- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Evolution: Artificial Selection презентация
Содержание
- 1. Evolution: Artificial Selection
- 4. Terminology
- 8. Non-Random Mating – small population have less
- 9. Hybridization is the process of crossing
- 10. Steps of Artificial Selection 1. Humans decide
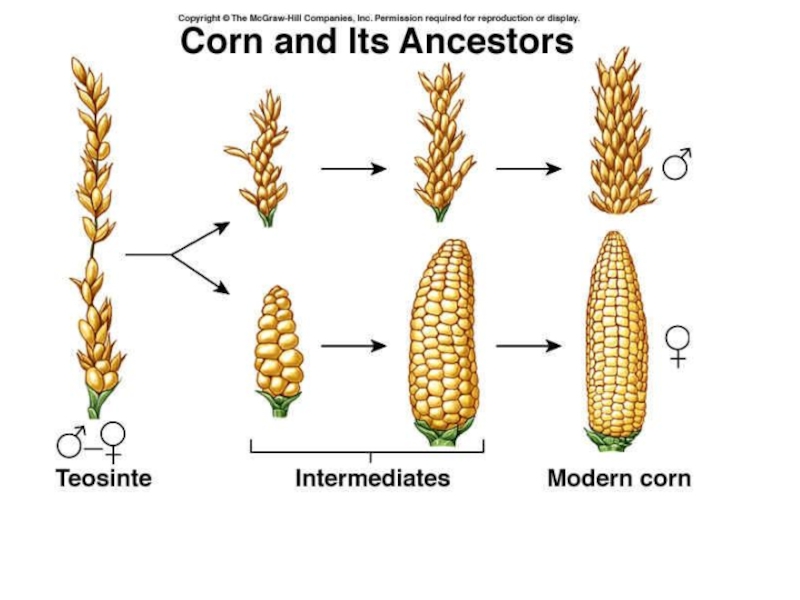
- 11. The evolution of corn by Artificial Selection
- 13. Artificial Selection – hybrid Banana’s that have
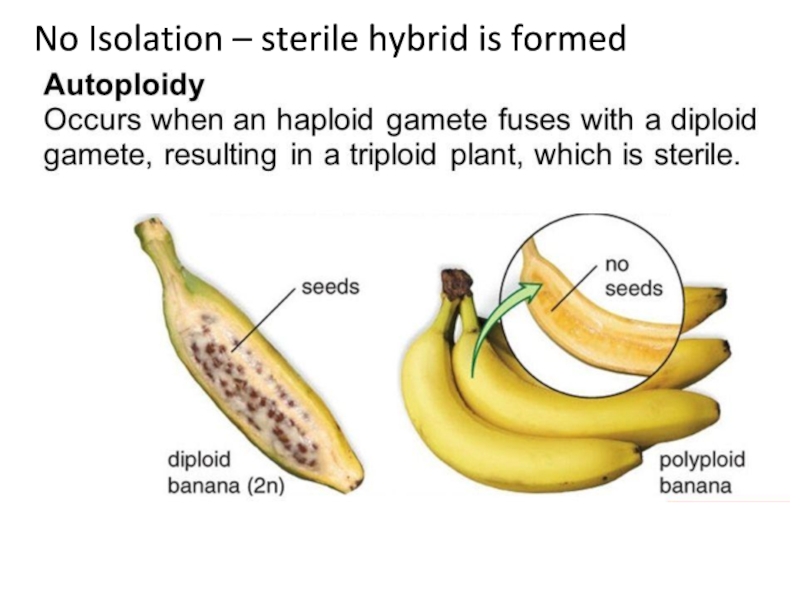
