- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Anatomy of bones in childhood презентация
Содержание
- 1. Anatomy of bones in childhood
- 2. The Anatomical and physiological particularities of bone
- 3. The First kernel of the large
- 4. After birth the size of skeleton increases
- 5. The fetus and newborn have a
- 6. The regeneration and healing processes
- 7. Periosteal tissues (a bone cover) provide
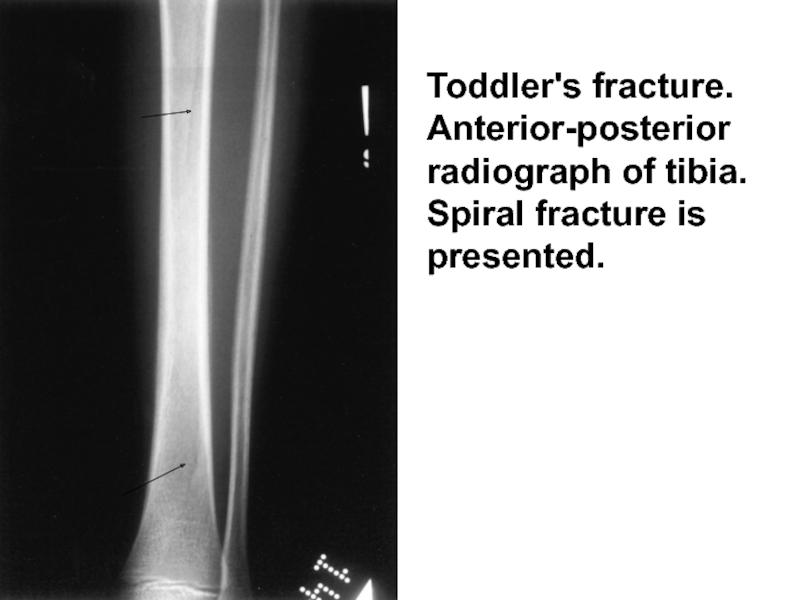
- 8. Toddler's fracture. Anterior-posterior radiograph of tibia. Spiral fracture is presented.
- 9. 3 parameters associated with bone tissue
- 10. The Short Notion about kernels of the
- 11. Wrist X-Ray in a 1 yr old
- 12. The bone, growth, teeth and passport
- 13. The skeleton examination and the most important semiotics of bone diseases in children.
- 14. Estimating the bone system the next clinical
- 15. The most common complaint is the
- 16. Complaints "Pains of the growing" are
- 17. Complaints The Flat foot Pains disturb
- 18. Complaints The most serious pain symptom
- 19. The big diagnostic importance has combination of
- 20. The big diagnostic importance has combination of
- 21. Visual inspection & palpation
- 23. In newborns and early infants the skull
- 24. During the difficult labor the skull bone
- 25. The pathological craniosynostosis This newborn girl
- 26. Three-week-old infant with premature sagittal craniosynostosis.
- 27. The kraniotabes is unusual softness of infantile
- 28. The Cephalhematoma is a wide-spreaded delivery trauma
- 29. The Neck.
- 30. Congenital torticollis Left photo is an example
- 31. The chest
- 32. In small children the thorax has rounded
- 33. The place of diaphragm fixing inside thorax
- 34. Other thorax deformations are typical for
- 35. Other thorax deformations The insulated
- 36. The spine.
- 37. Spinal curves In newborns the spine is
- 38. The spine deviations aside are never
- 39. Structural changes in idiopathic
- 40. The limbs and tubular bones.
- 41. In young children the tubular bones
- 42. Limb` deformations It is known that multiple
- 43. Skeleton` deformations If the deformations of skeleton
- 45. Often the palm abnormalities are symptoms of
- 46. The symptoms of innate displastic/dislocative hip (DDH) in infants and children.
