CSI v2.1—14-
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
SAFE Wireless LAN Security in Depth презентация
Содержание
- 1. SAFE Wireless LAN Security in Depth
- 2. Wireless LAN Security Concepts © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 3. The Need for Wireless Standard 802.11-based WLANs
- 4. Types of Wireless Technology Functional view: Peer-to-peer
- 5. 802.11 Wireless Technology Wi-Fi Alliance provides a
- 6. WLAN Radio Frequency Methods The 802.11 standard
- 7. Wireless Security As standardized by
- 8. WLAN Components The following are WLAN components:
- 9. SAFE Wireless LAN Caveats and Design
- 10. Several WLAN technologies are not covered. SAFE
- 11. SAFE WLAN Design Considerations (Axioms) SAFE WLAN
- 12. SAFE WLAN Design Considerations (Axioms) (Cont.)
- 13. Wireless LAN Security Extensions © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 14. WLAN Networks Are Targets: Security
- 15. EAP Authentication Process Wireless Computer with
- 16. EAP Benefits EAP provides three significant benefits
- 17. EAPs Current EAP types include: Cisco LEAP EAP-TLS PEAP EAP-TTLS EAP-SIM
- 18. LEAP Authentication Process Wireless Computer with LEAP
- 19. EAP-TLS Authentication Process Wireless Computer with EAP-TLS
- 20. Wireless Computer with PEAP Supplicant Wireless Computer
- 21. WEP Enhancements IEEE 802.11i includes two encryption
- 22. Cisco Wireless LAN Product Portfolio ©
- 23. Cisco Aironet WLAN Product Line Wireless LAN
- 24. Cisco Aironet WLAN Product Line (Cont.) Wireless
- 25. Cisco Aironet WLAN Product Line (Cont.) Wireless
- 26. “Air”/RF Management L2 mobility L3 mobility (future)
- 27. Cost-effective and scalable Improved productivity
- 28. Wireless LAN Design Approach © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 29. WLAN Network Design Fundamentals The two
- 30. Access Point Security Standard WLAN Design
- 31. Standard Wireless LAN Design © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 32. Key devices are: Wireless client adapter and
- 33. Attack Mitigation Roles for Standard EAP WLAN
- 34. EAP with TKIP Design Guidelines Give special
- 35. Key devices are: Wireless client adapter and
- 36. Attack Mitigation Roles for Standard VPN WLAN
- 37. Standard VPN WLAN Design Guidelines Use VPN
- 38. Enterprise Wireless LAN Design © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 39. Enterprise Network: EAP with TKIP Option Wireless
- 40. Enterprise Network EAP with TKIP Option: Design
- 41. Enterprise Network: IPSec VPN Option Wireless Computer
- 42. Enterprise IPSec VPN Option: Design Guidelines Design
- 43. Medium Wireless LAN Design © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 44. Medium Network: EAP with TKIP Option DHCP/RADIUS/OTP/PKI/AP
- 45. Medium Network EAP with TKIP Option: Design
- 46. Medium Network: IPSec VPN Option DHCP/RADIUS/OTP/PKI/AP Management
- 47. Medium Network VPN WLAN Design: Alternative DHCP/RADIUS/OTP/PKI/AP
- 48. Small Wireless LAN Design © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 49. Small Network EAP WLAN Design To corporate
- 50. Small WLAN Network: Design Guidelines Guideline includes:
- 51. Remote Wireless LAN Design © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 52. Remote WLAN Design Two primary types of
- 53. Software VPN Remote Network WLAN
- 54. Hardware VPN Remote Network WLAN Design
- 55. SAFE WLAN Implementation © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
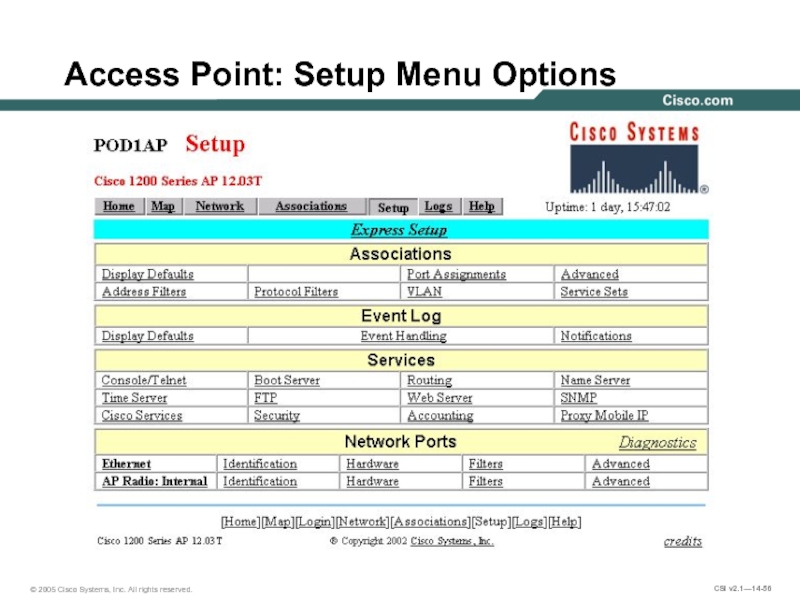
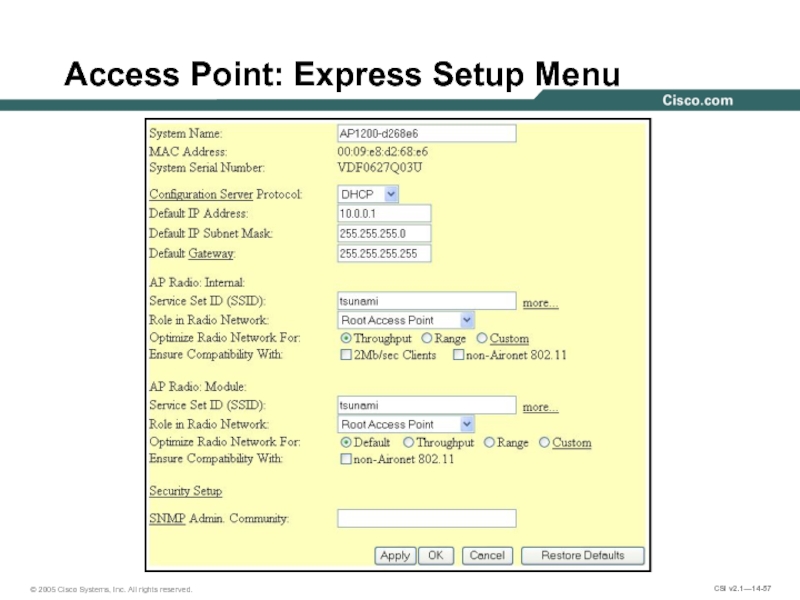
- 56. Access Point: Setup Menu Options
- 57. Access Point: Express Setup Menu
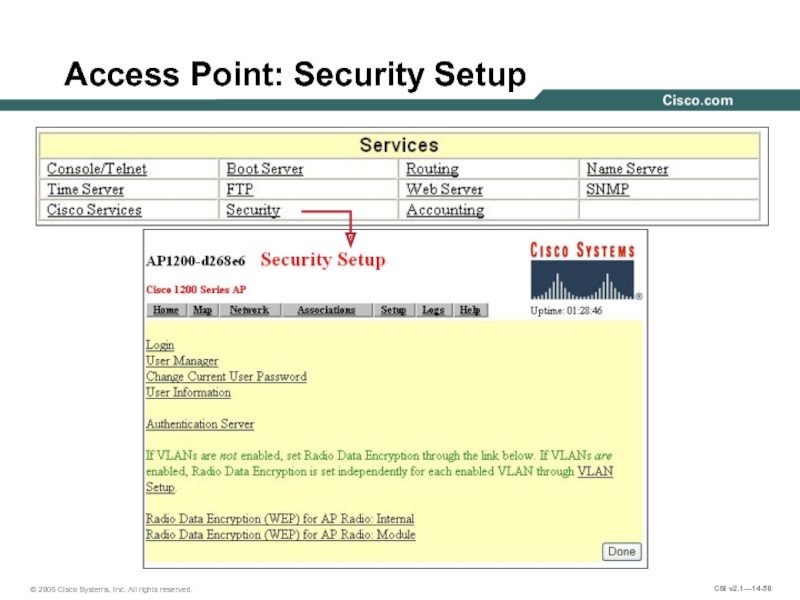
- 58. Access Point: Security Setup
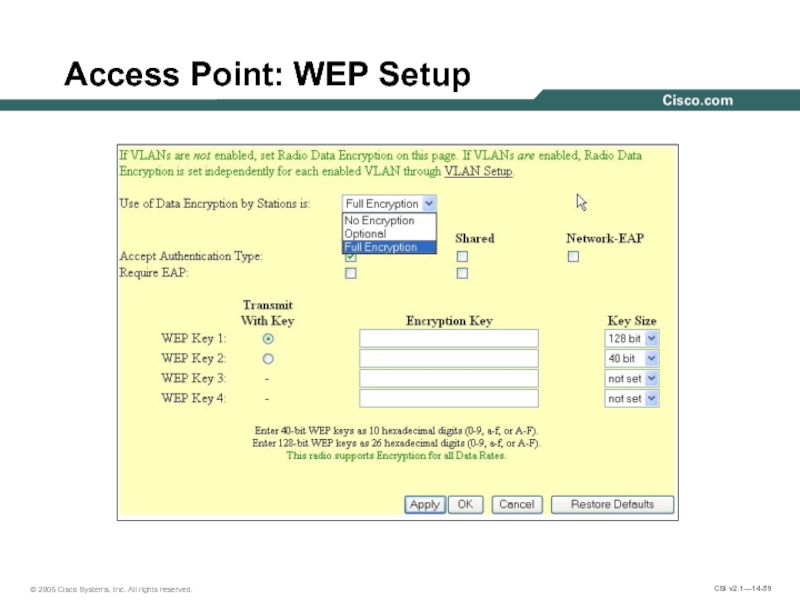
- 59. Access Point: WEP Setup
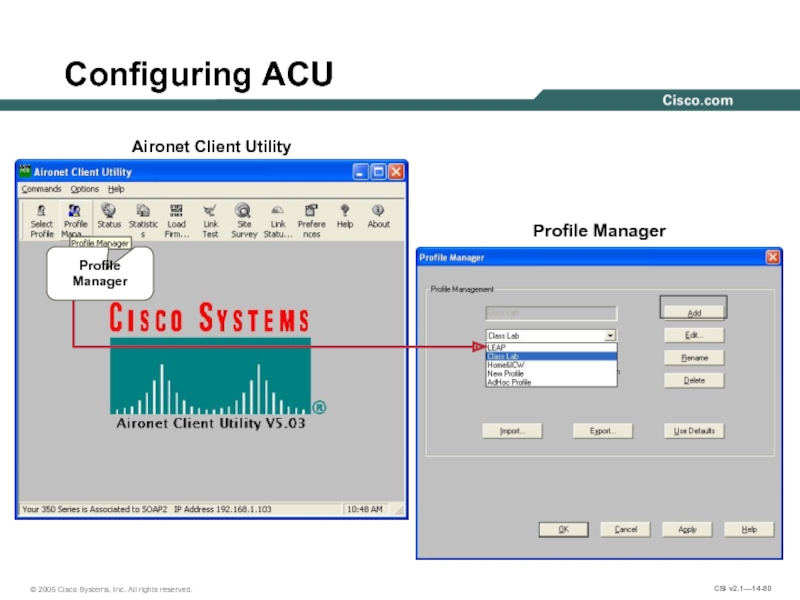
- 60. Configuring ACU Aironet Client Utility Profile Manager Profile Manager
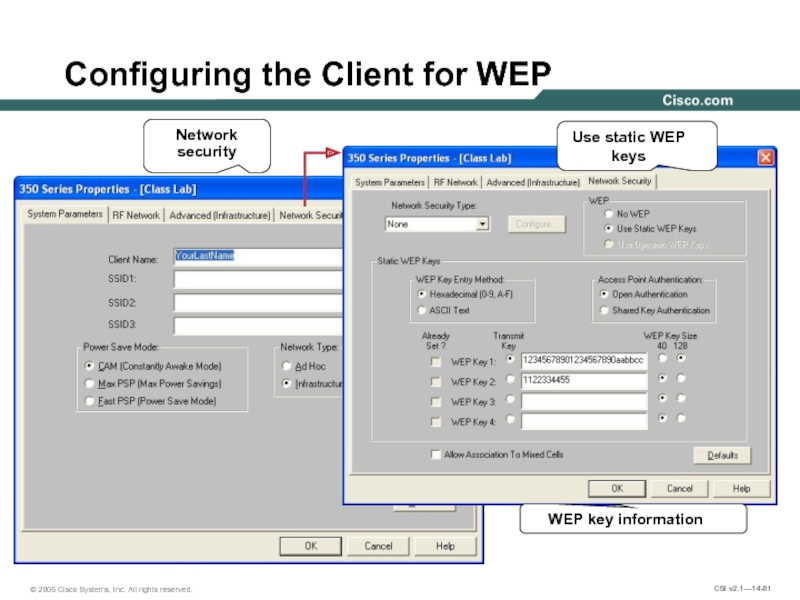
- 61. Configuring the Client for WEP Network security WEP key information Use static WEP keys
