- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Warm-Up презентация
Содержание
- 1. Warm-Up
- 2. Chapter 42 – Part I Circulation
- 3. What you need to know: Circulatory vessels,
- 4. Transport systems (circulation) linked with gas exchange
- 5. Circulatory System = Blood + Vessels +
- 6. Figure 42.10a Endothelium Artery Smooth muscle Connective
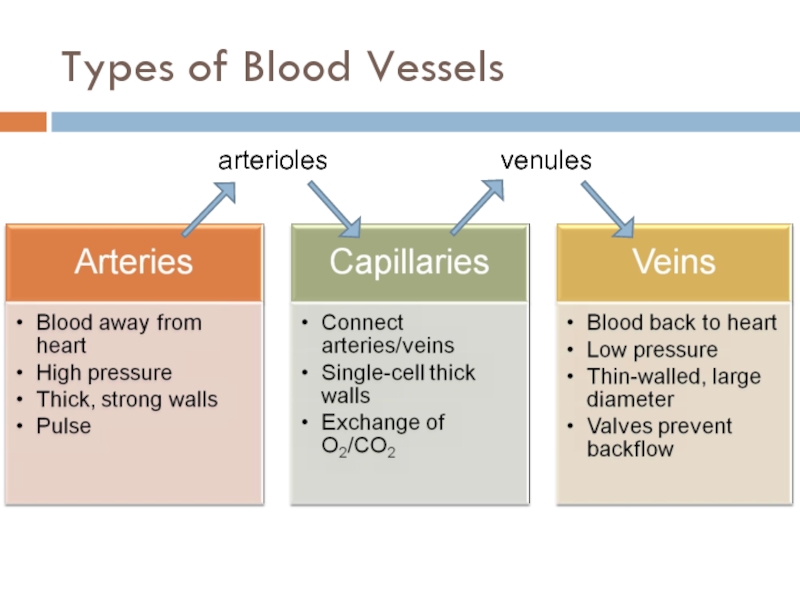
- 7. Types of Blood Vessels arterioles venules
- 8. Blood enters through an atrium and is
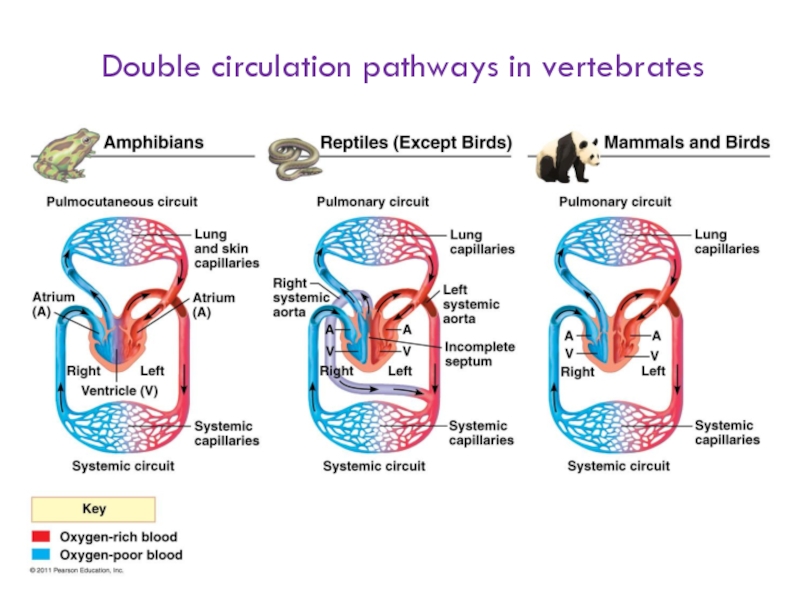
- 9. Double circulation pathways in vertebrates
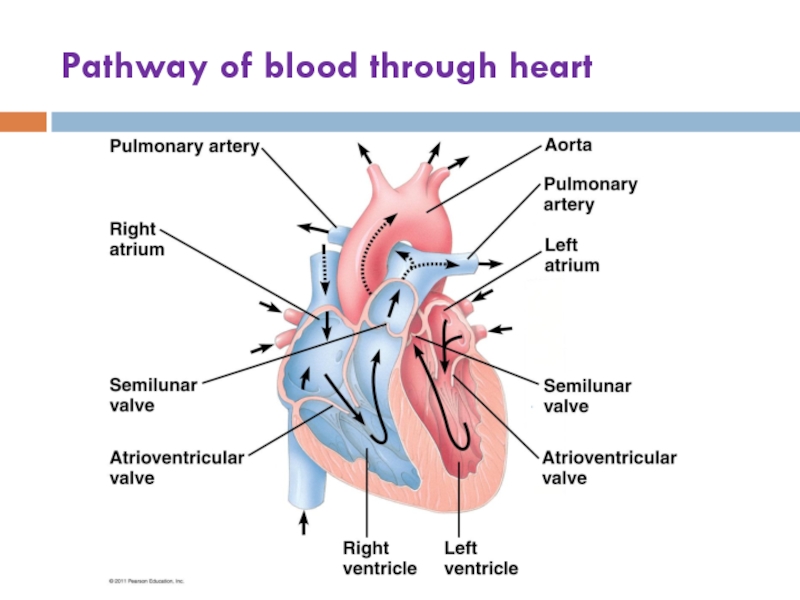
- 10. Pathway of blood through heart
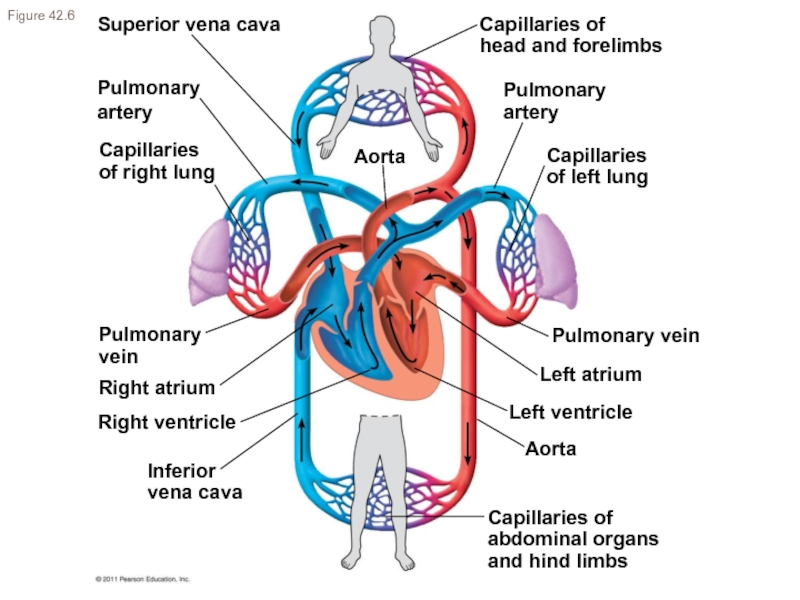
- 11. Superior vena cava Pulmonary artery Capillaries of
- 12. Cardiac cycle Systole: contraction or pumping phase
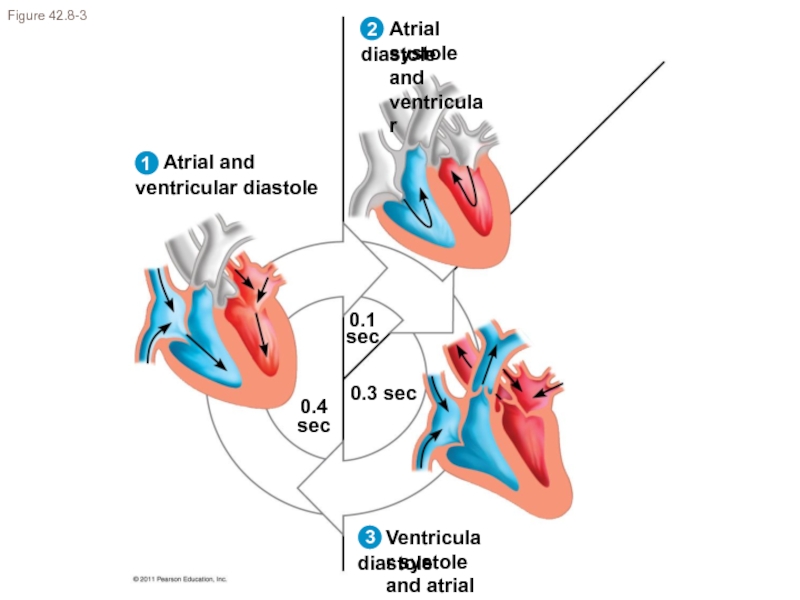
