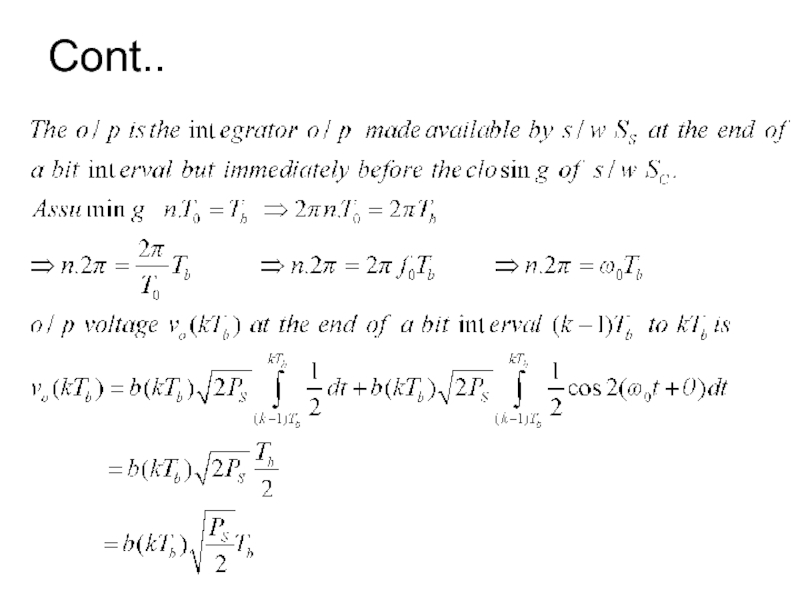- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Module IIITaub Ch.6 презентация
Содержание
- 1. Module IIITaub Ch.6
- 2. Examples of Modulation Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)
- 3. Description of binary ASK,PSK, and FSK
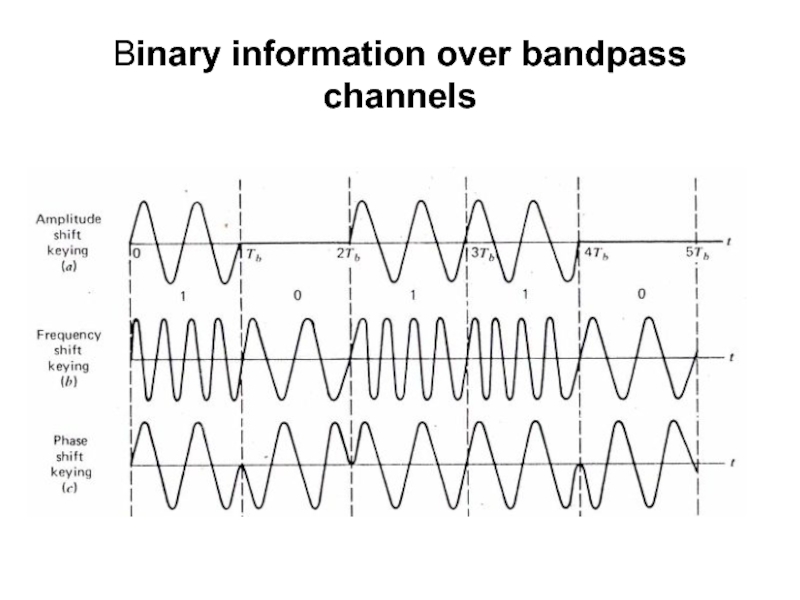
- 4. Binary information over bandpass channels
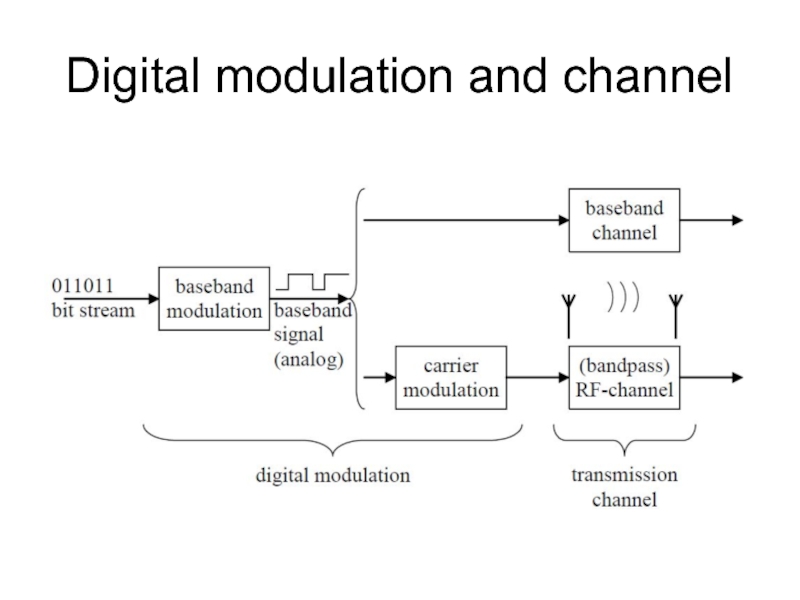
