degenerative disease
Trauma
Congenital abnormalities of the spine
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
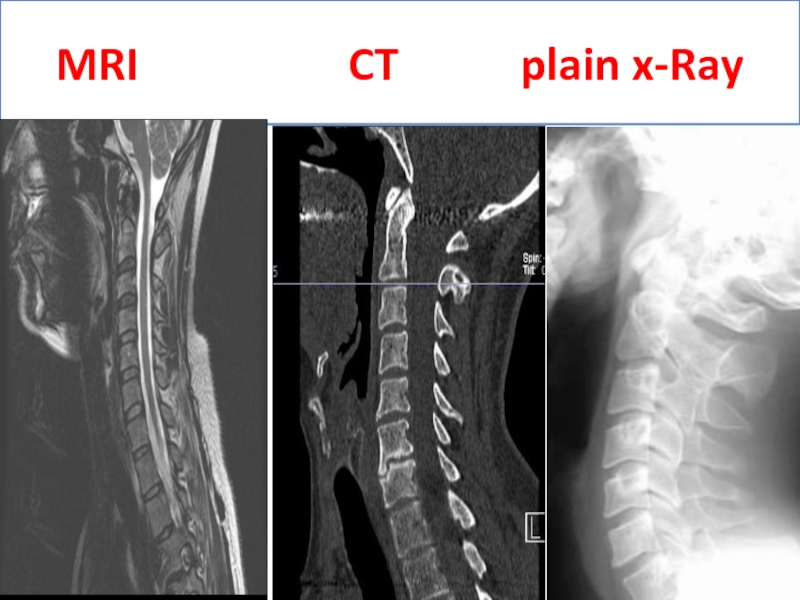
What are the indications for MRI & CT презентация
Содержание
- 1. What are the indications for MRI & CT
- 2. Preparations for CT & MRI: 1-Fasting for
- 3. Patient position: Is usually
- 4. Computed tomography (CT): . Usual scanning.
- 7. CT Myelography: Is considered as intrathecal contrast
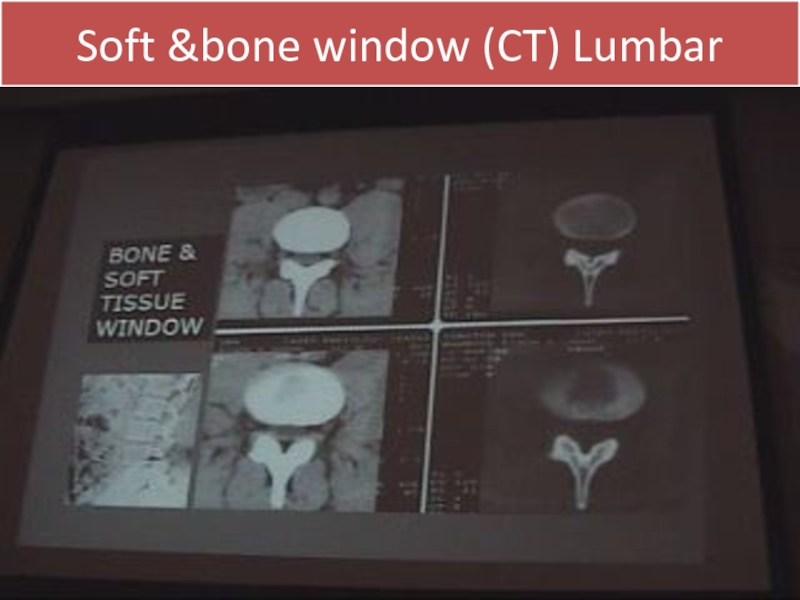
- 8. Soft &bone window (CT) Lumbar
- 10. 1. Lumbar spinal canal diameter: Spinal canal
- 11. Disc lesions: We detect it in soft
- 12. N.B: . Normally due to overload ,the
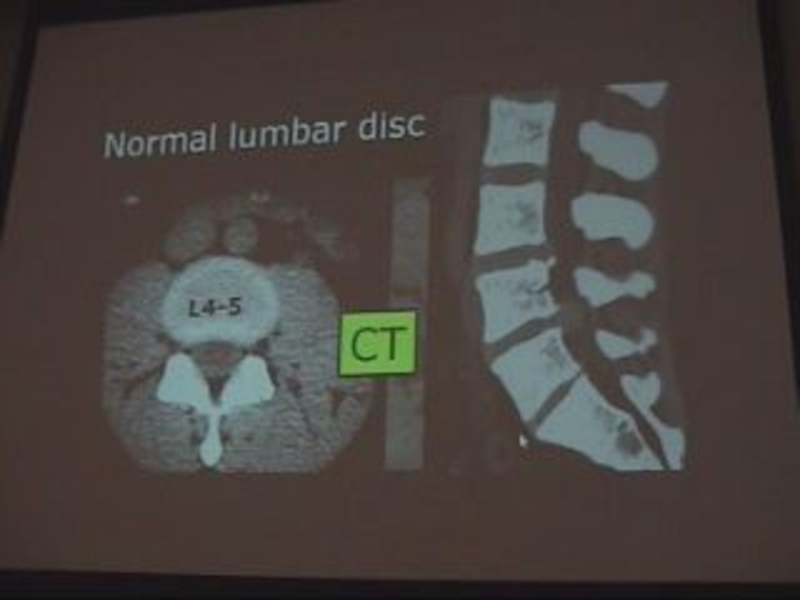
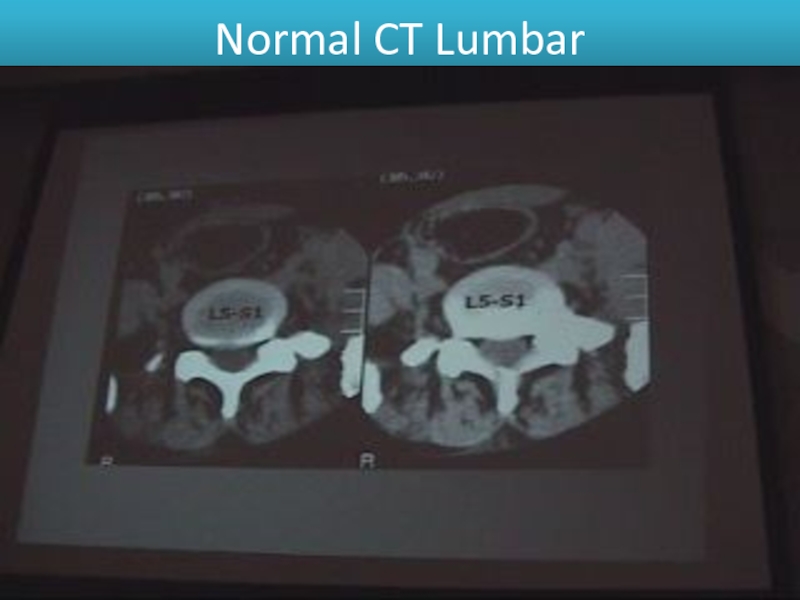
- 15. Normal CT Lumbar
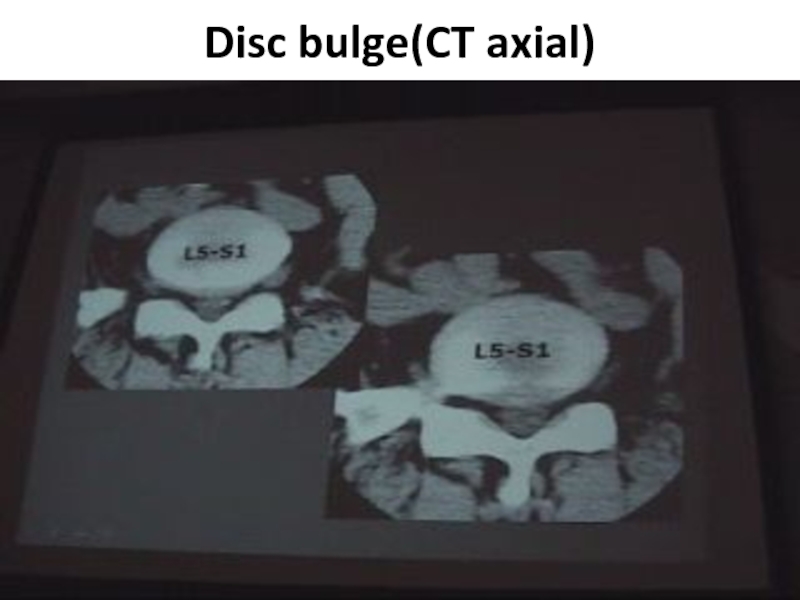
- 16. Disc bulge(CT axial)
