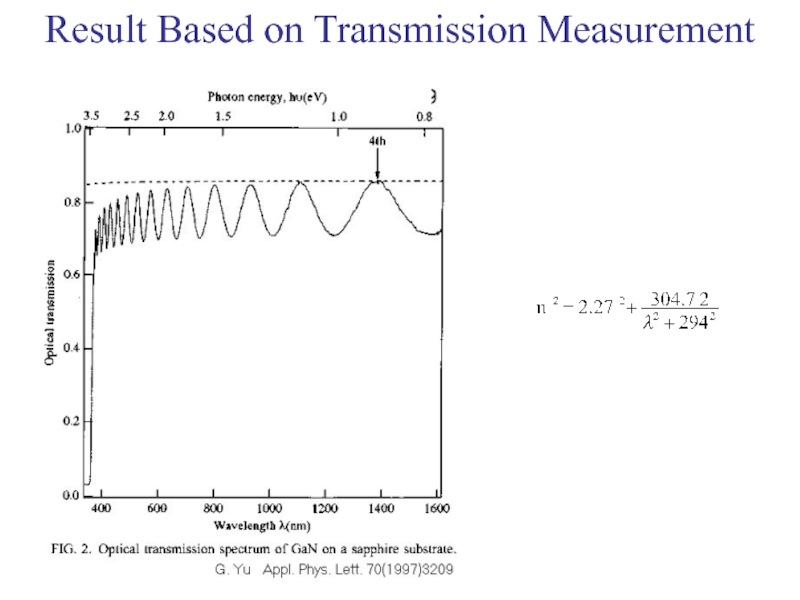
- 19. Result Based on Transmission Measurement
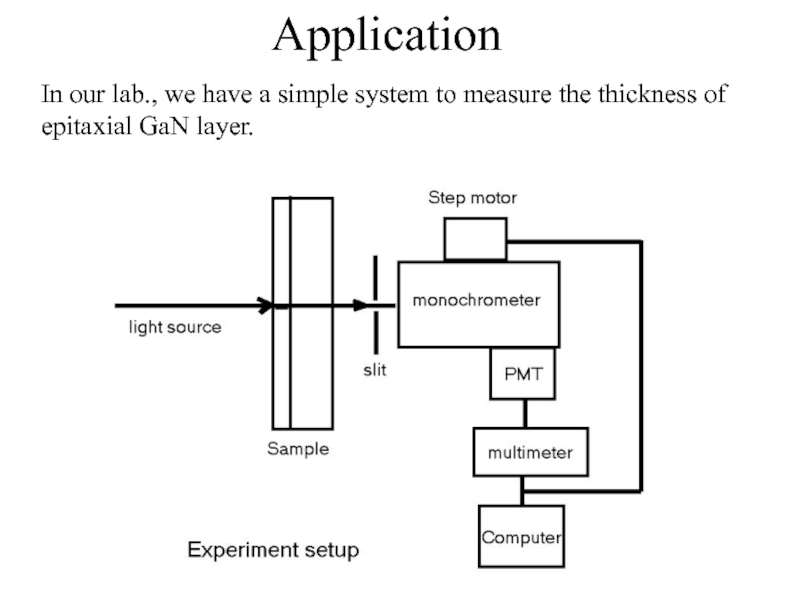
- 20. Application In our lab., we have a
- 21. n(λm)=m λm/2d Thickness Measurement Steps to calculate
- 22. Pochi Yeh, "Optical Wave in Layered
Слайд 1Jing Li
Outline
Introduction
Classical Model
Typical measurement methods
Application
Reference
Index of Refraction
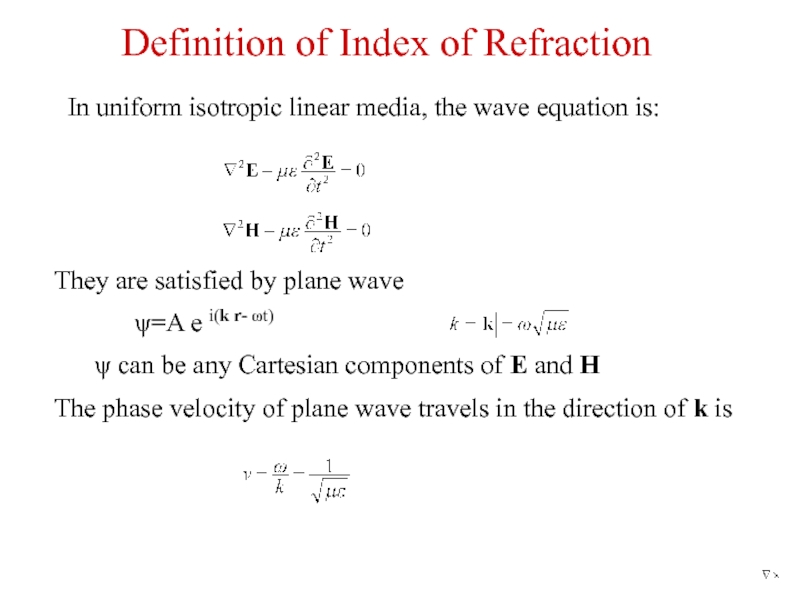
