11
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
How do you make a space your own? unit_5 презентация
Содержание
- 1. How do you make a space your own? unit_5
- 2. Warm- Up Questions What places or
- 3. p. 115- The Q Classroom Listening
- 4. Video: Frank Gehry Frank Owen Gehry
- 5. p. 116: Exercise E Look at
- 6. Listening 2: What your stuff says about
- 7. Exercises A, C, D Exercise D:
- 8. Vocabulary Listening 2 Clarify Clue Crucial
- 9. Listening 1 Vocabulary p. 123 Adjacent Affiliate
- 10. Organizing notes into a formal outline
- 11. p. 118: Listening You are going to
- 12. Vocabulary Skill: Words with multiple meanings Many
- 13. Speaking Skills: Giving Advice Knowing how to
- 14. Speaking: Conditionals (p. 134) Verbs in
- 15. present/ future real conditionals present/ future
- 16. present/ future unreal conditionals Present/ future
- 17. Past unreal conditionals The condition was
- 18. SHORTCUT 1. Future (Likely/Possible/Real): If +
- 20. p. 134 Exercises A and B
Слайд 2Warm- Up Questions
What places or spaces do you have that
you consider “yours?”
What are some differences in the way different groups— such as males ,females, adults and children – personalize their space?
Look at the photo on p. 113. How would you personalize this space?
What are some differences in the way different groups— such as males ,females, adults and children – personalize their space?
Look at the photo on p. 113. How would you personalize this space?
Слайд 4Video: Frank Gehry
Frank Owen Gehry (1929) is a Canadian born
American architect
A number of his buildings, including his private residence, have become world-renowned attractions. His works are cited as being among the most important works of contemporary architecture.
In 2010, Vanity Fair labeled him as "the most important architect of our age."
A couple of Gehry's best-known works include the Guggen heim Museum in Bilbao, Spain, the Walt Disney Concert Hall in downtown Los Angeles and the Louis Vuitton Foundation in Paris, France.
A number of his buildings, including his private residence, have become world-renowned attractions. His works are cited as being among the most important works of contemporary architecture.
In 2010, Vanity Fair labeled him as "the most important architect of our age."
A couple of Gehry's best-known works include the Guggen heim Museum in Bilbao, Spain, the Walt Disney Concert Hall in downtown Los Angeles and the Louis Vuitton Foundation in Paris, France.
Слайд 5p. 116: Exercise E
Look at the pictures of different kinds
of space. What does each space tell you about the person? Share your ideas with a partner.
Work in a group. Think of one of you personal spaces. Take turns describing your space and explaining what it shows about you.
Work in a group. Think of one of you personal spaces. Take turns describing your space and explaining what it shows about you.
Слайд 6Listening 2: What your stuff says about You!
Radio interview and call-in
show from NPR’s Talk of the Nation.
Dr. Sam Gosling – a psychology professor will discuss his book, Snoop: What Your Stuff Says About You
Preview: Dr. Gosling says that he looks for information about people in many places— and that he uses the word places very broadly, to refer not only to physical areas. What kind of places or things do you think Dr. Gosling might be interested in?
Dr. Sam Gosling – a psychology professor will discuss his book, Snoop: What Your Stuff Says About You
Preview: Dr. Gosling says that he looks for information about people in many places— and that he uses the word places very broadly, to refer not only to physical areas. What kind of places or things do you think Dr. Gosling might be interested in?
Слайд 7Exercises A, C, D
Exercise D:
What are some places Dr. Gosling
snoops around and why do they reveal so much about people?
Does Dr. Gosling believe that people are always correct in the conclusions they come to about the possessions and actions of others? Why or why not?
How does psychology play a role in figuring out “what your stuff says about you?”
Does Dr. Gosling believe that people are always correct in the conclusions they come to about the possessions and actions of others? Why or why not?
How does psychology play a role in figuring out “what your stuff says about you?”
Слайд 8Vocabulary
Listening 2
Clarify
Clue
Crucial
Domain
Extrovert
Framework
Introvert
Modify
Profile
Propose
Tentatively
Trait
Слайд 9Listening 1 Vocabulary
p. 123
Adjacent
Affiliate with
Belongings
Engage in
Gender
Ingrained in
Invade
Moderately
Radius
Refrain from
Remarkable
Suburban
Слайд 10Organizing notes into a formal outline
One of the most conventional
ways to organize information and relationships between points is an outline.
Many lecturers and speakers provide formal outlines so listeners can follow along more easily.
The advantage of an outline is that the main ideas and supporting details can be easily identified.
Main ideas (people, theories, events, etc.) stand out along the left margin, while supporting details and examples are clearly indented beneath them.
Various bullets, numbers or letters are used to list these points.
Many lecturers and speakers provide formal outlines so listeners can follow along more easily.
The advantage of an outline is that the main ideas and supporting details can be easily identified.
Main ideas (people, theories, events, etc.) stand out along the left margin, while supporting details and examples are clearly indented beneath them.
Various bullets, numbers or letters are used to list these points.
Слайд 11p. 118: Listening
You are going to listen to a short talk
on personal space. Before you listen, read the notes on p.118. Then listen to the lecture and organize the notes into a formal outline.
