- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Human resource management. Session 3. Designing jobs and conducting job analysis презентация
Содержание
- 1. Human resource management. Session 3. Designing jobs and conducting job analysis
- 2. Job Design. Job design is the process
- 3. Five approaches to job design: Work simplification
- 4. JOB ANALYSIS. Job analysis- the systematic process
- 5. Methods of gathering job information. Interviews. The
- 6. Methods of Job Analysis. Interview
- 7. Interview Methods Unstructured Interviews: Here the interview
- 8. Interview Outcomes However information from different
- 9. The uses of Job Analyses. Job analysis
- 10. Job analysis is useful for the following
- 11. The Techniques of Job Analysis. Task Inventory
- 12. The Techniques of Job Analysis (continue): Position
- 13. The Techniques of Job Analysis (continue):
- 14. JOB DESCRIPTION. Job description – a written
- 15. Problems with current job descriptions Too many
- 16. Problems with current job descriptions (continue). Managers
- 17. How to Write a Job Description There
- 18. Choosing the Correct Job Title Make
- 19. How to Write a Job Description (continue)
- 20. How to Write a Job Description (continue)
- 21. Elements of a Job Description. Job descriptions
- 22. Conducting the Interview Help the employee feel
- 23. Carefully Construct Interview Questions In developing interview
Слайд 2Job Design.
Job design is the process of organizing work into the
Five approaches to job design:
Work simplification.
Job enlargement.
Job rotation.
Job enrichment.
Team-based job design.
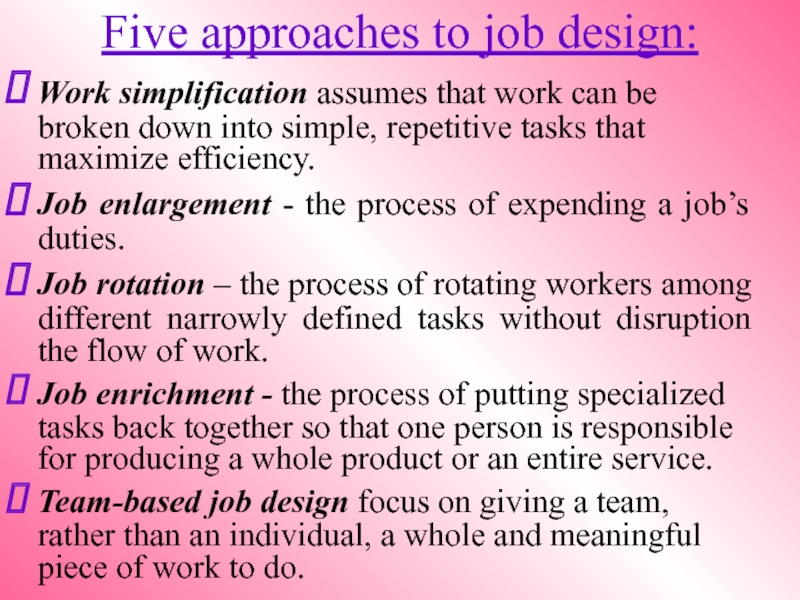
Слайд 3Five approaches to job design:
Work simplification assumes that work can be
Job enlargement - the process of expending a job’s duties.
Job rotation – the process of rotating workers among different narrowly defined tasks without disruption the flow of work.
Job enrichment - the process of putting specialized tasks back together so that one person is responsible for producing a whole product or an entire service.
Team-based job design focus on giving a team, rather than an individual, a whole and meaningful piece of work to do.
Слайд 4JOB ANALYSIS.
Job analysis- the systematic process of collecting information used to
A task is basic element of work that is a logical and necessary step in performing and job duty.
A duty consists of one or more tasks that constitute a significant activity performed in a job.
A responsibility is one or several duties that identify and describe the major purpose or reason for job’s existence.
Слайд 5Methods of gathering job information.
Interviews. The interviewer (usually member of HR
Observation. An individual observes the job incumbent actually performing the job and records the core job characteristics from observation.
Diaries. Several incumbents may be asked to keep diaries or logs of their daily job activities and record the amount of time spent on each activity.
Questionnaires. The job incumbent fills out a questionnaire that asks a series of questions about the job’s duties, responsibilities, and knowledge, skill, and ability requirements.
Слайд 6Methods of Job Analysis.
Interview
Advantages
Allows the incumbent to describe tasks and
Disadvantages
The incumbent may exaggerate or omit tasks and duties.
The Job Analysis Interview: method to collect a variety of information from an incumbent by asking the incumbent to describe the tasks and duties performed.
