- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease)
- 2. What is Leprosy? It is a disease
- 3. Introduction Leprosy is a chronic infectious
- 4. Introduction Multidrug therapy (MDT) treatment has
- 6. Gerhard Armauer Hansen Global Project on the
- 7. Leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprae
- 8. Cultivation Not possible Can be propagated in
- 9. Important Experimental Animal
- 10. Most Important experimental Animal
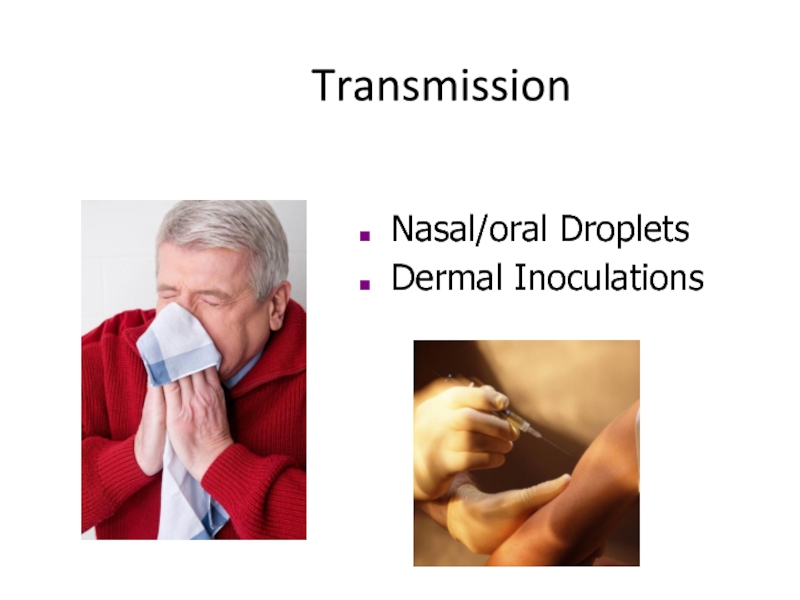
- 11. Transmission Nasal/oral Droplets Dermal Inoculations
- 12. Classification (Madrid)
- 13. Symptoms
- 14. Types of Leprosy Depending on clinical features,
- 15. WHO classification Two Groups: 1 Paucibacillary
- 16. WHO classification 2 Multibacillary M. leprae can
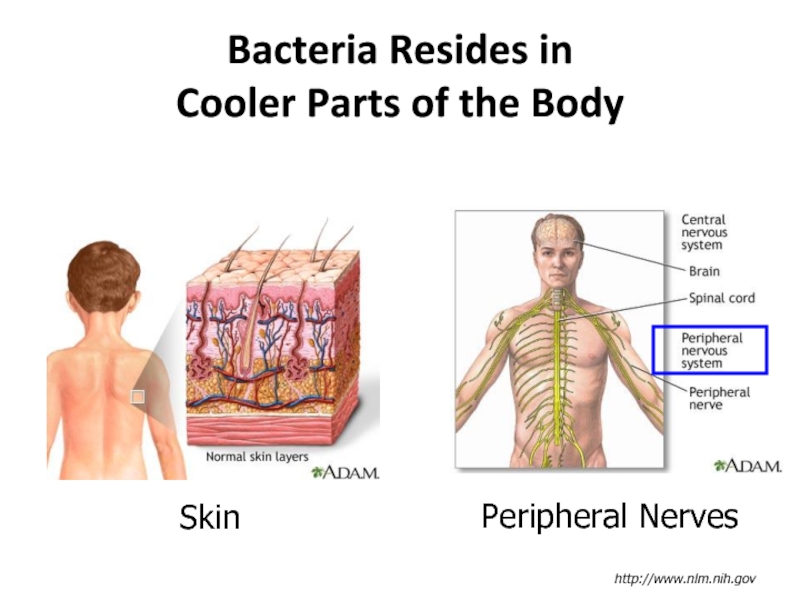
- 17. Bacteria Resides in Cooler Parts of the Body http://www.nlm.nih.gov Skin Peripheral Nerves
- 18. Symptoms & Diagnosis: (1) Skin Lesions
- 19. Immunocompromised individuals are more susceptible to disease
- 20. Mechanism of Nerve Damage Scollard, DM et
- 21. Sensory Loss Paralysis Deformities Outcomes of Nerve Damage Leprosy: eMedicine Infectious Diseases http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/220455-overview
- 22. Sensory Loss Can Lead to Secondary Infections
