- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Assessing the Internal Environment of the Firm презентация
Содержание
- 1. Assessing the Internal Environment of the Firm
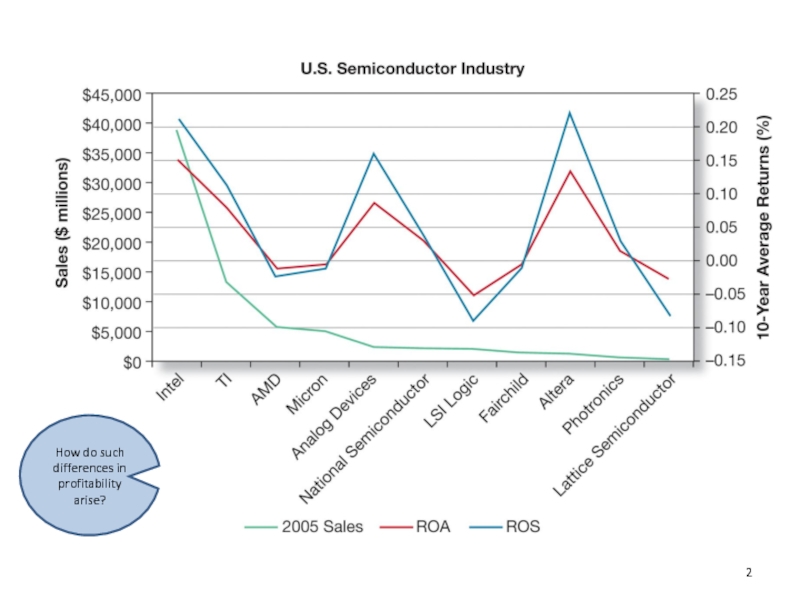
- 2. How do such differences in profitability arise?
- 3. Resource-Based View of the Firm Why some
- 4. Resource-Based View of the Firm Tangible resources
- 5. Resource-Based View of the Firm Intangible resources
- 6. Resource-Based View of the Firm Organizational capabilities
- 7. QUESTION Gillette combines several technologies to attain
- 8. Resource-Based View of the Firm Two Critical
- 9. Firm Resources and Sustainable Competitive Advantages Four
- 10. Firm Resources and Sustainable Competitive Advantages Can
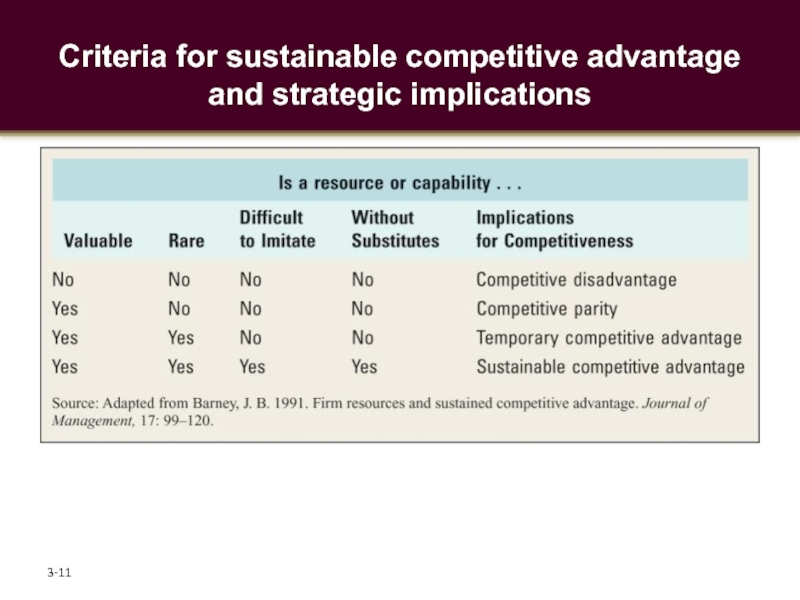
- 11. Criteria for sustainable competitive advantage and strategic implications 3-
- 13. Resources of Manchester United Manchester United is
- 14. Questions According to text, how well did
- 15. Biggest kit deals in Europe
- 16. Value-Chain Analysis Value-chain analysis a strategic
- 17. The Value Chain 3- Exhibit 3.1
- 18. Value-Chain Analysis Primary activities contribute to
- 19. Value-Chain Analysis Support activities activities of the
- 20. QUESTION In assessing its primary activities, an
- 21. Primary Activity: Inbound Logistics Associated with receiving,
- 22. Primary Activity: Operations Associated with transforming inputs
- 23. How Does Automation Affect Cost Structure? 3- Harley-Davidson Then and Now
- 24. Primary Activity: Outbound Logistics Associated with collecting,
- 25. Primary Activity: Marketing and Sales Associated with
- 26. Primary Activity: Service Associated with providing service
- 27. Support Activity: Procurement Function of purchasing inputs
- 28. Support Activity: Human Resource Management Activities
