- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The role of compliance in pharmaceutical cross-border trade презентация
Содержание
- 1. The role of compliance in pharmaceutical cross-border trade
- 2. Introduction Key Concepts: Globalisation, Global Trade/Cross-Border (Pharmaceutical)Trade
- 3. What is Globalisation? From the Business Perspective:
- 4. Globalisation: Context & Focus Focus of this
- 5. What is Global Trade? The worldwide business that involves: making and
- 6. Global Trade
- 7. What is Cross-Border Trade? The buying and selling of goods and services
- 8. Cross-Border Trade in Africa “One of the
- 9. Cross-Border Trade Environment For Pharmaceuticals Key Requirements
- 10. Cross-Border Pharmaceutical Trade in Africa Harmonisation of
- 11. Key Considerations for Successful Regional Harmonisation in
- 12. Industry’s Goals Improve Efficiency Harmonisation of
- 13. What is Trade Compliance Trade compliance is
- 14. Drivers of Increased Compliance Focus in Cross-Border
- 15. Pharmaceutical Regulatory Aspects of Compliance in Cross-Border
- 16. NAFDAC MANDATE NAFDAC was established by
- 17. NAFDAC Act CAP N1 LFN, 2004
- 18. NAFDAC controls the importation and exportation of
- 19. To control and inspect imported food, drugs,
- 20. Imposition of sanctions and administrative penalties for
- 21. A.) IMPORTS: The divisions in PID ensure
- 22. B.) EXPORTS: NAFDAC mandate covers the certification
- 23. Pre-Clearance Processes involves Pre-arrival notification.
- 24. The Federal Government in her wisdom made
- 25. All consignments imported into Nigeria are subjected
- 26. Customs Clearing
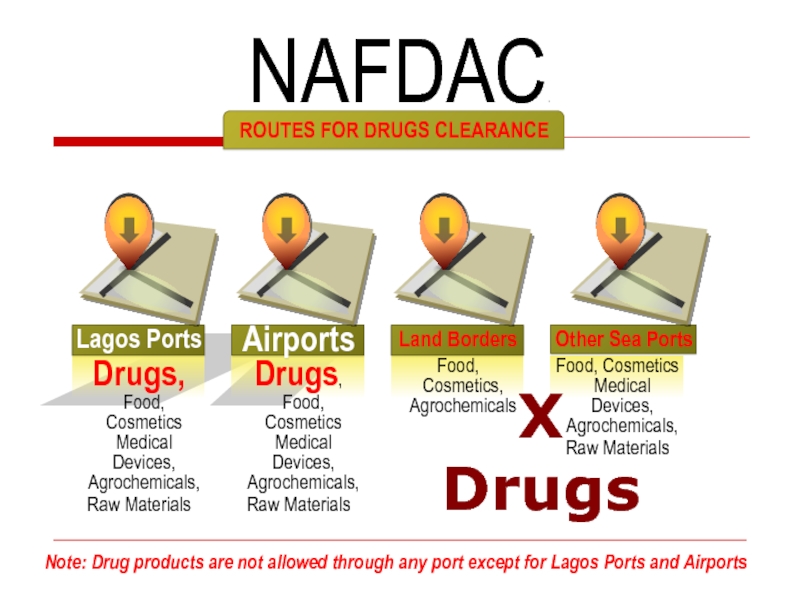
- 27. ROUTES FOR DRUGS CLEARANCE NAFDAC.
