- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Педагогический и методический менеджмент при обучении иностранному язіку презентация
Содержание
- 1. Педагогический и методический менеджмент при обучении иностранному язіку
- 2. План лекции 1 1. Современные требования к
- 3. John Dewey (1859-1952) the art of …
- 4. Современные требования к учителю ИЯ – составляющие
- 7. Основные понятия педагогического и методического менеджмента
- 8. Основные понятия педагогического и методического менеджмента
- 9. Виды управления процессом обучения Разомкнутое
- 12. Planning Wording the aim: discussion, prioritizing, ranking,
- 13. Motivating skills Formulation of
- 14. Motivating techniques to help the teacher to
- 15. Motivating techniques to help the teacher to formulate the aim Analysis Debates Illustration
- 16. Motivating techniques to help the teacher make
- 17. Organizing Group Work Skills Distribution of students
- 18. Distributing students into groups techniques Grouping according
- 19. Distributing roles and responsibilities techniques Discussion Expressing priorities Listing Role-mapping Table filling
- 20. Group uniting techniques Teams competitions Groupmates learning activities
- 21. Organization of work with information skills Organizing
- 22. Organization of work with information techniques
- 23. Control and correction monitoring – careful
- 24. Principles of Monitoring continuous scientific purposeful prognostic norm-referencing
- 25. Feedback giving students information about what actions
- 26. Formula of effective feedback (T. Russel)
- 27. Self-control and self-correction the ability
- 28. The process of self-control development (M.E. Braigina)
- 29. Monitoring and self-correction techniques asking and
- 30. Assessment The process of measuring, quantifying, and/or
- 31. To provide assessment and self-assessment
- 32. Correction Aim: to stimulate correction of
- 33. Reflexive analysis Analysis – a careful examination
- 34. ORGANIZING REFLEXIVE ANALYSIS SKILLS To organize the
- 35. Organizing Reflexive Analysis Techniques discussion, individual interview,
- 36. Thanks for your attention!
Слайд 1ПЕДАГОГИЧЕСКИЙ И МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЙ МЕНЕДЖМЕНТ ПРИ ОБУЧЕНИИ ИЯ
Старкова Д.А. «Теория и методика
Слайд 2План лекции 1
1. Современные требования к преподавателю ИЯ – составляющие профессиональной
2. Управленческая составляющая ПК преподавателя ИЯ
3. Основные понятия педагогического и методического менеджмента
4. Управленческий цикл и основные управленческие методические умения учителя ИЯ
Слайд 3John Dewey (1859-1952)
the art of … giving shape to human powers
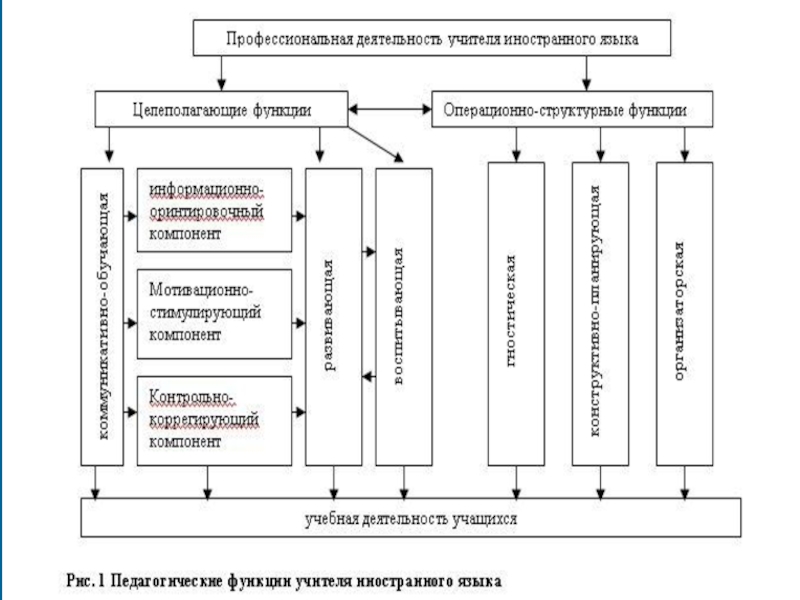
Слайд 4Современные требования к учителю ИЯ – составляющие профессиональной коммуникативной компетентности
Компетентностный подход
Профессиональная компетентность (определения разных ученых: Марковой А.К., Митиной Л.М., Кузьминой Н.В.)
