SUBJECT: “OBSTETRICKS”
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
PREECLAMPSIA 401c Tajimuratova I Tashkent Medical Academy DEPARTMENT OF OBSTETRICKS AND GYNECOLOGY SUBJECT: OBSTETRICKS. презентация
Содержание
- 1. PREECLAMPSIA 401c Tajimuratova I Tashkent Medical Academy DEPARTMENT OF OBSTETRICKS AND GYNECOLOGY SUBJECT: OBSTETRICKS.
- 2. PREECLAMPSIA Hypertensive disorder specific to pregnancy affects
- 3. PREECLAMPSIA Severity ranges from: a mild disorder
- 4. PREECLAMPSIA Predisposes women to other serious complications:
- 5. PREECLAMPSIA The etiology is unknown believed to
- 6. PREECLAMPSIA Classification of hypertension in pregnancy Gestational
- 7. PREECLAMPSIA Definition of hypertension a systolic blood
- 8. PREECLAMPSIA Criteria for severe preeclampsia Blood pressure:
- 9. PREECLAMPSIA Criteria for severe preeclampsia Pulmonary edema
- 10. PREECLAMPSIA Screening tests for gestational hypertension routine
- 11. PREECLAMPSIA Prevention of preeclampsia women at risk:
- 12. PREECLAMPSIA Mild preeclampsia - management < 37
- 13. PREECLAMPSIA Severe preeclampsia - expectant management gestational
- 14. PREECLAMPSIA Severe preeclampsia - guidelines for expedient
- 15. PREECLAMPSIA Severe preeclampsia - guidelines for expedient
- 16. PREECLAMPSIA Severe preeclampsia - management protocol admission
- 17. PREECLAMPSIA Severe preeclampsia - management protocol Expedited
- 18. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - diagnosis 10% before
- 19. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome parameters used to diagnose
- 20. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - diagnostic criteria hemolysis
- 21. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - differential diagnosis acute
- 22. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - differential diagnosis idiopathic
- 23. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - antepartum management assess
- 24. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - antepartum management evaluate
- 25. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - management for cesarean
- 26. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - management for cesarean
- 27. PREECLAMPSIA HELLP syndrome - management of women
- 28. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia occurrence of convulsions or coma
