CEIST Presentation
29th November 2007
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Occupational Health and Safety for Schools презентация
Содержание
- 1. Occupational Health and Safety for Schools
- 2. Overview Education has similar health and
- 3. What is occupational health and safety?
- 4. What is occupational health and safety?
- 5. The basics All employers must:
- 6. The basics All employees must: Comply with
- 7. The basics General Principles of Prevention:
- 8. The basics The replacement of dangerous
- 9. Types of occupational hazards Chemical hazards
- 10. Risk Assessment? Purpose: the
- 11. Safety Statement Reflects employers commitment to
- 12. Safety Statement Outlines the measures
- 13. Insured costs Covers civil liabilities only
- 14. Uninsured (hidden) costs Costs to injured
- 15. Human Costs Circa 60 fatalities per
- 16. Benefits to schools of good safety management
- 17. Reasons for poor safety systems in schools
- 18. Reasons for poor safety systems in schools
- 19. Safety Culture
- 20. Safety Culture Successful companies hold the
- 21. Safety Culture Indicators Accidents Absenteeism Sickness rates Staff turnover Legislative compliance Staff complaints.
- 22. Creating a Safety Culture within schools
- 23. Creating a Safety Culture within schools
- 24. Creating a Safety Culture within schools
- 25. Safety Management System Initial review
- 26. What is a safety management system? Key
- 27. Questions ??
Слайд 1
Occupational Health and Safety for Schools
Shay Bannon
Dip SHWW, Grad IOSH.
Слайд 2Overview
Education has similar health and safety concerns to other sectors
Employers
must manage safety
Employers must prepare a safety statement
Managers and staff have responsibilities
Co-operation essential to create a safety culture in schools.
Employers must prepare a safety statement
Managers and staff have responsibilities
Co-operation essential to create a safety culture in schools.
Слайд 3What is occupational health and safety?
It is :
the promotion and
maintenance of the highest degree of physical, mental and social well-being of employees and students
the prevention of adverse health effects due to working conditions
the protection of employees /students from risks resulting from factors adverse to health
the prevention of adverse health effects due to working conditions
the protection of employees /students from risks resulting from factors adverse to health
Слайд 4What is occupational health and safety?
the placing and maintenance of employees/students
in an occupational environment adapted to physical and mental needs
the adaptation of work to humans.
Occupational health and safety encompasses the social, mental and physical well-being of workers, that is the “whole person”.
the adaptation of work to humans.
Occupational health and safety encompasses the social, mental and physical well-being of workers, that is the “whole person”.
Слайд 5The basics
All employers must:
Actively manage safety and health
Undertake a risk assessment
Prepare
a safety statement
Comply with industry or task specific regulations
Inform all employee of their health and safety obligations.
Comply with industry or task specific regulations
Inform all employee of their health and safety obligations.
Слайд 6The basics
All employees must:
Comply with the law
Protect their own and the
health and safety of others
Co-operate with the Board
Attend necessary training
Not engage in improper conduct or other behaviour which could endanger own safety or that of others
Make correct use of equipment
Report hazards
Not intentionally interfere with or misuse equipment.
Co-operate with the Board
Attend necessary training
Not engage in improper conduct or other behaviour which could endanger own safety or that of others
Make correct use of equipment
Report hazards
Not intentionally interfere with or misuse equipment.
Слайд 7The basics
General Principles of Prevention:
Avoidance of risk
Evaluation of unavoidable risks (risk
assessment)
Combating risks at source
Adaptation of work to the individual especially with regard to design of places of work, the choice of work equipment and the choice of systems of work
Adaptation of work to technical progress
Combating risks at source
Adaptation of work to the individual especially with regard to design of places of work, the choice of work equipment and the choice of systems of work
Adaptation of work to technical progress
Слайд 8The basics
The replacement of dangerous articles, substances or systems of work
by safe or less dangerous articles, substances or systems of work
Priority of collective protective measures over individual protective measures
Development of an adequate prevention policy which takes account of technology, organisation of work, working conditions, social factors and the influence of factors relating to the working environment
Giving of appropriate training and instructions to employees .
Priority of collective protective measures over individual protective measures
Development of an adequate prevention policy which takes account of technology, organisation of work, working conditions, social factors and the influence of factors relating to the working environment
Giving of appropriate training and instructions to employees .
Слайд 9Types of occupational hazards
Chemical hazards
Physical hazards
Biological hazards
Psychological hazards
Hazards associated with
the non-application of ergonomic principles
Human.
Human.
Слайд 10Risk Assessment?
