- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
HSJ Chapter 6. Business-Level Strategy and the Industry Environment презентация
Содержание
- 1. HSJ Chapter 6. Business-Level Strategy and the Industry Environment
- 2. FRAGMENTED INDUSTRY Composed of a large number
- 3. FRAGMENTED INDUSTRY Focus strategy works best for a fragmented industry.
- 4. CONSOLIDATING W/VALUE INNOVATION Value innovator - Defines
- 5. VALUE INNOVATION Chaining: Obtaining the advantages of
- 6. VALUE INNOVATION Franchising: Strategy in which franchisor
- 7. FRANCHISING Advantages Finances the growth of the
- 8. VALUE INNOVATION Disadvantages Tight control of operations
- 9. HORIZONTAL MERGERS Merging with or acquiring competitors
- 10. EMBRYONIC & GROWTH INDUSTRIES Limited customer demand
- 11. EMBRYONIC & GROWTH INDUSTRIES Industry enters the
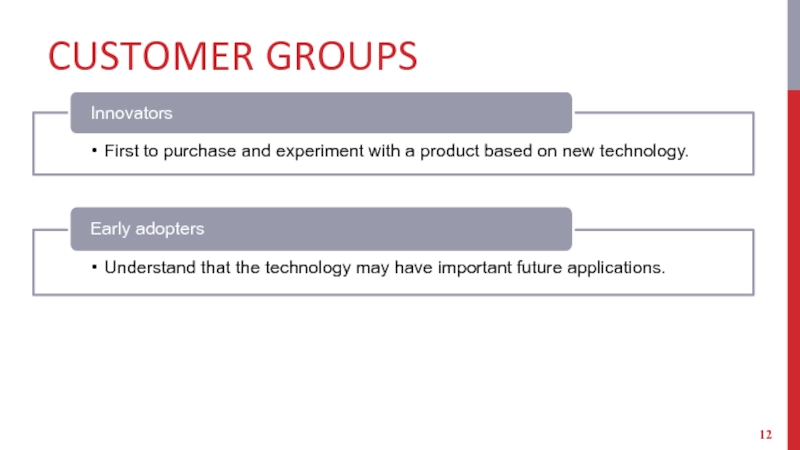
- 12. CUSTOMER GROUPS
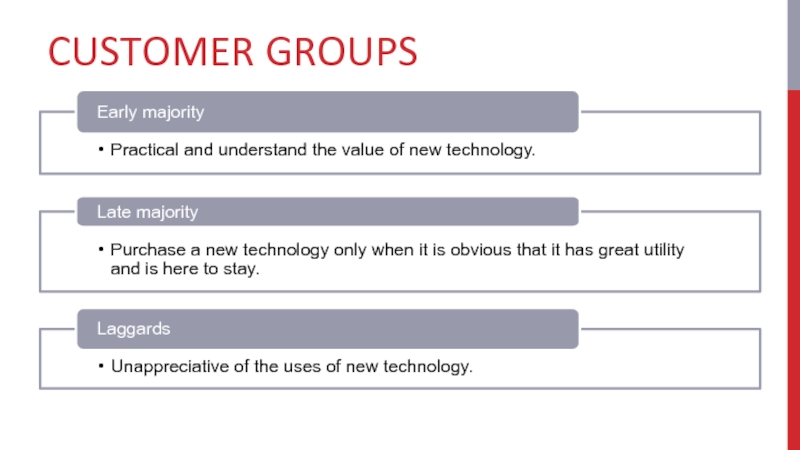