- 29. Support Activity: Technology Development Related to
- 30. Support Activity: General Administration Typically supports
- 31. Value Chain – Internet Startup Example 3-
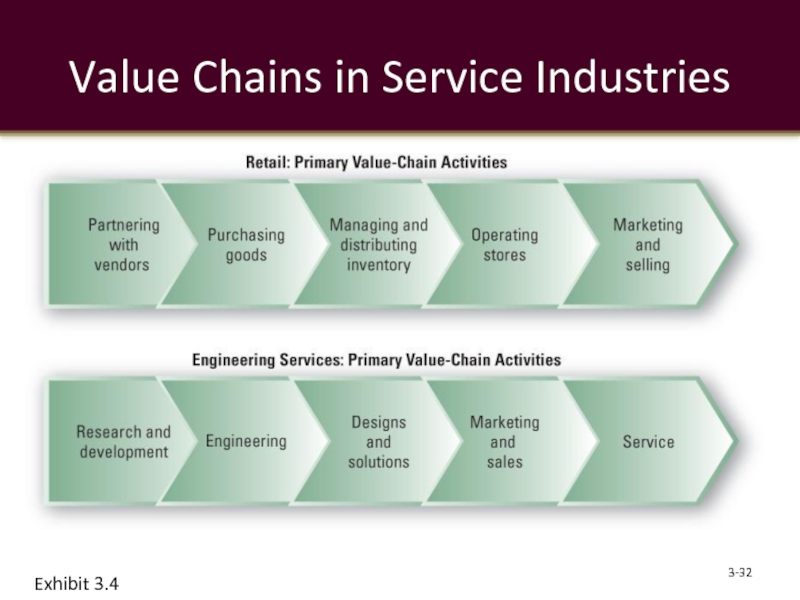
- 32. Value Chains in Service Industries 3- Exhibit 3.4
- 33. Value Chain and Competitive Advantage 3-
- 34. Value Chain and Competitive Advantage 3-
- 35. Innovation and Integration of Value Chain 3-
- 36. Key Takeaways 3-
- 37. Evaluating Firm Performance Financial ratio analysis Balance
- 38. Financial Ratio Analysis Five types of financial
- 39. Five Types of Financial Ratios 3-
Слайд 1Assessing the Internal
Environment of the Firm
Chapter Three
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2012 by The
Слайд 3Resource-Based View of the Firm
Why some firms outperform others?
Endowment of strategic
Determine the resources and capabilities that are likely sources of competitive advantage (internal and external focus)
Three key types of resources: Tangible, Intangible, and Organizational Capabilities
Central theme – competitive advantages are created and sustained through the bundling of several of these resources to unique combinations
3-
Слайд 4Resource-Based View of the Firm
Tangible resources – relatively easy to identify
Financial
Physical – company’s plant, equipment, and machinery
Technological
Organizational – company’s strategic planning process, employee development
3-
Слайд 5Resource-Based View of the Firm
Intangible resources – embedded in unique routines
Human – experience and capability of employees, trust and collaboration
Innovation and creativity – technical and scientific expertise
Reputation – brand name, reputation with suppliers/customers
What do firms such as BP and Toyota do when their intangible resource – reputation was damaged due to scandals?
