- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
WIUU Business Policy презентация
Содержание
- 1. WIUU Business Policy
- 2. Let us play a quick marketing game
- 3. Adidas – German quality
- 4. Business Policy “Without Business Policy and
- 5. Business Policy “Business policy is study
- 6. Evolution of Business Policy as discipline. Origin
- 7. Evolution of Business Policy has undergone four
- 8. Evolution of Business Policy has undergone four
- 9. Evolution of Business Policy has undergone four
- 10. Core concept of Strategy: A company’s concept
- 11. Core concept of Strategy: Military Origins of
- 12. Core Concept of Strategy A company’s Strategy
- 13. Crafting and Executing Strategy WIUU BBA Business Policy
- 14. Structure and Organization What is
- 15. Structure and Organization What is
- 16. 1. What Is Strategy and Why Is
- 17. What do we mean by strategy?
- 18. Strategy and the Quest for Competitive Advantage
- 19. 4 of the most frequently used strategic
- 20. Identifying a company’s strategy – what to
- 21. Why a Company’s Strategy Evolves over Time
- 22. A Company’s strategy is redefined constantly
- 23. Strategy CONTENT Planning SCOPE Business Unit Corporate
- 24. 1. What Is Strategy and Why Is
- 25. To discuss: CAN BUSINESS ETHICS BE
- 26. Just keeping a company’s strategic actions within
- 27. 1. What Is Strategy and Why Is
- 28. Be clear on how to earn money
- 29. 1. What Is Strategy and Why Is
- 30. 3 questions to distinguish a winning strategy
- 31. 1. What Is Strategy and Why Is
- 32. Questions?
- 33. 2. Leading the Process of Crafting &
- 34. The Strategy-Making, Strategy-Executing Process 1 2 3
- 35. 2. Leading the Process of Crafting &
- 36. Factors to Consider in Deciding on a
- 37. Characteristics of an Effectively Worded Vision Statement
- 38. Common Shortcomings in Company Vision Statements
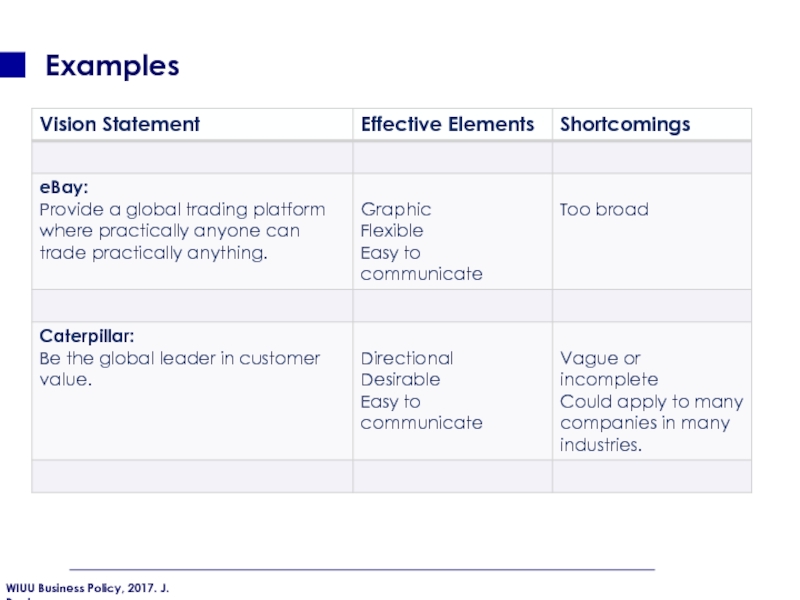
- 39. Examples
- 40. How a Strategic Vision Differs from a
- 41. 2. Leading the Process of Crafting &
- 42. Financial & Strategic objectives CORE CONCEPT
- 43. Examples of financial & strategic objectives Strategic
- 44. To discuss: ARE FINANCIAL OBJECTIVES ENOUGH
- 45. Good Strategy + competitiveness = future performance
- 46. Long term & short term targets needed
- 47. 2. Leading the Process of Crafting &
- 48. Company’s Strategy-Making Hierarchy Operating strategies within each
- 49. Strategic Vision + Objectives + Strategy =
- 50. 2. Leading the Process of Crafting &
- 51. 2. Leading the Process of Crafting &
- 52. Leading the strategic management process calls for
- 53. Staying on Top of How Well Things
- 55. Amazon. Task. (15min) Read page
- 56. Homework till 18th Nov.
- 57. Intro to 2nd class (and what
- 58. External Analysis
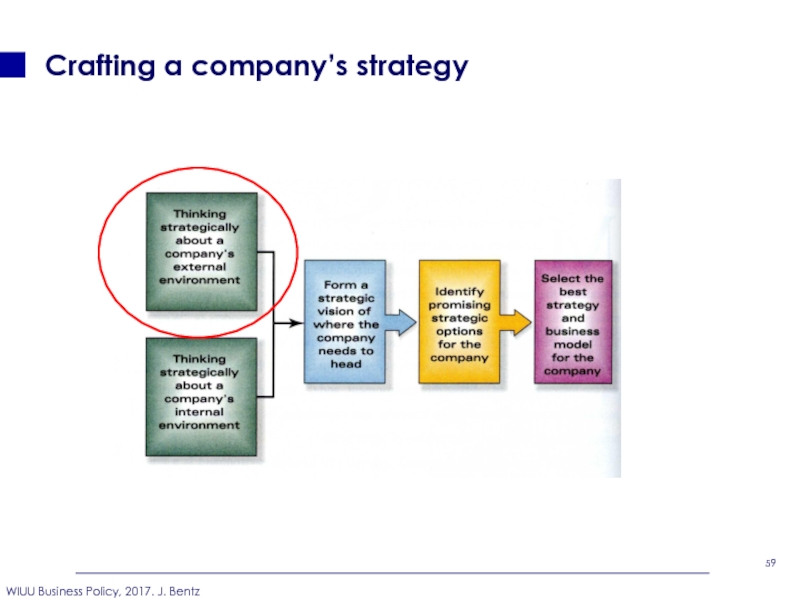
- 59. Crafting a company’s strategy
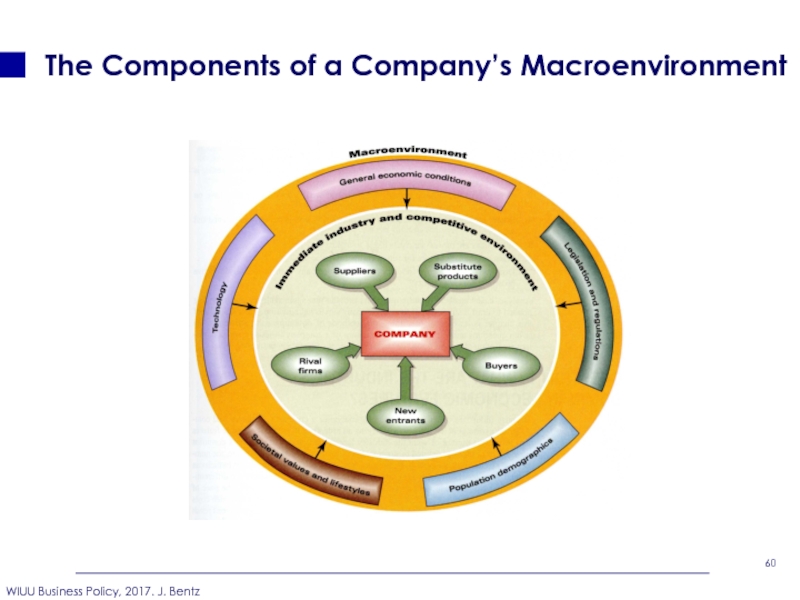
- 60. The Components of a Company’s Macroenvironment
- 61. Industry’s Dominant Economic Features
- 62. What to consider in identifying an Industry’s
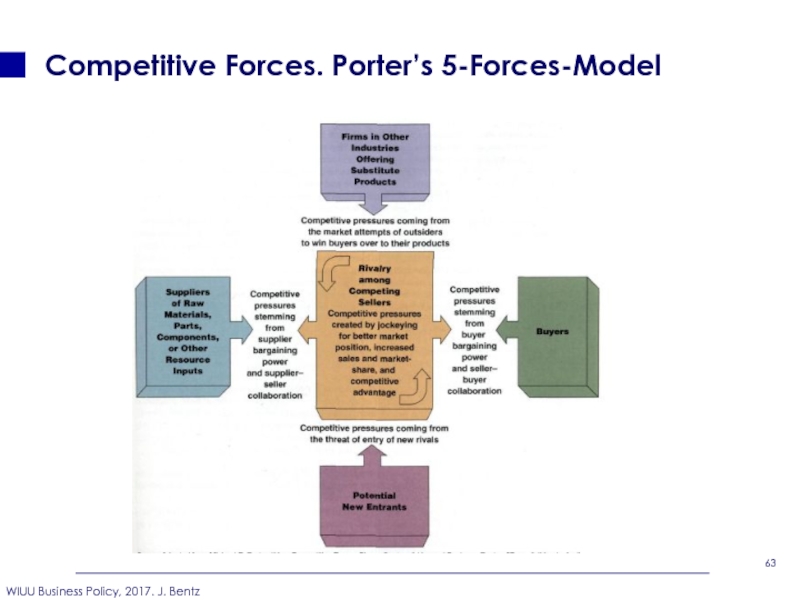
- 63. Competitive Forces. Porter’s 5-Forces-Model
- 64. Driving Industry Forces
- 65. What are the most common driving forces?
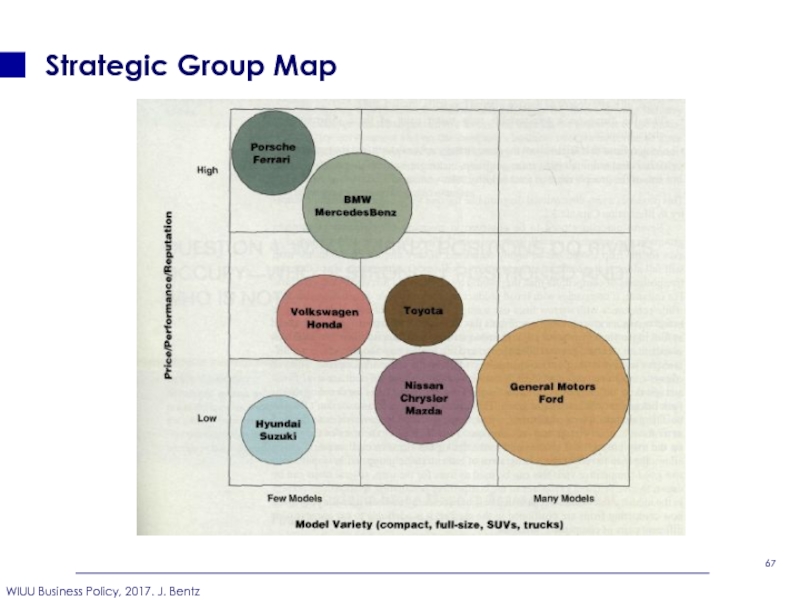
- 66. Strategic Group Map
- 67. Strategic Group Map
- 68. Strategic Group Map Let us discuss
- 69. Key Success Factors
- 70. What are the most common types of
- 71. Tools to Evaluate a Company’s External Environment
- 72. Questions?