Purpose: the identification of hazards and risks and
the preparation of measures to overcome these before an accident occurs
How? Analyse work activities; Identify hazards; Evaluate risks; Introduce protective/ preventative measures; Monitor and assess.
Hazard assessment is most beneficial when it is carried out by people who work in the area.
How? Analyse work activities; Identify hazards; Evaluate risks; Introduce protective/ preventative measures; Monitor and assess.
Hazard assessment is most beneficial when it is carried out by people who work in the area.
Слайд 11Safety Statement
Reflects employers commitment to ensuring safety, health and welfare of
all employees
Action document – based on risk assessments identified in the workplace
Must be a written document – in a language that is understood by all employees
Details the health and safety provisions that exist within the workplace
Highlights all potential hazards in the workplace
Specifies what must be done
Action document – based on risk assessments identified in the workplace
Must be a written document – in a language that is understood by all employees
Details the health and safety provisions that exist within the workplace
Highlights all potential hazards in the workplace
Specifies what must be done
Слайд 12Safety Statement
Outlines the measures that have been put in place to
reduce hazards in the workplace
Outlines emergency plans and procedures
Must be brought to the attention of all employees
Includes the names, job titles and details of anybody with assigned safety responsibilities
Should be reviewed annually and must be revised if any significant change happens in the working environment or nature of the work
Audits to ensure employee compliance and effectiveness of procedures.
Outlines emergency plans and procedures
Must be brought to the attention of all employees
Includes the names, job titles and details of anybody with assigned safety responsibilities
Should be reviewed annually and must be revised if any significant change happens in the working environment or nature of the work
Audits to ensure employee compliance and effectiveness of procedures.
Слайд 13Insured costs
Covers civil liabilities only (compensation claims for injury, ill health
and damage)
Can cover legal costs
Can cover interruption to work of school
Does not cover criminal liability or fines imposed by courts.
Claims cause insurance premiums to rise.
Can cover legal costs
Can cover interruption to work of school
Does not cover criminal liability or fines imposed by courts.
Claims cause insurance premiums to rise.
Слайд 14Uninsured (hidden) costs
Costs to injured person or their family
Treatment and
lost teaching time costs
Investigation costs, writing reports and filling forms
Costs of finding/training suitable/qualified replacement
Lower staff morale
Negative publicity (local media, newspapers, HSA etc.)
Costs to State (occupational injury benefit paid by taxes!!).
Investigation costs, writing reports and filling forms
Costs of finding/training suitable/qualified replacement
Lower staff morale
Negative publicity (local media, newspapers, HSA etc.)
Costs to State (occupational injury benefit paid by taxes!!).
Слайд 15Human Costs
Circa 60 fatalities per annum according to HSA
Injuries that
result in pain and suffering
Loss of income
Medical costs – doctors/prescriptions
Inconvenience of trips to consultants, doctors, hospitals – having to be driven – disruption to other family members
Potential for negative relationships with Board, Principal and staff
Possibility of long term medical problems and inability to return to work.
Loss of income
Medical costs – doctors/prescriptions
Inconvenience of trips to consultants, doctors, hospitals – having to be driven – disruption to other family members
Potential for negative relationships with Board, Principal and staff
Possibility of long term medical problems and inability to return to work.
Слайд 16Benefits to schools of good safety management
Fewer accidents/injuries/lost time/claims
Fewer disruptions
to delivery of learning and teaching
Protects welfare of staff and students
Boosts morale/staff feel valued
Lower or stable insurance costs due to fewer claims
Ensures legal compliance and reduces liability of Board and individuals
Happier and healthier working environment. Less absenteeism.
Protects welfare of staff and students
Boosts morale/staff feel valued
Lower or stable insurance costs due to fewer claims
Ensures legal compliance and reduces liability of Board and individuals
Happier and healthier working environment. Less absenteeism.
Слайд 17Reasons for poor safety systems in schools
No appreciation of costs of
accidents or injuries or the benefits of good health
Fear of unknown
Time! Time! Time! – competing pressures on all of us
Lack of funding and support for safety changes
Lack of knowledge of health and safety duties and responsibilities
Jargon
“Not my job” – extra hassle
Lack of communication and listening
Fear of unknown
Time! Time! Time! – competing pressures on all of us
Lack of funding and support for safety changes
Lack of knowledge of health and safety duties and responsibilities
Jargon
“Not my job” – extra hassle
Lack of communication and listening
Слайд 18Reasons for poor safety systems in schools
Poor leadership – fear of
devolved or shared leadership
Focus on students
Inadequate involvement of staff
Health and safety not planned in projects (i.e. purchasing of equipment; building projects)
No understanding of hazards or risk assessments
No competence within the school
A culture of lack of trust and fear exists within school
Not knowing where to start therefore No Safety Culture.