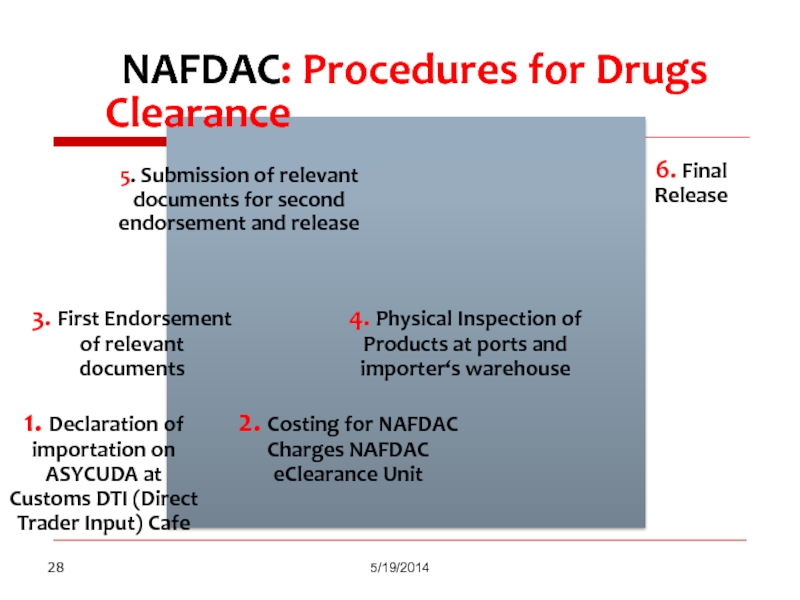
- 28. NAFDAC: Procedures for Drugs Clearance
- 29. NAFDAC: Documents Required for 1st Stamp for
- 30. NAFDAC: Documents Required for 2nd
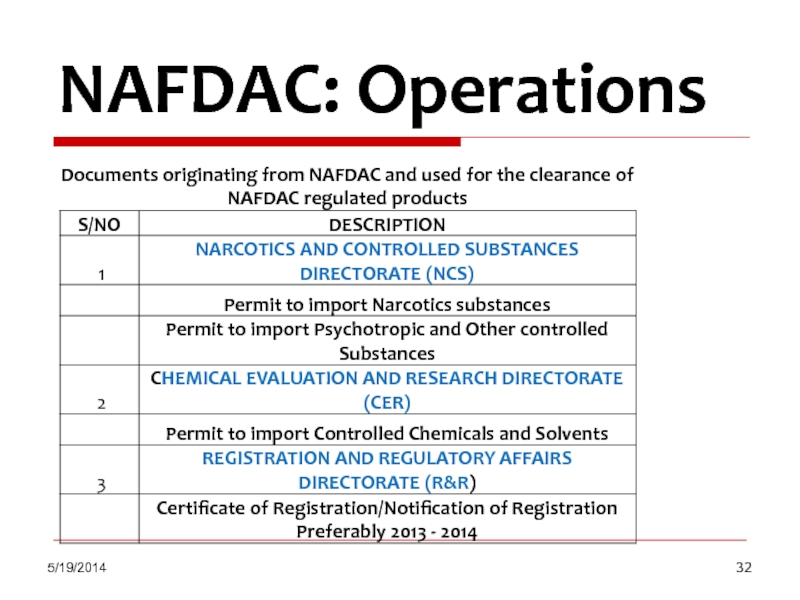
- 31. 5/19/2014 NAFDAC: Operations
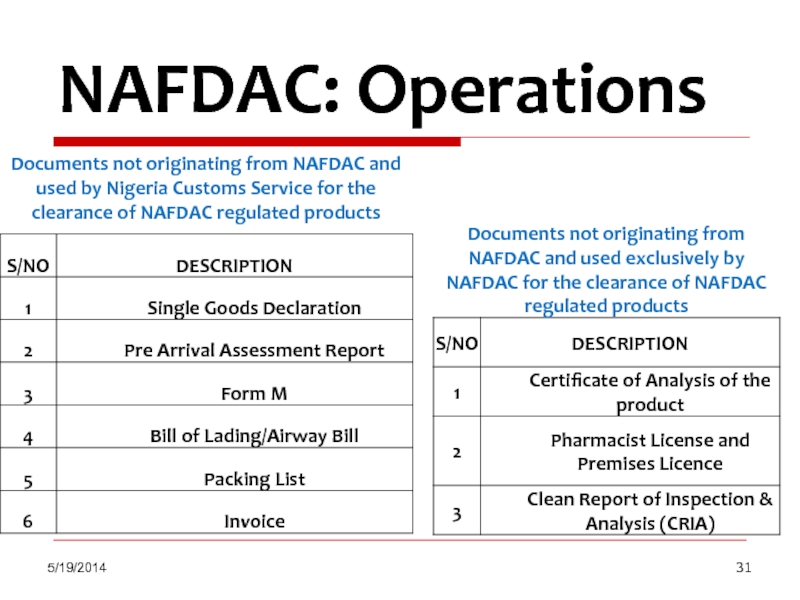
- 32. 5/19/2014 NAFDAC: Operations
- 33. Functions of Nigeria Customs Service in the
- 34. Functions of Nigeria Customs Service in the
- 35. Nigeria Customs Service (NCS):Trade Facilitation Objectives
- 36. Nigeria Customs Service (NCS): Trade Facilitation Objectives
- 37. I. Implementation of global best practices
- 38. What is PAAR? •P- Pre •A- Arrival
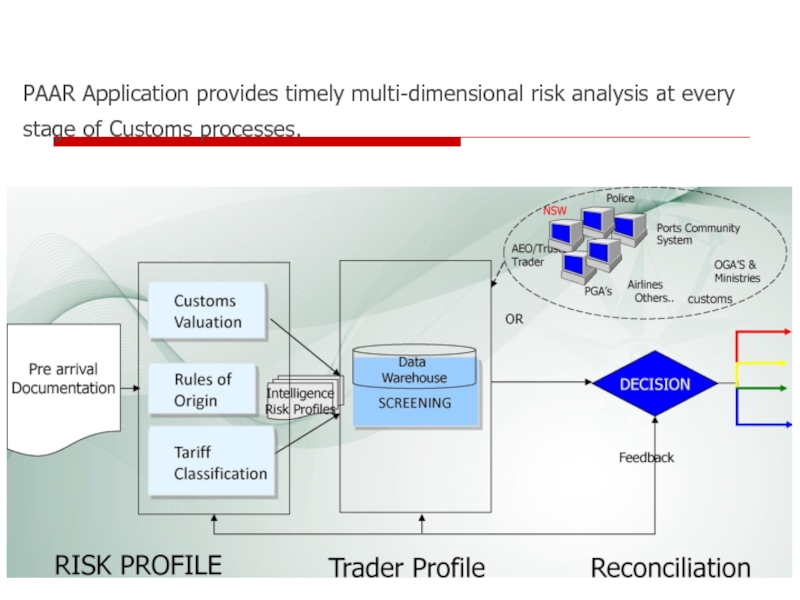
- 39. PAAR Application provides timely multi-dimensional risk analysis at every stage of Customs processes.
- 40. Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls Risk: The
- 41. Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls...2 Risk
- 42. Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls...3 Risk
- 43. Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls...4 Risk
- 44. Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls...5 Risk
- 45. Consumer Protection Service Failure Arising from Agencies
- 46. Best Practice: Customs Trade Compliance
- 47. Getting it Right: Facilitation, not Encumbrance!
- 48. Summary Globalisation: Has led to greatly
- 49. Summary Trade Compliance: Conventionally driven by
- 50. Thank You! Contact Information: Remi ADESEUN Chairman
Слайд 1The role of compliance in pharmaceutical cross-border trade
Phamaceutical Society of Nigeria
Global
Sheraton Hotel, Lagos (May 22,2014)
Presented by Remi ADESEUN, FPSN.
Слайд 2Introduction
Key Concepts: Globalisation, Global Trade/Cross-Border (Pharmaceutical)Trade
Focus on Africa
Compliance
Trade (General)
Pharmaceutical
Regulators
NAFDAC
Nigeria Customs Service
Industry
Best Practice
Summary
Remi ADESEUN
Слайд 3What is Globalisation?