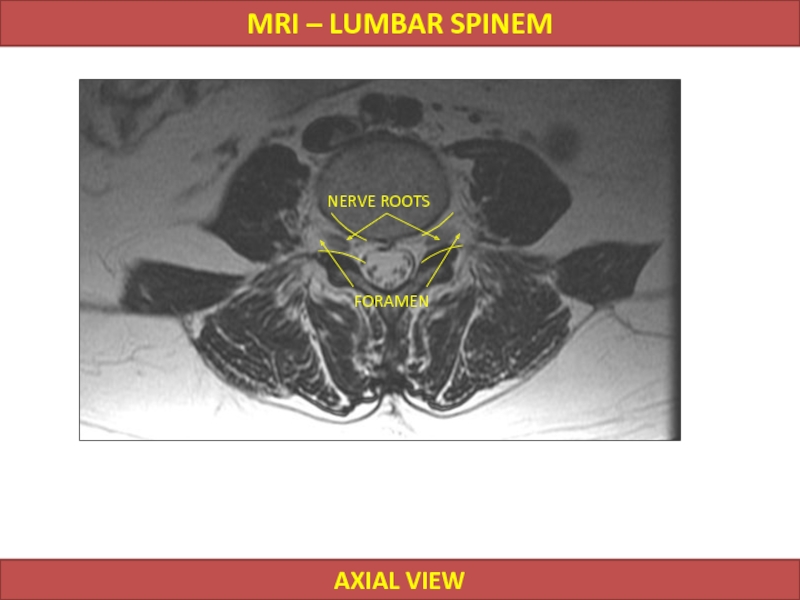
- 17. NERVE ROOTS MRI – LUMBAR SPINEM AXIAL VIEW FORAMEN
- 18. Manifestations of arthritis in any joint: (Spondylosis
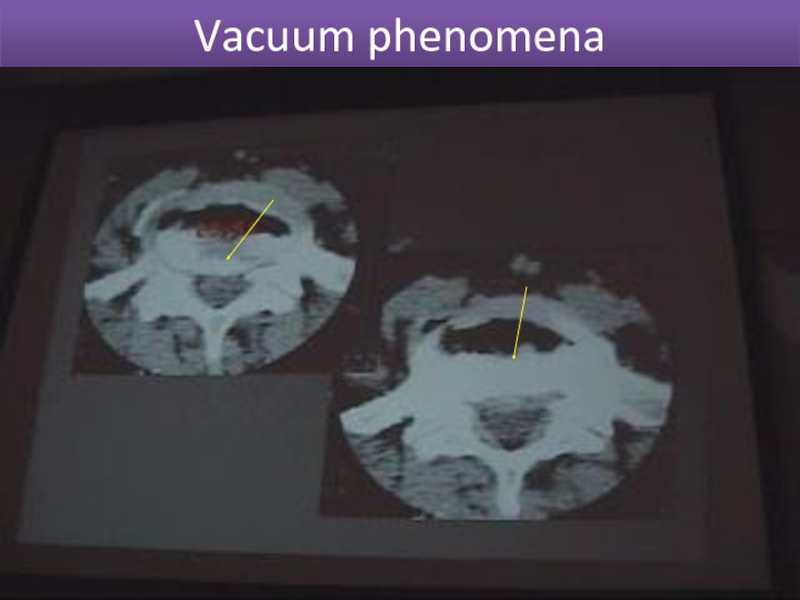
- 19. Vacuum phenomena
- 20. CT of cervical spine
- 21. We have 2 types of joints: Neurocentral
- 22. Cervical disc in CT: We see it
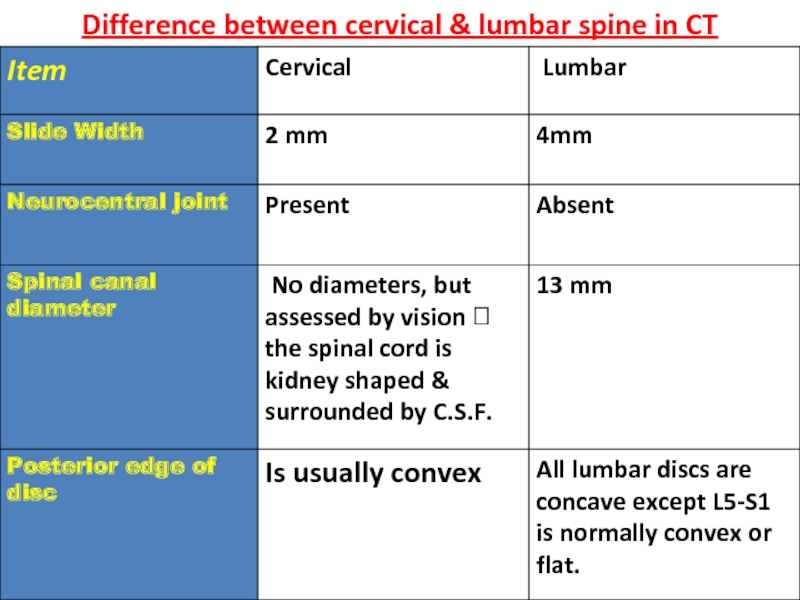
- 23. Difference between cervical & lumbar spine in CT
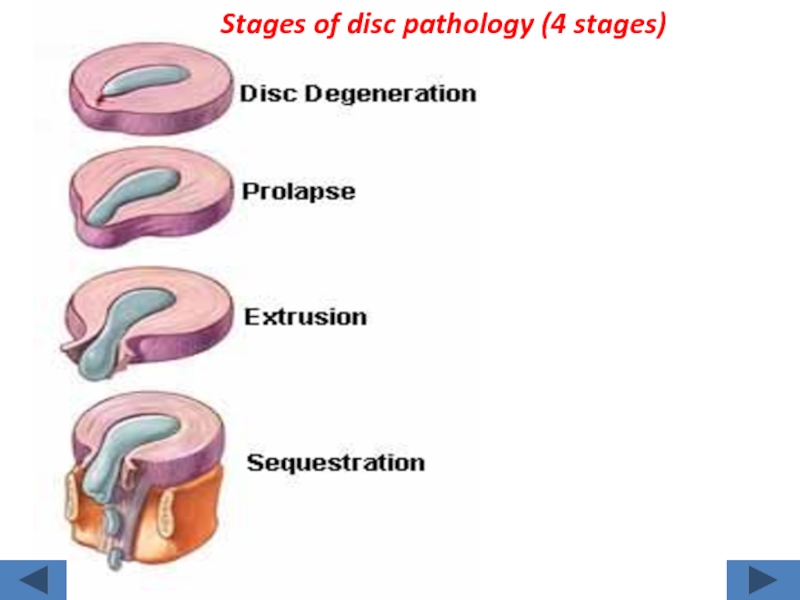
- 27. Stages of disc pathology (4 stages)
- 28. CT of the spine
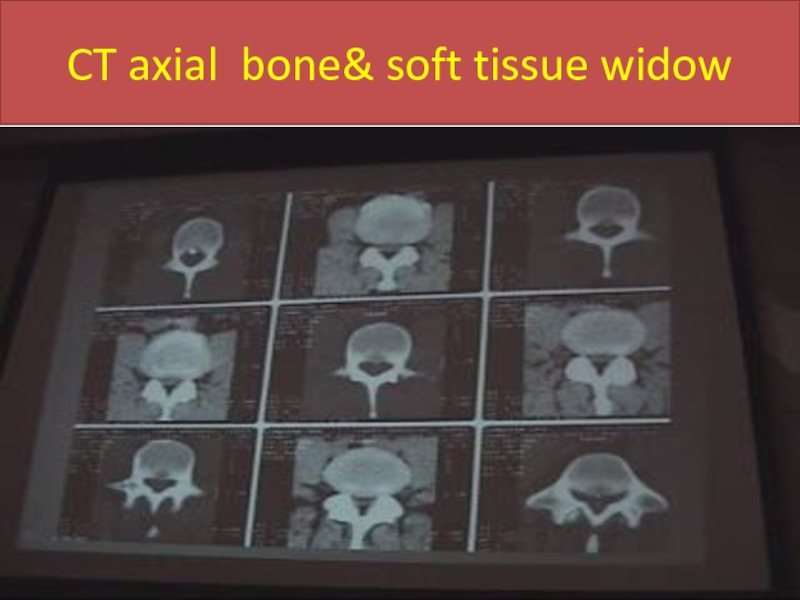
- 29. CT axial bone& soft tissue widow
- 31. CT machine
- 38. MRI
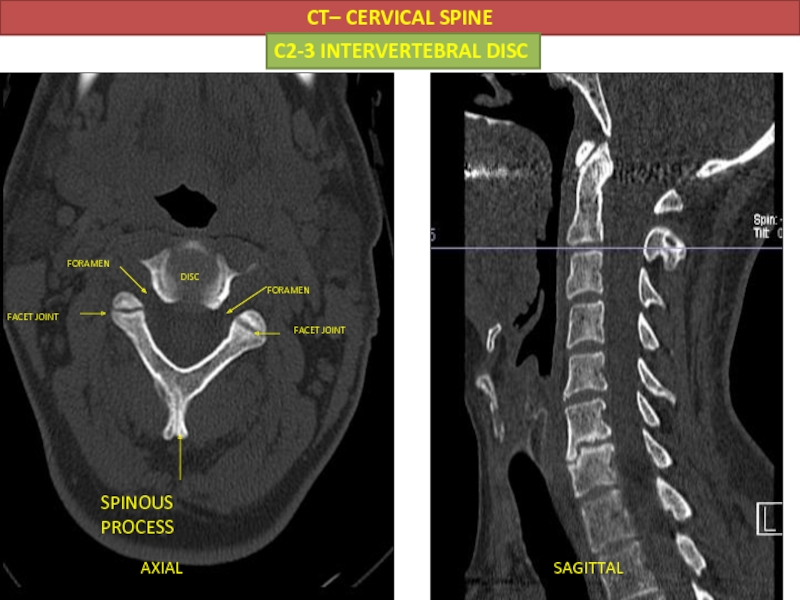
- 39. CT– CERVICAL SPINE AXIAL SAGITTAL C2-3 INTERVERTEBRAL
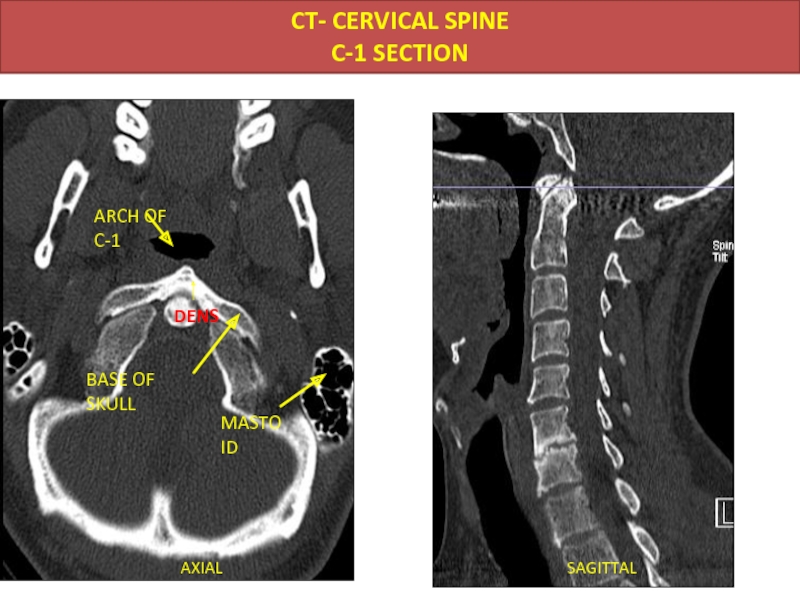
- 40. AXIAL SAGITTAL CT- CERVICAL SPINE C-1 SECTION