- 13. Figure 42.8-3 0.1 sec 0.4 sec 0.3 sec 2 1 3
- 14. Valves: prevent backflow of blood The
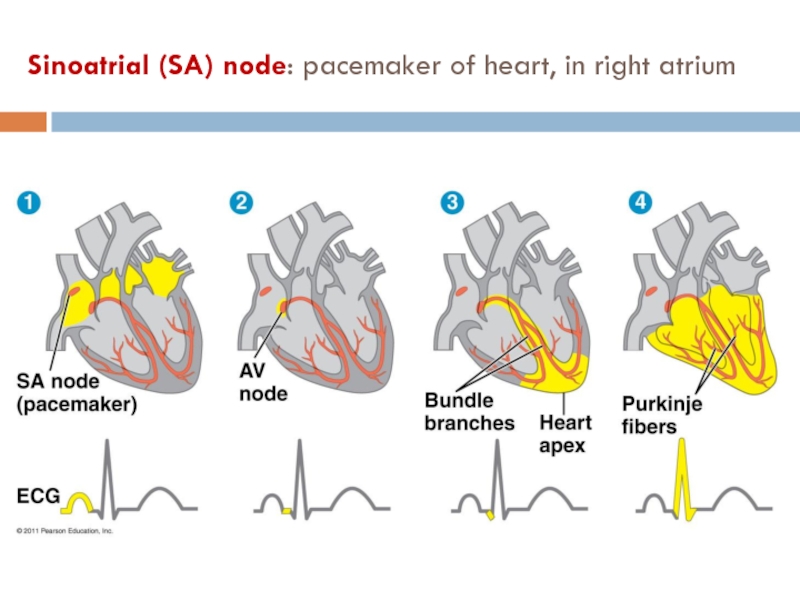
- 15. Sinoatrial (SA) node: pacemaker of heart, in right atrium
- 16. The pacemaker is regulated by two portions
- 17. Blood Pressure BP = systolic/diastolic pressure Systolic:
- 18. Blood pressure reading: 120/70 120 70
- 19. Direction of blood flow in vein (toward
- 20. Lymphatic System: returns lost fluid and proteins
- 21. Blood Plasma (55%) – water, ions, proteins,
- 22. Figure 42.17 Plasma 55% Constituent Major functions
- 23. Figure 42.18 Collagen fibers
- 24. Cardiovascular Disease Atherosclerosis: buildup of plaque deposits
- 25. Lumen of artery Smooth muscle Endothelium
Слайд 1Warm-Up
(Ch. 41) List the locations where each of the 4 macromolecules