Слайд 2In uniform isotropic linear media, the wave equation is:
They are satisfied
ψ=A e i(k r- ωt)
ψ can be any Cartesian components of E and H
The phase velocity of plane wave travels in the direction of k is
Definition of Index of Refraction
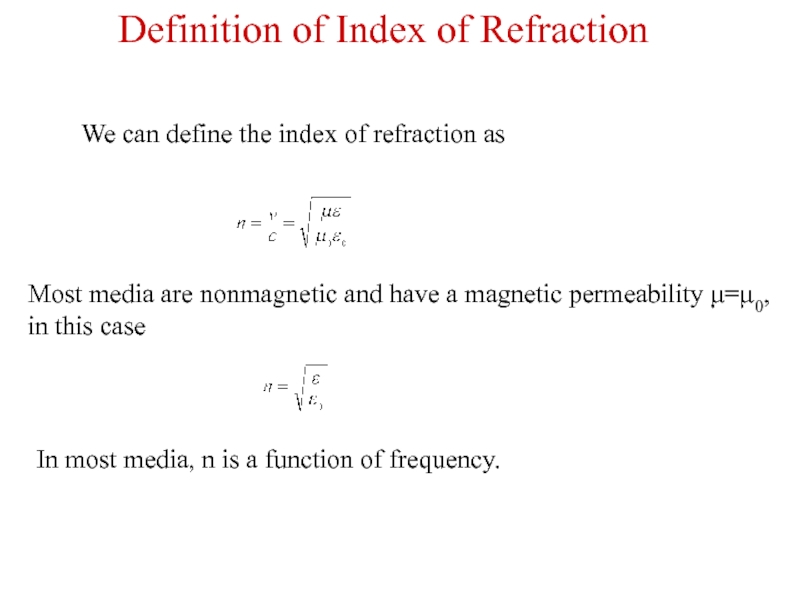
Слайд 3We can define the index of refraction as
Most media are nonmagnetic
In most media, n is a function of frequency.