- 73. Questions to the podcast: The 5
- 74. Business Policy Next Class We
- 75. What we would like to do today
- 76. Questions to the podcast: Can your
- 77. Business Policy Next Class We
- 78. Case study analysis Ben & Jerry’s
- 79. Case study analysis Ben & Jerry’s
- 80. Business Policy Midterm (closed book)
- 81. What we would like to do today
- 82. What you should keep in mind …
- 83. Value chain analysis
- 84. VALUE THE VALUE IS THE TOTAL AMOUNT
- 85. WHAT IS THE VALLUE CHAIN? Porter’s
- 86. TYPES OF VALUE CHAIN Value Chain is
- 87. WHAT IS VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS? Used
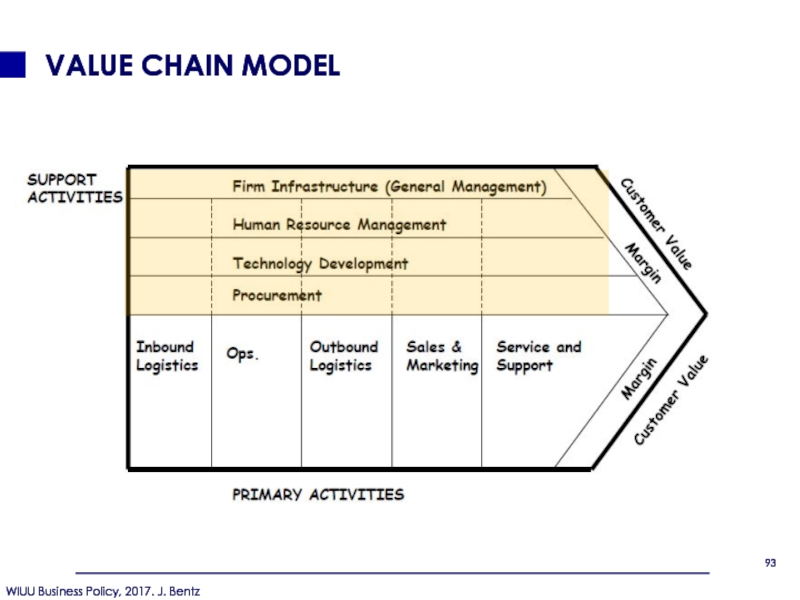
- 88. VALUE CHAIN MODEL
- 89. TYPES OF FIRM ACTIVITIES Primary activities:
- 90. VALUE CHAIN MODEL
- 91. PRIMARY ACTIVITIES INBOUND LOGISTICS CONCERNED WITH
- 92. PRIMARY ACTIVITIES MARKETING AND SALES Identification
- 93. VALUE CHAIN MODEL
- 94. SUPPORT ACTIVITIES FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE
- 95. USES OF THE VALUECHAIN The sources
- 96. VERTICAL LINKAGE LINKAGES CAN ALSO EXIST OUTSIDE
- 97. APPLYING THE VALUE CHAIN TO AN
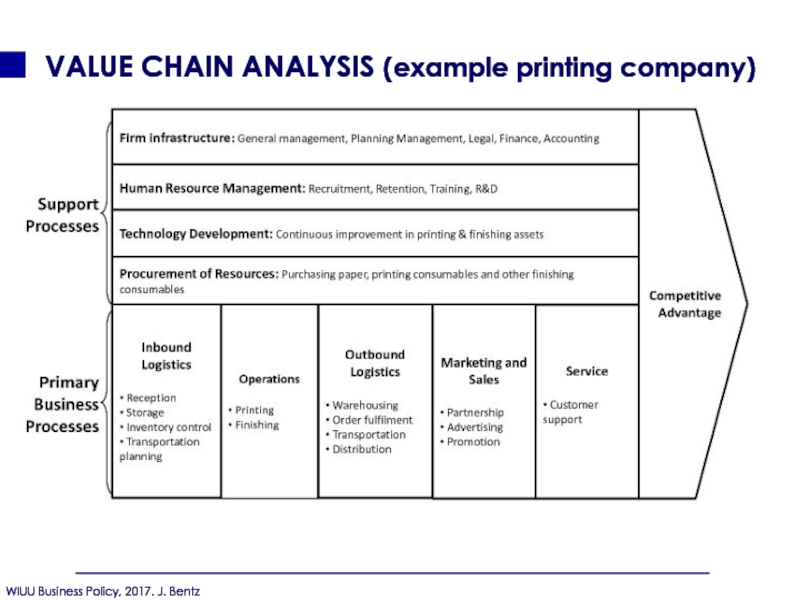
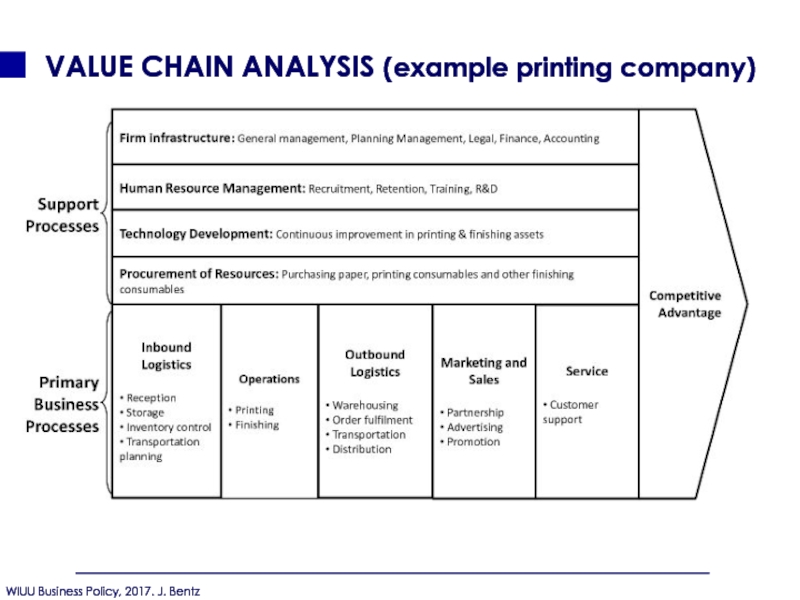
- 98. VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS (example printing company)
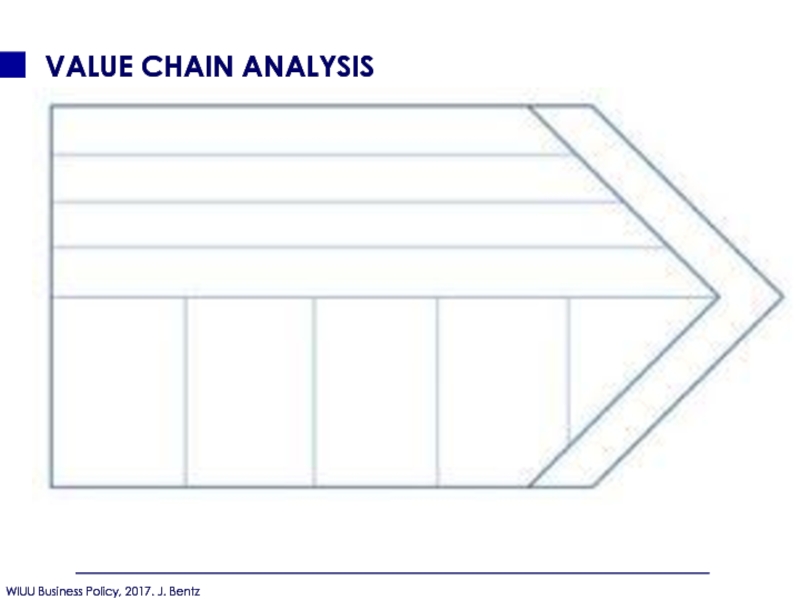
- 99. VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 100. Business Policy Next Class We
- 101. Business Policy 2017/2018 Mo. 22.1. 15.20 –
- 102. What we would like to do today
- 103. Business Policy https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Economic_Forum
- 105. Davos. World Economic Forum https://www.youtube.com/user/WorldEconomicForum Fourth industrial revolution https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kpW9JcWxKq0
- 106. Fourth industrial revolution Watch the
- 107. VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS (example printing company)
- 108. USES OF THE VALUECHAIN The sources
- 109. VERTICAL LINKAGE LINKAGES CAN ALSO EXIST OUTSIDE
- 110. Estimated Value chain costs for CD recording/ distribution through traditional trade
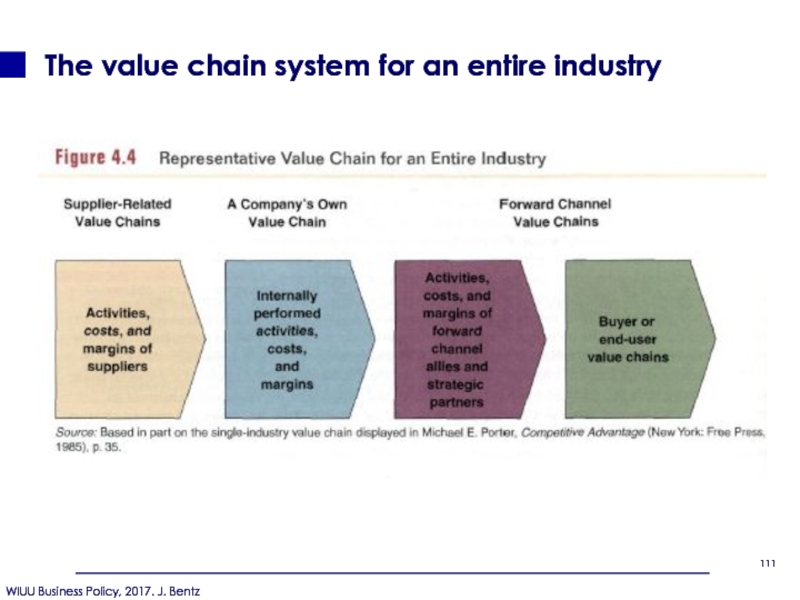
- 111. The value chain system for an entire industry
- 112. Benchmarking
- 113. Translating Company Performance of Value Chain Activities into Competitive Advantage
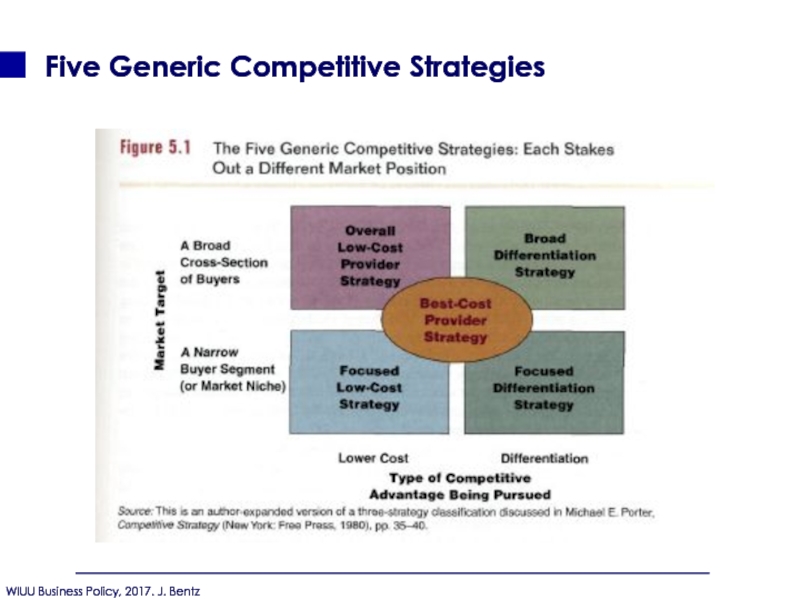
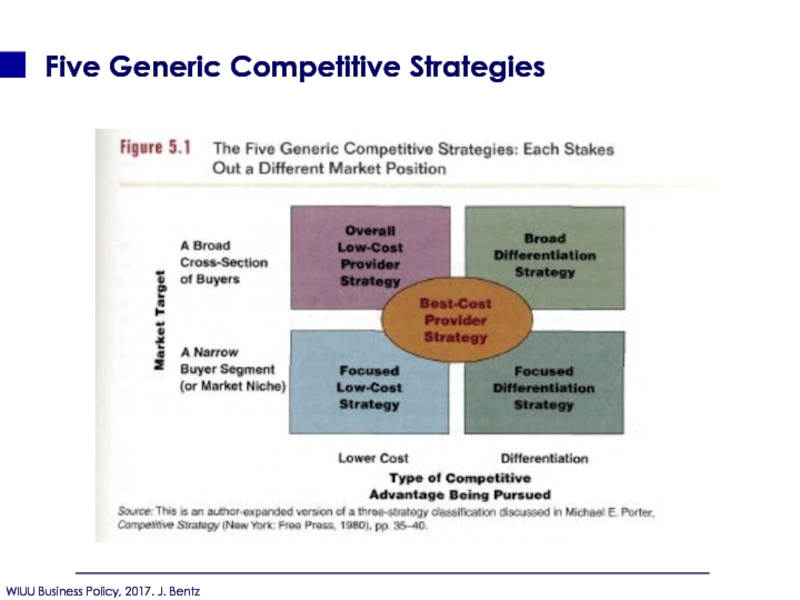
- 114. Five Generic Competitive Strategies
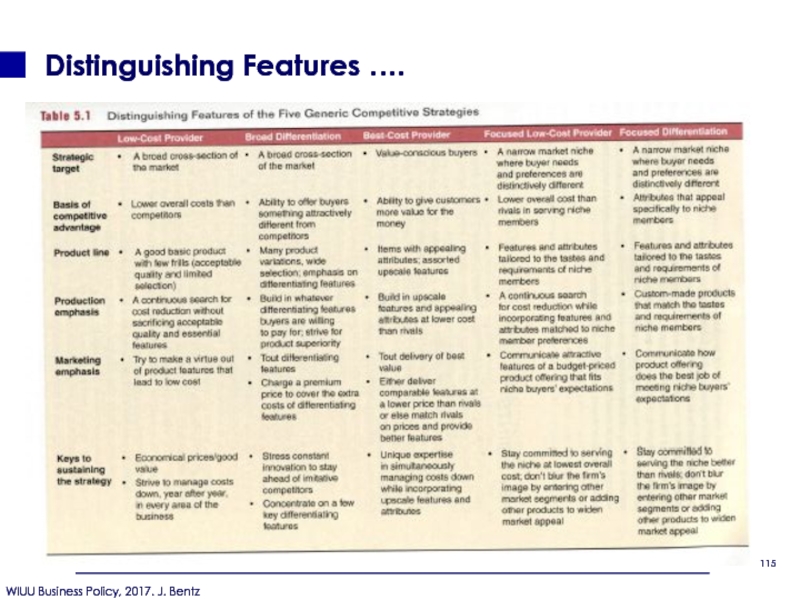
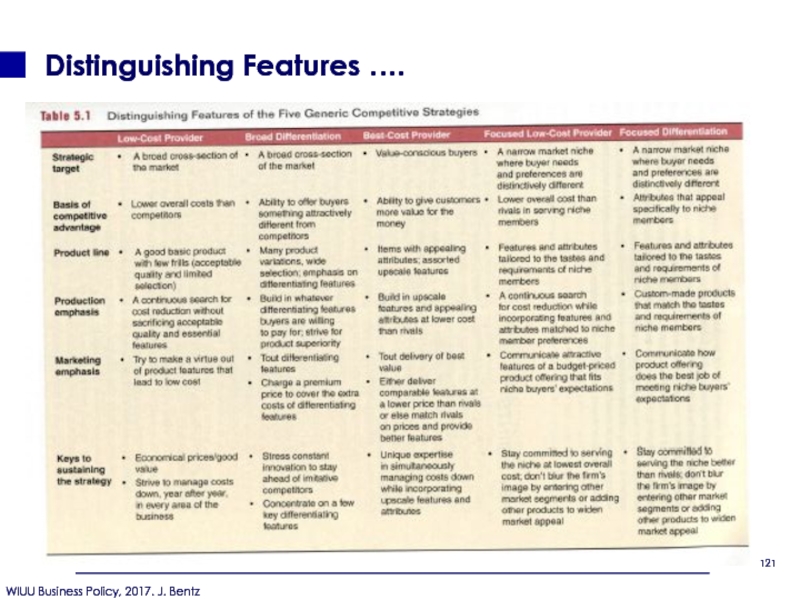
- 115. Distinguishing Features ….
- 116. And let us talk about supplementing strategies