(Ch. 41) Where do vertebrates store excess calories?
(Ch. 42) Draw and label the structure of a human heart.
(Ch. 42) List the pathway of a single red blood cell through the heart.
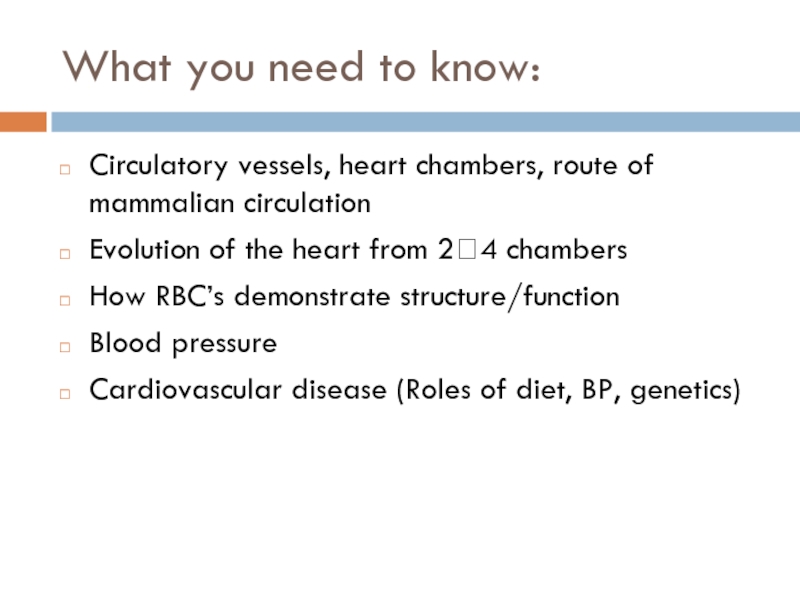
Слайд 3What you need to know:
Circulatory vessels, heart chambers, route of mammalian
Evolution of the heart from 2?4 chambers
How RBC’s demonstrate structure/function
Blood pressure
Cardiovascular disease (Roles of diet, BP, genetics)
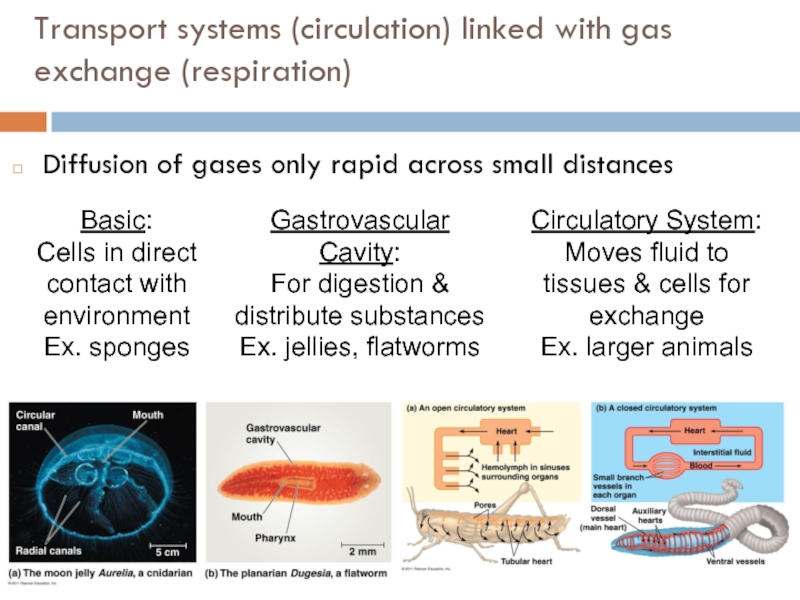
Слайд 4Transport systems (circulation) linked with gas exchange (respiration)
Diffusion of gases only
Basic:
Cells in direct contact with environment
Ex. sponges
Gastrovascular Cavity:
For digestion & distribute substances
Ex. jellies, flatworms
Circulatory System:
Moves fluid to tissues & cells for exchange
Ex. larger animals
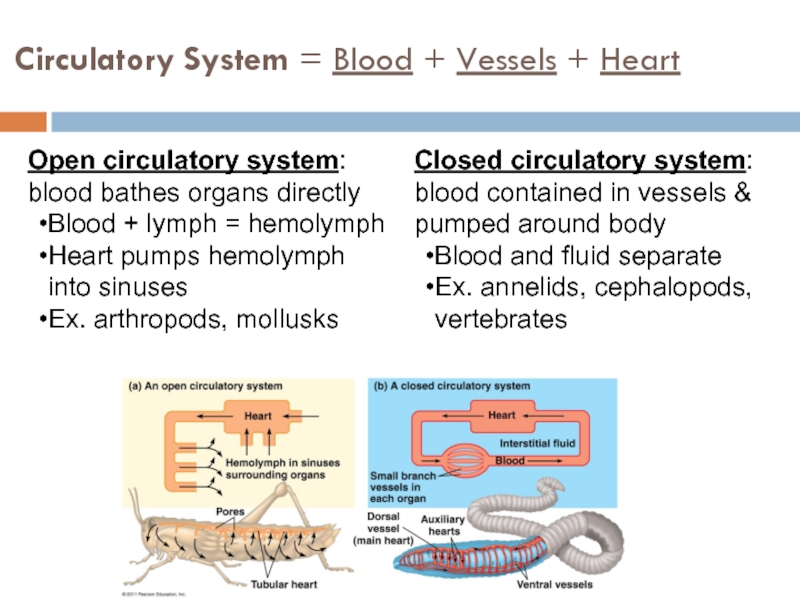