Definition of Index of Refraction
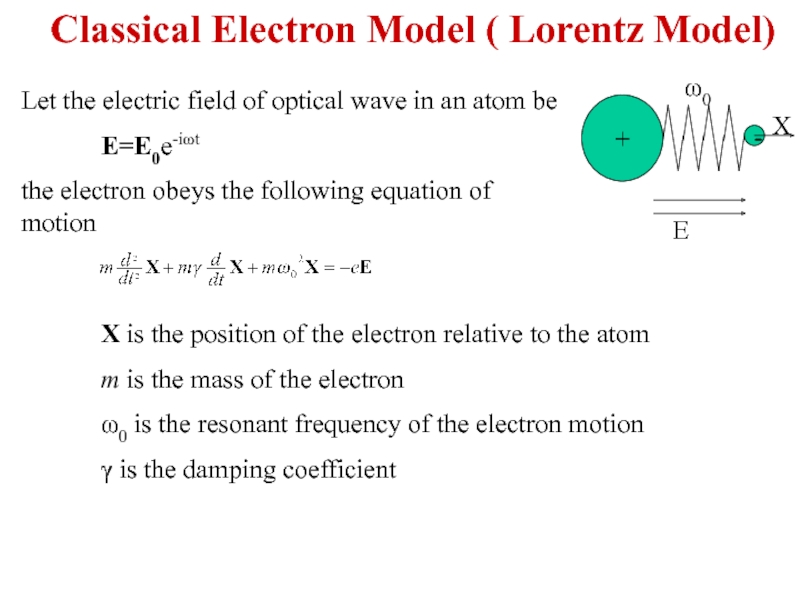
Слайд 4Let the electric field of optical wave in an atom be
E=E0e-iωt
the
X is the position of the electron relative to the atom
m is the mass of the electron
ω0 is the resonant frequency of the electron motion
γ is the damping coefficient
Classical Electron Model ( Lorentz Model)
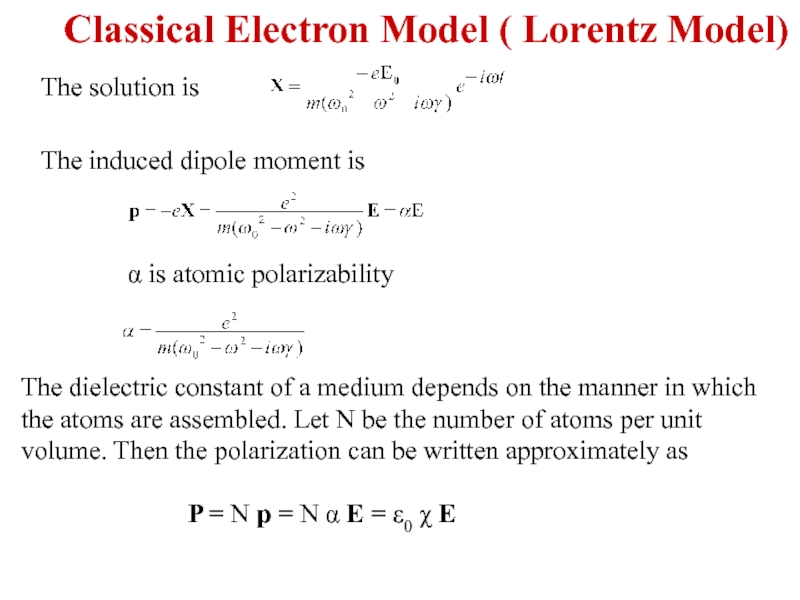
Слайд 5The solution is
The induced dipole moment is
α is atomic polarizability
The dielectric
P = N p = N α E = ε0 χ E
Classical Electron Model ( Lorentz Model)
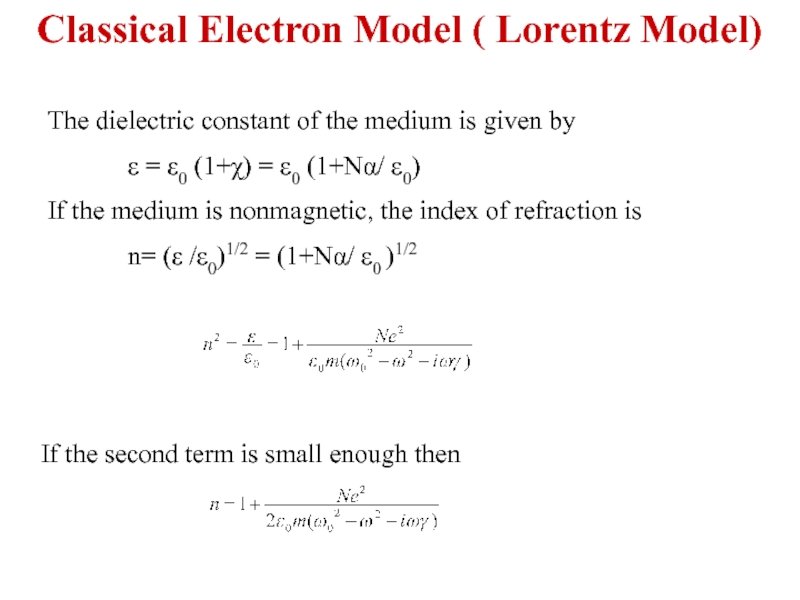
Слайд 6If the second term is small enough then
The dielectric constant of
ε = ε0 (1+χ) = ε0 (1+Nα/ ε0)
