- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Basic terms used in the industry of meat and meat products презентация
Содержание
- 1. Basic terms used in the industry of meat and meat products
- 2. Vocabulary Sheep – мелкий скот Brains, kidneys,
- 3. trimming – жиловка chuck – лопаточная часть
- 4. roast beef-ростбиф roast chicken-жареный цыплёнок Boiled-варёный Fried-жареный
- 5. Selection and grading of manufacturing-meat from cattle.
- 6. Similar to pork, valuable meat cuts (choice
- 8. Meat is an important food commodity which
- 9. Type of meat
- 10. Horse (horse meat) poultry (chicken meat) fish (fish products)
- 11. The structure of meat Animal flesh consists
- 12. What’s the connection? Meat muscle is made
- 13. meatandeducation.com 2011 Muscle fibres and cooking Connective
- 14. meatandeducation.com 2011 Muscle fibres and cooking Elastin
- 15. Muscle fibres Fine muscle fibres These
- 16. Fat – visible fat Fat is found
- 17. The colour of meat The colour of
- 18. Summary Which animal meat are used for
- 19. Eat right!
Vocabulary Sheep – мелкий скот Brains, kidneys, breast – мозги, почки, грудинка culinary destination – кулинарное назначение mutton – баранья лопатка grouse, partridges – рябчики, куропатки char-grilled – на углях cinnamon,
Слайд 2Vocabulary
Sheep – мелкий скот
Brains, kidneys, breast – мозги, почки, грудинка
culinary destination
– кулинарное назначение
mutton – баранья лопатка
grouse, partridges – рябчики, куропатки
char-grilled – на углях
cinnamon, cloves – корица, гвоздика
features – особенности
veal dairy - телятина молочная
without deep cuts - без глубоких надрезов
for forequarter - для передней четвертины
dirt – загрязнения