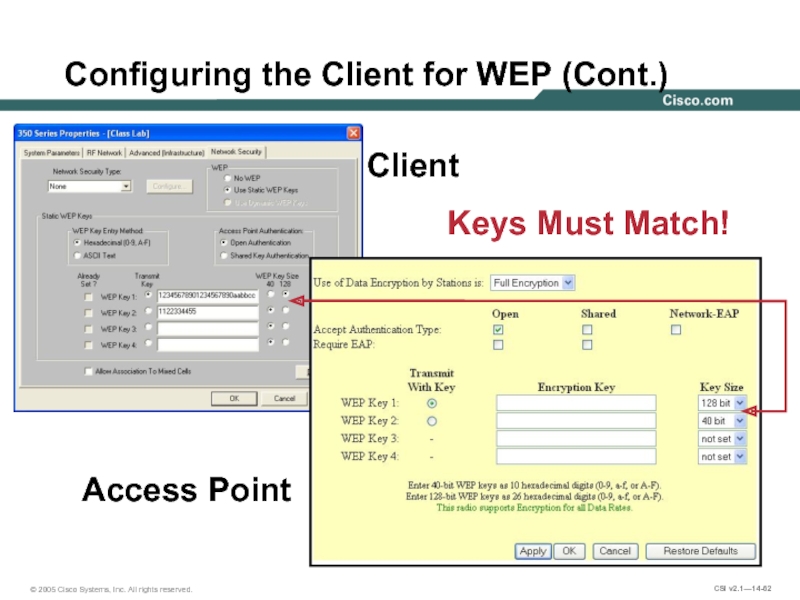
- 62. Configuring the Client for WEP (Cont.) Client Access Point Keys Must Match!
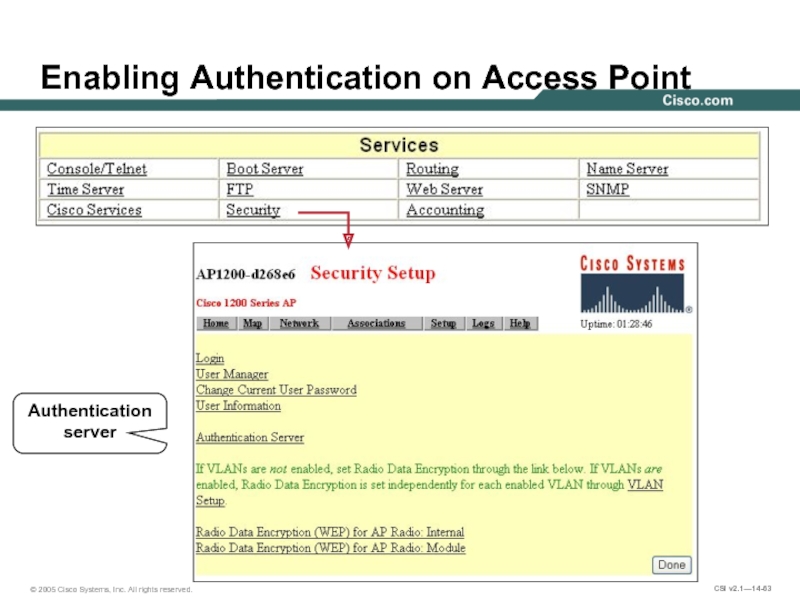
- 63. Enabling Authentication on Access Point Authentication server
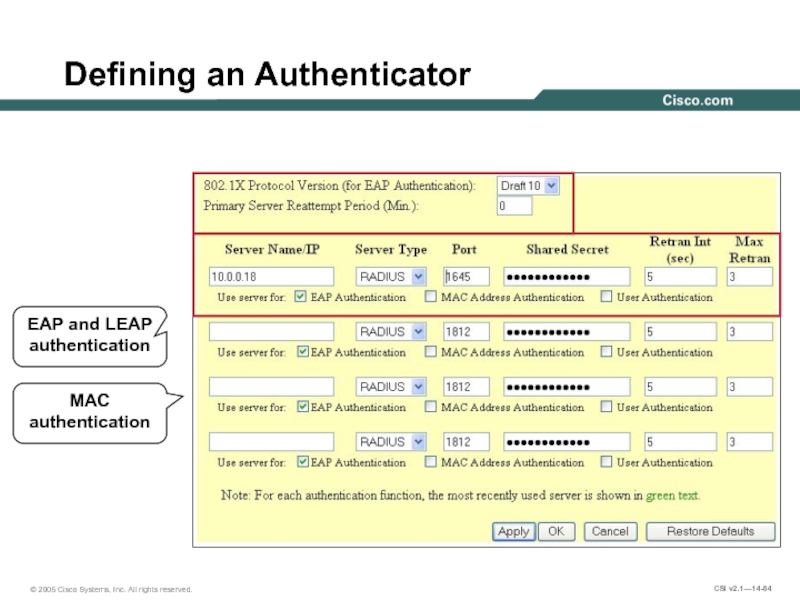
- 64. Defining an Authenticator EAP and LEAP authentication MAC authentication
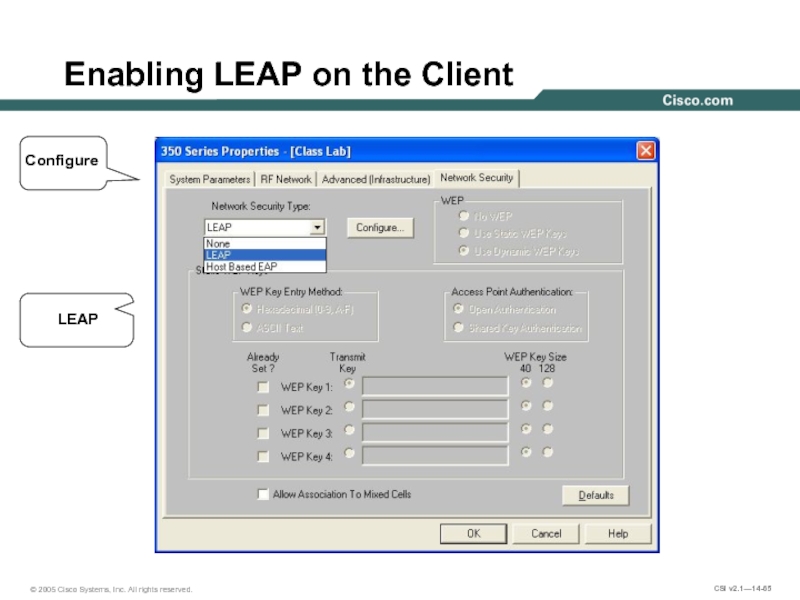
- 65. Enabling LEAP on the Client LEAP Configure
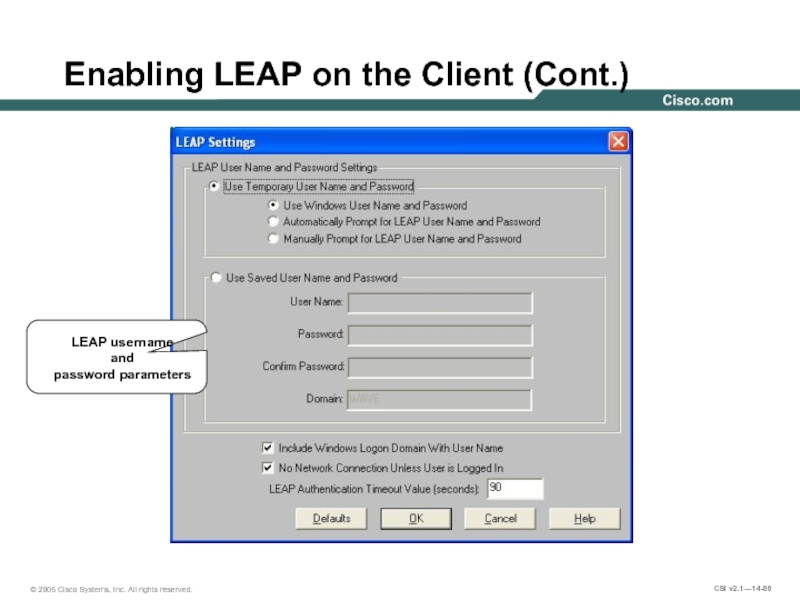
- 66. Enabling LEAP on the Client (Cont.) LEAP username and password parameters
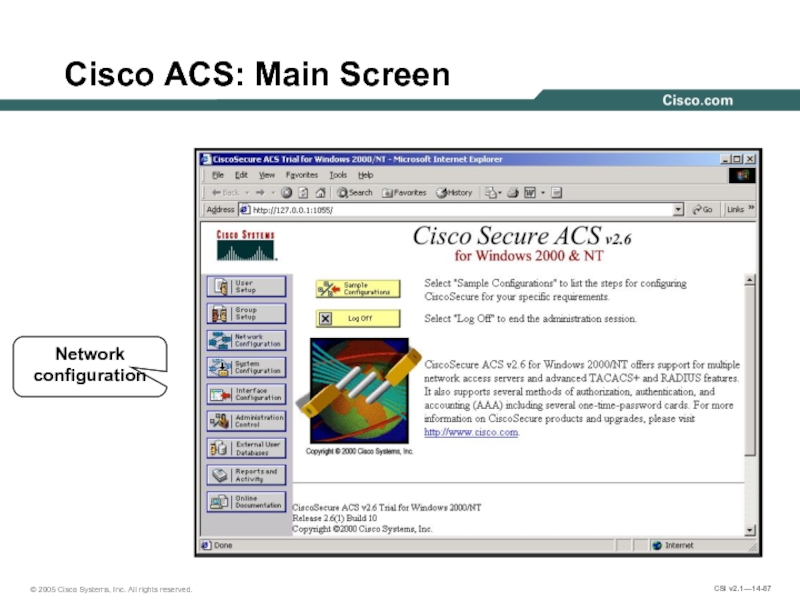
- 67. Cisco ACS: Main Screen Network configuration
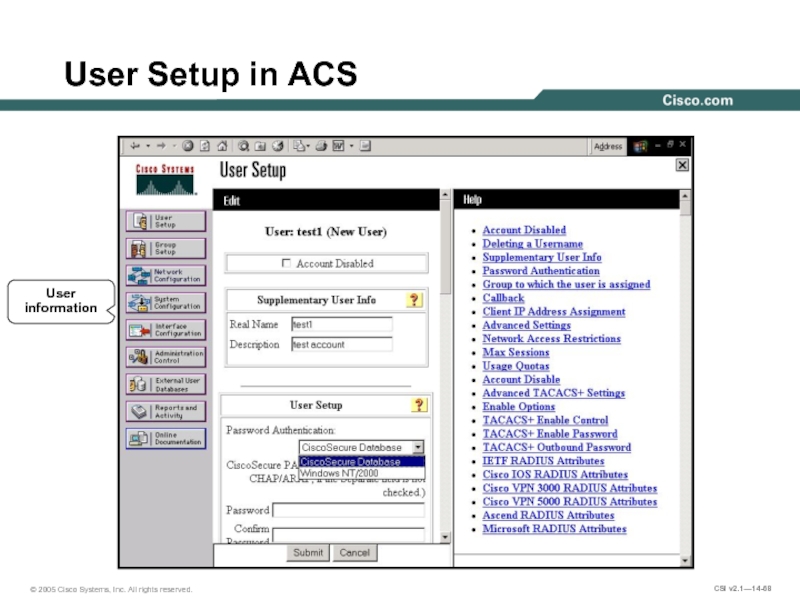
- 68. User Setup in ACS User information
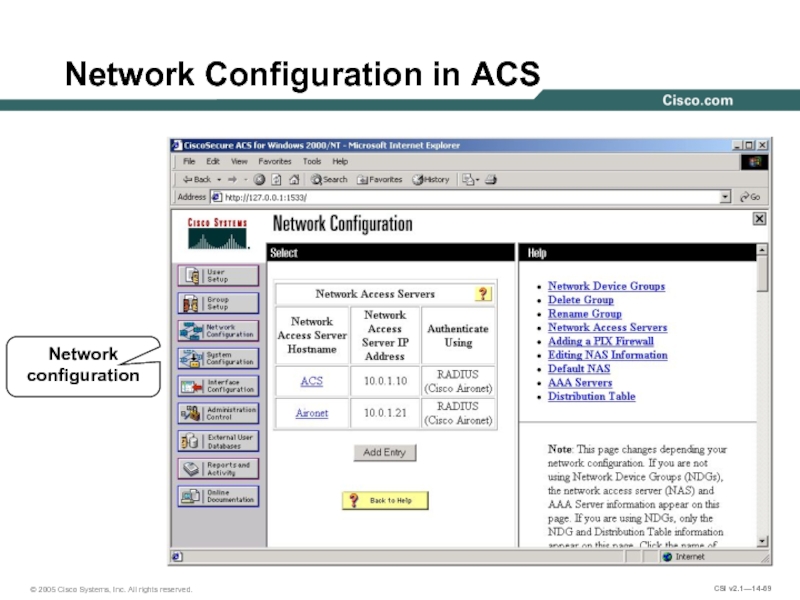
- 69. Network Configuration in ACS Network configuration
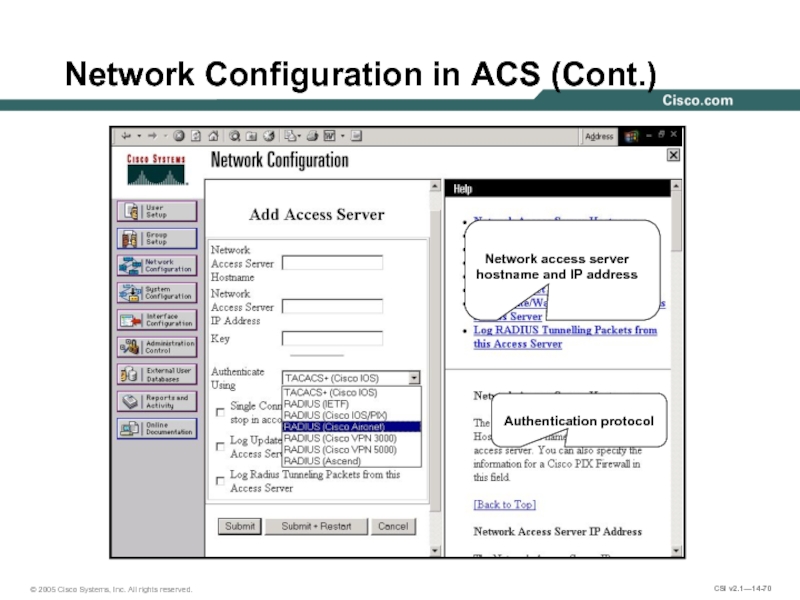
- 70. Network Configuration in ACS (Cont.) Network
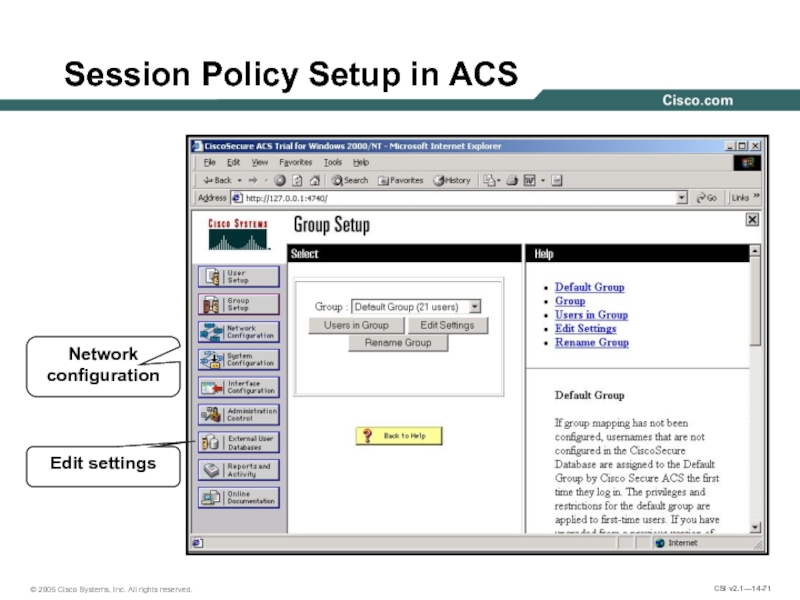
- 71. Session Policy Setup in ACS Network configuration Edit settings
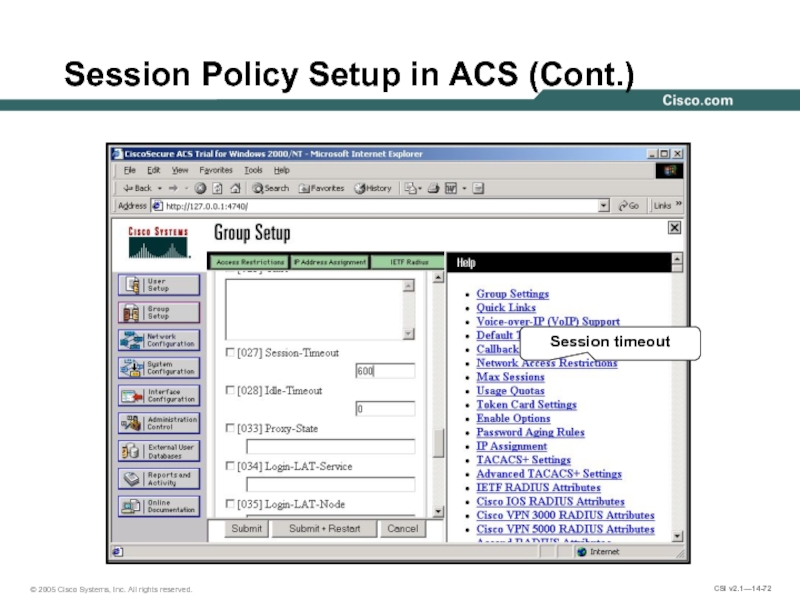
- 72. Session Policy Setup in ACS (Cont.) Session timeout
- 73. Summary IEEE 802.11 is the standard that
- 74. Summary (Cont.) There are numerous design considerations
- 75. Lab Visual Objective © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. CSI v2.1—14-
- 76. .100 Lab 1 Visual Objective 10.0.P.0 /24
- 77. .100 Labs 2 and 3 Visual Objective
- 78. .100 Lab 4 Visual Objective 10.0.P.0 /24
Слайд 1
Lesson 14
SAFE Wireless LAN Security in Depth
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc.
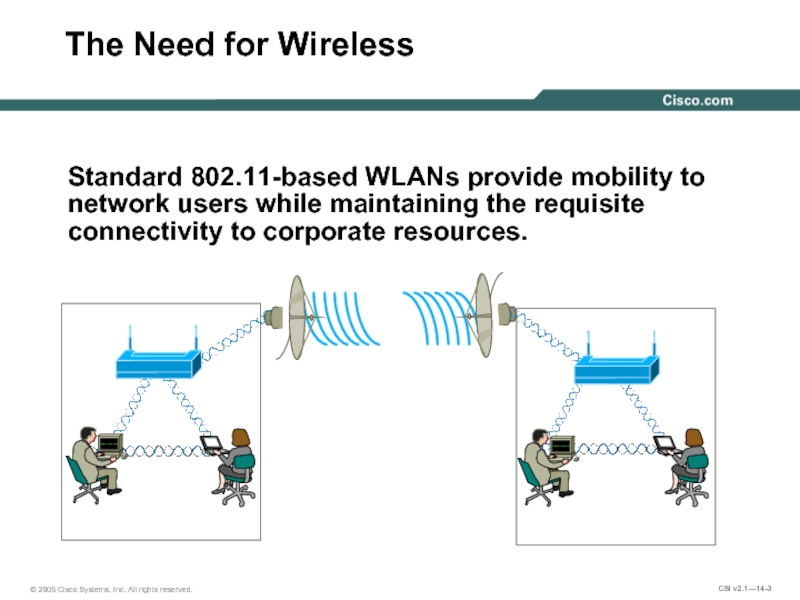
Слайд 3The Need for Wireless
Standard 802.11-based WLANs provide mobility to network users
Слайд 4Types of Wireless Technology
Functional view:
Peer-to-peer WLANs
Multiple-cell WLANs
Building-to-building wireless networks
Technology view:
802.11
HiperLAN
HomeRF SWAP
Bluetooth
Слайд 5802.11 Wireless Technology
Wi-Fi Alliance provides a branding for 802.11-based technology.
