- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Using Infrastructure Services презентация
Содержание
- 1. Using Infrastructure Services
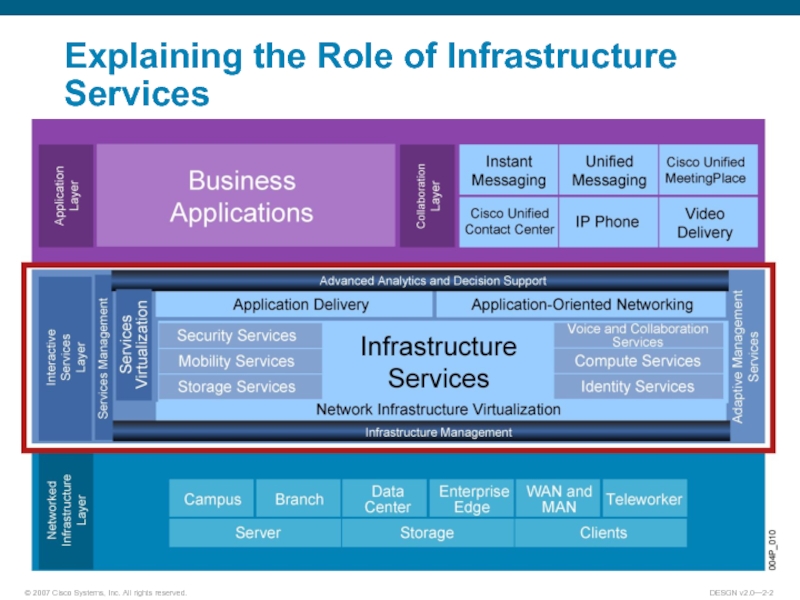
- 2. Explaining the Role of Infrastructure Services
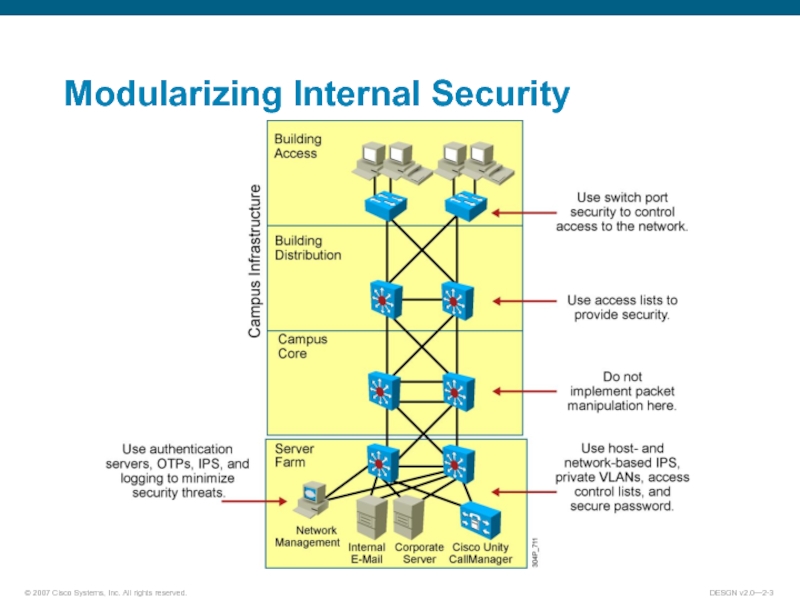
- 3. Modularizing Internal Security
- 4. Reasons for Internal Security The enterprise campus
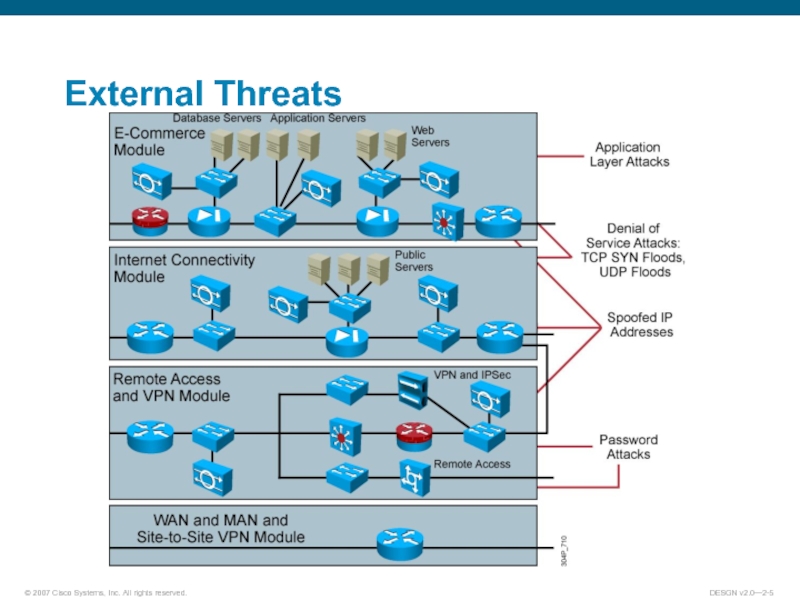
- 5. External Threats
- 6. Designing High Availability Analyze the business and
- 7. Designing Route Redundancy Design redundant routes: Minimize
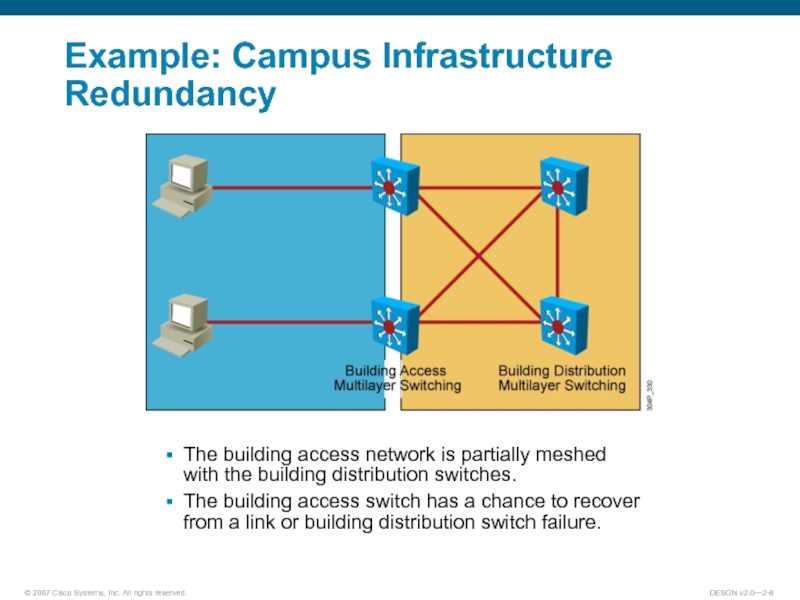
- 8. Example: Campus Infrastructure Redundancy The building access
- 9. Example: Enterprise Edge Redundancy The remote site
- 10. High Availability in the Server Farm Module
- 11. Example: Attachment Through a Redundant Transceiver Transceiver
- 12. Example: Attachment Through a Redundant NIC
- 13. Voice Transport Overview Two implementations: Voice over