- 29. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia precise cause unknown theories vasospasm ischemia edema multisystem organ failure
- 30. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia seizures usually occur without aura
- 31. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia 80% of convulsions occur before
- 32. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - risk factors low socioeconomic
- 33. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - management control convulsions correction
- 34. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - anticonvulsant therapy magnesium sulfate
- 35. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - magnesium sulfate side effects:
- 36. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - anticonvulsant therapy phenytoin used
- 37. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - phenytoin dosage - 1
- 38. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - diazepam side effects -
- 39. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - management of fetus fetal
- 40. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - radiographic evaluation should be
- 41. PREECLAMPSIA Eclampsia - management allow patient to
- 42. PREECLAMPSIA Counseling regarding future pregnancies - HELLP
Слайд 1
PREECLAMPSIA
401c Tajimuratova I
Tashkent Medical Academy
DEPARTMENT OF OBSTETRICKS AND GYNECOLOGY
Слайд 2PREECLAMPSIA
Hypertensive disorder specific to pregnancy
affects nearly 6% of all pregnancies
a major
cause of maternal and neonatal mortality and morbidity
15 to 20 % of maternal mortality in developed countries
15 to 20 % of maternal mortality in developed countries
Слайд 3PREECLAMPSIA
Severity ranges from:
a mild disorder (transient hypertension in the later part
of the pregnancy) to
a life-threatening disorder with seizures, HELLP syndrome, fetal hypoxia, and growth retardation
more severe disease: 0.56 per 1000 deliveries
a life-threatening disorder with seizures, HELLP syndrome, fetal hypoxia, and growth retardation
more severe disease: 0.56 per 1000 deliveries
Слайд 4PREECLAMPSIA
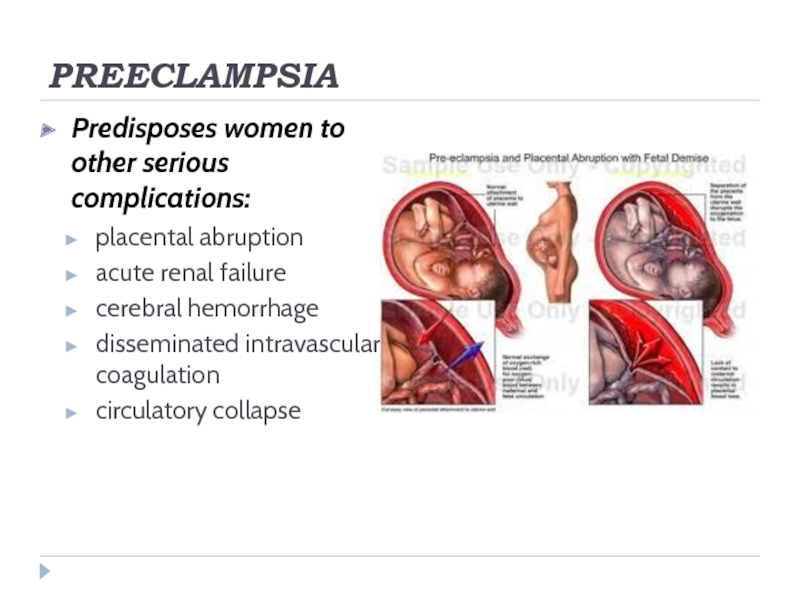
Predisposes women to other serious complications:
placental abruption
acute renal failure
cerebral hemorrhage
disseminated intravascular
coagulation
circulatory collapse
circulatory collapse
Слайд 5PREECLAMPSIA
The etiology is unknown
believed to be involved:
immune maladaptation
placental ischemia
oxidative stress
genetic susceptibility
Слайд 6PREECLAMPSIA
Classification of hypertension in pregnancy
Gestational hypertension
Preeclampsia / eclampsia
Chronic hypertension
Preeclampsia superimposed on
chronic hypertension
Слайд 7PREECLAMPSIA
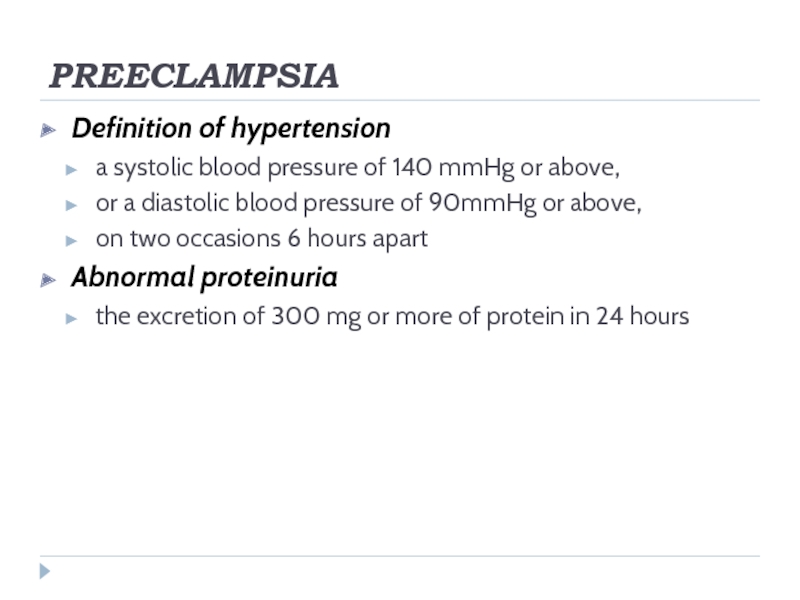
Definition of hypertension
a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or above,
or
a diastolic blood pressure of 90mmHg or above,
on two occasions 6 hours apart
Abnormal proteinuria
the excretion of 300 mg or more of protein in 24 hours
on two occasions 6 hours apart
Abnormal proteinuria
the excretion of 300 mg or more of protein in 24 hours
Слайд 8PREECLAMPSIA
Criteria for severe preeclampsia
Blood pressure: > 160 mmHg systolic or
> 110 mm Hg diastolic
Proteinuria: > 5 g in 24 hours
Persistent and severe cerebral or visual disturbances (headache, scotoma, blurred vision)
Persistent and severe epigastric pain or right upper quadrant pain
Proteinuria: > 5 g in 24 hours
Persistent and severe cerebral or visual disturbances (headache, scotoma, blurred vision)
Persistent and severe epigastric pain or right upper quadrant pain
Слайд 9PREECLAMPSIA
Criteria for severe preeclampsia
Pulmonary edema or cyanosis
Oliguria (< 500 mL of
urine in 24 hours)
Eclampsia (grand mal seizures)
HELLP syndrome
Eclampsia (grand mal seizures)
HELLP syndrome
Слайд 10PREECLAMPSIA
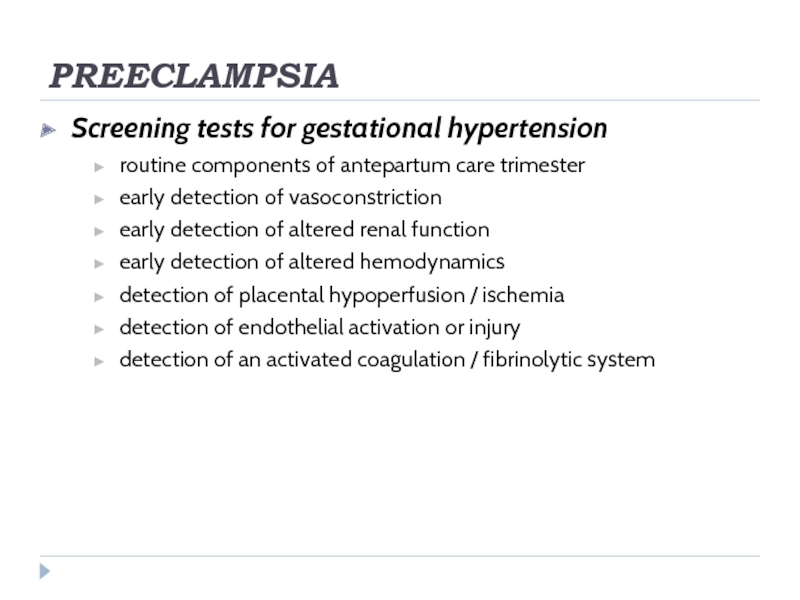
Screening tests for gestational hypertension
routine components of antepartum care trimester
early detection
of vasoconstriction
early detection of altered renal function
early detection of altered hemodynamics
detection of placental hypoperfusion / ischemia
detection of endothelial activation or injury
detection of an activated coagulation / fibrinolytic system
early detection of altered renal function
early detection of altered hemodynamics
detection of placental hypoperfusion / ischemia
detection of endothelial activation or injury
detection of an activated coagulation / fibrinolytic system
Слайд 11PREECLAMPSIA
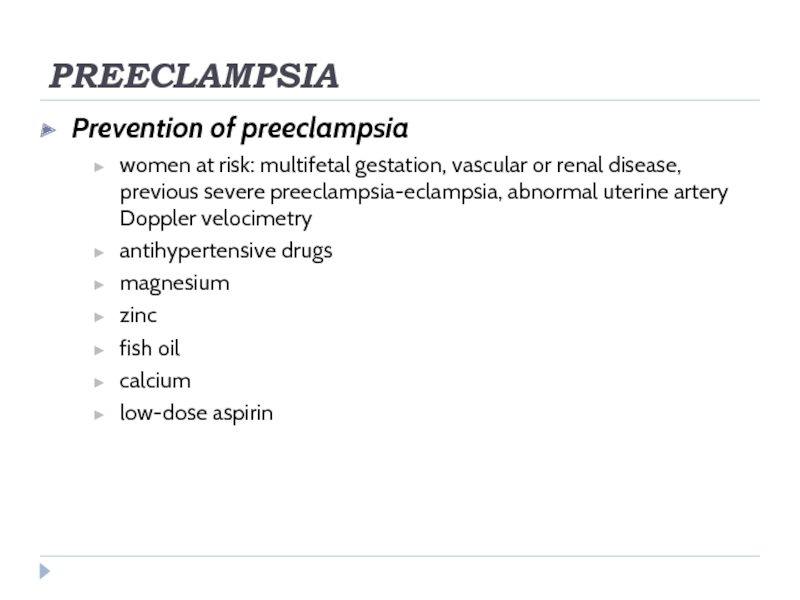
Prevention of preeclampsia
women at risk: multifetal gestation, vascular or renal disease,
previous severe preeclampsia-eclampsia, abnormal uterine artery Doppler velocimetry
antihypertensive drugs
magnesium
zinc
fish oil
calcium
low-dose aspirin
antihypertensive drugs
