- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Cell injury. (Subject 2) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Cell injury. (Subject 2)
- 2. Conception of cell injury Cell Adaptation
- 3. The relationships among cell states (Hypertrophy) Myocardial fiber Hypertension Ischemia (short time) Ischemia (long time)
- 4. Injury From Physical Agents Causes: Mechanical
- 5. Other causes of cell damage Chemicals –
- 6. Types of Cell Injury Acute (strong irritants)
- 7. Signs of Cell Injury Morphological Functional
- 8. General Principles of Cell Injury Factors, which
- 9. Major Processes of Cell Injury Decreased ATP
- 10. Example test Chose the example of specific
- 11. Example test Which factors determine the type
- 12. Example test Patient was made blood biochemical
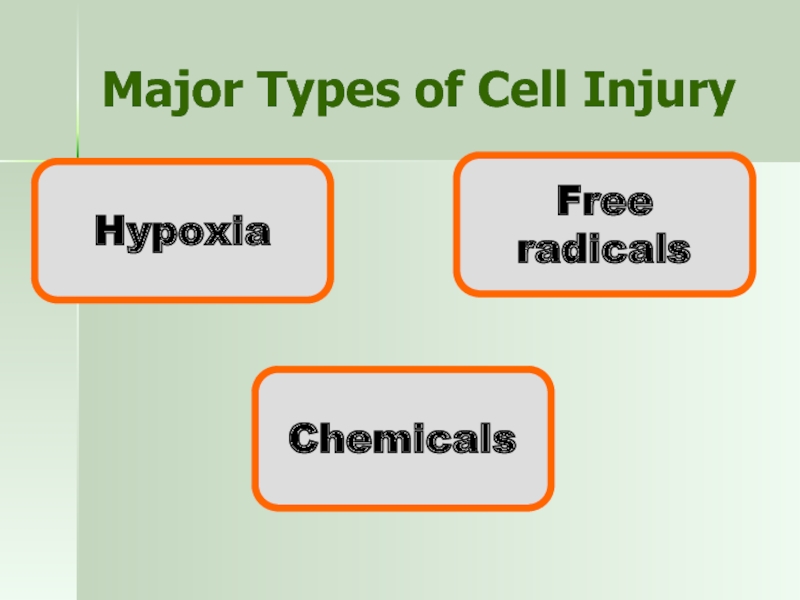
- 13. Major Types of Cell Injury Hypoxia Chemicals Free radicals
- 14. Reversible Hypoxic Injury Lack of oxygen Decreased
- 15. Irreversible Hypoxic Injury ↑ membranes permeability
- 16. Mechanisms of membranes damage Progressive loss
- 17. Reperfusion injury Neutrophiles Calcium ions Blood
- 18. Example test Disturbance of which process is
- 19. Example test Which factor directly causes the
- 20. Example test Which process is initiated by
- 21. Example test Which process determines irreversibility of
- 22. Example test Which tissue cells are most
- 23. Sources of free radicals
- 24. Reactive oxygen species Superoxide O2- Hydroxyl radical OH- Hydrogen peroxide H2O2
- 25. The effects of free radicals Positive: phagocytosis,
- 26. Antioxidative substances Enzymatic antioxidants Thioredoxin system
- 27. Example test Choose the effect which IS
- 28. Chemical injury mechanisms Direct cytotoxic effect
- 29. Outcomes of cell injury
- 30. Cell death Necrosis - death of a
- 31. Physiological apoptosis Frog plants amphibia human
- 32. Morphological signs of apoptosis Shrinkage of
- 33. Necrosis and apoptosis
- 34. Example test Give the correct definition of
- 35. Example test Which from the following is
- 36. Example test Every day, blood cells in
- 37. Cell Adaptation to Injury compensation of energy
- 38. Compensation of energy metabolism disturbance increased ATP
- 39. Protection of cells membranes activation of antioxidants