From the Business Perspective:
Globalisation is the worldwide movement toward
4 Basic Aspects according to IMF:
trade and transactions,
capital and investment movements,
migration and movement of people
the dissemination of knowledge.[7]
Ref:International Monetary Fund . (2000). "Globalization: Threats or Opportunity." 12th April 2000: IMF Publications.
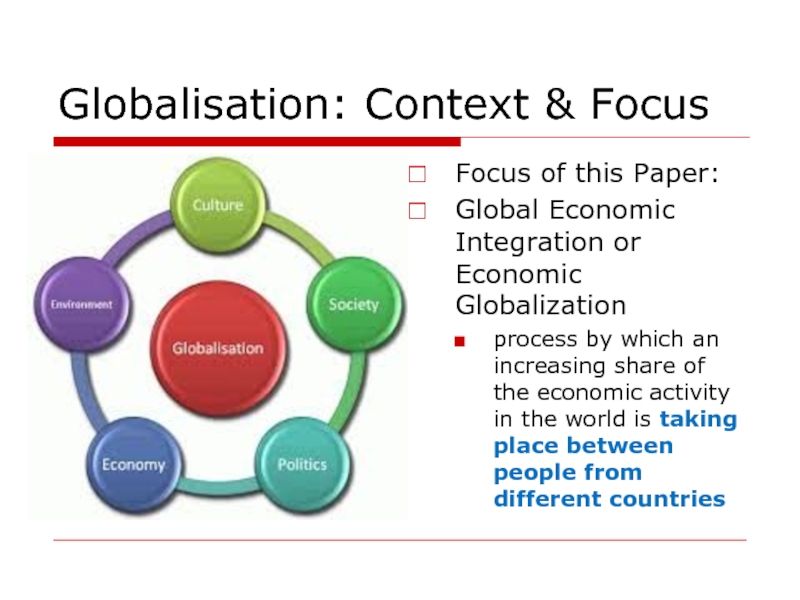
Слайд 4Globalisation: Context & Focus
Focus of this Paper:
Global Economic Integration or Economic
process by which an increasing share of the economic activity in the world is taking place between people from different countries
Слайд 5What is Global Trade?
The worldwide business that involves:
making and collecting payments
for transactions in goods and services,
and
Remi ADESEUN
Слайд 7What is Cross-Border Trade?
The buying and selling of goods and services
between businesses in neighboring countries,
with the seller being
Слайд 8Cross-Border Trade in Africa
“One of the biggest obstacles to industrialization in
only 10-12 percent of total trade, whereas regional trade accounts for 63% in EU, 40% in the US and 30% in Asean countries.”
Ref: http://kariobangi.com/2012/02/13/are-african-economies-too-similar/
Слайд 9Cross-Border Trade Environment For Pharmaceuticals
Key Requirements for Understanding
Extensive knowledge of Trade
Deep understanding of
import and export laws and regulations,
The Global Supply Chain
Trade Processes and Controls
Extensive knowledge of Pharmaceutical Laws and Regulations
Forward-thinking attitude/Global Mindset
Harmonisation of Regulatory Requirements
Слайд 10Cross-Border Pharmaceutical Trade in Africa
Harmonisation of Regulatory Requirements is a key
East Africa has made significant progress in this regard by making Product Registration in one Country acceptable for trade in another country
Leading to improved Compliance and enhanced Cross-Border Pharmaceutical Trade
Слайд 11Key Considerations for Successful Regional Harmonisation in Africa
A need to adopt
A need to invest in regulatory and industry capacity building,
Acknowledgment that NMRAs must follow through on their mandate to promote and protect public health
Sustainability, transparency and trust building
Use of existing structures and broader REC strategies to advocate for AMRH
National sovereignty must be respected,
Existing forums should be used to provide regulators with practical advocacy (African Medicines Regulators Conference (AFDRAC), International Conference for Drug Regulatory Authorities (ICDRA), International Conference on Harmonisation Global Cooperation Group (ICH-GCG)
Need for the Consortium to keep all stakeholders informed and involved
Need to capitalise on strategic niche roles of key players including:WHO, NEPAD, DFID, etc.