Профессиональная компетентность учителя ИЯ и профессиограмма
Слайд 6
Управленческая составляющая
профессиональной компетентности учителя ИЯ
Составляющие ПК учителя
Управленческая составляющая ПК учителя
Управленческая
Управленческий подход в образовании
Слайд 7Основные понятия педагогического и методического менеджмента
3 позиции определения понятия «управление»
Педагогическое управление
Методическое
Менеджмент
3 уровня менеджмента в образовании
Связь понятия «менеджмент» с понятием «эффективность»
Слайд 8Основные понятия педагогического и методического менеджмента
Принципы управления процессом обучения ИЯ
Организация и
Руководство и управление
Стили руководства
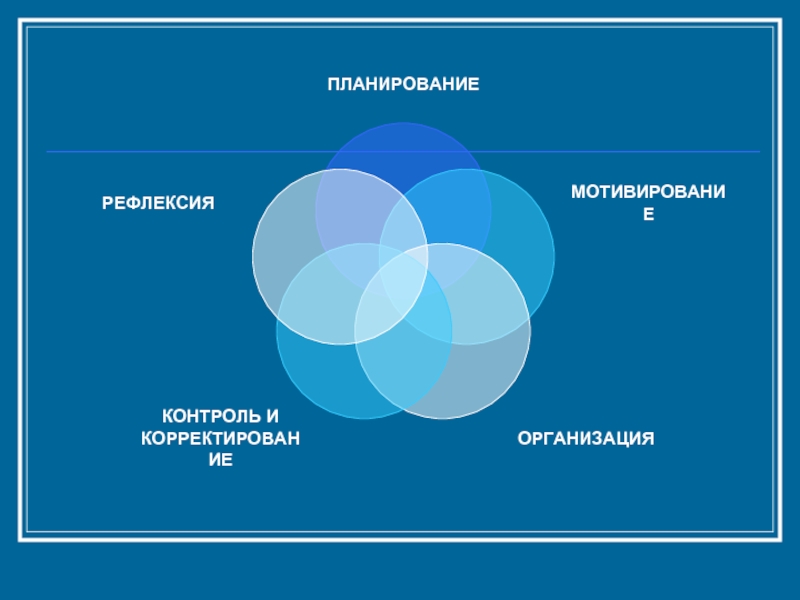
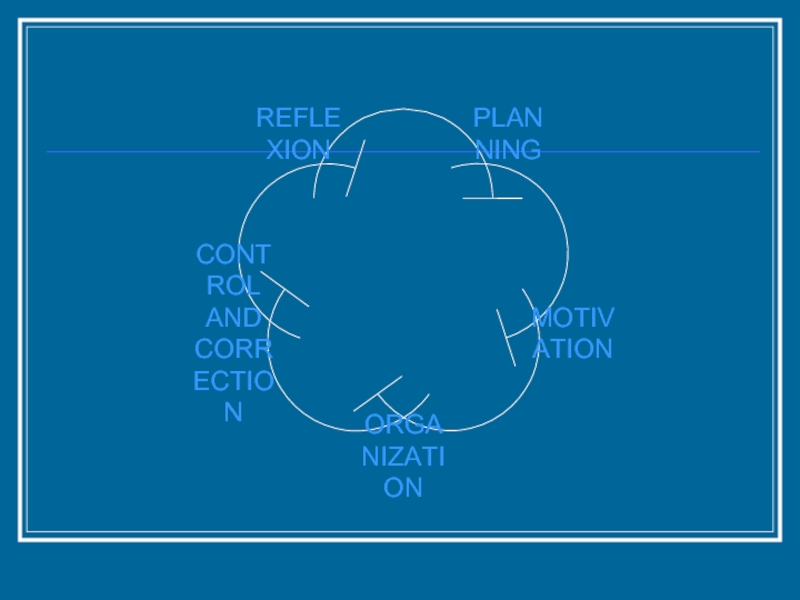
Функции управления
Управленческие методические умения
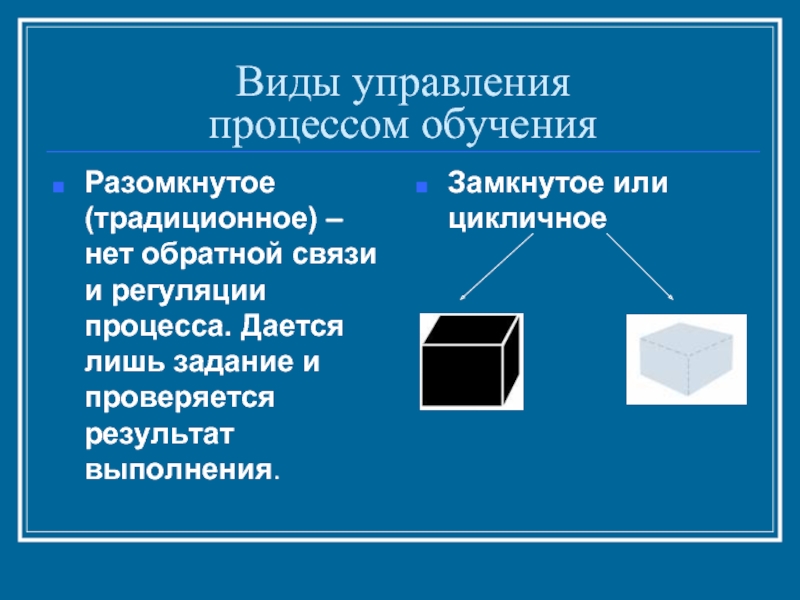
Слайд 9Виды управления
процессом обучения
Разомкнутое (традиционное) – нет обратной связи и
Замкнутое или цикличное
Слайд 12Planning
Wording the aim: discussion, prioritizing, ranking, note-taking
Thinking over ways of aim
Determining characteristics of the final product and criteria of assessment: association, listing, description
Слайд 13
Motivating skills
Formulation of problem
Formulation of aim
Interesting process of problem solving
Слайд 14Motivating techniques to help the teacher to formulate a problem
Debates
Discussion
Problem
Questionnairing
Quiz
Test
Слайд 16Motivating techniques to help the teacher make the process interesting
Decision making
Discussion
Extending
Problem solving
Слайд 17Organizing Group Work Skills
Distribution of students into groups
Distribution of roles and
Group uniting
Слайд 18Distributing students into groups techniques
Grouping according to some idea
Leader’s enrollment
Expressing
Слайд 19Distributing roles and responsibilities
techniques
Discussion
Expressing priorities
Listing
Role-mapping
Table filling
Слайд 21Organization of work with information skills
Organizing students’ search of information
Organizing students’
Organizing students’ product creation and presentation
Слайд 22Organization of work with information techniques
categorizing (grouping), comparing, compilation, description,