Слайд 5Circulatory System = Blood + Vessels + Heart
Open circulatory system: blood
Blood + lymph = hemolymph
Heart pumps hemolymph into sinuses
Ex. arthropods, mollusks
Closed circulatory system: blood contained in vessels & pumped around body
Blood and fluid separate
Ex. annelids, cephalopods, vertebrates
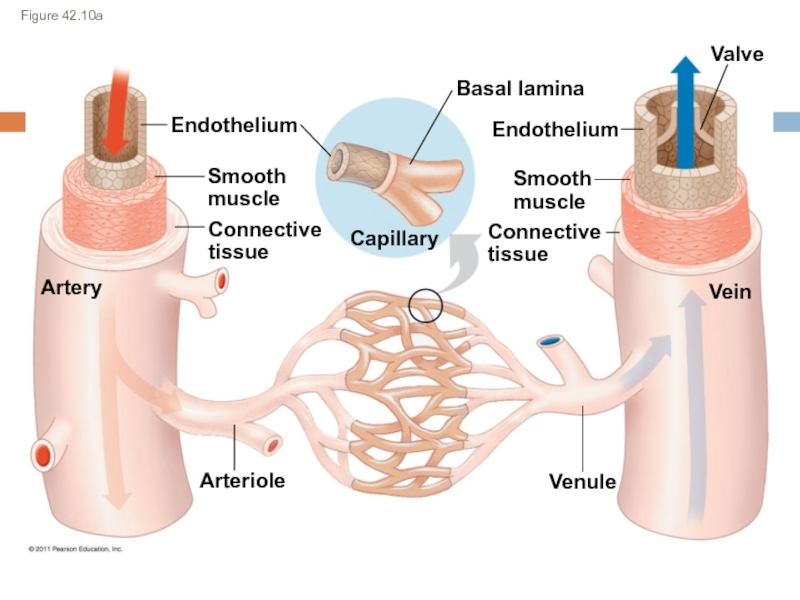
Слайд 6Figure 42.10a
Endothelium
Artery
Smooth
muscle
Connective
tissue
Capillary
Valve
Vein
Basal lamina
Endothelium
Smooth
muscle
Connective
tissue
Venule
Arteriole
Слайд 8Blood enters through an atrium and is pumped out through a
Fish = single circulation pathway, 2 chambers
Double circulation: amphibians, reptiles, mammals
Слайд 11Superior vena cava
Pulmonary
artery
Capillaries
of right lung
Pulmonary
vein
Aorta
Inferior
vena cava
Right ventricle
Capillaries of
abdominal organs