- 117. Individual work for now …. ☺
- 118. Business Policy Next Class We
- 119. Business Policy 2017/2018 Mo. 22.1. 15.20 –
- 120. Five Generic Competitive Strategies
- 121. Distinguishing Features ….
- 122. Individual work for now …. ☺
- 123. And let us talk about supplementing strategies
- 124. Supplementing strategies: Daimler - Chrysler In May
- 125. Supplementing strategies: Daimler - Chrysler In May
- 126. Davos. World Economic Forum https://www.youtube.com/user/WorldEconomicForum Meet
- 127. Strategies for competing in foreign markets (Chapter
- 128. Strategies for competing in foreign markets (Chapter
- 129. Strategies for competing in foreign markets (Chapter
- 130. Business Policy Next Class We
- 131. Business Policy Next Class We
- 132. Business Policy 2017/2018 Mo. 22.1. 15.20 –
- 133. Business Policy Projects 2017/2018 (17.2.) we have
- 134. Business Policy Projects 2017/2018 (17.2.) we have
- 135. The Pub (29.1.) Task/Questions: Identify the
- 136. Identify the industry in which the Pub
- 137. Identify the industry in which the Pub
- 138. 2) Conduct a Five Forces analysis of
- 139. 2) Conduct a Five Forces analysis of
- 140. 3) Conduct a value chain analysis of
- 141. 3) Conduct a value chain analysis of
- 143. 4) Conduct a SWOT analysis for The
- 144. 4) Conduct a SWOT analysis for The
- 145. 4) Conduct a SWOT analysis for The
- 146. 4) Conduct a SWOT analysis for The
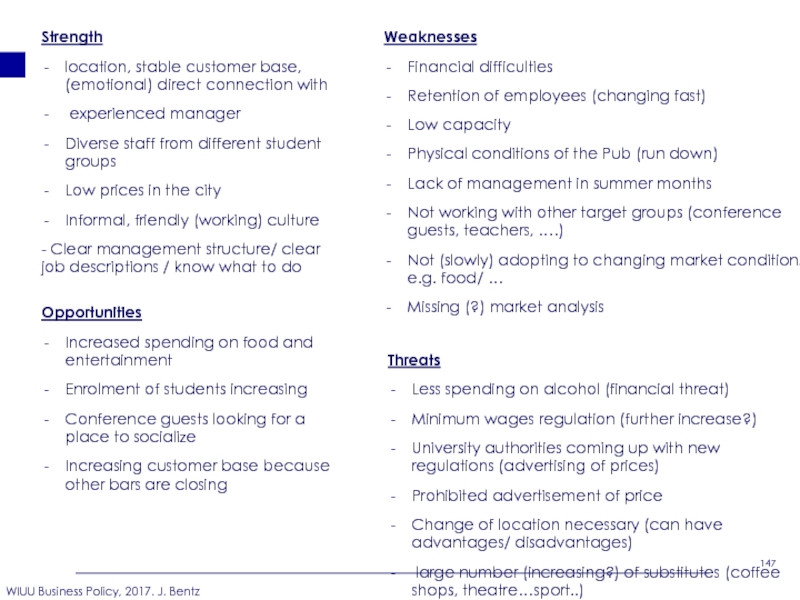
- 147. Strength location, stable customer base, (emotional) direct
- 148. 5) What should Scooter and the board
- 149. Questions to the podcast: Take complexity
- 150. Business Policy Next Class/ Exam
Слайд 2Let us play a quick marketing game
Quick task for warming
If YOU were a well known brand which would that be?
Which positive sides do you have/ which negative ones?
… 3 minutes to prepare.
Слайд 3
Adidas –
German quality
Always a step ahead in technology
Intelligent
Not cheap but affordable
One of the best in his field ☺
Down-to-earth, cheerful
BIG Ego (Self-confident)
Слайд 4Business Policy
“Without Business Policy and Strategy, an organisation
is like a
like a tramp; it has no place to go”
Слайд 5Business Policy
“Business policy is study of the function and
responsibility of
problems that affect the success of the in the
whole organisation and the decisions that
determine the direction of the organisation and
shape its future.”
Слайд 6Evolution of Business Policy as discipline.
Origin – 1911- Harvard Business School
Development of subject of Business Policy has always followed the demands of real life business.