- 40. Compensation of water-ion disbalance activation of ion
- 41. Mechanisms of cell genome repair revealing and
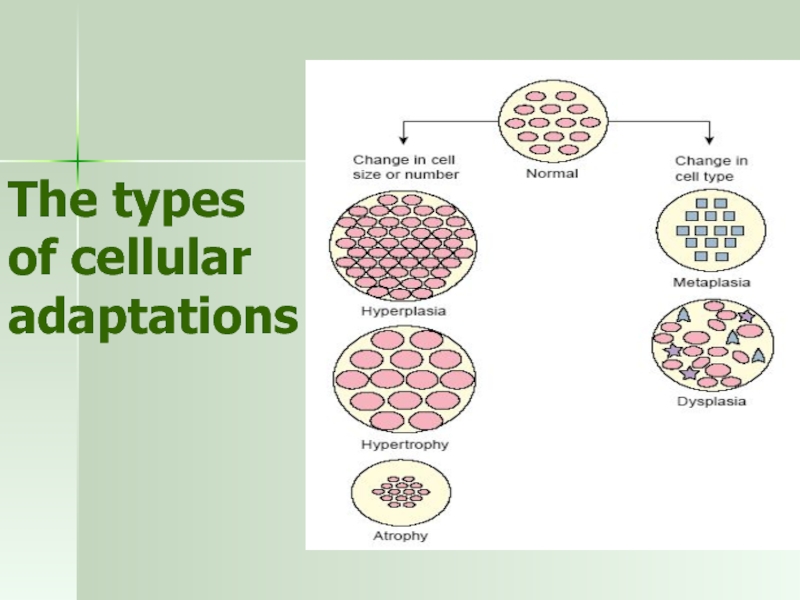
- 42. The types of cellular adaptations
- 43. Causes of atrophy decreased workload, loss
- 44. Hypertrophy increase in the size of cells
- 45. Hyperlasia increase in the number of cells
- 46. Metaplasia one adult cell type (epithelial
- 47. Dysplasia Deranged cell growth of a specific
- 48. Example test Cells may adapt to external
- 49. Example test Cells may adapt to external
- 50. Example test A 30-year-old man sustained a
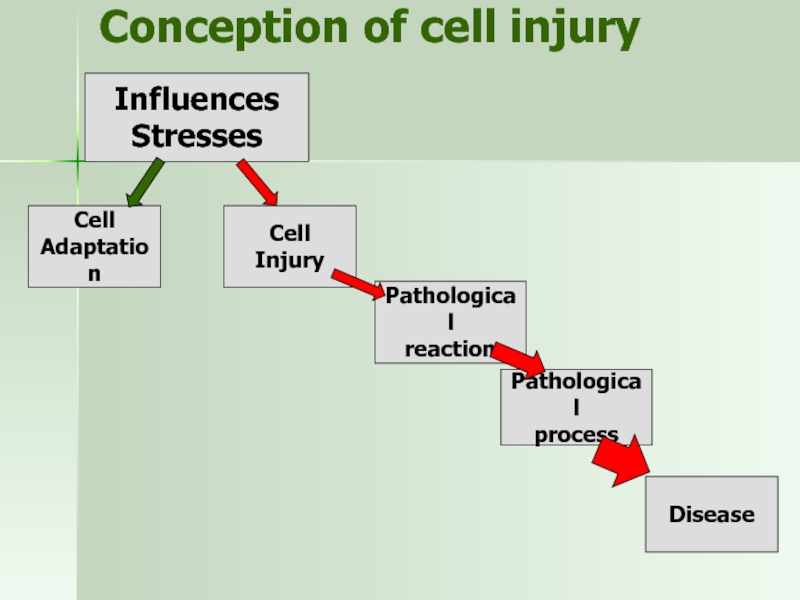
Слайд 2Conception of cell injury
Cell
Adaptation
Pathological
process
Disease
Pathological
reaction
Influences
Stresses
Cell Injury
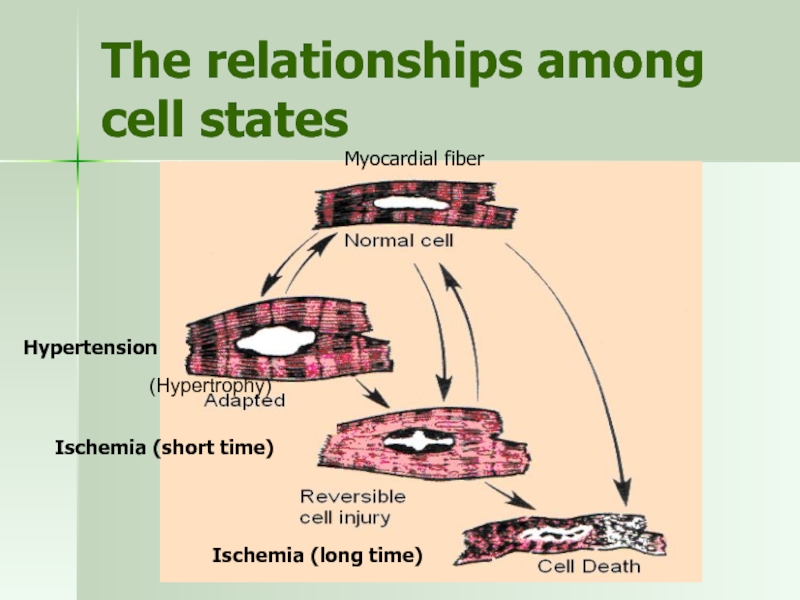
Слайд 3The relationships among cell states
(Hypertrophy)
Myocardial fiber
Hypertension
Ischemia (short time)
Ischemia (long time)
Слайд 4Injury From Physical Agents
Causes:
Mechanical forces - trauma.
Extremes of temperature –
Electrical injuries - disruption of nervous and cardiac impulses.
Ionizing radiation - radiation sickness, mutations, tumors.
Ultraviolet radiation- sunburn, ageing, skin cancers.
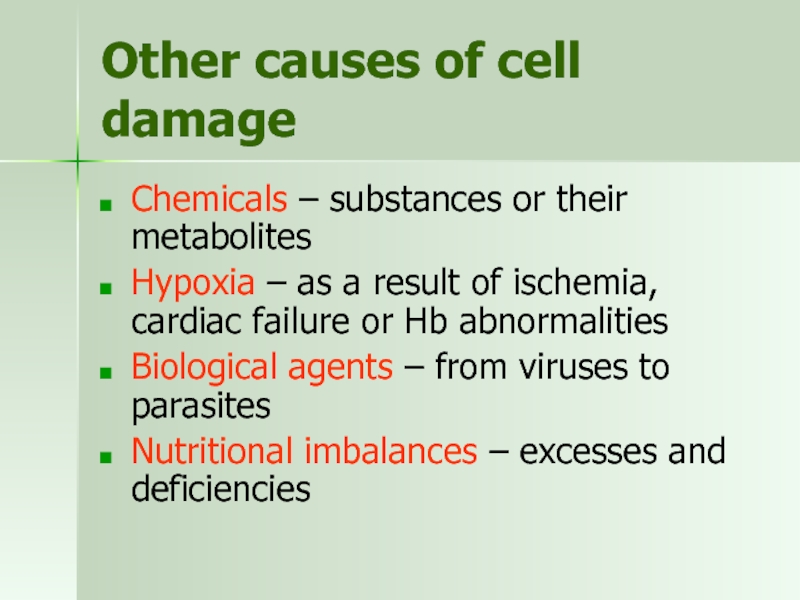
Слайд 5Other causes of cell damage
Chemicals – substances or their metabolites
Hypoxia –
Biological agents – from viruses to parasites
Nutritional imbalances – excesses and deficiencies
Слайд 6Types of Cell Injury
Acute
(strong irritants)
Chronic
(moderate irritants)
Reversible
(angina pectoris)
Irreversible
(myocardial infarction)
Non-specific
(hypoxic injury)
Specific
(immune
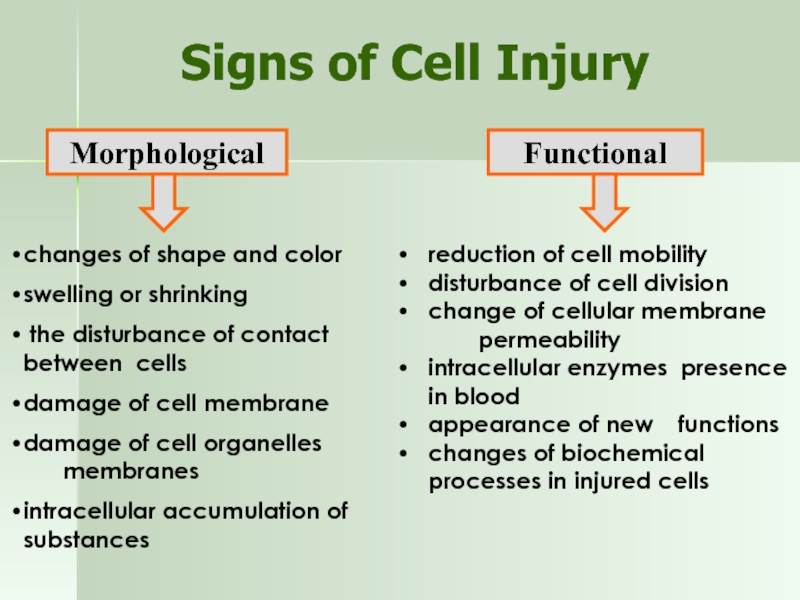
Слайд 7Signs of Cell Injury
Morphological
Functional
changes of shape and color
swelling or shrinking
the disturbance of contact between cells
damage of cell membrane
damage of cell organelles membranes
intracellular accumulation of substances
reduction of cell mobility
disturbance of cell division
change of cellular membrane permeability
intracellular enzymes presence in blood
appearance of new functions
changes of biochemical processes in injured cells
Слайд 8General Principles of Cell Injury
Factors, which determine cell response
Kind, severity, and
Type of affected cell, its prior state of health.