Слайд 23Control and correction
monitoring – careful watching some situation and checking
assessment – 1) a process in which you make a judgment about a person or situation, 2) calculation about the cost or value of something;
correction – a change in something in order to make it right or better
Слайд 25Feedback
giving students information about what actions have led to the necessary
Слайд 26Formula of effective feedback
(T. Russel)
1) give students the opportunity to
2) give students the opportunity to see and realize the result of their actions
3) together with your student agree on what must be changed
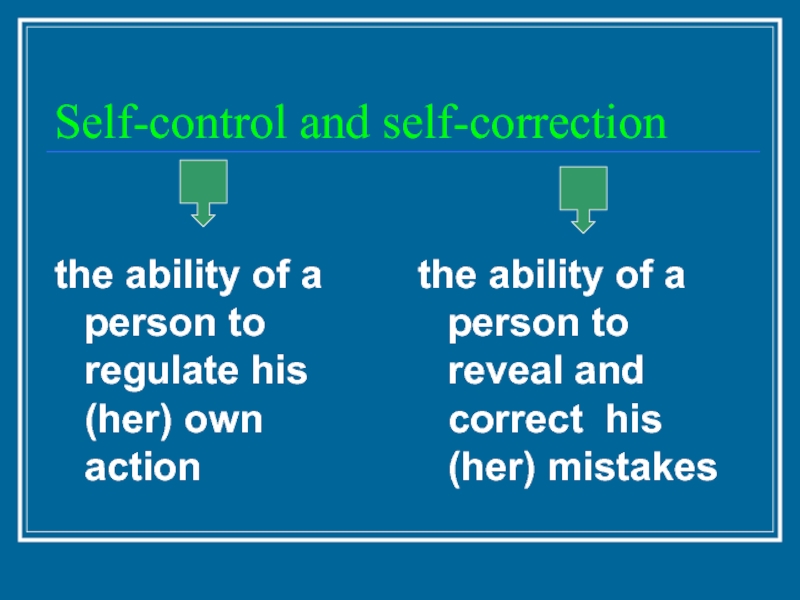
Слайд 27Self-control and self-correction
the ability of a person to regulate his (her)
the ability of a person to reveal and correct his (her) mistakes
Слайд 28The process of self-control development (M.E. Braigina)
to learn to understand and
to learn to observe and analyse the peers’ studying activity
to learn to observe one’s own studying activity, its analysis, correction and assessment
Слайд 29Monitoring and self-correction techniques
asking and answering questions
table-filling
observation
interview
note-taking
substitution
reordering
correction
paraphrasing
transformation
Слайд 30Assessment
The process of measuring, quantifying, and/or describing aspects related to the
Слайд 31
To provide assessment and self-assessment
Comparing
Level-determination
Note-taking
Observation
Rating
Table-filling
Слайд 32Correction
Aim: to stimulate correction of mistakes in the usage of the
Stimulating techniques:
underlining,
shaking head
repeating the phrase before the mistake
rules revision
skills drilling and practicing
Слайд 33Reflexive analysis
Analysis – a careful examination of some object in order
Reflexion – introspection, i.e. the process of deeply thinking about your own thoughts, feelings, qualities, behaviour
Слайд 34ORGANIZING REFLEXIVE ANALYSIS SKILLS
To organize the process of recollection of main
To stimulate students’/learners’ analysis of successful and problematic parts of work and determine one’s own progress
To make students/learners draw conclusions