If the medium is nonmagnetic, the index of refraction is
n= (ε /ε0)1/2 = (1+Nα/ ε0 )1/2
Classical Electron Model ( Lorentz Model)
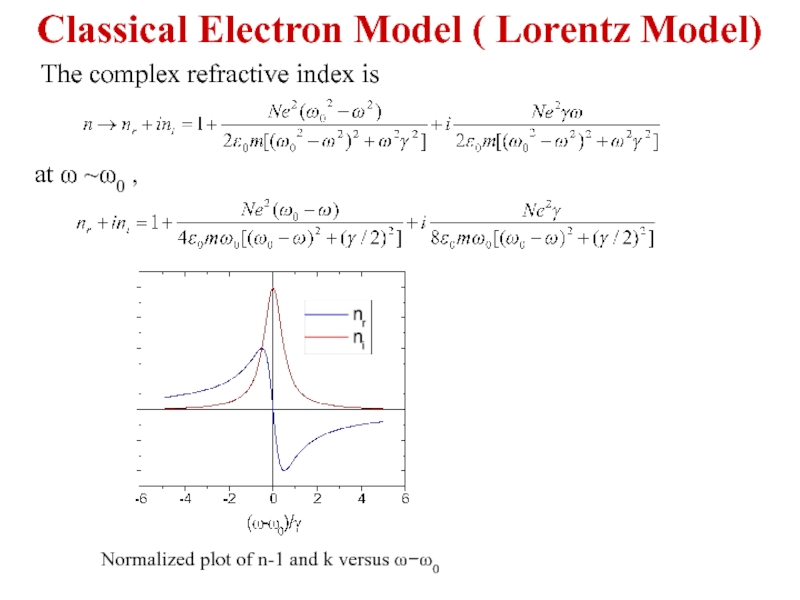
Слайд 7The complex refractive index is
Normalized plot of n-1 and k versus
at ω ~ω0 ,
Classical Electron Model ( Lorentz Model)
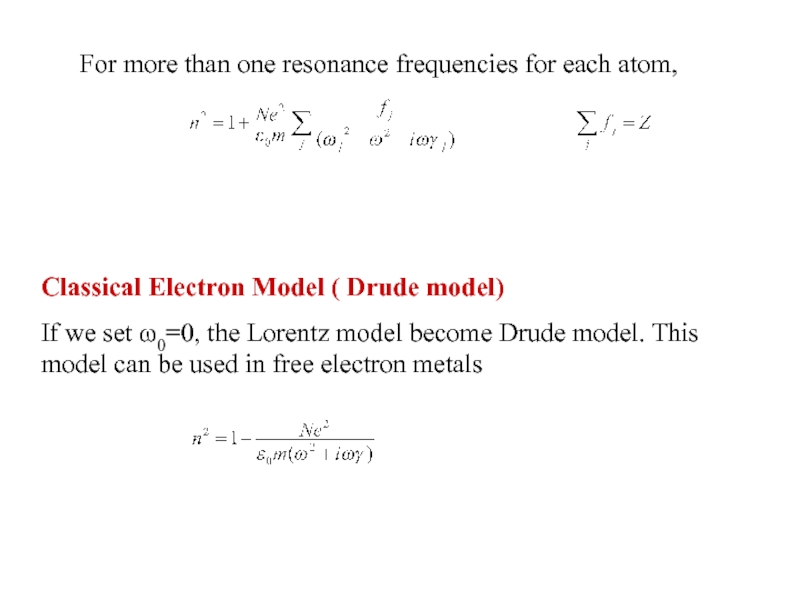
Слайд 8For more than one resonance frequencies for each atom,
Classical Electron Model
If we set ω0=0, the Lorentz model become Drude model. This model can be used in free electron metals
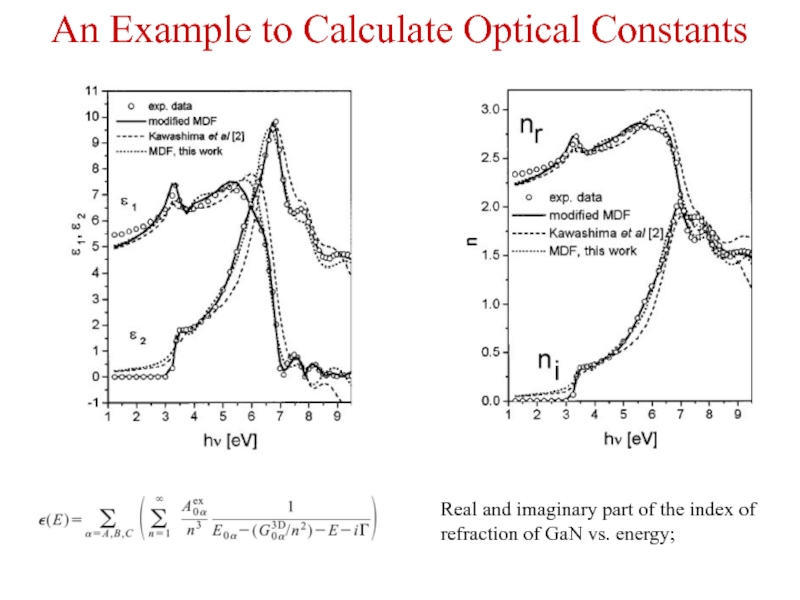
Слайд 10Real and imaginary part of the index of refraction of GaN
An Example to Calculate Optical Constants