Major sensitive cell components:
integrity of cell membrane
aerobic respiration
protein synthesis
genetic integrity
Слайд 9Major Processes of Cell Injury
Decreased ATP production
Injury by toxic oxygen radicals
Disturbances
Mitochondrial injury
Слайд 10Example test
Chose the example of specific cell injury from listed below:
myocardial
intestinal epithelial injury due to bacterial toxins
immune hemolysis of RBC
liver cell injury due to chemicals
skin damage due to mechanical trauma
Слайд 11Example test
Which factors determine the type of cell’s response to injuring
kind of injuring factor
injuring factor severity and time of duration
prior state of the cell
type of the affected cell
all is correct
Слайд 12Example test
Patient was made blood biochemical test in order to confirm
cell’s membrane damage
damage to plasma membrane sodium pump
depletion of ATP store in the cell
nonperoxidative mitochondrial injury
disturbance of cells aerobic respiration
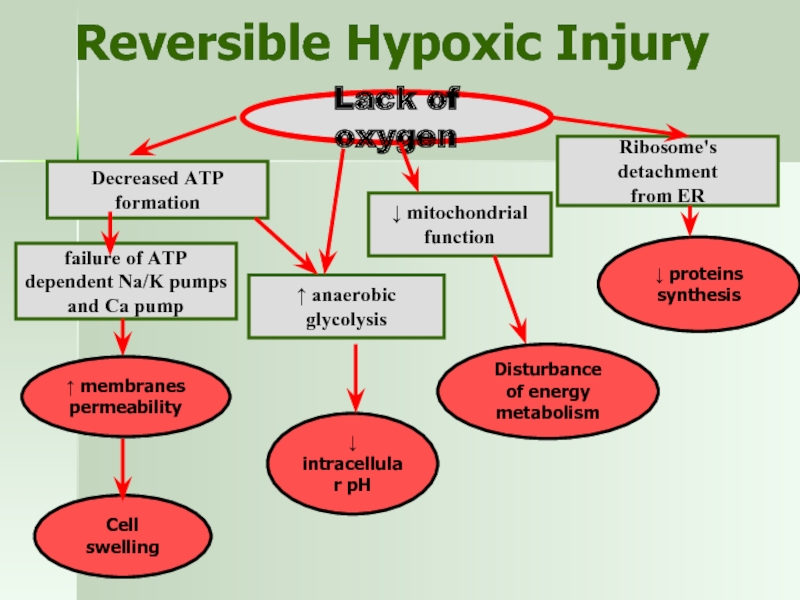
Слайд 14Reversible Hypoxic Injury
Lack of oxygen
Decreased ATP formation
failure of ATP
dependent Na/K
and Ca pump
Cell swelling
↓ mitochondrial
function
Disturbance
of energy metabolism
Ribosome's detachment
from ER
↓ proteins synthesis
↑ anaerobic glycolysis
↓ intracellular pH
↑ membranes
permeability
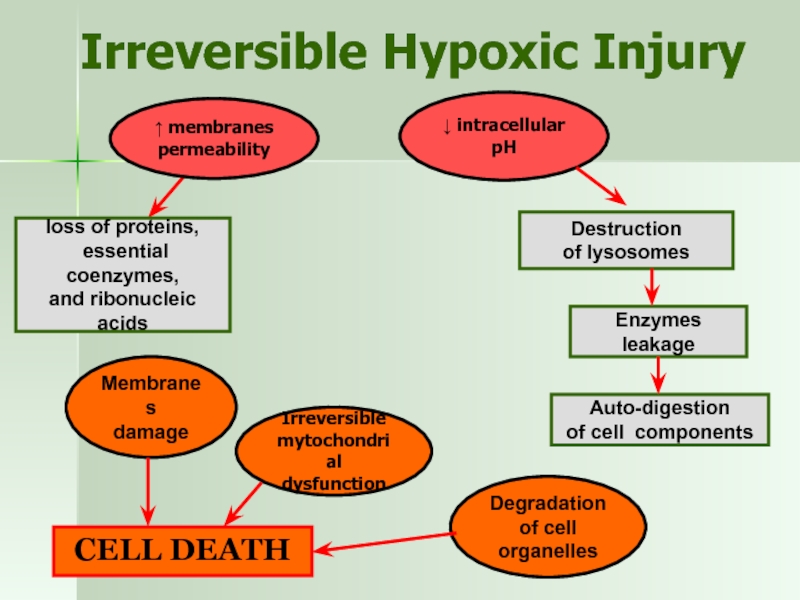