- 14. No Isolation – sterile hybrid is formed
- 15. These were all created by Artificial Selection
- 17. Artificial
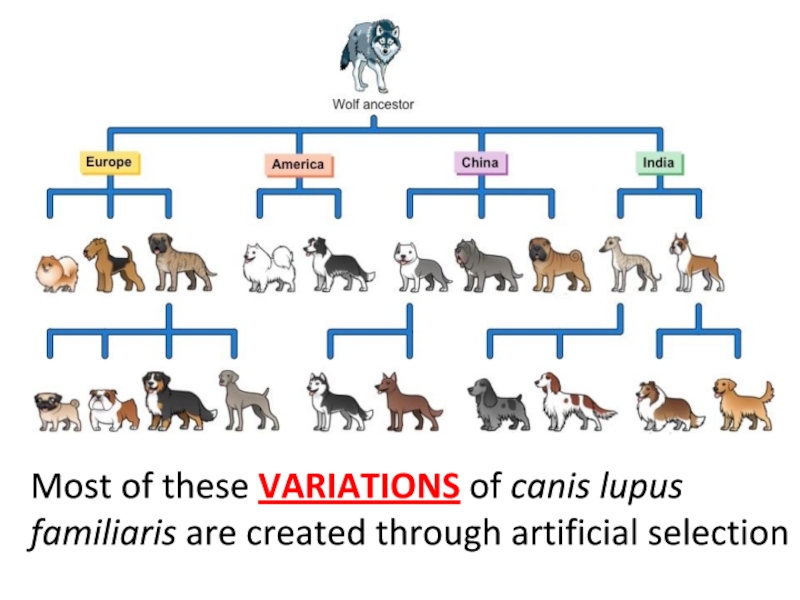
- 18. Most of these VARIATIONS of canis lupus familiaris are created through artificial selection
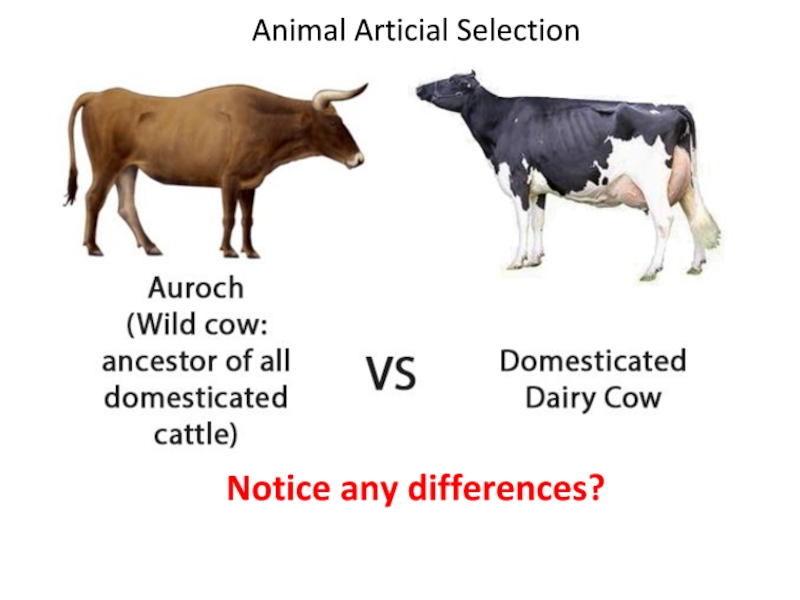
- 19. Notice any differences? Animal Articial Selection
- 21. Belgian Blue cattle ... they have a
- 22. 1. How as artificial selection improved these
- 23. What trait was artificially selected for in this cow?