3-
Слайд 6Resource-Based View of the Firm
Organizational capabilities – competencies/skills that a firm
Enable a firm to take full advantage of other resources it controls
Examples:
Outstanding customer service
Excellent product development capabilities
Ability to hire, motivate, and retain human capital
Marketing skill
Cooperative relationships
3-
Слайд 7QUESTION
Gillette combines several technologies to attain unparalleled success in the wet
3-
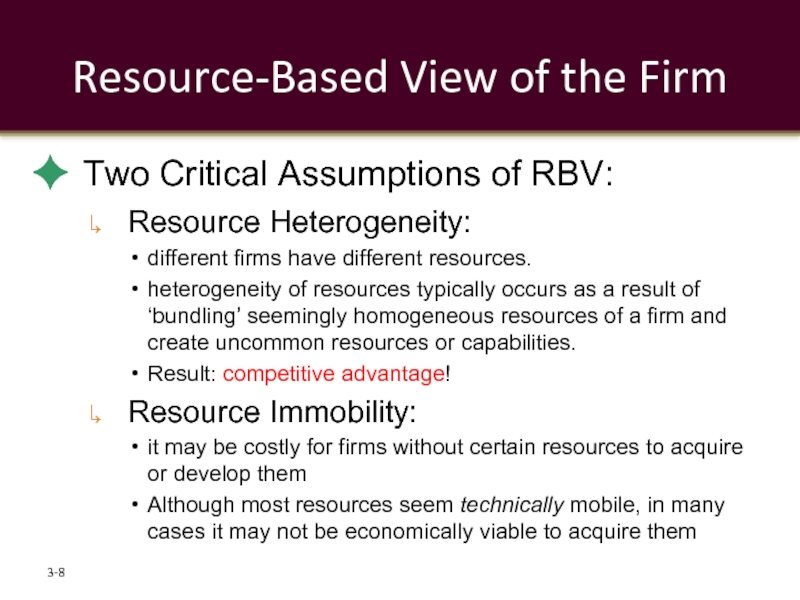
Слайд 8Resource-Based View of the Firm
Two Critical Assumptions of RBV:
Resource Heterogeneity:
different
heterogeneity of resources typically occurs as a result of ‘bundling’ seemingly homogeneous resources of a firm and create uncommon resources or capabilities.
Result: competitive advantage!
Resource Immobility:
it may be costly for firms without certain resources to acquire or develop them
Although most resources seem technically mobile, in many cases it may not be economically viable to acquire them
3-
Слайд 9Firm Resources and Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Four Key Attributes of Resources
Is the
Enable a firm to formulate and implement strategies that improve its efficiency or effectiveness
Is the resource rare?
Common strategies based on similar resources give no one firm an advantage
Competitive advantages are gained only from uncommon resources
3-
Слайд 10Firm Resources and Sustainable Competitive Advantages
Can the resource be imitated easily?
Physical
Path dependency (first mover advantage)
Causal ambiguity
Social complexity (org. relationships & culture)
Are substitutes readily available?
Similar resource(s)
Strategic substitutes
3-
Слайд 13Resources of Manchester United
Manchester United is one of the world's most
Fresh off its worst season in more than two decades, Manchester United is in talks with Nike and some of the biggest names in sports apparel for a contract that could top $600 million.
Profit tripled last year, revenues up by 26%.
What are some of Man. U’s critical resources?
Слайд 14Questions
According to text, how well did Manchester United play in 2013-14?
Based on the article, what is the most precious resource of Manchester United? How is Manchester United trying to leverage this resource? How does Manchester United try to add value to this resource, besides -- or instead of -- just winning some soccer games?
How many of you are fans of Manchester United? Why does this team have a special brand? What does it take for a sports team to build up a global brand outside the local community?
3-
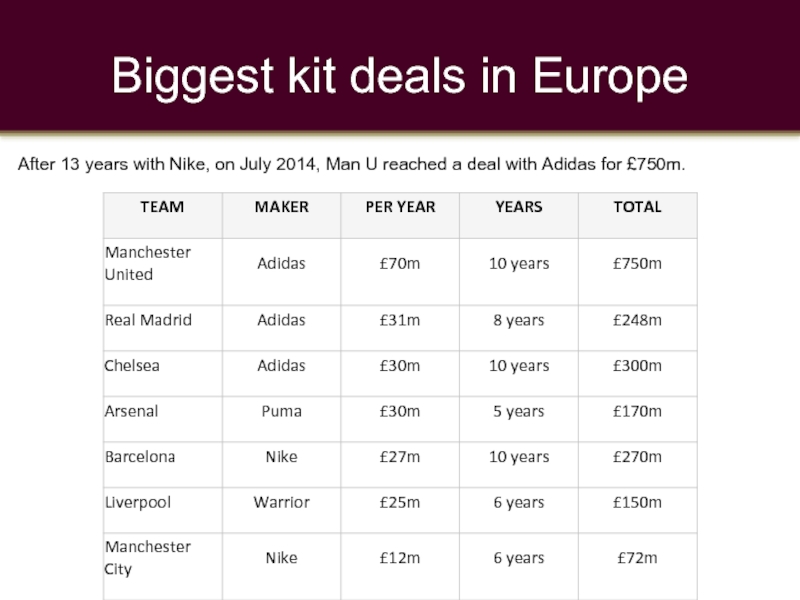
Слайд 15Biggest kit deals in Europe
After 13 years with Nike, on July
Слайд 16Value-Chain Analysis
Value-chain analysis
a strategic analysis of an organization that uses
View the organization as a sequential process of value-creating activities
Value is the amount that buyers are willing to pay for what a firm provides them
A firm is profitable when the value of its products or services exceeds the total costs involved in creating them
Creating value for buyers that exceeds the costs of production (i.e., margin) is a key driver of a firm’s competitive position.