Слайд 15Irreversible Hypoxic Injury
↑ membranes
permeability
Irreversible
mytochondrial
dysfunction
↓ intracellular pH
loss of proteins,
essential
and ribonucleic acids
Destruction
of lysosomes
Enzymes leakage
Auto-digestion
of cell components
Degradation
of cell organelles
Membranes
damage
CELL DEATH
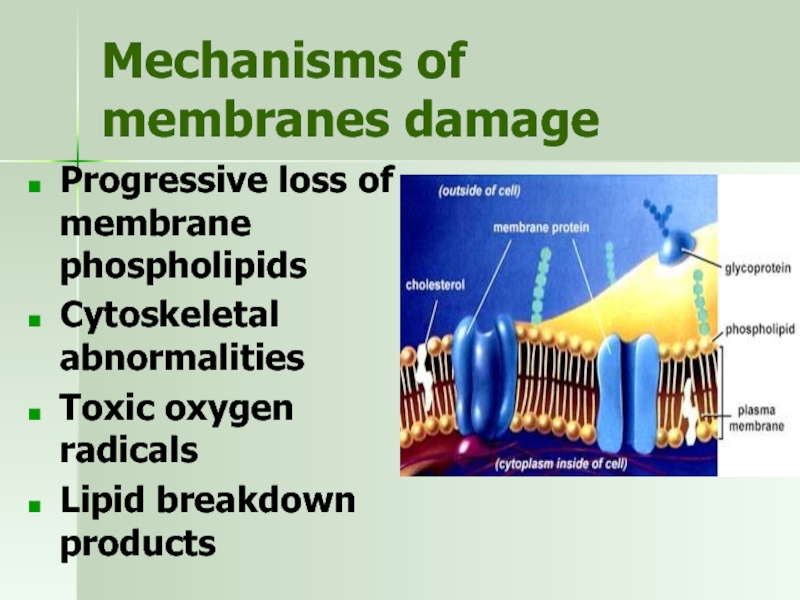
Слайд 16Mechanisms of membranes damage
Progressive loss of membrane phospholipids
Cytoskeletal abnormalities
Toxic oxygen radicals
Lipid breakdown products
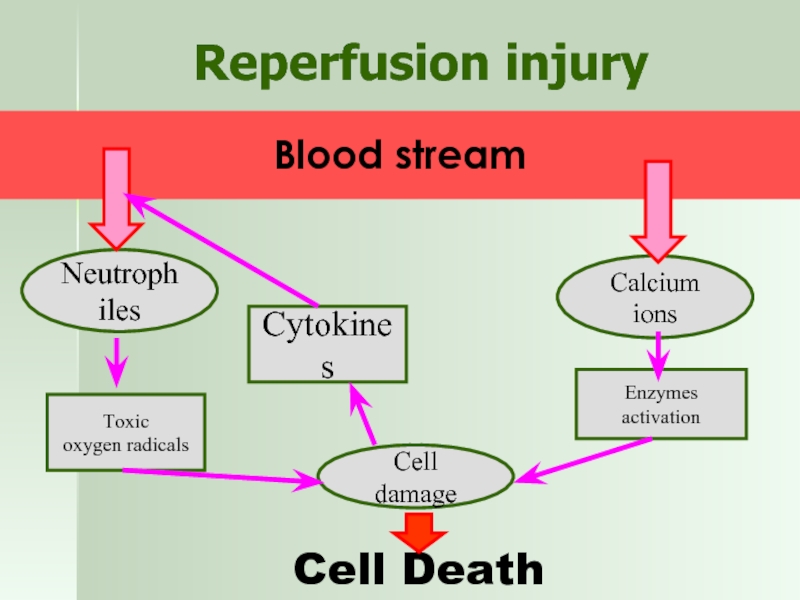
Слайд 17Reperfusion injury
Neutrophiles
Calcium ions
Blood stream
Toxic
oxygen radicals
Cell damage
Cytokines
Enzymes activation
Cell Death
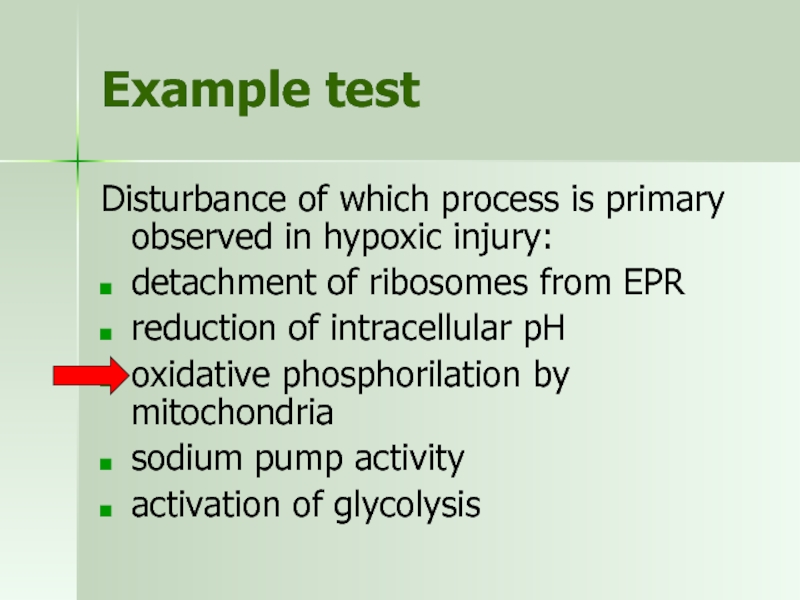
Слайд 18Example test
Disturbance of which process is primary observed in hypoxic injury:
detachment
reduction of intracellular pH
oxidative phosphorilation by mitochondria
sodium pump activity
activation of glycolysis
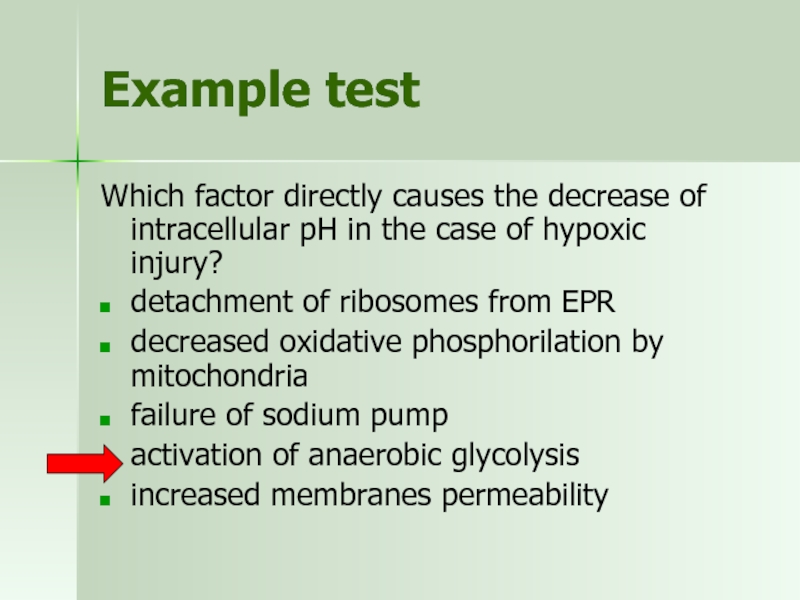
Слайд 19Example test
Which factor directly causes the decrease of intracellular pH in
detachment of ribosomes from EPR
decreased oxidative phosphorilation by mitochondria
failure of sodium pump
activation of anaerobic glycolysis
increased membranes permeability
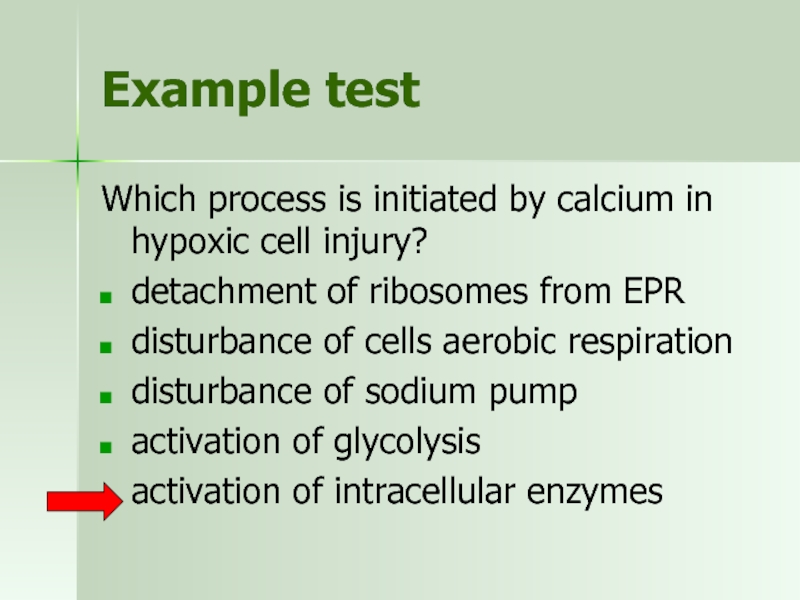
Слайд 20Example test
Which process is initiated by calcium in hypoxic cell injury?
detachment