- 24. Success Criteria 1. Define hybrid, inbreeding and
- 25. Choose One to Investigate Crop Plants Wheat
- 26. Make 1-2 slide presentation that clearly
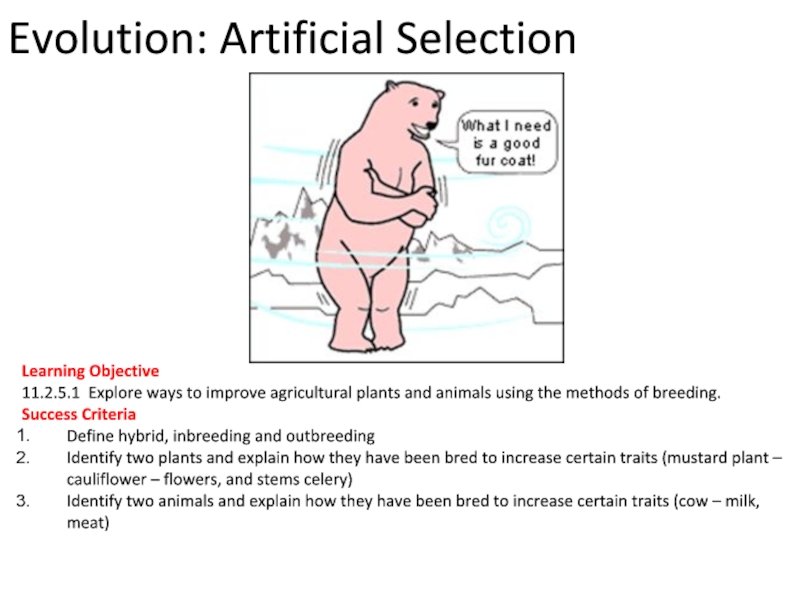
Слайд 1Evolution: Artificial Selection
Learning Objective
11.2.5.1 Explore ways to improve agricultural plants and
Success Criteria
Define hybrid, inbreeding and outbreeding
Identify two plants and explain how they have been bred to increase certain traits (mustard plant – cauliflower – flowers, and stems celery)
Identify two animals and explain how they have been bred to increase certain traits (cow – milk, meat)
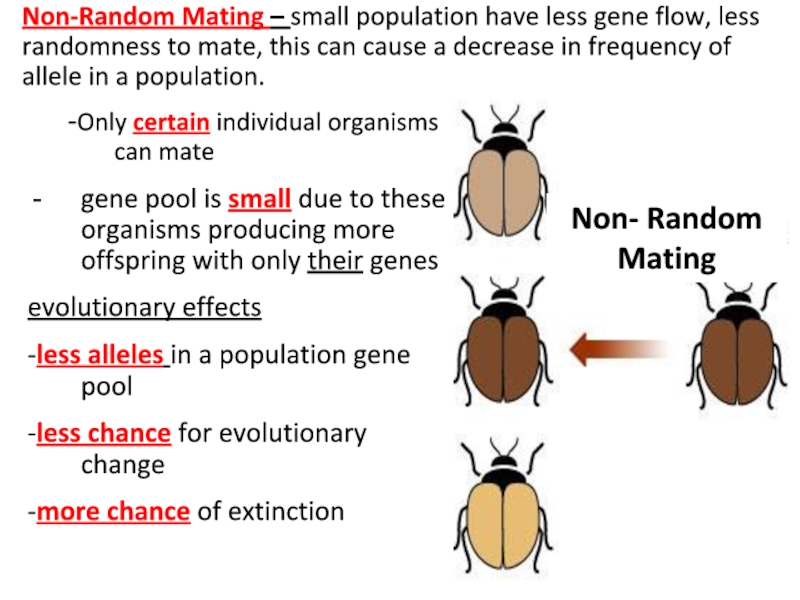
Слайд 8Non-Random Mating – small population have less gene flow, less randomness
Random
Mating
Non- Random
Mating
-Only certain individual organisms can mate
gene pool is small due to these organisms producing more offspring with only their genes
evolutionary effects
-less alleles in a population gene pool
-less chance for evolutionary change
-more chance of extinction
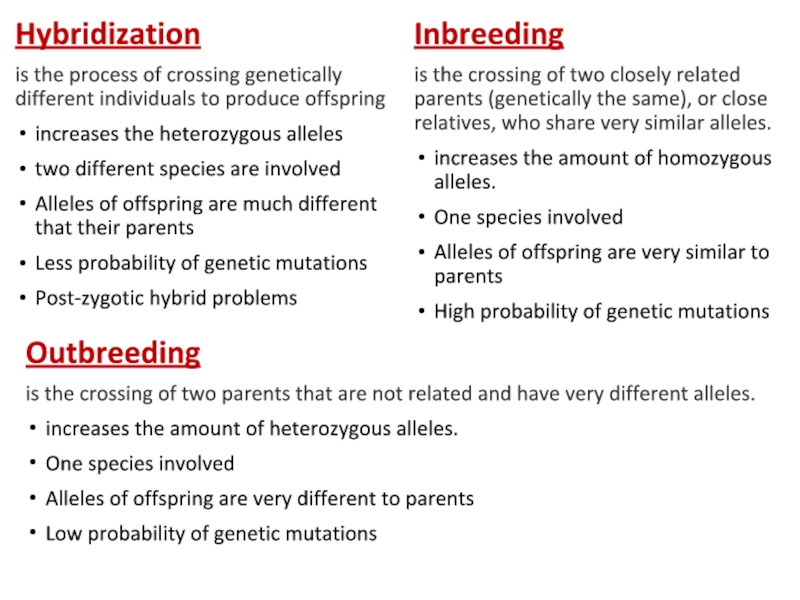
Слайд 9Hybridization
is the process of crossing genetically different individuals to produce
increases the heterozygous alleles
two different species are involved
Alleles of offspring are much different that their parents
Less probability of genetic mutations
Post-zygotic hybrid problems
Inbreeding
is the crossing of two closely related parents (genetically the same), or close relatives, who share very similar alleles.
