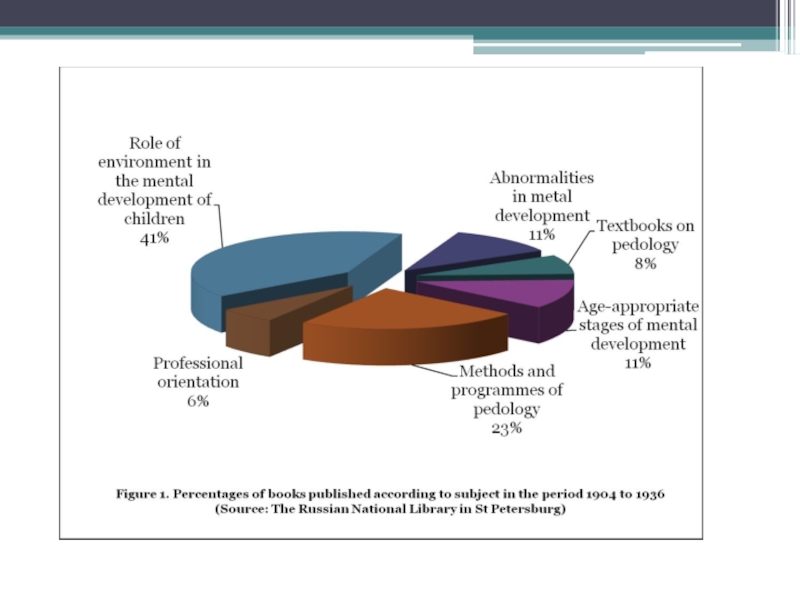
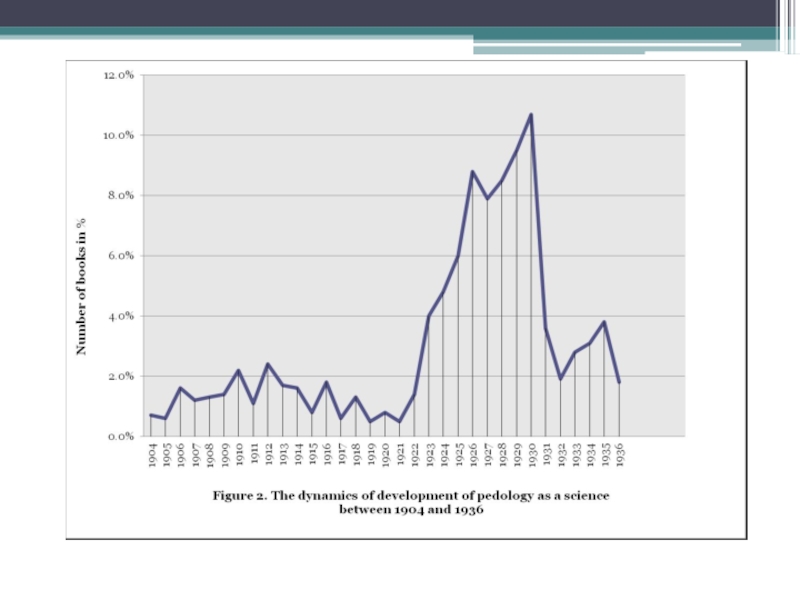
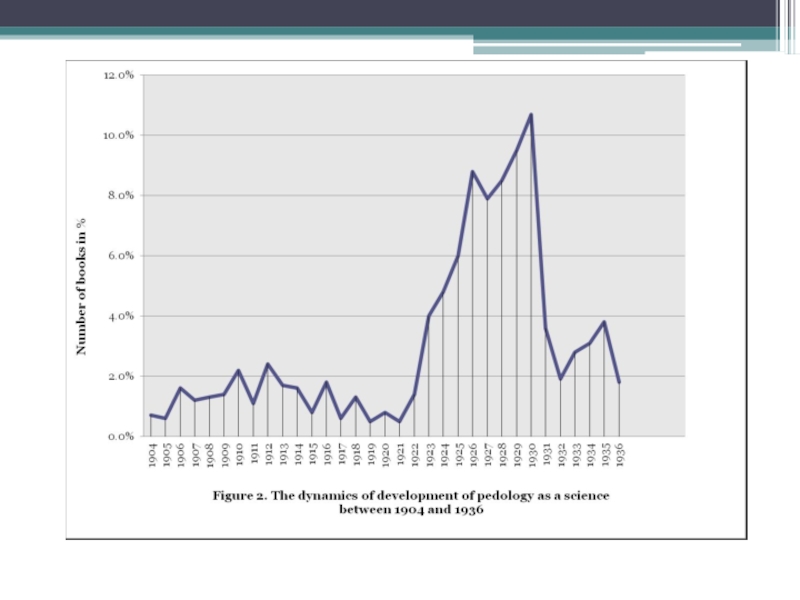
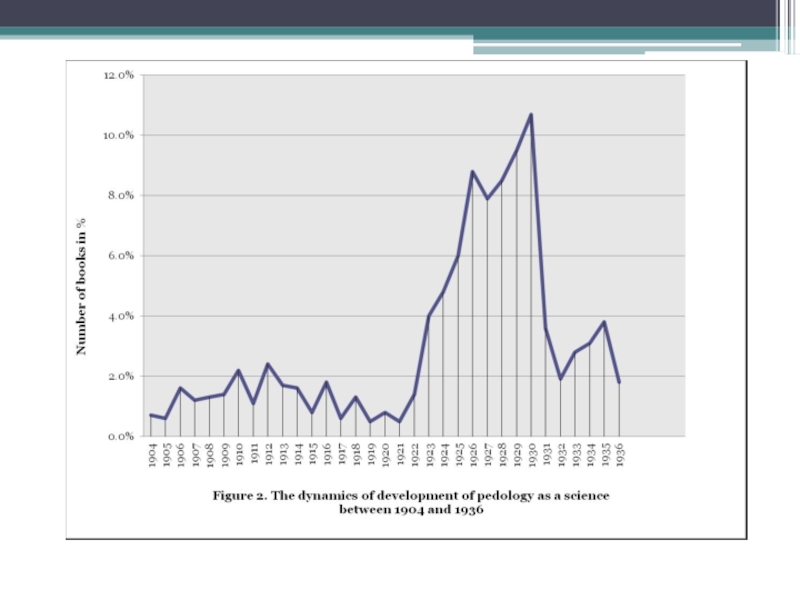
Elena Minkova
State Pedagogical University,
Nizhny Novgorod, Russia
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Grigory Rossolimo - a founder of Russian child neurology and psychology презентация
Содержание
- 1. Grigory Rossolimo - a founder of Russian child neurology and psychology
- 2. The
- 3. Grigory Rossolimo (1860-1928)
- 4. Sergei Korsakoff (1854 – 1900) 1854 -
- 5. Grigory Rossolimo and Anton Chekhov, his contemporary well-known writer-physician
- 6. Clinic for Nervous Diseases in Moscow, founded in 1890
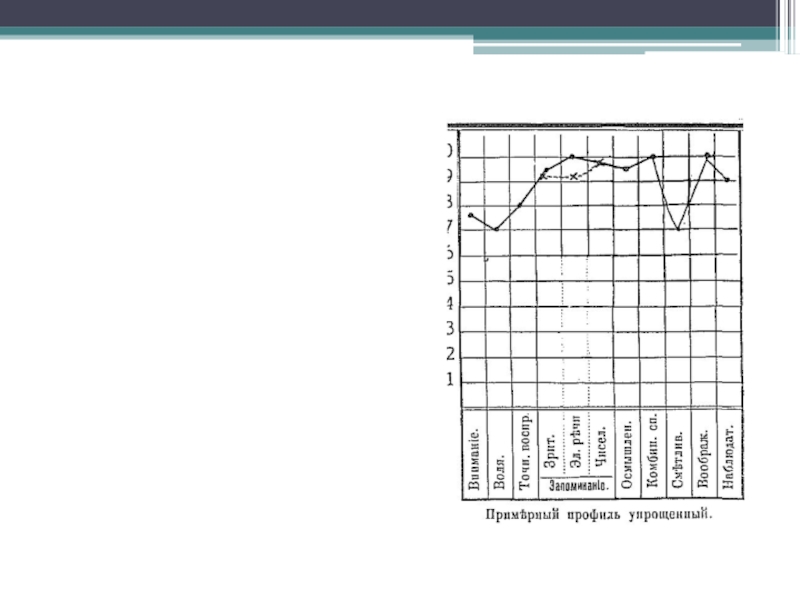
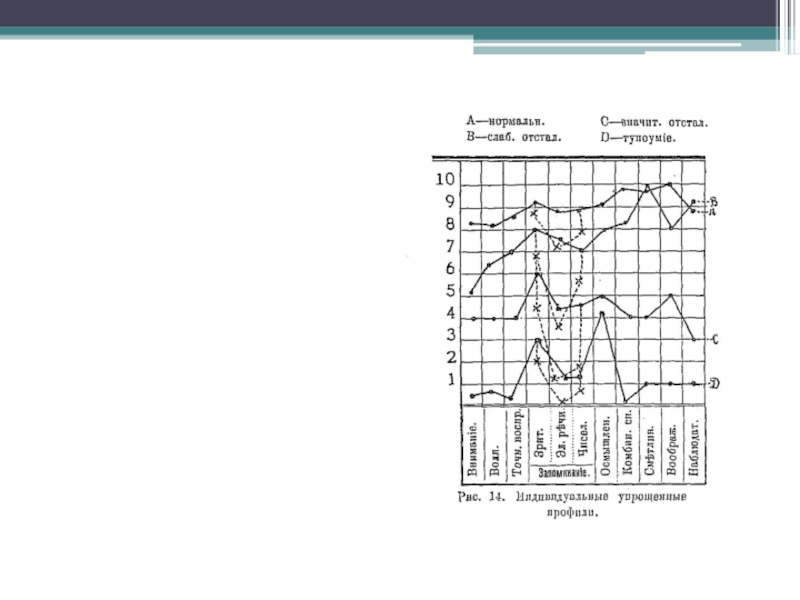
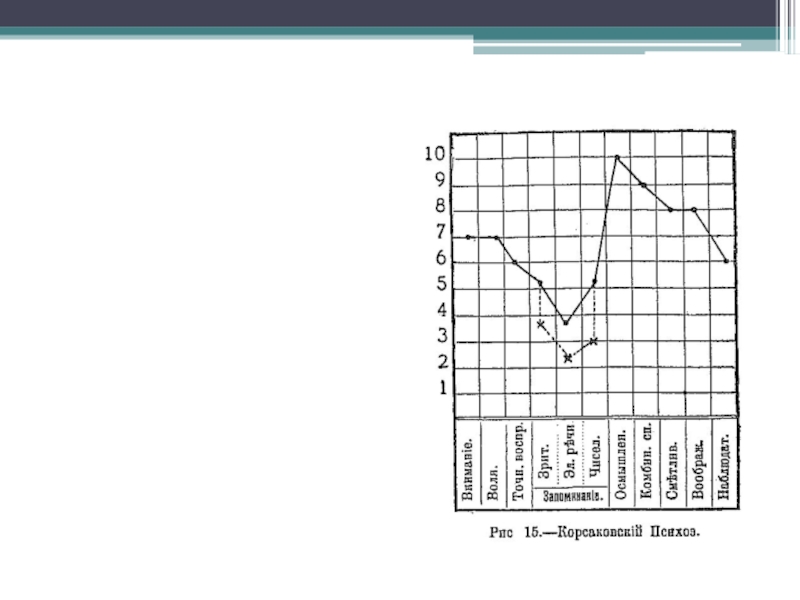