disturbance of cells aerobic respiration
disturbance of sodium pump
activation of glycolysis
activation of intracellular enzymes
Слайд 21Example test
Which process determines irreversibility of hypoxic injury?
inability to reverse mitochondrial
damage to plasma membrane sodium pump
inability to re-start protein synthesis
extremely low pH
depletion of ATP store in the cell
Слайд 22Example test
Which tissue cells are most sensitive to hypoxic injury?
skeletal muscles
smooth
myocardial cells
brain cells
liver cells
Слайд 25The effects of free radicals
Positive: phagocytosis, energy production
Negative:
Lipid peroxidation of membranes
Nonperoxidative
Lesions in DNA
Oxidation of proteins
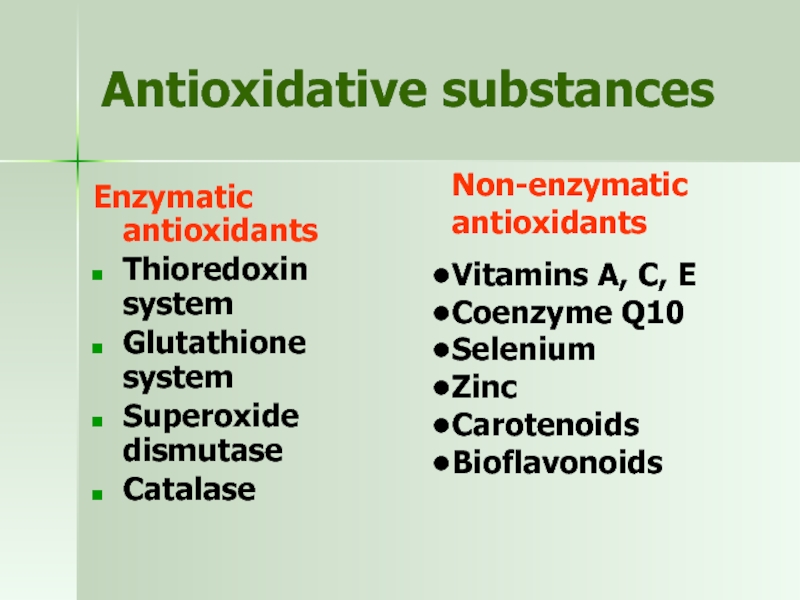
Слайд 26Antioxidative substances
Enzymatic antioxidants
Thioredoxin system
Glutathione system
Superoxide dismutase
Catalase
Non-enzymatic antioxidants
Vitamins A, C, E
Coenzyme Q10
Selenium
Zinc
Carotenoids
Bioflavonoids
Слайд 27Example test
Choose the effect which IS NOT directly caused by free
lipid peroxidation of membranes
nonperoxidative mitochondrial injury
disturbance of cells aerobic respiration
DNA lesions
cross-linking of proteins
Слайд 28Chemical injury mechanisms
Direct cytotoxic effect
mercury damages GIT and kidneys
cyanide breaks
Conversion to reactive toxic metabolites
free radicals
lipid peroxodation.
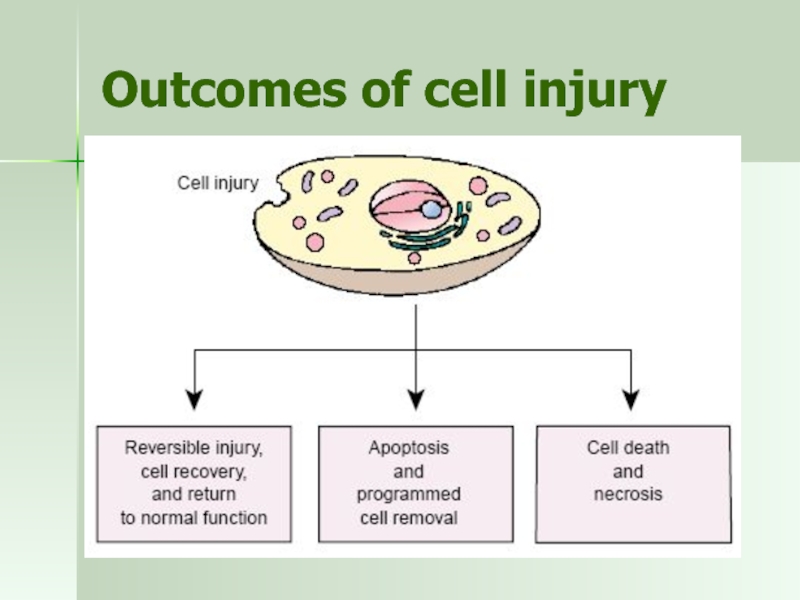
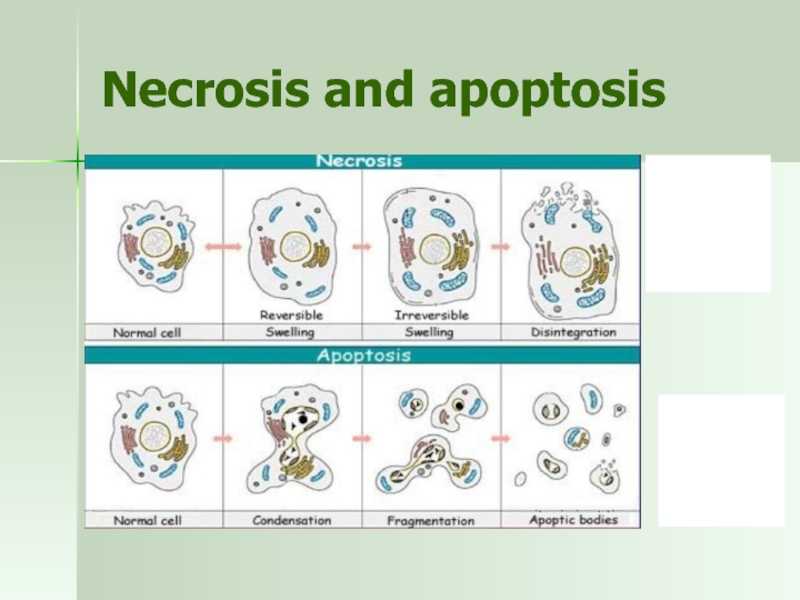
Слайд 30Cell death
Necrosis - death of a cell due to external forces
Apoptosis
gene-related
energy dependent
initiated by external and internal influences)
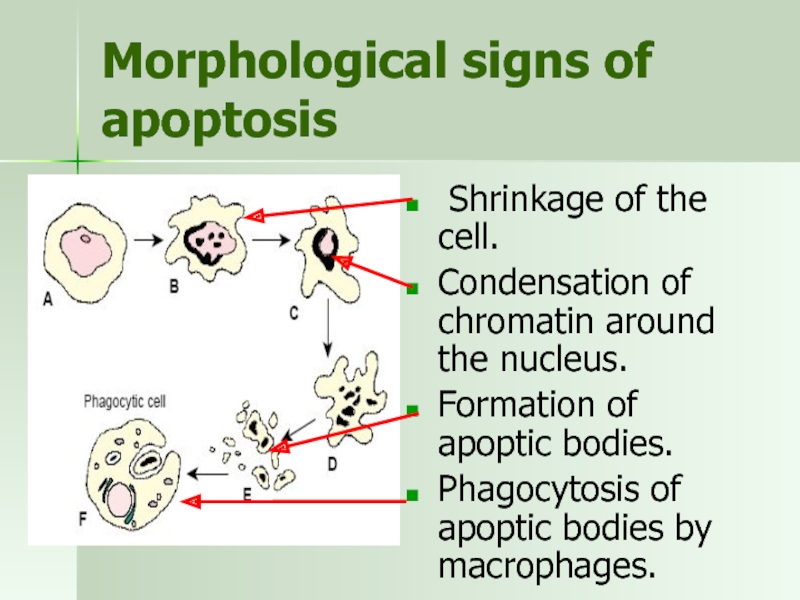
Слайд 32Morphological signs of apoptosis
Shrinkage of the cell.
Condensation of chromatin around
Formation of apoptic bodies.
Phagocytosis of apoptic bodies by macrophages.
Слайд 34Example test
Give the correct definition of apoptosis. Apoptosis is…
a process of
a programmed cell death
a death of the cell after injuring factor influence
a cell’s death as a result of enzymes action
an irreversible cell injury
Слайд 35Example test
Which from the following is the most typical morphological sign
condensation of nucleus and cytoplasm
presence of inflammatory reaction
compensatory increase of DNA-synthesis
swelling of mitochondrions
increase of cell’s size
Слайд 36Example test
Every day, blood cells in our body become senescent and
due to necrosis of heart muscle
due to apoptosis of heart muscle
due to atrophy of heart muscle
due to swelling of heart muscle
due to disturbances in calcium metabolism
Слайд 37Cell Adaptation to Injury
compensation of energy metabolism disturbance
protection of cells membranes
compensation
repair of cell genome
Слайд 38Compensation of energy metabolism disturbance
increased ATP formation, transport and effectiveness of
increase of enzymes activity taking part in reduction-oxidation reactions
decrease of cell’s functional activity and protein synthesis
Слайд 39Protection of cells membranes
activation of antioxidants action
activation of cells buffer system
activation
activation of cellular structures reparation
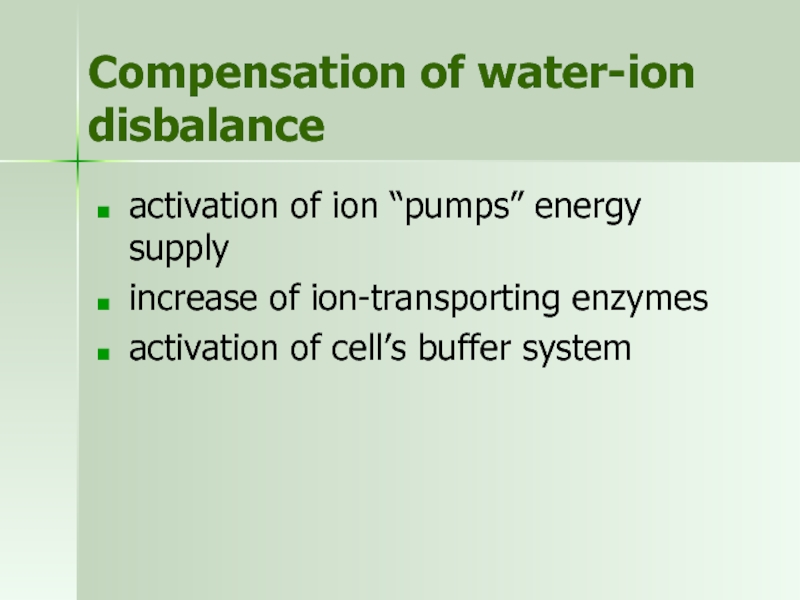
Слайд 40Compensation of water-ion disbalance
activation of ion “pumps” energy supply
increase of ion-transporting
activation of cell’s buffer system
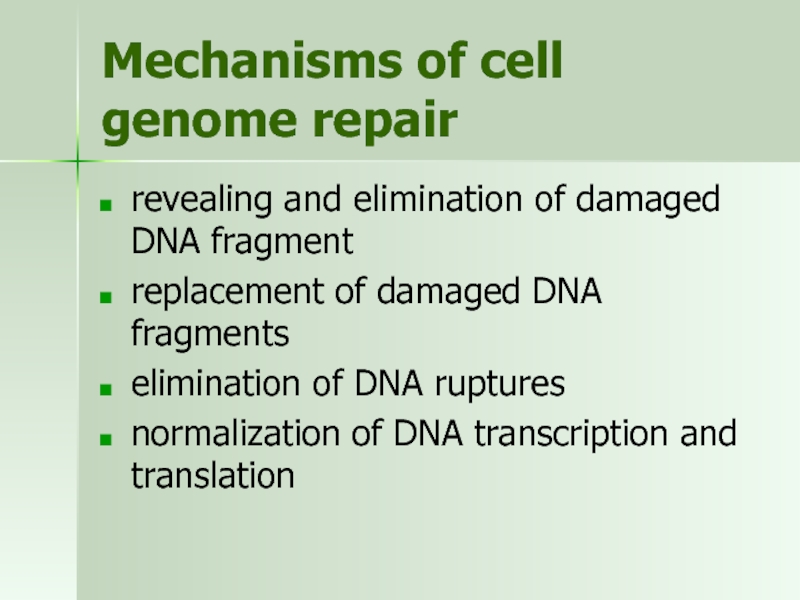
Слайд 41Mechanisms of cell genome repair
revealing and elimination of damaged DNA fragment
replacement
elimination of DNA ruptures
normalization of DNA transcription and translation
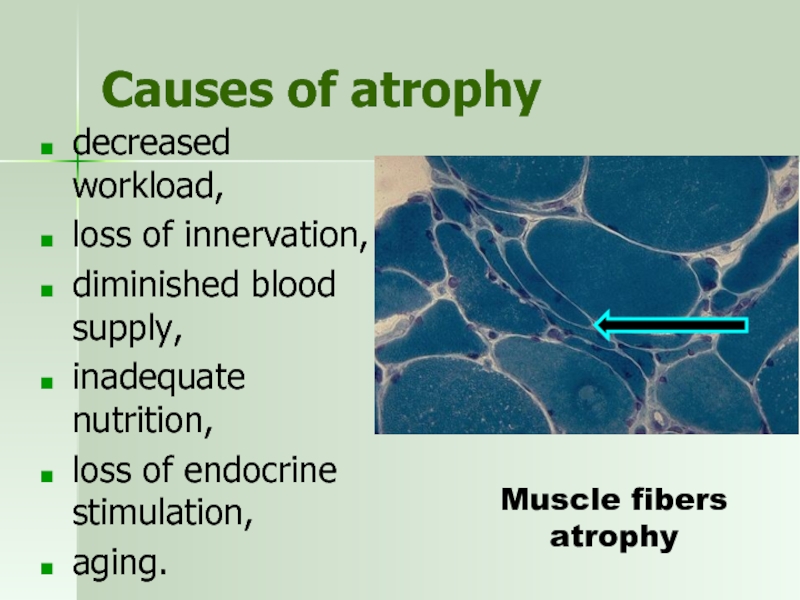
Слайд 43Causes of atrophy
decreased workload,
loss of innervation,
diminished blood supply,
inadequate
loss of endocrine stimulation,
aging.
Muscle fibers atrophy
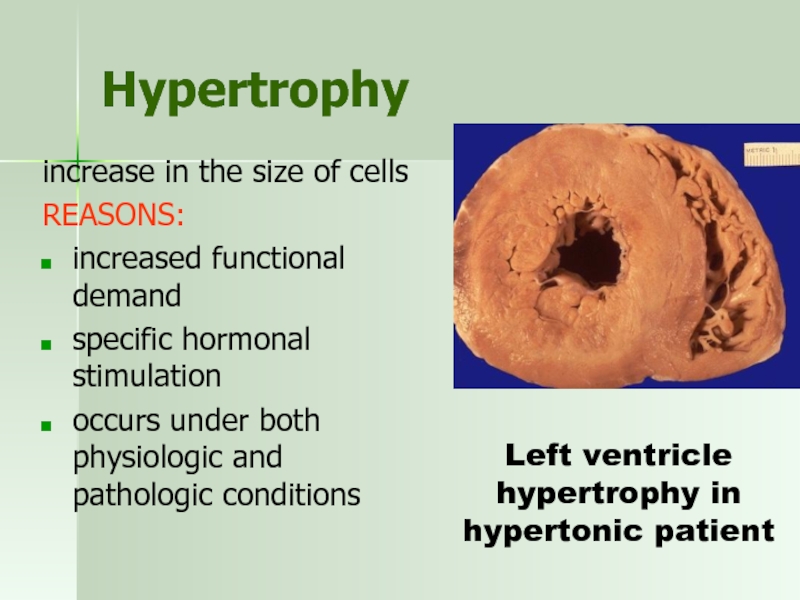
Слайд 44Hypertrophy
increase in the size of cells
REASONS:
increased functional demand
specific hormonal
occurs under both physiologic and pathologic conditions
Left ventricle hypertrophy in hypertonic patient
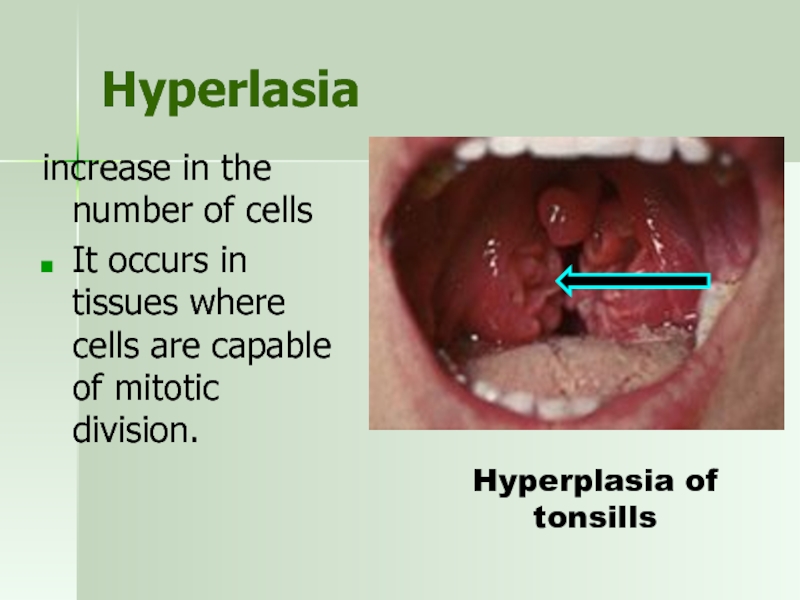
Слайд 45Hyperlasia
increase in the number of cells
It occurs in tissues where
Hyperplasia of tonsills
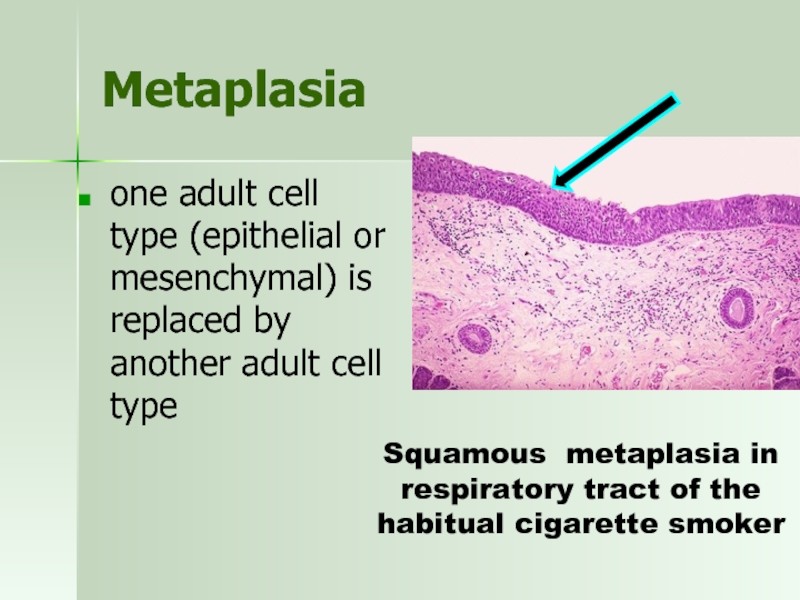
Слайд 46Metaplasia
one adult cell type (epithelial or mesenchymal) is replaced by
Squamous metaplasia in respiratory tract of the habitual cigarette smoker
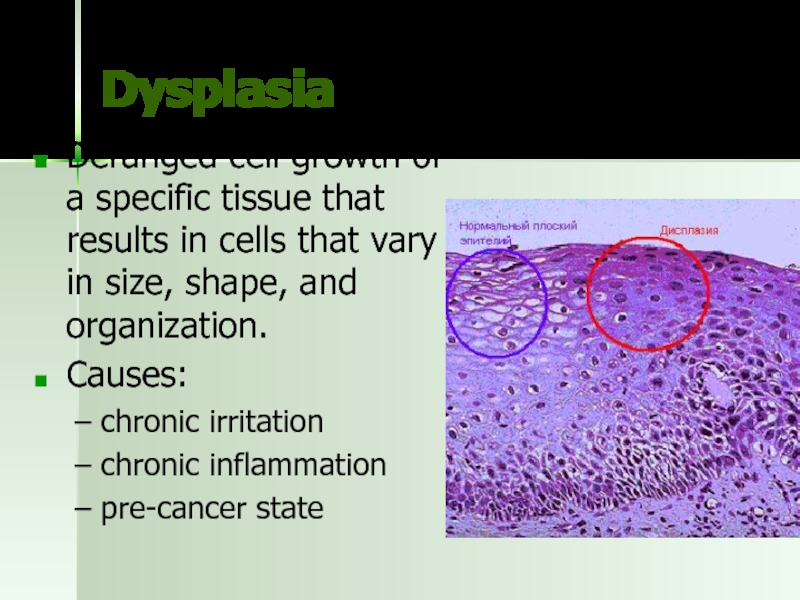
Слайд 47Dysplasia
Deranged cell growth of a specific tissue that results in cells
Causes:
chronic irritation
chronic inflammation
pre-cancer state
Слайд 48Example test
Cells may adapt to external and internal stimuli by undergoing
hypertrophy
atrophy
hyperplasia
metaplasia
dysplasia
Слайд 49Example test
Cells may adapt to external and internal stimuli by undergoing
hypertrophy
atrophy
hyperplasia
metaplasia
dysplasia
Слайд 50Example test
A 30-year-old man sustained a fracture of his leg 2
inadequate nutrition
loss of innervation
loss of endocrine stimulation
decreased workload
diminished blood supply