Слайд 11The real part and imaginary part of the complex dielectric function
P indicates that the integral is a principal value integral.
K-K relation can also be written in other form, like
Kramers-Kronig Relation
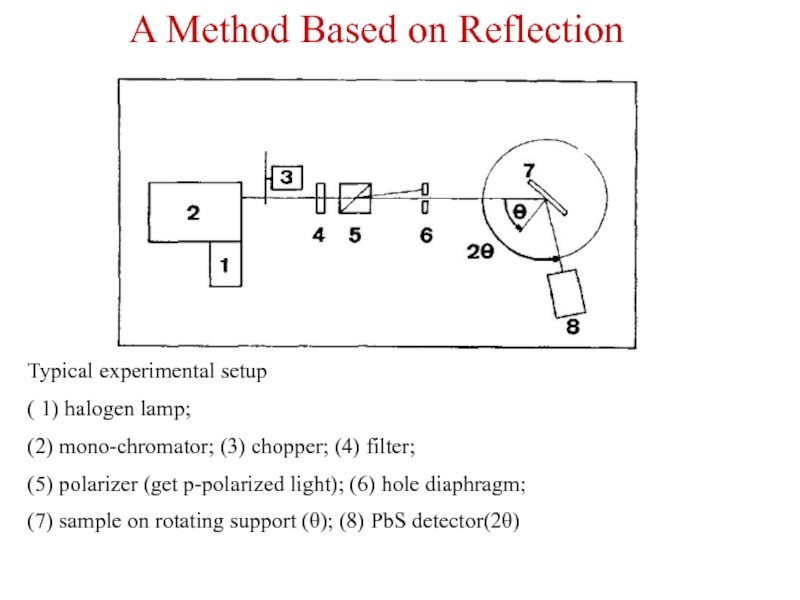
Слайд 12Typical experimental setup
( 1) halogen lamp;
(2) mono-chromator; (3) chopper; (4)
(5) polarizer (get p-polarized light); (6) hole diaphragm;
(7) sample on rotating support (θ); (8) PbS detector(2θ)
A Method Based on Reflection
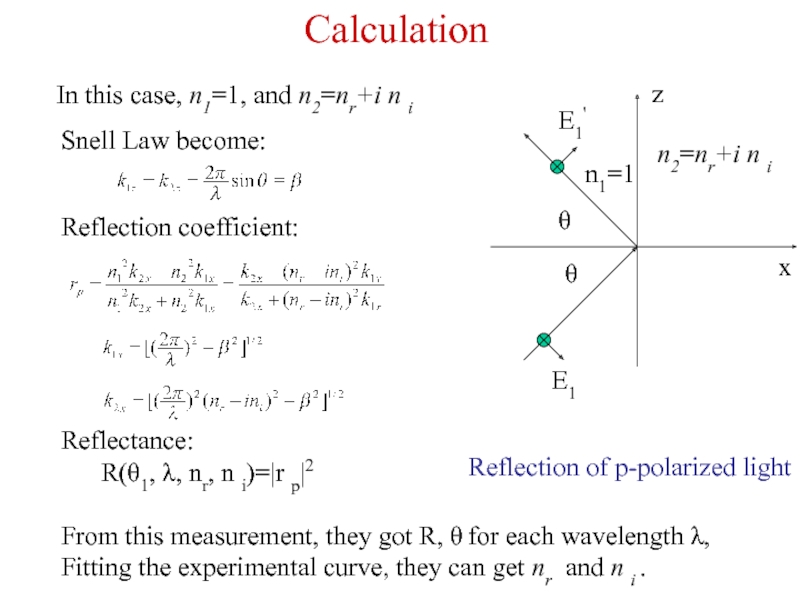
Слайд 13Snell Law become:
Reflection of p-polarized light
Reflection coefficient:
In this case, n1=1, and
Reflectance:
R(θ1, λ, nr, n i)=|r p|2