- 25. 1941: Discovery of Dapsone Targets dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS) Inhibits nucleic acid synthesis
- 26. 1964: Dapsone Resistance from Missense Mutations in
- 27. 1960’s: Rifampicin and Clofazimine Discovered Rifampicin (Rifampin):
- 28. 1981: WHO Proposes Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT) Combination of DAPSONE, RIFAMPICIN, and CLOFAZIMINE + +
- 29. The Nippon Foundation http://www.nippon-foundation.or.jp/eng/
- 30. 1995: WHO Distributes MDT Drugs for Free to Worldwide Patients
- 31. 1999: Global Alliance to Eliminate Leprosy As a Public Health Problem
- 32. Obstacles to Eliminating Leprosy in Endemic Countries
- 33. Overcoming Stigma Mass Media
- 34. Worobec, Sophie M. 2009. “Treatment of leprosy/Hansen's
- 35. In 2016 WHO has launched a new
Слайд 2What is Leprosy?
It is a disease of Historical importamce
Worlds oldest recorded
Stigmatized disease
Слайд 3Introduction
Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae, an
The disease mainly affects the skin, the peripheral nerves, mucosa of the upper respiratory tract and the eyes.
Leprosy is curable and treatment provided in the early stages averts disability.
Слайд 4Introduction
Multidrug therapy (MDT) treatment has been made available by WHO
It provides a simple yet highly effective cure for all types of leprosy.
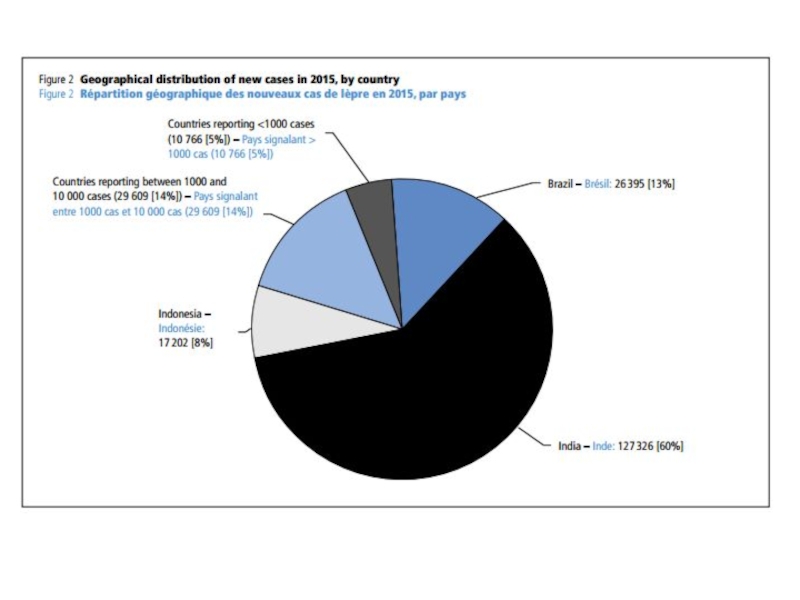