1930 -1960: Environment change: New Products:
Continuously changing market: Ford Foundation recommended a “Capstone” course of Business Policy which would give the students an opportunity to pull together what they have learned in the separate business fields and utilise this knowledge in the analysis of complex business problems.
~1990: The course has become an integral part of management education curriculum.
Слайд 7Evolution of Business Policy has undergone four Paradigms
Paradigm One: Ad-hoc Policy
1900 -1930: Era of Mass Production – Maximising output, normally a Single Product, Standardised and low cost product, catering to unique set of customers servicing limited geographical area – Informal control and co-ordination. The Strategic planning was centered on maximising output.
Paradigm Two – Integrated Policy Formulation.
1930-1940: Changes in Technology, Turbulence in Political environment, emergence of new industries, demand for novelty products even at higher costs, product differentiation, market segmentation in increasingly competitive and changing markets. These all made investment decisions increasingly difficult. This was era of integrating all functional areas and framing policies to guide managerial actions.
Слайд 8Evolution of Business Policy has undergone four Paradigms
Paradigm Three – The
1940- 1960: Planned policy became irrelevant due to increasingly complex and accelerating changes. Firms had to anticipate environmental changes. A strategy needed to be formed with critical look at basic concept of Business and its relationship to the existing environment then.
Слайд 9Evolution of Business Policy has undergone four Paradigms
Paradigm Four – The
1980 & onwards: The focus of Strategic Management is on the strategic process of business firms and responsibilities of general management.
Everything out side the four walls is changing rapidly and this phenomenon is called as “Discontinuity” by Mr. Peter Drucker. Past experiences are no guarantee as science and technology is moving faster. The future is no more extension of the past or the present.
What to produce, where to market, which new business to enter, which one to quit and how to get internally stronger and resourceful are the new stakes.
Strategic Planning is required to be done to endow the enterprise with certain fundamental competencies / distinctive strengths which could take care of eventualities resulting from unexpected environmental changes.
Слайд 10Core concept of Strategy:
A company’s concept of Strategy consists of the
Слайд 11Core concept of Strategy:
Military Origins of Strategy: Strategy is a term
Military origins of strategy are century old. It seems sensible to begin our examination of strategy with the military view.
Substitute "resources" for troops and the transfer of the concept to the business world begins to take form.
Strategy also refers to the means by which policy is effected, As per “Clauswitz” the war is the continuation of political relations via other means.
Слайд 12Core Concept of Strategy
A company’s Strategy consists of the competitive moves
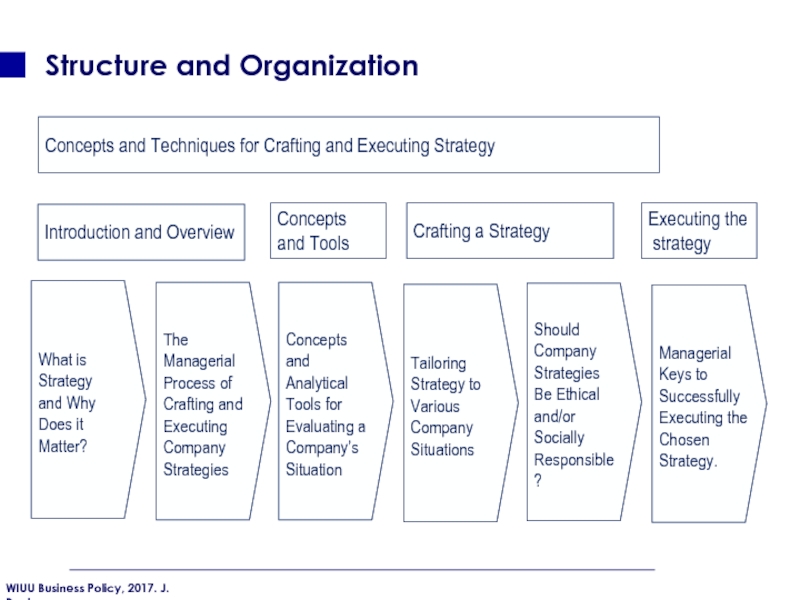
Слайд 14Structure and Organization
What is Strategy and Why Does it Matter?
The Managerial Process of Crafting and Executing Company Strategies
Concepts and Analytical Tools for Evaluating a Company’s Situation
Tailoring Strategy to Various Company Situations
Should Company Strategies Be Ethical and/or Socially Responsible?
Managerial Keys to Successfully Executing the Chosen Strategy.
Introduction and Overview
Crafting a Strategy
Concepts
and Tools
Executing the
strategy
Concepts and Techniques for Crafting and Executing Strategy
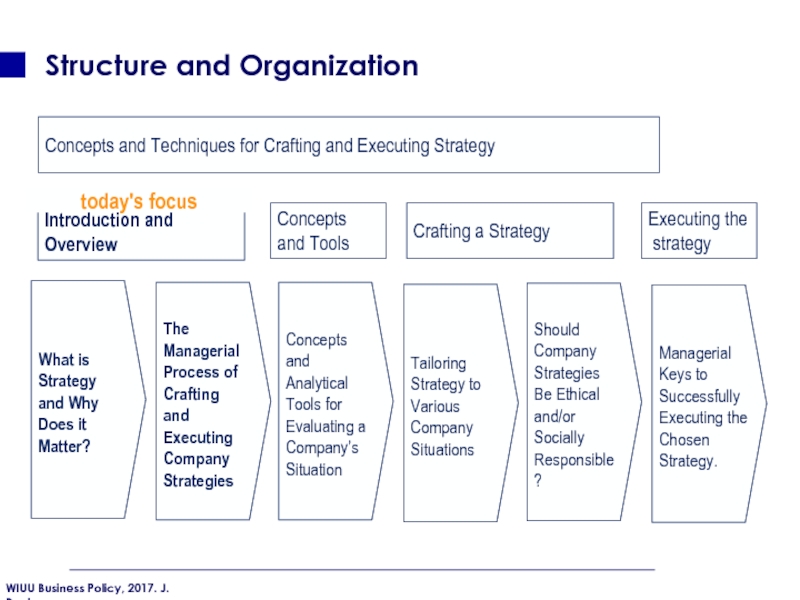
Слайд 15Structure and Organization
What is Strategy and Why Does it Matter?
The Managerial Process of Crafting and Executing Company Strategies
Concepts and Analytical Tools for Evaluating a Company’s Situation
Tailoring Strategy to Various Company Situations
Should Company Strategies Be Ethical and/or Socially Responsible?
Managerial Keys to Successfully Executing the Chosen Strategy.
Introduction and Overview
Crafting a Strategy
Concepts
and Tools
Executing the
strategy
Concepts and Techniques for Crafting and Executing Strategy
today's focus
Слайд 161. What Is Strategy and Why Is It Important? 1.1 What
CORE CONCEPT
A company’s strategy consists of the competitive moves and business approaches that managers are employing to grow the business, attract and please customers, compete successfully, conduct operations, and achieve the targeted levels of organizational performance.
Слайд 17What do we mean by strategy?
A Company’s strategy is all
How management intends to grow the business
How it will build a loyal clientele and outcompete rivals
How each functional piece of the business (research and development, supply chain activities, production, sales and marketing, distribution, finance, and Human resources) will be operated
How performance will be boosted.
Слайд 18Strategy and the Quest for Competitive Advantage
CORE CONCEPT
A company achieves sustainable
Слайд 194 of the most frequently used strategic approaches
Striving for being the
Creating a differentiation-based advantage keyed to such features as higher quality, wider product selection, added performance, value-added services more attractive design, technological superiority, or unusually good value for the money.
Focusing on serving the special needs and tastes of buyers comprising a narrow market niche.
Developing expertise and resource strengths that give the company competitively valuable capabilities that rivals can’t easily match, copy, or trump with substitute capabilities.
Слайд 20Identifying a company’s strategy – what to look for
The pattern of
Actions to diversify the company’s revenues and earnings by entering new segments
Actions to strengthen competitive capabilities and correct competitive weaknesses
Actions and approaches used in managing R&D, production, sales and marketing, finance, and other key activities.
Actions to strengthen competitiveness via strategic alliances and collaborative partnerships
Actions to strengthen market standing and competitiveness by acquiring or merging with other companies
Actions to capture emerging market opportunities and defend against external threats to the company’s business prospects
Actions to enter new geographic or product markets or exit existing ones
Actions to respond to changing market conditions or other external factors
Actions to gain sales & market share via lower prices, more performance, better design, quality or customer service, ….
Слайд 21Why a Company’s Strategy Evolves over Time
CORE CONCEPT
Changing circumstances and ongoing
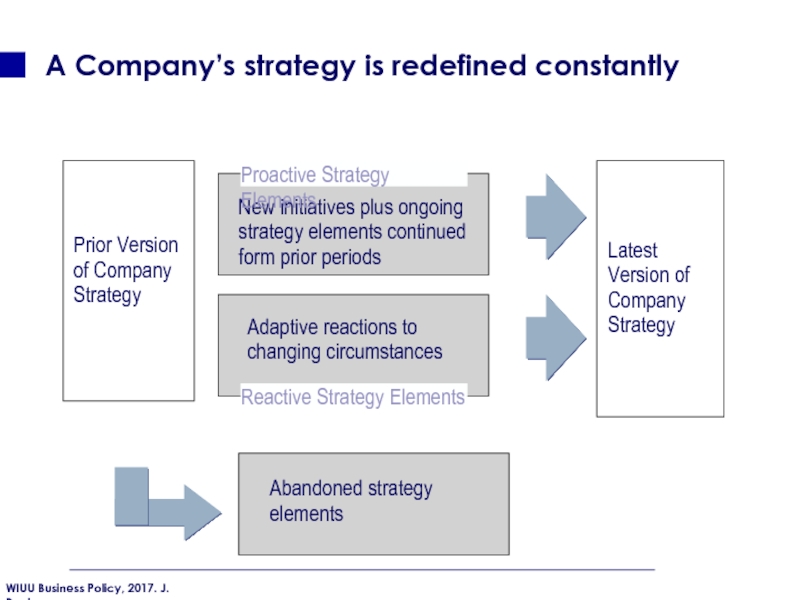
Слайд 22A Company’s strategy is redefined constantly
Prior Version of Company Strategy
Latest
Abandoned strategy elements
Adaptive reactions to changing circumstances
New initiatives plus ongoing strategy elements continued form prior periods
Reactive Strategy Elements
Proactive Strategy Elements
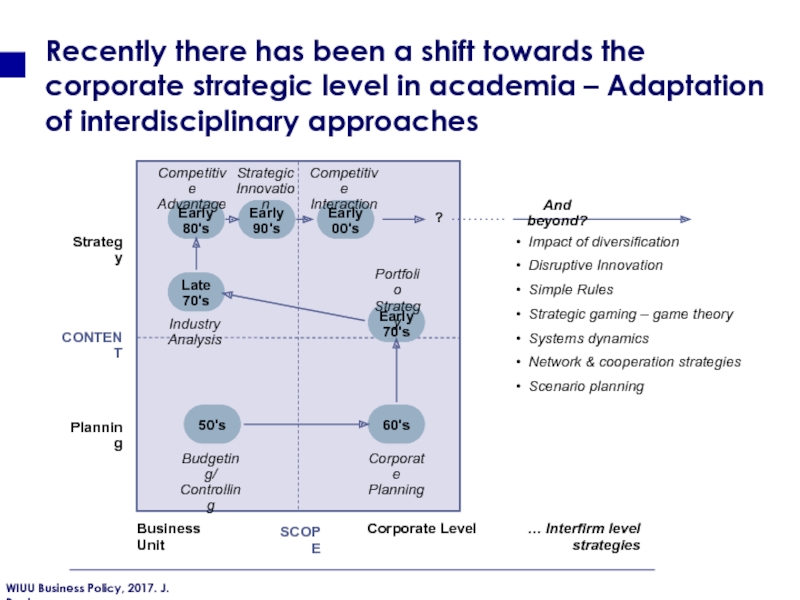
Слайд 23Strategy
CONTENT
Planning
SCOPE
Business Unit
Corporate Level … Interfirm level strategies
50's
60's
Early
70's
Early
00's
Early
80's
Early
90's
Late
70's
Corporate
Planning
Budgeting/
Controlling
Industry Analysis
Competitive
Advantage
Strategic
Innovation
Competitive
Interaction
Portfolio
Strategy
And beyond?