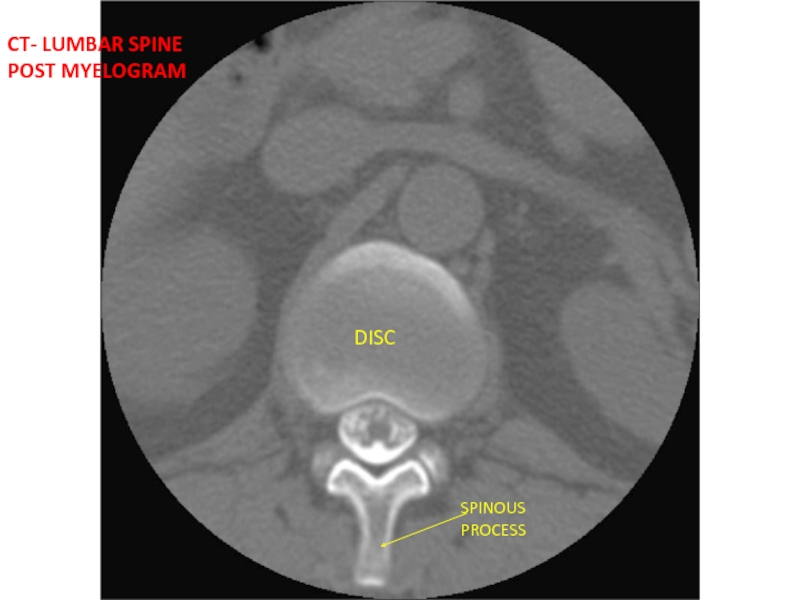
- 41. DISC SPINOUS PROCESS CT- LUMBAR SPINE POST MYELOGRAM
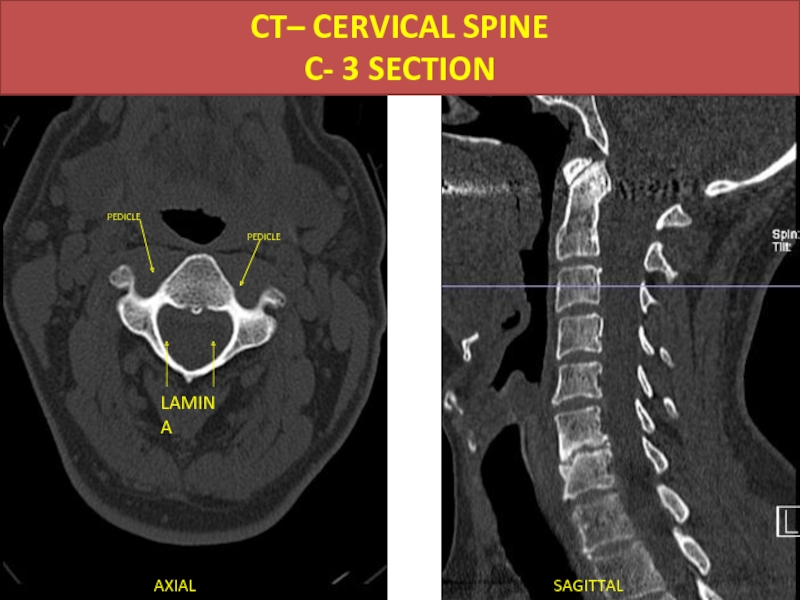
- 42. CT– CERVICAL SPINE C- 3 SECTION AXIAL SAGITTAL PEDICLE PEDICLE LAMINA
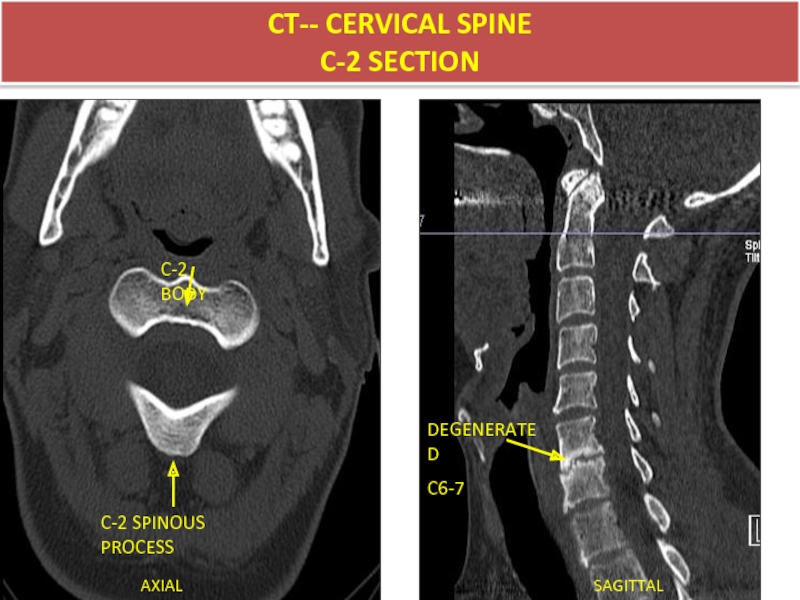
- 43. AXIAL SAGITTAL CT-- CERVICAL SPINE C-2 SECTION
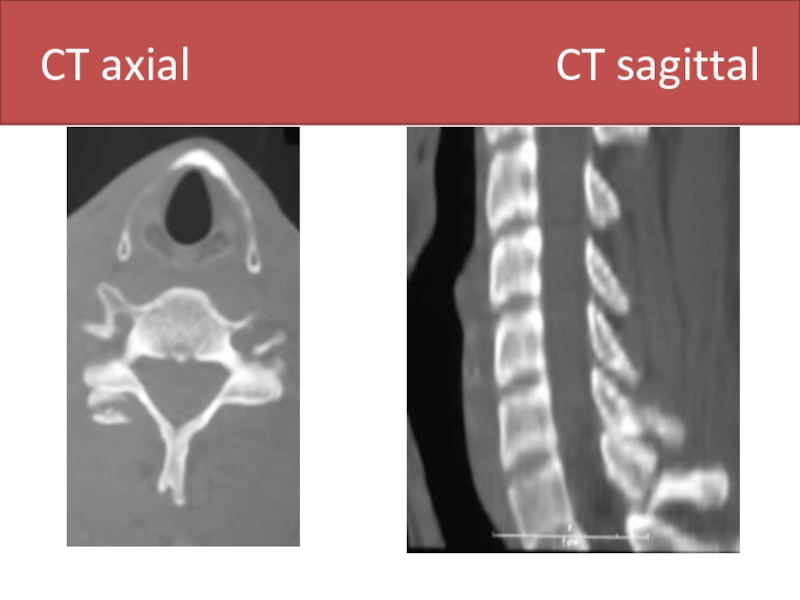
- 44. CT axial
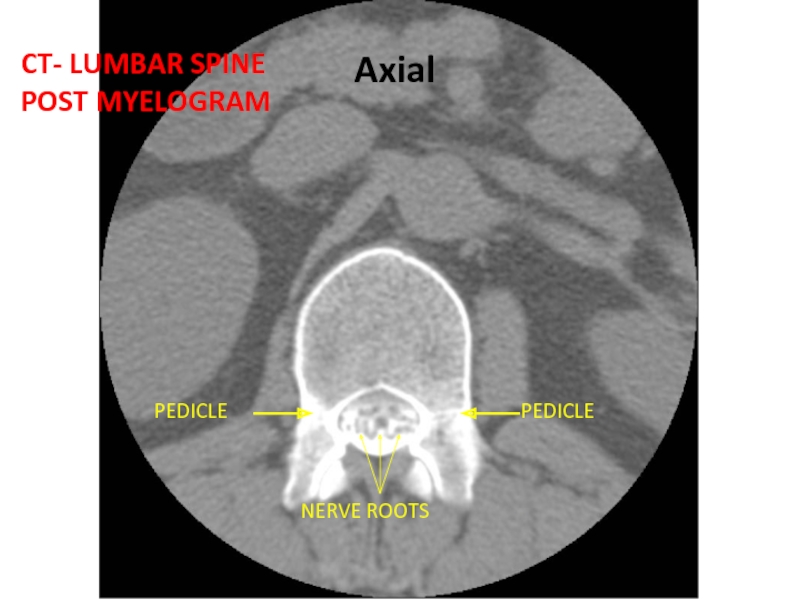
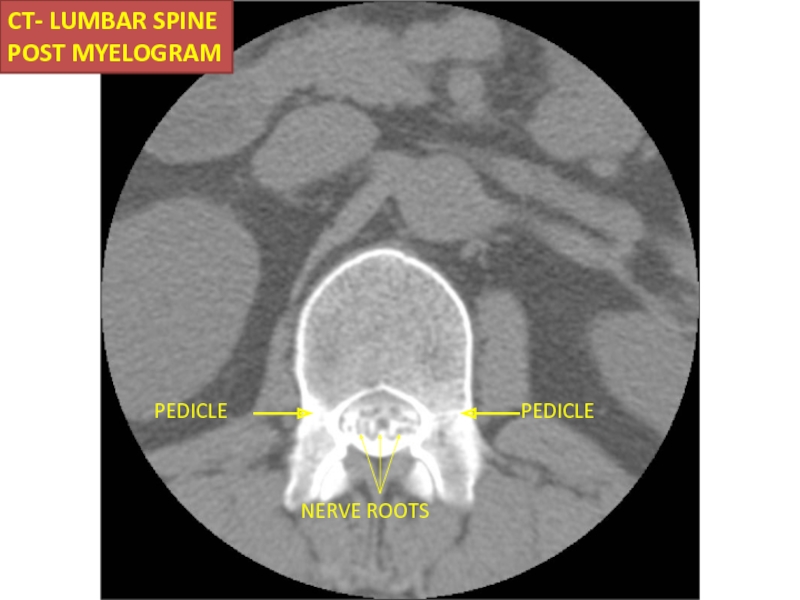
- 45. PEDICLE PEDICLE NERVE ROOTS CT- LUMBAR SPINE POST MYELOGRAM Axial
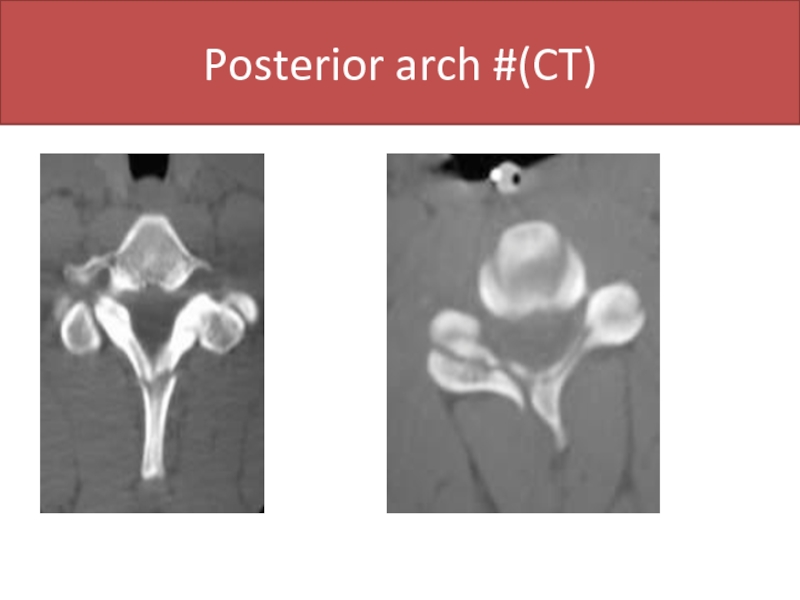
- 46. Posterior arch #(CT)
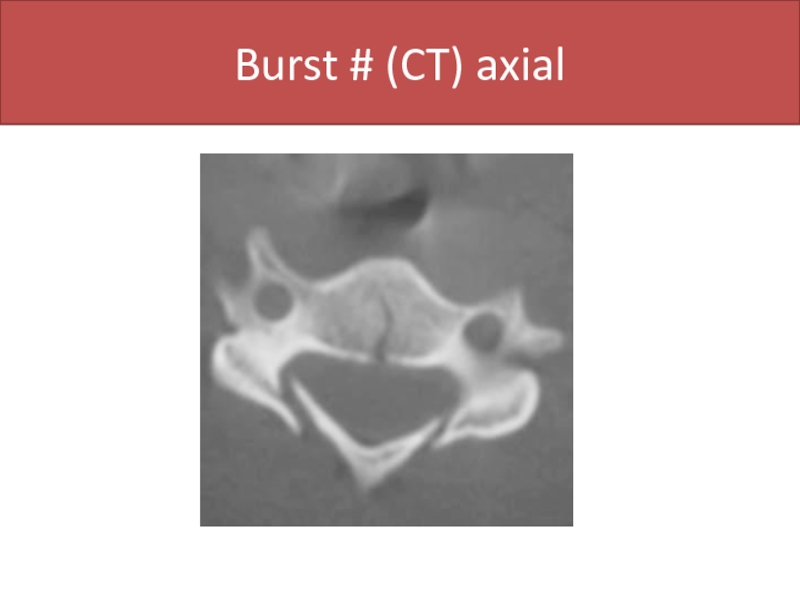
- 47. Burst # (CT) axial
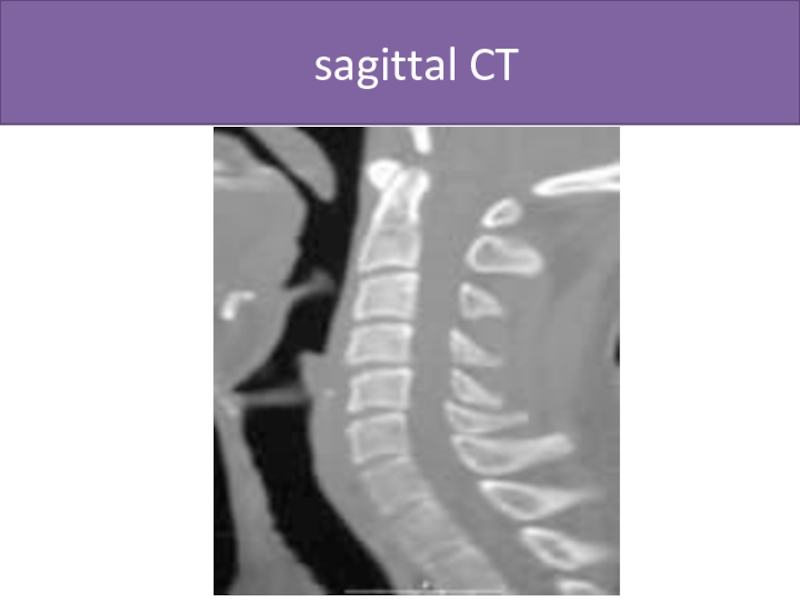
- 48. sagittal CT
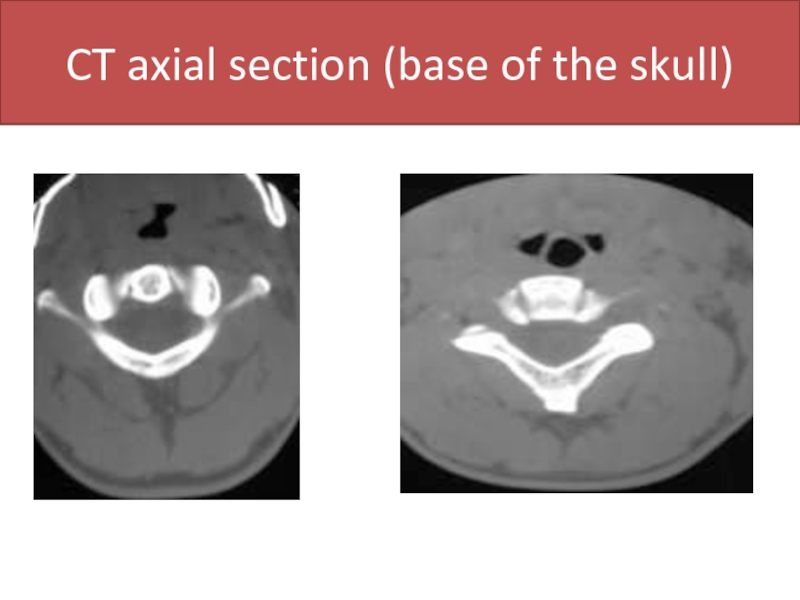
- 49. CT axial section (base of the skull)
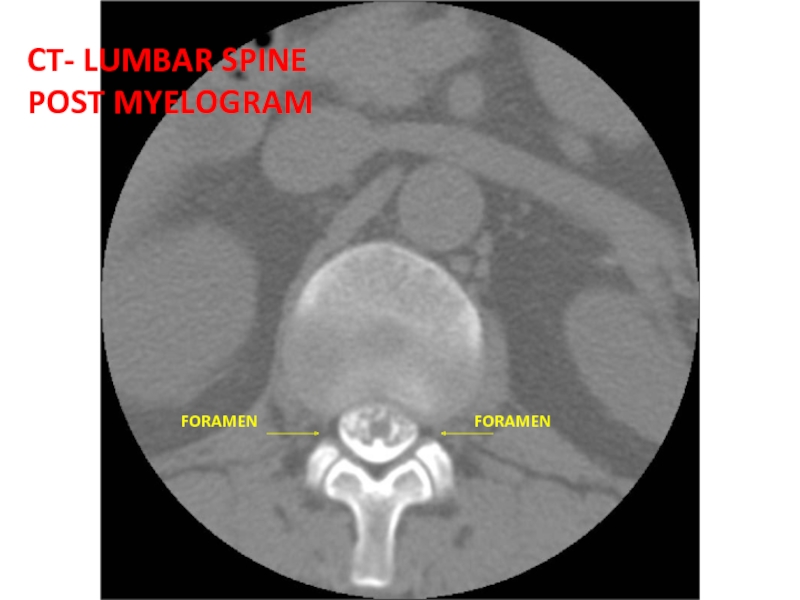