- 5. Digital modulation and channel
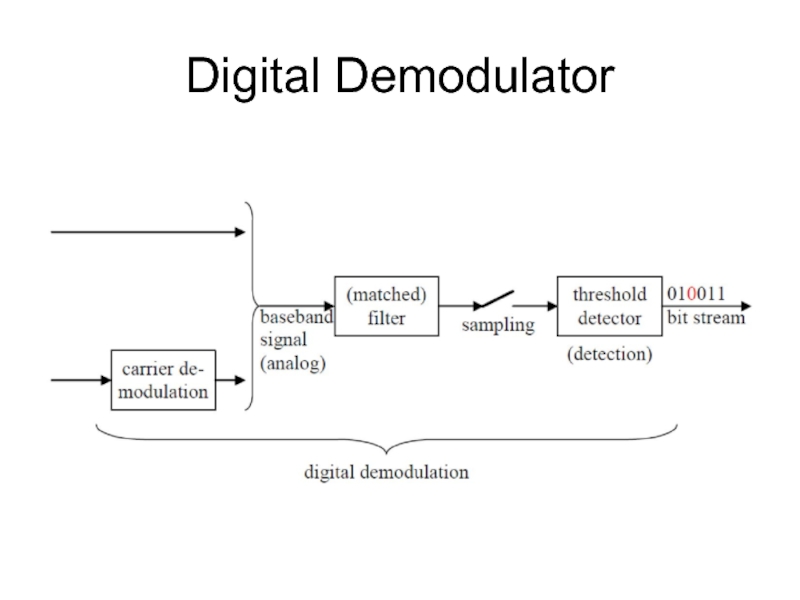
- 6. Digital Demodulator
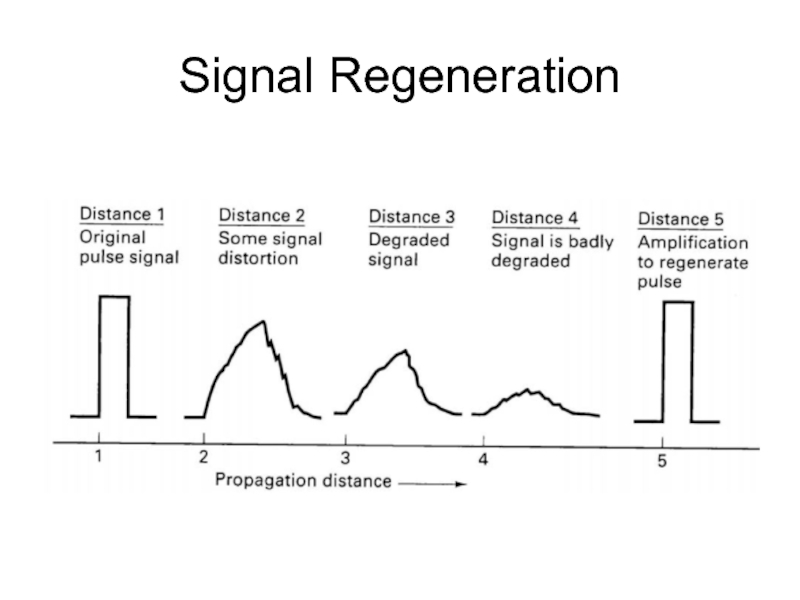
- 7. Signal Regeneration
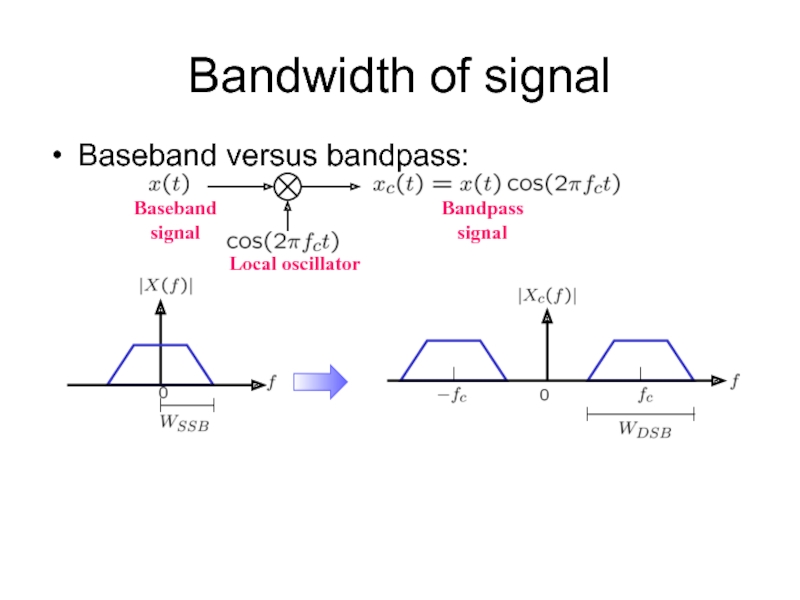
- 8. Bandwidth of signal Baseband versus bandpass:
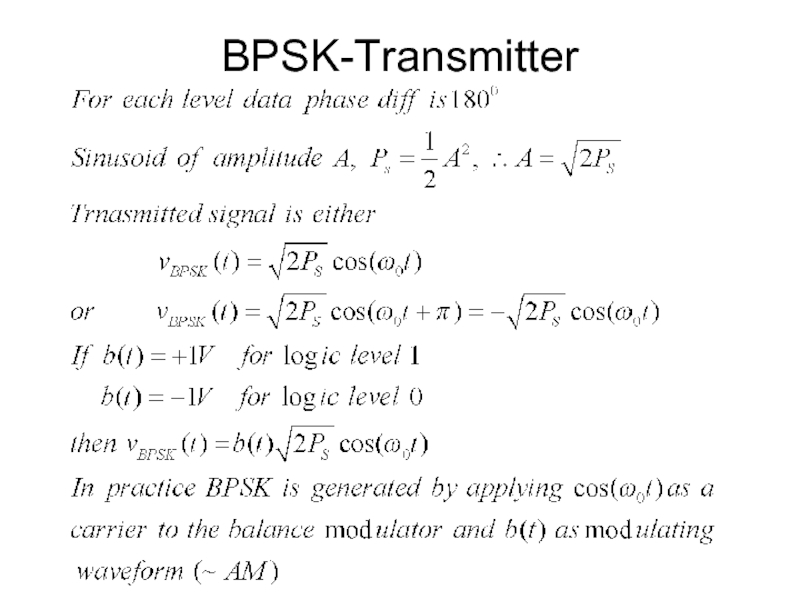
- 9. BPSK-Transmitter
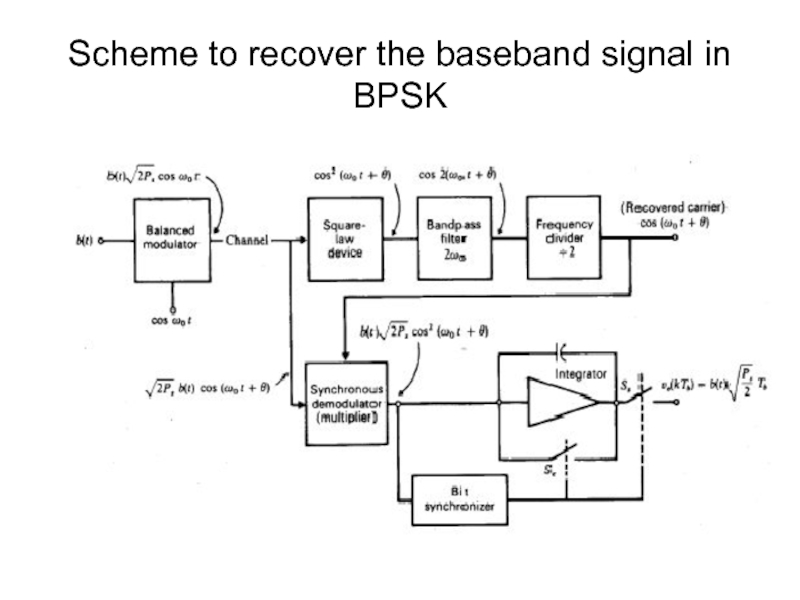
- 10. Scheme to recover the baseband signal in BPSK
- 11. BPSK-Receiver
- 12. Cont..