3-
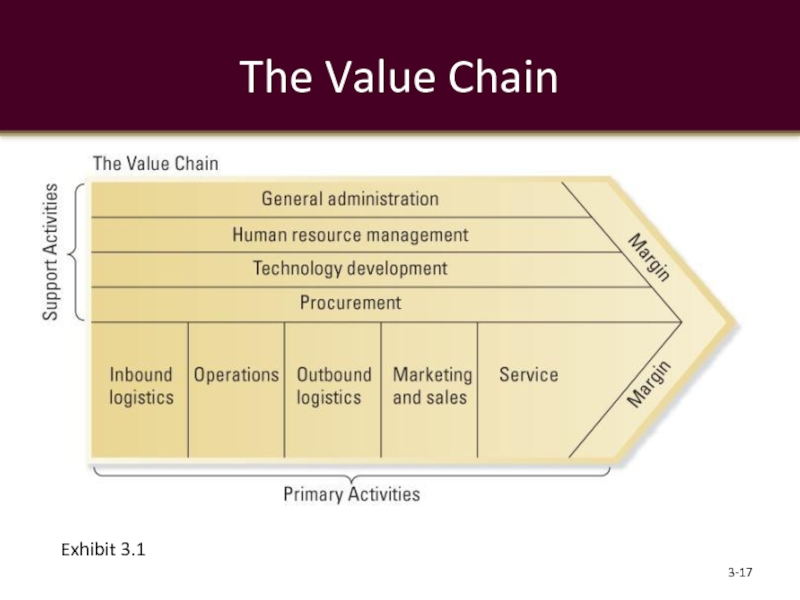
Слайд 18Value-Chain Analysis
Primary activities
contribute to the physical creation of the product
inbound logistics
operations
outbound logistics
marketing and sales
service
3-
Слайд 19Value-Chain Analysis
Support activities
activities of the value chain that either add value
procurement
technology development
human resource management
general administration
3-
Слайд 20QUESTION
In assessing its primary activities, an airline would examine:
A. Employee training programs
B. Baggage
3-
Слайд 21Primary Activity: Inbound Logistics
Associated with receiving, storing and distributing inputs to
Location of distribution facilities
Material and inventory control systems
Systems to reduce time to send “returns” to suppliers
Warehouse layout and designs
Toyota’s use of JIT system
Wal-mart’s Electronic Data Interchange system
3-
Слайд 22Primary Activity: Operations
Associated with transforming inputs into the final product form
Efficient
Incorporation of appropriate process technology
Quality production control systems
Efficient plant layout and workflow design
3-
Слайд 24Primary Activity: Outbound Logistics
Associated with collecting, storing, and distributing the product
Effective shipping processes to provide quick delivery and minimize damages
Shipping of goods in large lot sizes to minimize transportation costs.
Efficient finished goods warehousing processes
Ex: Cambell Soup’s e-network continuous replenishment program
3-
Слайд 25Primary Activity: Marketing and Sales
Associated with purchases of products and services
Innovative approaches to promotion and advertising
Proper identification of customer segments and needs
Selection of most appropriate distribution channels
Effective pricing strategies
Q: Internet advertising vs. traditional ads?
3-
Слайд 26Primary Activity: Service
Associated with providing service to enhance or maintain the
Quick response to customer needs and emergencies
Quality of service personnel and ongoing training
Warranty and
guarantee policies
3-
Слайд 27Support Activity: Procurement
Function of purchasing inputs used in the firm’s value
Procurement of raw material inputs
Development of collaborative “win-win” relationships with suppliers
Analysis and selection of alternate sources of inputs to minimize dependence on one supplier
3-
Слайд 28Support Activity:
Human Resource Management
Activities involved in the recruiting, hiring, training,
Effective recruiting, development, and retention mechanisms for employees
Quality relations with trade unions
Reward and incentive programs to motivate all employees
Q: Should employee performance metrics be eliminated? Why? Why not?