Focus on students
Inadequate involvement of staff
Health and safety not planned in projects (i.e. purchasing of equipment; building projects)
No understanding of hazards or risk assessments
No competence within the school
A culture of lack of trust and fear exists within school
Not knowing where to start therefore No Safety Culture.
Слайд 19Safety Culture
What is a
safety culture?
Culture is a combination of an organisation's:
Attitudes
Behaviours
Beliefs
Values
Ways of doing things
The other shared characteristics of a particular group of people.
Culture is a combination of an organisation's:
Attitudes
Behaviours
Beliefs
Values
Ways of doing things
The other shared characteristics of a particular group of people.
Слайд 20Safety Culture
Successful companies hold the view that health and safety is
a key value and way of life.
”The way we do things around here”
“Health and safety management protects people from harm and also contributes to business success”
“Most accidents are preventable”
”The way we do things around here”
“Health and safety management protects people from harm and also contributes to business success”
“Most accidents are preventable”
Слайд 21Safety Culture Indicators
Accidents
Absenteeism
Sickness rates
Staff turnover
Legislative compliance
Staff complaints.
Слайд 22Creating a Safety Culture within schools
Leadership and commitment from the top
that is genuine and visible (“Walk the walk”)
Conviction among staff that high standards of safety are desirable and achievable
Identification and assessment of hazards and the creation of preventative systems
Immediate rectification of identified deficiencies
Health and safety a line management issue
Conviction among staff that high standards of safety are desirable and achievable
Identification and assessment of hazards and the creation of preventative systems
Immediate rectification of identified deficiencies
Health and safety a line management issue
Слайд 23Creating a Safety Culture within schools
Safety Policy sets out high expectations
Comprehensive
set of safety practices
Setting of realistic and achievable targets that are monitored and measured
Active participation by all employees in decision making
“Ownership” of health and safety permeates all levels of the school – achieved through training, staff and student involvement and good communication
Setting of realistic and achievable targets that are monitored and measured
Active participation by all employees in decision making
“Ownership” of health and safety permeates all levels of the school – achieved through training, staff and student involvement and good communication
Слайд 24Creating a Safety Culture within schools
All incidents are thoroughly investigated
Safety behaviour
embedded in school planning process
Effective accountability systems – specific, measurable, achievable, reasonable, unambiguous
Good safety behaviour is a condition of employment
Existence of a continuous improvement culture
Annual health and safety report.
Effective accountability systems – specific, measurable, achievable, reasonable, unambiguous
Good safety behaviour is a condition of employment
Existence of a continuous improvement culture
Annual health and safety report.
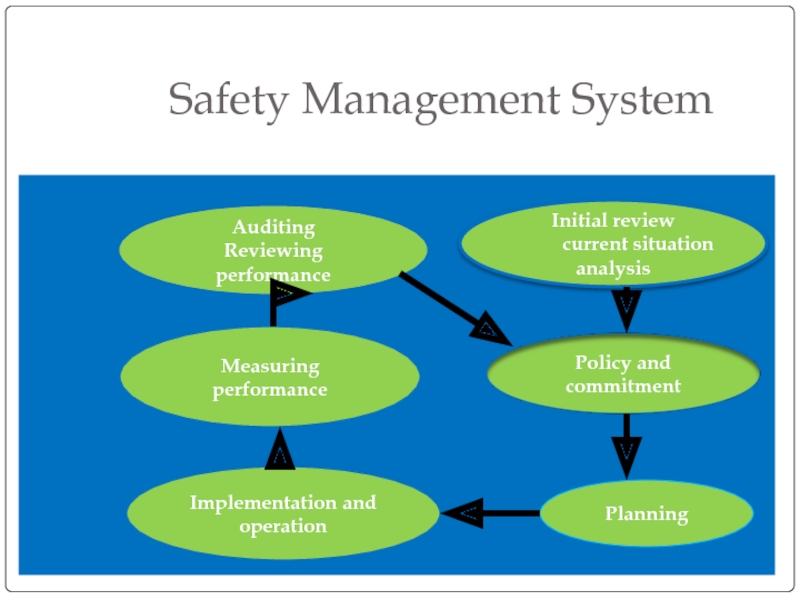
Слайд 25Safety Management System
Initial review
current situation analysis
Planning
Implementation
and operation
Measuring performance
Auditing
Reviewing performance
Слайд 26What is a safety management system?
Key elements:
Policy and commitment
Planning – objectives
and targets
Implementation and operation
Measuring performance
Monitoring
Audit and review
Implementation and operation
Measuring performance
Monitoring
Audit and review