increases the amount of homozygous alleles.
One species involved
Alleles of offspring are very similar to parents
High probability of genetic mutations
Outbreeding
is the crossing of two parents that are not related and have very different alleles.
increases the amount of heterozygous alleles.
One species involved
Alleles of offspring are very different to parents
Low probability of genetic mutations
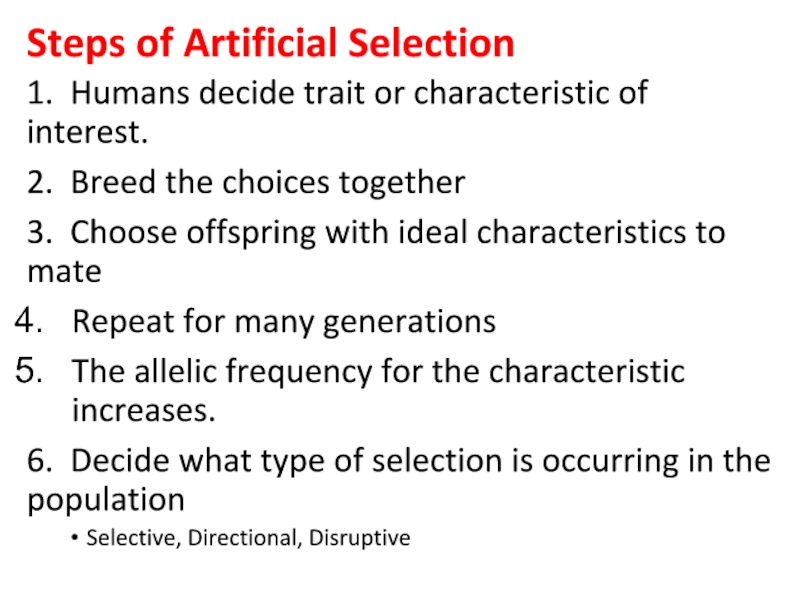
Слайд 10Steps of Artificial Selection
1. Humans decide trait or characteristic of interest.
2.
3. Choose offspring with ideal characteristics to mate
Repeat for many generations
The allelic frequency for the characteristic increases.
