- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
2. Java Basics. Java Statements презентация
Содержание
- 1. 2. Java Basics. Java Statements
- 2. Comments /* . . . */ -
- 3. How to Use Comments Comments should be
- 4. Variables Variables declaration: int k;
- 5. 1. What will this program output? public
- 6. 2. What will this program output? public
- 7. 3. What will this program output? public
- 8. 4. What will this program output? public
- 9. Constant Declaration final modifier: final int a
- 10. If-Then_Else Statement I if (boolean_expression) {
- 11. If-Then_Else Statement II if (boolean_expression) { statements;
- 12. If-Then-Else Example int a = 10; if
- 13. Switch Statement switch(integral-expression) { case integer-value1
- 14. Switch Example char c = ’b’; switch(c)
- 15. Switch Statement Expressions You can use enumerations
- 16. While and Do-While Statement while (boolean_expression) {
- 17. While Example double a = 100.;
- 18. Do-While Example double a = 0.5;
- 19. For Statement for (initialization; Boolean-expression; step) { statements; } * Infopulse Training Center
- 20. For Examples for (int i = 10,
- 21. Break and Continue Statements break quits the
- 22. Use Break with a Label L: for
- 23. Exercise 2.2.1. Find and print all divisors
- 24. Exercise 2.2.1. See 221Divisors project for the full text. * Infopulse Training Center
- 25. Exercise 2.2.2. Find and print all prime
- 26. Exercise 2.2.3. Find sum of an infinite
- 27. Manuals Learning the Java Language. Language Basics * Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 2Comments
/* . . . */ - multi line comment
// .
/** . . . */ - comment for documentation. It can include some additional tags (e.g. @version, @author, @param, @return).
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 3How to Use Comments
Comments should be used to give overviews of
Comments should contain only information that is relevant to reading and understanding the program
Doc comments describe Java classes, interfaces, constructors, methods, and fields
Java associates documentation comments with the first declaration after the comment
*
Infopulse Training Center
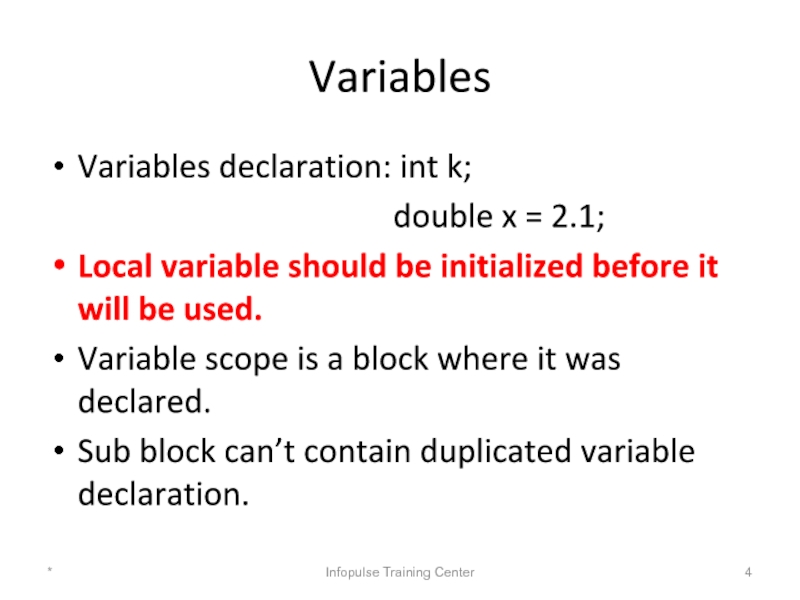
Слайд 4Variables
Variables declaration: int k;
Local variable should be initialized before it will be used.
Variable scope is a block where it was declared.
Sub block can’t contain duplicated variable declaration.