From this measurement, they got R, θ for each wavelength λ, Fitting the experimental curve, they can get nr and n i .
Calculation
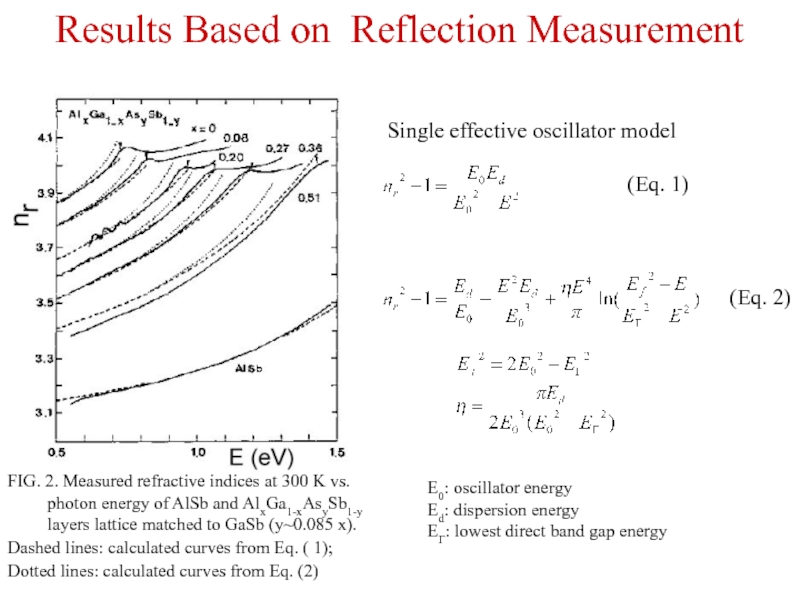
Слайд 14Results Based on Reflection Measurement
FIG. 2. Measured refractive indices at 300
Dashed lines: calculated curves from Eq. ( 1);
Dotted lines: calculated curves from Eq. (2)
E0: oscillator energy
Ed: dispersion energy
EΓ: lowest direct band gap energy
Single effective oscillator model
(Eq. 1)
(Eq. 2)
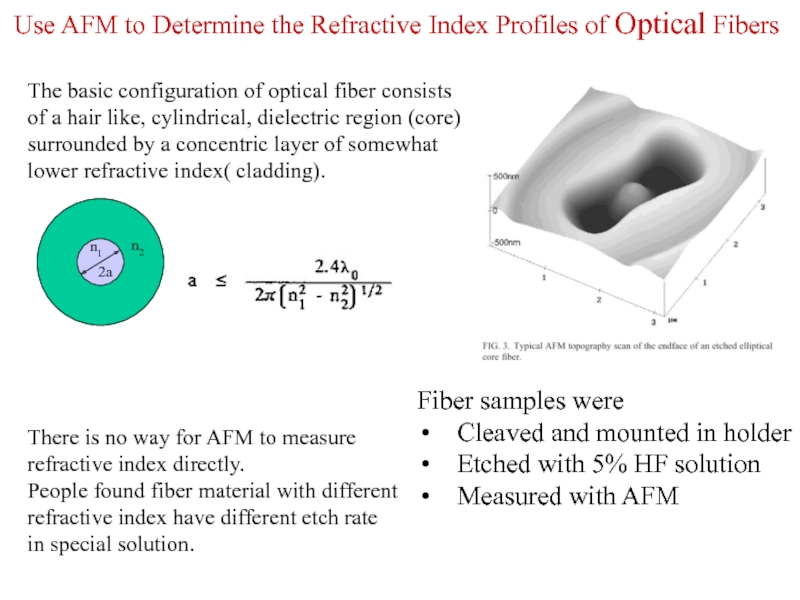
Слайд 15Use AFM to Determine the Refractive Index Profiles of Optical Fibers
Fiber
Cleaved and mounted in holder
Etched with 5% HF solution
Measured with AFM
There is no way for AFM to measure refractive index directly.