and hind limbs
Right
Aorta
Left ventricle
Left atrium
Pulmonary vein
Pulmonary
artery
Capillaries
of left lung
Capillaries of
head and forelimbs
Figure 42.6
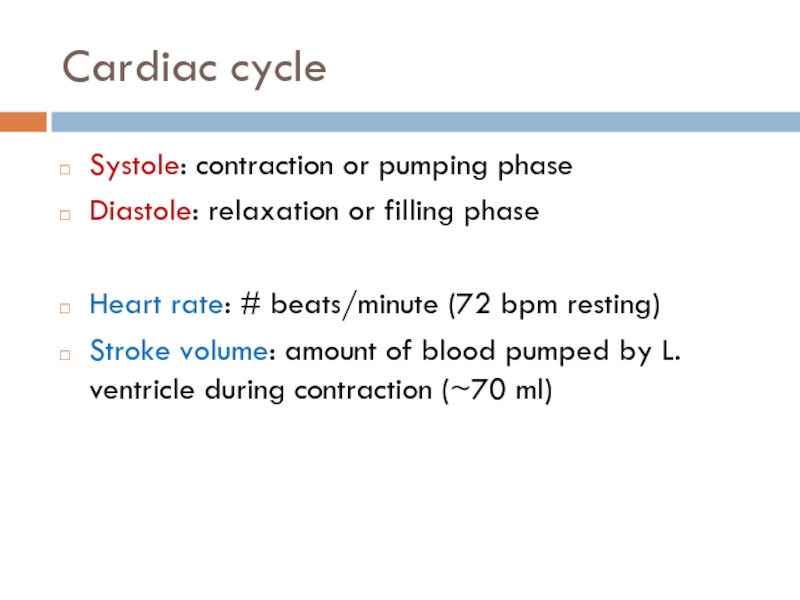
Слайд 12Cardiac cycle
Systole: contraction or pumping phase
Diastole: relaxation or filling phase
Heart rate:
Stroke volume: amount of blood pumped by L. ventricle during contraction (~70 ml)
Слайд 14Valves: prevent backflow of blood
The atrioventricular (AV) valves (tricuspid, bicuspid) separate
The semilunar valves control blood flow to the aorta and the pulmonary artery
“Lub-dup” sound = blood against closed AV valves (lub) / the semilunar (dup) valves
Heart murmur: backflow of blood through a defective valve
Слайд 16The pacemaker is regulated by two portions of the nervous system:
The sympathetic division speeds up the pacemaker
