- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Test TPO 13. Biological clocks. (Section 2) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Test TPO 13. Biological clocks. (Section 2)
- 2. Set the timer to “40:00”
- 3. Question 1 of 28
- 4. Question 2 of
- 5. Question 3
- 6. Question 4
- 7. Question 5
- 8. Question 6
- 9. Question 7
- 10. Question 8
- 11. Question 9
- 12. Question 10
- 13. Question 11
- 14. Question 12
- 15. Look at the four squares
- 16. Question 14
- 19. 15 of 28
- 20. 16 of 28
- 21. 17 of 28
- 22. 18 of 28
- 23. 19 of 28
- 24. 20 of 28
- 25. 21 of 28
- 26. 22 of 28
- 27. 23 of 28
- 28. 24 of 28
- 29. 25 of 28
- 30. 26 of 28
- 31. 27 of 28 Look at
- 32. Question 28
- 34. Congratulations! You have completed this practice test.
- 36. Are you sure you want to exit
- 37. Your answers will be saved with the
- 38. OK When your computer asks you if
- 39. OK When your computer asks you if
Слайд 2
Set the timer to “40:00” before doing the test.
If you
Слайд 3
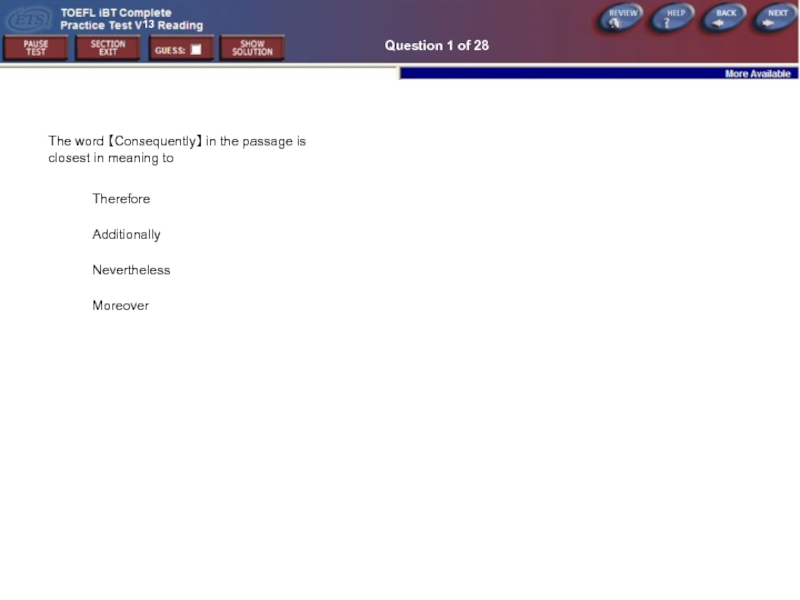
Question 1 of 28
The word 【Consequently】 in the passage is closest
Therefore
Additionally
Nevertheless
Moreover
Слайд 4
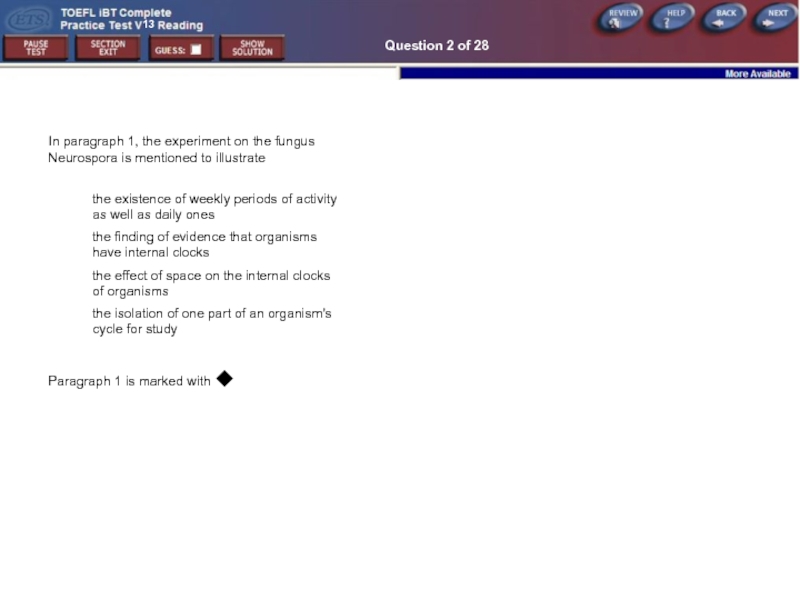
Question 2 of 28
In paragraph 1, the experiment on the fungus
the existence of weekly periods of activity as well as daily ones
the finding of evidence that organisms have internal clocks
the effect of space on the internal clocks of organisms
the isolation of one part of an organism's cycle for study
Paragraph 1 is marked with ◆
Слайд 5
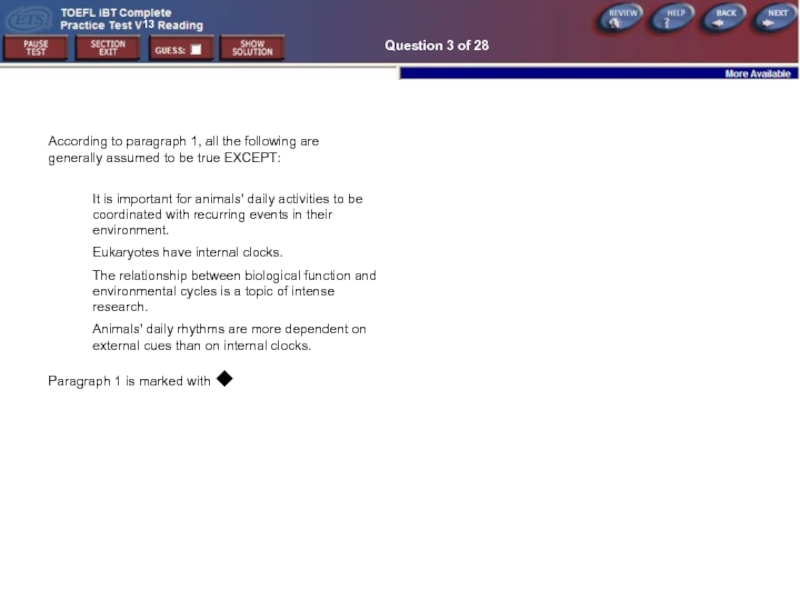
Question 3 of 28
According to paragraph 1, all the following are
It is important for animals' daily activities to be coordinated with recurring events in their environment.
Eukaryotes have internal clocks.
The relationship between biological function and environmental cycles is a topic of intense research.
Animals' daily rhythms are more dependent on external cues than on internal clocks.