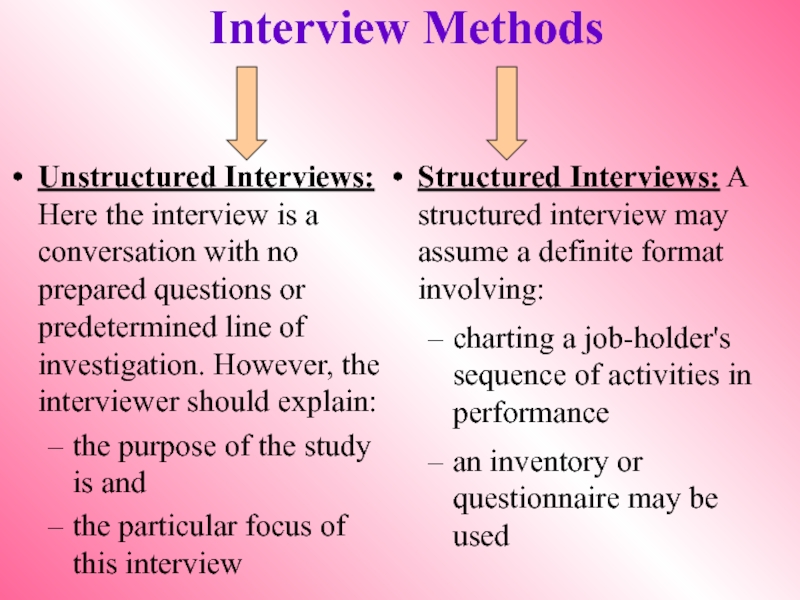
Слайд 7Interview Methods
Unstructured Interviews: Here the interview is a conversation with no
the purpose of the study is and
the particular focus of this interview
Structured Interviews: A structured interview may assume a definite format involving:
charting a job-holder's sequence of activities in performance
an inventory or questionnaire may be used
Слайд 8Interview Outcomes
However information from different interviews can be:
hard to bring together
there is potential for interviewer bias
certain areas of the work may fail to be picked up
an interview may stress one area and neglect others
there are problems in interpretation and analysis with the possibility of distorted impressions
the subjectivity of the data captured needs to be considered
Interviewing is a flexible method for all levels and types of job. An interview may focus on what a hypothetical job might involve.
Слайд 9The uses of Job Analyses.
Job analysis measures job content and the
For instance:
A company may be able to defend its policy of requiring sales representatives to have a valid driver’s license if it can show via job analysis that driving is an essential activity in the sales rep’s job.
The owner of a fast-food restaurant who pays an assistant manager a weekly salary (without any overtime pay) may be able to defend herself from charges of an overtime pay violation with a job analysis proving that the assistant manager job is exempt from the overtime provisions of the Fair Labor Standards Act.
Слайд 10Job analysis is useful for the following HR activities:
Recruitment. Job analysis
Selection. Job analysis can be used to determine whether an applicant for a specific job should be required to take a personality test or some other kind of test.
Performance appraisal. The performance standards used to judge employee performance for purposes of promotion, rewards, discipline, or layoff should be job related.
Compensation. Job analysis information can be used to compare the relative worth of each job’s contribution to the company’s overall performance.
Training and career development. Job analysis is an important input for determining training needs.
Слайд 11The Techniques of Job Analysis.
Task Inventory Analysis - is actually a
The Critical Incident Technique (CIT) is used to develop behavioral descriptions of a job.The technique involves the following four steps: (1) generate dimensions, (2) generate incidents, (3) retranslate, and (4) assign effectiveness values.
Слайд 12The Techniques of Job Analysis (continue):
Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ) is job
Information input.
Mental processes.
Work output..
Relationships with other persons.
Job context.
Other characteristics.
Слайд 13The Techniques of Job Analysis (continue):
Functional Job Analysis, a technique
1. What the job incumbent does to people, data, and things.
2. The methods and techniques the job incumbent uses to perform the job.
3. The machines, tools, and equipment used by the job incumbent.
4. The materials, projects, or services produced by the job incumbent.
Слайд 14JOB DESCRIPTION.
Job description – a written document that identifies, describes, and
Two types of a job descriptions:
1. Specific job descriptions.
2. General job descriptions
Слайд 15Problems with current job descriptions
Too many jobs don’t even have a
Many of the thousands of job descriptions suffer from a variety of ailments: inconsistency, jargon-laden writing, lack of appropriate information, lack of plain language and inadequate detail.
Job descriptions often include credentials and years of experience which can be considered a barrier.
Another significant problem is that many job descriptions are out of date because jobs change or evolve even if the job title has not changed (e.g., mergers, process improvements, reorganizations, job redesigns, technological changes, organizational changes, etc.)
Слайд 16Problems with current job descriptions (continue).
Managers perceive that writing a job
Many job descriptions are created by compensation staff and are useful for job evaluation purposes but not as useful for other areas in human resources
Слайд 17How to Write a Job Description
There are as many different formats
Job descriptions can include any or all of the following elements:
The date the job description was written. The job description should always be up to date. Rewrite it to reflect changes as often as needed.
Job status. Salaried or hourly? Full-time or part-time? Temporary or permanent?
Position title. Make sure your position titles reasonably and accurately reflect the actual title of the job.
Слайд 18Choosing the Correct Job Title
Make the title descriptive
Consider the
Think of your company hierarchy
Stay away from company jargon
Слайд 19How to Write a Job Description (continue)
Job summary. This section should
Detailed duties and responsibilities. This is a more detailed description of the duties involved and separates the essential functions of the job from the incidental job functions.
Skills required to perform the job. This can include compensable factors such as education, experience, and abilities.
Слайд 20How to Write a Job Description (continue)
Importance of job duties and
When and how often the tasks are performed. You might want to mention that certain tasks are only done once a month, quarter, year etc.
Job environment. Job environments can impact significantly on workers' motivation and job satisfaction.
Слайд 21Elements of a Job Description.
Job descriptions have four key elements:
Identification Information.
Job
Job Duties and Responsibilities.
Job Specifications and Minimum Qualifications.
Слайд 22Conducting the Interview
Help the employee feel welcome and at ease.
Break
Arrange a private place for the interview, and make arrangements so that you are not interrupted and so the employee may speak candidly about their job.
Give the employee an overview of the interview procedure. Take a few minutes to recap the essential functions of the job, and to explain why this analysis is important.
Let the employee know that you may need a few minutes every now and then to jot down their comments or your thoughts -- explain that your notes will be helpful later as you prepare the description of the job.
Слайд 23Carefully Construct Interview Questions
In developing interview questions, it is important to
Realistic given the requirements of the job
Complex enough to allow adequate demonstration of the KSAs being assessed
Stated in a straightforward unambiguous manner