- 14. IP Telephony Components
- 15. Modular Approach in Voice Network Design
- 16. Example: Voice Network Solution
- 17. Evaluating the Existing Data Infrastructure for Voice
- 18. Wireless LAN Overview Supports connecting mobile clients
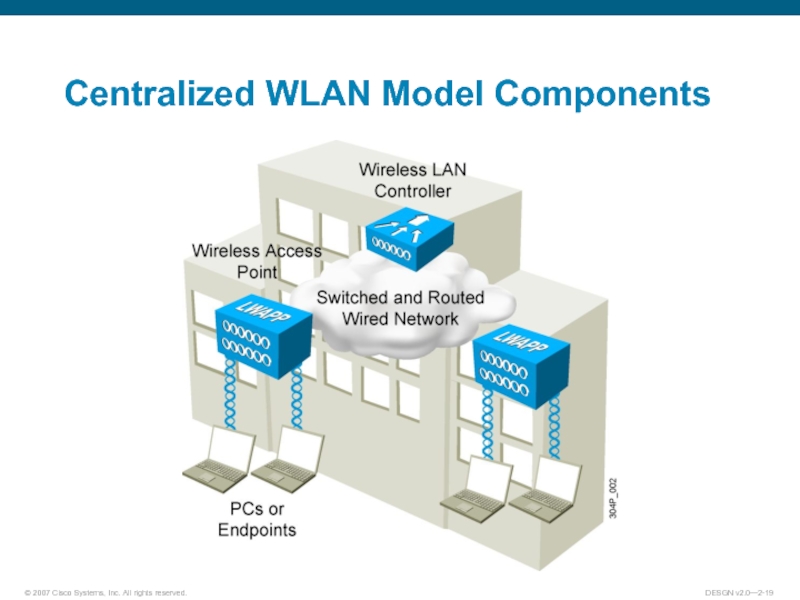
- 19. Centralized WLAN Model Components
- 20. Application Networking Services Introduction Traditional networks handled
- 21. ANS Can Resolve Application Issues Wide-area application
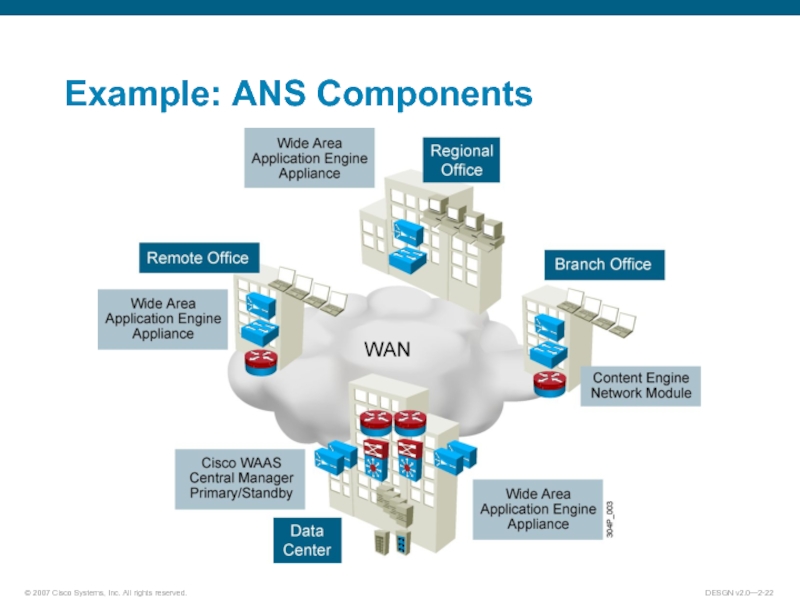
- 22. Example: ANS Components
- 23. Summary Network infrastructure services add intelligence to
- 24. Summary (Cont.) Voice infrastructure services throughout the
Слайд 4Reasons for Internal Security
The enterprise campus is protected by security functions
in the enterprise edge:
If the enterprise edge security fails, the unprotected enterprise campus is vulnerable.
The potential attacker can gain physical access to the enterprise campus.
Some network solutions require indirect external access to the enterprise campus.
All vital elements in the enterprise campus must be protected independently.
If the enterprise edge security fails, the unprotected enterprise campus is vulnerable.
The potential attacker can gain physical access to the enterprise campus.
Some network solutions require indirect external access to the enterprise campus.
All vital elements in the enterprise campus must be protected independently.
Слайд 6Designing High Availability
Analyze the business and technical goals.
Identify critical applications, systems,
internetworking devices, and links.
Document the trade-offs between redundancy and cost and simplicity versus complexity.
Duplicate any component whose failure could disable critical applications.
Duplicate vital links and connect them to different devices.
Document the trade-offs between redundancy and cost and simplicity versus complexity.
