- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain: Approach to Diagnosis and Management презентация
Содержание
- 1. Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain: Approach to Diagnosis and Management
- 2. Disclosures None
- 3. Objectives Identify the neurogenic and mechanical factors
- 4. Outline Basics Definition, Incidence, Prognosis Anatomy Factors Neurogenic Mechanical Diagnosis Management Suggested Treatment Algorithm
- 5. Basics CVA: 795,000 per year; 3rd for
- 6. HSP Risk Factors Impaired motor control Diminished
- 7. HSP Prognosis Lower Barthel score at
- 8. Anatomy Shoulder: complex ball-and-socket joint Agility at
- 9. Mechanisms of Injury Cause is likely multifactorial
- 10. Neurogenic Factors Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) injury
- 11. UMN Disorders Weakness Disrupts cervicothoraic posture, shoulder
- 12. UMN Disorders Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
- 13. Mechanical Factors Shoulder subluxation Rotator cuff injury
- 14. Diagnosis History, physical examination, special tests/maneuvers Imaging
- 15. Diagnosis: Exam Observation ROM AROM, then PROM
- 16. Diagnosis: Exam Special tests Neer, Hawkins, Jobe,
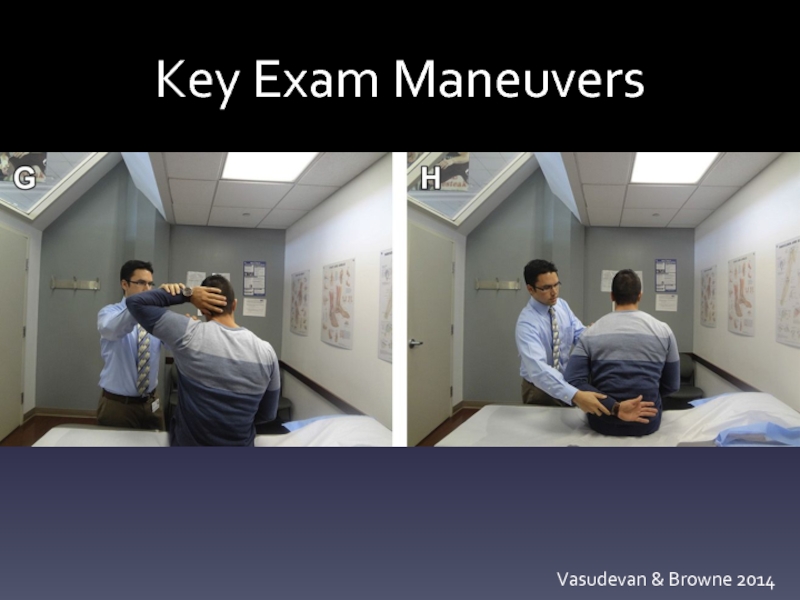
- 18. Key Exam Maneuvers Vasudevan & Browne 2014
- 19. Diagnosis: Imaging Radiography AP: assess for fracture,
- 20. Diagnosis: Imaging Relationship of imaging and HSP
- 21. Management Prevention through positioning Flaccid stage: risk
- 22. Physical Therapy Mechanical Factors PROM exercises within
- 23. Physical Therapy Neurogenic Factors TENS: high intensity
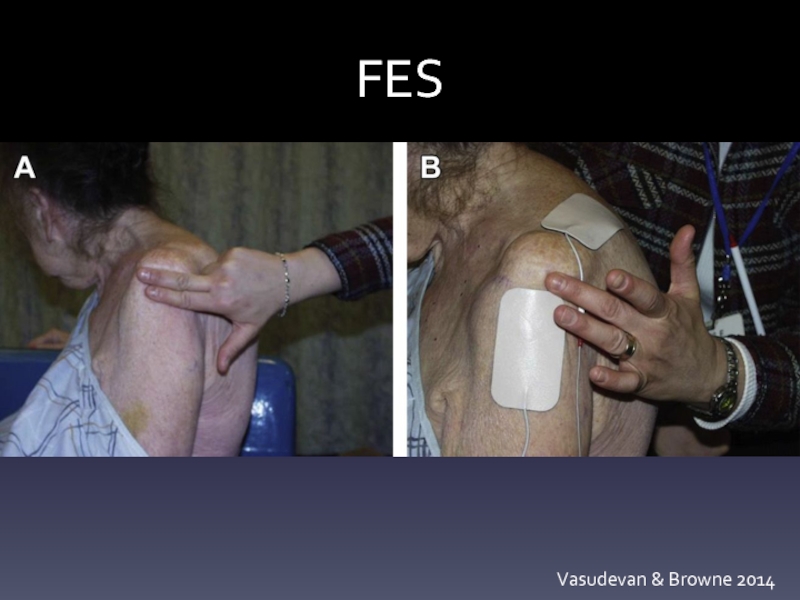
- 24. FES Vasudevan & Browne 2014
- 25. Physical Therapy Neurogenic Factors EMG biofeedback and
- 26. Interventional Neurogenic Factors Botulinum toxin (presynaptic Ach
- 27. Pharmacotherapy NSAIDs, topical lidocaine, antiepileptic agents, TCAs,
- 28. Complementary and alternative medicine Acupuncture Works via
- 29. Surgery Typically for adhesive capsulitis (release of
- 30. Suggested Protocol Step 1: Identify neurogenic factors
- 31. Suggested Protocol Strapping/Taping: perpendicular to inhibit, parallel
- 32. Suggested Protocol Physical Therapy and Modalities Strive
- 33. Suggested Protocol Pharmacotherapy Neurogenic: Neuropathic pain: AEDs,
- 34. Suggested Protocol Injection therapy Neurogenic: Botulinum Toxin:
- 35. Suggested Protocol Complementary and alternative medicine Acupuncture
- 36. Suggested Protocol Surgery (after 6 mos failed
- 37. Summary HSP is a common complication of
- 38. Objectives Identify the neurogenic and mechanical factors
- 39. References Contact me for a list john.vasudevan@uphs.upenn.edu
- 40. THANK YOU!
Слайд 1Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain:
Approach to Diagnosis & Management
John Vasudevan, MD