People found fiber material with different refractive index have different etch rate in special solution.
The basic configuration of optical fiber consists of a hair like, cylindrical, dielectric region (core) surrounded by a concentric layer of somewhat lower refractive index( cladding).
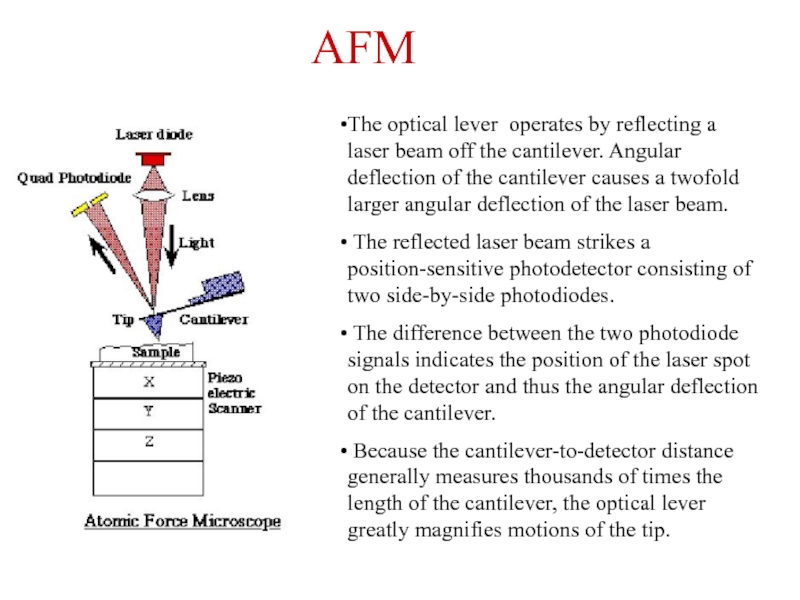
Слайд 16The optical lever operates by reflecting a laser beam off the
The reflected laser beam strikes a position-sensitive photodetector consisting of two side-by-side photodiodes.
The difference between the two photodiode signals indicates the position of the laser spot on the detector and thus the angular deflection of the cantilever.