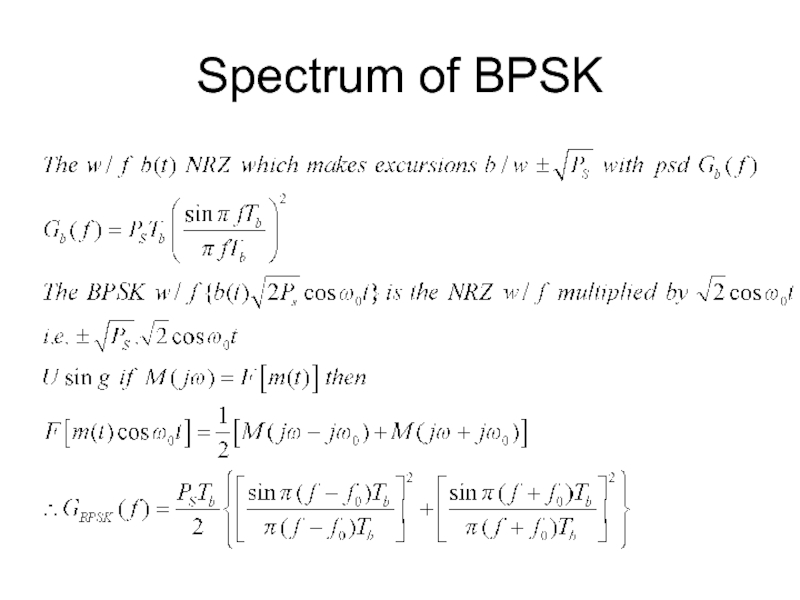
- 13. Spectrum of BPSK
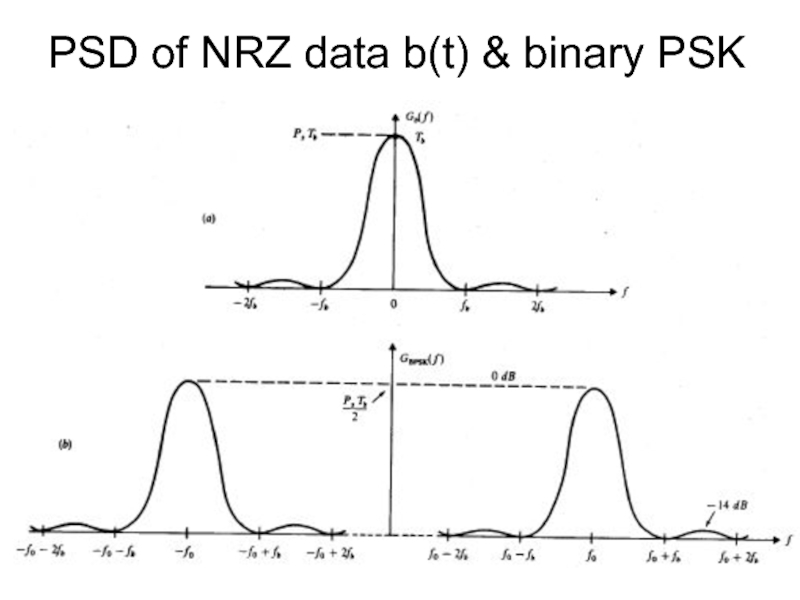
- 14. PSD of NRZ data b(t) & binary PSK
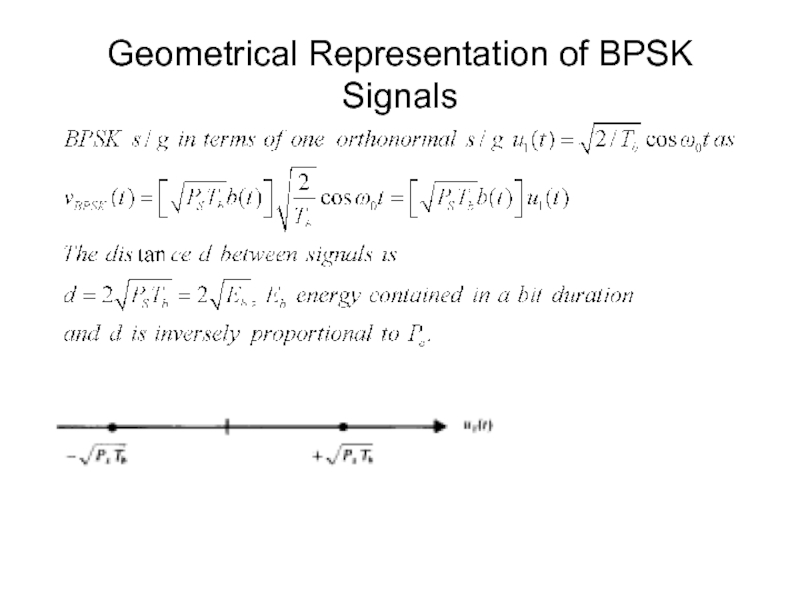
- 15. Geometrical Representation of BPSK Signals
- 16. Differential Phase-Shift Keying Merit – it eliminate
- 17. Means of generating a DPSK signal
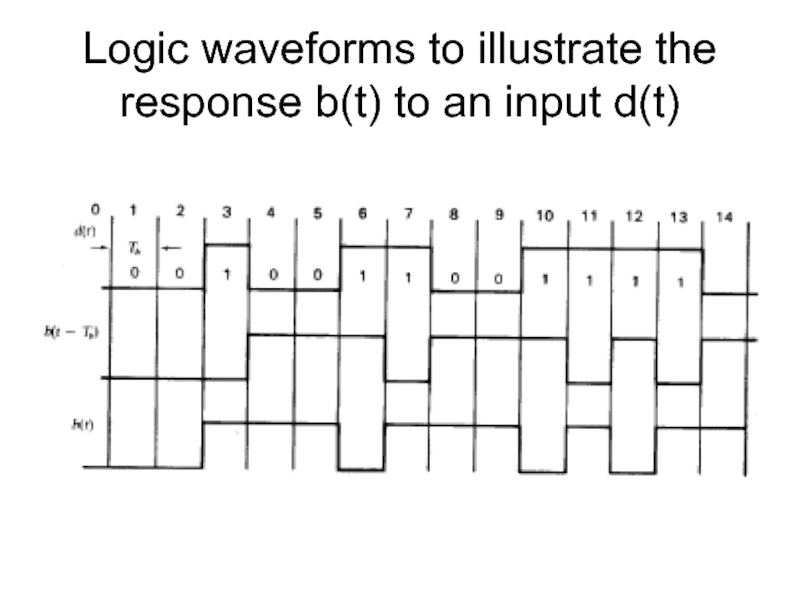
- 18. Logic waveforms to illustrate the response b(t) to an input d(t)
- 19. Method of recovering data from the DPSK signal
- 20. Cont.. The transmitted data d(t) can be
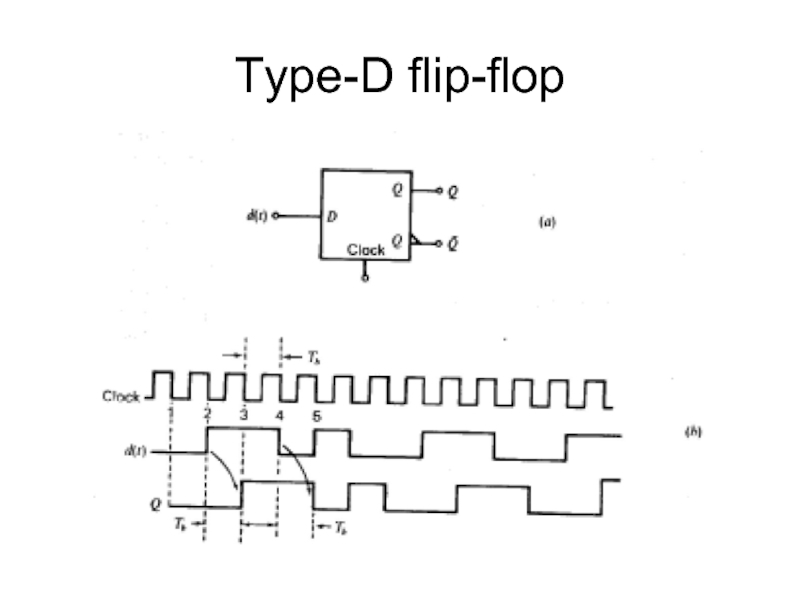