- 50. FORAMEN CT- LUMBAR SPINE POST MYELOGRAM FORAMEN
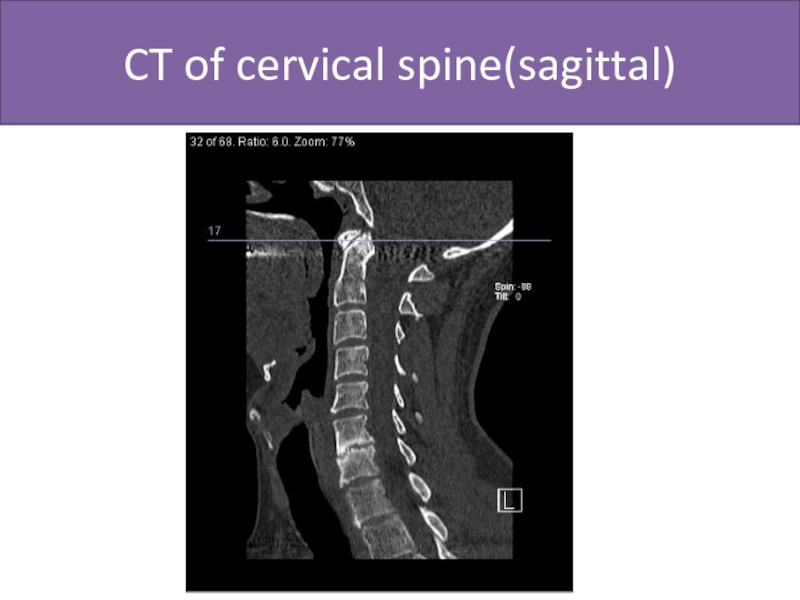
- 51. CT of cervical spine(sagittal)
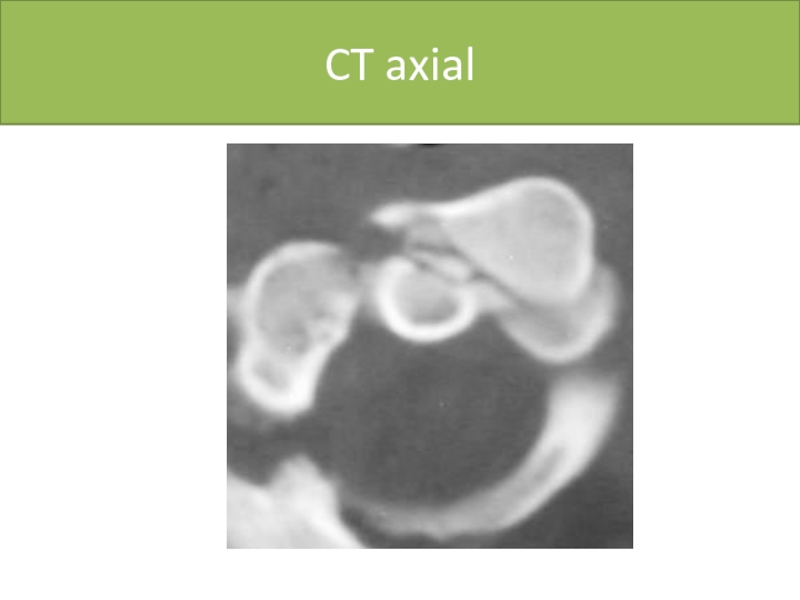
- 52. CT axial
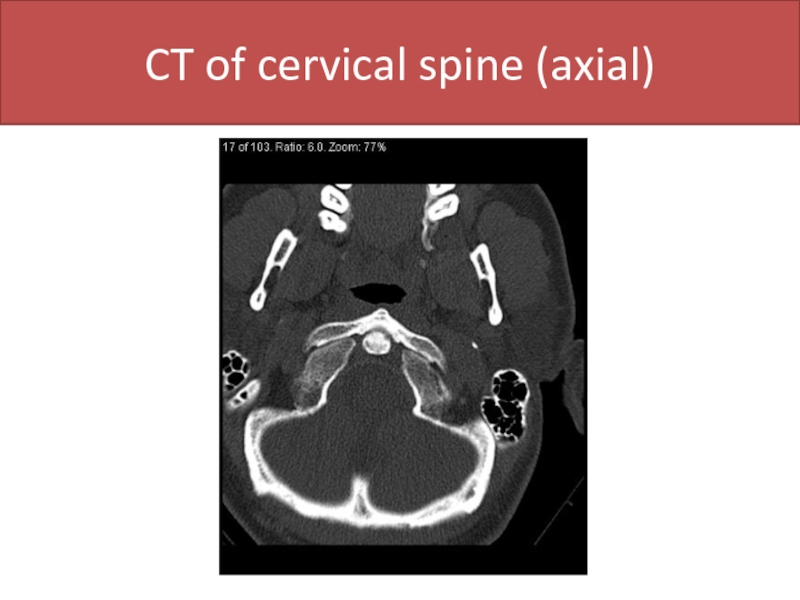
- 53. CT of cervical spine (axial)
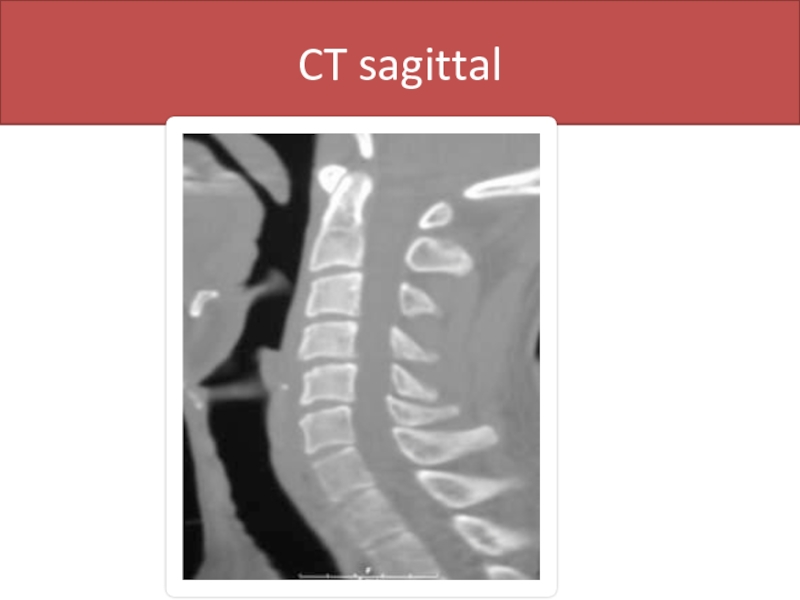
- 54. CT sagittal
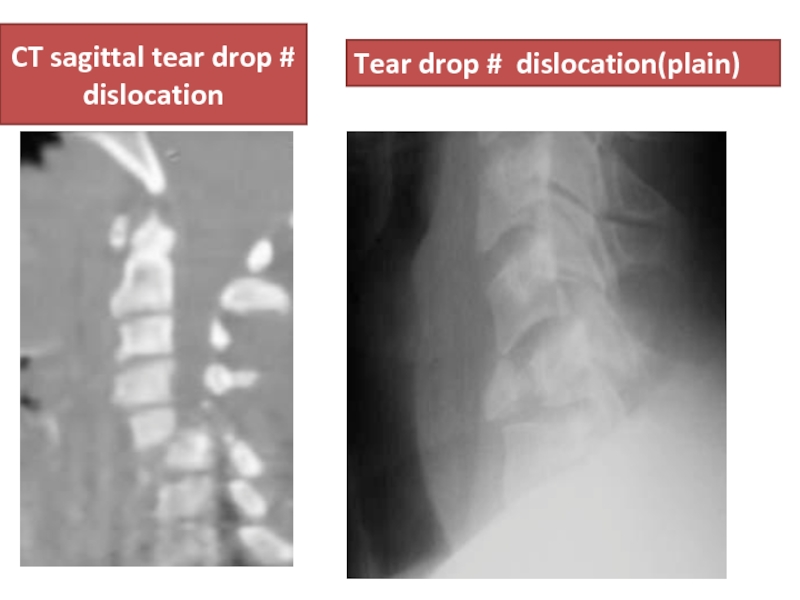
- 55. CT sagittal tear drop # dislocation Tear drop # dislocation(plain)
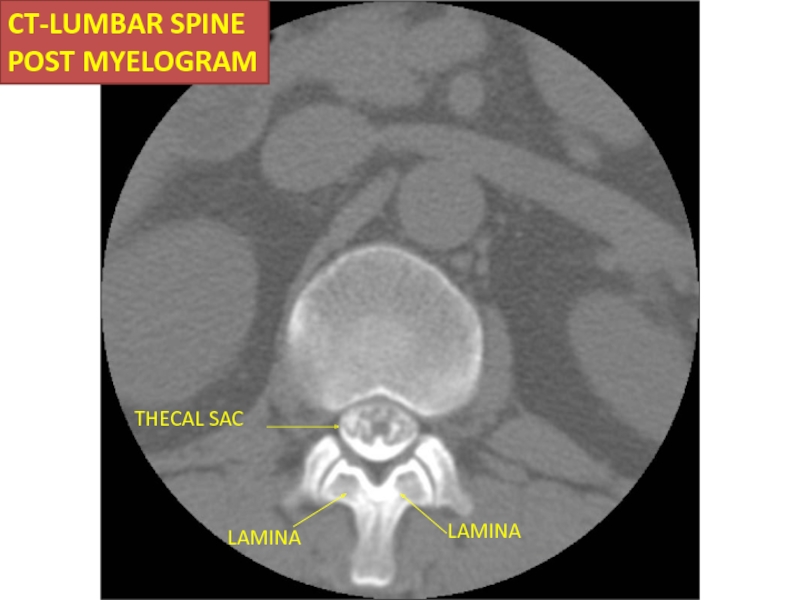
- 56. THECAL SAC LAMINA LAMINA CT-LUMBAR SPINE POST MYELOGRAM
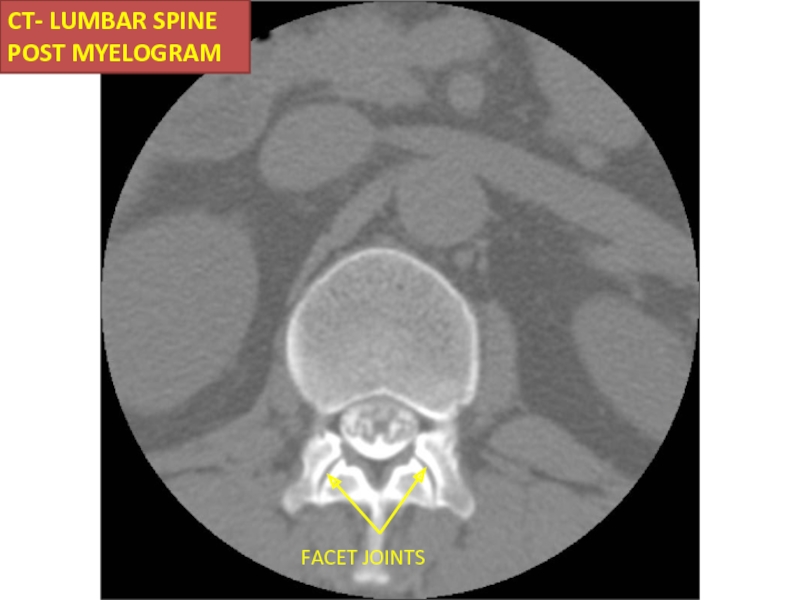
- 57. FACET JOINTS CT- LUMBAR SPINE POST MYELOGRAM
- 58. PEDICLE PEDICLE NERVE ROOTS CT- LUMBAR SPINE POST MYELOGRAM
Слайд 1
What are the indications for MRI & CT:
Disc lesions
Post-operative spine(after surgery)
Tumors
Any
Слайд 2Preparations for CT & MRI: 1-Fasting for 4-6 hours 2-Contrast material Urographin ,telebrix