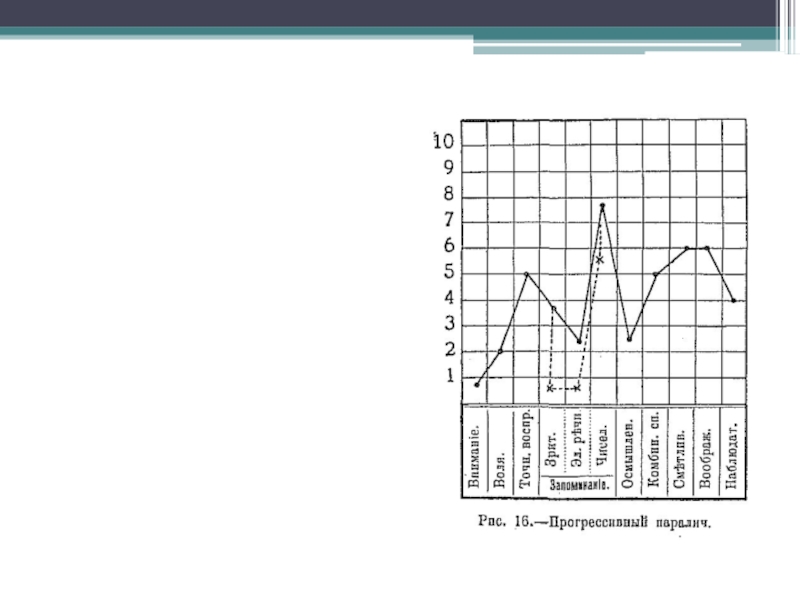
- 7. Method of psychological profile.
- 8. Tombstone on the grave of Rossolimo in Novodevichie cemetery (Sculptor V.I. Kovrigin) “
- 10. Laboratories opened and working by February 1917
- 12. 1904 - the first pedological courses were
- 13. The subjects taught at the first pedological
- 15. National Research Institute for Scientific Pedagogy at
- 16. 1923 - The First All-Russian Psycho-Neurological of
- 17. Pavel Blonsky (1884 - 1941) 1884
- 18. Lev Vygotsky (1896 -1934) 1896
- 19. Aron Zalkind (1888-1936) 1888 - Born
- 21. Mikhail Basov (1892-1931) 1892 - Born
- 22. Four main principles of Pedology
Слайд 1Grigory Rossolimo - a founder of Russian child neurology and psychology
Слайд 2 The main aim of this paper