- 21. Type-D flip-flop
- 22. Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying (QPSK) BW for BPSK
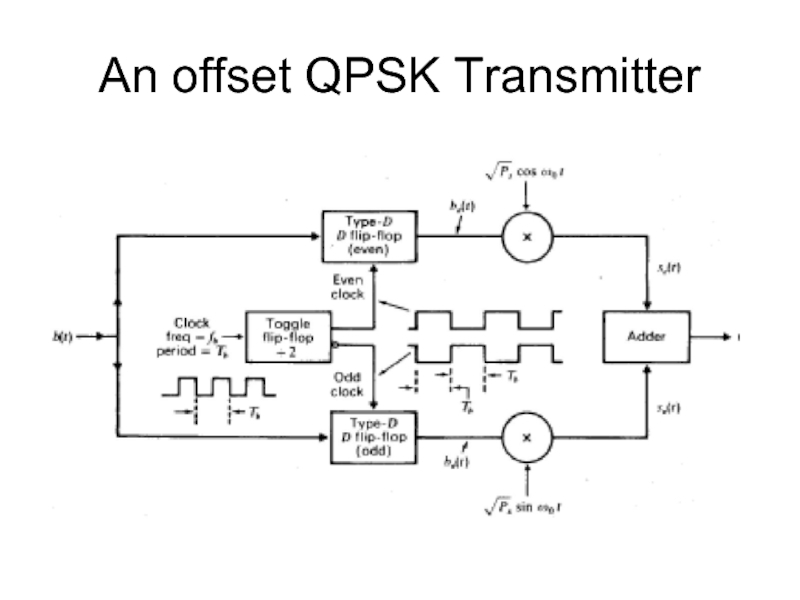
- 23. An offset QPSK Transmitter
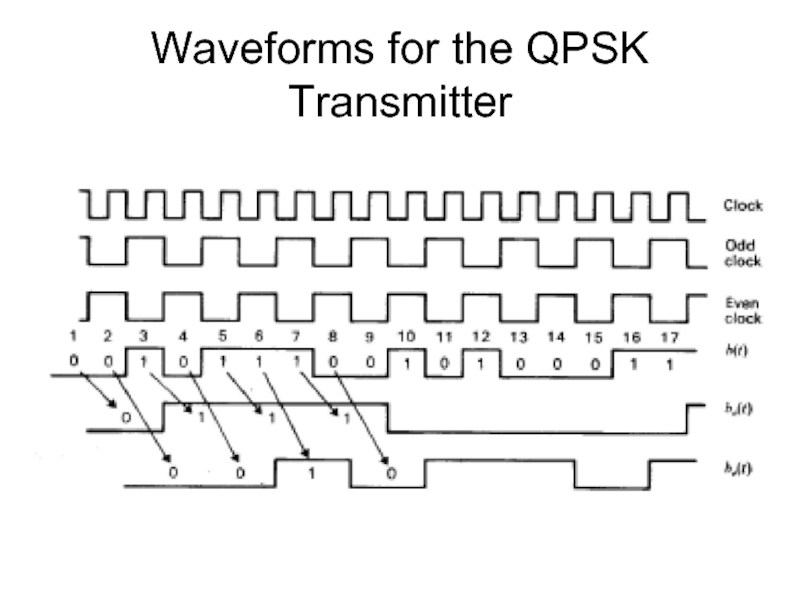
- 24. Waveforms for the QPSK Transmitter
- 25. OQPSK
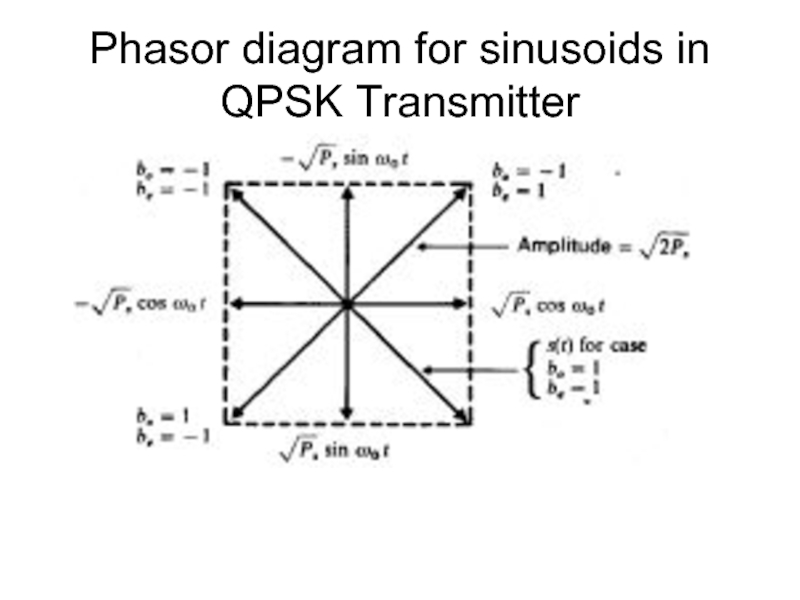
- 26. Phasor diagram for sinusoids in QPSK Transmitter
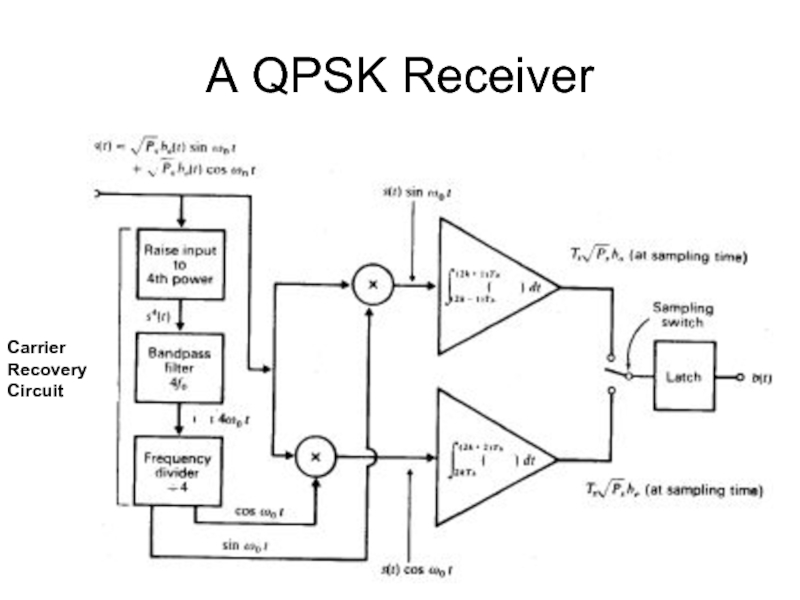
- 27. A QPSK Receiver Carrier Recovery Circuit
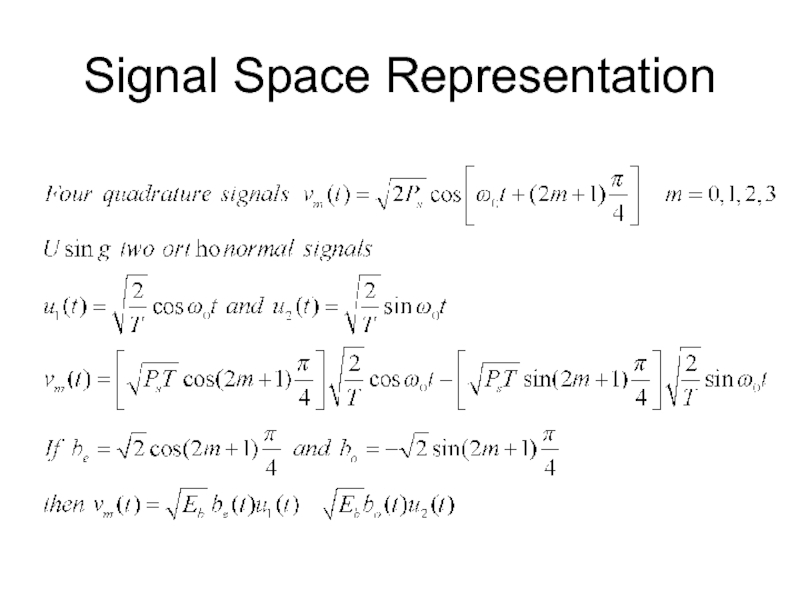
- 28. Signal Space Representation
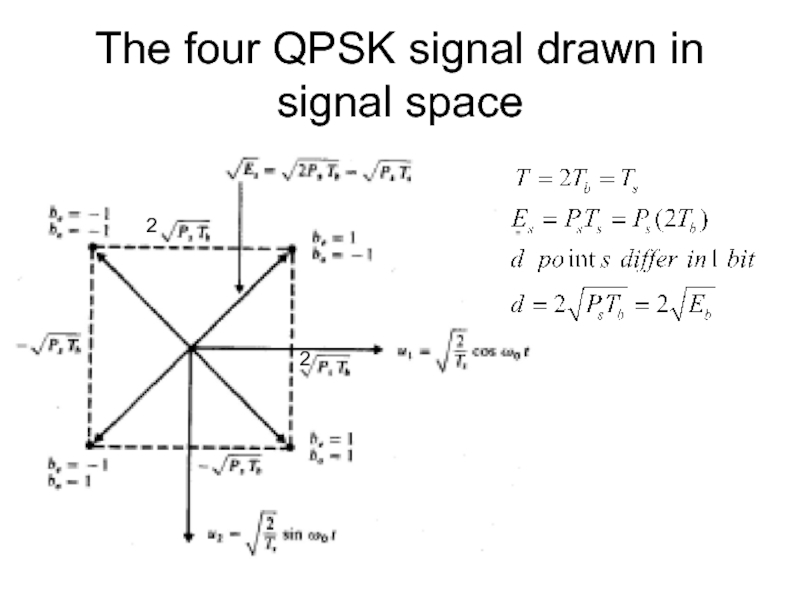