The parasympathetic division slows down the pacemaker
The pacemaker is also regulated by hormones (epinephrine) and temperature
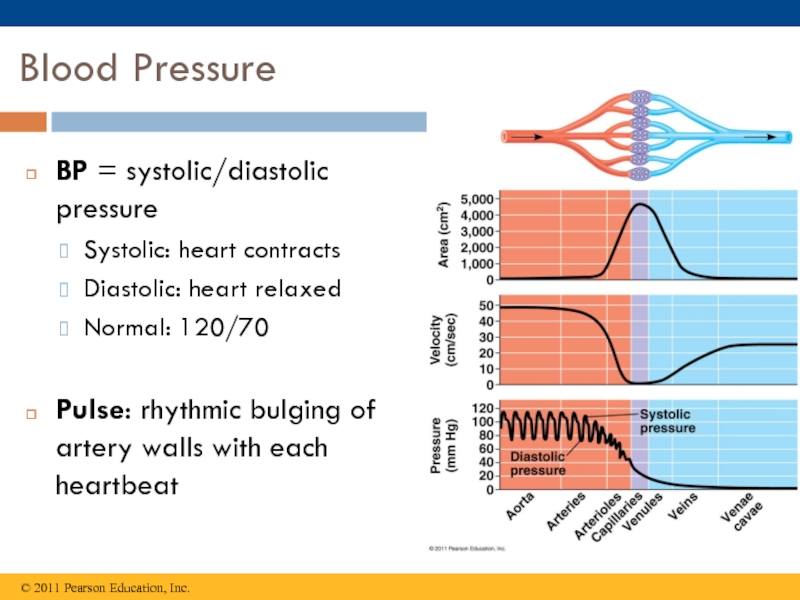
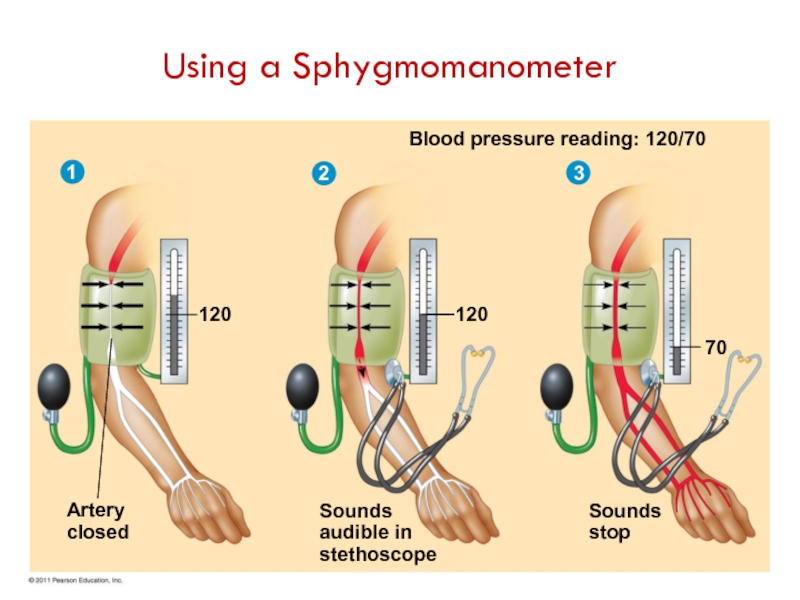
Слайд 17Blood Pressure
BP = systolic/diastolic pressure
Systolic: heart contracts
Diastolic: heart relaxed
Normal: 120/70
Pulse: rhythmic
Слайд 18
Blood pressure reading: 120/70
120
70
Sounds
stop
Sounds
audible in
stethoscope
120
Artery
closed
1
2
3
Using a Sphygmomanometer
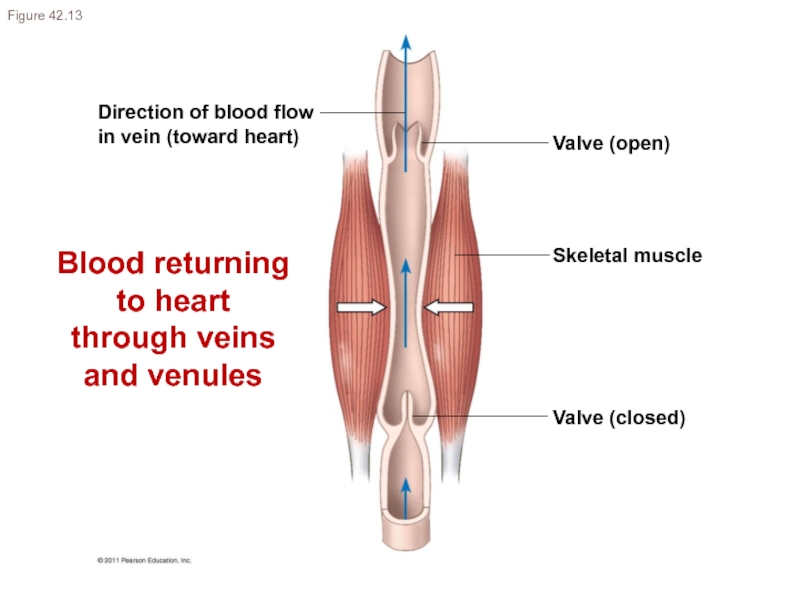
Слайд 19Direction of blood flow
in vein (toward heart)
Valve (open)
Skeletal muscle
Valve (closed)
Figure 42.13
Blood
Слайд 20Lymphatic System: returns lost fluid and proteins to blood as lymph
Lymph
Immune system role
Слайд 21Blood
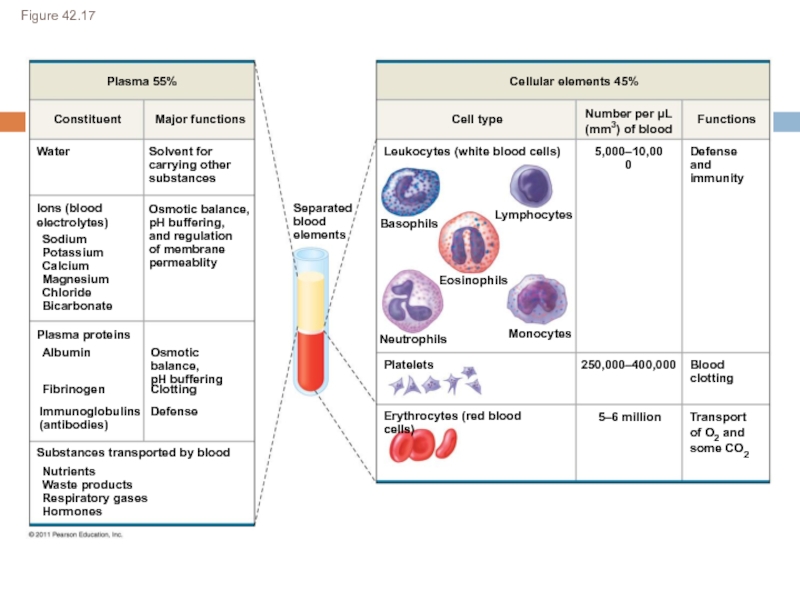