provide characteristic features of his work in experimental psychology, following the path of his scientific work in chronological order
analyze his key findings in his primary research: the method of psychological profiles
highlight Rossolimo's enduring contribution to the development of Russian and world psychology and defectology
Слайд 3 Grigory Rossolimo (1860-1928)
1860 - Born in Odessa
1887 - Earned his medical doctorate
1890 - Head of the Clinic for Nervous Diseases
1890 - Chairman of the Society of Neurologists and Psychiatrists in Moscow
1901 - Founder and Editor of Journal “Neuropsychiatry"
1911 - 1917 - Founded Russia's first clinic of nervous diseases of childhood
1911 - Arranged Institute of Child Psychology and Neurology which he funded himself
1917 - Professor of Nervous Diseases at the 1st State University in Moscow, Director of the clinic and the Neurological Institute
1928 - Died in Moscow
Слайд 4Sergei Korsakoff
(1854 – 1900)
1854 - Born in Vladimir
1875 - Graduated
1876 – 1879 –Postgraduated from the clinic for nervous diseases
1887 -Earned his medical doctorate
1892 – Appointed professor extraordinarius at a new university psychiatric clinic
1899 - Head of the Clinic for Nervous Diseases
1900 - Died in Moscow
Слайд 10Laboratories opened and working by February 1917
Laboratory of Experimental Psychology
Moscow Medical and Pedagogical Experimental Station, under the direction of V.P. Kashenko (later renamed to Moscow Medical and Pedagogical Clinic);
Psychological Institute at the 2nd Moscow State University, under the direction G.I. Chelpanov;
The Central Pedological Institute, under the direction N. A. Ribnikov.