1-2 mg/kg
Administration of contrast:
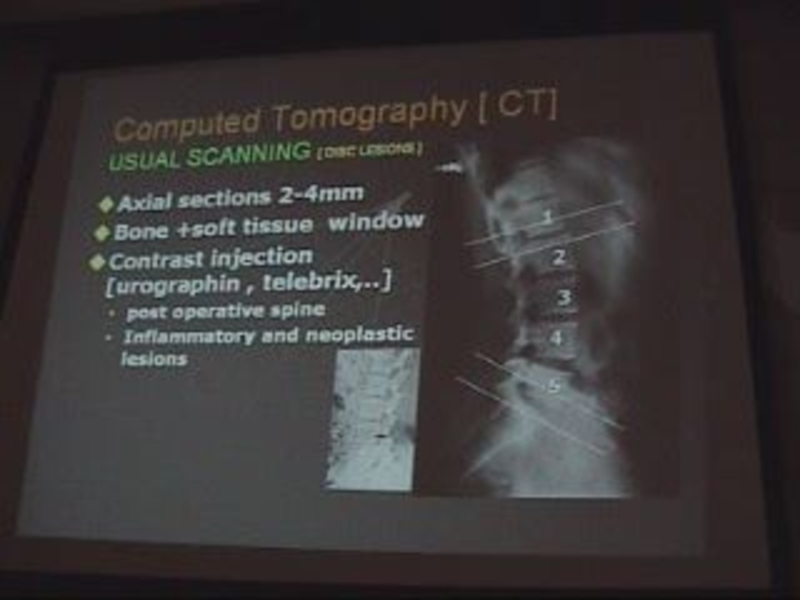
Yes: In post-operative lumbar spine, inflammatory disorders& neoplastic lesions.
No: disc lesions, trauma.
Anesthesia
Used with children & uncooperative patients.
Administration of contrast:
Yes: In post-operative lumbar spine, inflammatory disorders& neoplastic lesions.
No: disc lesions, trauma.
Anesthesia
Used with children & uncooperative patients.
Слайд 3Patient position:
Is usually supine, sometimes side lying, &
rarely prone.
How to see:
Scanogram: primitive picture to detect the site of lumbar spine
How to see:
Scanogram: primitive picture to detect the site of lumbar spine
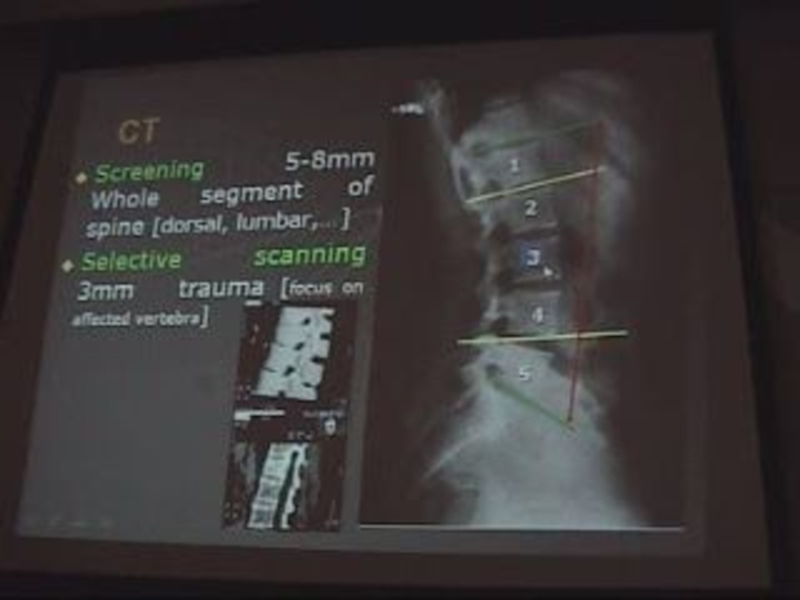
Слайд 4Computed tomography (CT):
. Usual scanning.
. Axial slides 2-4 mm.
2