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 51. What will this program output?
public class InitTest {
public
int a = 5;
int b;
if (a < 0) b = 10;
if (a >= 0) b = 50 ;
System.out.println(b);
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 62. What will this program output?
public class Oblzm {
public
int i = 5;
{
int j = 2;
System.out.println("Result is " + i * j);
}
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 73. What will this program output?
public class Oblzm {
public
int i = 5;
{
int j = 2;
}
System.out.println("Result is “ + i * j);
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 84. What will this program output?
public class Oblzm {
public
int i = 5;
{
int j = 2;
int i = 4;
System.out.println("Result is " + i * j);
}
}
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 9Constant Declaration
final modifier: final int a = 42;
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 10If-Then_Else Statement I
if (boolean_expression) {
statements
}
if (boolean_expression) {
statements
} else {
statements
}
*
Infopulse
Слайд 11If-Then_Else Statement II
if (boolean_expression) {
statements;
} else if (boolean_expression) {
statements;
} else if
statements;
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
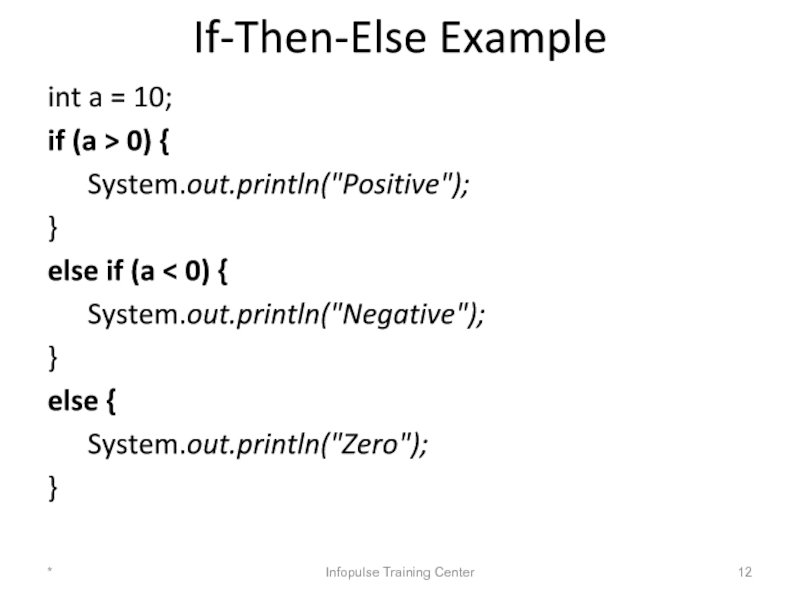
Слайд 12If-Then-Else Example
int a = 10;
if (a > 0) {
System.out.println("Positive");
}
else if (a
System.out.println("Negative");
}
else {
System.out.println("Zero");
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
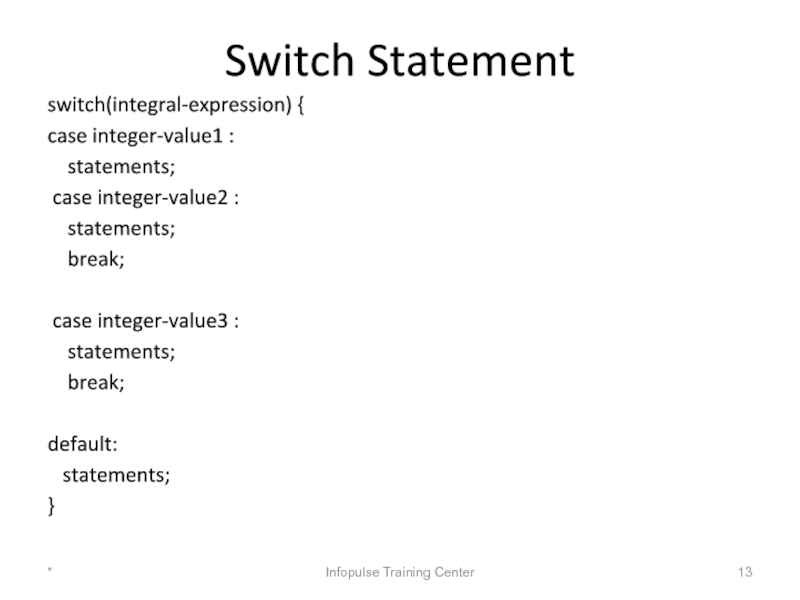
Слайд 13Switch Statement
switch(integral-expression) {
case integer-value1 :
statements;
case integer-value2
statements;
break;
case integer-value3 :
statements;
break;
default:
statements;
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
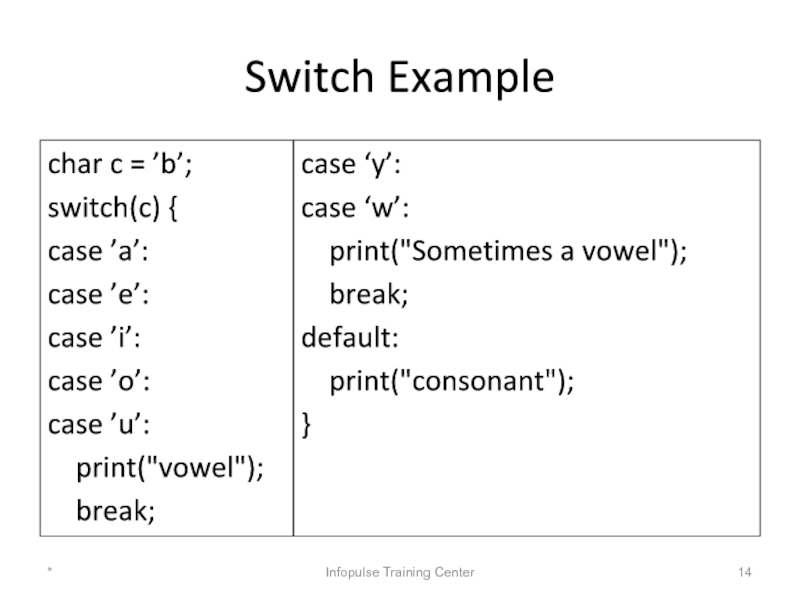
Слайд 14Switch Example
char c = ’b’;
switch(c) {
case ’a’:
case ’e’:
case
case ’o’:
case ’u’:
print("vowel");
break;
case ‘y’:
case ‘w’:
print("Sometimes a vowel");
break;
default:
print("consonant");
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
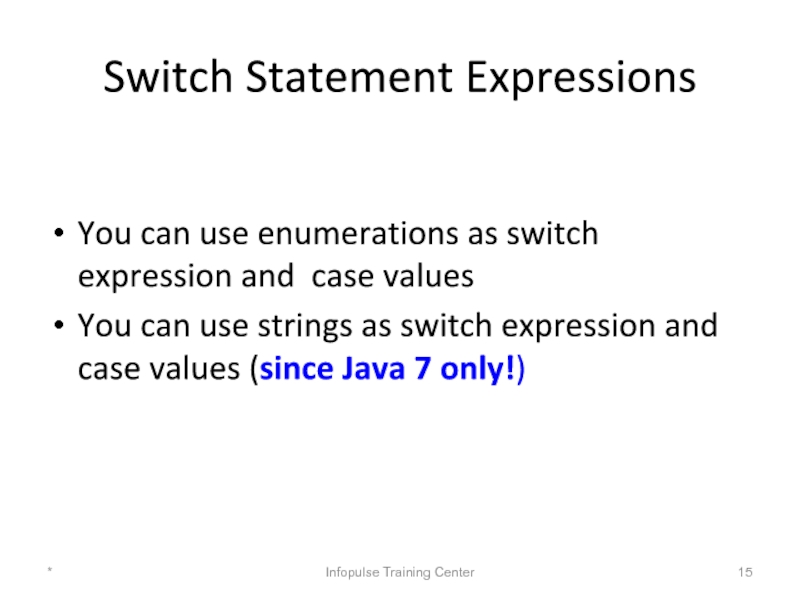
Слайд 15Switch Statement Expressions
You can use enumerations as switch expression and case
You can use strings as switch expression and case values (since Java 7 only!)