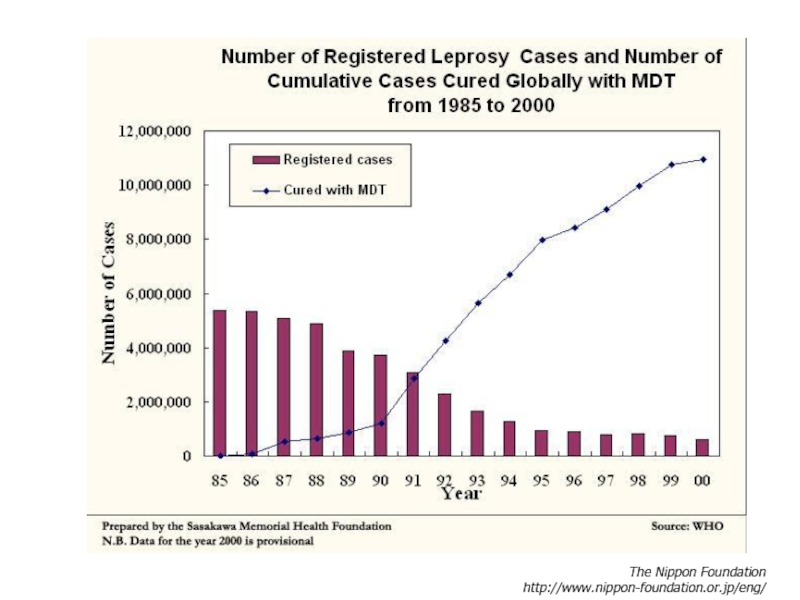
Elimination of leprosy as public health problem (with a prevalence less than 1 case per 10 000 persons) was achieved globally in the year 2000.
More than 16 million leprosy patients have been treated with MDT over the past 20 years.
Слайд 6Gerhard Armauer Hansen
Global Project on the History of Leprosy
http://www.leprosyhistory.org/graphics/gallery/hansen.jpg
1868 - Identifies
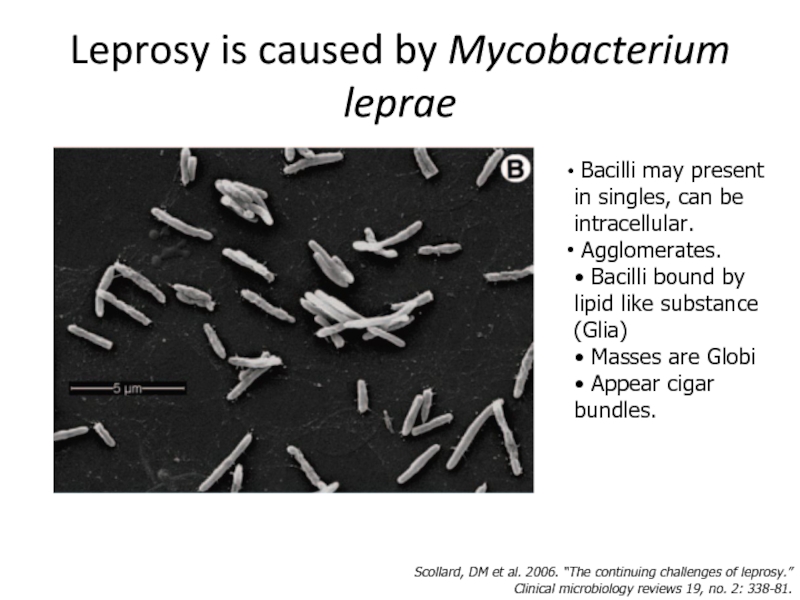
Слайд 7Leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprae
Scollard, DM et al. 2006.
Clinical microbiology reviews 19, no. 2: 338-81.
Bacilli may present in singles, can be intracellular.
Agglomerates.
• Bacilli bound by lipid like substance (Glia)
• Masses are Globi
• Appear cigar bundles.
Слайд 8Cultivation
Not possible
Can be propagated in Foot pads of Mice
Granulomas develop at
Nine banded armadillo highly susceptible.
Chimpanzees
Generation time 12 -13 days.
Average may be 8- 42 days
Слайд 14Types of Leprosy
Depending on clinical features, leprosy is classified as:
Indeterminate Leprosy
Paucibacillary Leprosy (PB)
Borderline Tuberculoid Leprosy (BT)
Borderline borderline Leprosy (BB)
Borderline lepromatous Leprosy (BL)
Multibacillary Leprosy (MB)
Слайд 15WHO classification
Two Groups:
1 Paucibacillary
2 Multibacillary
Paucibacillary (PB): the number of M.