mm in cervical spine / 4 mm in lumbar spine
Has bone & soft tissue window.
CT screening:
. Whole segment of the spine
5 mm in cervical spine, 8 mm in lumbar spine.
. Selective Scanning
Every 3 mm especially in trauma, also in cervical disc lesions.
N.B:
If I want to see one vertebra e.g. L3 I have to take 1 vertebra above (L2 )& 1 below (L4).
Has bone & soft tissue window.
CT screening:
. Whole segment of the spine
5 mm in cervical spine, 8 mm in lumbar spine.
. Selective Scanning
Every 3 mm especially in trauma, also in cervical disc lesions.
N.B:
If I want to see one vertebra e.g. L3 I have to take 1 vertebra above (L2 )& 1 below (L4).
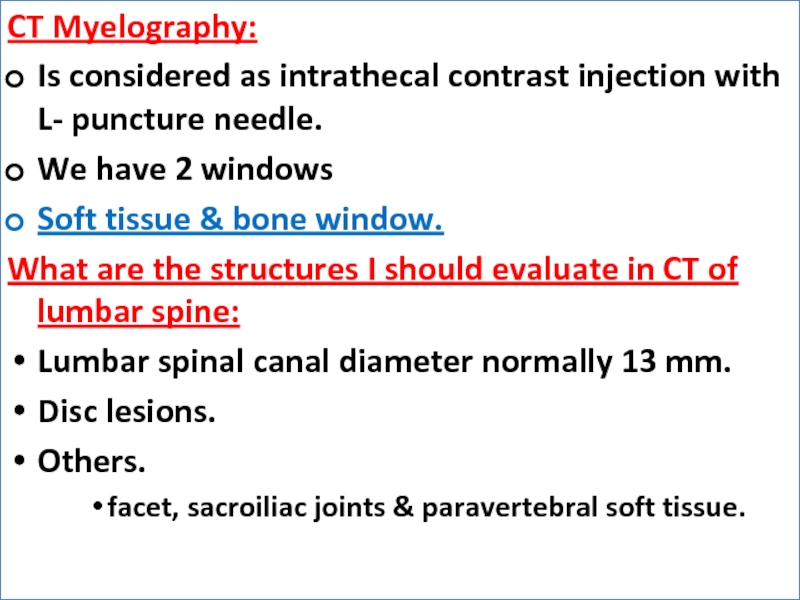
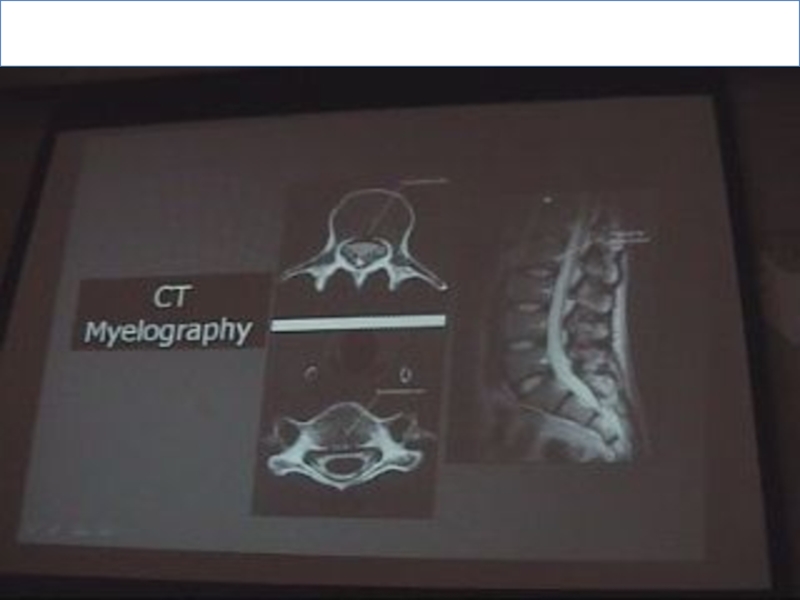
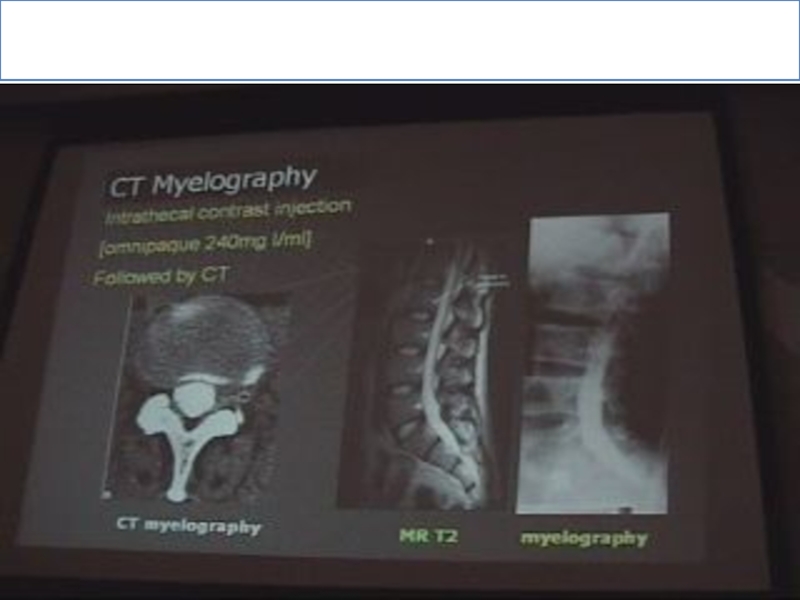
Слайд 7CT Myelography:
Is considered as intrathecal contrast injection with L- puncture needle.