Paragraph 1 is marked with ◆
Слайд 6
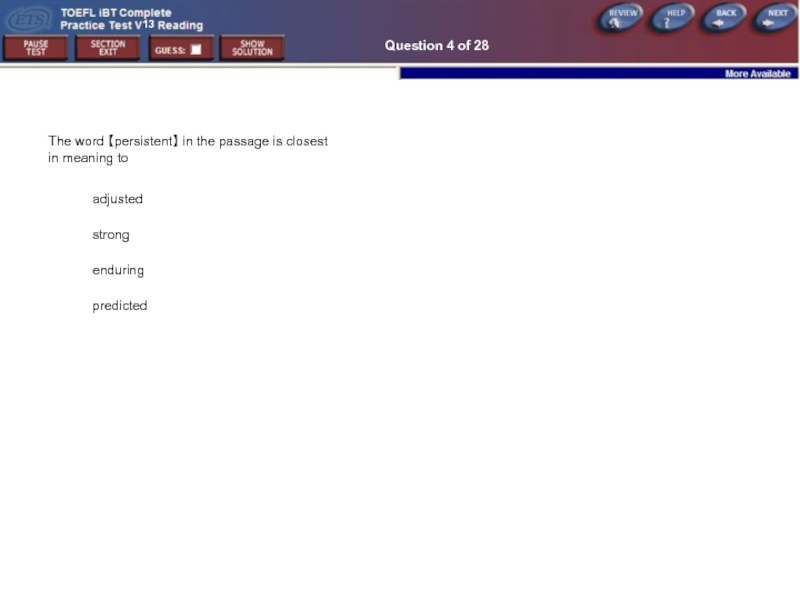
Question 4 of 28
The word 【persistent】 in the passage is closest
adjusted
strong
enduring
predicted
Слайд 7
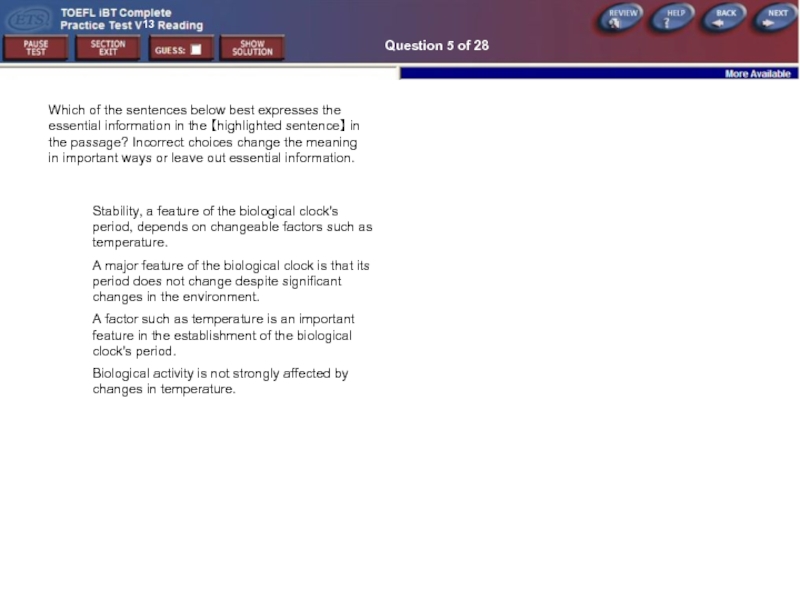
Question 5 of 28
Which of the sentences below best expresses the
Stability, a feature of the biological clock's period, depends on changeable factors such as temperature.
A major feature of the biological clock is that its period does not change despite significant changes in the environment.
A factor such as temperature is an important feature in the establishment of the biological clock's period.
Biological activity is not strongly affected by changes in temperature.
Слайд 8
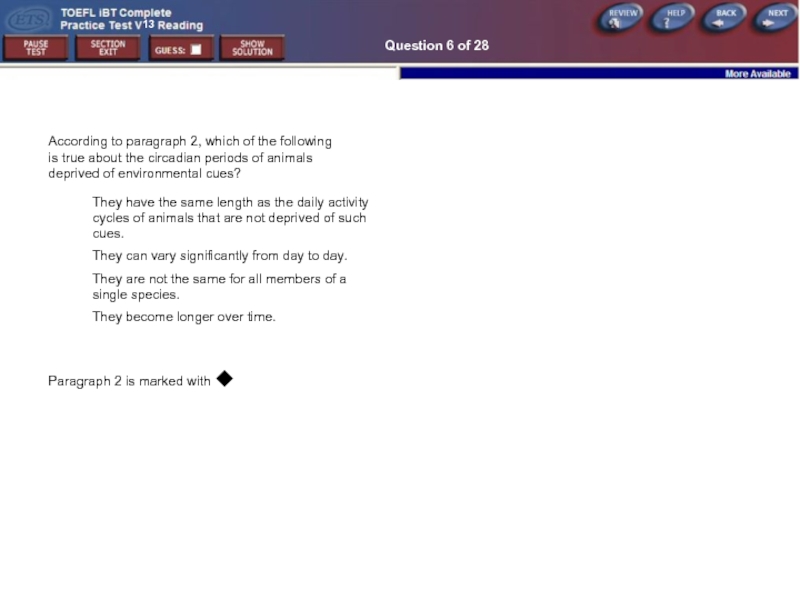
Question 6 of 28
According to paragraph 2, which of the following
They have the same length as the daily activity cycles of animals that are not deprived of such cues.
They can vary significantly from day to day.
They are not the same for all members of a single species.
They become longer over time.
Paragraph 2 is marked with ◆
Слайд 9
Question 7 of 28
According to paragraph 2, what will an animal
Disorientation
Change in period of the internal rhythms
Reversal of day and night activities Increased
Sensitivity to environmental factors
Paragraph 2 is marked with ◆
Слайд 10
Question 8 of 28
In paragraph 2, the author provides evidence for
listing the daily activities of an animal's cycle: sleeping, feeding, moving, reproducing, metabolizing, and producing enzymes and hormones
describing the process of establishing the period of a biological clock
presenting cases in which an animal's daily schedule remained stable despite lack of environmental cues
contrasting animals whose daily schedules fluctuate with those of animals whose schedules are constant
Paragraph 2 is marked with ◆
Слайд 11
Question 9 of 28
The word 【duration】 in the passage is closest
length
feature
process
repetition
Слайд 12
Question 10 of 28
In paragraph 2, why does the author mention
To illustrate that an animal's internal clock seldom has a 24-hour cycle
To argue that different horseshoe crabs will shift from daytime to nighttime vision at different times
To illustrate the approximate range of the circadian rhythm of all animals
To support the idea that external cues are the only factors affecting an animal's periodic behavior
Paragraph 2 is marked with ◆
Слайд 13
Question 11 of 28
The word 【it】 in the passage refers to
an
the daily rhythm of an animal
the local solar day
a cycle whose period is precisely 24 hours
Слайд 14
Question 12 of 28
The word 【sustained】 in the passage is closest
intense
uninterrupted
natural
periodic
Слайд 15
Look at the four squares [■]that indicate where the following sentence
Because the internal signals that regulate waking and going to sleep tend to align themselves with these external cues, the external clock appears to dominate the internal clock.
Where would the sentence best fit?
■ 1
■ 2
■ 3
■ 4
Question 13 of 28
Слайд 16
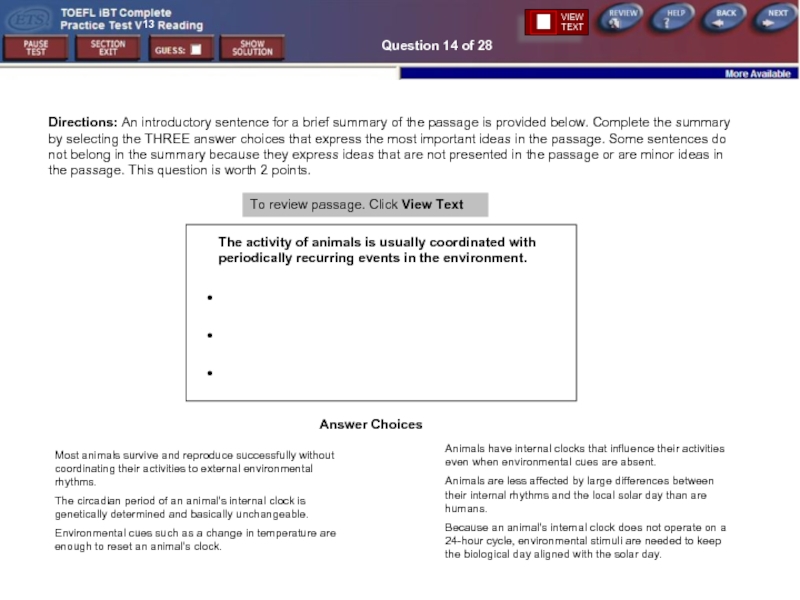
Question 14 of 28
Directions: An introductory sentence for a brief summary
Answer Choices
To review passage. Click View Text
The activity of animals is usually coordinated with periodically recurring events in the environment.
●
●
●
Most animals survive and reproduce successfully without coordinating their activities to external environmental rhythms.
The circadian period of an animal's internal clock is genetically determined and basically unchangeable.
Environmental cues such as a change in temperature are enough to reset an animal's clock.
Animals have internal clocks that influence their activities even when environmental cues are absent.
Animals are less affected by large differences between their internal rhythms and the local solar day than are humans.
Because an animal's internal clock does not operate on a 24-hour cycle, environmental stimuli are needed to keep the biological day aligned with the solar day.
Слайд 19
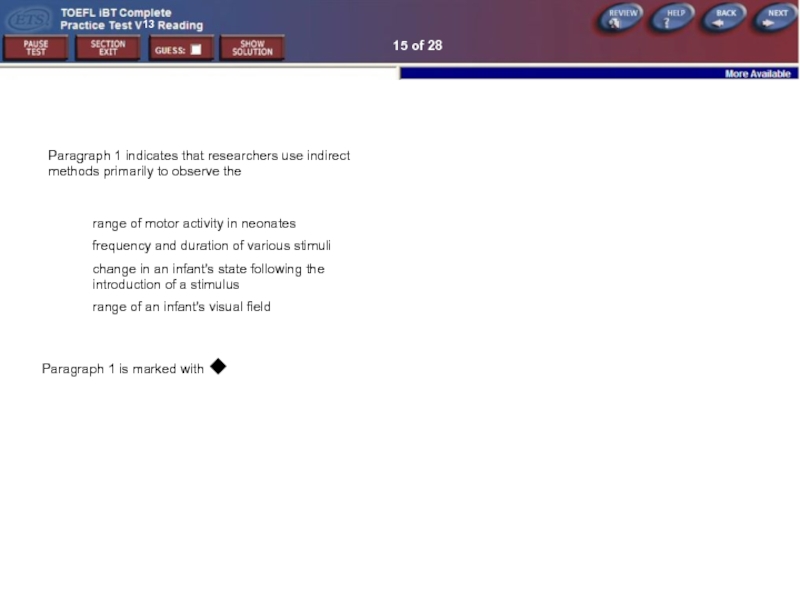
15 of 28
Paragraph 1 indicates that researchers use indirect methods primarily
range of motor activity in neonates
frequency and duration of various stimuli
change in an infant's state following the introduction of a stimulus
range of an infant's visual field
Paragraph 1 is marked with ◆
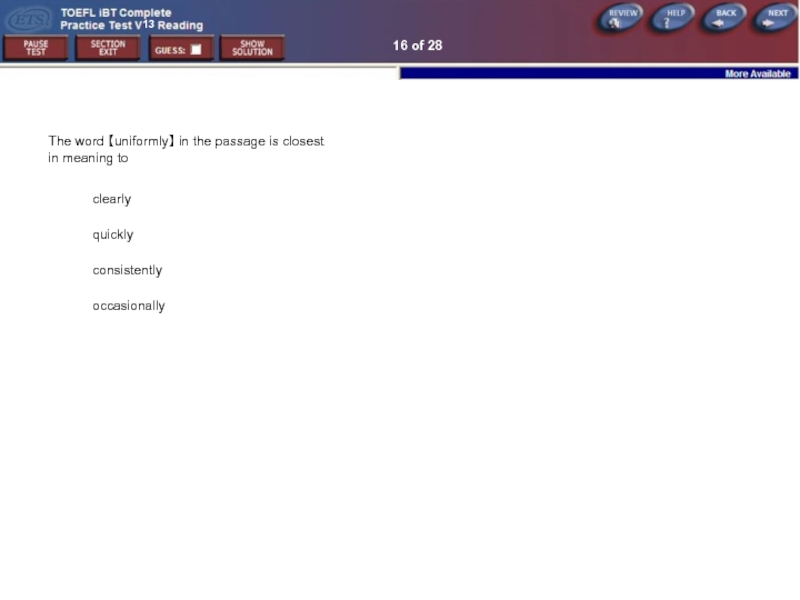
Слайд 2016 of 28
The word 【uniformly】 in the passage is closest in
clearly
quickly
consistently
occasionally
Слайд 21
17 of 28
Why does the author mention 【repetitive following movements of
To identify a response that indicates a neonate's perception of a stimulus
To explain why a neonate is capable of responding to stimuli only through repetitive movements
To argue that motor activity in a neonate may be random and unrelated to stimuli
To emphasize that responses to stimuli vary in infants according to age
Слайд 22
18 of 28
Which of the following is NOT mentioned in paragraph
It is impossible to be certain of the actual cause of an infant's response.
Infants' responses, which occur quickly and diffusely, are often difficult to measure.
Infants do not respond well to stimuli presented in an unnatural laboratory setting.
It may be difficult for observers to agree on the presence or the degree of a response.
Paragraph 2 is marked with ◆
Слайд 23
19 of 28
The word 【potent】 in the passage is closest in
artificial
powerful
common
similar
Слайд 24
20 of 28
Which of the sentences below best expresses the essential
Researchers using observational assessment techniques on infants must not overgeneralize and must base their conclusions on data from many studies.
On the basis of the data from one or two studies, it seems that some infants develop a particular perceptual ability not observed in others.
To use data from one or two studies on infant's perceptual abilities, it is necessary to use techniques that will provide conclusive evidence.
When researchers fail to make generalizations from their studies, their observed data is often inconclusive.
Слайд 25
21 of 28
What is the author's primary purpose in paragraph 3?
To
To describe new techniques for observing infant perception that overcome problems identified in the previous paragraph
To present and evaluate the conclusions of various studies on infant perception
To point out the strengths and weaknesses of three new methods for quantifying an infant's reaction to stimuli
Paragraph 3 is marked with ◆
Слайд 26
22 of 28
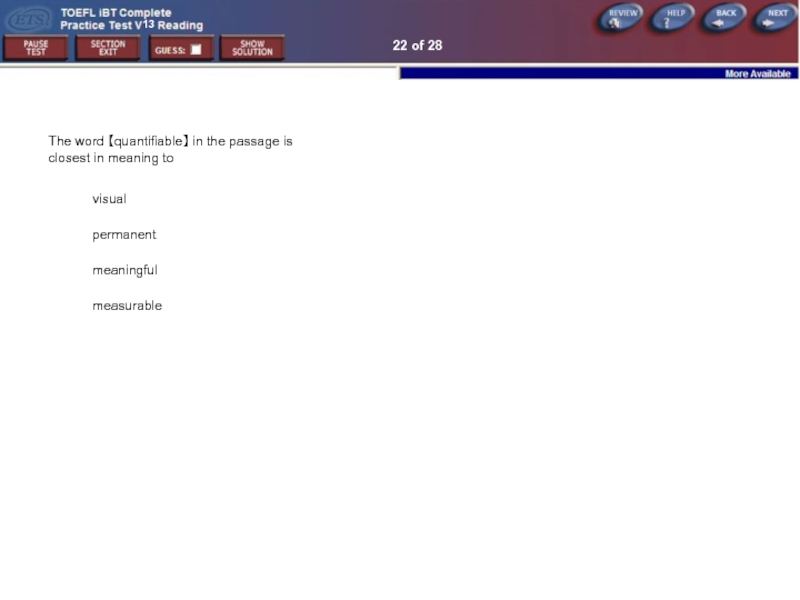
The word 【quantifiable】 in the passage is closest in
visual
permanent
meaningful
measurable
Слайд 27
23 of 28
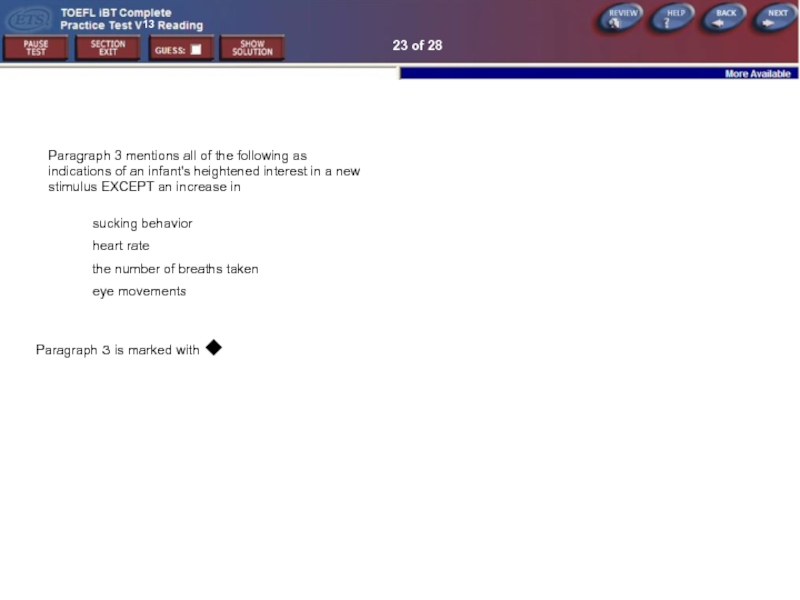
Paragraph 3 mentions all of the following as indications
sucking behavior
heart rate
the number of breaths taken
eye movements
Paragraph 3 is marked with ◆
Слайд 28
24 of 28
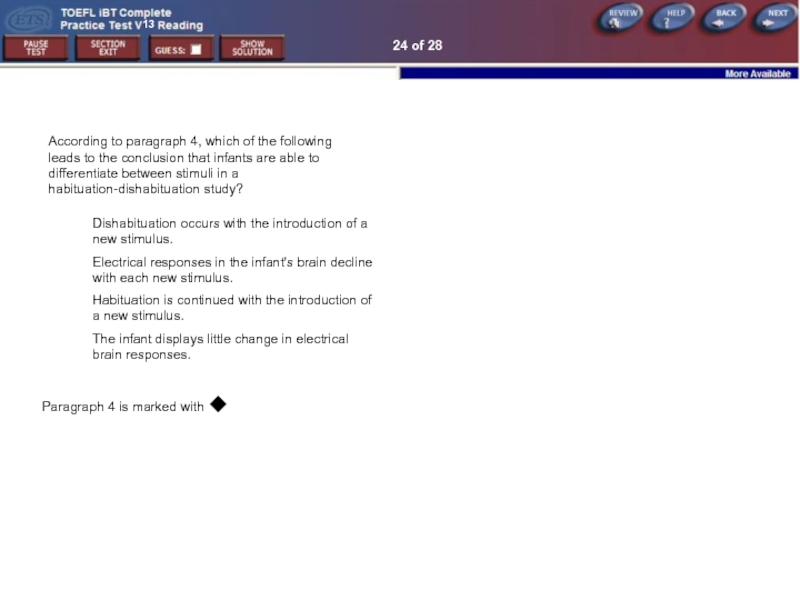
According to paragraph 4, which of the following leads
Dishabituation occurs with the introduction of a new stimulus.
Electrical responses in the infant's brain decline with each new stimulus.
Habituation is continued with the introduction of a new stimulus.
The infant displays little change in electrical brain responses.
Paragraph 4 is marked with ◆
Слайд 29
25 of 28
In paragraph 4, what does the author suggest about
An infant's potential to respond to a stimulus may be related to the size of its brain.
Changes in the electrical patterns of an infant's brain are difficult to detect.
Different areas of an infant's brain respond to different types of stimuli.
An infant is unable to perceive more than one stimulus at a time.
Paragraph 4 is marked with ◆
Слайд 30
26 of 28
Paragraph 5 indicates that researchers who used the techniques
infants find it difficult to perceive some types of stimuli
neonates of only a few days cannot yet discriminate between stimuli
observational assessment is less useful for studying infant perception than researchers previously believed
a neonate is able to perceive stimuli better than researchers once thought
Paragraph 5 is marked with ◆
Слайд 31
27 of 28
Look at the four squares [■]that indicate where the
The repetition allows researchers to observe the infant's behavior until they reach agreement about the presence and the degree of the infant's response.
Where would the sentence best fit?
■ 1
■ 2
■ 3
■ 4
Слайд 32
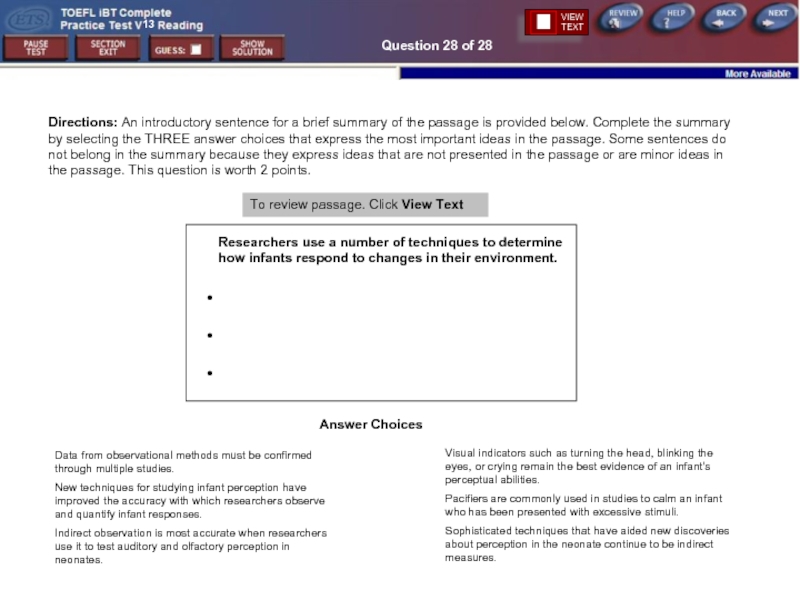
Question 28 of 28
Directions: An introductory sentence for a brief summary
To review passage. Click View Text
Researchers use a number of techniques to determine how infants respond to changes in their environment.
●
●
●
Answer Choices
Data from observational methods must be confirmed through multiple studies.
New techniques for studying infant perception have improved the accuracy with which researchers observe and quantify infant responses.
Indirect observation is most accurate when researchers use it to test auditory and olfactory perception in neonates.
Visual indicators such as turning the head, blinking the eyes, or crying remain the best evidence of an infant's perceptual abilities.
Pacifiers are commonly used in studies to calm an infant who has been presented with excessive stimuli.
Sophisticated techniques that have aided new discoveries about perception in the neonate continue to be indirect measures.
Слайд 34Congratulations!
You have completed this practice test.
Save / exit the test
Review
Obtain answer keys
Слайд 36Are you sure you want to exit the test?
YES
NO
Exit the test.
Return to the last question and resume doing the test.
Слайд 37Your answers will be saved with the file.
Your answers will
Do you want to save your answers?
YES
NO



![Look at the four squares [■]that indicate where the following sentence could be added to](/img/tmb/3/246450/0701ef5512d79f814c108ea67243fea9-800x.jpg)




![27 of 28Look at the four squares [■]that indicate where the following sentence could be](/img/tmb/3/246450/5e2c82f8293aaabba64817daa9fb9f2b-800x.jpg)