University of Pennsylvania
2015
Слайд 3Objectives
Identify the neurogenic and mechanical factors which contribute to HSP
Prescribe appropriate
Understand the level of evidence supporting treatments for HSP
Слайд 4Outline
Basics
Definition, Incidence, Prognosis
Anatomy
Factors
Neurogenic
Mechanical
Diagnosis
Management
Suggested Treatment Algorithm
Слайд 5Basics
CVA: 795,000 per year; 3rd for mortality, 1st for disability; costs
Hemiplegia: present in 50%, persists in 70%
HSP: commonly reported 70% (range 16-84%)
Roger 2012; Aoyagi 2004; Bohannon 1986
Слайд 6HSP Risk Factors
Impaired motor control
Diminished proprioception
Tactile extinction
Abnormal sensation
Elbow flexor spasticity
Restricted ROM
Trophic changes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Adhesive capsulitis
Complex regional pain syndrome
Supraspinatus or long head biceps injury
Roosink 2011; Barlak 2009; Dromerick 2008
Слайд 7HSP Prognosis
Lower Barthel score at 12 weeks
Lower chance of return
Resolution within first 5 weeks predicts good long-term function
Roy 1994; Murie-Fernandez 2012; Higgins 2005
Слайд 8Anatomy
Shoulder: complex ball-and-socket joint
Agility at the cost of stability
Static stabilizers
Glenohumeral ligaments
Dynamic
Rotator cuff
Periscapular musculature
Kalichman 2011; Smith 2012
Слайд 9Mechanisms of Injury
Cause is likely multifactorial
Weakness, spasticity, sensory loss, instability
Classification
Better by
Слайд 10Neurogenic Factors
Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) injury
Paralysis, spasticity, central post-stroke pain, central
Lower Motor Neuron (LMN) injury
Peripheral neuropathy, brachial plexus injury, complex regional pain syndrome
Слайд 11UMN Disorders
Weakness
Disrupts cervicothoraic posture, shoulder stability
Spasticity
Overactive pectorals, subscapularis, biceps
85% with spasticity
Subscapular nerve block can reduce pain
Brachial plexus injury
Traction injury suspected
Suprascapular and axillary nerves most affected
Van Ouwenaller 1986; Hecht 1992; Kaplan 1977; Moskowitz 1963; Chino 1980
Слайд 12UMN Disorders
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
Type 1 (previously RSD), Type 2
Incidence up to 23% of all HSP cases
Central post-stroke pain (CPSP)
Also termed thalamic pain syndrome, thought due to lesion in spinothalamic tract
Alterations in serotonin and norepinephrine
Van Ouwenaller 1986
Слайд 13Mechanical Factors
Shoulder subluxation
Rotator cuff injury
Glenohumeral joint disorders
Adhesive capsulitis
Myofascial pain
Direct trauma
Слайд 14Diagnosis
History, physical examination, special tests/maneuvers
Imaging (XR, MRI, US)
Electrodiagnosis
Diagnostic injections (nerve, muscle,
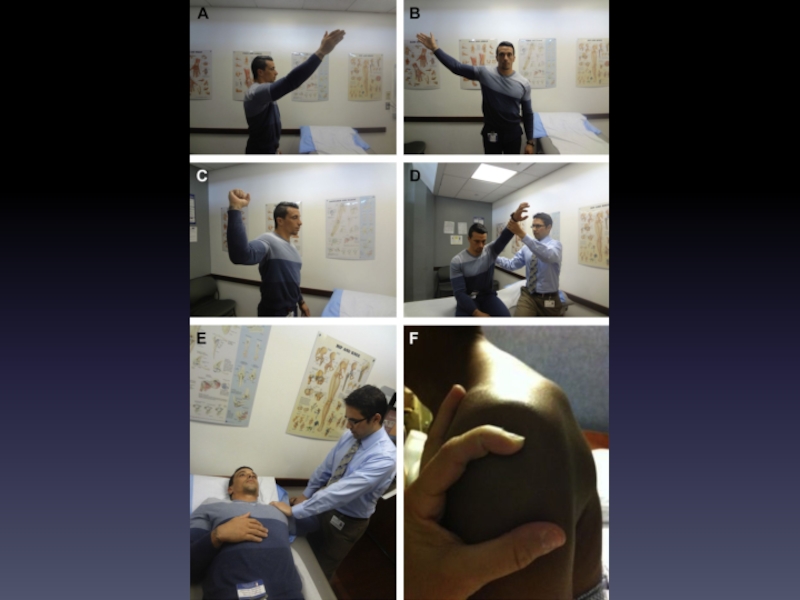
Слайд 15Diagnosis: Exam
Observation
ROM
AROM, then PROM
Palpation
Assess for bulk, focal tenderness
Sensation
Dermatomes, peripheral nerves (e.g.,
Reflexes
C5-C8, UMN signs, spasticity
Strength
Слайд 16Diagnosis: Exam
Special tests
Neer, Hawkins, Jobe, O’Brien, HBB/HBN
Instability: Apprehension, Sulcus
Diagnostic Injections
Nerve blocks
Joint/tendon injections (GHJ, SA/SD bursa, etc)
Trigger point injections
Слайд 19Diagnosis: Imaging
Radiography
AP: assess for fracture, subluxation
ER: calcific tendinopathy; IR: Hill-Sachs lesion
Scapular
Axillary: shoulder instability
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Arthrography: labral tear, adhesive capsulitis
Ultrasonography
May help assess for adhesive capsulitis
Advantage of serial assessments at low cost
More injuries noted for those admitted at Brunnstrom I-III vs IV-VI
Pong 2009; Huang 2010; Lee 2009
Слайд 20Diagnosis: Imaging
Relationship of imaging and HSP
Lo et al study:
HSP cohort:
Arthrography helpful to detect adhesive capsulitis
Most cases within 2 months from CVA onset
MRI findings in chronic stroke: synovial capsule thickening/enhancement, rotator cuff enhancement
No difference in cuff tendinopathy, joint effusion, subacromial bursal fluid, ACJ arthrosis, muscle atrophy
Lo 2003; Tavora 2010
Слайд 21Management
Prevention through positioning
Flaccid stage: risk for injury
Suggested: abduction, ER, flexion
But no
Strapping and slings
Tape perpendicular to inhibit, parallel to promote
Only small studies to support vs. sham taping
Slings and arm troughs help minimize shoulder subluxation
Improvements in HR, gait speed, decreased O2 rate with sling use in a cross-over study
Wanklyn 1996, Braus 1994, Murie-Fernandez 2012; Thelan 2008; Han 2011
Слайд 22Physical Therapy
Mechanical Factors
PROM exercises within pain-free range can reduce reports of
Overhead pulley exercises increase cuff injury risk
Neither Bobath nor Brunnstrom superior
CPM: increased shoulder stability but no change to motor impairment, pain, tone, disability
Robotic devices: improved function at 8 months
Caldwell 1969; Kumar 1990; Walsh 2001; Lynch 2005; Masiero 2007
Слайд 23Physical Therapy
Neurogenic Factors
TENS: high intensity > low intensity or placebo
FES: to
More effective in acute vs chronic HSP after 6 wks Tx
FES + PT is superior to PT alone (RCT, n=50)
Cochrane: improves pain-free ROM and reduces subluxation, does not affect pain or impairment
Intramuscular FES: reduced pain at 1 year, but no change to strength/sensation
Leandri 1990; Walsh 2001; Want 2000; Koyuncu 2010; Price 2001; Chae 2005; David 2010
Слайд 25Physical Therapy
Neurogenic Factors
EMG biofeedback and relaxation: 150 min x 5 days
Williams 1982
Слайд 26Interventional
Neurogenic Factors
Botulinum toxin (presynaptic Ach inhibitor)
Several small studies show favorable results
One study vs corticosteroid
Some studies include intraarticular toxin
Nocioceptive effect?
Sympathetic blocks (for CRPS)
Central pain covered later in this talk
Rehab considerations: pain/edema control, isometric and stress-loading exercises, concurrent psychotherapy
Yelnik 2007; Kong 2007; De Boer 2008; Lim 2008; Castiglione 2011
Слайд 27Pharmacotherapy
NSAIDs, topical lidocaine, antiepileptic agents, TCAs, SSRIs, antispasmodics
The problem: not a
Corticosteroid injection
Glenohumeral joint or subacromial bursa
Can reduce pain and increase pain-free ROM
Suprascapular nerve block
Potentially superior to corticosteroid at 1 month
Lakse 2009; Chae 2009; Dekker 1997; Snels 2000; Yasar 2011, Allen 2010
Слайд 28Complementary and alternative medicine
Acupuncture
Works via neurohormonal mechanism: β-endorphin dynorphin A/B, substance
Benefit in addition to standard PT
Aromatherapy: limited study
Shin 2007; Lee 2012; Shin 2007
Слайд 29Surgery
Typically for adhesive capsulitis (release of capsular adhesions, manipulation under anesthesia)
HSP relieved in all 13 patients after contracture release in one small study
Braun 1971
Слайд 30Suggested Protocol
Step 1: Identify neurogenic factors
Step 2: Identify mechanical factors
Step 3:
Step 4: Symptom control and rehabilitation
Step 5: pathology based intervention
Слайд 31Suggested Protocol
Strapping/Taping: perpendicular to inhibit, parallel to promote
Slings:
Flaccid: sitting, ambulating, transferring
Spastic:
Avoid axillary supports
Слайд 32Suggested Protocol
Physical Therapy and Modalities
Strive for maximal pain-free ROM
Avoid overhead pulley
TENS: best at high intensity
FES: apply to deltoid and supraspinatus for temporary reduction in shoulder subluxation
EMG biofeedback: to encourage early and active participation, maximize psychological control
Слайд 33Suggested Protocol
Pharmacotherapy
Neurogenic:
Neuropathic pain: AEDs, TCAs, SSRIs
Spasticity: antispasmodics
Mechanical
NSAIDs and acetaminophen
Rare opioids or
Слайд 34Suggested Protocol
Injection therapy
Neurogenic:
Botulinum Toxin: IM, possibly even IA
Stellate Ganglion Block
Mechanical
Corticosteroid to
Suprascapular nerve block
Trigger point injections
Слайд 35Suggested Protocol
Complementary and alternative medicine
Acupuncture may be superior in combination with
Aromatherapy has limited positive support
Слайд 36Suggested Protocol
Surgery (after 6 mos failed conservative Tx)
Neurogenic: release of contractures
Mechanical:
Слайд 37Summary
HSP is a common complication of CVA which is known to
HSP is a multifactorial process often encompassing a combination of neurogenic and mechanical factors
They key to management is prevention as able, and concurrent treatment of all contributing factors
Слайд 38Objectives
Identify the neurogenic and mechanical factors which contribute to HSP
Prescribe appropriate
Understand the level of evidence supporting treatments for HSP