action to ensure desired results.
It sees to it that the right things happen, in the right ways, and at the right time.
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Controlling as a Management Function презентация
Содержание
- 1. Controlling as a Management Function
- 2. May 16, 2006 LIS580- Spring 2006 What
- 3. Controlling as a Management Function Controlling Done
- 4. Controlling as a Management Function Controlling It
- 5. Controlling as a Management Function Cybernetic Control
- 6. The Control Process Establish objectives and standards.
- 7. The Control Process
- 8. Establish Objectives and Standards The control
- 9. Establish Objectives and Standards There are
- 10. Measuring Actual Performance Measurements must be accurate
- 11. Comparing Results with Objectives and Standards The
- 12. Taking Corrective Action Taking any action
- 13. Taking Corrective Action Management-by Exception can save
- 14. Effective Controls The Best Controls in Organizations
- 15. Effective Controls The Best Controls in Organizations
- 16. Types of Control
- 17. Types of Control Preliminary Sometimes called
- 18. Types of Control Concurrent
- 19. Types of Control Postaction Sometimes
- 20. Types of Controls Managers have two broad
- 21. Types of Control Internal Controls Allows motivated
- 22. Types of Control External Controls It occurs
- 23. Qualities of an Effective Control System Prentice Hall, 2002
- 24. Organizational Control Systems Management Processes Strategy
- 25. Organizational Control Systems Compensation and Benefits Attract
- 26. Organizational Control Systems Employee Discipline Discipline
- 27. The “Hot Stove Rule” Immediate Focus on
- 28. Organizational Control Systems Information and Financial
- 29. Operations Management and Control Purchasing Economic
- 30. Operations Management and Control Project Management Program
- 31. Operations Management and Control Statistical Quality Control
Слайд 1Controlling as a Management Function
Controlling
A process of monitoring performance and taking
Слайд 2May 16, 2006
LIS580- Spring 2006
What is Control?
The process of monitoring activities
to ensure that they are being accomplished as planned and of correcting any significant deviations
An effective control system ensures that activities are completed in ways that lead to the attainment of the organization’s goals
An effective control system ensures that activities are completed in ways that lead to the attainment of the organization’s goals
Prentice Hall, 2002
Слайд 3Controlling as a Management Function
Controlling
Done well, it ensures that the overall
directions of individuals and groups are consistent with short and long range plans.
It helps ensure that objectives and accomplishments are consistent with one another throughout an organization.
It helps ensure that objectives and accomplishments are consistent with one another throughout an organization.
Слайд 4Controlling as a Management Function
Controlling
It helps maintain compliance with essential organizational
rules and policies.
Слайд 5Controlling as a Management Function
Cybernetic Control System
One that is self-contained in
its performance monitoring and correction capabilities. (thermostat)
The control process practiced in organizations is not cybernetic, but it does follow similar principles.
The control process practiced in organizations is not cybernetic, but it does follow similar principles.
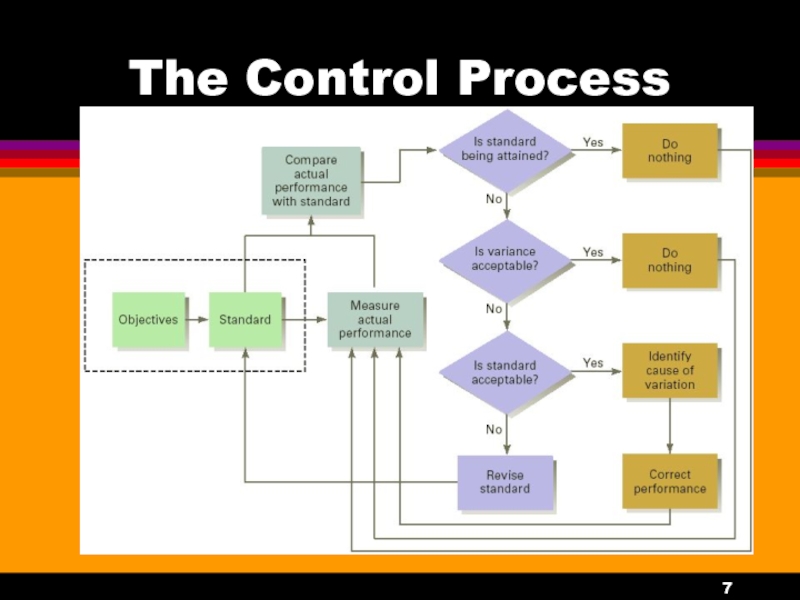
Слайд 6The Control Process
Establish objectives and standards.
Measure actual performance.
Compare results with objectives
and standards.
Take necessary action.
Take necessary action.
Слайд 8Establish Objectives and Standards
The control process begins with planning and the
establishment of performance objectives.
Performance objectives are defined and the standards for measuring them are set.
Performance objectives are defined and the standards for measuring them are set.
Слайд 9Establish Objectives and Standards
There are two types of standards:
Output Standards -
measures performance results in terms of quantity, quality, cost, or time.
Input Standards - measures work efforts that go into a performance task.
Input Standards - measures work efforts that go into a performance task.
Слайд 10Measuring Actual Performance
Measurements must be accurate enough to spot deviations or
variances between what really occurs and what is most desired.
Without measurement, effective control is not possible.
Without measurement, effective control is not possible.
Слайд 11Comparing Results with Objectives and Standards
The comparison of actual performance with
desired performance establishes the need for action.
Ways of making such comparisons include:
Historical / Relative / Engineering
Benchmarking
Ways of making such comparisons include:
Historical / Relative / Engineering
Benchmarking
Слайд 12Taking Corrective Action
Taking any action necessary to correct or improve things.
Management-by-Exception
focuses managerial attention on substantial differences between actual and desired performance.
Слайд 13Taking Corrective Action
Management-by Exception can save the managers time, energy, and
other resources, and concentrates efforts on areas showing the greatest need.
There are two types of exceptions:
Problems - below standard
Opportunities - above standard
There are two types of exceptions:
Problems - below standard
Opportunities - above standard
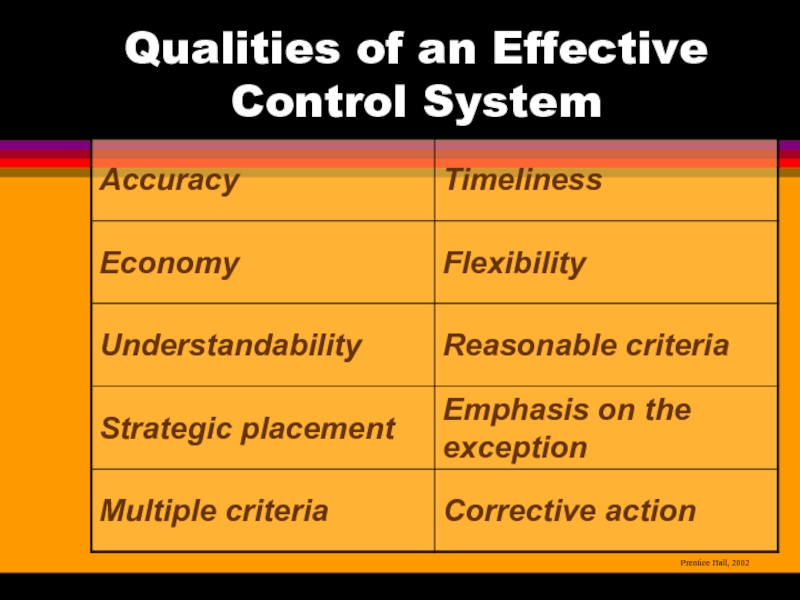
Слайд 14Effective Controls
The Best Controls in Organizations
are
Strategic and results oriented
Understandable
Encourage self-control
Слайд 15Effective Controls
The Best Controls in Organizations are
Timely and exception oriented
Positive in
nature
Fair and objective
Flexible
Fair and objective
Flexible
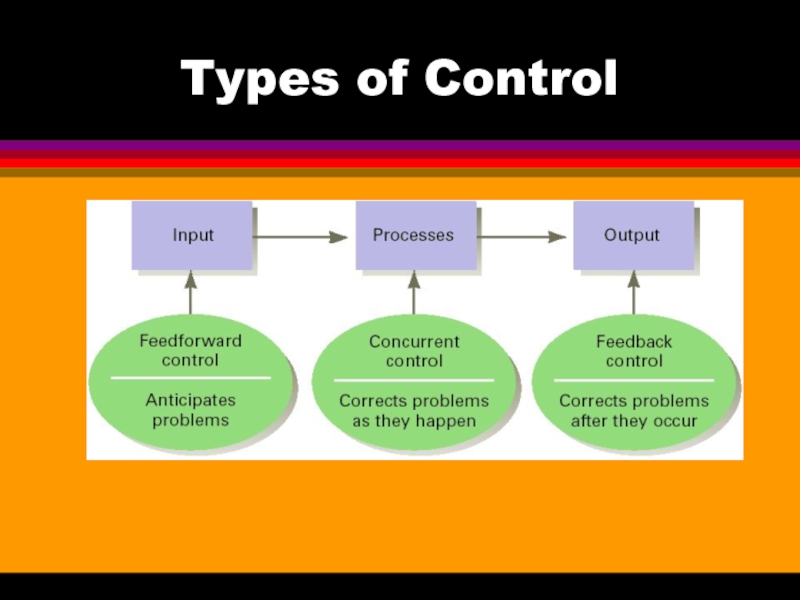
Слайд 17Types of Control
Preliminary
Sometimes called the feedforward controls, they are accomplished
before a work activity begins.
They make sure that proper directions are set and that the right resources are available to accomplish them.
They make sure that proper directions are set and that the right resources are available to accomplish them.
Слайд 18Types of Control
Concurrent
Focus on what happens during the
work process. Sometimes called steering controls, they monitor ongoing operations and activities to make sure that things are being done correctly.
Слайд 19Types of Control
Postaction
Sometimes called feedback controls, they take place
after an action is completed. They focus on end results, as opposed to inputs and activities.
Слайд 20Types of Controls
Managers have two broad options with respect to control.
They
can rely on people to exercise self-control (internal) over their own behavior.
Alternatively, managers can take direct action (external) to control the behavior of others.
Alternatively, managers can take direct action (external) to control the behavior of others.
Слайд 21Types of Control
Internal Controls
Allows motivated individuals to exercise self-control in fulfilling
job expectations.
The potential for self-control is enhanced when capable people have clear performance objectives and proper resource support.
The potential for self-control is enhanced when capable people have clear performance objectives and proper resource support.
Слайд 22Types of Control
External Controls
It occurs through personal supervision and the use
of formal administrative systems.
Performance appraisal systems, compensation and benefit systems, employee discipline systems, and management-by-objectives.
Performance appraisal systems, compensation and benefit systems, employee discipline systems, and management-by-objectives.
Слайд 24Organizational Control Systems
Management Processes
Strategy and objectives
Policies and procedures
Selection and training
Performance
appraisal
Job design and work structures
Performance modeling, norms, and organization culture
Job design and work structures
Performance modeling, norms, and organization culture
Слайд 25Organizational Control Systems
Compensation and Benefits
Attract talented people and retain them.
Motivate people
to exert maximum effort in their work.
Recognize the value of their performance contributions.
Recognize the value of their performance contributions.
Слайд 26Organizational Control Systems
Employee Discipline
Discipline is defined as influencing behavior through
reprimand.
Progressive Discipline ties reprimand to the severity and frequency of the employee’s infractions.
Positive Discipline tries to involve people more positively and directly in making decisions to improve their behavior.
Progressive Discipline ties reprimand to the severity and frequency of the employee’s infractions.
Positive Discipline tries to involve people more positively and directly in making decisions to improve their behavior.
Слайд 27The “Hot Stove Rule”
Immediate
Focus on activity not personality
Consistent
Informative
Occur in a supportive
setting
Support realistic rules
Support realistic rules
To be Effective Discipline Should be:
Слайд 28Organizational Control Systems
Information and Financial
Activity-based costing - the true cost
of all products and services.
Economic value added - examine the value added by all activities.
Understand the implication of key financial measures of (ratios) organizational performance
Economic value added - examine the value added by all activities.
Understand the implication of key financial measures of (ratios) organizational performance
Слайд 29Operations Management and Control
Purchasing
Economic Order Quantity
automatic reorder points
Just-In-Time Scheduling
Слайд 30Operations Management and Control
Project Management
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) -
Identifies and controls the many separate events in complex projects.
Слайд 31Operations Management and Control
Statistical Quality Control
Based on the establishment of upper
and lower control limits, that can be graphically and statistically monitored to ensure that products meet standards.