Standard 802.11-based
The 802.11 standard specifically takes advantage of two frequency bands:
2.4-to-2.4835-GHz UHF band used for 802.11 and 802.11b networks
5.15-to-5.825-GHz SHF band used for 802.11a-based networks
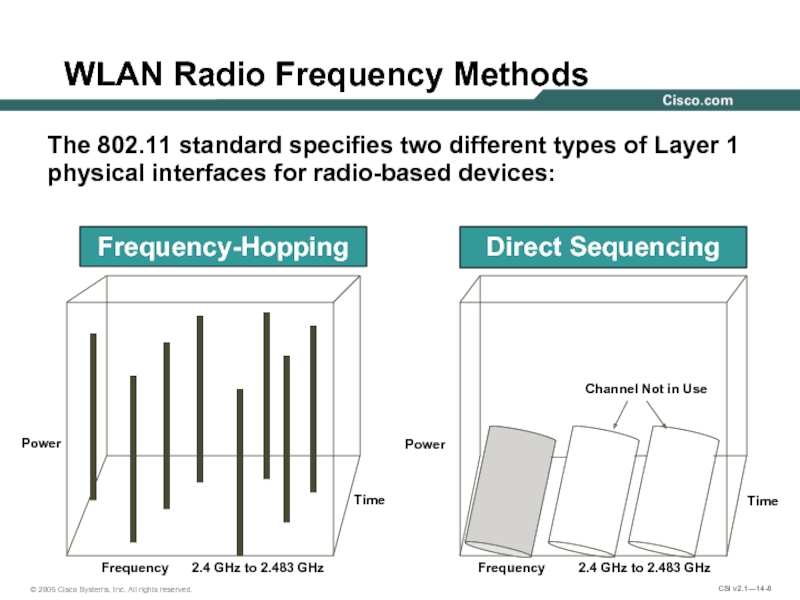
Слайд 6WLAN Radio Frequency Methods
The 802.11 standard specifies two different types of
Frequency
Power
Time
Power
2.4 GHz to 2.483 GHz
Direct Sequencing
Frequency-Hopping
Frequency
2.4 GHz to 2.483 GHz
Time
Channel Not in Use
Слайд 7
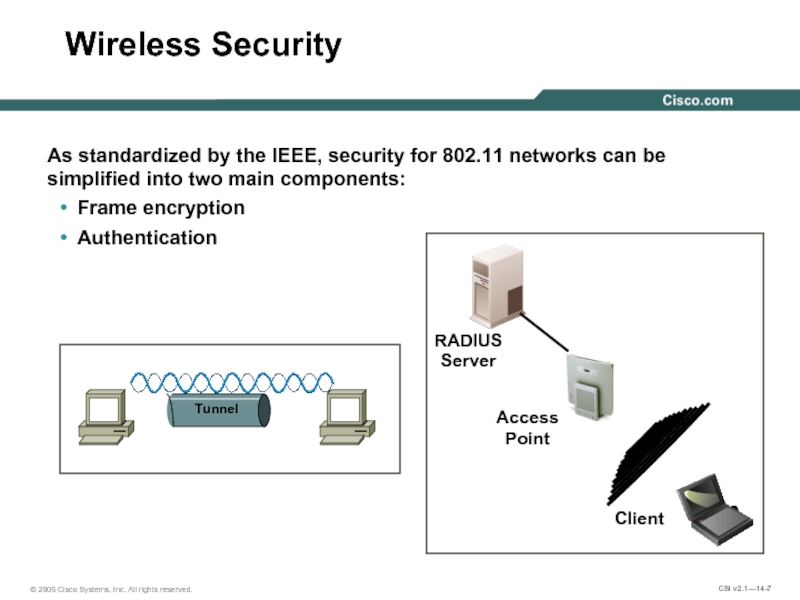
Wireless Security
As standardized by the IEEE, security for 802.11 networks can
Frame encryption
Authentication
Tunnel
Client
Access
Point
RADIUS
Server
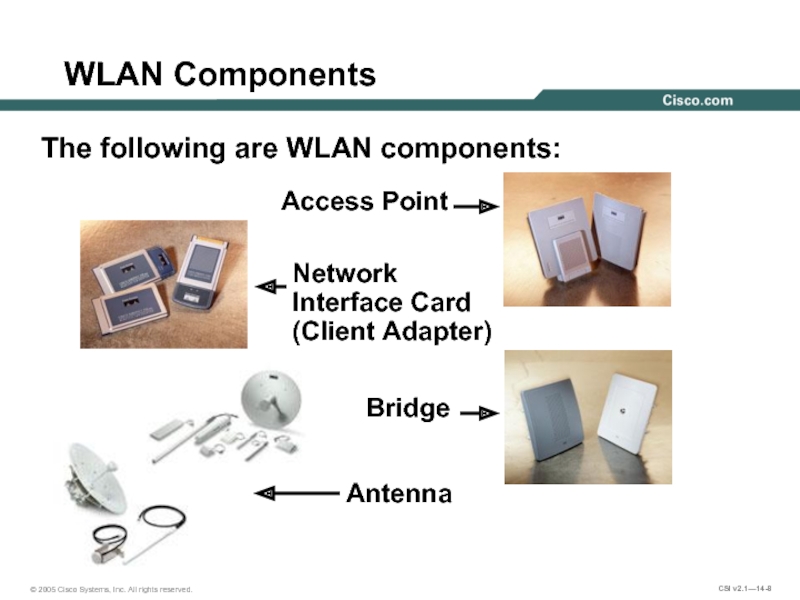
Слайд 8WLAN Components
The following are WLAN components:
Access Point
Bridge
Antenna
Network Interface Card
(Client Adapter)
Слайд 9
SAFE Wireless LAN Caveats and Design Considerations (Axioms)
© 2005 Cisco Systems,
CSI v2.1—14-
Слайд 10Several WLAN technologies are not covered.
SAFE guidelines do not guarantee a
A security policy is in place.
SAFE WLAN Caveats
SAFE WLAN is based on the following caveats:
Слайд 11SAFE WLAN Design Considerations (Axioms)
SAFE WLAN is based on the following
Wireless networks are targets.
Wireless networks are weapons.
Слайд 12
SAFE WLAN Design Considerations (Axioms) (Cont.)
Traditional 802.11 WLAN security
elements are:
Authentication
Key
WEP
802.11 is insecure
Слайд 14
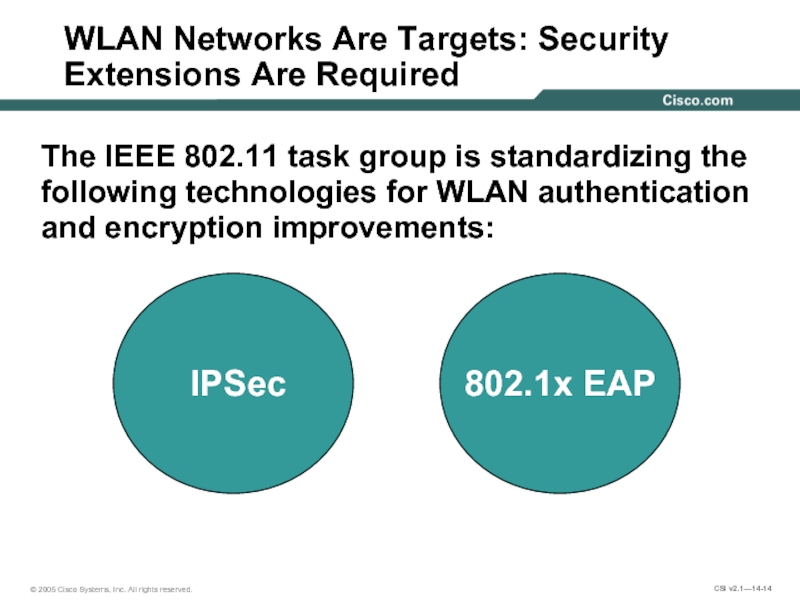
WLAN Networks Are Targets: Security Extensions Are Required
The IEEE 802.11 task
IPSec
802.1x EAP
Слайд 15
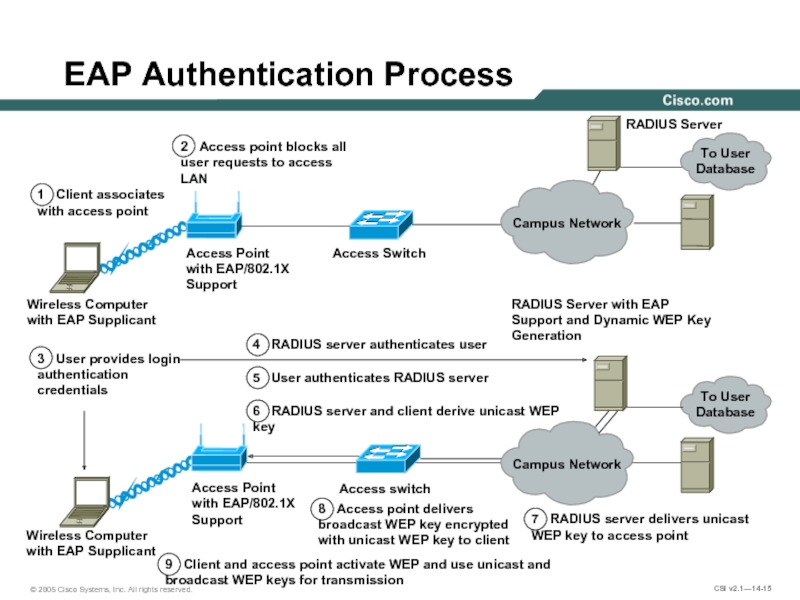
EAP Authentication Process
Wireless Computer
with EAP Supplicant
Wireless Computer
with EAP Supplicant
Access Point
with EAP/802.1X
Support
Access Point
with EAP/802.1X
Support
Access Switch
Access switch
RADIUS Server
To User
Database
RADIUS Server with EAP
Support and Dynamic WEP Key Generation
1 Client associates
with access point
2 Access point blocks all user requests to access LAN
8 Access point delivers broadcast WEP key encrypted with unicast WEP key to client
7 RADIUS server delivers unicast WEP key to access point
6 RADIUS server and client derive unicast WEP key
5 User authenticates RADIUS server
4 RADIUS server authenticates user
3 User provides login
authentication
credentials
9 Client and access point activate WEP and use unicast and broadcast WEP keys for transmission
Campus Network
Campus Network
To User
Database
Слайд 16EAP Benefits
EAP provides three significant benefits over basic 802.11 security:
Mutual authentication
Centralized management and distribution of encryption keys
Centralized policy control
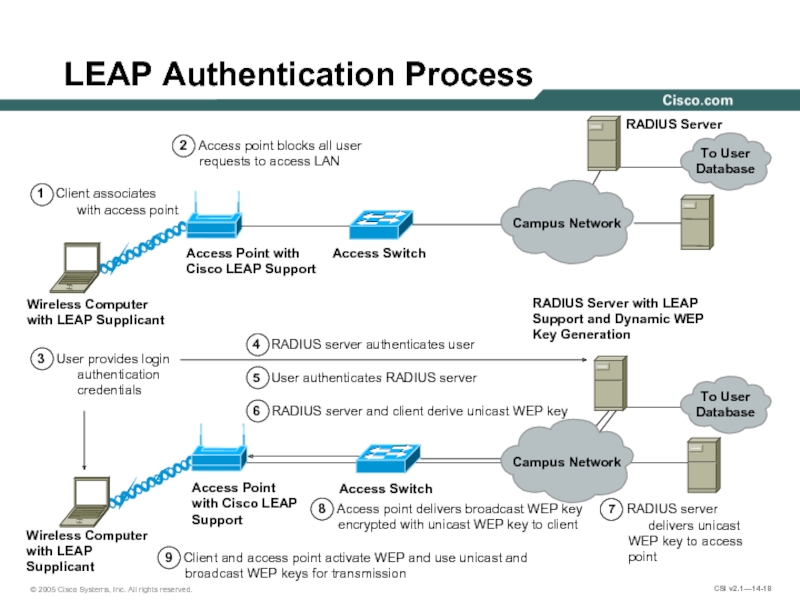
Слайд 18LEAP Authentication Process
Wireless Computer
with LEAP Supplicant
Wireless Computer
with LEAP
Supplicant
Access Point with
Cisco LEAP Support
Access Point
with Cisco LEAP
Support
Access Switch
Access Switch
RADIUS Server
RADIUS Server with LEAP
Support and Dynamic WEP Key Generation
1 Client associates
with access point
2 Access point blocks all user requests to access LAN
8 Access point delivers broadcast WEP key encrypted with unicast WEP key to client
7 RADIUS server
delivers unicast WEP key to access point
6 RADIUS server and client derive unicast WEP key
5 User authenticates RADIUS server
4 RADIUS server authenticates user
3 User provides login
authentication
credentials
9 Client and access point activate WEP and use unicast and broadcast WEP keys for transmission
To User
Database
Campus Network
Campus Network
To User
Database
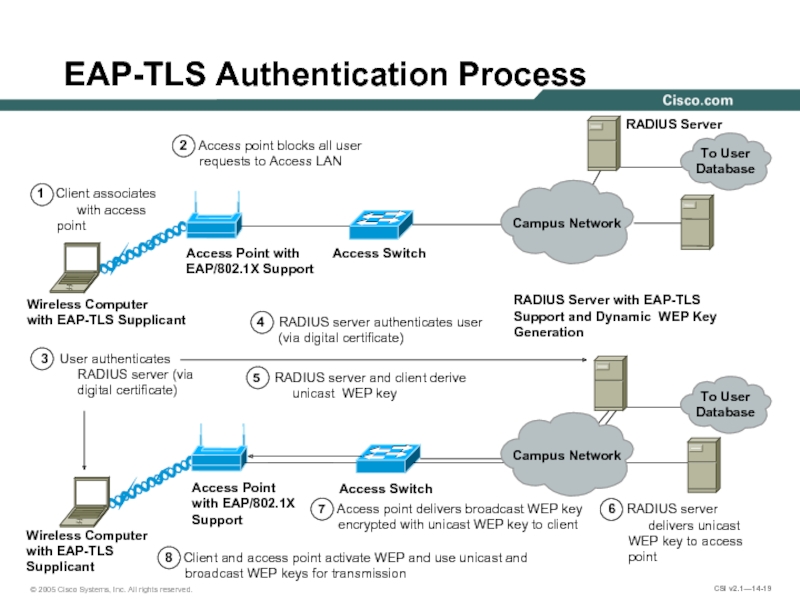
Слайд 19EAP-TLS Authentication Process
Wireless Computer
with EAP-TLS Supplicant
Wireless Computer
with EAP-TLS
Supplicant
Access Point with
EAP/802.1X Support
Access Point
with EAP/802.1X
Support
Access Switch
Access Switch
RADIUS Server