- 29. The four QPSK signal drawn in signal space 2 2
- 30. M-ary PSK
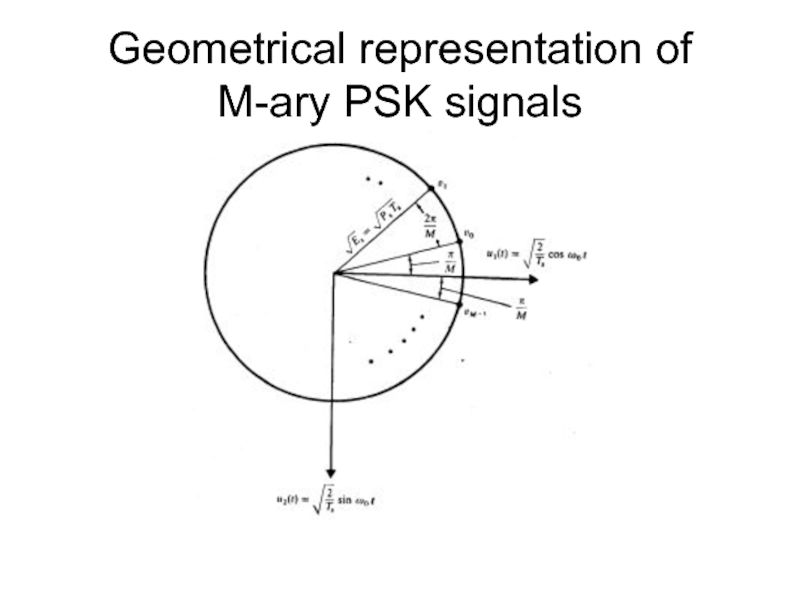
- 31. Geometrical representation of M-ary PSK signals
- 32. Cont..
- 33. Cont..
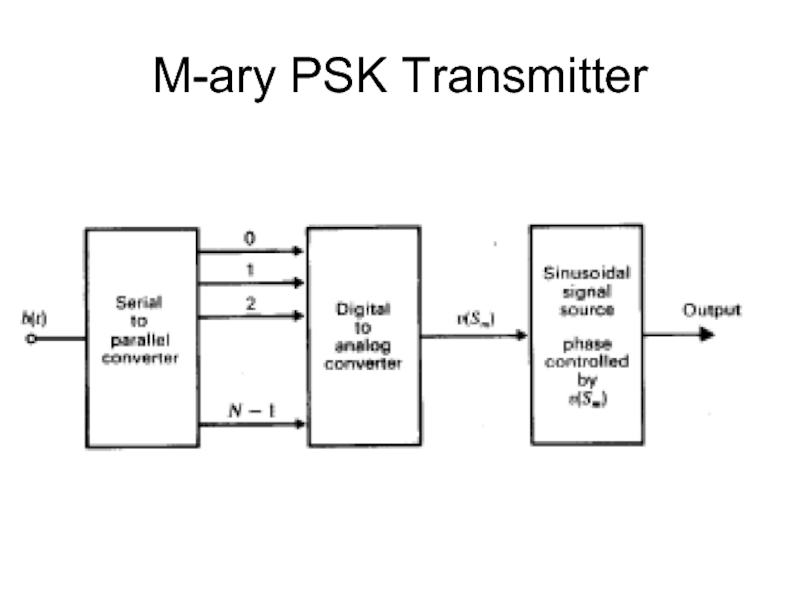
- 34. M-ary PSK Transmitter
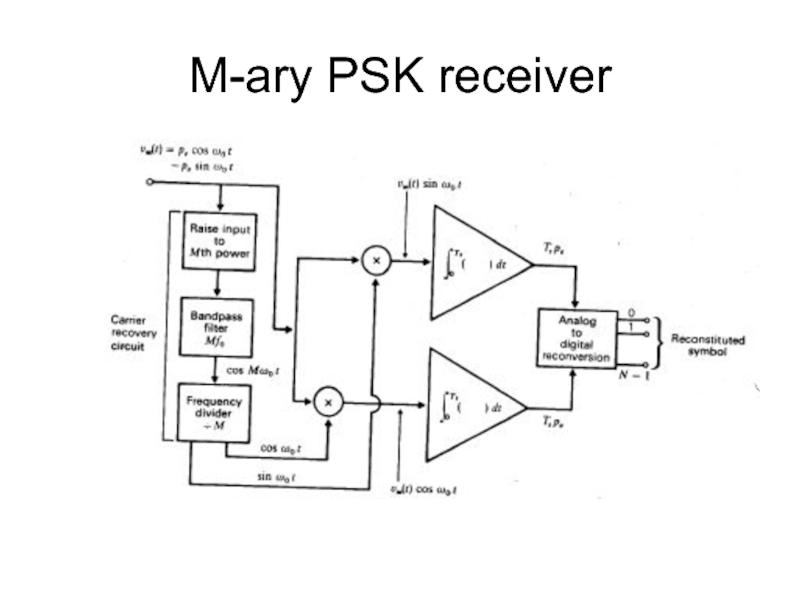
- 35. M-ary PSK receiver
- 36. BFSK
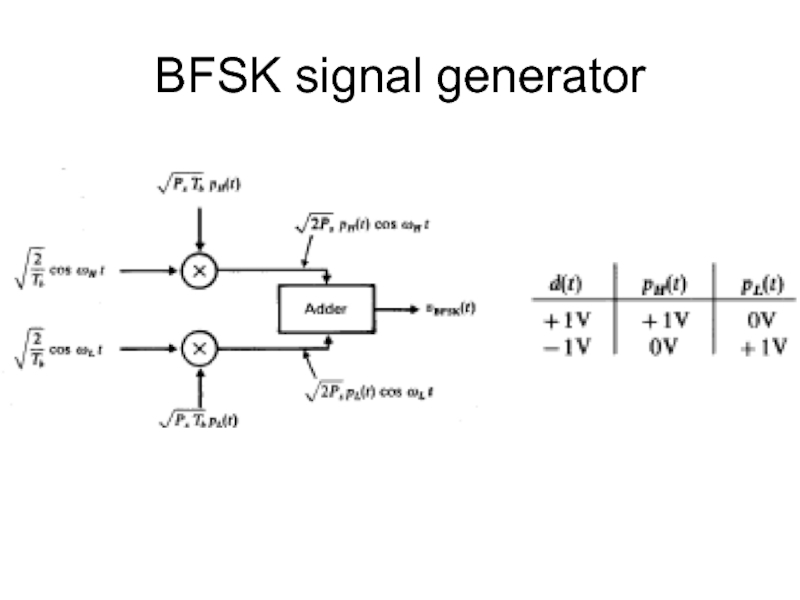
- 37. BFSK signal generator
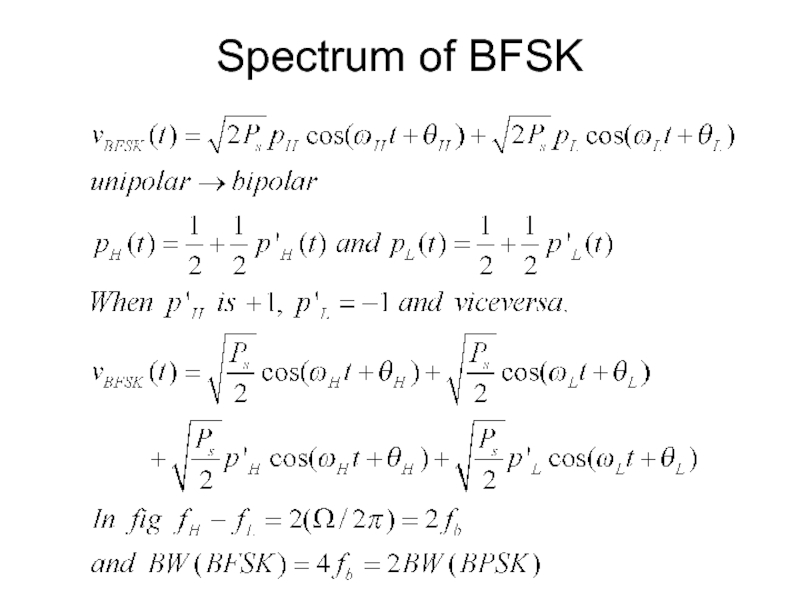
- 38. Spectrum of BFSK
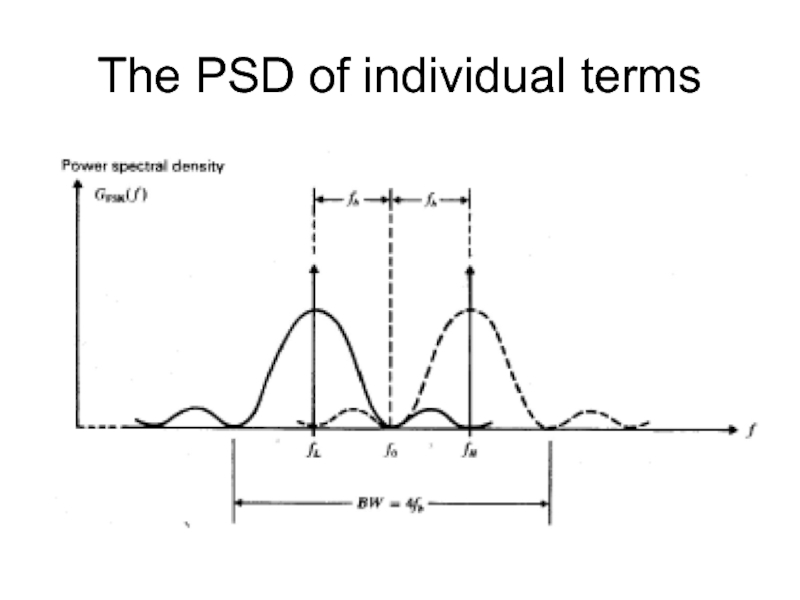
- 39. The PSD of individual terms
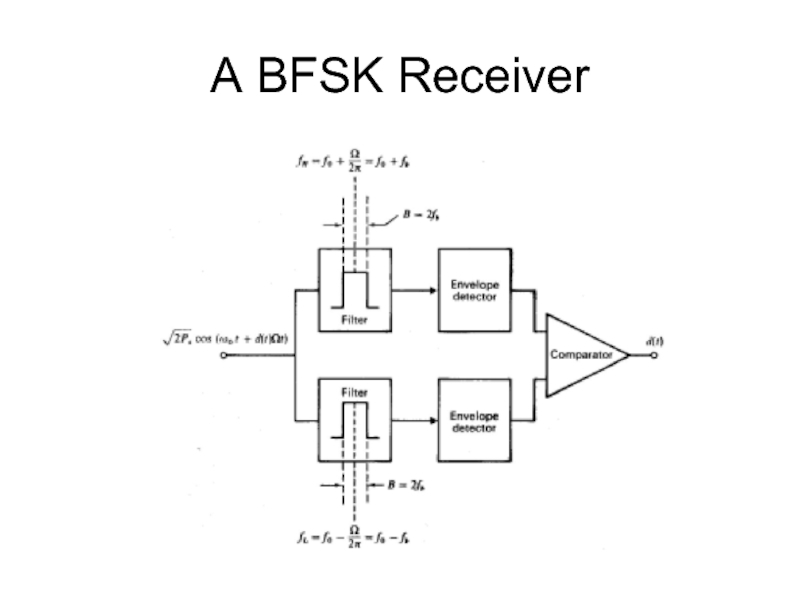
- 40. A BFSK Receiver