magnesium
zinc
fish oil
calcium
low-dose aspirin
Слайд 12PREECLAMPSIA
Mild preeclampsia - management
< 37 weeks gestation
inpatient or outpatient management
worsening disease:
delivery, magnesium sulfate
> 40 weeks gestation
delivery, magnesium sulfate
37 - 39 weeks gestation
inducible cervix: delivery, magnesium sulfate
cervix not inducible: inpatient or outpatient management
> 40 weeks gestation
delivery, magnesium sulfate
37 - 39 weeks gestation
inducible cervix: delivery, magnesium sulfate
cervix not inducible: inpatient or outpatient management
Слайд 13PREECLAMPSIA
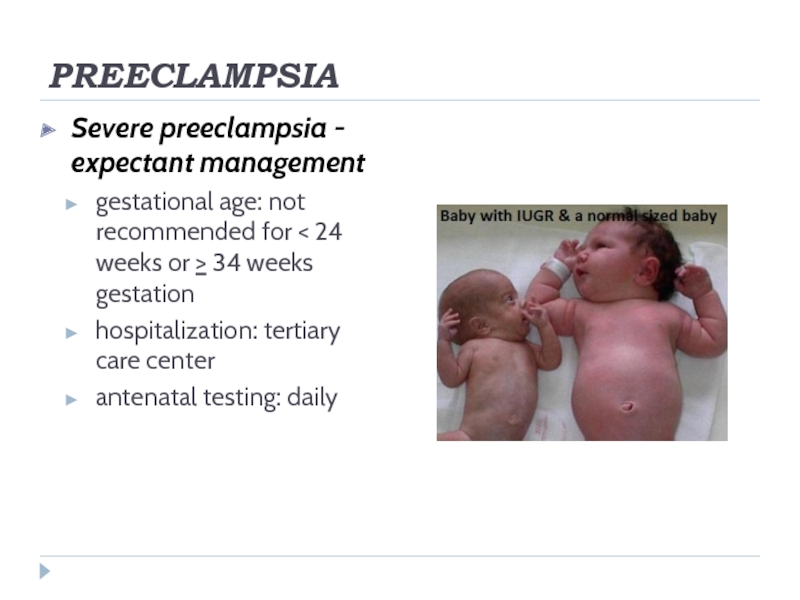
Severe preeclampsia - expectant management
gestational age: not recommended for < 24
weeks or > 34 weeks gestation
hospitalization: tertiary care center
antenatal testing: daily
hospitalization: tertiary care center
antenatal testing: daily
Слайд 14PREECLAMPSIA
Severe preeclampsia - guidelines for expedient delivery
maternal indications
eclampsia, thrombocytopenia, pulmonary edema,
acute renal failure
persistent severe headache or visual changes
elevated liver enzymes with persistent severe epigastric pain or right upper quadrant tenderness
labor or rupture of membranes
vaginal bleeding, abruptio placenta
persistent severe headache or visual changes
elevated liver enzymes with persistent severe epigastric pain or right upper quadrant tenderness
labor or rupture of membranes
vaginal bleeding, abruptio placenta
Слайд 15PREECLAMPSIA
Severe preeclampsia - guidelines for expedient delivery
fetal indications
repetitive severe variables or
late decelerations
biophysical profile < 4 on two occasions 4 hours apart
amniotic fluid index < 2 cm
intrauterine growth restriction
fetal death
> 34 weeks gestation
biophysical profile < 4 on two occasions 4 hours apart
amniotic fluid index < 2 cm
intrauterine growth restriction
fetal death
> 34 weeks gestation
Слайд 16PREECLAMPSIA
Severe preeclampsia - management protocol
admission to labor and delivery for 24
hours
magnesium sulfate IV for 24 hours
antihypertensives if diastolic blood pressure > 110 mmHg
meet guidelines for expedited delivery?
yes? delivery
magnesium sulfate IV for 24 hours
antihypertensives if diastolic blood pressure > 110 mmHg
meet guidelines for expedited delivery?
yes? delivery
Слайд 17PREECLAMPSIA
Severe preeclampsia - management protocol
Expedited delivery? no?