?
Impact of
Disruptive Innovation
Simple Rules
Strategic gaming – game theory
Systems dynamics
Network & cooperation strategies
Scenario planning
Recently there has been a shift towards the corporate strategic level in academia – Adaptation of interdisciplinary approaches
Слайд 241. What Is Strategy and Why Is It Important? 1.2 Strategy
CORE CONCEPT
Ethics go beyond legality: to meet the standard of being ethical, a strategy must entail actions that can pass moral scrutiny in the sense of not being shady, unconscionable, or injurious to others or unnecessarily harmful to the environment.
Слайд 25
To discuss:
CAN BUSINESS ETHICS BE AN ELEMENT OF COMPETITIVE
DO YOU SEE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN WESTERN EUROPE & UKRAINE?
1.2 Strategy & Ethics: Passing the test of moral security?
Слайд 26Just keeping a company’s strategic actions within the bounds of what
Ethical and moral standards are not governed by what is legal
Ethical behavior includes, but is not limited to corporate responsibility – in regards to community, environment
In many countries consumers care about companies ethics (!)
e.g. KitKat from Nestle.
http://www.nowpublic.com/environment/nestle-kit-kat-palm-oil-crisis-greenpeace-uses-facebook-youtube-2595022.html
Слайд 271. What Is Strategy and Why Is It Important? 1.3 The
CORE CONCEPT
A company’s business model explains the rationale for why its business approach and strategy will be a moneymaker. Absent the ability to deliver good profitability, the strategy is not feasible and the survival of the business is in doubt.
Слайд 28Be clear on how to earn money (your Business Model)
Magazines: Generating
Razors (Gillette): Selling the razor at an attractively low price and then making money on repeat purchase of razor blades.
Printer Manufacturer: Selling printers at a low (virtually break-even) price and making large profits on the repeat purchase of printer supplies, especially ink cartridges.
Fitness Club:
Слайд 291. What Is Strategy and Why Is It Important? 1.4 What
CORE CONCEPT
A winning strategy must fit the enterprise’s external and internal situation, build sustainable competitive advantage, and improve company performance.
Слайд 303 questions to distinguish a winning strategy from a flawed:
How
Is the strategy helping the company achieve a sustainable competitive advantage?
Is the strategy resulting in better company performance?
Слайд 311. What Is Strategy and Why Is It Important? 1.5 Why
Good Strategy + Good Strategy Execution = Good Management
Слайд 332. Leading the Process of Crafting & Executing Strategy 2.1 What
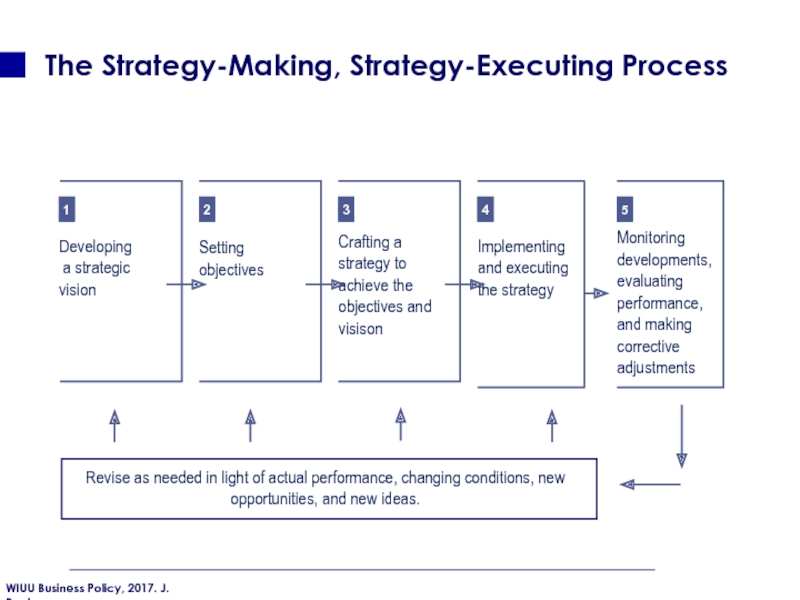
Process consists of five interrelated steps:
Developing a strategic vision of where the company needs to head and what its future product/customer/market/technology focus should be.
Setting objective and using them as yardsticks for measuring the company’s performance and progress
Crafting a strategy to achieve the objectives and move the company along the strategic course that management has charted
Implementing and executing the chosen strategy efficiently and effectively.
Evaluating performance and initiating corrective adjustments in the company’s long-term direction, objectives, strategy, or execution in light of actual experience, changing conditions, new ideas, and new opportunities.
Слайд 34The Strategy-Making, Strategy-Executing Process
1
2
3
4
5
Developing
a strategic vision
Setting objectives
Crafting a strategy
Implementing and executing the strategy
Monitoring developments, evaluating performance, and making corrective adjustments
Revise as needed in light of actual performance, changing conditions, new opportunities, and new ideas.
Слайд 352. Leading the Process of Crafting & Executing Strategy 2.2 Phase
CORE CONCEPT
A strategic vision describes the route a company intends to take in developing and strengthening its business. It lays out the company’s strategic course in preparing for the future.
Слайд 36Factors to Consider in Deciding on a Company’s Future Direction
Internal
External Considerations
Is the outlook for the company promising if the company sticks with it’s present product/market/customer/technology focus and strategic direction?
Are changes under way in the competitive landscape acting to enhance or weaken the company's prospects?
What, if any, new customer groups and/or geographic markets should the company get in position to serve?
Are there any emerging market opportunities the company ought to pursue?
Should we plan to abandon any of the markets, market segments, or customer groups we are currently serving?
What are our ambitions for the company – what industry standing do we want to have?
Will our present business generate sufficient growth and profitability to please shareholders?
What resource strengths does the company have that will aid its ability to add new products/services/ and/or get into new businesses?
Is the company stretching its resources too thin by trying to compete in too many product categories or market arenas, some of which are unprofitable?
Is the company's technological focus too broad or too narrow?
Слайд 40How a Strategic Vision Differs from a Mission Statement
The distinction between
Слайд 412. Leading the Process of Crafting & Executing Strategy 2.3 Phase
CORE CONCEPT
Objectives are an organization’s performance targets – the results and outcomes management wants to achieve. They function as yardsticks for measuring how well the organization is doing.
Слайд 42Financial & Strategic objectives
CORE CONCEPT
Financial objectives relate to the financial performance
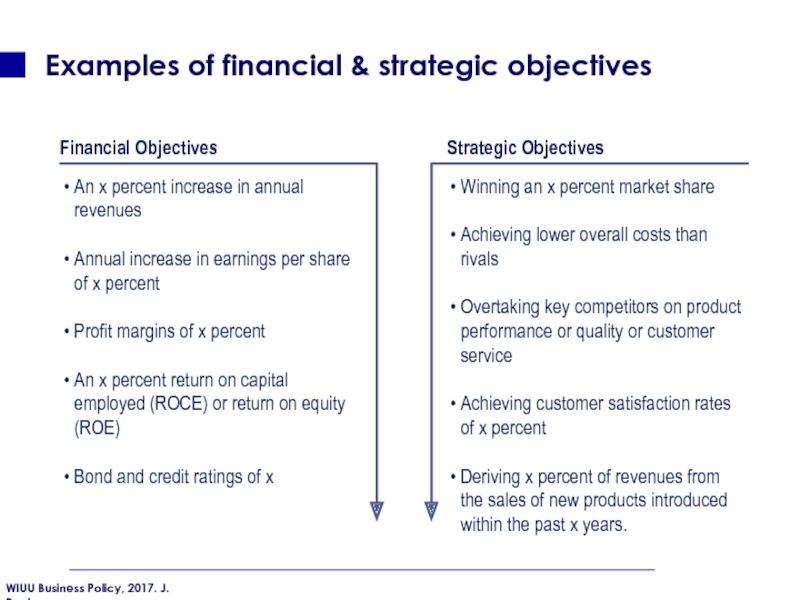
Слайд 43Examples of financial & strategic objectives
Strategic Objectives
Financial Objectives
An x percent
Annual increase in earnings per share of x percent
Profit margins of x percent
An x percent return on capital employed (ROCE) or return on equity (ROE)
Bond and credit ratings of x
Winning an x percent market share
Achieving lower overall costs than rivals
Overtaking key competitors on product performance or quality or customer service
Achieving customer satisfaction rates of x percent
Deriving x percent of revenues from the sales of new products introduced within the past x years.
Слайд 44
To discuss:
ARE FINANCIAL OBJECTIVES ENOUGH TO STEER THE
BUSINESS?
Financial
Слайд 45Good Strategy + competitiveness = future performance
CORE CONCEPT
A company that pursues
Слайд 46Long term & short term targets needed
CORE CONCEPT
A company exhibits
Слайд 472. Leading the Process of Crafting & Executing Strategy 2.3 Phase
CORE CONCEPT
In most companies, crafting and executing strategy is a collaborative effort in which every manager has a role for the area he or she heads. It is flawed thinking to view crafting and executing strategy as something only high-level managers do.