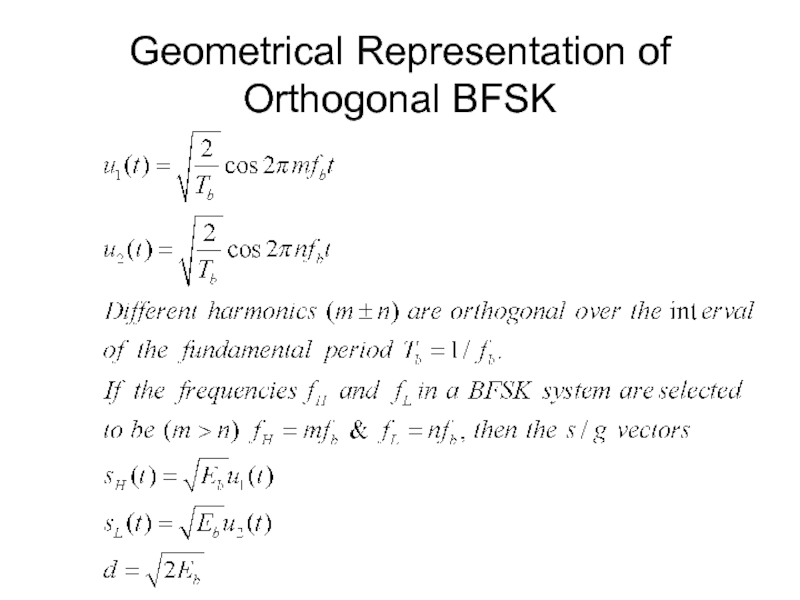
- 41. Geometrical Representation of Orthogonal BFSK
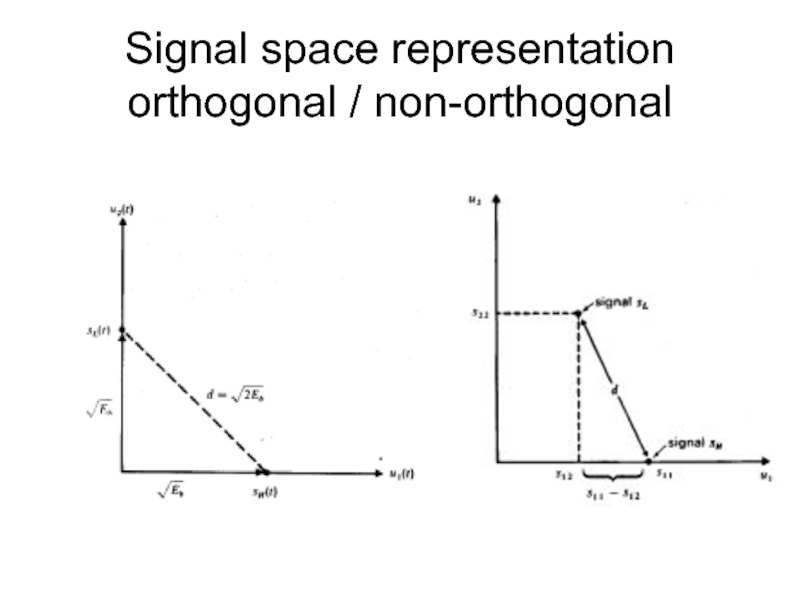
- 42. Signal space representation orthogonal / non-orthogonal
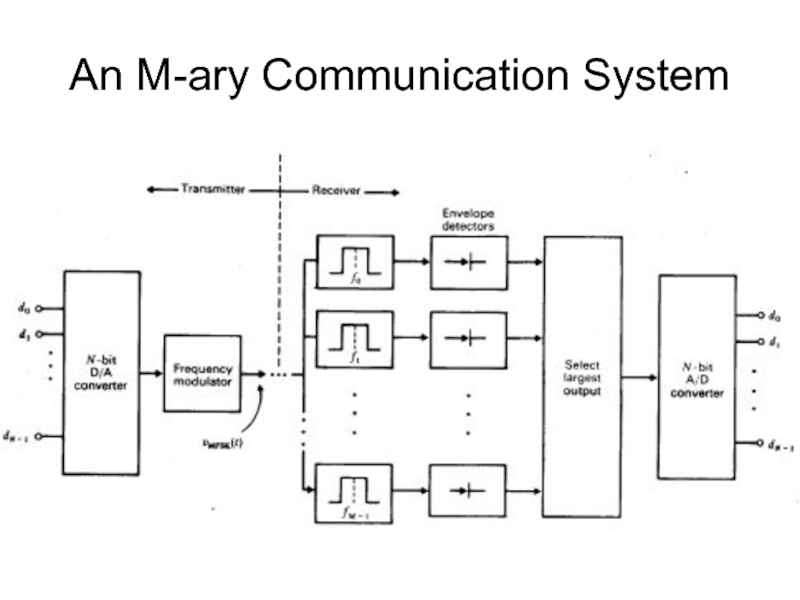
- 43. An M-ary Communication System
- 44. M-ary FSK
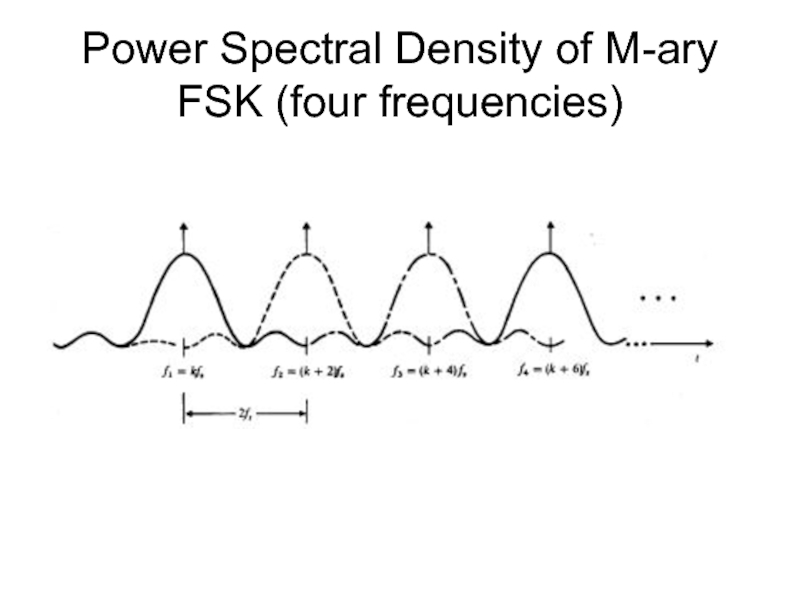
- 45. Power Spectral Density of M-ary FSK (four frequencies)
- 46. Geometrical Representation of orthogonal M-ary FSK (M=3)
- 47. MSK
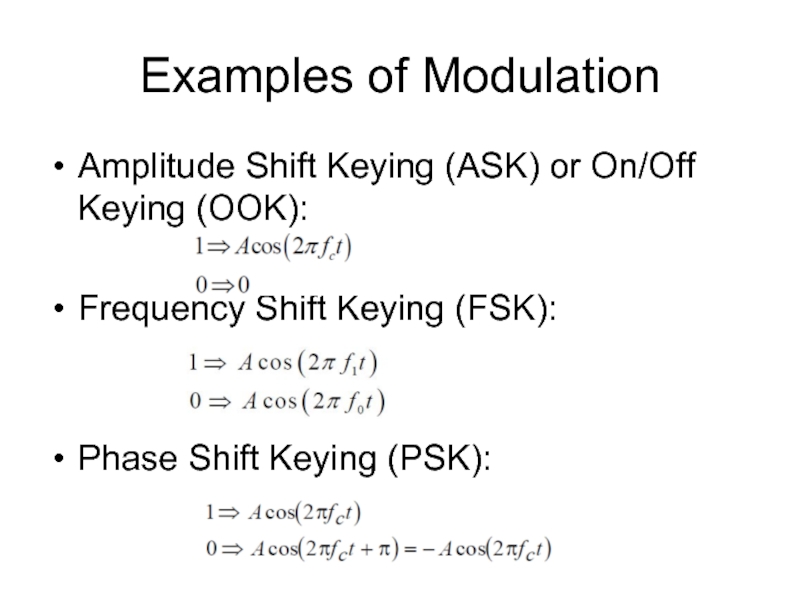
Слайд 2Examples of Modulation
Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) or On/Off Keying (OOK):
