Serna
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Sir Isaac Newton. Life and Accomplishments презентация
Содержание
- 1. Sir Isaac Newton. Life and Accomplishments
- 2. Table of Contents The Beginning of His
- 3. The beginning of his life Born on
- 4. Early life Newton received a bachelor’s degree
- 5. Reflecting Telescope In 1668 Newton made the
- 6. Calculus Newton invented Calculus in 1669,
- 7. Motion and Gravity Newton wondered why objects
- 8. First Law of Motion A body
- 9. Second Law of Motion When a
- 10. Third Law of Motion If body
- 11. Force Newton believed that when an object
- 12. Comets Newton showed that comets acted upon
- 13. Principia and Opticks most popular works
- 14. A Great Man Isaac Newton died on March 31, 1727 in London, England
- 15. References Book Isaac Newton (The Last
Слайд 2Table of Contents
The Beginning of His Life
Early Life
Reflecting Telescope
Calculus
Motion and Gravity
First Law of Motion
Second Law of Motion
Third Law of Motion
Force
Comets
Principia and Opticks
A Great Man
References
Слайд 3The beginning of his life
Born on January 4, 1643
In Woolsthorpe, Lincolnshire,
England
Where he was raised by his Grandmother
Where he was raised by his Grandmother
Woolsthorpe Manor: house where Newton grew up
Слайд 4Early life
Newton received a bachelor’s degree at Trinity College, Cambridge in
1665
The next two years Newton returned home where he came up with most of his discoveries.
He returned to Trinity College in 1667, where he became a professor of mathematics in 1669.
The next two years Newton returned home where he came up with most of his discoveries.
He returned to Trinity College in 1667, where he became a professor of mathematics in 1669.
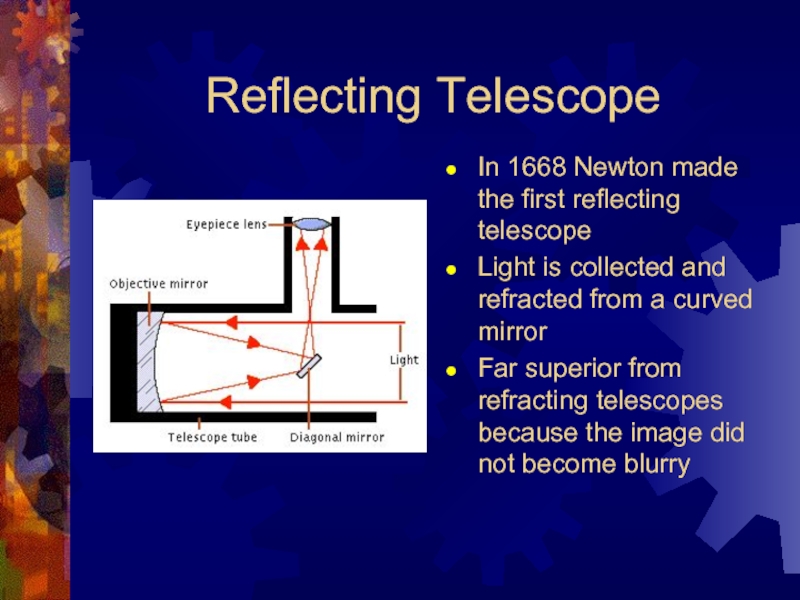
Слайд 5Reflecting Telescope
In 1668 Newton made the first reflecting telescope
Light is
collected and refracted from a curved mirror
Far superior from refracting telescopes because the image did not become blurry
Far superior from refracting telescopes because the image did not become blurry
Слайд 6Calculus
Newton invented Calculus in 1669, but didn’t publish his work
until 1704
Calculus is divided into two parts Differential and Integral Calculus
Differential Calculus: Deals with the change in rate of objects
Integral Calculus: Deals with measuring quantities and dividing into smaller ones
Calculus is divided into two parts Differential and Integral Calculus
Differential Calculus: Deals with the change in rate of objects
Integral Calculus: Deals with measuring quantities and dividing into smaller ones
Слайд 7Motion and Gravity
Newton wondered why objects fell to earth while sitting
under an apple tree he saw an apple fall in front of him
Although many believe this story is untrue
That is when Newton came up with the three laws of motion
Although many believe this story is untrue
That is when Newton came up with the three laws of motion
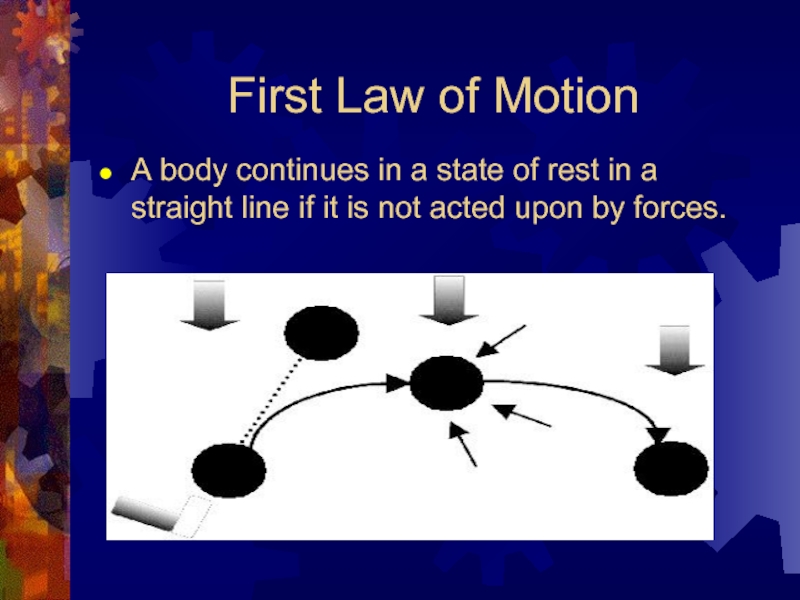
Слайд 8First Law of Motion
A body continues in a state of
rest in a straight line if it is not acted upon by forces.