3-
Слайд 29Support Activity:
Technology Development
Related to a wide range of activities and
Effective R&D activities for process and product initiatives
Positive collaborative relationships between R&D and other departments
Excellent professional qualifications of personnel
3-
Слайд 30Support Activity:
General Administration
Typically supports the entire value chain and not
Ability of top management to anticipate and act on key environmental trends and events
Excellent relationships with diverse stakeholder groups
Effective use of information technology to integrate value-creating activities
3-
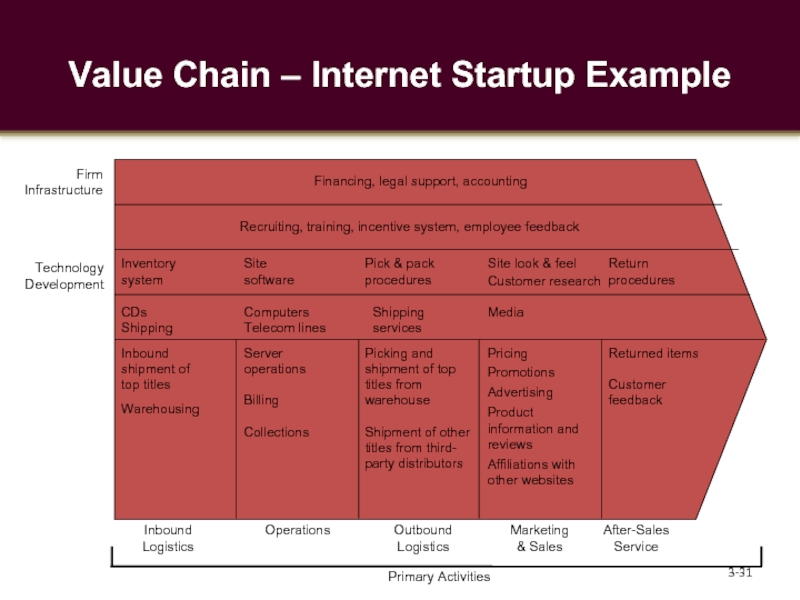
Слайд 31Value Chain – Internet Startup Example
3-
Inbound shipment of top titles
Warehousing
Server operations
Billing
Collections
Picking
Shipment of other titles from third- party distributors
Pricing
Promotions
Advertising
Product information and reviews
Affiliations with other websites
Returned items
Customer feedback
Financing, legal support, accounting
Recruiting, training, incentive system, employee feedback
Technology
Development
Firm
Infrastructure
Inbound
Logistics
Operations
Outbound
Logistics