Because the cantilever-to-detector distance generally measures thousands of times the length of the cantilever, the optical lever greatly magnifies motions of the tip.
AFM
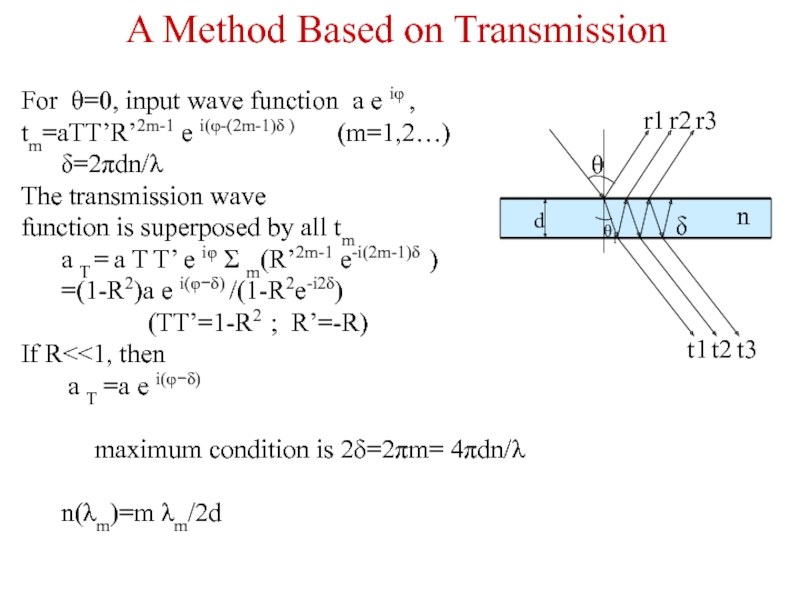
Слайд 18For θ=0, input wave function a e iφ ,
tm=aTT’R’2m-1 e
δ=2πdn/λ
The transmission wave
function is superposed by all tm
a T = a T T’ e iφ Σ m(R’2m-1 e-i(2m-1)δ )
=(1-R2)a e i(φ−δ) /(1-R2e-i2δ)
(TT’=1-R2 ; R’=-R)
If R<<1, then
a T =a e i(φ−δ)
maximum condition is 2δ=2πm= 4πdn/λ
n(λm)=m λm/2d
A Method Based on Transmission
Слайд 20Application
In our lab., we have a simple system to measure the
Слайд 21n(λm)=m λm/2d
Thickness Measurement
Steps to calculate thickness
Get peak position λm
d=(λm λm-1)/2/[λm-1 n(λm)
Average d
get m min= n(λ max)*2d/ λ max
Calculate d : d=m λm/2/n(λm) (from m min for each peak)
Average d again
Limit
Minimum thickness:~500/n
Error<λ/2n
Слайд 22
Pochi Yeh, "Optical Wave in Layered Media", 1988, John Wiley &
E. E. Kriezis, D. P. Chrissoulidis & A. G. Papafiannakis, Electromagnetics and Optics, 1992, World Scientific Publishing Co.,
Aleksandra B. Djurisic and E. H. Li, J. OF Appl. Phys., 85 (1999) 2848 (mode for GaN)
C. Alibert, M. Skouri, A. Joullie, M. Benounab andS. Sadiq , J. Appl. Phys., 69(1991)3208 (Reflection)
Kun Liu, J. H. Chu, and D. Y. Tang, J. Appl. Phys. 75 (1994)4176 (KK relation)
G. Yu, G. Wang, H. Ishikawa, M. Umeno, T. Soga, T. Egawa, J. Watanabe, and T. Jimbo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70 (1997) 3209
Jagat, http://www.phys.ksu.edu/~jagat/afm.ppt (AFM)
Reference



![n(λm)=m λm/2dThickness MeasurementSteps to calculate thicknessGet peak position λmd=(λm λm-1)/2/[λm-1 n(λm) − λm n(λm-1)]Average dget](/img/tmb/4/392796/f9e76c1f10966b80bf3d930839277642-800x.jpg)