Слайд 48Company’s Strategy-Making Hierarchy
Operating strategies within each business
Add detail and completeness
Provide a game plan for managing specific lower-echelon activities with strategic significance
Functional area strategies within each business
Add relevant detail to the hows of overall business strategy
Provide a game plan for managing a particular activity in ways
that support the overall business strategy
Business Strategy (one for each Businesses the company has)
How to strengthen market position and
gain competitive advantage
Actions to build competitive capabilities
Corporate Strategy
The overall companywide game plan
for a managing a set of businesses
CEO
+ other senior executives
General Manager of Business
Unit + other key people
Head of functional areas
+ other key people
Operating Managers
e.g. Brand Manager
Слайд 49Strategic Vision + Objectives + Strategy = Strategic Plan
CORE CONCEPT
A company’s
Слайд 502. Leading the Process of Crafting & Executing Strategy 2.4 Phase
Managing the strategy execution process includes the following principal aspects:
Staffing the organization with the needed skills and expertise
Allocating sufficient resources to activities critical to strategic success.
Using the best-known practices to perform core business activities and pushing for continuous improvement.
Installing information and operating systems that enable company personnel to do their jobs better and quicker.
Motivating people to pursue the target objectives energetically
Tying rewards and incentives directly to the achievement of performance objectives
Crating a company culture and work climate supporting the strategy (chance)
Слайд 512. Leading the Process of Crafting & Executing Strategy 2.5 Phase
CORE CONCEPT
A company’s vision, objectives, strategy, and approach to strategy execution are never final; managing strategy is an ongoing process, not an every-now-and-then-task.
Слайд 52Leading the strategic management process calls for SIX actions of senior
Staying on top of how well things are going
Making sure the company has a good strategic plan
Putting constructive pressure on organizational units to achieve good results and operating excellence
Pushing corrective actions to improve both the company’s strategy and how well it is being executed
Leading the development of stronger core competencies and competitive capabilities
Displaying ethical integrity and leading social responsibility initiatives.
2. Leading the Process of Crafting & Executing Strategy
2.6 Leading the Strategic Management Process
Слайд 53Staying on Top of How Well Things are Going
CORE CONCEPT
Management
Слайд 55Amazon. Task. (15min)
Read page 1,2,3
Do small groups of 2-3
Answer following questions:
Why is Jeff concerned about day 2?
What is ‘customer focus’
How does he approach decision making?
(Keep the document for next classes)
Слайд 62What to consider in identifying an Industry’s Economic Features?
Let us
Tobacco industry in Ukraine
Cosmetic industry in Ukraine
Industry’s Dominant Economic Features
Слайд 65What are the most common driving forces?
Let us discuss examples.
Tobacco industry in Ukraine
Cosmetic industry in Ukraine
Driving Industry Forces
Слайд 68Strategic Group Map
Let us discuss examples.
Tobacco industry in Ukraine
Cosmetic industry in Ukraine
☺
Слайд 70What are the most common types of industry key success factors
Let us discuss examples.
Tobacco industry in Ukraine
Cosmetic industry in Ukraine
Key Success Factors
Слайд 71Tools to Evaluate a Company’s External Environment
Industry’s Dominant Economic Features?
Competitive
Driving Industry Forces
Strategic Group Map
Key Success Factors (for future competitive success)
-> Describing the industry landscape.
(e.g. market size, # of rivals, supply/ demand conditions, # if buyers)
-> To identify the nature and strength of competitive pressure in a given industry.
-> The major underlying causes of changing industry and competitive conditions.
-> is a cluster of industry rivals that have similar competitive approaches and market positions.
-> are the factors with the greatest impact on future competitive success in the marketplace.
Слайд 73Questions to the podcast: The 5 competitive forces that shape strategy.
Why are the driving forces different for different industries?
Why are industry profits so low in airline industry?
What is positive-sum-competition?
What is zero-sum-competition?
Is the 5-forces-analysis is just a static-snapshot?
Why does Mr. Porter recommends to share the strategy with suppliers?
Слайд 74Business Policy
Next Class
We meet at Saturday 2nd December. 10.00-13.15.
Homework
Read
Study case study Ben & Jerry’s
Assign for group work (team members) and topic
Слайд 75What we would like to do today ….
Housekeeping
Projectwork/ detailed
Strategy Stress Test
Ben & Jerry‘s case analysis (group work)
Presentation & feedback
Homework
Quiz
Слайд 76Questions to the podcast: Can your business plan survive this stress-test?
Why do so many business ideas fail right at the beginning?
What does the ‘strategy stress-test’ do?
What is more important – the strategy or the implementation?
What are the 6 steps of ‘strategy stress-test’
Слайд 77Business Policy
Next Class
We meet at Saturday 9th December. 10.00-13.15.
Homework
Define
Be ready to discuss Ben & Jerry case (based on questions given next page)
Слайд 78Case study analysis Ben & Jerry’s
Discuss the following questions &
Summary on the case (what is happening, which challenges does the protagonist face)
Describe the Industry’s dominant economic features
Describe competitive forces with the help of Porters 5-forces analysis
Describe the forces which are driving industry change
Prepare a strategic group map - what market positions do rival occupy – how strong are they?
What are the strategic moves you expect competition to make next?
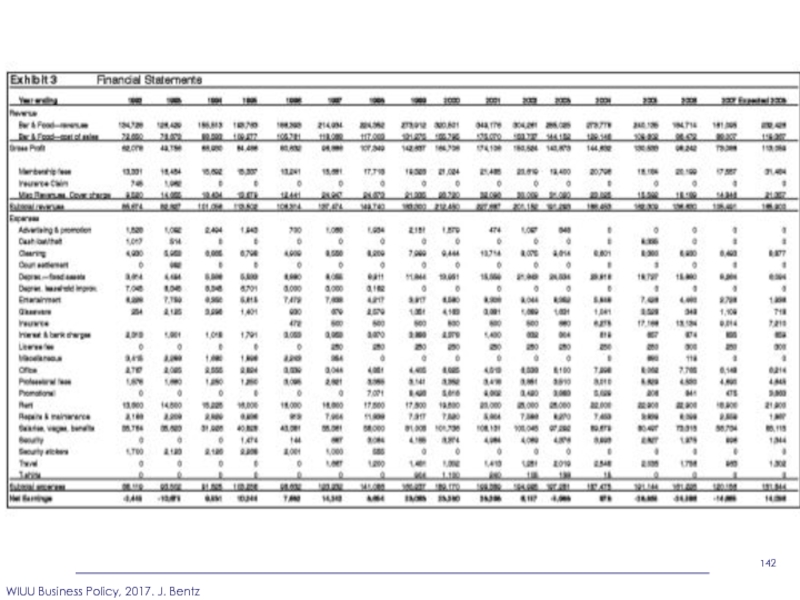
Analyze Ben & Jerry’s financials
SWOT for Ben & Jerry’s based on previous analysis
Discussion in class ….
Слайд 79Case study analysis Ben & Jerry’s
Discuss the following questions &
Summary on the case (what is happening, which challenges does the protagonist face)
Describe the Industry’s dominant economic features
Describe competitive forces with the help of Porters 5-forces analysis
Describe the forces which are driving industry change
Prepare a strategic group map - what market positions do rival occupy – how strong are they?
What are the strategic moves you expect competition to make next?
Analyze Ben & Jerry’s financials
SWOT for Ben & Jerry’s based on previous analysis
Discussion in class ….
Слайд 80Business Policy
Midterm (closed book)
Reading book till chapter 4
Podcasts/ Videos (Porter
Ben & Jerry case
+ class discussions
… with multiple choice plus many open questions.
Слайд 81What we would like to do today ….
Mid-term exam 10.15
--Break--
Class 12.00 – 13.00
Слайд 82What you should keep in mind …
‘list’ – name the
‘define’ – definition
‘describe’ / ‘explain’ – details, maybe example
‘evaluate’ – describe + explain + pros/ cons
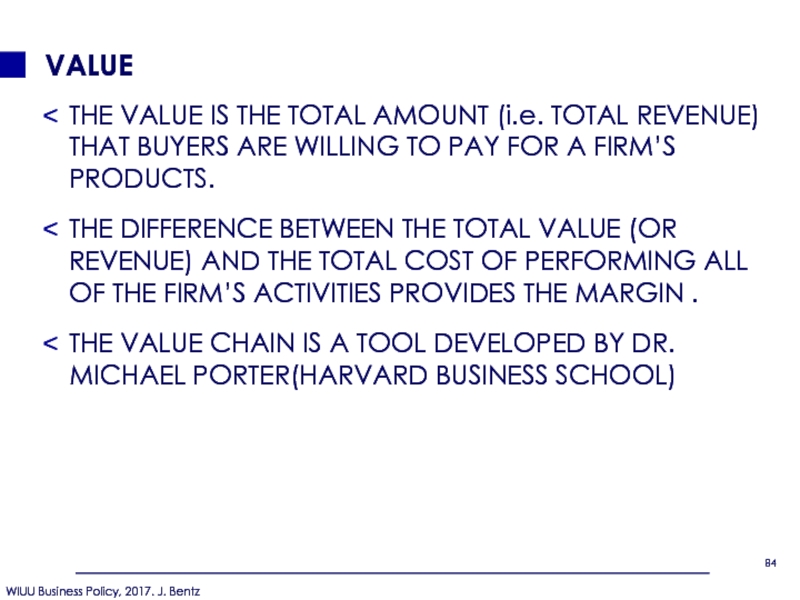
Слайд 84VALUE
THE VALUE IS THE TOTAL AMOUNT (i.e. TOTAL REVENUE) THAT BUYERS
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE TOTAL VALUE (OR REVENUE) AND THE TOTAL COST OF PERFORMING ALL OF THE FIRM’S ACTIVITIES PROVIDES THE MARGIN .
THE VALUE CHAIN IS A TOOL DEVELOPED BY DR. MICHAEL PORTER(HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL)
Слайд 85WHAT IS THE VALLUE CHAIN?
Porter’s definition includes all activities to
The value chain is concentrating on the activities starting with raw materials till the conversion into final goods or services.
Two categories:
Primary Activities (operations, distribution, sales)
Support Activities (R&D, Human Resources)
Слайд 86TYPES OF VALUE CHAIN
Value Chain is categorized into types based on
Manufacturing based.
Service based.
Both manufacturing and service based.
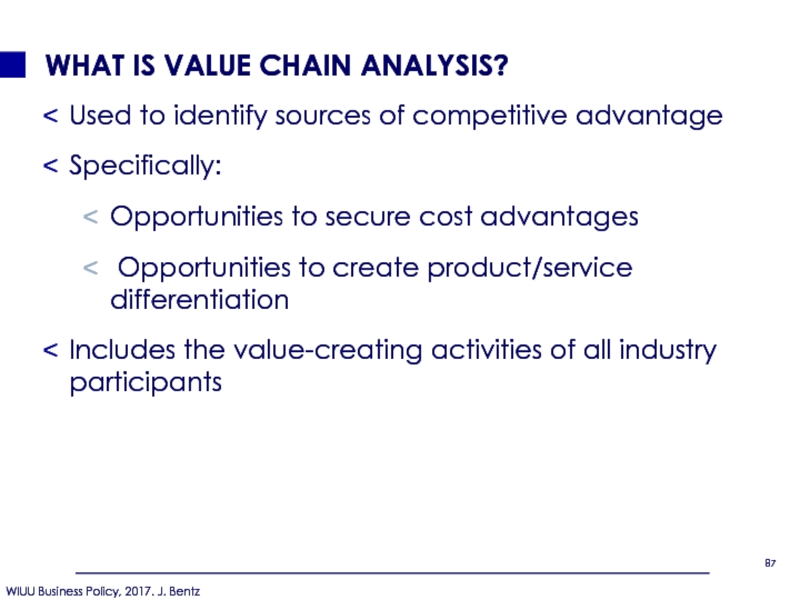
Слайд 87WHAT IS VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS?
Used to identify sources of competitive
Specifically:
Opportunities to secure cost advantages
Opportunities to create product/service differentiation
Includes the value-creating activities of all industry participants
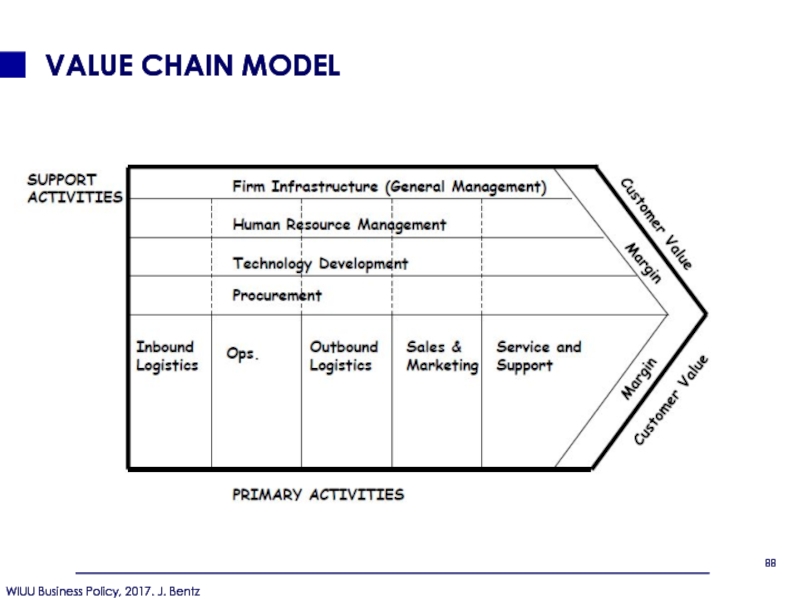
Слайд 89TYPES OF FIRM ACTIVITIES
Primary activities:
Those that are involved in the
Inbound logistics
Operations
Outbound logistics
Sales and marketing
Service and support
Support Activities:
Those that merely support the primary activities
Human resources (general and admin.)
Tech. development/ IT
Procurement
Слайд 91PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
INBOUND LOGISTICS
CONCERNED WITH RECEIVING, STORING, DISTRIBUTING INPUTS (e.g. HANDLING
OPERATIONS
COMPRISE THE TRANSFORMATION OF THE INPUTS INTO THE FINAL PRODUCT FORM (E.G. PRODUCTION, ASSEMBLY, AND PACKAGING)
OUTBOUND LOGISTICS
INVOLVE THE COLLECTING, STORING, AND DISTRIBUTING THE PRODUCT TO THE BUYERS (e.g. PROCESSING OF ORDERS, WAREHOUSING OF FINISHED GOODS, AND DELIVERY)
Слайд 92PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
MARKETING AND SALES
Identification of customer needs and generation of
SERVICE -INVOLVES HOW TO MAINTAIN THE VALUE OF THE PRODUCT AFTER IT IS PURCHASED (e.g. INSTALLATION, REPAIR, MAINTENANCE, AND TRAINING)
Слайд 94SUPPORT ACTIVITIES
FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE
The activities such as Organization structure,
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Involved in recruiting, hiring, training, development and compensation.
TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT
These activities are intended to improve the product and the process, can occur in many parts of the firm.
PROCUREMENT
Concerned with the tasks of purchasing inputs such as raw materials, equipment, and even labor.
Слайд 95USES OF THE VALUECHAIN
The sources of the competitive advantage of
The value chain is a tool for systematically examining the activities of a firm and how they interact with one another and affect each other’s cost and performance.
A firm gains a competitive advantage by performing these activities better or at lower cost than competitors.
Helps you to stay out of the “No Profit Zone”
Presents opportunities for integration
Aligns spending with value processes
Слайд 96VERTICAL LINKAGE
LINKAGES CAN ALSO EXIST OUTSIDE THE FIRM; FOR INSTANCE THERE
e.g. THE ACTIVITIES OF THE RAW MATERIALS SUPPLIERS AFFECT THE ACTIVITIES OF THE FIRM. SIMILARLY, THE ACTIVITIES OF THE DISTRIBUTOR ALSO AFFECT THE FIRM.
Слайд 97 APPLYING THE VALUE CHAIN TO AN INDUSTRY
THE VALUE CHAINS OF
IN FACT, THE DIFFERENCES IN THE VALUE CHAINS AMONG THE DIFFERENT INDUSTRY PLAYERS PROVIDE THE SOURCE OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES BETWEEN THESE PLAYERS.
Слайд 100Business Policy
Next Class
We meet at Monday 22nd Januar . 15.20-18.30.
Homework
Read & study carefully book till chapter 8
Слайд 101Business Policy 2017/2018
Mo. 22.1. 15.20 – 18.30
Sa. 27.1. 10.00 – 13.00
Mo.
Sa 3.2. 10.00 – 13.00
Mo 5.2. 15.20 – 18.30 (voluntarily, BP presentations/ Q&A)
Sa 10.2. 10.00 – 13.00 (final exam)
Sa 17.2. 10.00 – 15.00 (BP presentations in groups)
Слайд 102What we would like to do today ….
Housekeeping
Economic Forum
Value Chain (follow up last class)
Generic strategies
Supplementing strategies
Individual work (assignment)
Projectwork update (team leaders)
Слайд 105Davos. World Economic Forum
https://www.youtube.com/user/WorldEconomicForum
Fourth industrial revolution
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kpW9JcWxKq0
Слайд 106Fourth industrial revolution
Watch the video and think about:
Challenges for the
Which technologies will change our life …
Fourth industrial revolution
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kpW9JcWxKq0
Слайд 108USES OF THE VALUECHAIN
The sources of the competitive advantage of
The value chain is a tool for systematically examining the activities of a firm and how they interact with one another and affect each other’s cost and performance.
A firm gains a competitive advantage by performing these activities better or at lower cost than competitors.
Helps you to stay out of the “No Profit Zone”
Presents opportunities for integration
Aligns spending with value processes
Слайд 109VERTICAL LINKAGE
LINKAGES CAN ALSO EXIST OUTSIDE THE FIRM; FOR INSTANCE THERE
e.g. THE ACTIVITIES OF THE RAW MATERIALS SUPPLIERS AFFECT THE ACTIVITIES OF THE FIRM. SIMILARLY, THE ACTIVITIES OF THE DISTRIBUTOR ALSO AFFECT THE FIRM.
Слайд 116And let us talk about supplementing strategies
Strategic alliances
Merger and
Outsourcing
What are the opportunities & risks?
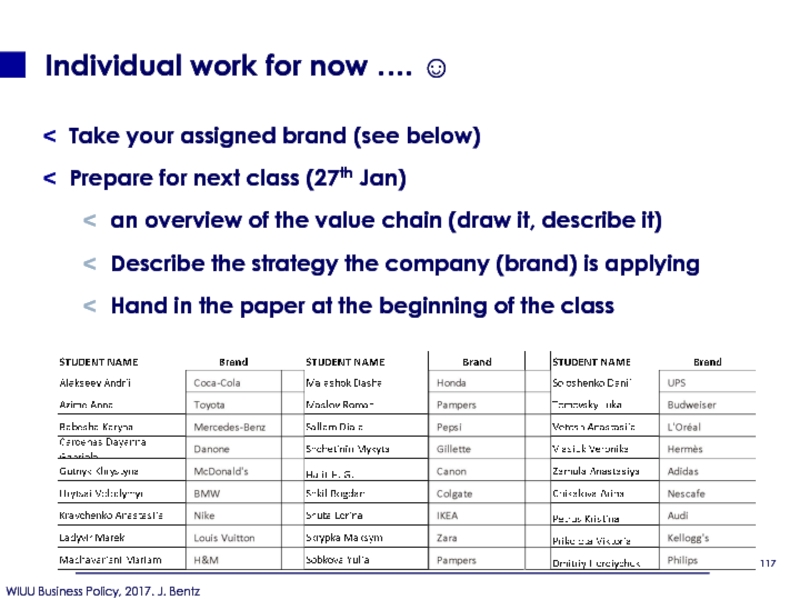
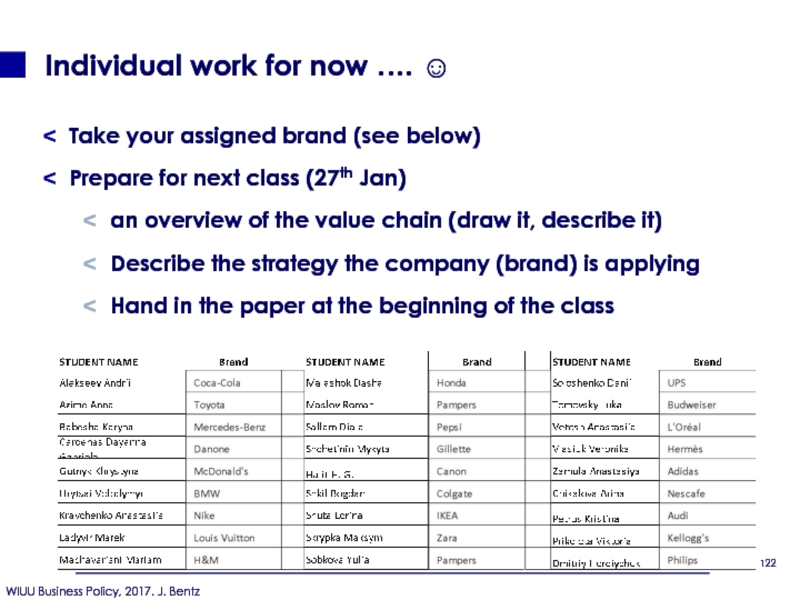
Слайд 117Individual work for now …. ☺
Take your assigned brand (see
Prepare for next class (27th Jan)
an overview of the value chain (draw it, describe it)
Describe the strategy the company (brand) is applying
Hand in the paper at the beginning of the class
Слайд 118Business Policy
Next Class
We meet at Saturday 27th Jan. 10.00-13.15.