Слайд 121904 - the first pedological courses were opened at the University
1907 - Bechterev founded the Pedological Institute
1908 - a Froebel Institute was set up in Kiev by Sikorsky
1921 - three pedological institutes formed in Moscow: The Central Pedological Institute, Medical Pedological Institute and a psycho-pedological branch at the 2nd Moscow State University
Слайд 13The subjects taught at the first pedological courses in St. Petersburg
Pedagogy Anatomy
General Psychology Nervous and mental
Pathology
Study of defective
children Child Hygiene
Criminal Anthropology Psychophysiology of sensory organs
Comparative
Child Psychology Psychology
Слайд 15National Research Institute for Scientific Pedagogy at Second Moscow State University
Academy of Communist Education (1923, has tree pedological laboratories: Molozhavy, Blonsky, Zalkind)
State Institute of Experimental Psychology (1924, Kornilov)
Department of Children's Health Hospital for Nervous Diseases at the First Moscow State University (1923, Rossolimo)
National Institute of Social Hygiene People's Commissariat of Health (1923, Molkov)
The higher educational courses at the Second Moscow State University (1924, Zalkind)
Research Institute of Occupational Diseases (1923, Bogolepova)
Слайд 161923 - The First All-Russian Psycho-Neurological of Human Behavior Congress (also
1923 - The Second Congress of Social Legal Protection of Minors
1924 -The Second All-Russian Psycho-Neurological Congress
1925 - The First All-Russian Congress of Teachers
1927 - The Second All-Union Pedological Conference (also known as “Pedological Meeting”
1928 - All-Union Pedological Congress
1930 - The Third All-Russian Child Welfare Congress
1930 - The First All-Union Congress on the Study
Слайд 17Pavel Blonsky
(1884 - 1941)
1884 - Born in Kiev
1907 - Graduated
department of the history and philology faculty, Kiev University
1908 - Taught education and psychology in girls’ high schools in Moscow
1913 - Obtained Master’s degree, became an assistant professor at Moscow University, began to give lectures on educational psychology
1918 - He was made a professor at Moscow University
1922 - Worked with Krupskaya in the scientific education section of the State Academic Council (GUS)
1941 - Died in Moscow
“
Слайд 18Lev Vygotsky
(1896 -1934)
1896 - Born in Orsha
1917 - Graduated
1924 -1928 - Worked at the Moscow State Institute of Experimental Psychology
1925 - Defended his doctoral thesis on “Psychology of Art”
1925 – Participated in the Congress of Defectology in London
1927 – 1934 - Taught courses in several universities in Moscow, Leningrad, Harkov
1929- 1934 - Founded and worked at the Institute of Defectology.
1934 - Died in Moscow
Слайд 19Aron Zalkind
(1888-1936)
1888 - Born in Kharkov
1911 - Graduated from the
1917 - 1920 - Was director of the Petrograd Psychotherapeutic Institute
1925 - Was forced to distance himself from psychoanalysis and publicly repented of his "connections" with Freudianism, directed his scientific aspirations towards the developmental problems of Pedology
1930 - Director of the Institute of Psychology, Pedology and Psychotechnics
1936 - Died in Moscow
Слайд 21Mikhail Basov
(1892-1931)
1892 - Born in the village of Loginovo, Tver
1915 - Worked in Psychoneurological Institute in Petrograd under Lazursky’s leadership
1924-1931 - Professor of Pedology and psychology at the State Institute of Pedology, Leningrad and at the Leningrad Pedagogical Institute in the name of Herzen
1920-1930 - Was accused of being anti-Marxist and to re-instate his name he leaves science and takes up mechanical fitter apprenticeship
1931 - Received a small injury at the factory which caused blood infection and later death
Слайд 22 Four main principles of Pedology
The principle of the holistic approach
The genetic principle, to include Vygotsky's proposed idea of the zone of proximal development;
The principle of taking into consideration the social context, that is, the living conditions of the child;
The principle of making a diagnosis of the level of a child's development with the purpose of providing the child and the child's parents with psychological assistance.