Слайд 12Industry’s Goals
Improve Efficiency
Harmonisation of Regulatory Requirements
Speedier Port Clearance
Reduce Cost
Mitigate
Слайд 13What is Trade Compliance
Trade compliance is the process by which goods
It should be the goal of the Customs Service to maximize trade compliance while facilitating the importation of legitimate cargo.
Слайд 14Drivers of Increased Compliance Focus in Cross-Border Pharmaceutical Trade
tremendous increase in
the growing awareness of trans-national organized crime and, more recently,
the threat of terrorism.
increased awareness in Customs administrations that national and and international co-operation is essential
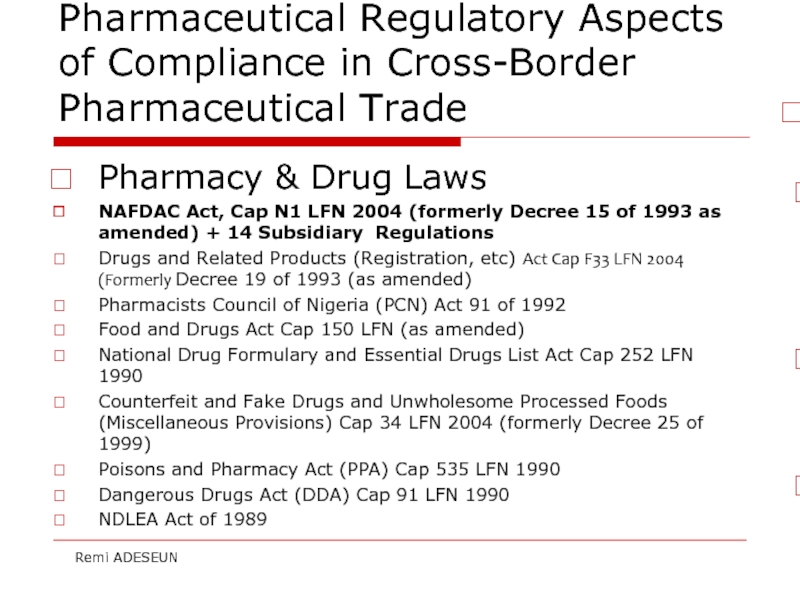
Слайд 15Pharmaceutical Regulatory Aspects of Compliance in Cross-Border Pharmaceutical Trade
Pharmacy & Drug
NAFDAC Act, Cap N1 LFN 2004 (formerly Decree 15 of 1993 as amended) + 14 Subsidiary Regulations
Drugs and Related Products (Registration, etc) Act Cap F33 LFN 2004 (Formerly Decree 19 of 1993 (as amended)
Pharmacists Council of Nigeria (PCN) Act 91 of 1992
Food and Drugs Act Cap 150 LFN (as amended)
National Drug Formulary and Essential Drugs List Act Cap 252 LFN 1990
Counterfeit and Fake Drugs and Unwholesome Processed Foods (Miscellaneous Provisions) Cap 34 LFN 2004 (formerly Decree 25 of 1999)
Poisons and Pharmacy Act (PPA) Cap 535 LFN 1990
Dangerous Drugs Act (DDA) Cap 91 LFN 1990
NDLEA Act of 1989
Drug Laws
Poisons and Pharmacy Act (PPA) Cap 535 LFN 1990
Dangerous Drugs Act (DDA) Cap 91 LFN 1990
NDLEA Act of 1989
Remi ADESEUN
Слайд 16NAFDAC
MANDATE
NAFDAC was established by Decree No. 15 of 1993 (now
This mandate places on Ports Inspection Directorate (PID) the responsibility of carrying out the following functions and exercising powers as described in sections 5d,5e and 5g of the NAFDAC Act.