Duplicate any component whose failure could disable critical applications.
Duplicate vital links and connect them to different devices.
Слайд 7Designing Route Redundancy
Design redundant routes:
Minimize the effect of link failures.
Minimize
the effect of an internetworking device failure.
Make the connection redundant:
Parallel physical links between switches and routers
Backup LAN and WAN links
Make the network redundant:
Full mesh to provide complete redundancy and good performance
Partial mesh, which is cheaper and more scalable
Make the connection redundant:
Parallel physical links between switches and routers
Backup LAN and WAN links
Make the network redundant:
Full mesh to provide complete redundancy and good performance
Partial mesh, which is cheaper and more scalable
Слайд 8Example: Campus Infrastructure Redundancy
The building access network is partially meshed
with
the building distribution switches.
The building access switch has a chance to recover from a link or building distribution switch failure.
The building access switch has a chance to recover from a link or building distribution switch failure.
Слайд 9Example: Enterprise Edge Redundancy
The remote site establishes a backup connection
via
an IPsec tunnel across the Internet.
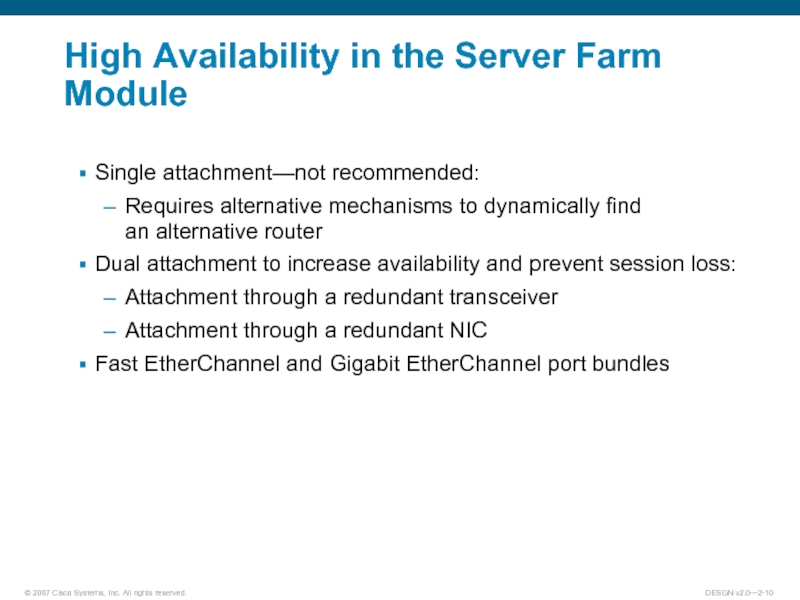
Слайд 10High Availability in the Server Farm Module
Single attachment—not recommended:
Requires alternative mechanisms
to dynamically find
an alternative router
Dual attachment to increase availability and prevent session loss:
Attachment through a redundant transceiver
Attachment through a redundant NIC
Fast EtherChannel and Gigabit EtherChannel port bundles
Dual attachment to increase availability and prevent session loss:
Attachment through a redundant transceiver
Attachment through a redundant NIC
Fast EtherChannel and Gigabit EtherChannel port bundles
Слайд 11Example: Attachment Through a Redundant Transceiver
Transceiver activates backup link on primary
link failure.
Transceiver cannot detect failures beyond physical link.
Transceiver cannot detect failures beyond physical link.
Слайд 12Example: Attachment Through a
Redundant NIC
Device driver presents two NIC cards
as a single logical interface.
This setup uses one MAC address on both interfaces.
Backup card is activated when the primary link is gone.
This setup uses one MAC address on both interfaces.
Backup card is activated when the primary link is gone.