Слайд 16WHO classification
2 Multibacillary
M. leprae can multiple in the body almost without
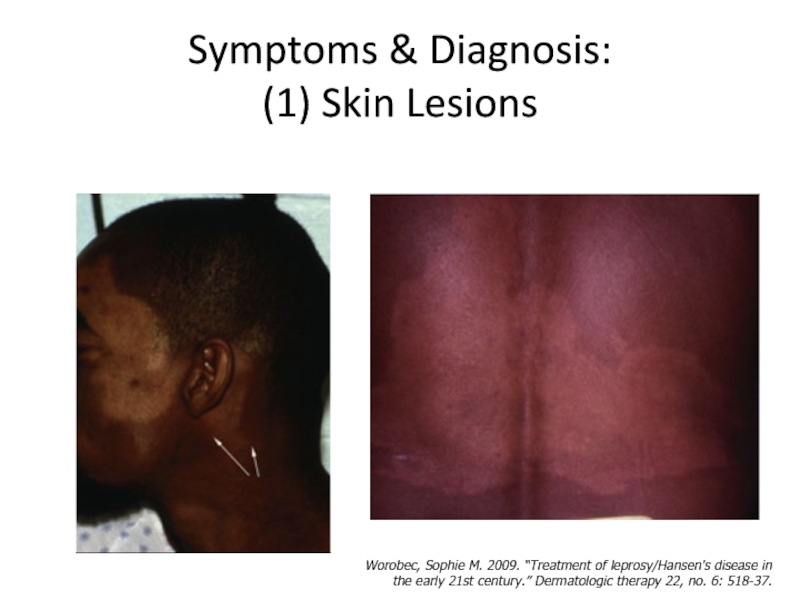
Слайд 18Symptoms & Diagnosis:
(1) Skin Lesions
Worobec, Sophie M. 2009. “Treatment of
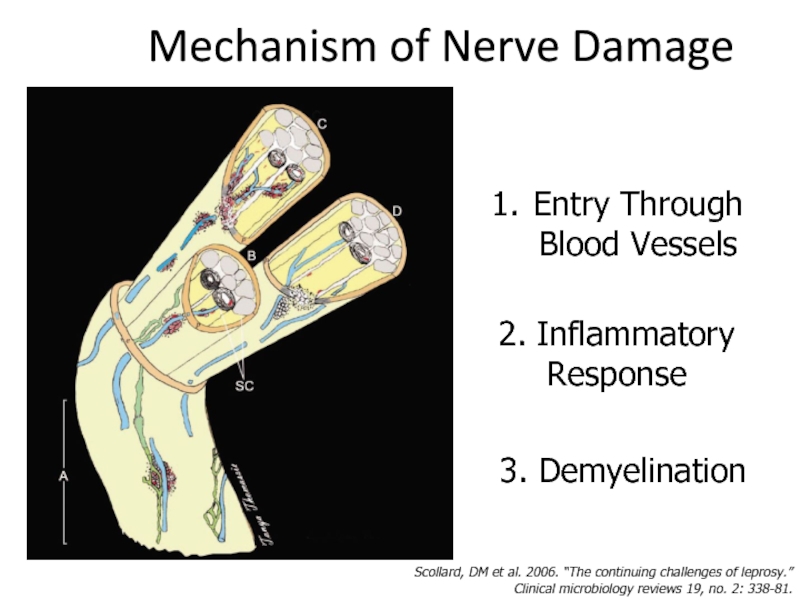
Слайд 20Mechanism of Nerve Damage
Scollard, DM et al. 2006. “The continuing challenges
Clinical microbiology reviews 19, no. 2: 338-81.