Frequency Shift
Keying (FSK):
Phase Shift Keying (PSK):
Phase Shift Keying (PSK):
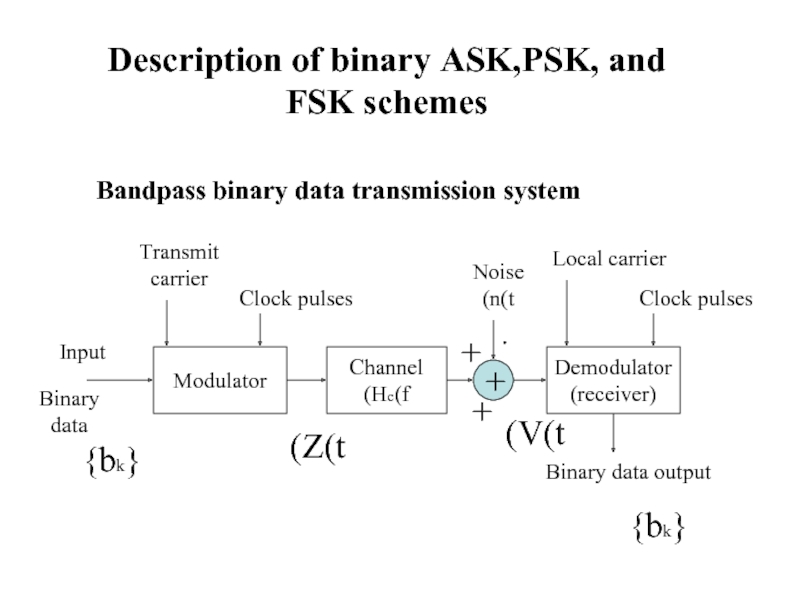
Слайд 3
Description of binary ASK,PSK, and
FSK schemes
Bandpass binary data transmission
system
Modulator
Channel
Hc(f)
Demodulator
(receiver)
{bk}
Binary
data
Input
{bk}
Transmit
carrier
Clock pulses
Noise
n(t)
Clock pulses
Local carrier
Binary data output
Z(t)
+
+
V(t)
ּ+
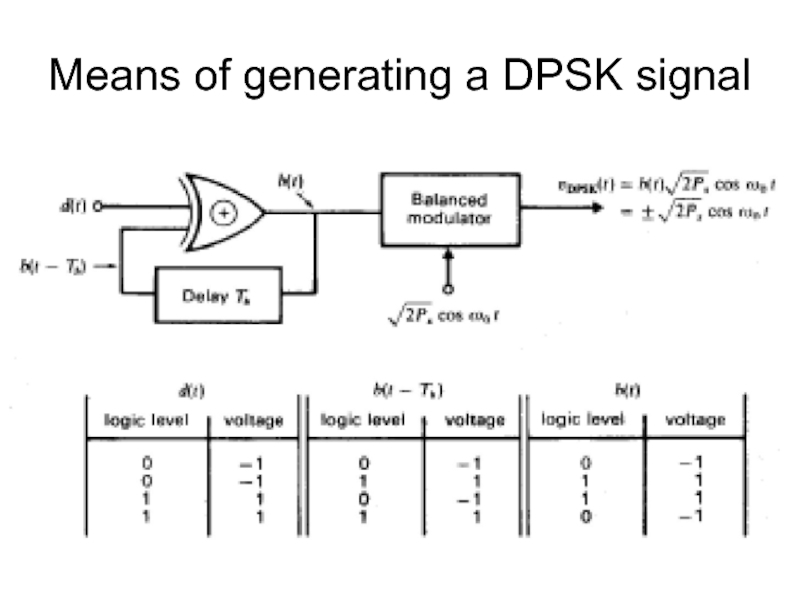
Слайд 16Differential Phase-Shift Keying
Merit – it eliminate the ambiguity about whether the
demodulated data is or is not inverted.