Homework
Hand
Hand in your individual brand assignment
Слайд 119Business Policy 2017/2018
Mo. 22.1. 15.20 – 18.30
Sa. 27.1. 10.00 – 13.00
Mo.
Sa 3.2. 10.00 – 13.00
Mo 5.2. 15.20 – 18.30 (voluntarily, BP presentations/ Q&A)
Sa 10.2. 10.00 – 13.00 (final exam)
Sa 17.2. 10.00 – 15.00 (BP presentations in groups)
Слайд 122Individual work for now …. ☺
Take your assigned brand (see
Prepare for next class (27th Jan)
an overview of the value chain (draw it, describe it)
Describe the strategy the company (brand) is applying
Hand in the paper at the beginning of the class
Слайд 123And let us talk about supplementing strategies
Strategic alliances
Merger and
Outsourcing
What are the opportunities & risks?
Слайд 124Supplementing strategies: Daimler - Chrysler
In May 1998 Daimler Benz AG and
In small groups please describe
the (legal) details of the merger
the economic/ strategic reasons for the merger (what do managers expect as a result?)
1
Слайд 125Supplementing strategies: Daimler - Chrysler
In May 2007 Daimler Benz AG and
In small groups please think about
what went wrong
what are the financial implications
2
Слайд 126Davos. World Economic Forum
https://www.youtube.com/user/WorldEconomicForum
Meet the Leader with Jack Ma (2018)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4zzVjonyHcQ
Слайд 127Strategies for competing in foreign markets (Chapter 7)
Why companies expand
To gain access to new customers
To achieve lower costs and enhance the firm’s competitiveness
To capitalize on its core competencies
To spread its business risk across a wider market base
Слайд 128Strategies for competing in foreign markets (Chapter 7)
Factors that shape
Cross country differences in culture, demographic and market conditions
Ability to gain competitive advantage based on where activities are located
The risk of adverse exchange rate shifts
The impact of host government policies
Слайд 129Strategies for competing in foreign markets (Chapter 7)
Strategy options for
Maintain a one country production base and export goods
License foreign firms to use the companies technology or to produce and distribute the company’s products
Employ a franchise strategy
Use strategic alliances and Joint Ventures
Set-up local affiliates maybe incl. production
Слайд 130Business Policy
Next Class
We meet at Monday 29th Jan. 15.20-18.00.
Homework
Read
Assignment questions/ task: “Identify the industry in which The Pub operates and conduct a macro economic analysis for The Pub. What are the changing forces affecting the industry?” [PESTEL & Porter 5-forces, driving industry forces]
Слайд 131Business Policy
Next Class
We meet at Saturday 03rd Feb 10.00 –
Homework
Read & prepare THE PUB case study
Assignment questions/ task:
prepare SWOT analysis
Слайд 132Business Policy 2017/2018
Mo. 22.1. 15.20 – 18.30
Sa. 27.1. 10.00 – 13.00
Mo.
Sa 3.2. 10.00 – 13.00
Mo 5.2. 15.20 – 18.30 (voluntarily, BP presentations/ Q&A)
Sa 10.2. 10.00 – 13.00 (final exam)
Sa 17.2. 10.00 – 15.00 (BP presentations in groups)
Слайд 133Business Policy Projects 2017/2018 (17.2.)
we have 7 groups to present, each
10.00. Group #1. ‘Creative Agency’
10.40. Group #2. ‘Special coffee-shop’
11.30. Group #3. ‘FYNO’
12.10. Group #4. Educator Hub’ → finish 13.00 (then E, D)
13.00. Group #5. ‘Magnetic car’
13.40. Group #6. ‘Co-working Dedication’
14.20. Group #7. ‘Electric shelf labeling’
Variant 1
Слайд 134Business Policy Projects 2017/2018 (17.2.)
we have 7 groups to present, each
09.10. Group #5. ‘Magnetic car’
10.00. Group #1. ‘Creative Agency’
10.40. Group #2. ‘Special coffee-shop’
11.30. Group #3. ‘FYNO’
12.10. Group #4. Educator Hub’ → finish 13.00 (then E, D)
13.00. Group #6. ‘Electric shelf labeling’
13.40. Group #7. ‘Co-working Dedication’
Variant 2
Слайд 135The Pub (29.1.)
Task/Questions:
Identify the industry in which the Pub operates
Conduct a Five Forces analysis of the industry in which The Pub operates. Is this an attractive industry?
Conduct a value chain analysis of The Pub. Identify the value and non-value adding activities of The Pub in its current location.
Conduct a SWOT analysis for The Pub in its current location. Is The Pub well positioned to take advantage of the opportunities available and minimize the threats it faces? How would this change when it moved to its new location?
What should Scooter and the board of directors do to ensure the future sustainability of The Pub?
Слайд 136Identify the industry in which the Pub operates and conduct a
Political
Government. Provincial law/ politics. Change: advertising of prices is now allowed but forbidden by the university.
University. Interested in reducing drinking (alc)
Economical
- Minimum wages increasing, leading to higher expenses for the Pub
Financial crises, disposable income of students low/ decreasing.
Industry (drinking & food) increasing
Sociocultural
Low brand loyalty
Socialising increasing vs. drinking (advertising against drinking)
Students want more food, less drinking
Increase of enrolment Undergrads
Слайд 137Identify the industry in which the Pub operates and conduct a
Technological
Growing internet penetration/ usage
Environmental
Opportunity to use more environmental applicances
Legal
- Legal drinking age 19 years
Слайд 1382) Conduct a Five Forces analysis of the industry in which
Suppliers (low)
Food / drinks:
Labour: low skilled worker, students,
University: location, financing
Buyers (medium/ high)
Students. Medium to high bargaining power
Teachers, staff, visiting people have different preferences but less bargaining power
Substitutes (high)
- (dance) clubs, sport, reading .. club, gaming
Слайд 1392) Conduct a Five Forces analysis of the industry in which
New Entrants (low)
Barriers for entrants are low, alc license, no big capital investment needed.
Not very attractive industry, decreasing drinking, low profitability
Rivalry (high)
- Some bars are closing, dying industry, other pubs will run activities to attract students and other people
Summary: hard to survive, low profits and increasing competition, declining industry.
Слайд 1403) Conduct a value chain analysis of The Pub. Identify the
Support Activities:
General Management
- Experienced Scooter, good/ strong relation with university, informal/ not structured management style, long holiday break in summer is limiting the development of the Pub.
Board of directors. Takes most decisions, monitoring situation, hands-off, slow in decision taking
HR
Hiring students form university, trying to reduce turnover rate, people like to work at the Pub, informal communication style, friendly, informal, fun place to work (= workforce is motivated), no formal job descriptions, high salary expenses for Scooter.
Technological
- Website (low technology)
Procurement
- - Buying from local liquor shop
Слайд 1413) Conduct a value chain analysis of The Pub. Identify the
Primary Activities:
Inbound/Outbound Logistics. N/a
Operations
One cash register only, slow service and consumer complaints.
No credit card accepted
Dance/ DJ. DJ booth, dance floor at current location
No kitchen (= no food)
Marketing & Sales
Membership cards to increase loyalty, email updates
No discounts at night
Clear target group with access (students)
Cross marketing activities
Lowest prices in town but are not allowed to advertise
Service
No ATM available?
Слайд 1434) Conduct a SWOT analysis for The Pub in its current
Strength
location, stable customer base, (emotional) direct connection with
experienced manager
Diverse staff from different student groups
Low prices in the city
Informal, friendly (working) culture
- Clear management structure/ clear job descriptions / know what to do
Слайд 1444) Conduct a SWOT analysis for The Pub in its current
Strength
….
Weaknesses
Financial difficulties
Retention of employees (changing fast)
Low capacity
Physical conditions of the Pub (run down)
Lack of management in summer months
Not working with other target groups (conference guests, teachers, ….)
Not (slowly) adopting to changing market conditions e.g. food/ …
Missing (?) market analysis
Слайд 1454) Conduct a SWOT analysis for The Pub in its current
Strength Weaknesses
Opportunities
Increased spending on food and entertainment
Enrolment of students increasing
Conference guests looking for a place to socialize
Increasing customer base because other bars are closing
Слайд 1464) Conduct a SWOT analysis for The Pub in its current
Strength Weaknesses Opportunities
Threats
Less spending on alcohol (financial threat)
Minimum wages regulation (further increase?)
University authorities coming up with new regulations (advertising of prices)
Prohibited advertisement of price
Change of location necessary (can have advantages/ disadvantages)
large number (increasing?) of substitutes (coffee shops, theatre…sport..)
Слайд 147Strength
location, stable customer base, (emotional) direct connection with
experienced manager
Diverse staff from different student groups
Low prices in the city
Informal, friendly (working) culture
- Clear management structure/ clear job descriptions / know what to do
Weaknesses
Financial difficulties
Retention of employees (changing fast)
Low capacity
Physical conditions of the Pub (run down)
Lack of management in summer months
Not working with other target groups (conference guests, teachers, ….)
Not (slowly) adopting to changing market conditions e.g. food/ …
Missing (?) market analysis
Opportunities
Increased spending on food and entertainment
Enrolment of students increasing
Conference guests looking for a place to socialize
Increasing customer base because other bars are closing
Threats
Less spending on alcohol (financial threat)
Minimum wages regulation (further increase?)
University authorities coming up with new regulations (advertising of prices)
Prohibited advertisement of price
Change of location necessary (can have advantages/ disadvantages)
large number (increasing?) of substitutes (coffee shops, theatre…sport..)
Слайд 1485) What should Scooter and the board of directors do to
Moving to another location (….)
Partnerships with student café and other organizations
Special meal for students
Discount programs for students, “bring a friend”
See photo
Слайд 149Questions to the podcast:
Take complexity out of your company.
Is
Which are the 4 sources of complexity?
How can you identify complexity?
Do all managers cause complexity? Why yes / no?
Слайд 150Business Policy
Next Class/ Exam
Book. Chapter 1 – 8
Podcasts/ Videos
Porter
Strategy stress test
Take Complexity Out of Your Company (listen)
Readings:
Stop competing being the Best
Five Common Strategy Mistakes (read)