- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Basics in organization of family medicine in Ukraine and Worldwide презентация
Содержание
- 1. Basics in organization of family medicine in Ukraine and Worldwide
- 2. First term primary health care (PHC) is
- 3. 2. Charlestown center of a family medicine
- 4. 3. Family medicine center Hamptons. USA
- 6. Family medicine in the world continues to
- 7. Were created powerful international association of
- 8. World Organization of National Colleges, Academies -
- 9. The main aim of Wonca is the
- 10. Workgroups Education (EURACT) Research Environment Ethical Issues
- 11. General practice / family medicine is an
- 13. (European Wonca, 2005) Competence of a
- 14. (European Wonca, 2005) Competence of a
- 15. 4. A comprehensive approach: - control disease
- 16. Characteristics of general practice - family medicine:
- 17. Characteristics of general practice - family medicine:
- 18. 5. Responsible for the consistency and continuity
- 19. 8. Solves both the problem of
- 20. Diagnostic techniques include - interviewing the
- 21. After collecting data, the FD: - arrives
- 22. Educational program and program of research in general practice / family medicine
- 23. Models of the family doctor practice in
- 24. USA MEDICINE The share of GP is
- 25. MEDICINE in CANADA The relationship between family
- 26. MEDICINE in CANADA FD spend their morning
- 27. MEDICINE in United Kingdom The share of
- 28. France medicine This system is ranked as
- 29. The main problems of family medicine To
Слайд 1“Basics in organization of family medicine in Ukraine and Worldwide”
ZSMU
Department of
Слайд 2First term primary health care (PHC) is found in scientific studies
In May 1978 at the International Conference on PHC, held in Alma-Ata, the World Health Organization (WHO) first defines the concept of PHC, which indicated the priority PHC and affected the national system of health care around the world.
Слайд 6Family medicine in the world continues to develop.
Today, the development of
Switching health care systems in many European countries on the principles of a family medicine has proved its efficiency and economic benefits.
Слайд 7Were created powerful
international association of family doctors WONCA and regional
They periodically hold international conferences and congresses where new achievements and successes of family medicine in the world are illuminated.
Слайд 8World Organization of National Colleges, Academies - Wonca
World Organization of
consists of national colleges, academies and organizations of general practitioners / family doctors.
Now it counts about 300,000 members representing 126 organizations from 102 countries.
WONCA President
Prof Richard G Roberts
WONCA Еurope President
Anthony Mathie
Слайд 9 The main aim of Wonca is the improvement of living standards
raising service standards in family medicine,
promoting intensive exchange of information,
support scientific and clinical research, and
the development of educational standards.
Слайд 10Workgroups
Education (EURACT)
Research
Environment
Ethical Issues
Informatics
Women and Family Medicine
Mental Health
High-quality and safe care
Rural Practice
WICC
Special Interest Groups
Cancer and Palliative Care
Difficulties in Health
Geriatric help
Medicine of migration and tourism
international health
International Movement of family doctors Vasco da Gama includes 32 countries
Purpose:
Holding conferences and exchange programs for young family doctors
Identifying problems of young family doctors and finding their solutions
Participation in the development of measures to improve the quality of education
cooperation with all WONCA
Institutions.
Слайд 11General practice / family medicine is an academic and scientific discipline
Family Medicine is a separate discipline rather than a set of parts of other disciplines because it requires its own scientific base.
Research is an integral part of any scientific discipline (they are also part of family medicine).
(European Wonca, 2002, 2005)
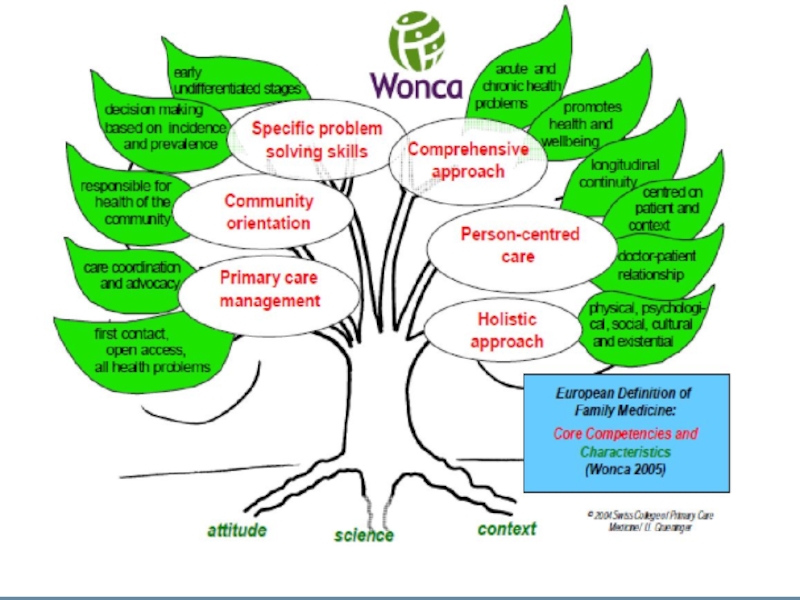
Слайд 13(European Wonca, 2005)
Competence of a GP – Family doctor
1. Management
- first contact,
- open and unrestricted access,
help with all the health problems
effective use of resources through the coordination of assistance and cooperation with other primary care professionals,
managing the interface between general and specific help,
take the role of defender of the patient when needed, ie , to protect patients from harm that may be inflicted as a result of unnecessary investigation and treatment
Слайд 14(European Wonca, 2005)
Competence of a GP – Family doctor
2. Patient-centered
- focused on the individual, his / her family,
- establishing a long relationship,
- effective communication,
long continuous assistance
3. Addressing specific problems :
making specific decisions,