- 13. CUSTOMER GROUPS
- 16. CROSSING THE CHASM New strategies are required
- 17. CROSSING THE CHASM
- 19. ACCELERATING CUSTOMER DEMAND
- 20. ACCELERATING CUSTOMER DEMAND
- 21. ACCELERATING CUSTOMER DEMAND
- 22. ACCELERATING CUSTOMER DEMAND
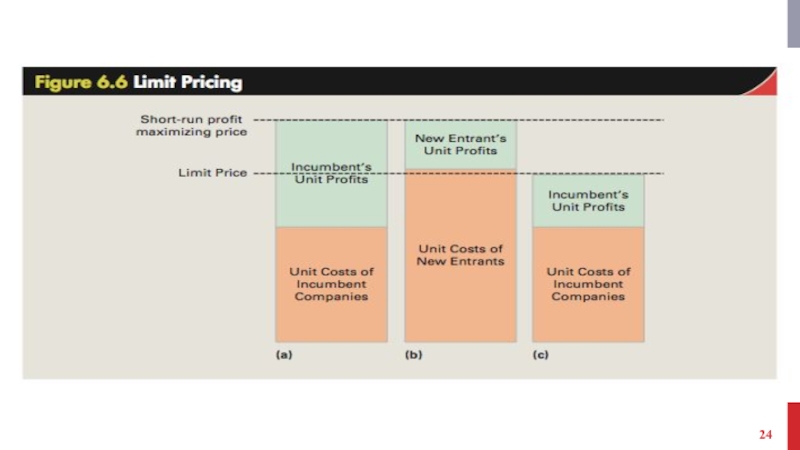
- 23. DETER ENTRY/MATURE INDUSTRIES
- 25. DETER ENTRY/MATURE INDUSTRIES
- 26. STRATEGIES TO MANAGE RIVALRY
- 27. STRATEGIES TO MANAGE RIVALRY
- 28. STRATEGIES TO MANAGE RIVALRY
- 29. STRATEGIES TO MANAGE RIVALRY
- 31. CAPACITY CONTROL Companies devise strategies to control
- 32. CAPACITY CONTROL Choosing a capacity-control strategy Each
- 34. CHOOSING A STRATEGY Leadership strategy: When a
- 35. CHOOSING A STRATEGY Harvest strategy: When a
- 37. BEST BUY case Share prices have gained
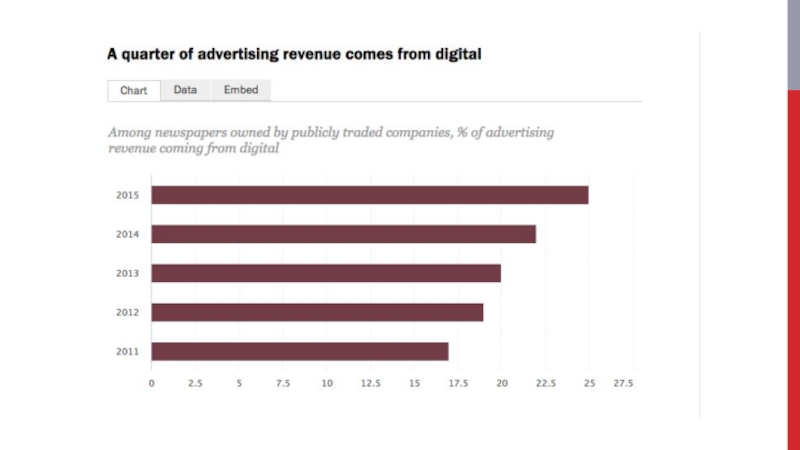
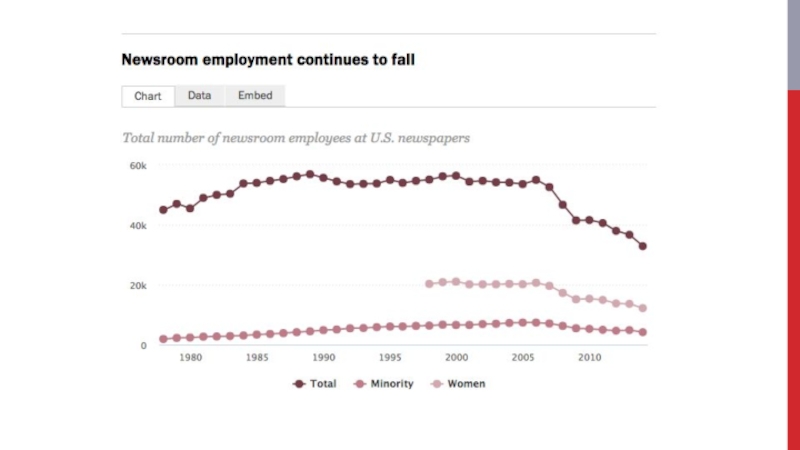
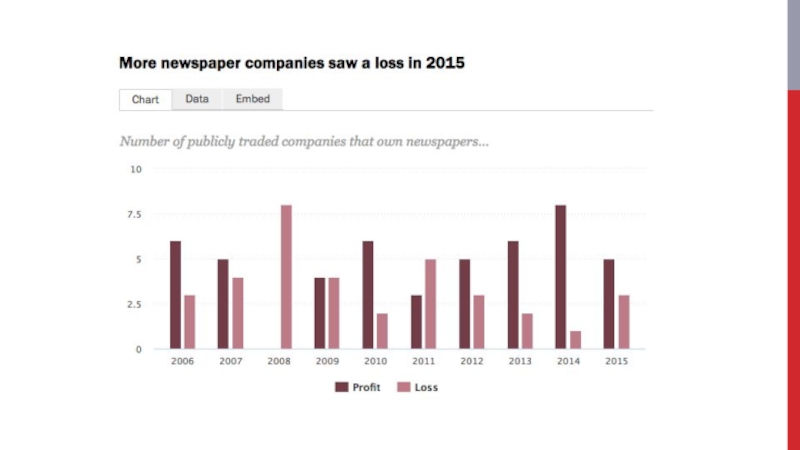
- 40. Newspaper industry Old triad model: Classifieds Display advertising Subscription revenue