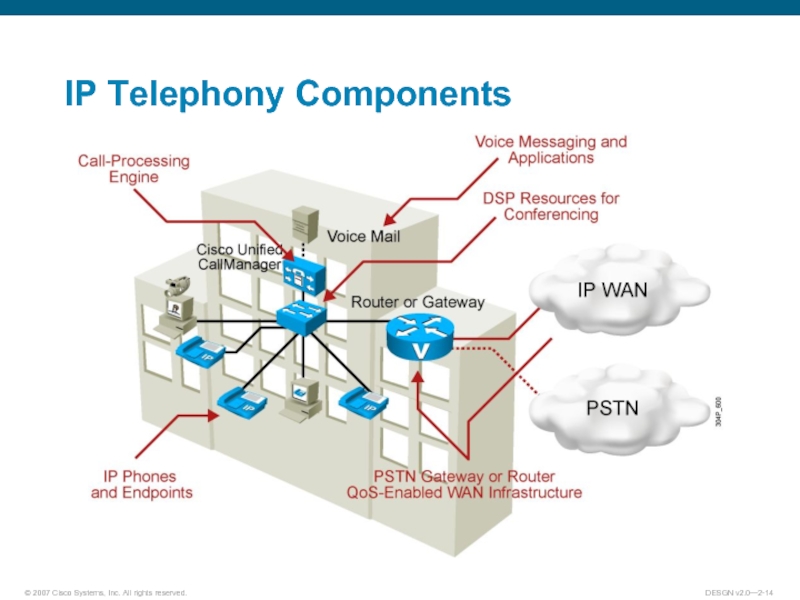
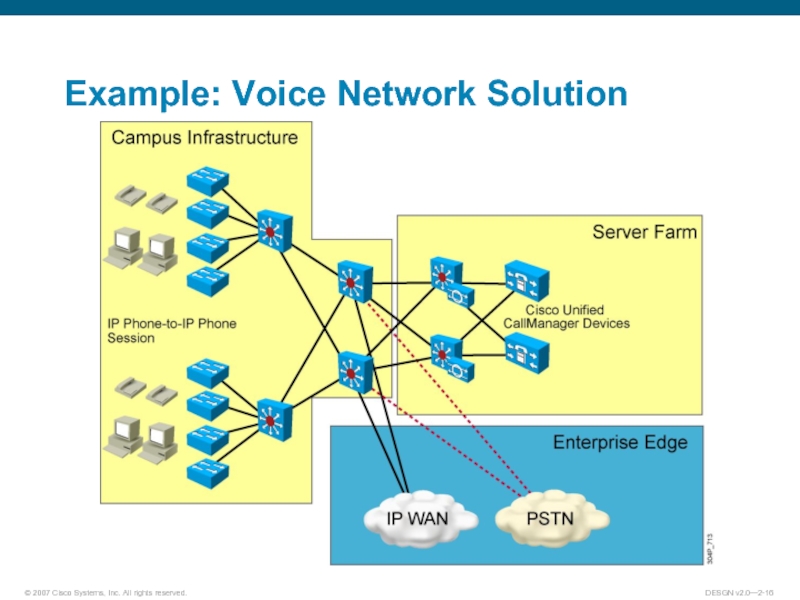
Слайд 13Voice Transport Overview
Two implementations:
Voice over IP: Uses analog phones. Transports voice
packets over the IP network using voice-enabled routers.
IP telephony: Implements voice in the network using Cisco Unified CallManager and IP phones.
Both implementations require properly designed networks.
All modules of the enterprise network are involved in the voice network solution.
IP telephony: Implements voice in the network using Cisco Unified CallManager and IP phones.
Both implementations require properly designed networks.
All modules of the enterprise network are involved in the voice network solution.