the prevalence of certain accident must cope simultaneously considering individual approach with both acute and chronic health problems with at all stages,
a wide range of complaints and illnesses, comorbidities
Слайд 154. A comprehensive approach:
- control disease stage differentiation diagnosis,
- risk
- health promotion and prevention as important as cure,
- care and palliative care
5. Targeting Society: responsible for public health
6. Holistic approach:
health problems in their biomedical, psychological, social, culture and
existential dimension
Слайд 16Characteristics of general practice - family medicine:
Available for the entire population
2. Ensures efficient use of resources of the entire health system by coordinating the efforts of various specialists, as well as by patients' rights when necessary;
Слайд 17Characteristics of general practice - family medicine:
3. Provides individual assistance to
4. Has a unique opportunity consulting all family members, regardless of age, examines the state of health of the family in several generations. Based on effective relationship between doctor and family.
Слайд 185. Responsible for the consistency and continuity of care,
6. Has its own unique type of clinical thinking and decision-making path, which is determined by statistical and epidemiological indicators of health and illness;
7. Solves the problem of diseases in preclinical often non-differentiable stage;
Слайд 19
8. Solves both the problem of acute and chronic diseases;
9. Personalized
10. Responsible for the quality and effectiveness of care provided to the individual as well as to the community;
11. Solve health problems in their physical, psychological, social, cultural and existential definitions;
Слайд 20Diagnostic techniques include
- interviewing the patient to collect information on
- prior medical history and other health details, followed by a physical examination.
Many FDs are trained in basic medical testing:
interpreting results of blood or other patient samples,
electrocardiograms, or x-rays
More complex and time-intensive diagnostic procedures are usually obtained by referral to specialists, due to either special training with a technology, or increased experience and patient volume that renders a risky procedure safer for the patient.
Слайд 21After collecting data, the FD:
- arrives at a differential diagnosis and, with the
formulates a plan including components of further testing,
specialist referral,
medication, therapy, diet or life-style changes
patient education, and follow up results of treatment.
FD also counsel and educate patients on safe health behaviors, self-care skills and treatment options, and provide screening tests and immunizations
Слайд 23Models of the family doctor practice in the world
Private Practice: physician
2. Group practice when several doctors grouped, saving money, organize interchangeably among themselves, to some specialization of medical practice.
3. Medical centers (Scandinavian model), which is actually a clinic of a GP, sometimes a hospital for the elder patients.
Слайд 24USA MEDICINE
The share of GP is nearly 40%
Every year on health
Average salary of a family doctor is from 44 to 60 thousand dollars a year.
At 49.7 - 60-hour weeks (47.4 weeks per year) FD takes about 175-182 patients and makes 27 visits to hospital.
Слайд 25MEDICINE in CANADA
The relationship between family doctors and narrow specialists is
3 of 4 Canadians surveyed prefer to get any medical help from a family doctor in the first place.
In a small town with a population of about 4,000 people there are surgeon, internist and 6 competent GP.
They work as well in a local hospital with capacity of 60-80 beds.
Слайд 26MEDICINE in CANADA
FD spend their morning in the hospital after 12
When hospitalization is necessary, FD assists with helping a patient during the whole period of staying in the hospital.
Usually FD has 60 or more hours a week, visiting 182 patients.
Слайд 27MEDICINE in United Kingdom
The share of FD is about 70%
Every citizen
Each FD usually gives more than 8 000 consultations per year
Approximately 85% of the consultations held in the office of the FD, 5% and 10% home visit, and by phone
The patient usually can not be consulted by a doctor of secondary level (eg, hospital), without referring to a FD in a first place.
About 13% of the population each year seek treatment in inpatient institutions, 50% of which require emergency measures.
Слайд 28France medicine
This system is ranked as №1 in the WHO rating
FD
Any medical care, except emergency, performed only after the patient’s visit to FD
It’s only possible to buy medicines prescribed by a FD
Only students with the highest level of success can become narrow specialists, others are FD
Слайд 29The main problems of family medicine
To create algorithms, based on scientific
To develop research protocols
To conduct research projects that reflect the nature and problems of discipline.