We
have 2 windows
Soft tissue & bone window.
What are the structures I should evaluate in CT of lumbar spine:
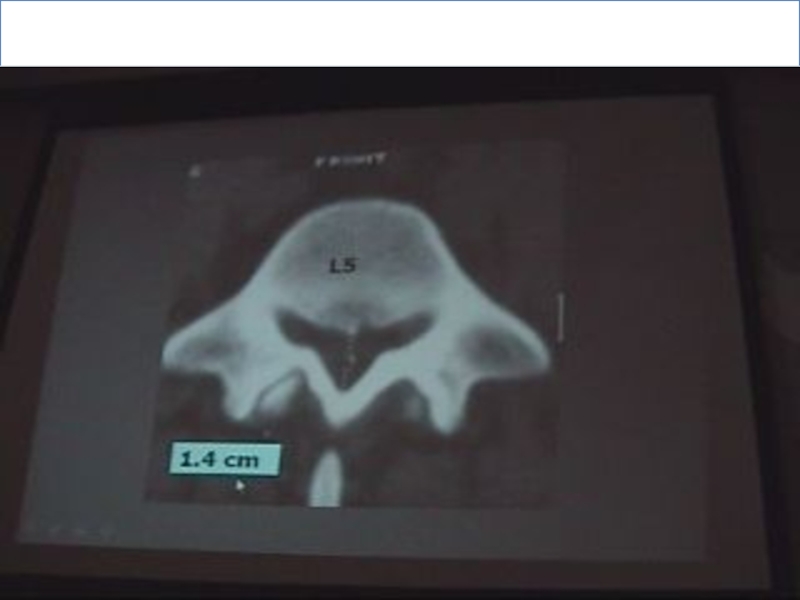
Lumbar spinal canal diameter normally 13 mm.
Disc lesions.
Others.
facet, sacroiliac joints & paravertebral soft tissue.
Soft tissue & bone window.
What are the structures I should evaluate in CT of lumbar spine:
Lumbar spinal canal diameter normally 13 mm.
Disc lesions.
Others.
facet, sacroiliac joints & paravertebral soft tissue.
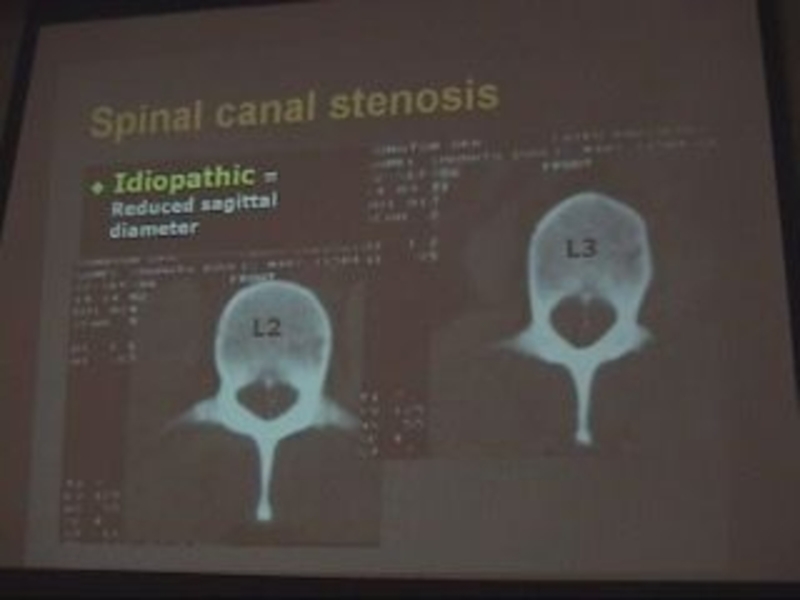
Слайд 101. Lumbar spinal canal diameter:
Spinal canal is bony structure, so we
see it in bone window.
The spinal canal must be closed (at the level of pedicles).
We measure the AP diameter.
Types of canal stenosis:
1-Relative:
11-12 mm & this doesn’t need operation but it needs operation if there’s disc.
2- Absolute:
8 -10 mm & it must be operated.
The spinal canal must be closed (at the level of pedicles).
We measure the AP diameter.
Types of canal stenosis:
1-Relative:
11-12 mm & this doesn’t need operation but it needs operation if there’s disc.
2- Absolute:
8 -10 mm & it must be operated.
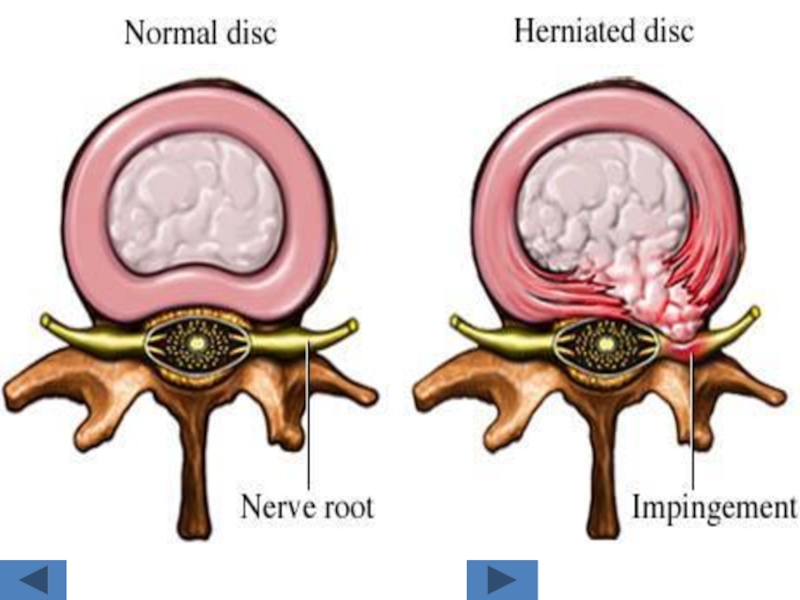
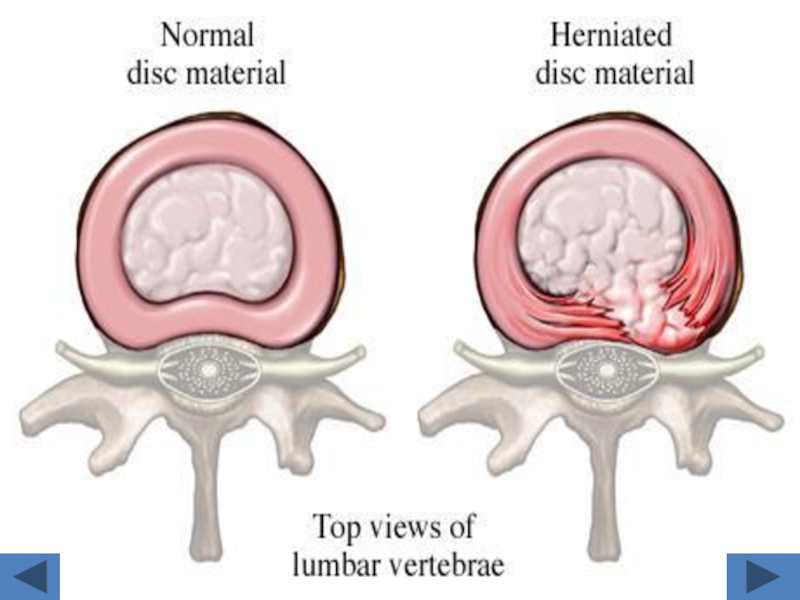
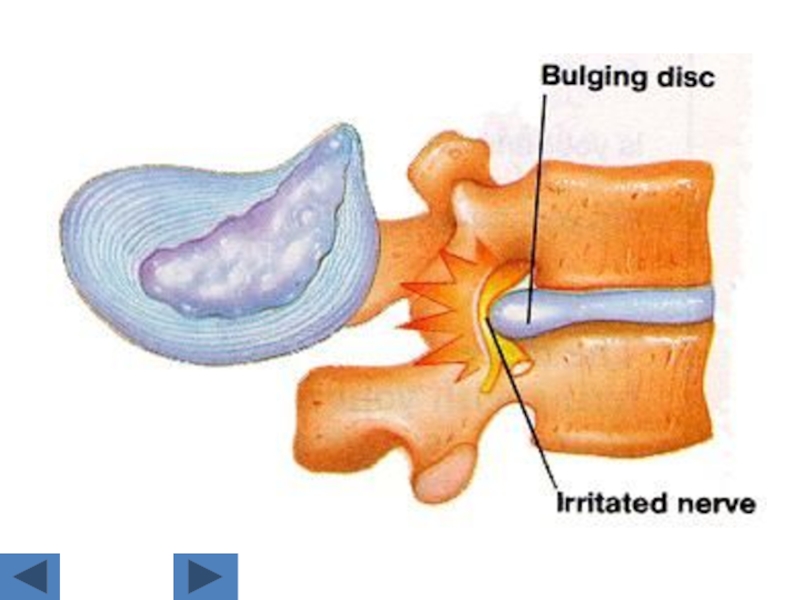
Слайд 11Disc lesions:
We detect it in soft tissue window.