< 23 weeks: counseling for
termination of pregnancy
23-32 weeks: steroids, antihypertensive medications, daily maternal and fetal evaluation, delivery at 34 weeks
32-33 weeks: amniocentesis
immature fluid - steroids, delivery in 48 hours
23-32 weeks: steroids, antihypertensive medications, daily maternal and fetal evaluation, delivery at 34 weeks
32-33 weeks: amniocentesis
immature fluid - steroids, delivery in 48 hours
Слайд 18PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - diagnosis
10% before 27 weeks
20% after 37 weeks
70% between
27 and 37 weeks
slow initial phase with accelerated final phase versus secondary expression of sepsis, ARDS, renal failure
slow initial phase with accelerated final phase versus secondary expression of sepsis, ARDS, renal failure
Слайд 19PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome
parameters used to diagnose preeclampsia are not reflective of disease
severity
target organ systems
liver
brain
kidneys
coagulation system
increased maternal and perinatal risk
target organ systems
liver
brain
kidneys
coagulation system
increased maternal and perinatal risk
Слайд 20PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - diagnostic criteria
hemolysis
abnormal peripheral smear
lactate dehydrogenase > 600 U/L
elevated
liver enzymes
serum aspartate aminotransferase > 70 U/L
lactate dehydrogenase > 600 U/L
low platelets
platelet count < 100,000/mm3
serum aspartate aminotransferase > 70 U/L
lactate dehydrogenase > 600 U/L
low platelets
platelet count < 100,000/mm3
Слайд 21PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - differential diagnosis
acute fatty liver of pregnancy
appendicitis
diabetes insipidus
gallbladder disease
gastroenteritis
glomerulonephritis
hemolytic
uremic syndrome
hepatic encephalopathy
hepatic encephalopathy
Слайд 22PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - differential diagnosis
idiopathic thrombocytopenia
kidney stones
pancreatitis
pyelonephritis
systemic lupus erythematosus
thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura
viral
hepatitis
Слайд 23PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - antepartum management
assess and stabilize the maternal condition
correct coagulopathy
if DIC is present
give intravenous magnesium sulfate to prevent seizures
provide treatment for severe hypertension to prevent stroke
transfer to tertiary center if appropriate
if subcapsular hematoma of liver, computed tomography or ultrasound of the abdomen
give intravenous magnesium sulfate to prevent seizures
provide treatment for severe hypertension to prevent stroke
transfer to tertiary center if appropriate
if subcapsular hematoma of liver, computed tomography or ultrasound of the abdomen
Слайд 24PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - antepartum management
evaluate fetal well-being
non stress test
biophysical profile
timing of
delivery
if > 34 weeks gestation, deliver
if < 34 weeks gestation, administer corticosteroids, then deliver in 48 hours
if > 34 weeks gestation, deliver
if < 34 weeks gestation, administer corticosteroids, then deliver in 48 hours
Слайд 25PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - management for cesarean birth
use general anesthesia if platelet
count is < 75,000 / mm3
transfuse 5 to 10 units of platelets before surgery if platelet count is < 50,000 / mm3
leave vesicouterine peritoneum open
install subfascial drain
transfuse 5 to 10 units of platelets before surgery if platelet count is < 50,000 / mm3
leave vesicouterine peritoneum open
install subfascial drain
Слайд 26PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - management for cesarean birth
schedule secondary closure of skin
incision or subcutaneous drain
administer postoperative transfusions as needed
perform intensive monitoring for at least 48 hours postpartum
consider dexamethasone (10 mg IV every 12 hours) until postpartum resolution of disease occurs
administer postoperative transfusions as needed
perform intensive monitoring for at least 48 hours postpartum
consider dexamethasone (10 mg IV every 12 hours) until postpartum resolution of disease occurs
Слайд 27PREECLAMPSIA
HELLP syndrome - management of women with a subcapsular liver hematoma
general
considerations - blood bank aware for potential need of many units of blood
general or vascular surgeon consultation
avoid direct and indirect manipulation of liver
closely monitor hemodynamic status
management of hematoma depends on whether it is ruptured or not
general or vascular surgeon consultation
avoid direct and indirect manipulation of liver
closely monitor hemodynamic status
management of hematoma depends on whether it is ruptured or not
Слайд 28PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia
occurrence of convulsions or coma unrelated to other associated conditions
all new
onset seizures during pregnancy - eclampsia until proven otherwise
incidence: 1 in 500 pregnancies
3% in multiple gestations