Avoids the need to provide the synchronous carrier required at the demodulator for detecting a BPSK signal.
Arbitrarily assuming that in the first interval b(0)=0. In the demodulator, the data will be correctly determined regardless of our assumption concerning b(0) - Invariant feature of the system.
i.e no change in b(t) occur whenever d(t)=0, and a change in b(t) occurs whenever d(t)=1.
When d(t)=0 the phase of the carrier does not change at the beginning of the bit interval, while when d(t)=1 there is a phase change of magnitude π.
Avoids the need to provide the synchronous carrier required at the demodulator for detecting a BPSK signal.
Arbitrarily assuming that in the first interval b(0)=0. In the demodulator, the data will be correctly determined regardless of our assumption concerning b(0) - Invariant feature of the system.
i.e no change in b(t) occur whenever d(t)=0, and a change in b(t) occurs whenever d(t)=1.
When d(t)=0 the phase of the carrier does not change at the beginning of the bit interval, while when d(t)=1 there is a phase change of magnitude π.
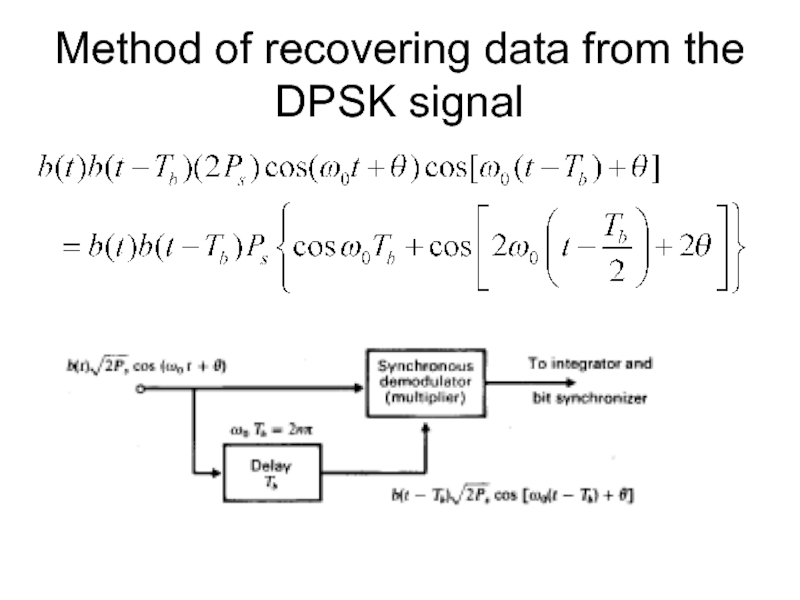
Слайд 20Cont..
The transmitted data d(t) can be readily determined from the product
b(t)b(t-Tb).
If d(t)=0 then there was no phase change and b(t)=b(t-Tb) both being +1V or both being -1V. In this case b(t)b(t-Tb)=1.
If however d(t)=1 then there was a phase change and either b(t)=1V with b(t-Tb)= -1V or vice versa.
In either case b(t)b(t-Tb)= -1.
If d(t)=0 then there was no phase change and b(t)=b(t-Tb) both being +1V or both being -1V. In this case b(t)b(t-Tb)=1.
If however d(t)=1 then there was a phase change and either b(t)=1V with b(t-Tb)= -1V or vice versa.
In either case b(t)b(t-Tb)= -1.
Слайд 22Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying (QPSK)
BW for BPSK must be nominally 2fb.
QPSK allows
bits to be transmitted at half the BW.
In a QPSK system the type D flip-flop is used as a one bit storage device.
In a QPSK system the type D flip-flop is used as a one bit storage device.
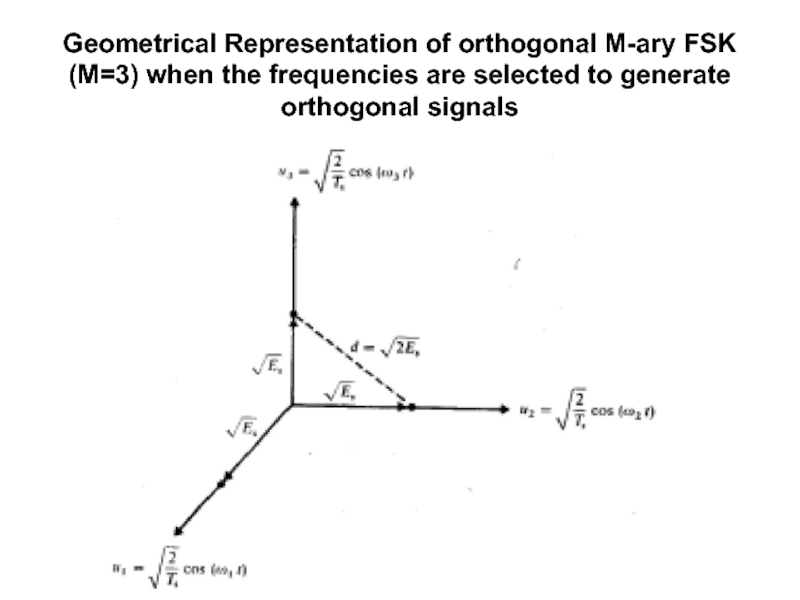
Слайд 46Geometrical Representation of orthogonal M-ary FSK (M=3) when the frequencies are
selected to generate orthogonal signals