Слайд 17NAFDAC Act CAP N1 LFN, 2004
5d) undertake inspection of imported food,
5e) compile standard specifications and guidelines for the production, importation, exportation, sale and distribution of food, drugs, cosmetics, medical devices, bottled water and chemicals;
5g) control the exportation and issue quality certification of food, drugs, cosmetics, medical devices, bottled water and chemicals intended for export.
NAFDAC
Слайд 18 NAFDAC controls the importation and exportation of all the products covered
No NAFDAC regulated product shall be imported into and exported out of Nigeria unless it has been duly registered and/or issued a permit or certificate in accordance with the provisions of Act Cap F33 LFN 2004 and the accompanying guidelines.
NAFDAC
Слайд 19To control and inspect imported food, drugs, cosmetics, medical devices, and
To control the export of food, drugs, cosmetics, medical devices, and chemicals and issue quality certification of the above products for export.
Duties also include compilation of guidelines & regulation for importation/exportation of regulated products.
Collaborate with other relevant Agencies, Organizations and the Private Sector at the Ports and Land Borders.
Sampling of relevant products for lab analysis before final release
Implementation of Government fiscal policy on the prohibition of imports of regulated products through the ports and land borders.
NAFDAC: Functions
Слайд 20Imposition of sanctions and administrative penalties for violations including outright seizures
Operation of 24-hour surveillance at designated airports.
Organizing seminars, workshops and meetings to sensitize, update and create awareness on NAFDAC regulations as it concerns imports and exports.
Holding Consultative meetings with sectoral groups and stakeholders to encourage regulatory compliance.
NAFDAC: Functions
Слайд 21A.) IMPORTS:
The divisions in PID ensure proper documentation and endorsement of
The Ports (sea and Air) and Land border offices conduct physical inspection of goods, Hold assignments, fast track activities and final release of goods at the various ports and land borders.
Import Activities occur as:
Pre-clearance Activities
Clearance Activities
Post Clearance Activities
NAFDAC: Operations
Слайд 22B.) EXPORTS:
NAFDAC mandate covers the certification of finished pharmaceutical products that
The following Certificates are issued on satisfying the requirements for export:
Combined Certificate of manufacture and free sale (for registered products)
Certificate of Pharmaceutical Products (COPP).
Free sale Certificates for products not manufactured in Nigeria but sold in Nigeria.
Export Certificate for goods transported through Land Borders for ECOWAS Market.
NAFDAC: Operations
Слайд 23
Pre-Clearance Processes involves
Pre-arrival notification.
Clearance Processes involves
E-Clearance Assessment
Payment of NAFDAC Charges
Documentation
Physical Inspection
Second Endorsement
Release of Goods to importers’ ware house
NAFDAC: Operations
Слайд 24 The Federal Government in her wisdom made laws which empowers several
In the light of this, the Federal Government in 2005 adopted the Destination Inspection (DI) Scheme.
The objectives of the Destination Inspection Scheme include:
To improve clearance of goods by using latest technology tools for documentary checks risk assessment and on the job training.
Facilitate trade through Risk Management and the use of non-intrusive inspection (x-ray scanners) of imports thereby minimizing the need for physical examination.
To enhance Government import revenue collection and the detection of illegal and false declaration of imports.
Ports Inspection Directorate
NAFDAC: Operations
Слайд 25 All consignments imported into Nigeria are subjected to some form of
NAFDAC is connected with Nigeria Customs Service on the Nigeria Trade Hub at www.nigeriatradehub.gov.ng and http://trade.gov.ng for ports operations.