incidence: 1 in 500 pregnancies
3% in multiple gestations
Слайд 29PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia
precise cause unknown
theories
vasospasm
ischemia
edema
multisystem organ failure
Слайд 30PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia
seizures usually occur without aura
hypertension not severe in 20%
edema absent
in 30%
proteinuria absent in 20%
hyperreflexia is not predictive of seizure
headache or visual changes - most common precipitating event
proteinuria absent in 20%
hyperreflexia is not predictive of seizure
headache or visual changes - most common precipitating event
Слайд 31PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia
80% of convulsions occur before or during the delivery
1/3 of cases
may be not preventable
atypical
less than 20 weeks gestation
more than 48 hours postpartum
atypical
less than 20 weeks gestation
more than 48 hours postpartum
Слайд 32PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - risk factors
low socioeconomic status
extremes in childbearing age
African-American
no prenatal care
substance
abuse
Слайд 33PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - management
control convulsions
correction of hypoxia and acidosis
blood pressure control
delivery after
maternal stabilization
Слайд 34PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - anticonvulsant therapy
magnesium sulfate
mechanism of action - smooth muscle relaxation
by displacement of calcium
dosage - 4-6 g intravenous loading dose, followed by 2 g per hour
may be given intramuscularly
dosage - 4-6 g intravenous loading dose, followed by 2 g per hour
may be given intramuscularly
Слайд 35PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - magnesium sulfate
side effects:
maternal hypotonia
respiratory depression
cardiac arrest
neonatal depression
contraindicated in myasthenia
gravis
use with caution in renal insufficiency
use with caution in renal insufficiency
Слайд 36PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - anticonvulsant therapy
phenytoin
used extensively in Europe
may be used in myasthenia
gravis
mechanism of action - may increase gamma aminobutyric acid-mediated chloride conduction in postsynaptic membranes
may inhibit neurotransmitter inhibitory systems
mechanism of action - may increase gamma aminobutyric acid-mediated chloride conduction in postsynaptic membranes
may inhibit neurotransmitter inhibitory systems
Слайд 37PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - phenytoin
dosage - 1 g loading dose over 1 hour
cardiac
monitoring during administration
side effects
arrhythmias with rapid administration
hepatitis
Steven-Johnson syndrome
side effects
arrhythmias with rapid administration
hepatitis
Steven-Johnson syndrome
Слайд 38PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - diazepam
side effects - loss of consciousness, hypotension, respiratory depression
caution
- may increase risk of aspiration
causes prolonged depression of the neonate
sodium thiopentotal
long acting barbiturate
used when sedation, paralysis and intubation needed
causes prolonged depression of the neonate
sodium thiopentotal
long acting barbiturate
used when sedation, paralysis and intubation needed
Слайд 39PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - management of fetus
fetal bradycardia during seizure
~ 5 minutes
after the onset of the seizure
may be associated with rebound tachycardia
recovery phase may show late decelerations
monitor for uterine hypertonicity
allow for fetal recovery
monitor for signs of abruption
may be associated with rebound tachycardia
recovery phase may show late decelerations
monitor for uterine hypertonicity
allow for fetal recovery
monitor for signs of abruption
Слайд 40PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - radiographic evaluation
should be reserved for women with neurological deficit,
recurrent seizures, or atypical presentation
abnormal CT findings - 50%
edema, hemorrhage, infarction
cerebral angiography has limited use
90% of EEG evaluations may be abnormal
abnormal CT findings - 50%
edema, hemorrhage, infarction
cerebral angiography has limited use
90% of EEG evaluations may be abnormal
Слайд 41PREECLAMPSIA
Eclampsia - management
allow patient to have seizure
use bite block as needed
to prevent maternal injury
establish airway
administer magnesium sulfate as soon as possible
obtain arterial blood gases
monitor urine output
control hypertension
establish airway
administer magnesium sulfate as soon as possible
obtain arterial blood gases
monitor urine output
control hypertension
Слайд 42PREECLAMPSIA
Counseling regarding future pregnancies - HELLP syndrome
information available varies
recurrent risk
of preeclampsia: 43% (19%)
recurrent risk of HELLP syndrome: 19-27% (3%)
If HELLP syndrome < 32 weeks
recurrent risk of preeclampsia / eclampsia is 61%
recurrent risk of HELLP syndrome: 19-27% (3%)
If HELLP syndrome < 32 weeks
recurrent risk of preeclampsia / eclampsia is 61%