RADIUS Server with EAP-TLS
Support and Dynamic WEP Key Generation
1 Client associates
with access point
2 Access point blocks all user requests to Access LAN
7 Access point delivers broadcast WEP key encrypted with unicast WEP key to client
6 RADIUS server
delivers unicast WEP key to access point
5 RADIUS server and client derive
unicast WEP key
4 RADIUS server authenticates user (via digital certificate)
3 User authenticates
RADIUS server (via
digital certificate)
8 Client and access point activate WEP and use unicast and broadcast WEP keys for transmission
To User
Database
Campus Network
Campus Network
To User
Database
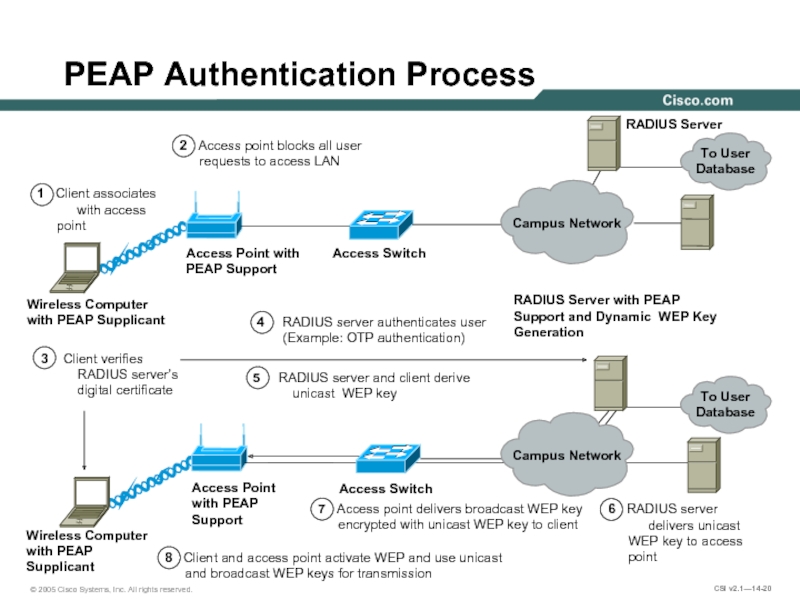
Слайд 20Wireless Computer
with PEAP Supplicant
Wireless Computer
with PEAP
Supplicant
Access Point with
PEAP Support
Access Point
with
Support
Access Switch
Access Switch
RADIUS Server
RADIUS Server with PEAP
Support and Dynamic WEP Key Generation
1 Client associates
with access point
2 Access point blocks all user requests to access LAN
7 Access point delivers broadcast WEP key encrypted with unicast WEP key to client
6 RADIUS server
delivers unicast WEP key to access point
5 RADIUS server and client derive
unicast WEP key
4 RADIUS server authenticates user (Example: OTP authentication)
3 Client verifies
RADIUS server’s
digital certificate
8 Client and access point activate WEP and use unicast and broadcast WEP keys for transmission
To User
Database
Campus Network
Campus Network
To User
Database
PEAP Authentication Process
Слайд 21WEP Enhancements
IEEE 802.11i includes two encryption enhancements in its draft standard
TKIP: A set of software enhancements to RC4-based WEP
AES: A stronger alternative to RC4
Слайд 22
Cisco Wireless LAN Product Portfolio
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
CSI v2.1—14-
Слайд 23Cisco Aironet WLAN Product Line
Wireless LAN Aironet
access points
Cisco Aironet 1300
Cisco Aironet 1230AG Series
Cisco Aironet 1200 Series
Cisco Aironet 1130AG Series
Cisco Aironet 1100 Series
Cisco Aironet 350 Series
Aironet wireless and workgroup bridges
Cisco Aironet 1400 Series
Cisco Aironet 1300 Series
Cisco Aironet 350 Series
Cisco Aironet antennas and accessories
Cisco Aironet Wireless LAN Client Adapters
Слайд 24Cisco Aironet WLAN Product Line (Cont.)
Wireless network management
Cisco Mobile Wireless Center
Cisco
CiscoWorks for Mobile Wireless
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
Wireless security servers
Cisco Secure Access Control Server for Unix
Cisco Secure Access Control Server for Windows
Cisco Secure Access Control Server Solution Engine
Слайд 25Cisco Aironet WLAN Product Line (Cont.)
Wireless integrated switches and routers
Cisco 3200
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series switches
Wireless IP telephony
Cisco 7900 Series IP phones
Cisco 3200 Series Wireless
and Mobile Router
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches
Cisco 7900 Series IP Phones
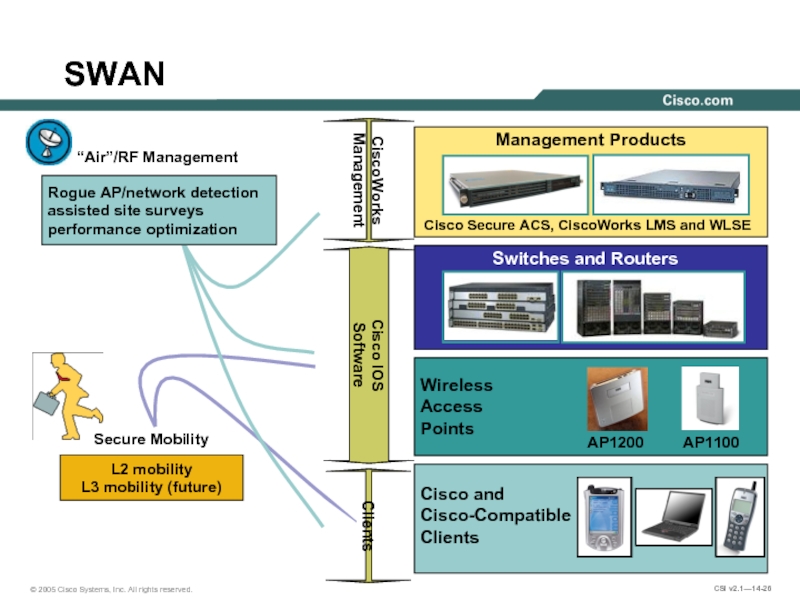
Слайд 26“Air”/RF Management
L2 mobility
L3 mobility (future)
Cisco IOS
Software
CiscoWorks
Management
Clients
Secure Mobility
Rogue AP/network detection
assisted site surveys
performance
Management Products
Wireless
Access
Points
AP1200
AP1100
Cisco Secure ACS, CiscoWorks LMS and WLSE
Switches and Routers
SWAN
Слайд 27 Cost-effective and scalable
Improved productivity and accuracy
Improved security and
Cisco Compatible Program for
WLAN Client Devices
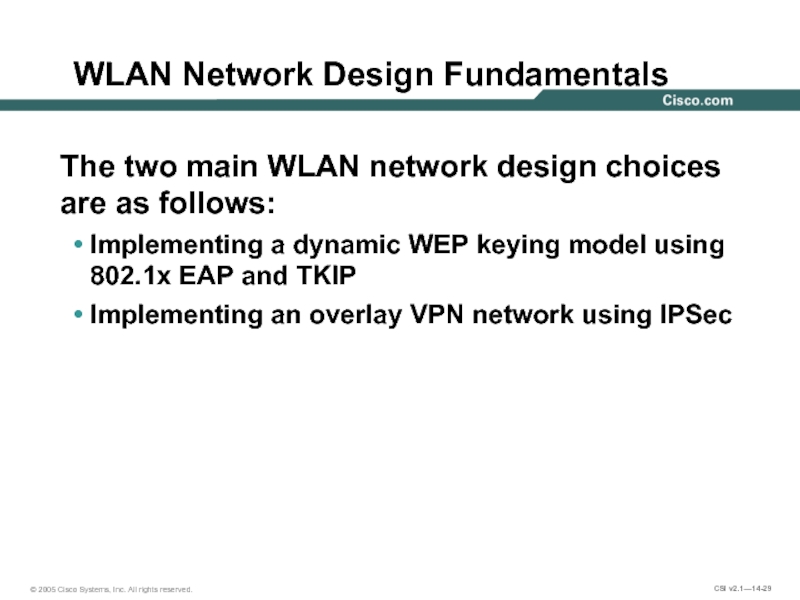
Слайд 29 WLAN Network Design Fundamentals
The two main WLAN network design choices
Implementing a dynamic WEP keying model using 802.1x EAP and TKIP
Implementing an overlay VPN network using IPSec
Слайд 30
Access Point Security
Standard WLAN Design Guidelines
All designs include the following WLAN
Client Security
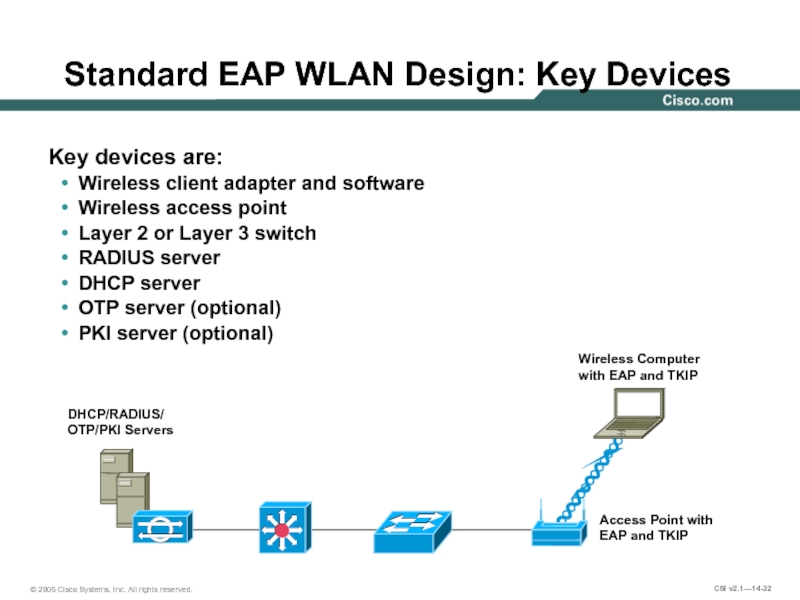
Слайд 32Key devices are:
Wireless client adapter and software
Wireless access point
Layer 2 or
RADIUS server
DHCP server
OTP server (optional)
PKI server (optional)
Standard EAP WLAN Design: Key Devices
DHCP/RADIUS/
OTP/PKI Servers
Access Point with
EAP and TKIP
Wireless Computer
with EAP and TKIP
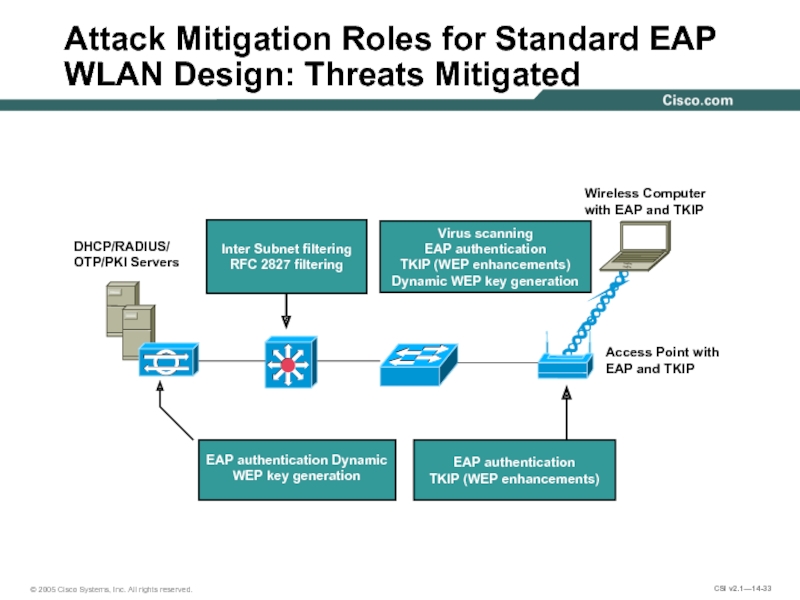
Слайд 33Attack Mitigation Roles for Standard EAP WLAN Design: Threats Mitigated
DHCP/RADIUS/
OTP/PKI Servers
Access
EAP and TKIP
Wireless Computer
with EAP and TKIP
EAP authentication Dynamic WEP key generation
EAP authentication
TKIP (WEP enhancements)
Inter Subnet filtering
RFC 2827 filtering
Virus scanning
EAP authentication
TKIP (WEP enhancements)
Dynamic WEP key generation
Слайд 34EAP with TKIP Design Guidelines
Give special consideration to the location of
Rekeying for both unicast and broadcast keys is recommended.
Follow EAP-specific design guidelines.
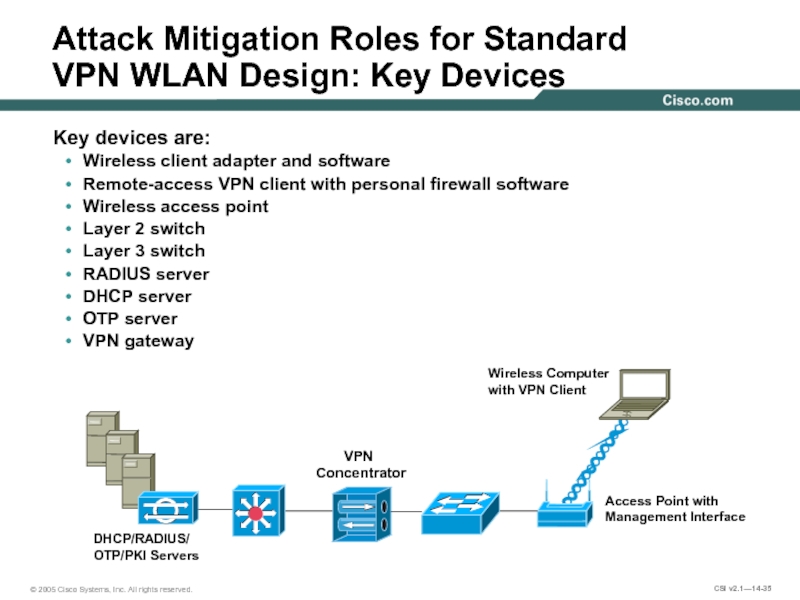
Слайд 35Key devices are:
Wireless client adapter and software
Remote-access VPN client with personal
Wireless access point
Layer 2 switch
Layer 3 switch
RADIUS server
DHCP server
OTP server
VPN gateway
Attack Mitigation Roles for Standard VPN WLAN Design: Key Devices
DHCP/RADIUS/
OTP/PKI Servers
Access Point with
Management Interface
Wireless Computer
with VPN Client
VPN Concentrator
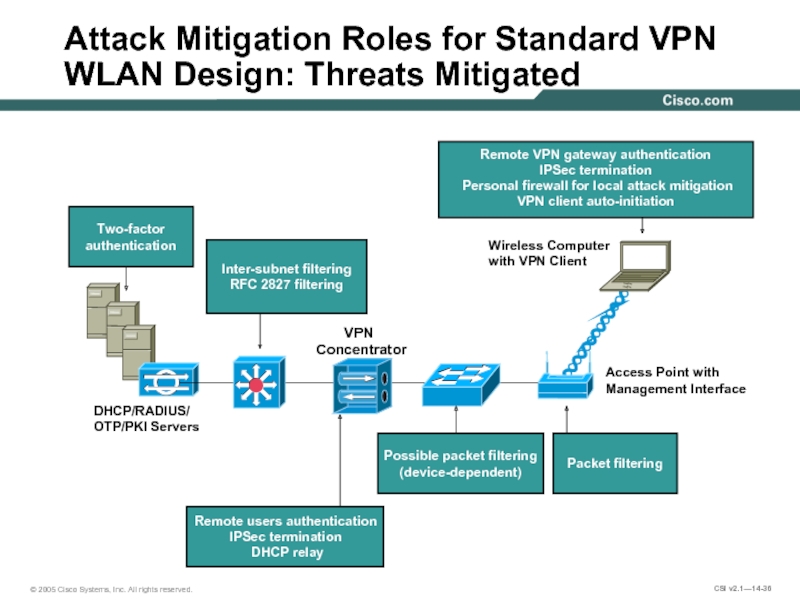
Слайд 36Attack Mitigation Roles for Standard VPN WLAN Design: Threats Mitigated
DHCP/RADIUS/
OTP/PKI Servers
Access
Management Interface
Wireless Computer
with VPN Client
Remote users authentication IPSec termination
DHCP relay
Packet filtering
Inter-subnet filtering
RFC 2827 filtering
VPN Concentrator
Two-factor
authentication
Possible packet filtering
(device-dependent)
Remote VPN gateway authentication
IPSec termination
Personal firewall for local attack mitigation VPN client auto-initiation
Слайд 37Standard VPN WLAN Design Guidelines
Use VPN gateway to perform authentication.
Separate WLAN
Prevent network access if RADIUS or DHCP service fails.
Implement protocol and port filtering.
Secure DNS and DHCP servers.
Implement VACLs and control ICMP.
Use auto-initiate feature of the VPN client.
Implement personal firewall and disable split tunneling.
Alternatives include:
Implementing static WEP keys
Using a layer of 802.1x EAP with the IPSec-based VPN
Using dedicated hosts for the VPN, WLAN, DHCP, and DNS
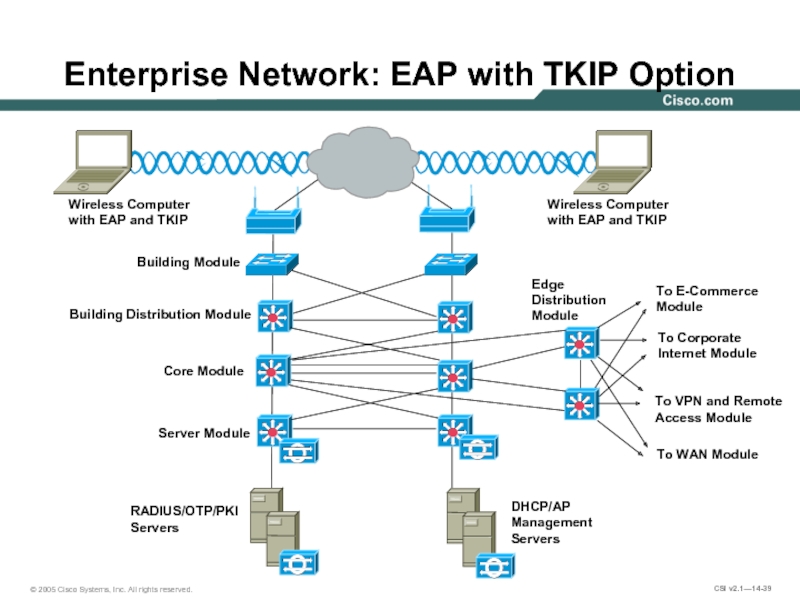
Слайд 39Enterprise Network: EAP with TKIP Option
Wireless Computer
with EAP and TKIP
Wireless Computer
with
Building Module
Building Distribution Module
Core Module
Server Module
RADIUS/OTP/PKI
Servers
DHCP/AP
Management
Servers
Edge
Distribution
Module
To E-Commerce
Module
To Corporate
Internet Module
To VPN and Remote
Access Module
To WAN Module
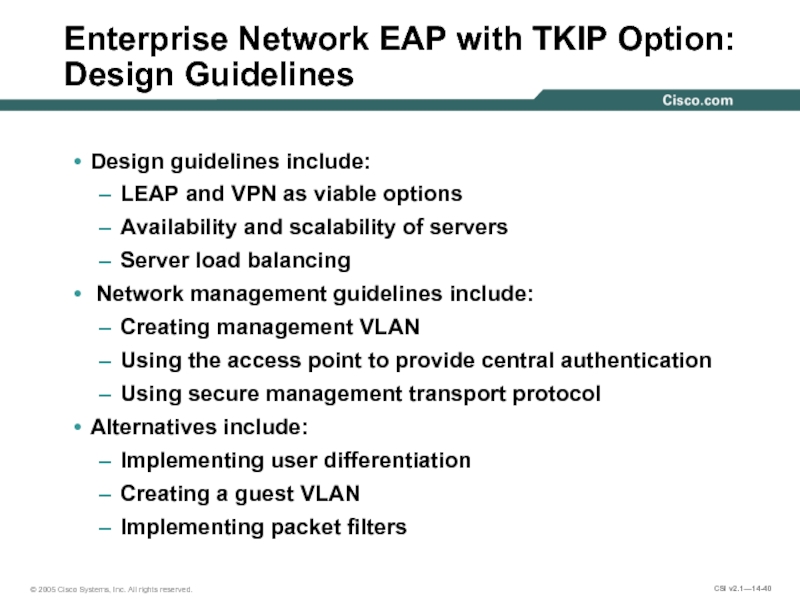
Слайд 40Enterprise Network EAP with TKIP Option: Design Guidelines
Design guidelines include:
LEAP and
Availability and scalability of servers
Server load balancing
Network management guidelines include:
Creating management VLAN
Using the access point to provide central authentication
Using secure management transport protocol
Alternatives include:
Implementing user differentiation
Creating a guest VLAN
Implementing packet filters
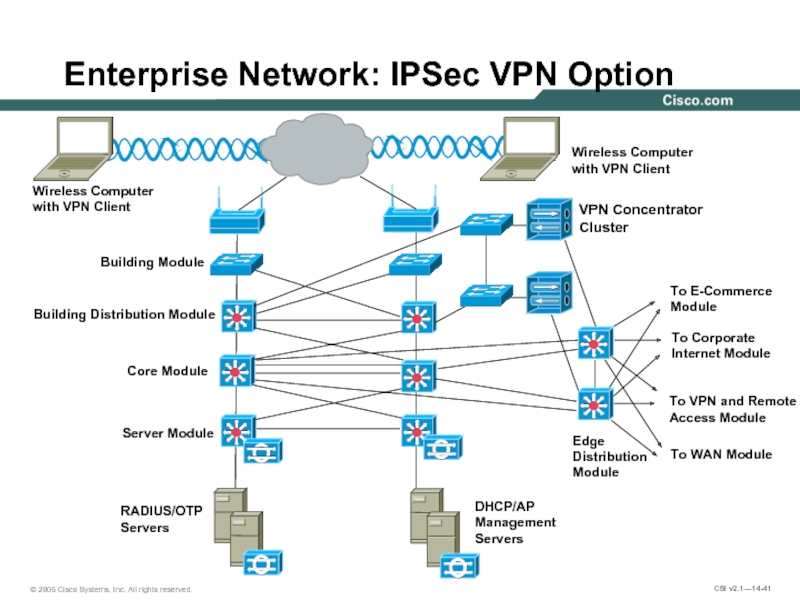
Слайд 41Enterprise Network: IPSec VPN Option
Wireless Computer
with VPN Client
Building Module
Building Distribution Module
Core
Server Module
RADIUS/OTP
Servers
DHCP/AP
Management
Servers
Edge
Distribution
Module
To E-Commerce
Module
To Corporate
Internet Module
To VPN and Remote
Access Module
To WAN Module
VPN Concentrator Cluster
Wireless Computer
with VPN Client
Слайд 42Enterprise IPSec VPN Option: Design Guidelines
Design guidelines include:
Balance the necessary cost-security
Consider client traffic to be insecure before the IPSec tunnel is established.