To facilitate legitimate trade, NCS in collaboration with regulatory agencies have listed all regulated products into HS Codes, clearing lanes as follows on the next slide:
NAFDAC: Operations
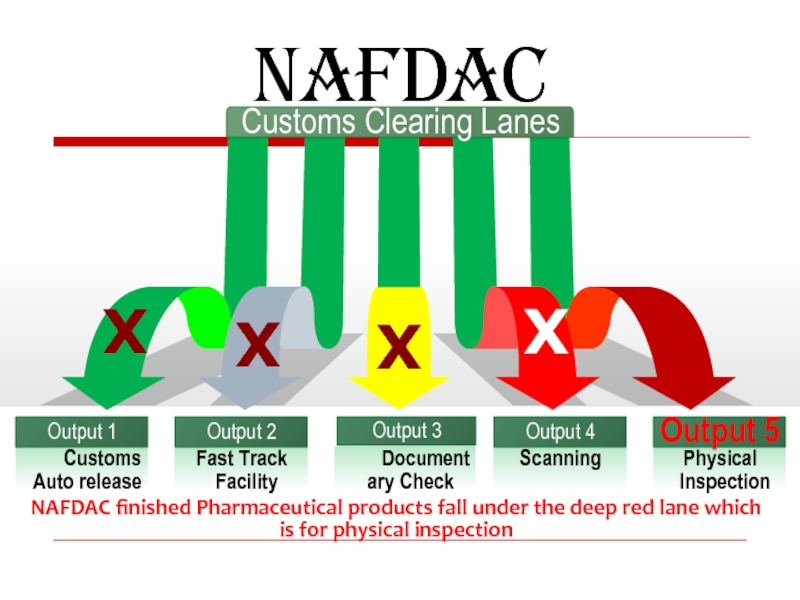
Слайд 26
Customs Clearing Lanes
NAFDAC
NAFDAC finished Pharmaceutical products fall under the deep red
X
X
X
X
Слайд 27
ROUTES FOR DRUGS CLEARANCE
NAFDAC.
Note: Drug products are not allowed through any
X
Drugs
Слайд 28
NAFDAC: Procedures for Drugs Clearance
5/19/2014
1. Declaration of importation on
2. Costing for NAFDAC Charges NAFDAC eClearance Unit
3. First Endorsement of relevant documents
4. Physical Inspection of Products at ports and importer‘s warehouse
5. Submission of relevant documents for second endorsement and release
6. Final Release
Слайд 29NAFDAC: Documents Required for 1st Stamp for Finished Pharmaceutical Products
Letter
Certificate of Analysis (Original Copy)
NAFDAC Certificate of Registration or Notification preferably 2013 – 2014
Electronic SGD
CRIA (Original) e.g
*India – QCS, Silis Labs, ACS
*China – NHU, Hanlin Shangai, Quangzhou Test Tech.
*Egypt - ITG
Photocopy of Payment Advice
Form C-30
Annual License to practice as a Pharmacist
Retention of Premises
NAFDAC receipt of payment
Permit to Import & Permit to Clear Controlled Substances
Packing list
Bill of lading/Airway bill
Invoice
Pre-Shipment Information for Finished Pharmaceutical Products
Form M
5/19/2014
Слайд 30 NAFDAC: Documents Required for 2nd Stamp for Finished Pharmaceutical Products &
Certificate of Analysis/CRIA
Invoice
Electronic SGD
Bill of Lading/Airway Bill
Form M
Packing List
PAAR (Pre-Arrival Assessment Report)
Physical Examination Sheet
NAFDAC Reg. Certificate
Permit to Import & Permit to Clear (Original where applicable)
5/19/2014
Слайд 33Functions of Nigeria Customs Service in the Nigerian Economy:
Revenue Collection
Customs &
[ii] Anti – smuggling operations Applicable at: Borders, sea and airports – checks contrabands, hazardous goods, national security interest.
Physical interception, examination of goods and documents.
Слайд 34Functions of Nigeria Customs Service in the Nigerian Economy:
Agency Function (Inter-Agency)
NCS
Nigeria Police Force – seizure of arms and ammunitions.
National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control [NAFDAC] – prevents illegal importation of foods, drugs and chemicals.
National Drug Law Enforcement Agency [NDLEA] – prevents importation and exportation of hard drugs.
