- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Forecasting. Successful operations of the company презентация
Содержание
- 1. Forecasting. Successful operations of the company
- 2. Successful operations of the company Effective planning Accurate forecasting
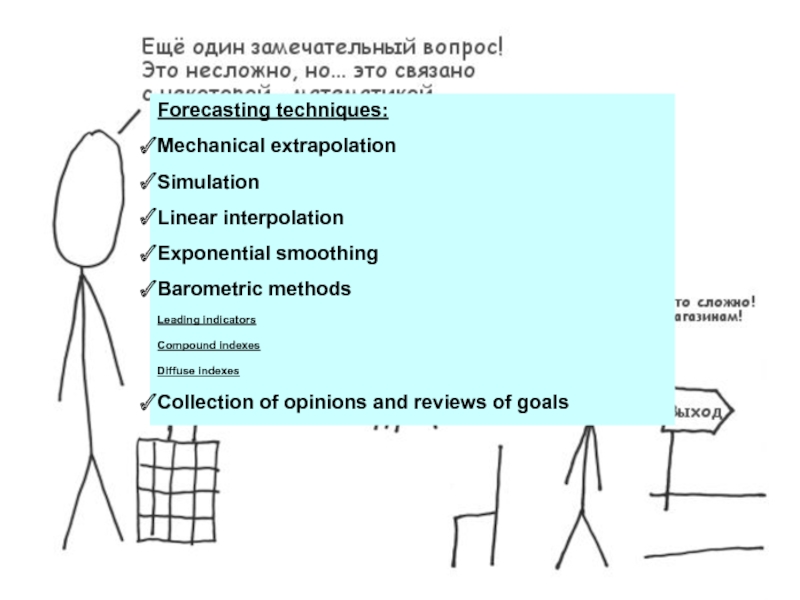
- 3. Forecasting techniques: Mechanical extrapolation Simulation
- 4. Mechanical extrapolation Forecasting techniques Originally extrapolation methods
- 5. However, they are widely used by professional
- 6. Mechanical extrapolation The simplest models: All future
- 7. Mechanical extrapolation Forecasting techniques: The simplest models:
- 8. The vast majority of all economic, political
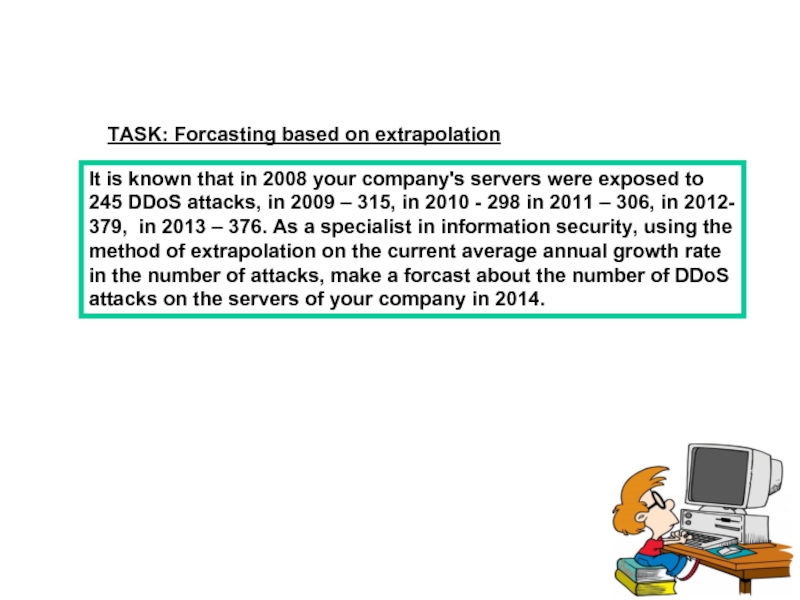
- 9. TASK: Forcasting based on extrapolation It is
- 10. 2. The average annual growth rate is
- 11. 3. Chain growth rate is the ratio
- 12. Time series analysis: Time series consist of
- 13. Why fluctuation is typical for the time
- 14. 1) Trend (Т) Is a long-term increase
- 15. 3) Cyclic changes (С) Cover periods of
- 16. Seasonal changes and the method of moving
- 17. Regroup presented data: Time series analysis: Mechanical
- 18. Step 1: Moving
- 19. Step 5: Make normatization: the average value
- 20. Q1: 316 (для 1989) * 0,99 =
- 21. Designing of trend As a forecasting method
- 22. ] Y – the observed value
- 23. Trend estimates are more reliable if they
- 25. Cyclical changes(С) Cyclic changes are regular fluctuations that occur in a few years Forecasting techniques:
Слайд 3Forecasting techniques:
Mechanical extrapolation
Simulation
Linear interpolation
Exponential smoothing
Barometric methods
Leading indicators
Compound indexes
Diffuse indexes
Collection of opinions and reviews of goals
Слайд 4Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques
Originally extrapolation methods are mechanical
and not closely linked to
Слайд 5However, they are widely used by professional economists who make forecasting
Because
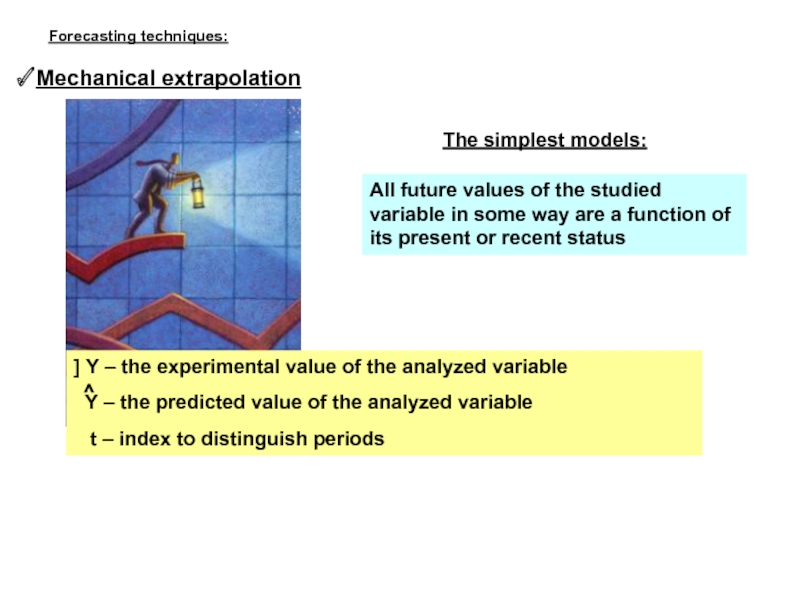
Слайд 6Mechanical extrapolation
The simplest models:
All future values of the studied variable in
^
Forecasting techniques:
] Y – the experimental value of the analyzed variable
Y – the predicted value of the analyzed variable
t – index to distinguish periods
^
Слайд 7Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
The simplest models:
Unchanging model
The predicted value of the
Y t+1 = Y t
^
Proportionaly - changing model
The value of a variable changes from current to next period will be proportional to the value of a variable changes from the previous period to the current period
Y t+1 = Y t + k ∆ Y t
^
Evaluation of k based on retrospective information.
K = 1 is a uniformly changing the model
Слайд 8The vast majority of all economic, political and social decisions are
For most short-term predictions the simplest models are the most easy ways of forecasting, since they are easy to use and requires minimal information for calculating
Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
The simplest models:
Слайд 9TASK: Forcasting based on extrapolation
It is known that in 2008 your
Слайд 102. The average annual growth rate is an indicator of the
Guidelines for decision :
1. The forecast value of the parameter on the basis of extrapolation in the current average annual growth rate is determined by the formula
Кn+1 – the forecast value of the parameter;
Кn – parameter value in the reporting period;
Тср.г. – the average annual rate of growth of parameter.
Тц1, Тц2,…,Тцn – the parameter of chain growth for periods; n is the number of periods.
Слайд 113. Chain growth rate is the ratio of each next level
4. The rate of growth, like a chain, and the average, characterize the relative rate of change of the level of series during the relevant period (or unit time)
Тпр.ц – chain increment rate;
Тц – chain growth rate.
Тпр.ср.г. – chain increment rate;
Тср.г. – среднегодовой темп роста.
Слайд 12Time series analysis:
Time series consist of values corresponding to certain points
Ordered in time indicators: sales, production volume, prices….
Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
Слайд 13Why fluctuation is typical for the time series?
Usually there are four
Trend (T)
Seasonal changes (S)
Cyclic changes (C)
Irregular forces (I)
Time series analysis:
Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
Слайд 141) Trend (Т)
Is a long-term increase or decrease of series
Seasonal changes
Due to weather conditions and habits appear almost at the same time of a year (for example, New Year, Easter and other holidays, during which various purchases are made)
Time series analysis:
Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
Слайд 153) Cyclic changes (С)
Cover periods of several years, reflect the level
Irregular forces (I)
Strikes, war. Inconsistent in their effect on individual series, but, nevertheless, be taken into account
Time series analysis:
Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
Слайд 16Seasonal changes and the method of moving average
Moving average is calculated
Seasonal changes can be taken into account in the forecast using the seasonal index, which can be calculated by the method of moving average
Time series analysis:
Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
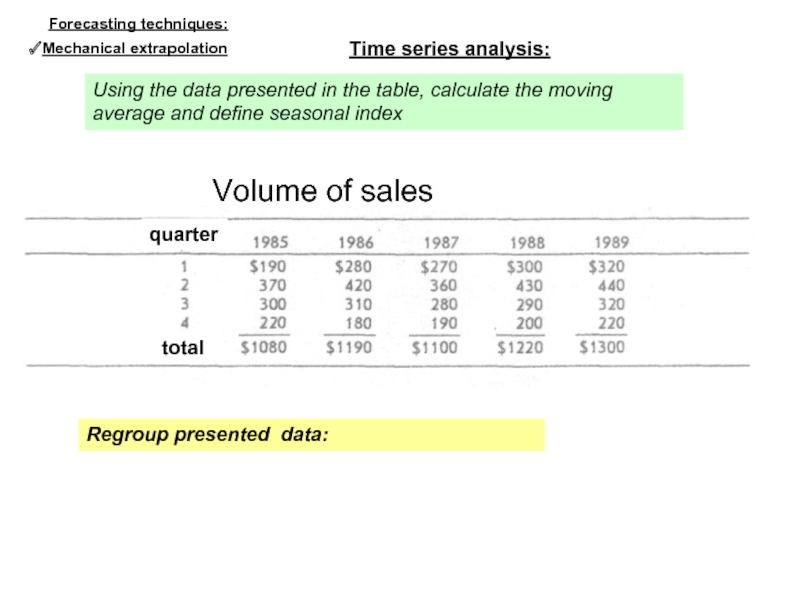
Слайд 17Regroup presented data:
Time series analysis:
Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
Using the data presented in
Volume of sales
quarter
total
Слайд 18
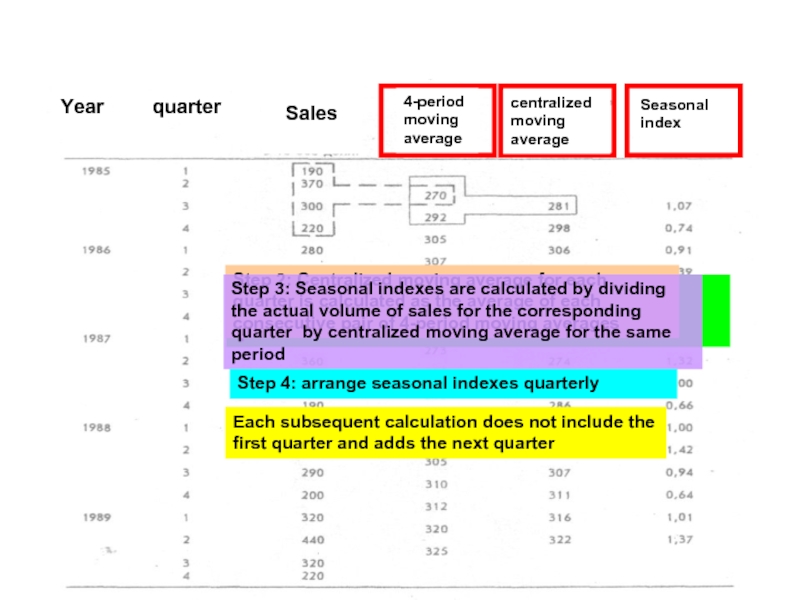
Step 1: Moving average over the four periods is calculated using
Each subsequent calculation does not include the first quarter and adds the next quarter
Step 2: Centralized moving average for each quarter is calculated as the average of each consecutive pair of 4-period moving averages
Step 3: Seasonal indexes are calculated by dividing the actual volume of sales for the corresponding quarter by centralized moving average for the same period
Step 4: arrange seasonal indexes quarterly
quarter
Year
Sales
4-period
moving
average
centralized
moving
average
Seasonal
index
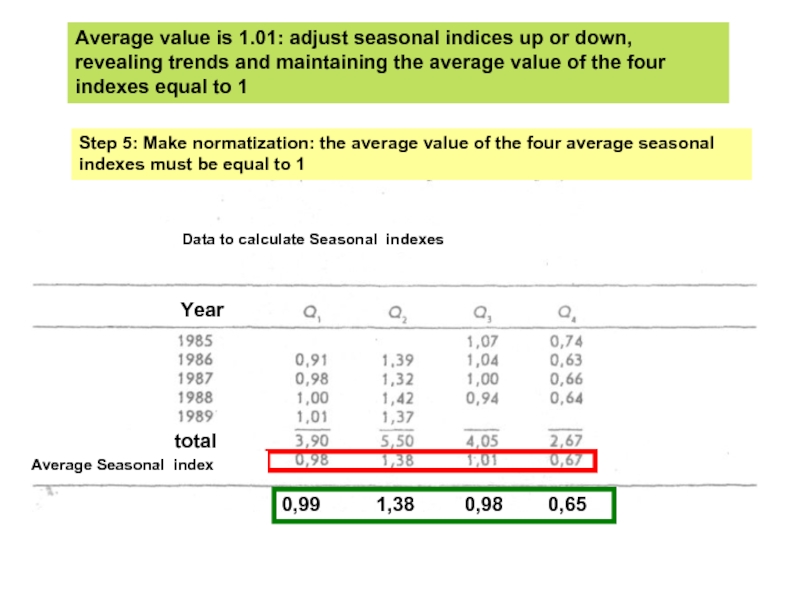
Слайд 19Step 5: Make normatization: the average value of the four average
Average value is 1.01: adjust seasonal indices up or down, revealing trends and maintaining the average value of the four indexes equal to 1
0,99 1,38 0,98 0,65
Year
Average Seasonal index
total
Data to calculate Seasonal indexes
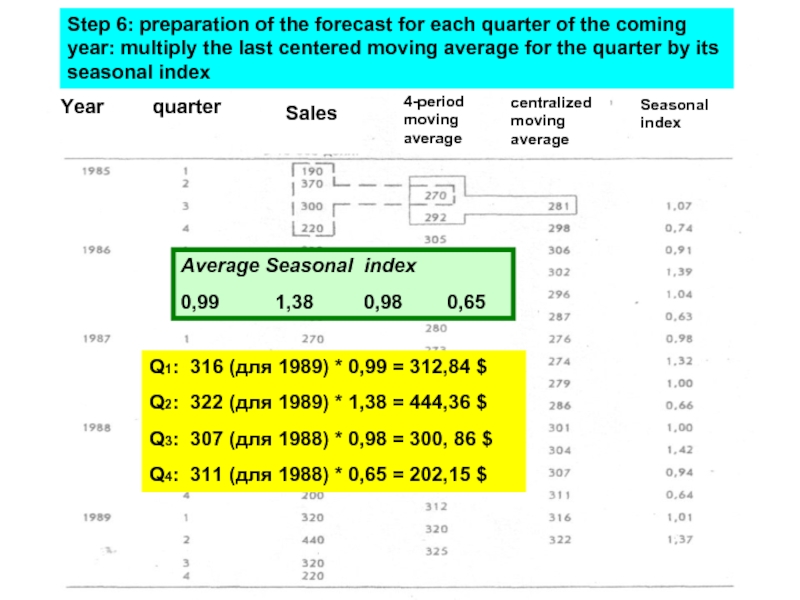
Слайд 20Q1: 316 (для 1989) * 0,99 = 312,84 $
Q2: 322 (для
Q3: 307 (для 1988) * 0,98 = 300, 86 $
Q4: 311 (для 1988) * 0,65 = 202,15 $
Average Seasonal index
0,99 1,38 0,98 0,65
4-period
moving
average
centralized
moving
average
Seasonal
index
Sales
Step 6: preparation of the forecast for each quarter of the coming year: multiply the last centered moving average for the quarter by its seasonal index
quarter
Year
Слайд 21Designing of trend
As a forecasting method assumes that started change in
The most widely used method of trend detection is regression analysis, namely the method of least squares
The method consists of the selection of a regression line according to the observations so that the squares of their deviations from the regression line were minimal
Time series analysis:
Mechanical extrapolation
Forecasting techniques:
Слайд 22
] Y – the observed value of the analyzed variable
Y
^
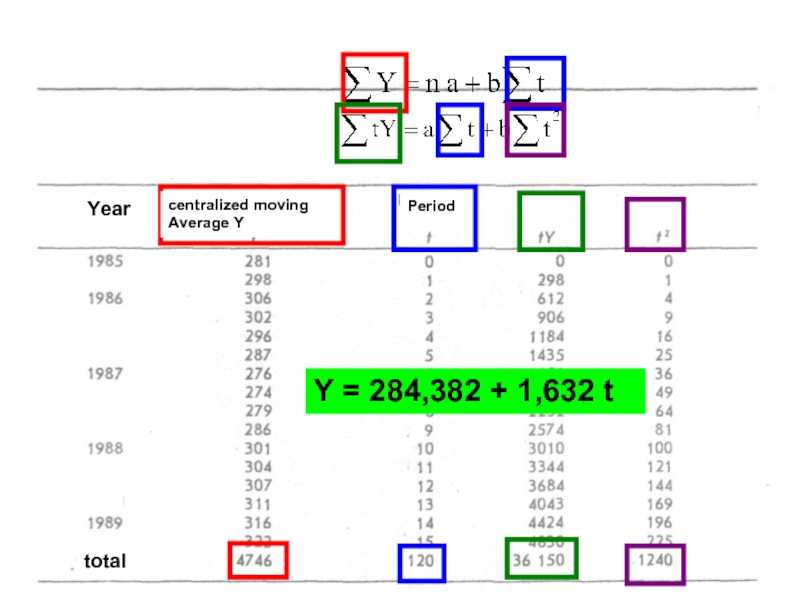
Regression line is presented by: Y = a + bt, where a and b - parameters of evaluation, t – number of period
^
To find the values of the parameters a and b, it is necessary to solve the system of equations
Слайд 23Trend estimates are more reliable if they are based on data
Seasonal effects are smoothed by a moving average
Слайд 25Cyclical changes(С)
Cyclic changes are regular fluctuations that occur in a few
Forecasting techniques:










![] Y – the observed value of the analyzed variable Y – the predicted value](/img/tmb/1/26279/108ef995b51328b0b103000848787985-800x.jpg)