blood clots – сгустки крови
boning – обвалка
mutton – баранья лопатка
grouse, partridges – рябчики, куропатки
char-grilled – на углях
cinnamon, cloves – корица, гвоздика
features – особенности
veal dairy - телятина молочная
without deep cuts - без глубоких надрезов
for forequarter - для передней четвертины
dirt – загрязнения
blood clots – сгустки крови
boning – обвалка
Слайд 3trimming – жиловка
chuck – лопаточная часть
neck – шейная часть
spinal ribs –
спинно-реберная часть
lumbar – поясничная часть
posterior pelvic – заднетазовая часть
shoulder and shoulder of – плечевая и заплечевая часть
breast area (ribs) – грудная часть (грудинка)
the undercut portion - подлопаточная часть
tenderloin – вырезка
loin-корейка
bacon-бекон
bacon and eggs-яичница с беконом
chop-отбивная
ham-ветчина
baked ham-буженина
lumbar – поясничная часть
posterior pelvic – заднетазовая часть
shoulder and shoulder of – плечевая и заплечевая часть
breast area (ribs) – грудная часть (грудинка)
the undercut portion - подлопаточная часть
tenderloin – вырезка
loin-корейка
bacon-бекон
bacon and eggs-яичница с беконом
chop-отбивная
ham-ветчина
baked ham-буженина
Слайд 4roast beef-ростбиф
roast chicken-жареный цыплёнок
Boiled-варёный
Fried-жареный
Stewed-тушёный
chicken breast-куриная грудка
chicken wings-куриные крылышки
chicken legs-куриные ноги
tenderloin (steak)
— филе (постное)
veal — телятина
rib eye (steak) — стейк без костей (нежное)
sirloin (steak) — стейк без костей (большой кусок)
spare ribs — ребрышки
baked / fried — жареный
broiled / roast — приготовленный на гриле
veal — телятина
rib eye (steak) — стейк без костей (нежное)
sirloin (steak) — стейк без костей (большой кусок)
spare ribs — ребрышки