Entry Through Blood Vessels
2. Inflammatory Response
3. Demyelination
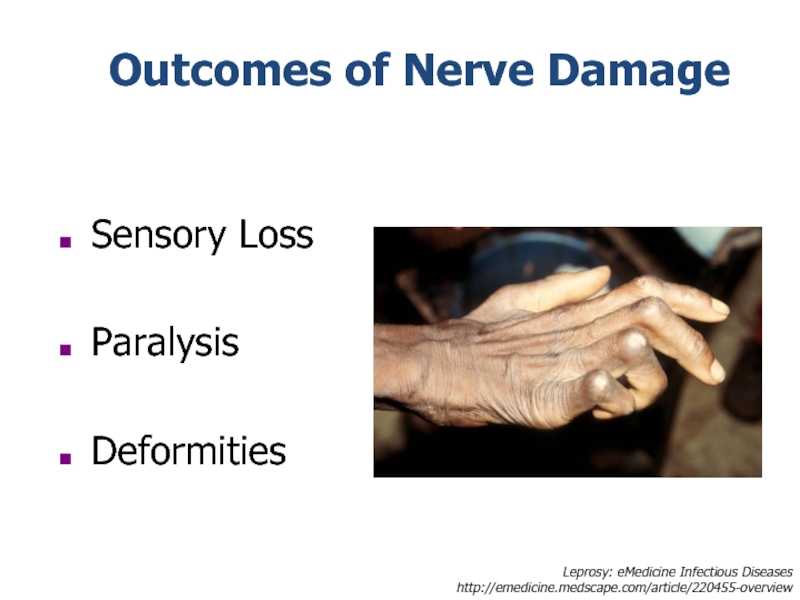
Слайд 21Sensory Loss
Paralysis
Deformities
Outcomes of Nerve Damage
Leprosy: eMedicine Infectious Diseases
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/220455-overview
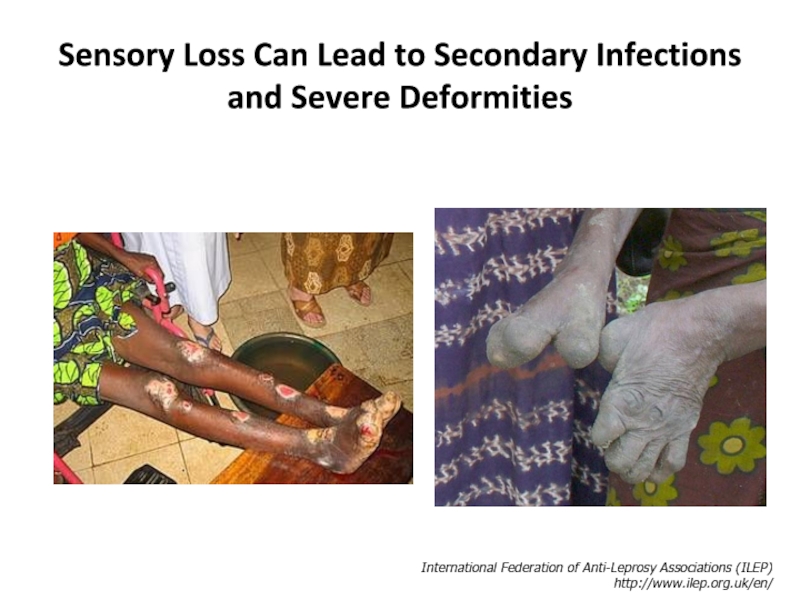
Слайд 22Sensory Loss Can Lead to Secondary Infections and Severe Deformities
International Federation
http://www.ilep.org.uk/en/
Слайд 251941: Discovery of Dapsone
Targets dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS)
Inhibits nucleic acid synthesis
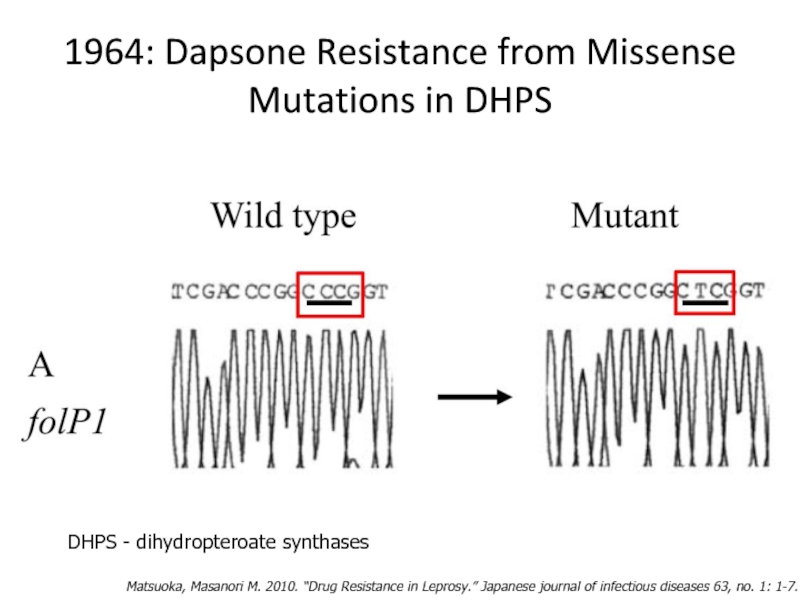
Слайд 261964: Dapsone Resistance from Missense Mutations in DHPS
Matsuoka, Masanori M. 2010. “Drug
DHPS - dihydropteroate synthases
Слайд 271960’s: Rifampicin and Clofazimine Discovered
Rifampicin (Rifampin): Inhibit RNA synthesis
Clofazimine:
Anti-inflammatory
Слайд 281981: WHO Proposes Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT)
Combination of DAPSONE, RIFAMPICIN, and CLOFAZIMINE
+
+
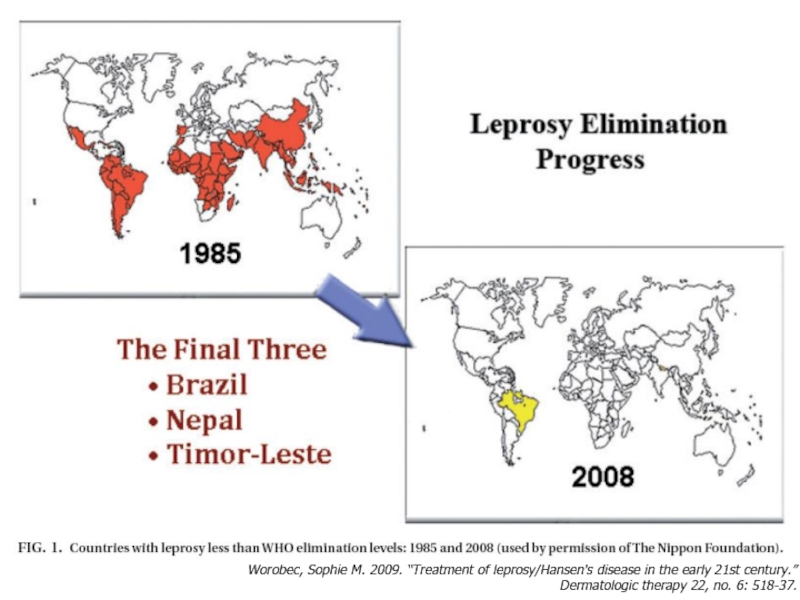
Слайд 32Obstacles to Eliminating Leprosy in Endemic Countries
World Health Organization. 2001. “Leprosy:
WHO Publications on Leprosy.
STIGMA
Слайд 34Worobec, Sophie M. 2009. “Treatment of leprosy/Hansen's disease in the early
Dermatologic therapy 22, no. 6: 518-37.
Слайд 35In 2016 WHO has launched a new global strategy – “The
The targets of the new global strategy to be met by 2020 are:
Zero disabilities among new paediatric patients.
A grade-2 disability rate of less than 1 case per 1 million people.
Zero countries with legislation allowing discrimination on basis of leprosy.