Posterior border of the
disc is more important as it has relation to the disc.
The normal posterior border of the disc is CONCAVE.
The abnormal is STRAIGHT OR CONVEX.
The normal posterior border of the disc is CONCAVE.
The abnormal is STRAIGHT OR CONVEX.
Слайд 12N.B:
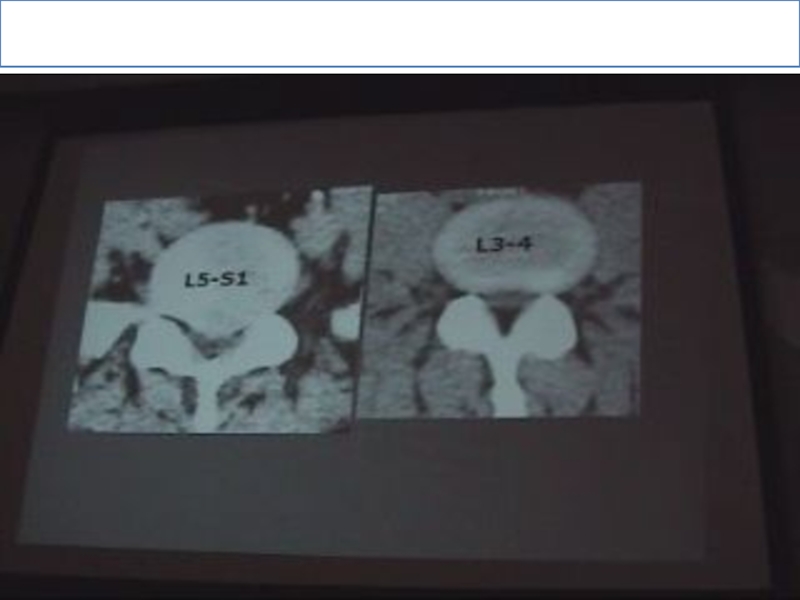
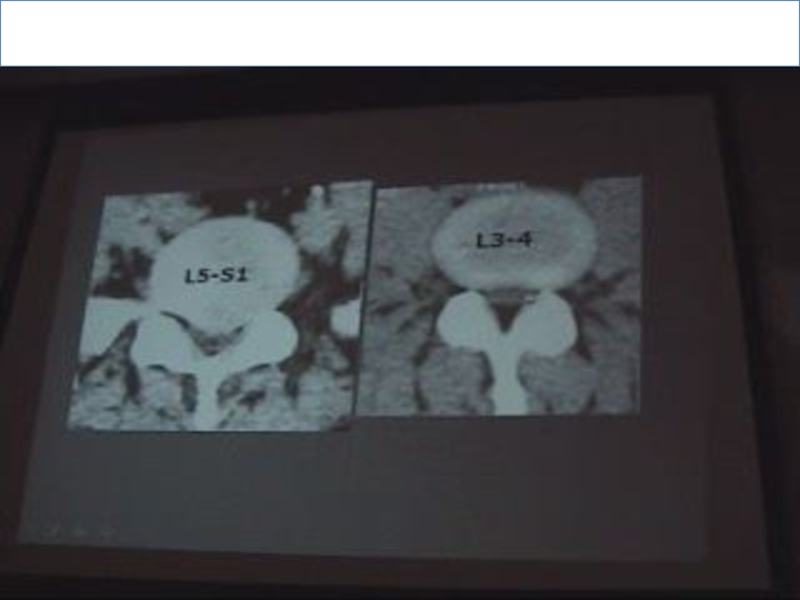
. Normally due to overload ,the disc of L5-S1 is CONVEX
& the abnormal is also convex, so to judge if it’s normal or no? look at the next slide if: the posterior border of the disc is convex so it is ABNORMAL.
. The angle of inclination in L5-S1 is more than 30 & the device accept up till 30 only so part of the slide will contain bone & part will contain disc.
. The angle of inclination in L5-S1 is more than 30 & the device accept up till 30 only so part of the slide will contain bone & part will contain disc.
Слайд 18Manifestations of arthritis in any joint:
(Spondylosis in spine and osteoarthritis of
other joints)
Osteophytic lipping.
Narrow joint space.
Subarticular bone sclerosis
Sub cortical pseudo cystic changes.
Intra articular air.(vaccum phenomena)
Osteophytic lipping.
Narrow joint space.
Subarticular bone sclerosis
Sub cortical pseudo cystic changes.
Intra articular air.(vaccum phenomena)
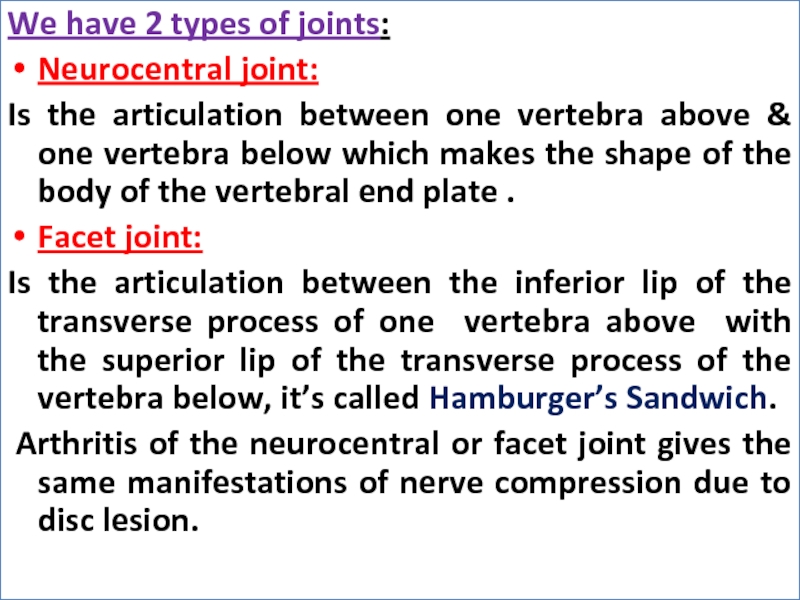
Слайд 21We have 2 types of joints:
Neurocentral joint:
Is the articulation between one
vertebra above & one vertebra below which makes the shape of the body of the vertebral end plate .
Facet joint:
Is the articulation between the inferior lip of the transverse process of one vertebra above with the superior lip of the transverse process of the vertebra below, it’s called Hamburger’s Sandwich.
Arthritis of the neurocentral or facet joint gives the same manifestations of nerve compression due to disc lesion.
Facet joint:
Is the articulation between the inferior lip of the transverse process of one vertebra above with the superior lip of the transverse process of the vertebra below, it’s called Hamburger’s Sandwich.
Arthritis of the neurocentral or facet joint gives the same manifestations of nerve compression due to disc lesion.
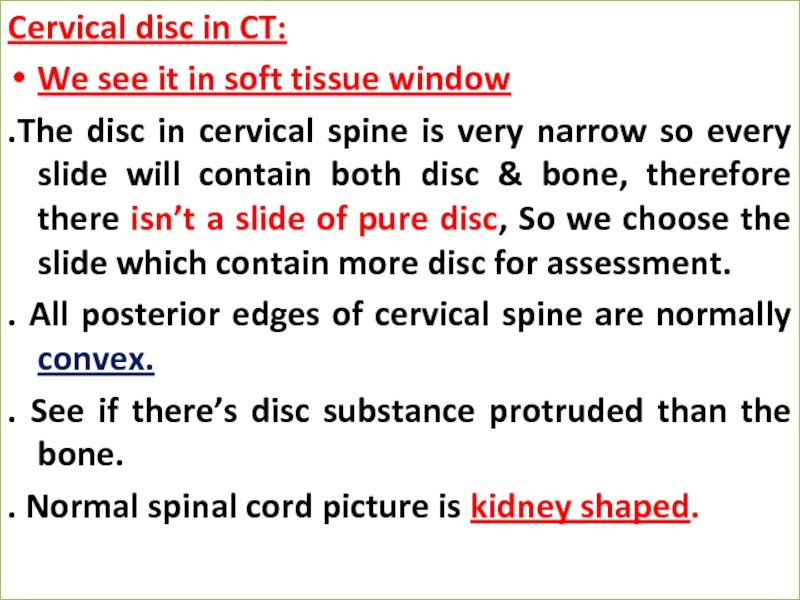
Слайд 22Cervical disc in CT:
We see it in soft tissue window
.The
disc in cervical spine is very narrow so every slide will contain both disc & bone, therefore there isn’t a slide of pure disc, So we choose the slide which contain more disc for assessment.
. All posterior edges of cervical spine are normally convex.
. See if there’s disc substance protruded than the bone.
. Normal spinal cord picture is kidney shaped.
. All posterior edges of cervical spine are normally convex.
. See if there’s disc substance protruded than the bone.
. Normal spinal cord picture is kidney shaped.