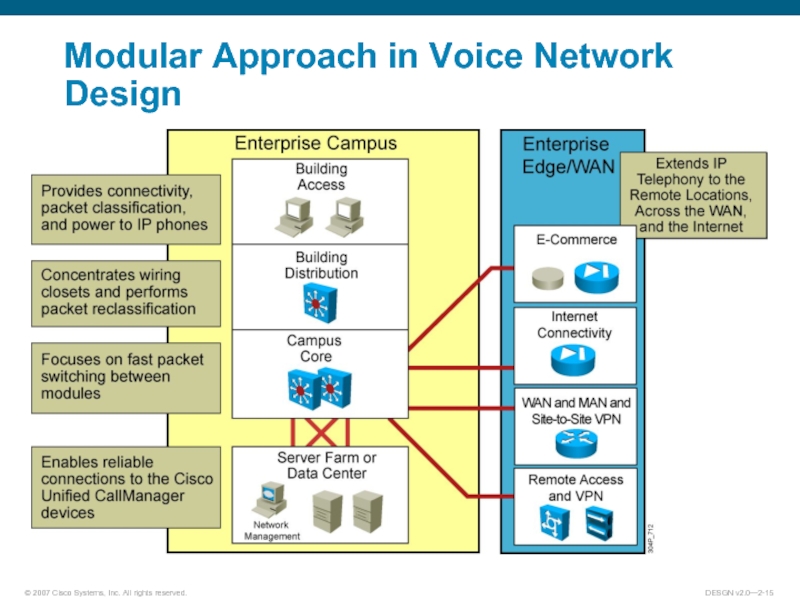
Слайд 17Evaluating the Existing Data Infrastructure for Voice Design
Document and evaluate
the existing data infrastructure
in each enterprise network module in terms of:
New voice performance requirements
Availability requirements
Feature requirements
Potential network capacity or impact
New voice performance requirements
Availability requirements
Feature requirements
Potential network capacity or impact
Слайд 18Wireless LAN Overview
Supports connecting mobile clients to the enterprise network
Transports packets
over radio waves
Has connectivity and privacy issues not found in wired networks
Can have implications for all modules of the enterprise network
Has connectivity and privacy issues not found in wired networks
Can have implications for all modules of the enterprise network
Слайд 20Application Networking Services Introduction
Traditional networks handled static web pages,
e-mail, and
routine client-server applications.
Applications are evolving into complex and highly visible services.
Application deployment issues are emerging.
Consolidation of data centers can result in lower productivity for remote users.
A web-based ordering system may suffer because of poor responsiveness.
Business partners may need immediate and secure electronic access to back-office applications.
A purchasing application may need to track large orders.
Applications are evolving into complex and highly visible services.
Application deployment issues are emerging.
Consolidation of data centers can result in lower productivity for remote users.
A web-based ordering system may suffer because of poor responsiveness.
Business partners may need immediate and secure electronic access to back-office applications.
A purchasing application may need to track large orders.
Слайд 21ANS Can Resolve Application Issues
Wide-area application services can compress, cache,
and
optimize content.
Optimization of the web streams can reduce latency, suppress unnecessary reloading of web objects, and offload the web server.
Security and remote connectivity services can validate requests, route them appropriately, and encrypt and prioritize responses.
Application messaging services interpret purchase orders and log large orders according to business policy rules.
Optimization of the web streams can reduce latency, suppress unnecessary reloading of web objects, and offload the web server.
Security and remote connectivity services can validate requests, route them appropriately, and encrypt and prioritize responses.
Application messaging services interpret purchase orders and log large orders according to business policy rules.
Слайд 23Summary
Network infrastructure services add intelligence to the network infrastructure, supporting application
awareness within the network.
Security is a network infrastructure service that increases the integrity of the network by protecting network resources and users from internal and external threats.
High-availability services protect the integrity of mission-critical information with networking platforms and topologies that offer a sufficient level of resiliency.
Security is a network infrastructure service that increases the integrity of the network by protecting network resources and users from internal and external threats.
High-availability services protect the integrity of mission-critical information with networking platforms and topologies that offer a sufficient level of resiliency.
Слайд 24Summary (Cont.)
Voice infrastructure services throughout the enterprise are needed to support
IP telephony.
Wireless services support mobile clients and integrate with the wired network.
Cisco ANS optimizes website performance, content delivery, and the security and connectivity of applications.
Wireless services support mobile clients and integrate with the wired network.
Cisco ANS optimizes website performance, content delivery, and the security and connectivity of applications.