Marketing
& Sales
After-Sales
Service
Primary Activities
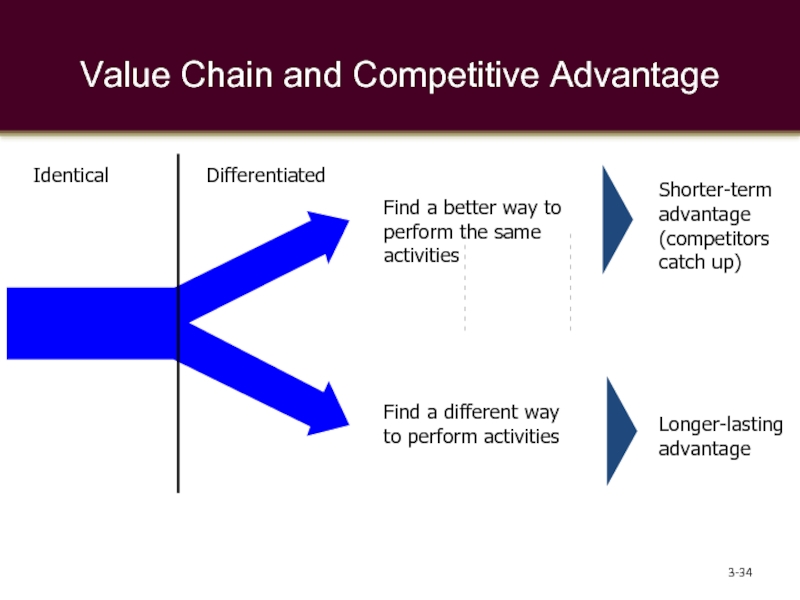
Слайд 34Value Chain and Competitive Advantage
3-
Identical
Differentiated
Find a different way to perform activities
Find a better way to perform the same activities
Shorter-term advantage (competitors catch up)
Longer-lasting advantage
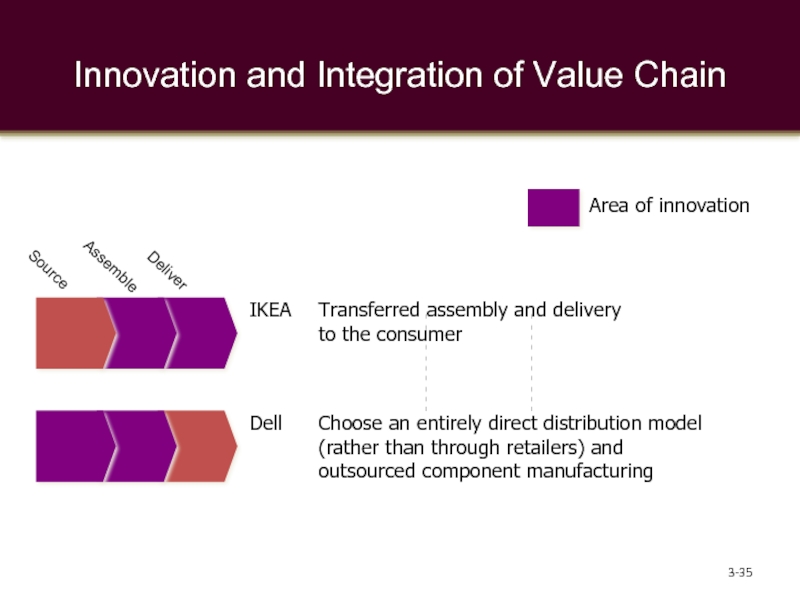
Слайд 35Innovation and Integration of Value Chain
3-
Transferred assembly and delivery to the
Choose an entirely direct distribution model (rather than through retailers) and outsourced component manufacturing
IKEA
Dell
Source
Assemble
Deliver
Area of innovation
Слайд 37Evaluating Firm Performance
Financial ratio analysis
Balance sheet
Income statement
Historical comparison
Comparison with industry norms
Comparison
Stakeholder perspective
Employees
Customers
Owners
3-
Слайд 38Financial Ratio Analysis
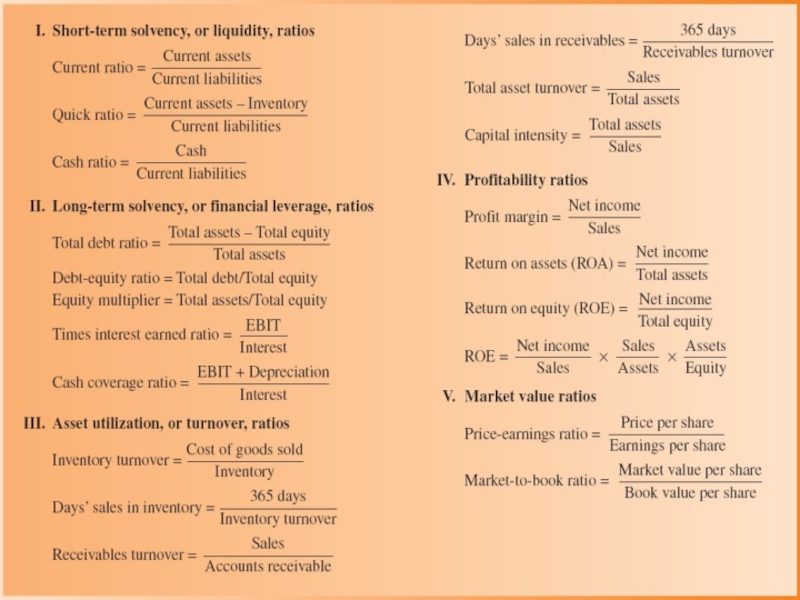
Five types of financial ratios
Short-term solvency or liquidity
Long-term solvency
Asset management (or turnover)
Profitability
Market value
Historical comparisons
Comparison with industry norms
Comparison with key competitors
3-