Слайд 12Vocabulary Skill: Words with multiple meanings
Many words in English have more
than one meaning, so you cannot assume that the one definition you know will fit every situation.
Ex: chair, contact, web, propose, etc.
P. 131 Exercise A
P. 133 Exercise B
Ex: chair, contact, web, propose, etc.
P. 131 Exercise A
P. 133 Exercise B
Слайд 13Speaking Skills: Giving Advice
Knowing how to make suggestions and give advice
without sounding pushy or demanding is an important conversational skill.
P. 137 CHART (forms of advice)
Exercise A and B
P. 137 CHART (forms of advice)
Exercise A and B
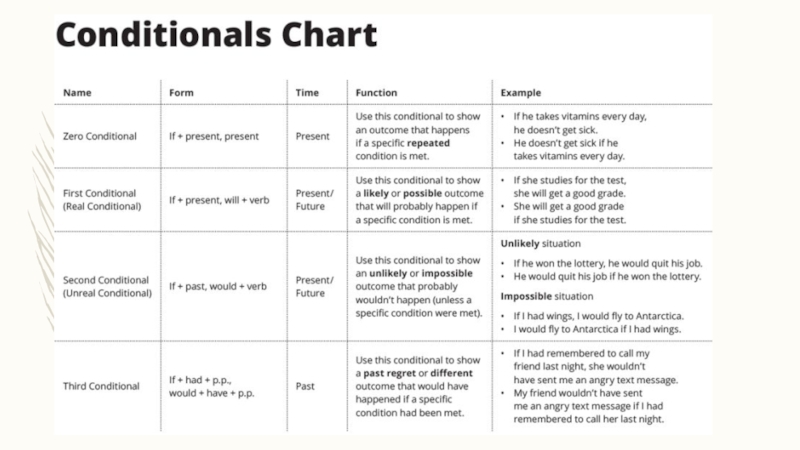
Слайд 14Speaking: Conditionals
(p. 134)
Verbs in conditional sentences show:
Time frame (present,
present/ future, or past)
Whether the conditions are real (true) or unreal (not true; imaginary)
3 types we will discuss:
1) present/ future real conditionals
2) present/ future unreal conditionals
3) past unreal conditionals
Whether the conditions are real (true) or unreal (not true; imaginary)
3 types we will discuss:
1) present/ future real conditionals
2) present/ future unreal conditionals
3) past unreal conditionals
Слайд 15present/ future real conditionals
present/ future real conditionals: there is a
real possibility the condition will happen, or it can, should, or might happen.
if clause = present tense form
Result = will, can , might, should + base verb
Ex: If he wants to make friends, he should join a club.
He will not enjoy large events if he is an introvert.
If she studies for the quiz, she can earn a high score.
Click on this link to get more practice on present/ future real conditionals: http://english-zone.com/grammar/if-then1.html
if clause = present tense form
Result = will, can , might, should + base verb
Ex: If he wants to make friends, he should join a club.
He will not enjoy large events if he is an introvert.
If she studies for the quiz, she can earn a high score.
Click on this link to get more practice on present/ future real conditionals: http://english-zone.com/grammar/if-then1.html
Слайд 16present/ future unreal conditionals
Present/ future unreal conditionals: the condition is
not true now, so the results are not true either.
If clause = past tense form
Result= would, might + base verb
Ex: If she wanted to reveal more about her personality, she would display photos.
He might sit at the front of the classroom if he weren’t so shy.
If he won the lottery, he would quit his job.
If she had wings, she would fly to Artarctica.
Follow this link for more practice on present/ future unreal conditions:
http://english-zone.com/members/teach/if-then3.html
If clause = past tense form
Result= would, might + base verb
Ex: If she wanted to reveal more about her personality, she would display photos.
He might sit at the front of the classroom if he weren’t so shy.
If he won the lottery, he would quit his job.
If she had wings, she would fly to Artarctica.
Follow this link for more practice on present/ future unreal conditions:
http://english-zone.com/members/teach/if-then3.html
Слайд 17Past unreal conditionals
The condition was not true before; the result
in the past or the present is not true either.
if clause = past perfect form
result = would, could, might + base verb (present results)
would have, could have, might have + past participle (past results)
Ex: If they had asked everyone about painting the room, no one would be angry now.
If everyone had contributed some money, we could have redecorated.
If I had remembered to call my friend last night, she wouldn’t have sent me an angry message.
Click for more practice: http://english-zone.com/members/teach/if-then5.html
if clause = past perfect form
result = would, could, might + base verb (present results)
would have, could have, might have + past participle (past results)
Ex: If they had asked everyone about painting the room, no one would be angry now.
If everyone had contributed some money, we could have redecorated.
If I had remembered to call my friend last night, she wouldn’t have sent me an angry message.
Click for more practice: http://english-zone.com/members/teach/if-then5.html
Слайд 18
SHORTCUT
1. Future (Likely/Possible/Real): If + Present, Will + Verb
2. Future (Unlikely/Impossible/Unreal):
If + Past, Would + Verb
3. Past: If + Had + P.P., Would + Have + P.P.
3. Past: If + Had + P.P., Would + Have + P.P.