Слайд 35Nigeria Customs Service (NCS):Trade Facilitation Objectives
Generation of Trade Statistics
Trade Facilitation
Trade facilitation
Developments in the WTO with emphasis on trade liberalization and facilitation.
Development of Free Trade Areas across the regions of the world – removing tariff and non-tariff barriers to speed up economic development .
NCS strategic positions at the entry and exit points of Nigerian borders; lead agency role
Слайд 36Nigeria Customs Service (NCS): Trade Facilitation Objectives
To improve the trade environment
To attract Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
To make Nigeria’s borders competitive by un-impeded flow of goods, services and investment funds through the borders.
Слайд 37I. Implementation of global best practices as a core objective
II. Revised Kyoto Convention (RKC) on the simplification and harmonization of Customs procedures- Pre-lodgement and Pre-registration.
III. WCO guidelines on immediate release of consignment - PreArrival processing.
IV. Facilitation of trade through provision of adequate & accurate information in the Nigeria Trade Hub Portal (NTH).
NCS New PAAR Policy
Слайд 38What is PAAR?
•P- Pre
•A- Arrival
•A- Assessment
•R- Report
•Pre-Arrival Assessment Regime
Слайд 39PAAR Application provides timely multi-dimensional risk analysis at every stage of
Слайд 40Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls
Risk: The potential for non-compliance with Customs
Risk analysis: Systematic use of available information to determine how often defined risks may occur and the magnitude of their likely consequences.
Risk areas: Those Customs procedures and categories of international traffic which present a risk.
Слайд 41Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls...2
Risk assessment: The systematic determination of risk
Risk indicators: Specific criteria which, when taken together, serve as a practical tool to select and target movements for their potential for non-compliance with Customs law.
Слайд 42Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls...3
Risk management: Logical and systematic method of
Слайд 43Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls...4
Risk profile: A predetermined, comprehensive and relevant
Слайд 44Risk Management Approach in Customs Controls...5
Risk profiling: The means by which Customs
Standardized Risk Assessments (SRAs): These Assessments produce risk indicator products for use by Customs officials for the purpose of targeting goods and conveyances in their daily work.
Слайд 45Consumer Protection
Service Failure
Arising from Agencies and Service Providers
Remedy
Waive Penalties for Infractions
Dispute Resolution Mechanism
No Agency must be allowed to be Prosecutor, Judge and Jury
Слайд 46Best Practice:
Customs Trade Compliance
Focused Assessments (FA)
a detailed review of
Goal: determine the company's current level of compliance, and whether or not there are sufficient systems in place to ensure a high level of compliance with Customs laws and regulations for future transactions.
Outcome: Compliant or Non-Compliant.
If Non-Compliant, the company will be required to formulate a compliance improvement plan (CIP), and tender any revenue found to be owing.
Слайд 48Summary
Globalisation:
Has led to greatly increased volume of Global and Cross-Border Trade
Increased
Developing nations need to take advantage of Globalisation for prosperity while avoiding inequalities of wealth distribution
All need to be aware of the risks that have come with Globalisation and mitigate against them
Cross-Border Trade:
Essentialy between Neighbours
Regional Cooperation is enlightened self-interest and should be encouraged
Inventory the relevant National laws/regulations and harmonise across the region
Keep all stakeholders actively informed and involved
Слайд 49Summary
Trade Compliance:
Conventionally driven by Customs
Customs should regularly compile and communicate
Goal should be facilitation of Trade not encumbrance
Policy implementation must be customer-centric and culture must be to protect consumer rights while pursuing National Interest
Dispute Resolution Systems and Structure must be established
Cross-Border Pharmaceutical Trade (CBPT):
Deference should be given to the difference between Professionally Regulated Pharmaceutical Trade and Trade in General Goods
There should be greater inter-agency collaboration especially between Customs and NAFDAC given the key role the latter plays in regulating CBPT
Companies need to establish Compliance Management Desks and give it appropriate Executive Oversight