Plasma (55%) – water, ions, proteins, gases, nutrients, wastes, hormones
Cells (45%)
Develop from stem cells in bone marrow
Red blood cells (erythrocytes): O2 transport via hemoglobin
White blood cells (leukocytes): fight infection
Platelets (cell fragments): blood clotting
Слайд 22Figure 42.17
Plasma 55%
Constituent
Major functions
Water
Ions (blood
electrolytes)
Sodium
Potassium
Calcium
Magnesium
Chloride
Bicarbonate
Solvent for
carrying other
substances
Osmotic balance,
pH buffering,
and regulation
of membrane
permeablity
Plasma
Osmotic balance,
pH buffering
Albumin
Fibrinogen
Immunoglobulins
(antibodies)
Clotting
Defense
Substances transported by blood
Nutrients
Waste products
Respiratory gases
Hormones
Separated
blood
elements
Basophils
Neutrophils
Monocytes
Lymphocytes
Eosinophils
Platelets
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
5–6 million
250,000–400,000
Blood
clotting
Transport
of O2 and
some CO2
Defense and
immunity
Functions
Number per μL
(mm3) of blood
Cell type
Cellular elements 45%
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
5,000–10,000
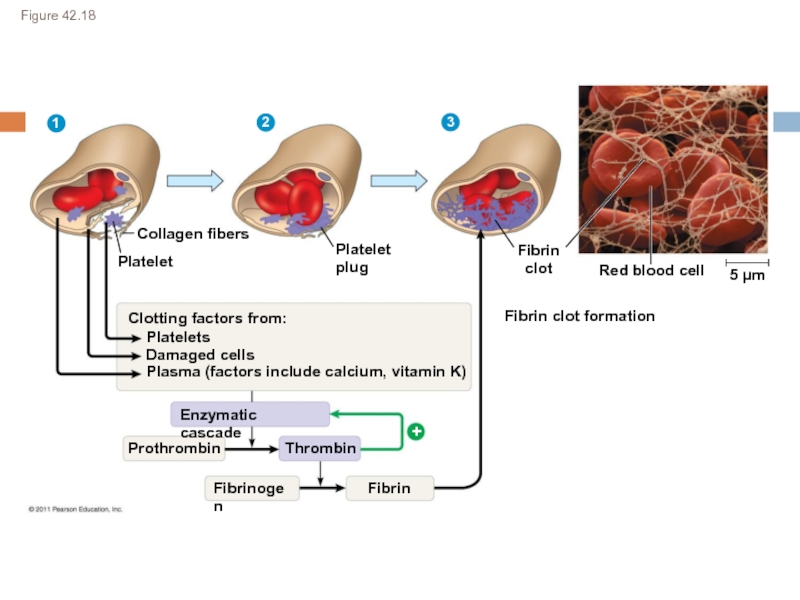
Слайд 23Figure 42.18
Collagen fibers
1
2
3
Platelet
Platelet
plug
Fibrin
clot
Fibrin clot formation
Red blood cell
5 μm
Clotting factors from:
Platelets
Damaged cells
Plasma
Enzymatic cascade
Prothrombin
Thrombin
Fibrinogen
Fibrin
+
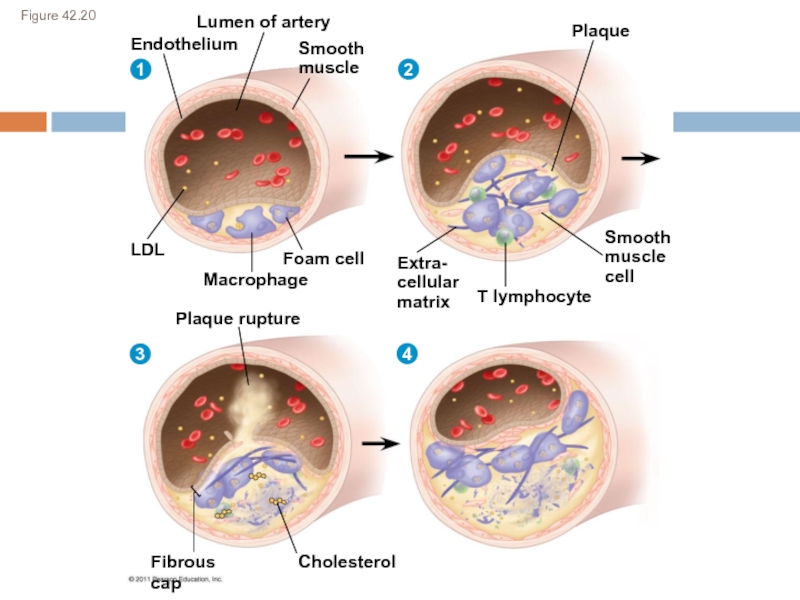
Слайд 24Cardiovascular Disease
Atherosclerosis: buildup of plaque deposits within arteries
Heart attack (myocardial infarction):
Stroke: rupture or blockage of arteries in the head
Hypertension: high blood pressure; promotes atherosclerosis and increases the risk of heart attack and stroke