Слайд 2FRAGMENTED INDUSTRY
Composed of a large number of small- and medium-sized companies.
Reasons
for fragmentation
Lack of scale economies
Brand loyalty in the industry is primarily local
Low entry barriers due to lack of scale economies and national brand loyalty
Lack of scale economies
Brand loyalty in the industry is primarily local
Low entry barriers due to lack of scale economies and national brand loyalty
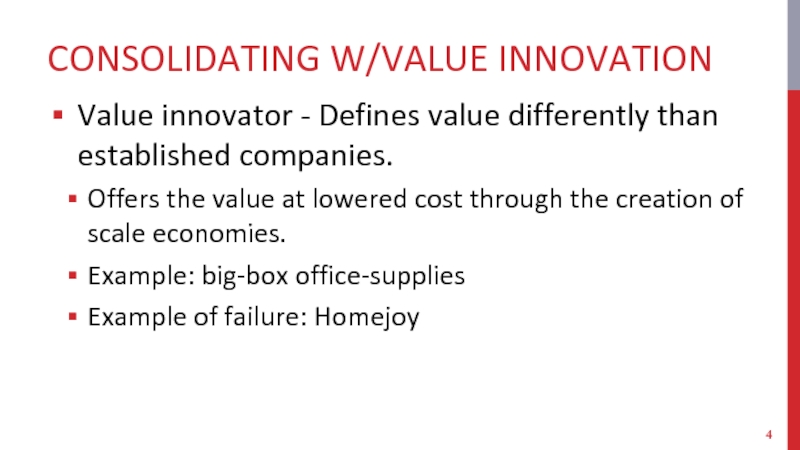
Слайд 4CONSOLIDATING W/VALUE INNOVATION
Value innovator - Defines value differently than established companies.
Offers
the value at lowered cost through the creation of scale economies.
Example: big-box office-supplies
Example of failure: Homejoy
Example: big-box office-supplies
Example of failure: Homejoy
Слайд 5VALUE INNOVATION
Chaining: Obtaining the advantages of cost leadership by establishing a
network of linked merchandising outlets.