baked / fried — жареный
broiled / roast — приготовленный на гриле
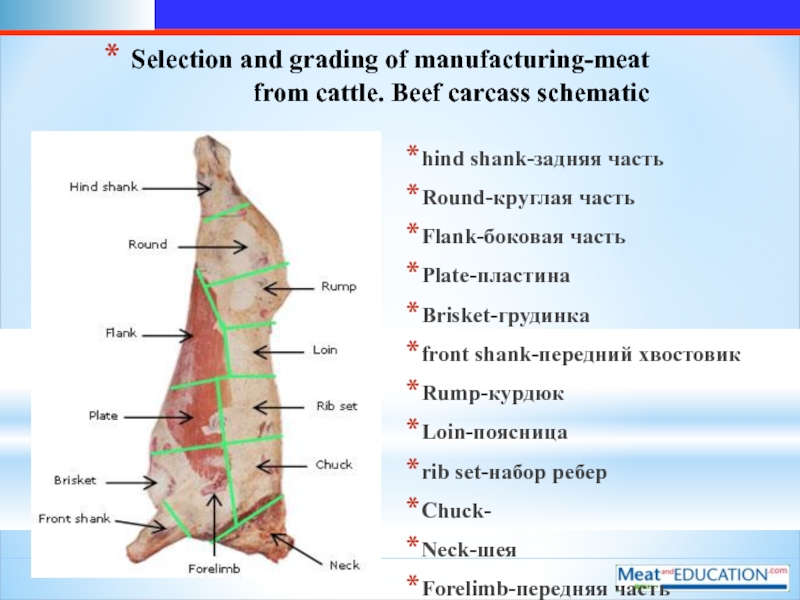
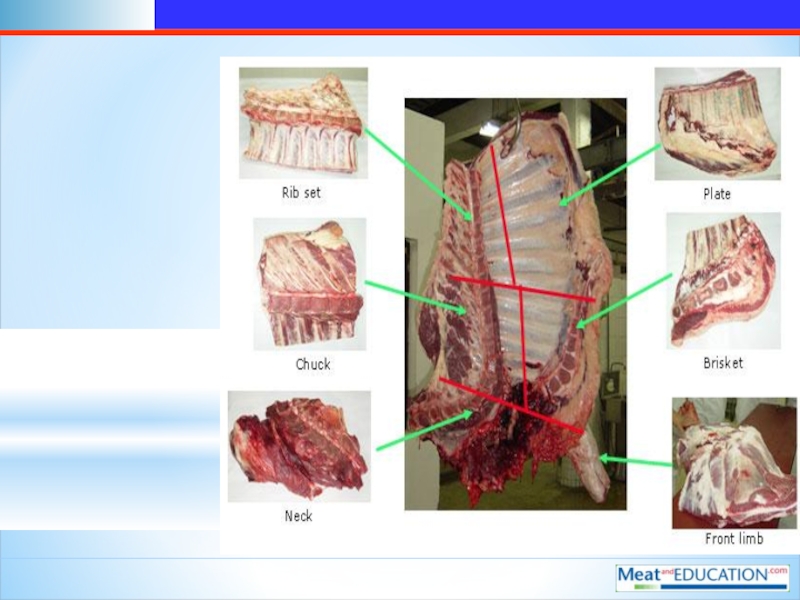
Слайд 5Selection and grading of manufacturing-meat from cattle. Beef carcass schematic
hind
shank-задняя часть
Round-круглая часть
Flank-боковая часть
Plate-пластина
Brisket-грудинка
front shank-передний хвостовик
Rump-курдюк
Loin-поясница
rib set-набор ребер
Chuck-
Neck-шея
Forelimb-передняя часть
Round-круглая часть
Flank-боковая часть
Plate-пластина
Brisket-грудинка
front shank-передний хвостовик
Rump-курдюк
Loin-поясница
rib set-набор ребер
Chuck-
Neck-шея
Forelimb-передняя часть
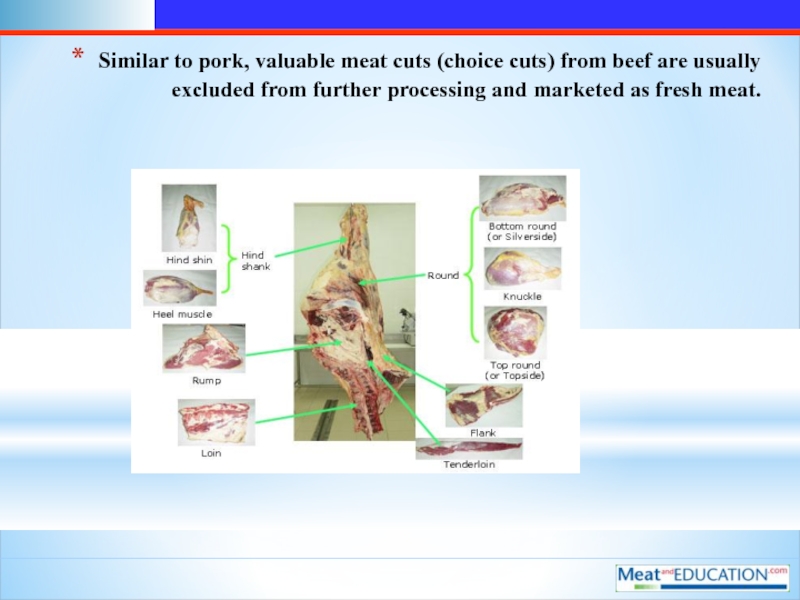
Слайд 6Similar to pork, valuable meat cuts (choice cuts) from beef are
usually excluded from further processing and marketed as fresh meat.
Слайд 8Meat is an important food commodity which provides nutrients essential for
health.
A variety of different textures, colours and flavours of meat are available for you to choose.
This module contains an overview of the origin, structure and composition of different types of meat.
A variety of different textures, colours and flavours of meat are available for you to choose.
This module contains an overview of the origin, structure and composition of different types of meat.
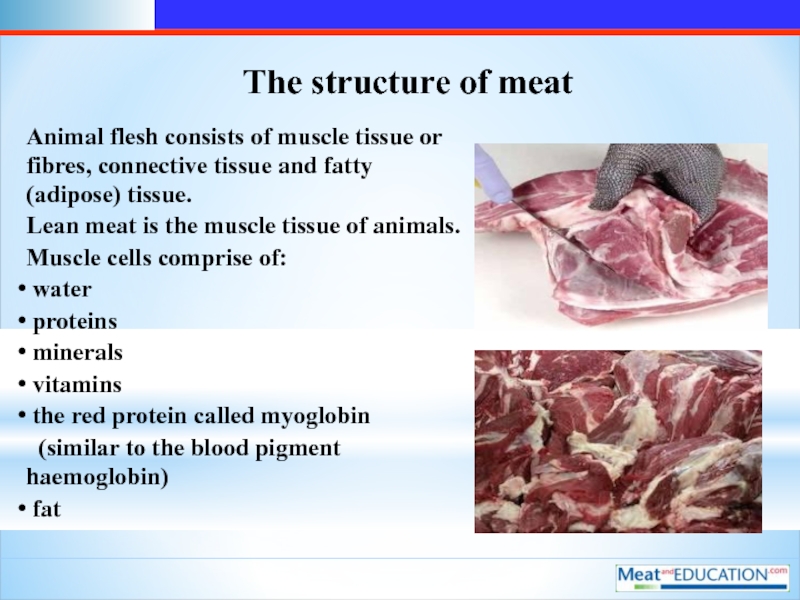
Слайд 11The structure of meat
Animal flesh consists of muscle tissue or fibres,
connective tissue and fatty (adipose) tissue.
Lean meat is the muscle tissue of animals.
Muscle cells comprise of:
water
proteins
minerals
vitamins
the red protein called myoglobin
(similar to the blood pigment haemoglobin)
fat
Lean meat is the muscle tissue of animals.
Muscle cells comprise of:
water
proteins
minerals
vitamins
the red protein called myoglobin
(similar to the blood pigment haemoglobin)
fat
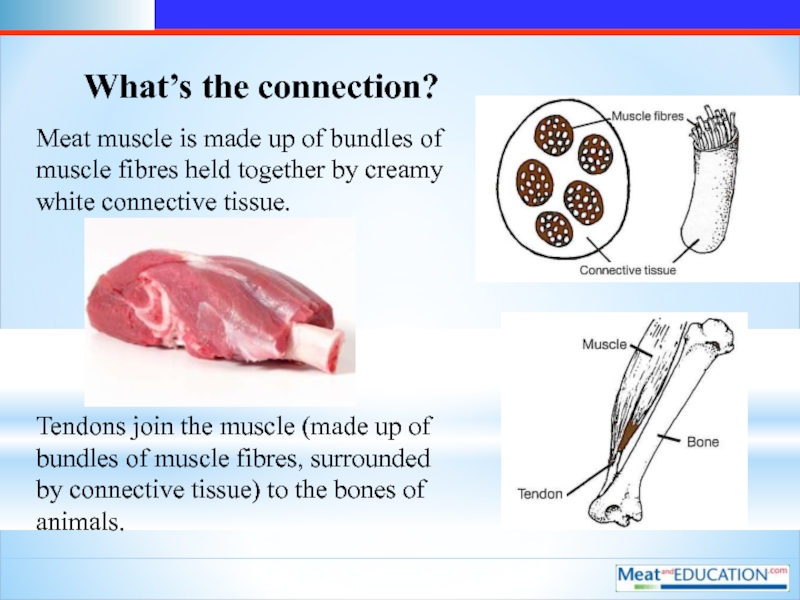
Слайд 12What’s the connection?
Meat muscle is made up of bundles of
muscle fibres held together by creamy white connective tissue.
Tendons join the muscle (made up of bundles of muscle fibres, surrounded by connective tissue) to the bones of animals.
Tendons join the muscle (made up of bundles of muscle fibres, surrounded by connective tissue) to the bones of animals.
Слайд 13meatandeducation.com 2011
Muscle fibres and cooking
Connective tissue is made up of two
proteins called collagen and elastin.
Collagen
The connective tissue in and around the muscle fibres and tendons is mostly collagen. When meat is cooked, the collagen becomes soft and soluble, and forms gelatine.
Collagen
The connective tissue in and around the muscle fibres and tendons is mostly collagen. When meat is cooked, the collagen becomes soft and soluble, and forms gelatine.
Слайд 14meatandeducation.com 2011
Muscle fibres and cooking
Elastin
This is much more elastic connective
tissue.
It is yellow in colour and remains tough, even when cooked. The ligaments which join two bones together are mostly made up of elastin.
It is yellow in colour and remains tough, even when cooked. The ligaments which join two bones together are mostly made up of elastin.
Слайд 15Muscle fibres
Fine muscle fibres
These tend to come from the muscles
of young animals, or in older animals from the muscles which do least work.
They contain little collagen and are tender even when cooking times short, e.g. grilling.
They contain little collagen and are tender even when cooking times short, e.g. grilling.
Muscle fibres are very small – and can only be seen under a microscope. The length of muscle fibres varies.
Слайд 16Fat – visible fat
Fat is found in meat underneath the skin
(subcutaneous fat) and between the muscles (intermuscular fat) and is a creamy-white colour.
This type of fat is called visible fat.
Visible fat (called suet) is also found around the animal’s organs, such as the kidneys.
This type of fat is called visible fat.
Visible fat (called suet) is also found around the animal’s organs, such as the kidneys.
Visible fat
Слайд 17The colour of meat
The colour of meat is largely due to
the red protein called myoglobin and some haemoglobin (blood) left in the muscle. Some muscles contain more of these red pigments than others.
Colour differences can be due to age and exercise, but are mainly due to the metabolism of the species and the function of the particular muscle.
Meat from muscles which have been used a lot and are from older animals is usually a darker colour.
Colour differences can be due to age and exercise, but are mainly due to the metabolism of the species and the function of the particular muscle.
Meat from muscles which have been used a lot and are from older animals is usually a darker colour.
Слайд 18Summary
Which animal meat are used for food?
What is in the muscle
tissue of animals?
From which is connective tissue?
What determines the color of the meat?
From what is lean?
From which is connective tissue?
What determines the color of the meat?
From what is lean?