- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Exceptions презентация
Содержание
- 1. Exceptions
- 2. Exception Exceptions in Java are special objects
- 3. Syntax try { // some
- 4. Checked vs. unchecked exceptions ‘Checked’ exceptions are
- 5. Exceptions hierarchy
- 6. Exceptions hierarchy : Throwable Every exception class
- 7. Exceptions hierarchy : Error Classes that
- 8. Exceptions hierarchy : Exception Exception classes that
- 9. Exceptions hierarchy : RuntimeException RuntimeException indicates occurrence
- 10. Catching exceptions Exceptions are caught in order
- 11. Creating your own exceptions When creating your
- 12. Common exceptions ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException int i =
- 13. Common exceptions ClassCastException In Java you
- 14. Common exceptions NullPointerException If you try
Слайд 2Exception
Exceptions in Java are special objects describing exceptional state occured in
some place within program‘s code. If execution flow has run into some exceptional state an Exception object is created and passed to handler method.
Exceptions may be thrown manually in custom code as well.
Exceptions may be thrown manually in custom code as well.
Слайд 3Syntax
try {
// some code that might run into exceptional
state
}
catch (CustomException е) {
// handle CustomException
}
catch (FileNotFoundException е) {
// handle FileNotFoundException
throw e; // rethrowing exception up the call stack
}
finally {
// some code that will run anyway
}
}
catch (CustomException е) {
// handle CustomException
}
catch (FileNotFoundException е) {
// handle FileNotFoundException
throw e; // rethrowing exception up the call stack
}
finally {
// some code that will run anyway
}
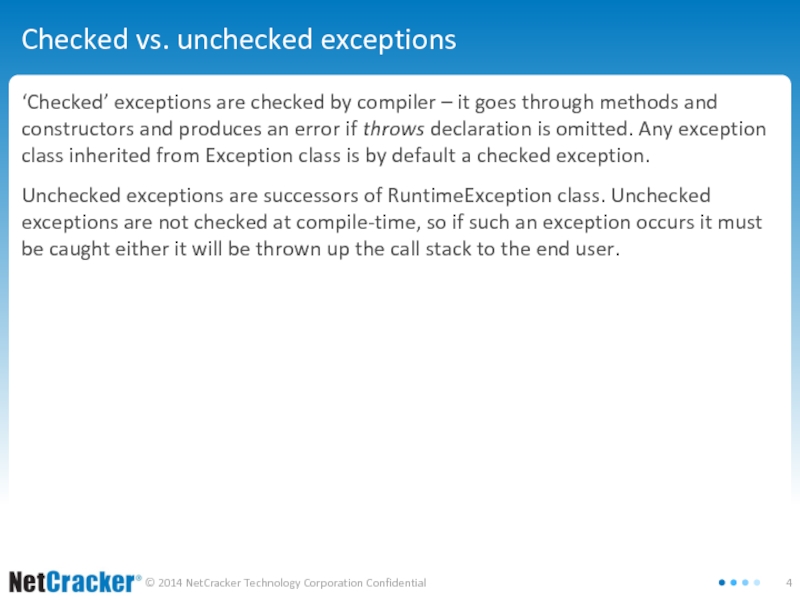
Слайд 4Checked vs. unchecked exceptions
‘Checked’ exceptions are checked by compiler – it
goes through methods and constructors and produces an error if throws declaration is omitted. Any exception class inherited from Exception class is by default a checked exception.
Unchecked exceptions are successors of RuntimeException class. Unchecked exceptions are not checked at compile-time, so if such an exception occurs it must be caught either it will be thrown up the call stack to the end user.
Unchecked exceptions are successors of RuntimeException class. Unchecked exceptions are not checked at compile-time, so if such an exception occurs it must be caught either it will be thrown up the call stack to the end user.
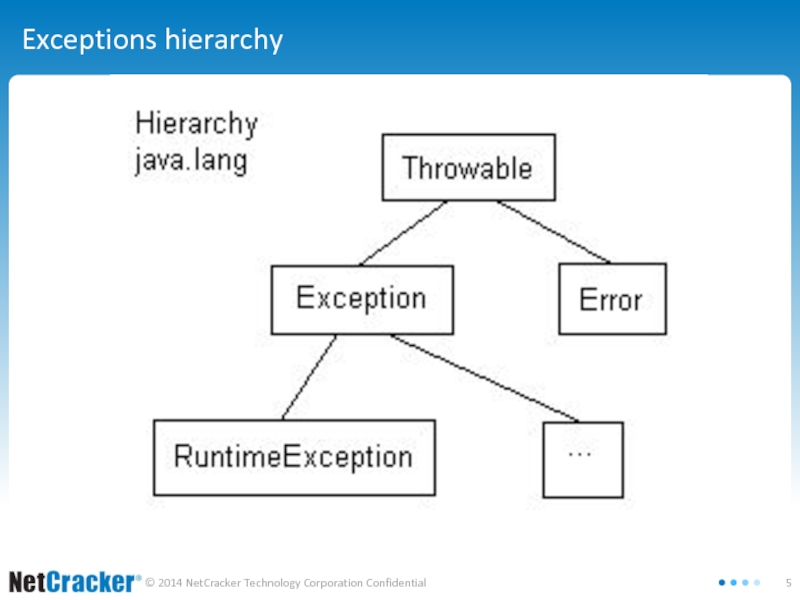
Слайд 6Exceptions hierarchy : Throwable
Every exception class inherits Throwable class
Throwable has two
predefined constructors:
Throwable(); - default constructor
- Throwable(String message) you can define a message describing exceptional state.
Message passed to the constructor can be obtained by getMessage() method. If the default constructor is used, this method will return null.
toString() method returns brief string representation of the exception occured.
You can get information about stacktrace of any exception by using printStackTrace() method – it prints entire call stack to the standard output;
Throwable(); - default constructor
- Throwable(String message) you can define a message describing exceptional state.
Message passed to the constructor can be obtained by getMessage() method. If the default constructor is used, this method will return null.
toString() method returns brief string representation of the exception occured.
You can get information about stacktrace of any exception by using printStackTrace() method – it prints entire call stack to the standard output;
Слайд 7Exceptions hierarchy : Error
Classes that extend Error are to represent
internal errors within JVM.
Errors should not be thrown from custom code.
You should not extend Error in your custom code either.
Classes that extend Error usually contain Error in their names.
Errors should not be thrown from custom code.
You should not extend Error in your custom code either.
Classes that extend Error usually contain Error in their names.
Слайд 8Exceptions hierarchy : Exception
Exception classes that extend Exception class are to
designate common exceptional state that could and should be handled.
These exceptions may be raised using throw operator
You can find appropriate exception class in JDK or create your own
These exceptions may be raised using throw operator
You can find appropriate exception class in JDK or create your own
Слайд 9Exceptions hierarchy : RuntimeException
RuntimeException indicates occurrence of a serious exceptional state,
though not as serious as Error
All RuntimeException children are unchecked exceptions
RuntimeException and its child classes can be inherited, thrown and caught within custom code
All RuntimeException children are unchecked exceptions
RuntimeException and its child classes can be inherited, thrown and caught within custom code
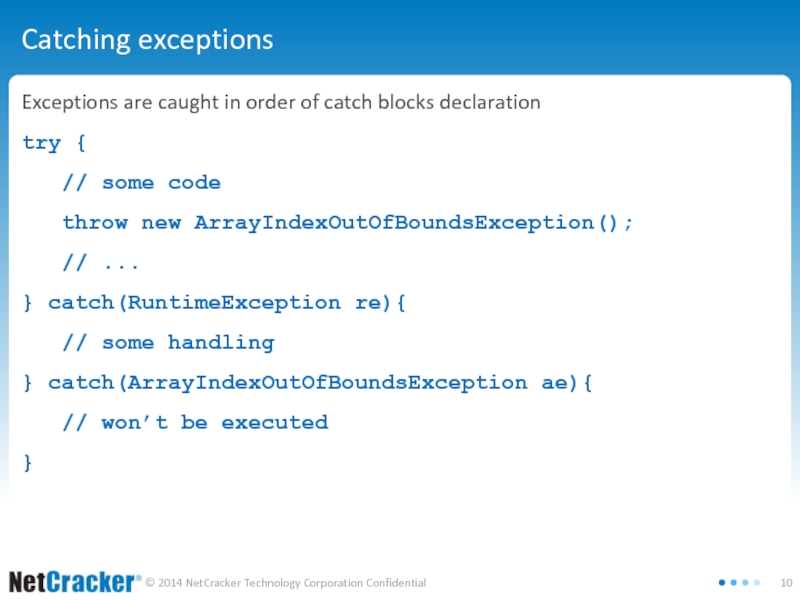
Слайд 10Catching exceptions
Exceptions are caught in order of catch blocks declaration
try {
//
some code
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
// ...
} catch(RuntimeException re){
// some handling
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ae){
// won’t be executed
}
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
// ...
} catch(RuntimeException re){
// some handling
} catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ae){
// won’t be executed
}
Слайд 11Creating your own exceptions
When creating your own exception you must keep
in mind:
Which situations may cause raising your exception
Is it possible that catching your exception will catch some other exceptions intentionally or unintentionally
Which exception class your exception will inherit
In most cases your exception won’t need anything special except two constructors and getMessage() method override
Which situations may cause raising your exception
Is it possible that catching your exception will catch some other exceptions intentionally or unintentionally
Which exception class your exception will inherit
In most cases your exception won’t need anything special except two constructors and getMessage() method override
Слайд 12Common exceptions
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
int i = 0;
int[] nArray = new int[5];
while(true) {
try
{
nArray[i] = i;
} catch(Exception ex) {
System.out.println("\n" + ex.toString());
break;
}
System.out.print(i);
i++;
}
nArray[i] = i;
} catch(Exception ex) {
System.out.println("\n" + ex.toString());
break;
}
System.out.print(i);
i++;
}
Слайд 13Common exceptions
ClassCastException
In Java you can not cast instance of one class
to another arbitrary class. If classes belong to different hierarchies or you are trying to cast parent class instance to child class, you will get ClassCastException
Object ch = new Character('*');
try {
System.out.println((Byte)ch);
}
catch(Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex.toString());
}
Object ch = new Character('*');
try {
System.out.println((Byte)ch);
}
catch(Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex.toString());
}
Слайд 14Common exceptions
NullPointerException
If you try to call method or address a field
from null reference, NullPointerException will occur.
int[] nNulArray = new int[5];
nNulArray = null;
try{
i = nNulArray.length;
}
catch(Exception ex){
System.out.println(ex.toString());
}
int[] nNulArray = new int[5];
nNulArray = null;
try{
i = nNulArray.length;
}
catch(Exception ex){
System.out.println(ex.toString());
}








![Common exceptionsArrayIndexOutOfBoundExceptionint i = 0;int[] nArray = new int[5];while(true) { try { nArray[i] = i;](/img/tmb/4/395214/bc0b0a9e76bd7465b3daadc0fc51a2ce-800x.jpg)