Interconnected by information technology that functions as one large company.
Aids in building a national brand.
Interconnected by information technology that functions as one large company.
Aids in building a national brand.
Слайд 6VALUE INNOVATION
Franchising: Strategy in which franchisor grants the franchisee the right
to use the franchisor’s name, reputation, and business model.
In return for a fee and a percentage of the profits.
In return for a fee and a percentage of the profits.
Слайд 7FRANCHISING
Advantages
Finances the growth of the system, resulting in rapid expansion.
Franchisees have
a strong incentive to ensure that the operations are run efficiently.
New offerings developed by a franchisee can be used to improve the performance of the entire system.
New offerings developed by a franchisee can be used to improve the performance of the entire system.
Слайд 8VALUE INNOVATION
Disadvantages
Tight control of operations is not possible.
Major portion of the
profit go to the franchisee.
When franchisees face a higher cost of capital, it raises system costs and lowers profitability.
When franchisees face a higher cost of capital, it raises system costs and lowers profitability.
Слайд 9HORIZONTAL MERGERS
Merging with or acquiring competitors and combining them into a
single large enterprise.
Слайд 10EMBRYONIC & GROWTH INDUSTRIES
Limited customer demand for products of an embryonic
industry is due to:
limited performance and poor quality of the first products.
customer unfamiliarity with the product.
poorly developed distribution channels.
lack of complementary products.
high production costs because of small volumes of production.
limited performance and poor quality of the first products.
customer unfamiliarity with the product.
poorly developed distribution channels.
lack of complementary products.
high production costs because of small volumes of production.
Слайд 11EMBRYONIC & GROWTH INDUSTRIES
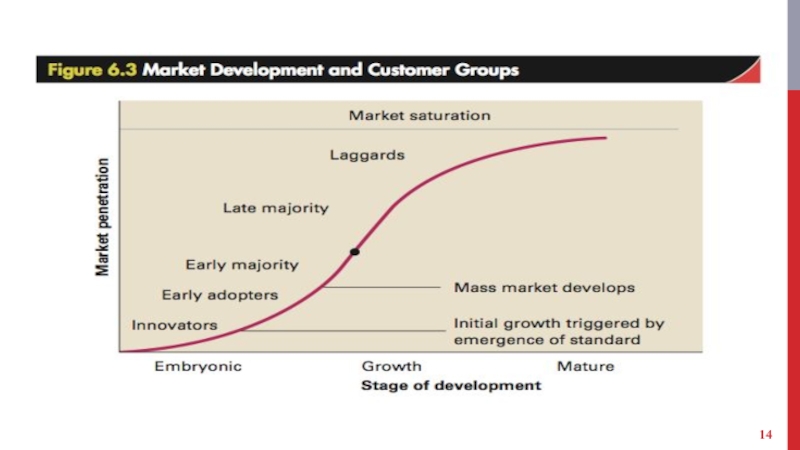
Industry enters the growth stage when a mass
market starts to develop for its products.
Mass market: One in which large numbers of customers enter the market.
Occurs when:
Product value increases, due to ongoing technological progress and development of complementary products.
Production cost decreases, resulting in low prices and high demand.
Mass market: One in which large numbers of customers enter the market.
Occurs when:
Product value increases, due to ongoing technological progress and development of complementary products.
Production cost decreases, resulting in low prices and high demand.
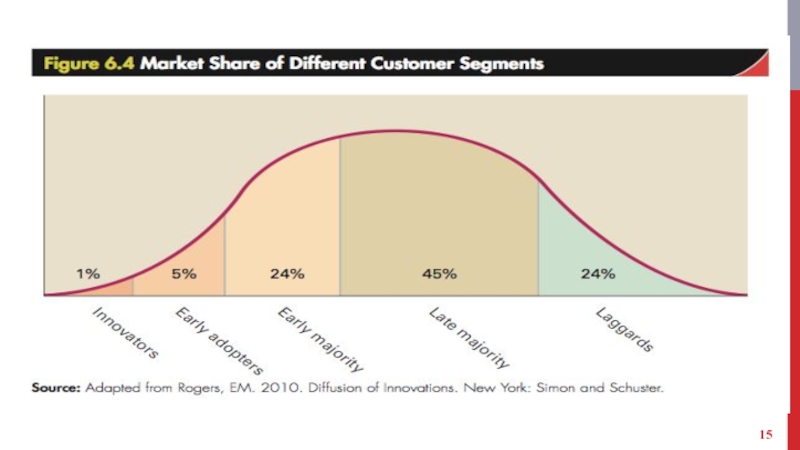
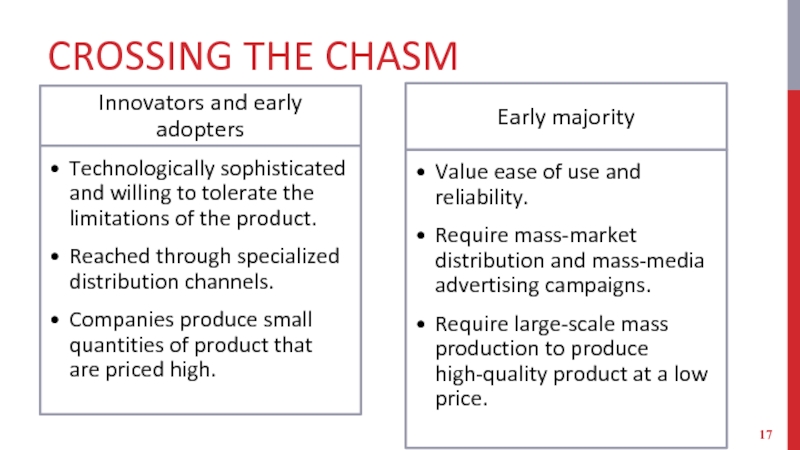
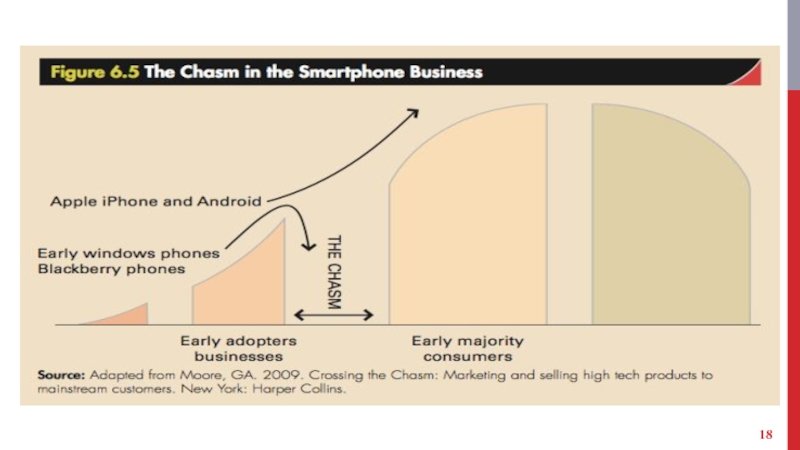
Слайд 16CROSSING THE CHASM
New strategies are required to strengthen a company’s business
model as a market develops.
Customers in each segment have very different needs.
Competitive chasm - Transition between the embryonic market and mass market.
Failure to do so results in the company going out of business.
Customers in each segment have very different needs.
Competitive chasm - Transition between the embryonic market and mass market.
Failure to do so results in the company going out of business.
Слайд 31CAPACITY CONTROL
Companies devise strategies to control or benefit from capacity expansion
programs.
Factors causing excess capacity.
New technologies that produce more than the old ones.
New entrants in an industry.
Economic recession that causes global overcapacity.
High growth of and demand in an industry that triggers rapid expansion.
Factors causing excess capacity.
New technologies that produce more than the old ones.
New entrants in an industry.
Economic recession that causes global overcapacity.
High growth of and demand in an industry that triggers rapid expansion.
Слайд 32CAPACITY CONTROL
Choosing a capacity-control strategy
Each company individually must try to preempt
its rivals.
Companies must collectively coordinate with each to be aware of the mutual effects of their actions.
Must avoid collusion
Companies must collectively coordinate with each to be aware of the mutual effects of their actions.
Must avoid collusion
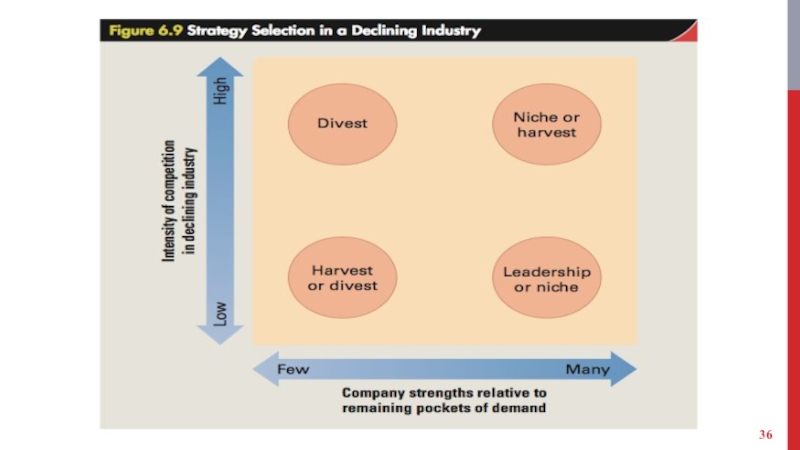
Слайд 34CHOOSING A STRATEGY
Leadership strategy: When a company develops strategies to become
the dominant player in a declining industry.
Niche strategy: When a company focuses on pockets of demand that are declining more slowly than the industry as a whole to maintain profitability.
Niche strategy: When a company focuses on pockets of demand that are declining more slowly than the industry as a whole to maintain profitability.
Слайд 35CHOOSING A STRATEGY
Harvest strategy: When a company reduces to a minimum
the assets it employs in a business to reduce its cost structure and extract maximum profits from its investment.
Divestment strategy: When a company decides to exit an industry by selling off its business assets to another company.
Divestment strategy: When a company decides to exit an industry by selling off its business assets to another company.
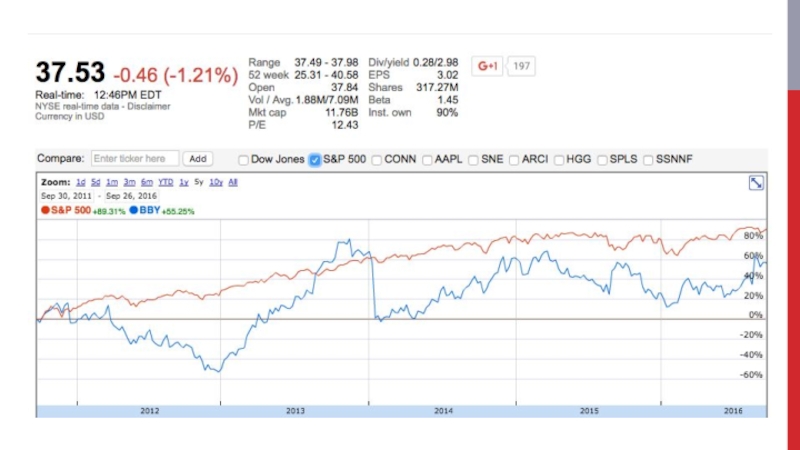
Слайд 37BEST BUY case
Share prices have gained 26% in 2016; 2.7% dividend
yield, too
16% earnings growth last quarter even with flat YoY revenue
16% earnings growth last quarter even with flat YoY revenue