6. Decide what type of selection is occurring in the population
Selective, Directional, Disruptive
Слайд 13Artificial Selection – hybrid Banana’s that have been bred until they
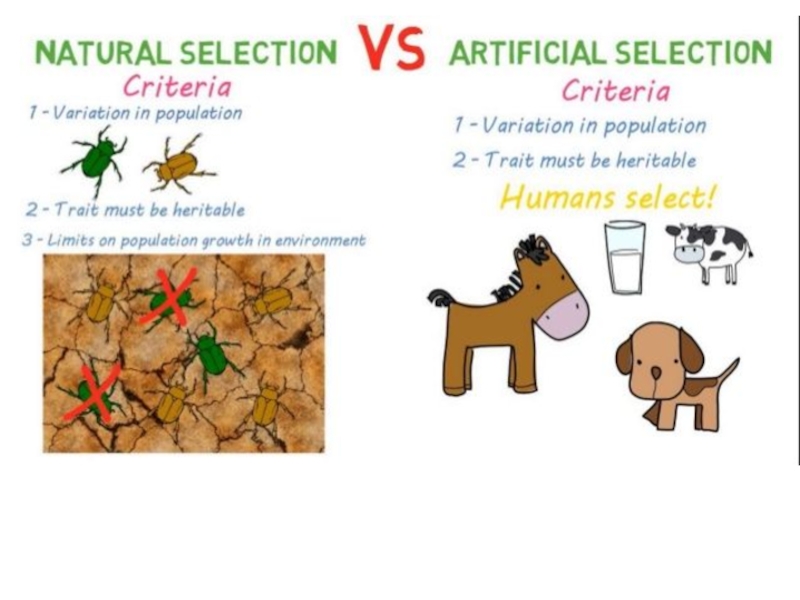
In contrast to natural selection artificial selection is intentional breeding or organisms for certain favorable traits, or combination of traits.
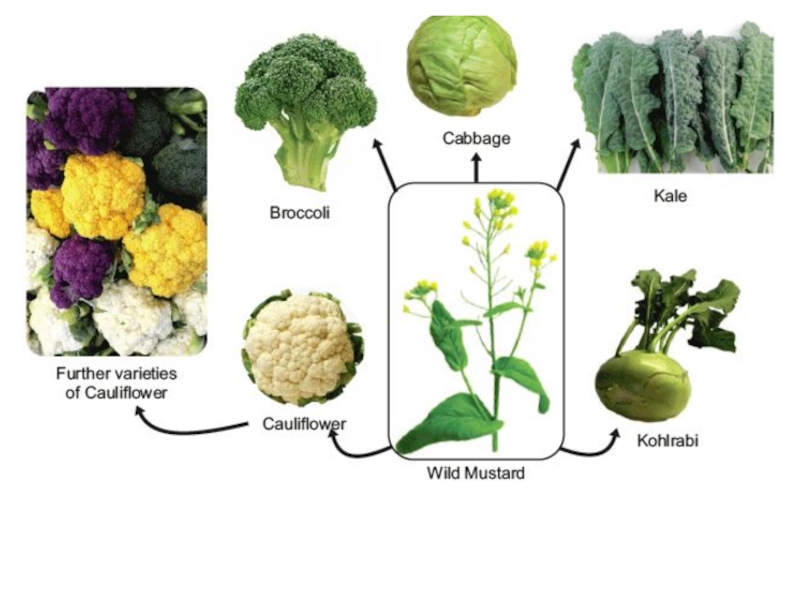
Слайд 15These were all created by Artificial Selection
From this plant.
Wild mustard
Sinapis
HOW?
Слайд 17 Artificial
In contrast to natural selection this is the
intentional breeding or organisms for certain favorable traits, or ombination of traits.
Broccoli: Flower development is suppressed
Cauliflower: flowers are sterile
Cabbage: selection for the terminal bud (head only forms)
Kale: selection is for leaves only
Undomesticated
banana-lots of seeds compared
to artificially
selected with little to no seeds
Слайд 21Belgian Blue cattle ... they have a mutation that creates twice
Слайд 221. How as artificial selection improved these cows?
Is it an
Reproductive success?
Слайд 24Success Criteria
1. Define hybrid, inbreeding and outbreeding
2. Identify two plants
3. Identify two animals and explain how they have been bred to increase certain traits (cow – milk, meat)
Слайд 25Choose One to Investigate
Crop Plants
Wheat
Millet
Carrots
Potatoes
Broccoli
Animals
Horses
Sheep
Goats
Cattle
Dogs
Cats
11.2.5.1
Слайд 26Make 1-2 slide presentation that clearly investigates artificial selection
Criteria
√ Name the trait that was selected.
√ Tell why the trait was selected
√ Clear use of terminology explaining the mechanism.
√ Picture of before artificial selection and after artificial selection.
√ Work shows understanding of differences between the two types of artificial selection.
You are investigating inbreeding and hybrids as method of artificial selection, not genetic engineering or Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO)