- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Corticosteroids. Steroids: the worst drugs for adverse effects презентация
Содержание
- 1. Corticosteroids. Steroids: the worst drugs for adverse effects
- 2. Steroids: the worst drugs for adverse effects
- 4. Corticosteroids History Synthesis Pharmacological
- 5. History 1855 – Addison's disease 1856 –
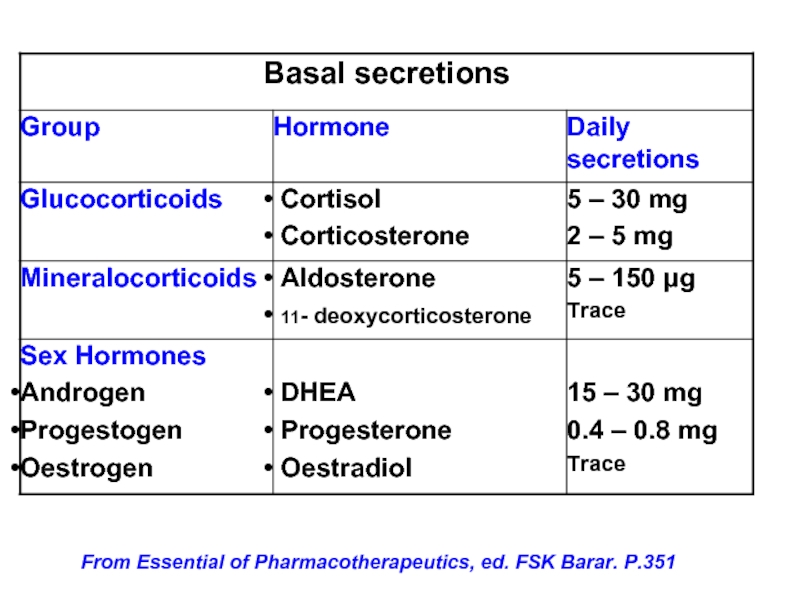
- 8. From Essential of Pharmacotherapeutics, ed. FSK Barar. P.351
- 9. Cholesterol Pregnenolone Progesterone Corticosterone
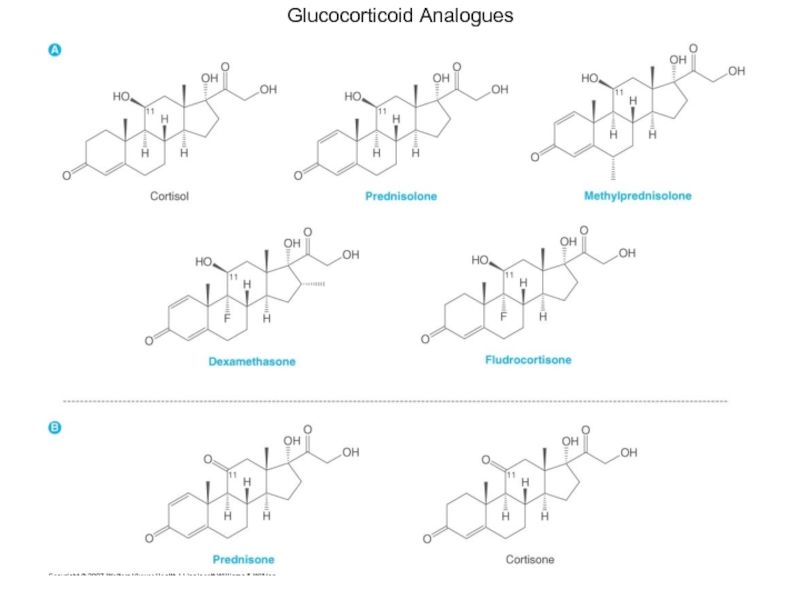
- 10. Glucocorticoid Analogues
- 11. Pharmacological Actions Direct (Intended) Actions Anti-inflammatory Anti-allergy
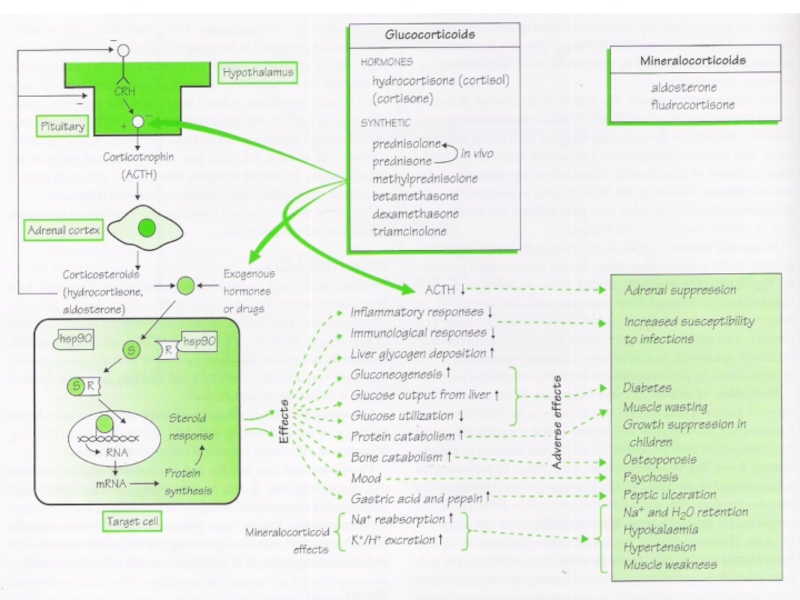
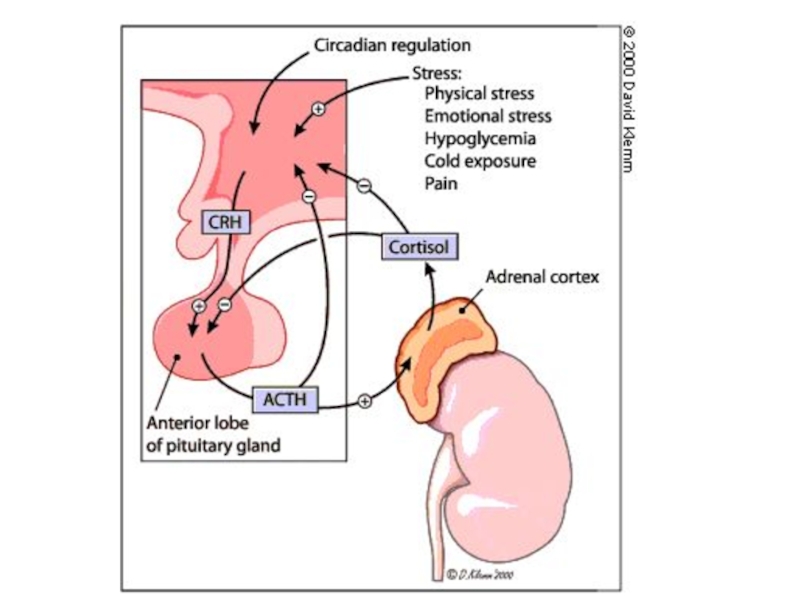
- 12. Pharmacological Actions Negative feedback mechanism. Steroids and
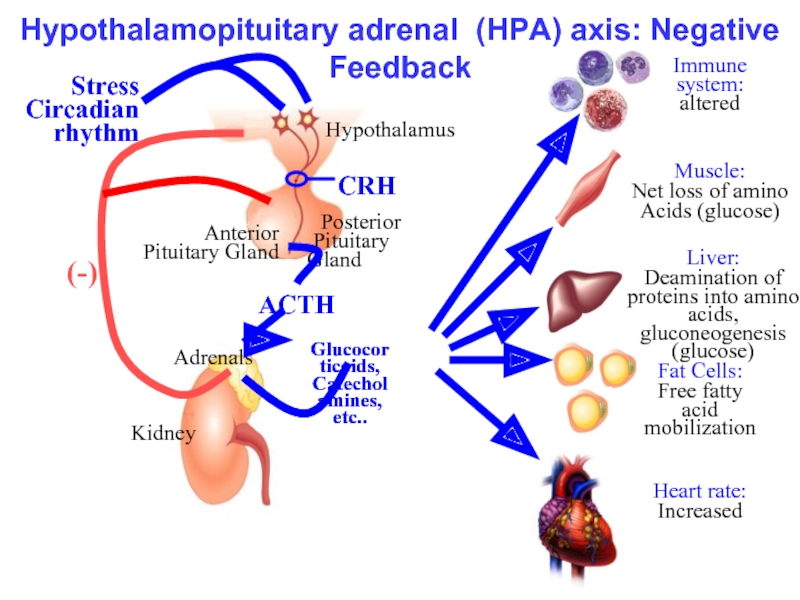
- 13. Hypothalamopituitary adrenal (HPA) axis: Negative Feedback
- 17. Pharmacological Actions For most clinical purposes, synthetic
- 18. Pharmacological Actions Betamethasone and dexamethasone: very potent,
- 19. Pharmacological Actions Carbohydrate Protein Lipid Electrolyte and
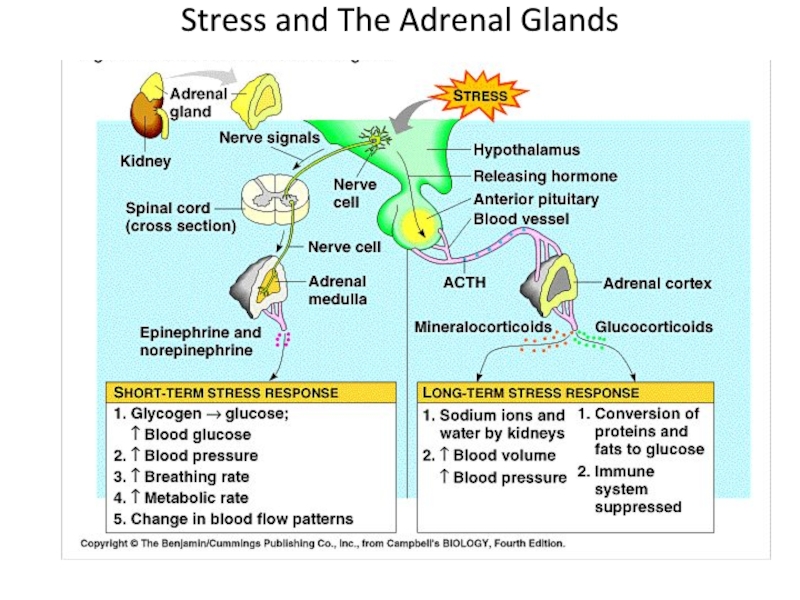
- 20. Stress and The Adrenal Glands
- 21. Actions: Carbohydrate and protein metabolism Gluconeogenesis
- 22. Redistribution of Fat Buffalo hump Moon face
- 23. Actions: Electrolyte and water balance Aldosterone is
- 24. Restrict capillary permeability Maintain tone of arterioles
- 25. Addison's disease: weakness and fatigue is due
- 26. Direct: Mood Behaviour Brain excitability Indirect:
- 27. Pseudotumor cerebri (Intracranial hypertension) Glucocorticoids Mineralocorticoids
- 28. Aggravate peptic ulcer. May be due to:
- 29. RBC: Hb and RBC content
- 30. Recruitment of WBC and
- 31. Phospholipids Arachidonic acids lipoxygenase Cycylooxygenase Leukotriene Prostaglandins,
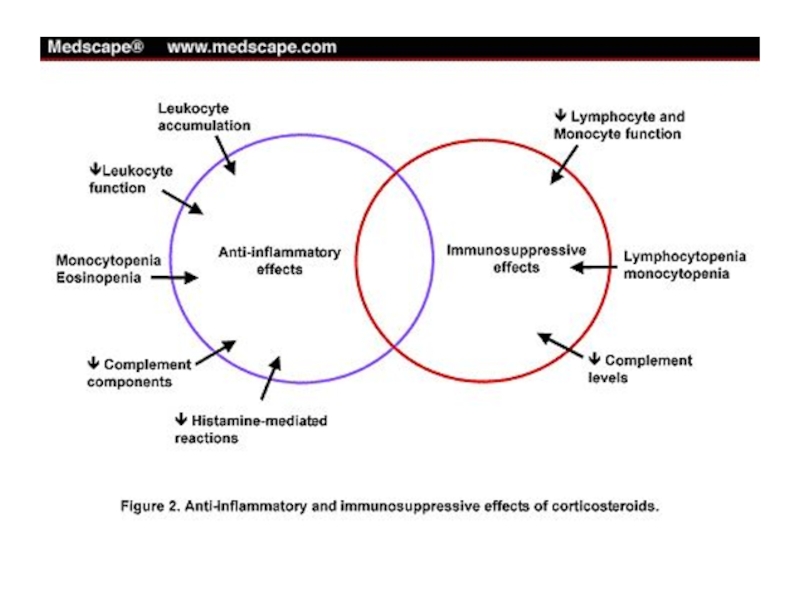
- 32. Anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids Corticosteroid inhibitory effect
- 33. Immunosuppressive and anti-allergic actions Suppresses all types
- 35. Inhibit cell division or synthesis of DNA
- 36. Intestinal absorption
- 37. Not bronchodilators Most potent and most
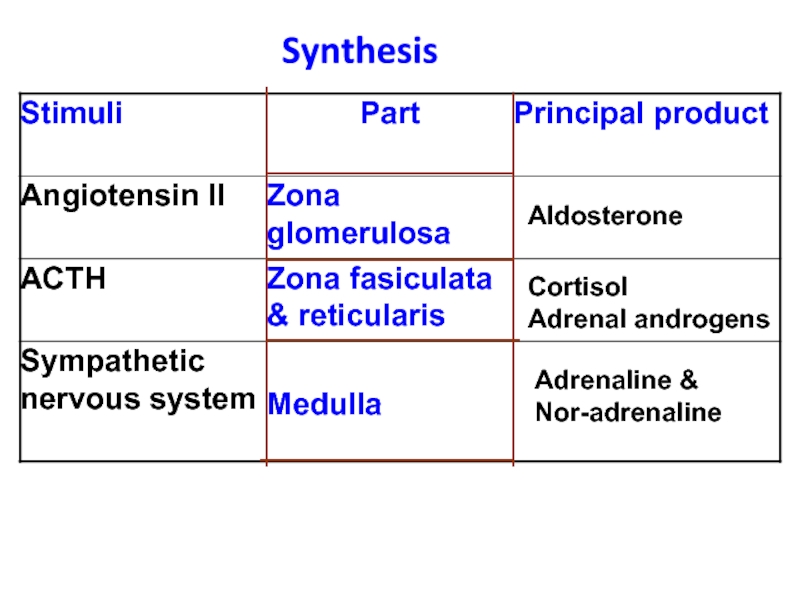
- 40. Synthesis Aldosterone Cortisol Adrenal androgens Adrenaline & Nor-adrenaline
- 41. Stimuli Sense Organs Other Brain Centers
Слайд 4Corticosteroids
History
Synthesis
Pharmacological Actions
Pharmacokinetics
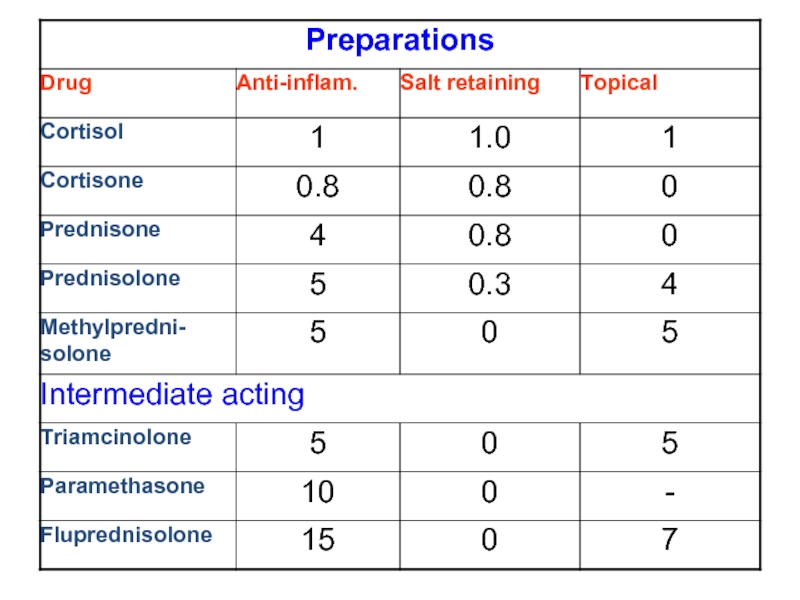
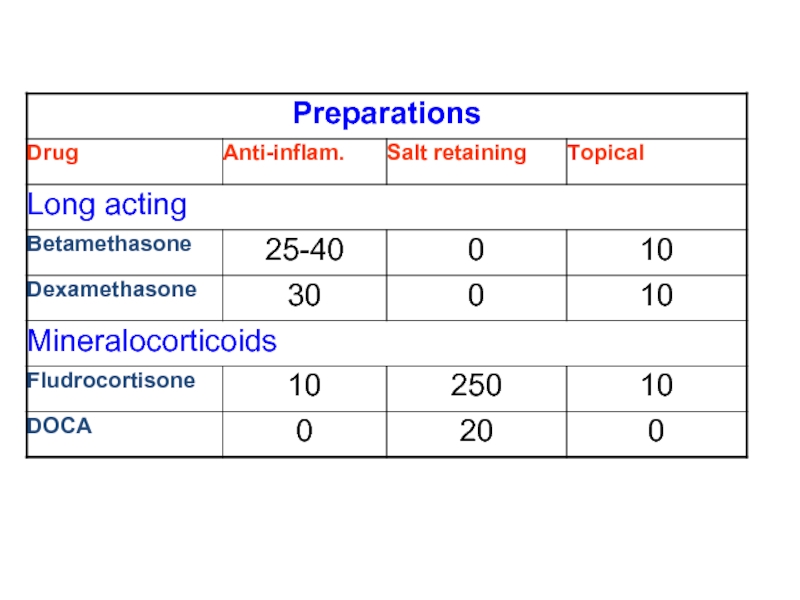
Preparations
Therapeutic principles
Dosage schedule & Steroid withdrawal
Uses:
Therapeutic
Diagnostic
Adverse reactions
Contraindications
Precautions during therapy
Glucocorticoid antagonists
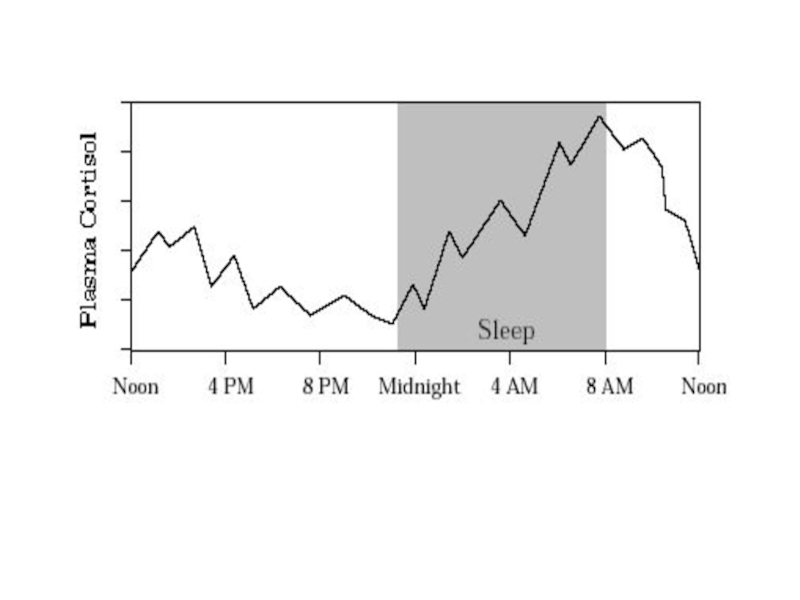
Слайд 5History
1855 – Addison's disease
1856 – Adrenal glands essential for life
1930 –
1932 – Cushing’s syndrome
1949 – Hench et al (Steroids in rheumatoid arthritis)
1952 – Aldosterone
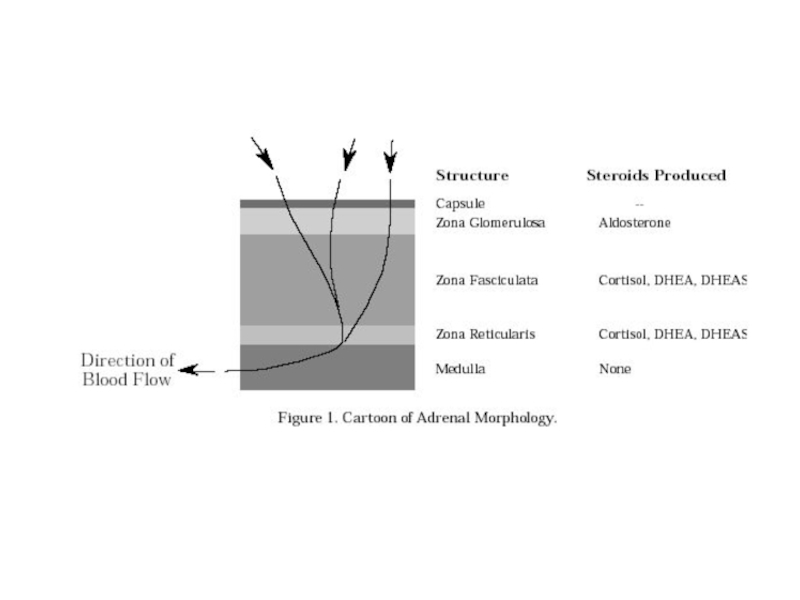
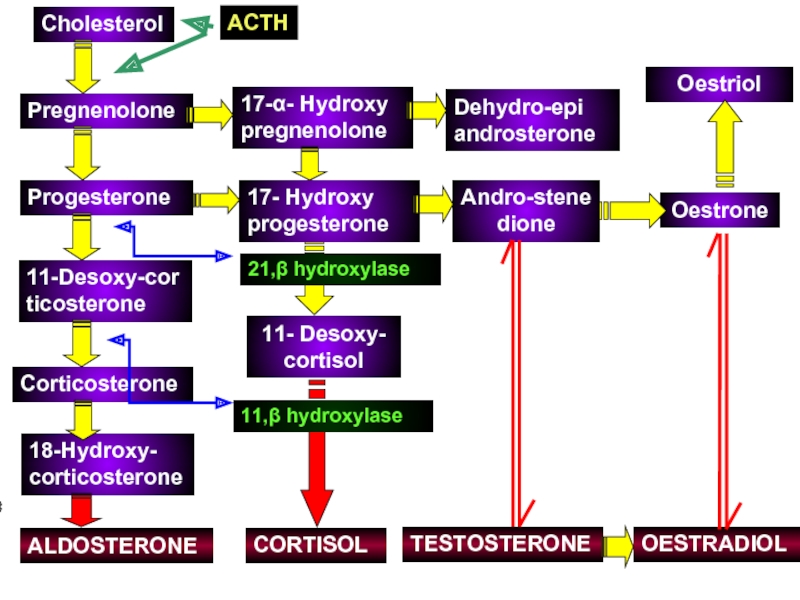
Слайд 9Cholesterol
Pregnenolone
Progesterone
Corticosterone
11-Desoxy-corticosterone
18-Hydroxy- corticosterone
ALDOSTERONE
17-α- Hydroxy pregnenolone
11- Desoxy- cortisol
17- Hydroxy progesterone
21,β hydroxylase
CORTISOL
11,β hydroxylase
Dehydro-epi androsterone
Andro-stenedione
Oestrone
Oestriol
TESTOSTERONE
OESTRADIOL
ACTH
Слайд 11Pharmacological Actions
Direct (Intended) Actions
Anti-inflammatory
Anti-allergy
Anti-immunity
Permissive Actions
Lipolytic effects
Effect on bp
Effect on bronchial muscles
(e.g.,sympathomimetic
Слайд 12Pharmacological Actions
Negative feedback mechanism.
Steroids and drugs designed to mimic them are
Glucocorticoids (e.g., prednisolone) used to suppress inflammation, allergy and immune responses.
Anti-inflammatory therapy is used in many illnesses (e.g., RA, UC, BA, eye and skin inflammations).
-Useful in, say, tissue transplantation and lymphopoiesis (leukemias and lymphomas).
Striking improvements can be obtained, but severe adverse, but highly predictable, effects are ensue.
Слайд 17Pharmacological Actions
For most clinical purposes, synthetic glucocorticoids are used because they
Hydrocortisone used for: orally for replacement therapy, i.v. for shock and asthma, topically for eczema (ointment) and enemas (ulcerative colitis).
Prednisolone the most widely used drug given orally in inflammation and allergic diseases.
Слайд 18Pharmacological Actions
Betamethasone and dexamethasone: very potent, w/o salt-retaining properties; thus, very
Beclometasone, diproprionate, budesonide: pass membranes poorly; more active when applied topically (severe eczema for local anti-inflammatory effects) than orally; used in asthma, (aerosol).
Triamcinolone: used for severe asthma and for local joint inflammation (intra-articular inj.).
Слайд 19Pharmacological Actions
Carbohydrate
Protein
Lipid
Electrolyte and H2O
CVS
Skeletal Muscle
CNS
Stomach
Blood
Anti-inflammatory
Immunosuppressant
Respiratory
Growth and Cell Division
Calcium metabolism
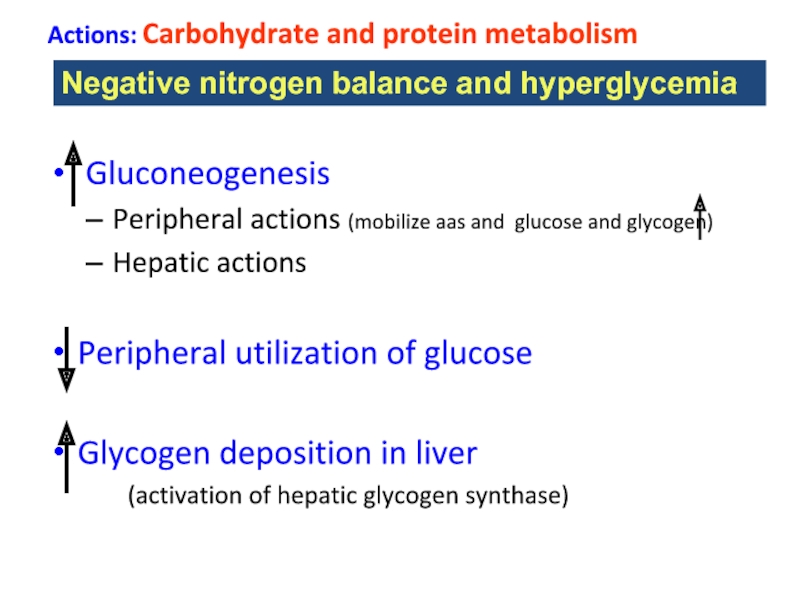
Слайд 21Actions: Carbohydrate and protein metabolism
Gluconeogenesis
Peripheral actions (mobilize aas and glucose
Hepatic actions
Peripheral utilization of glucose
Glycogen deposition in liver
(activation of hepatic glycogen synthase)
Negative nitrogen balance and hyperglycemia
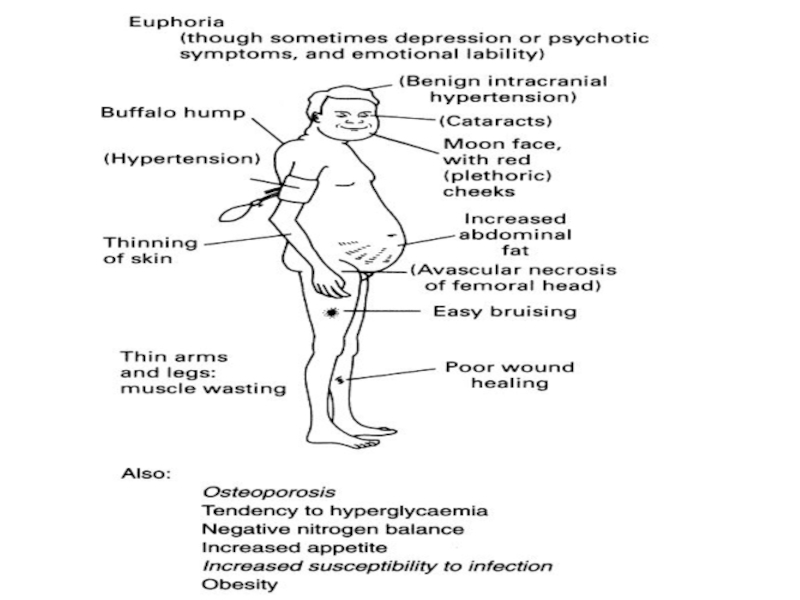
Слайд 22Redistribution of Fat
Buffalo hump
Moon face
Promote adipokinetic agents activity
(glucagon, growth hormone, adrenaline,
Actions: Lipid metabolism
Слайд 23Actions: Electrolyte and water balance
Aldosterone is more important
Act on DT and
Na+ reabsorption
Urinary excretion of K+ and H+
Addison’s disease ??
Na+ loss
Shrinkage of ECF
Cellular hydration
Hypodynamic state of CVS
Circulatory collapse, renal failure, death
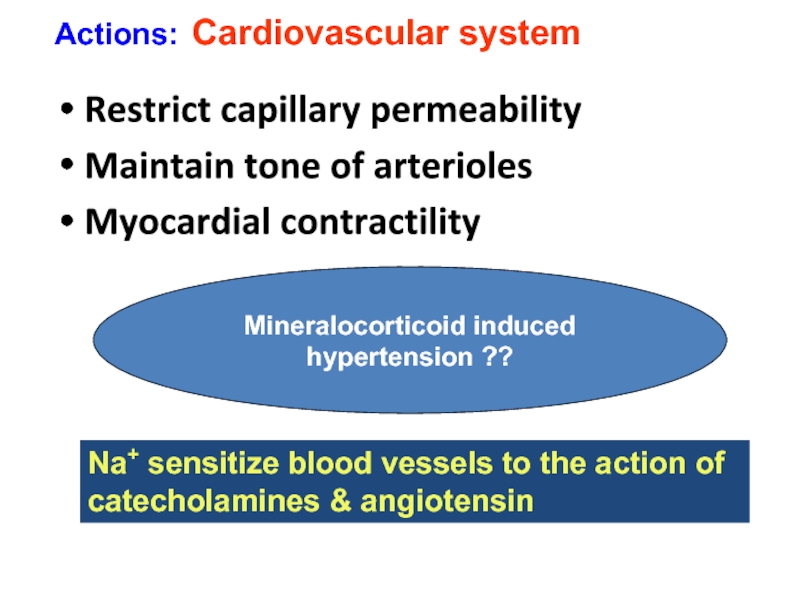
Слайд 24Restrict capillary permeability
Maintain tone of arterioles
Myocardial contractility
Actions: Cardiovascular system
Mineralocorticoid induced hypertension
Na+ sensitize blood vessels to the action of
catecholamines & angiotensin
Слайд 25Addison's disease: weakness and fatigue is due to
Prolonged use:
Actions:
Needed for maintaining the normal function of Skeletal muscle
inadequacy of circulatory system
Steroid myopathy
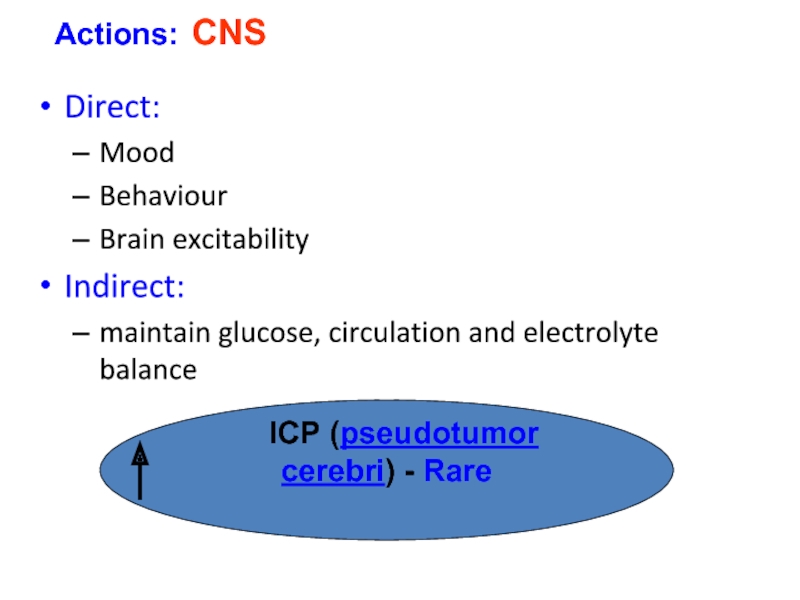
Слайд 26Direct:
Mood
Behaviour
Brain excitability
Indirect:
maintain glucose, circulation and electrolyte balance
Actions: CNS
Слайд 27Pseudotumor cerebri
(Intracranial hypertension)
Glucocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids
Amiodarone
Vitamin A
Oral contraceptives
Tetracyclines
From Harrison. 15th edition, volume 1,
Слайд 28Aggravate peptic ulcer. May be due to:
Acid and pepsin
immune response to H.Pylori
Actions: Stomach
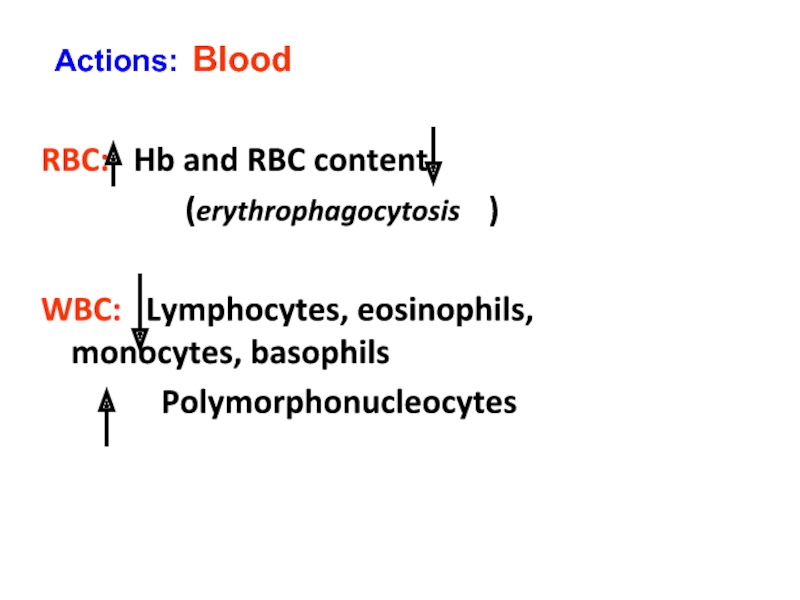
Слайд 29RBC: Hb and RBC content
(erythrophagocytosis
WBC: Lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes, basophils
Polymorphonucleocytes
Actions: Blood
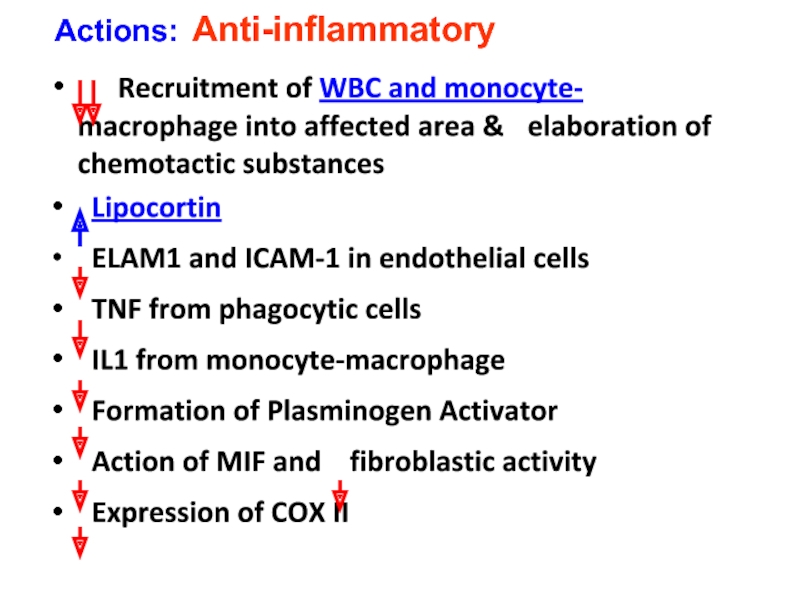
Слайд 30 Recruitment of WBC and monocyte- macrophage into affected
Lipocortin
ELAM1 and ICAM-1 in endothelial cells
TNF from phagocytic cells
IL1 from monocyte-macrophage
Formation of Plasminogen Activator
Action of MIF and fibroblastic activity
Expression of COX II
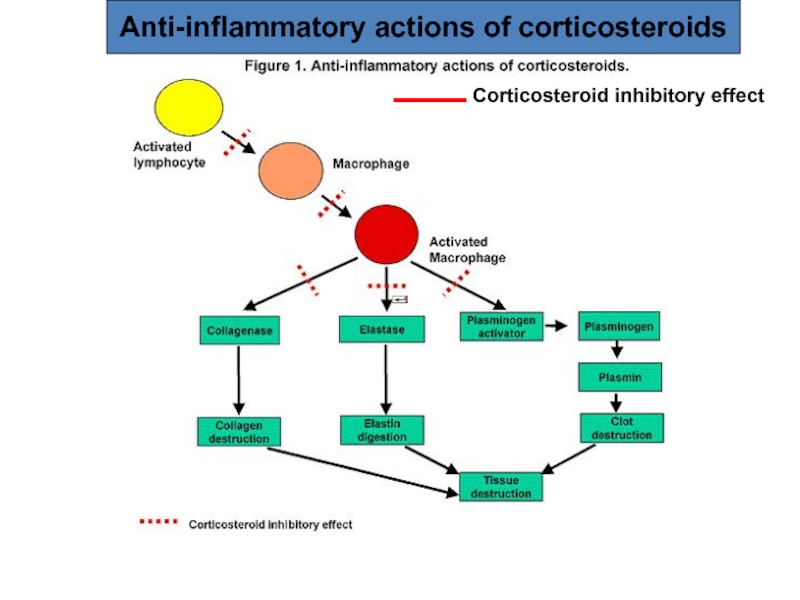
Actions: Anti-inflammatory
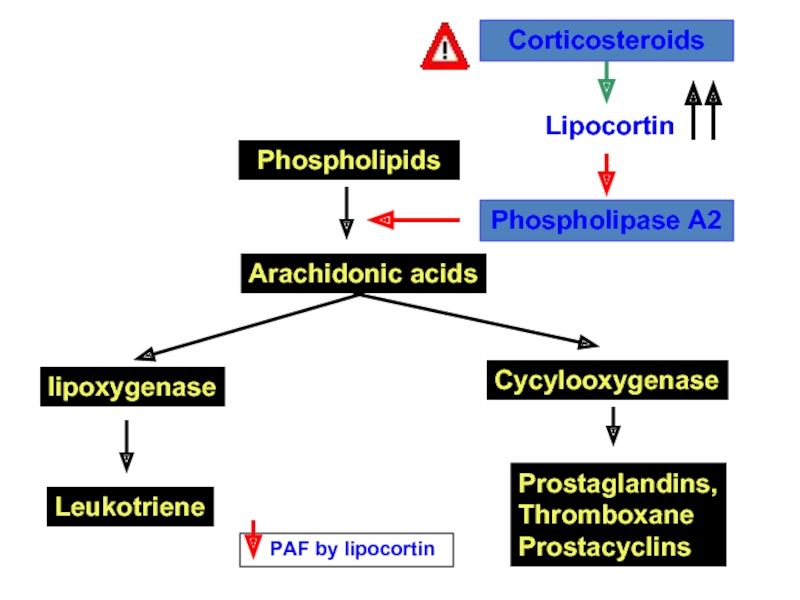
Слайд 31Phospholipids
Arachidonic acids
lipoxygenase
Cycylooxygenase
Leukotriene
Prostaglandins,
Thromboxane
Prostacyclins
Phospholipase A2
Lipocortin
Corticosteroids
PAF by lipocortin
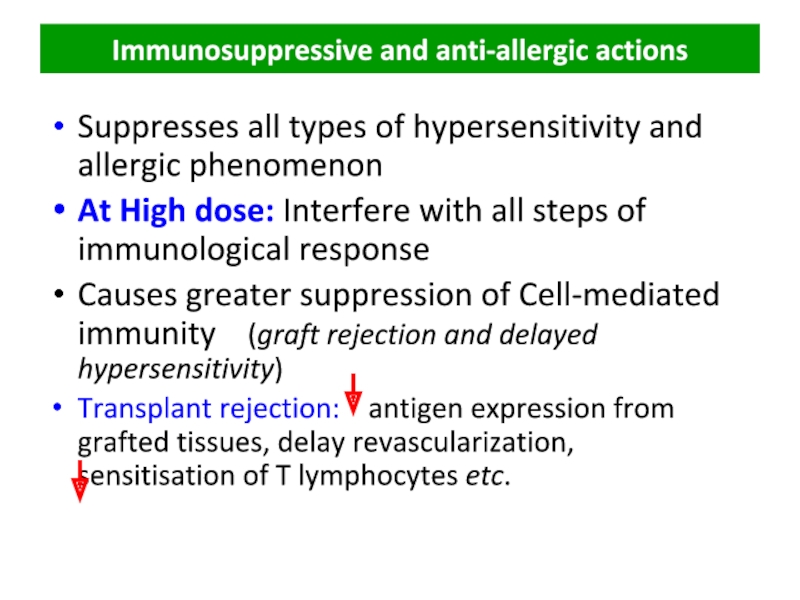
Слайд 33Immunosuppressive and anti-allergic actions
Suppresses all types of hypersensitivity and allergic phenomenon
At
Causes greater suppression of Cell-mediated immunity (graft rejection and delayed hypersensitivity)
Transplant rejection: antigen expression from grafted tissues, delay revascularization, sensitisation of T lymphocytes etc.
Слайд 35Inhibit cell division or synthesis of DNA
Delay the process of healing
Retard
Actions: Growth and Cell division
Слайд 36 Intestinal absorption
Renal excretion
Excessive loss of calcium
Actions: Calcium metabolism
Слайд 37Not bronchodilators
Most potent and most effective anti-inflammatory
Effects not seen immediately
Inhaled corticosteroids are used for long term control
Actions: Respiratory system
Слайд 41Stimuli
Sense Organs
Other Brain
Centers
Hippocampus
Hypothalamus
Pituitary
Thyroid
Gonads
Adrenal
Cortex
Nerves of the
CNS and ANS
Glucocorticoids
Thymus
Gland
Other Immune
System
Centers
Thymosin
From thymus
Nervous System
Endocrine System
Immune
Interleukin-1
[-]
[-]
[-]
[-]
[-]
[-]
[+]
INTERCELLULAR COMMUNICATION – THE EFFECTS OF GLUCOCORTICOIDS
Light
Sound
Smell
Taste
Touch

















![StimuliSense OrgansOther BrainCentersHippocampusHypothalamusPituitaryThyroidGonadsAdrenalCortexNerves of theCNS and ANSGlucocorticoidsThymusGlandOther ImmuneSystemCentersThymosinFrom thymusNervous SystemEndocrine SystemImmune SystemInterleukin-1[-][-][-][-][-][-][+]INTERCELLULAR COMMUNICATION – THE](/img/tmb/2/179988/9c5d0b24e7b81f043fbcfff2eed35f31-800x.jpg)