Use the auto-initiate feature of the VPN client.
Filter with ACLs.
Create redundant servers and VPN gateways for high availability and scalability.
Alternatives include:
Implement NIDS and firewalls.
Physically separate WLAN access.
Create multiple SSIDs and VLANs.
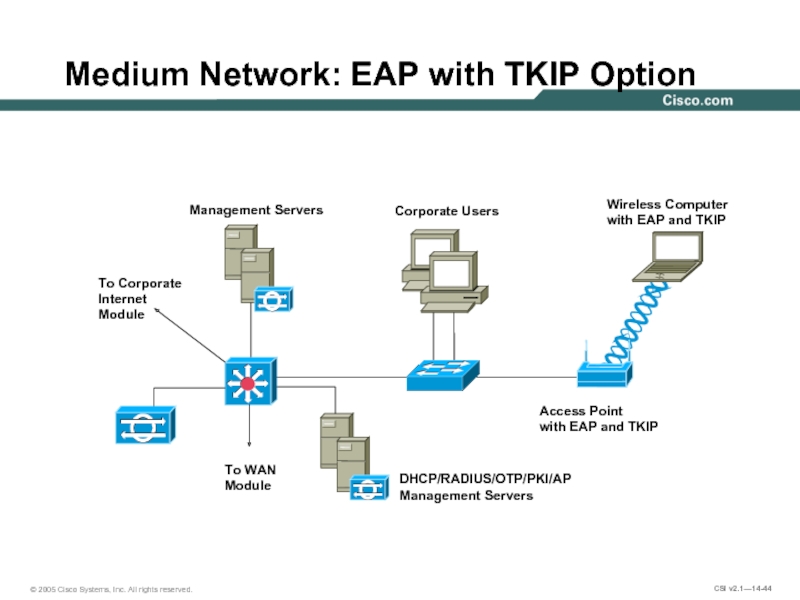
Слайд 44Medium Network: EAP with TKIP Option
DHCP/RADIUS/OTP/PKI/AP
Management Servers
To WAN
Module
To Corporate
Internet
Module
Management Servers
Corporate Users
Wireless
with EAP and TKIP
Access Point
with EAP and TKIP
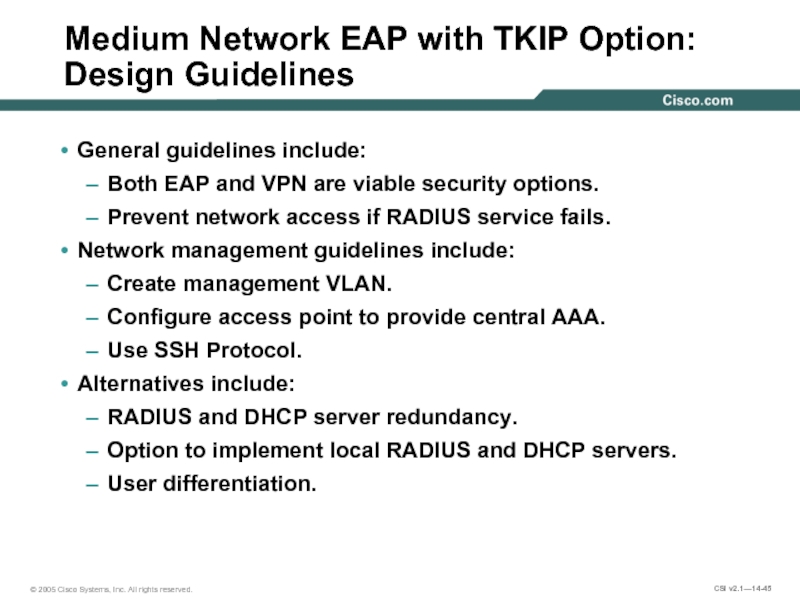
Слайд 45Medium Network EAP with TKIP Option: Design Guidelines
General guidelines include:
Both EAP
Prevent network access if RADIUS service fails.
Network management guidelines include:
Create management VLAN.
Configure access point to provide central AAA.
Use SSH Protocol.
Alternatives include:
RADIUS and DHCP server redundancy.
Option to implement local RADIUS and DHCP servers.
User differentiation.
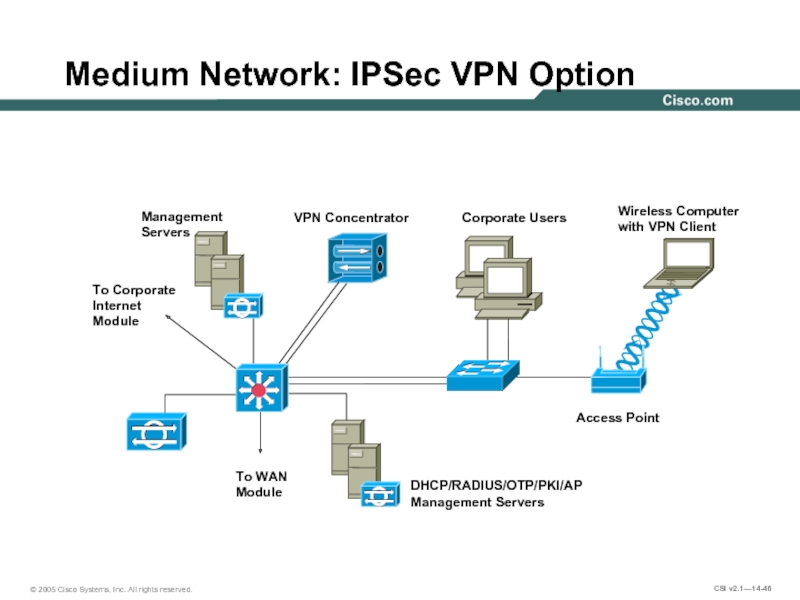
Слайд 46Medium Network: IPSec VPN Option
DHCP/RADIUS/OTP/PKI/AP
Management Servers
To WAN
Module
To Corporate
Internet
Module
Management
Servers
Corporate Users
Wireless Computer
with
Access Point
VPN Concentrator
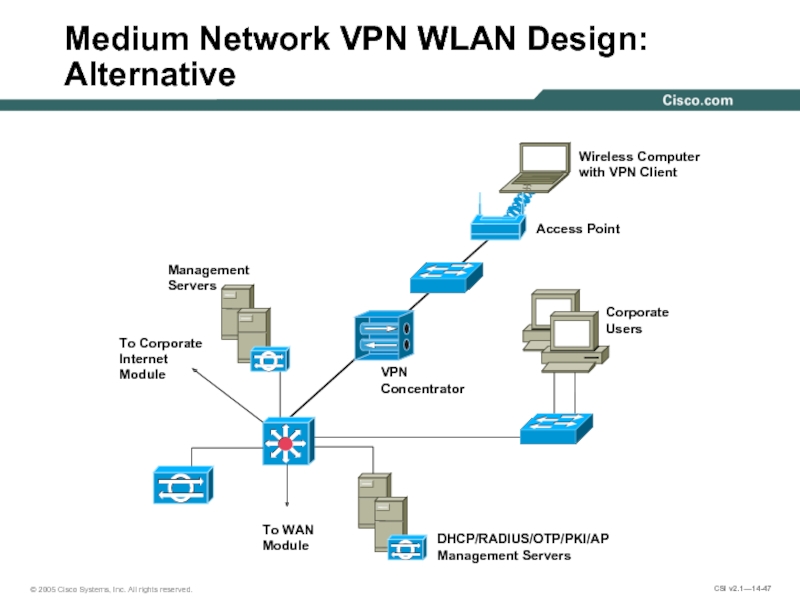
Слайд 47Medium Network VPN WLAN Design: Alternative
DHCP/RADIUS/OTP/PKI/AP
Management Servers
To WAN
Module
To Corporate
Internet
Module
Management
Servers
Corporate
Users
Wireless
with VPN Client
Access Point
VPN
Concentrator
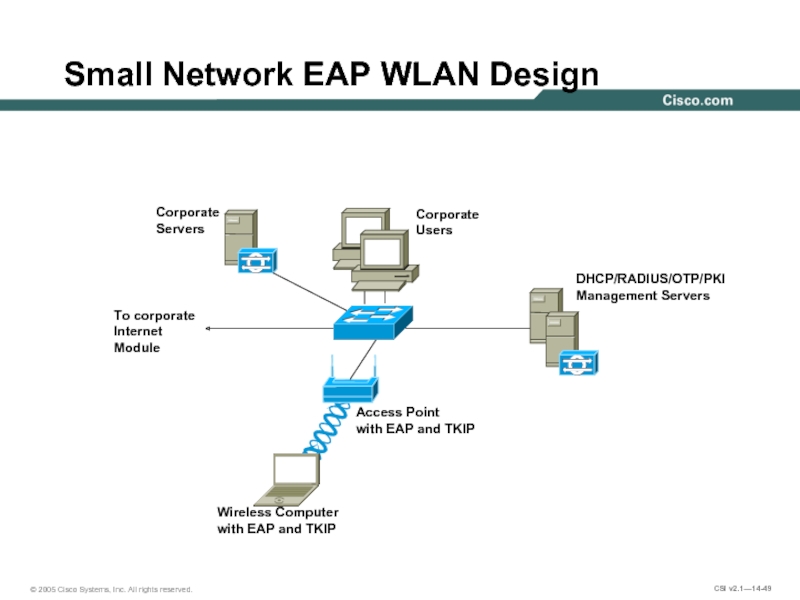
Слайд 49Small Network EAP WLAN Design
To corporate
Internet
Module
Corporate
Servers
Corporate
Users
Wireless Computer
with EAP and
Access Point
with EAP and TKIP
DHCP/RADIUS/OTP/PKI
Management Servers
Слайд 50Small WLAN Network: Design Guidelines
Guideline includes:
Single IP subnet
Network guideline includes:
Implementing EAP
Alternative:
Using static WEP keys, but not recommended
Слайд 52Remote WLAN Design