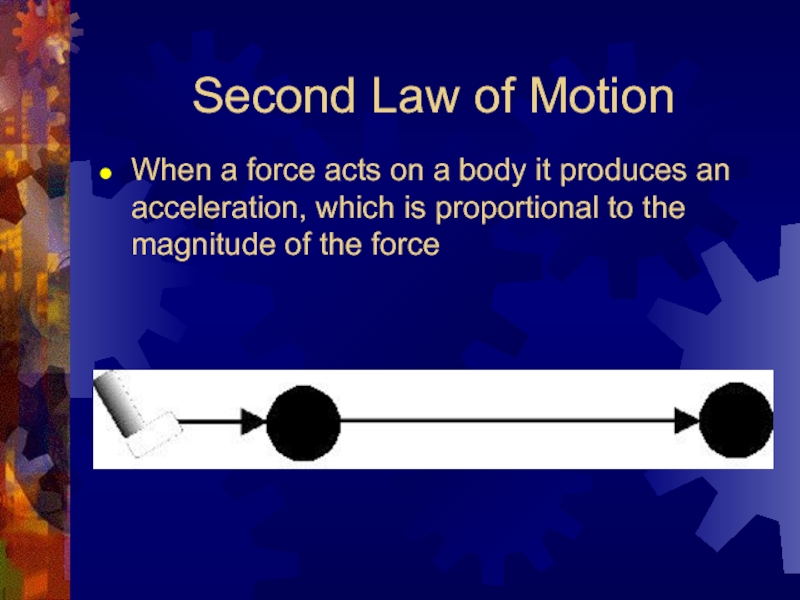
Слайд 9Second Law of Motion
When a force acts on a body
it produces an acceleration, which is proportional to the magnitude of the force
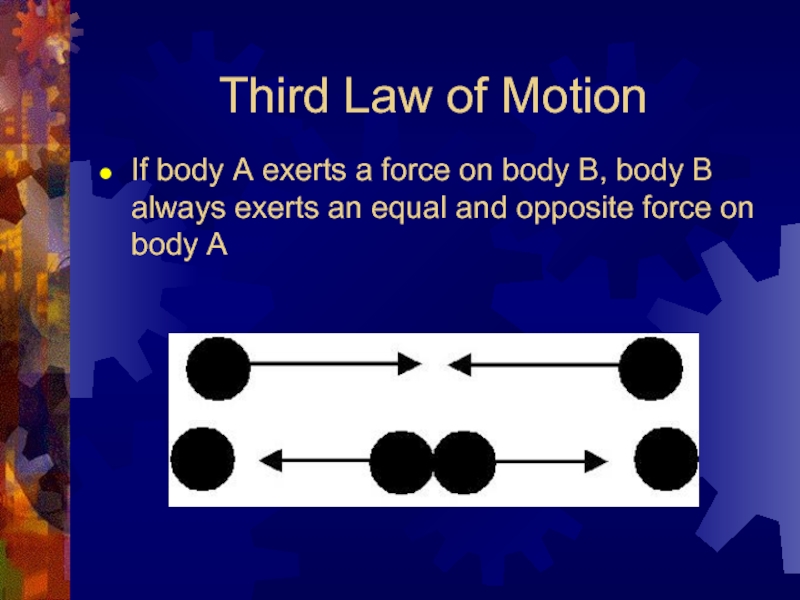
Слайд 10Third Law of Motion
If body A exerts a force on
body B, body B always exerts an equal and opposite force on body A
Слайд 11Force
Newton believed that when an object goes around another there are
two balanced forces.
Centripetal force: pulls the revolving object towards the pivoting point
Centrifugal force: pulls the object away from pivoting point
Centripetal force: pulls the revolving object towards the pivoting point
Centrifugal force: pulls the object away from pivoting point
Слайд 12Comets
Newton showed that comets acted upon by the same forces as
the planets
Proved when Edmund Halley predicted the next time a comet would pass by again
Proved when Edmund Halley predicted the next time a comet would pass by again
Слайд 13Principia and Opticks
most popular works
Newton summarized his discoveries in Philosophiae
naturalis principia mathematica (mathematical principles of natural philosophy) (1687)
It shows his principle of universal gravitation and provided an explanation both of falling bodies on the Earth and of the motions of planets, comets and other bodies of the universe.
Opticks (1704) presented his discoveries of light and elaborated his theory that light is composed of corpuscles, or particles.
It shows his principle of universal gravitation and provided an explanation both of falling bodies on the Earth and of the motions of planets, comets and other bodies of the universe.
Opticks (1704) presented his discoveries of light and elaborated his theory that light is composed of corpuscles, or particles.
Слайд 15References
Book
Isaac Newton (The Last Sorcerer), by Michael White
Encyclopedia Article
The
New Encyclopedia Britannica Volume 8. Micropaedia/Ready Reference pg. 663
A source of scientific period
The Scientists of The Scientific Revolution pg. 69-87
Internet source
Newton, Isaac. The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. 2001 @ www. Bartleby.com
A source of scientific period
The Scientists of The Scientific Revolution pg. 69-87
Internet source
Newton, Isaac. The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. 2001 @ www. Bartleby.com