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 16While and Do-While Statement
while (boolean_expression) {
statements;
}
do {
statements;
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
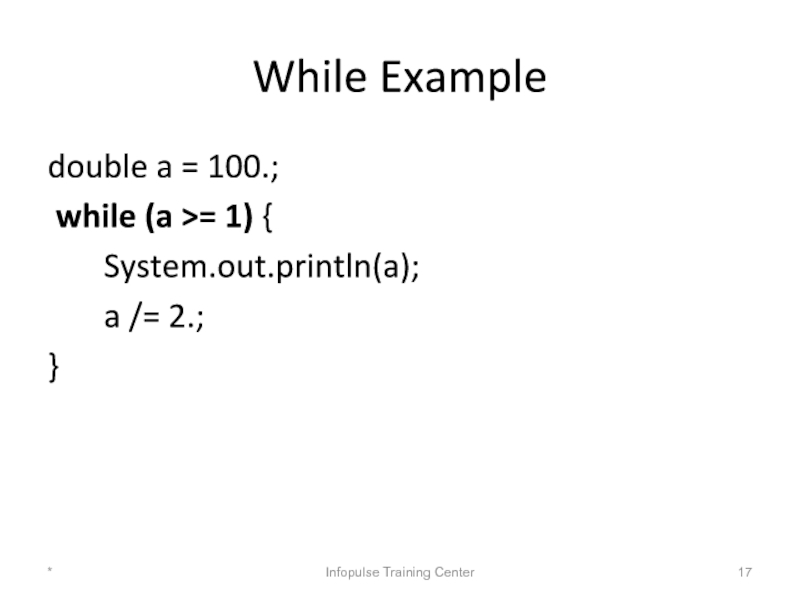
Слайд 17While Example
double a = 100.;
while (a >= 1) {
a /= 2.;
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
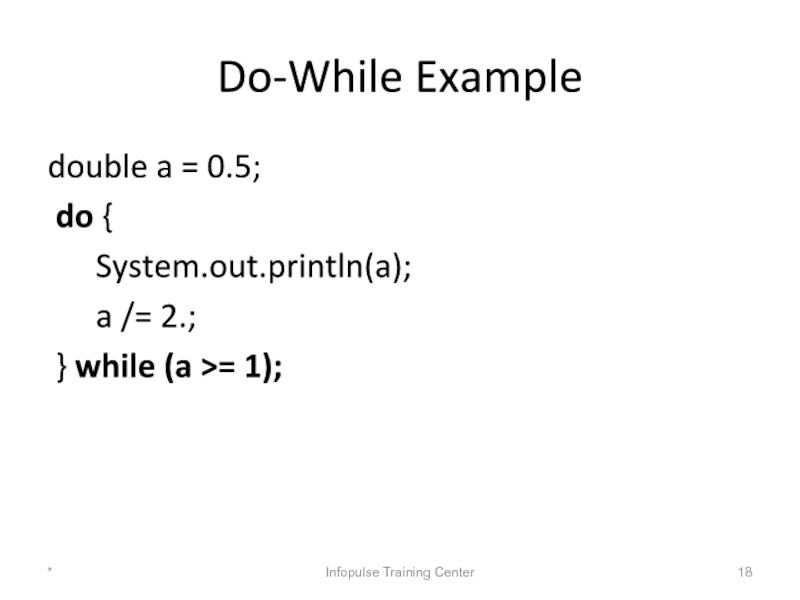
Слайд 18Do-While Example
double a = 0.5;
do {
System.out.println(a);
} while (a >= 1);
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 19For Statement
for (initialization; Boolean-expression; step) {
statements;
}
*
Infopulse Training Center
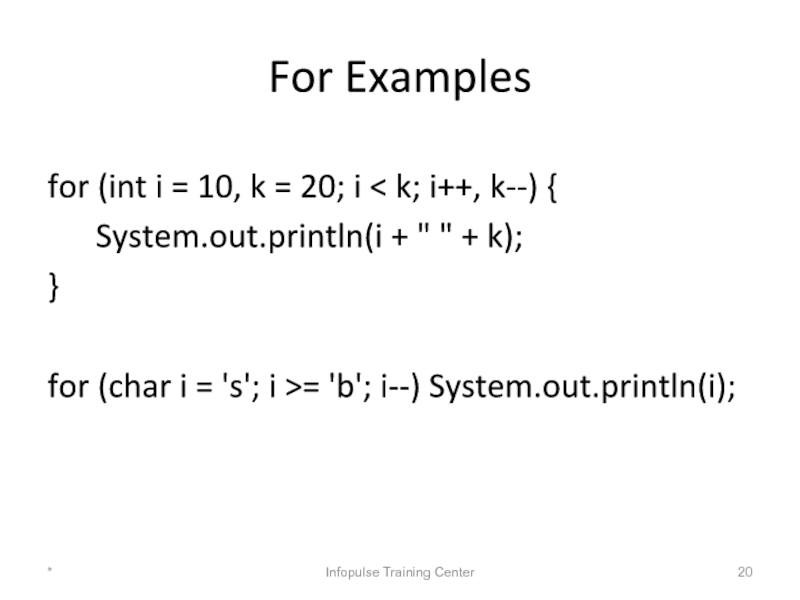
Слайд 20For Examples
for (int i = 10, k = 20; i
System.out.println(i + " " + k);
}
for (char i = 's'; i >= 'b'; i--) System.out.println(i);
*
Infopulse Training Center
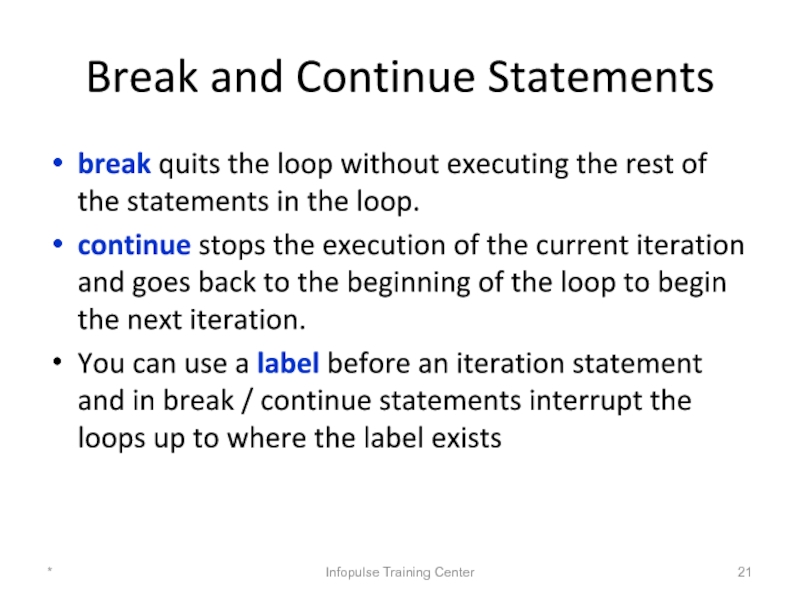
Слайд 21Break and Continue Statements
break quits the loop without executing the rest
continue stops the execution of the current iteration and goes back to the beginning of the loop to begin the next iteration.
You can use a label before an iteration statement and in break / continue statements interrupt the loops up to where the label exists
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 23Exercise 2.2.1.
Find and print all divisors of a given natural number
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 25Exercise 2.2.2.
Find and print all prime divisors of a given natural
*
Infopulse Training Center
Слайд 26Exercise 2.2.3.
Find sum of an infinite row for a given x
Compare
*
Infopulse Training Center



![1. What will this program output?public class InitTest { public static void main (String[] args)](/img/tmb/4/382569/bfbe55f8f54dfe3ab099f83a59dc5b55-800x.jpg)
![2. What will this program output?public class Oblzm { public static void main (String args[]){](/img/tmb/4/382569/75102a76d1f0952d40f884b15f8d1dca-800x.jpg)
![3. What will this program output?public class Oblzm { public static void main (String args[]){](/img/tmb/4/382569/d1b8c509a3b28f1e1c610923fe4cabf7-800x.jpg)
![4. What will this program output?public class Oblzm { public static void main (String args[]){](/img/tmb/4/382569/153f7f2856566f0ab2955c7750060480-800x.jpg)