Two primary types of remote VPN connectivity defined by
Software-based VPNs
Hardware-based VPNs
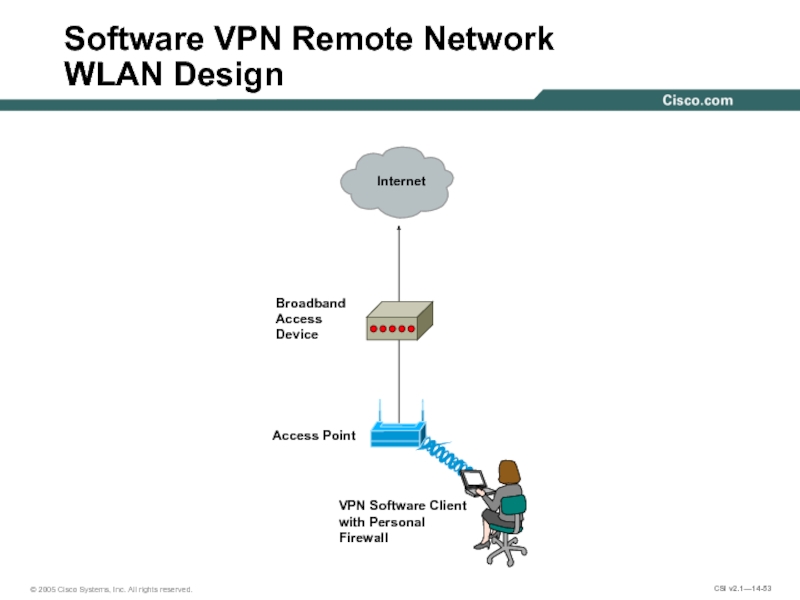
Слайд 53
Software VPN Remote Network
WLAN Design
Access Point
VPN Software Client
with Personal
Firewall
Broadband
Access
Device
Internet
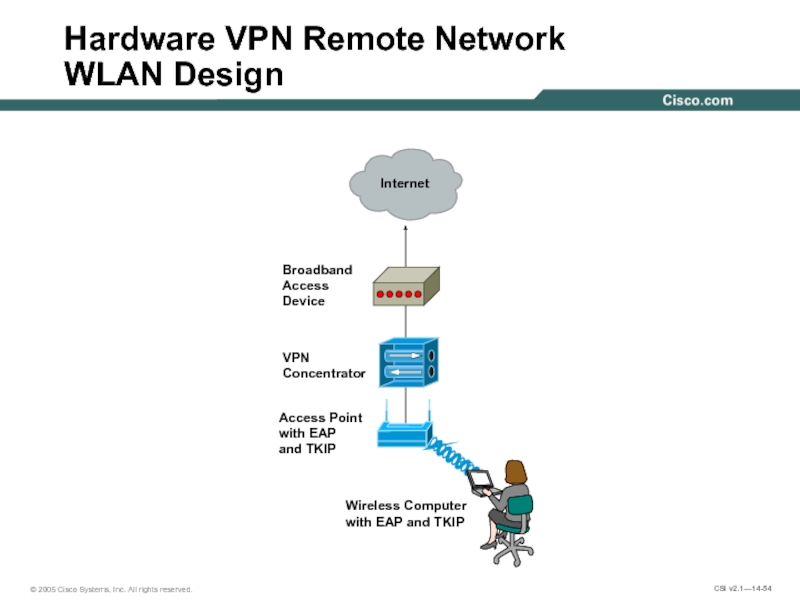
Слайд 54Hardware VPN Remote Network
WLAN Design
Access Point
with EAP
and TKIP
Wireless Computer
with
VPN
Concentrator
Broadband
Access
Device
Internet
Слайд 70Network Configuration in ACS (Cont.)
Network access server
hostname and IP address
Authentication
Слайд 73Summary
IEEE 802.11 is the standard that is used by wireless technologies.
Security
Encryption
Authentication
There are four WLAN components.
There are security extensions for SAFE WLAN.
There are two main network WLAN design choices:
Implementing a dynamic WEP keying model using 802.1x EAP and TKIP
Implementing an overlay VPN network using IPSec
Слайд 74Summary (Cont.)
There are numerous design considerations for small, medium, enterprise, and
The mitigation roles identified for each threat are integral to a successful WLAN implementation.
The design process is often a series of trade-offs. Some of these trade-offs are made at the module level, whereas others are made at the component level.
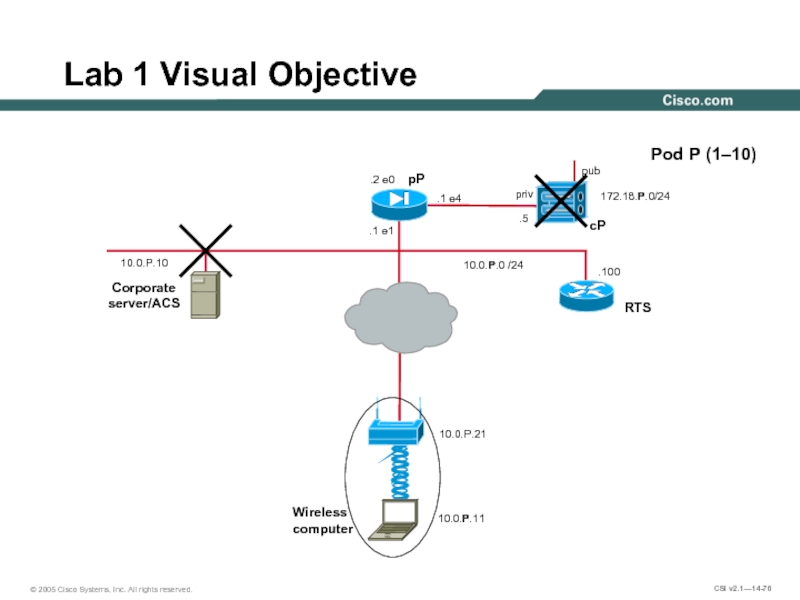
Слайд 76.100
Lab 1 Visual Objective
10.0.P.0 /24
Pod P (1–10)
pP
pub
cP
Corporate server/ACS
10.0.P.10
priv
.5
.2 e0
172.18.P.0/24
.1 e4
.1 e1
RTS
10.0.P.11
Wireless
computer
10.0.P.21
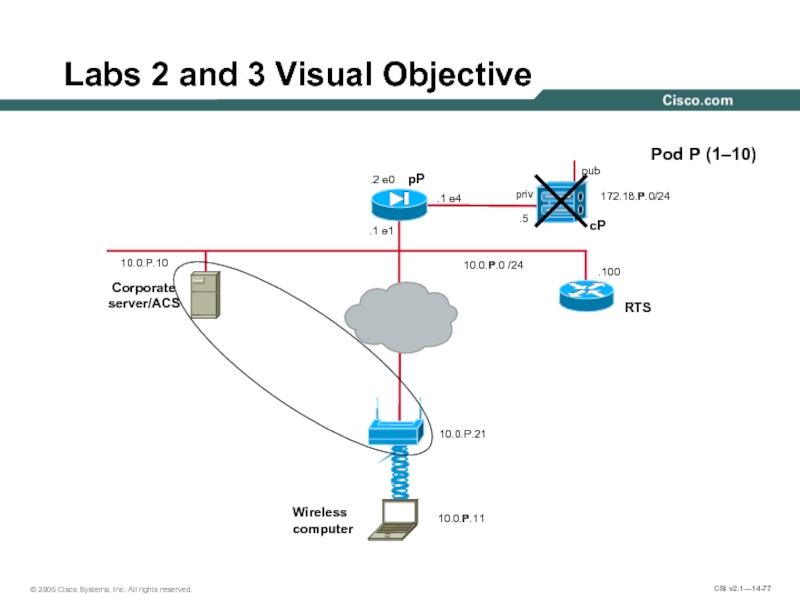
Слайд 77.100
Labs 2 and 3 Visual Objective
10.0.P.0 /24
Pod P (1–10)
pP
pub
cP
Corporate server/ACS
10.0.P.10
priv
.5
.2 e0
172.18.P.0/24
.1
.1 e1
RTS
10.0.P.11
Wireless
computer
10.0.P.21
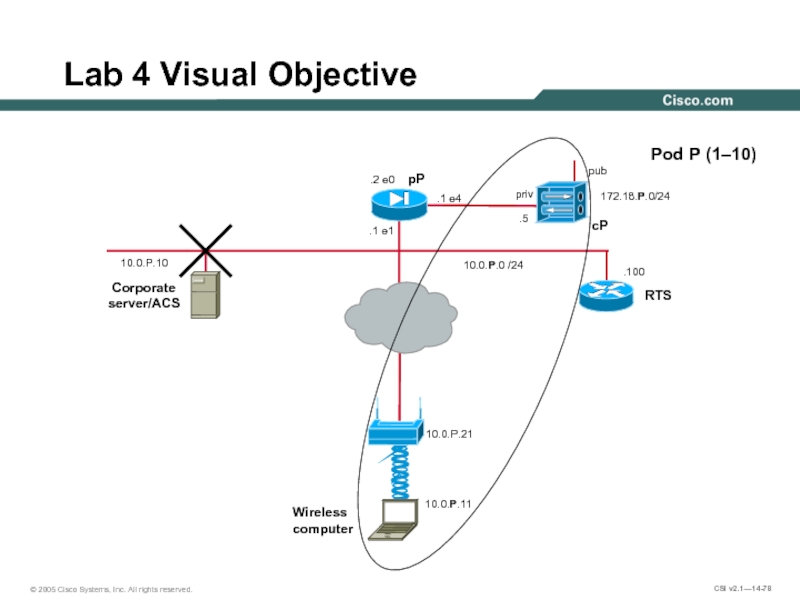
Слайд 78.100
Lab 4 Visual Objective
10.0.P.0 /24
Pod P (1–10)
pP
pub
cP
Corporate server/ACS
10.0.P.10
priv
.5
.2 e0
172.18.P.0/24
.1 e4
.1 e1
RTS
10.0.P.11
Wireless
computer
10.0.P.21