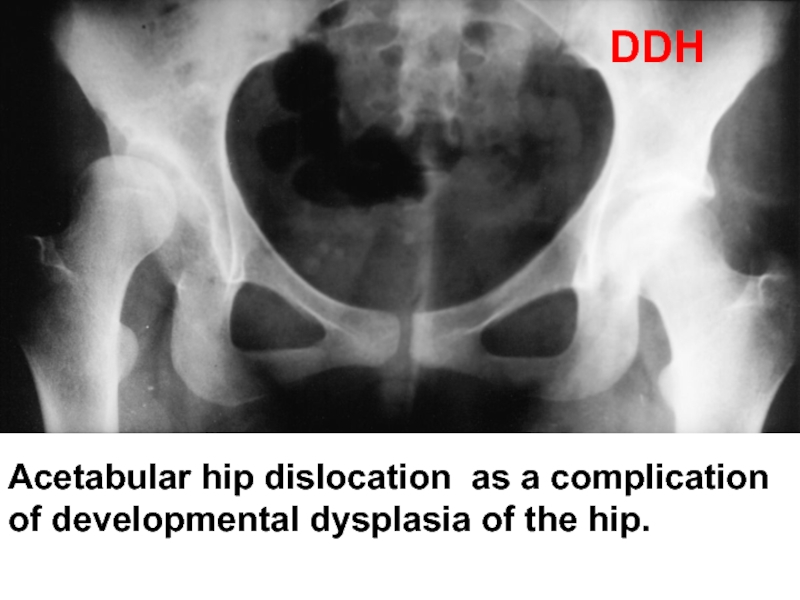
- 47. Acetabular hip dislocation as a complication of developmental dysplasia of the hip. DDH
- 48. DDH evaluation Limitation of
- 49. DDH evaluation Barlow test is the most
- 50. DDH evaluation The Ortolani test
- 51. DDH evaluation An asymmetric
- 52. DDH evaluation In older or
- 53. The teeth and teeth formula in children. The semiotics of teeth diseases.
- 54. The teeth are a skin appurtenance
- 55. The appearing of baby teeth (or
- 56. A 12 -15 mo old child as
- 57. A 18 - 20 mo old child
- 58. Unlike infantile teeth a succedaneous (secondary) teeth
- 59. The incisors are changing at age
- 60. What is the “difficult" teething?
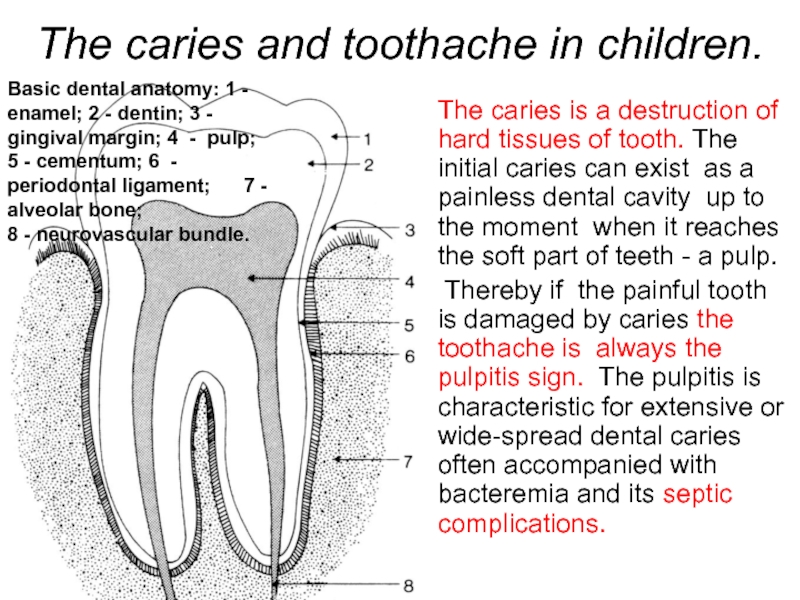
- 61. The caries and toothache in children. The
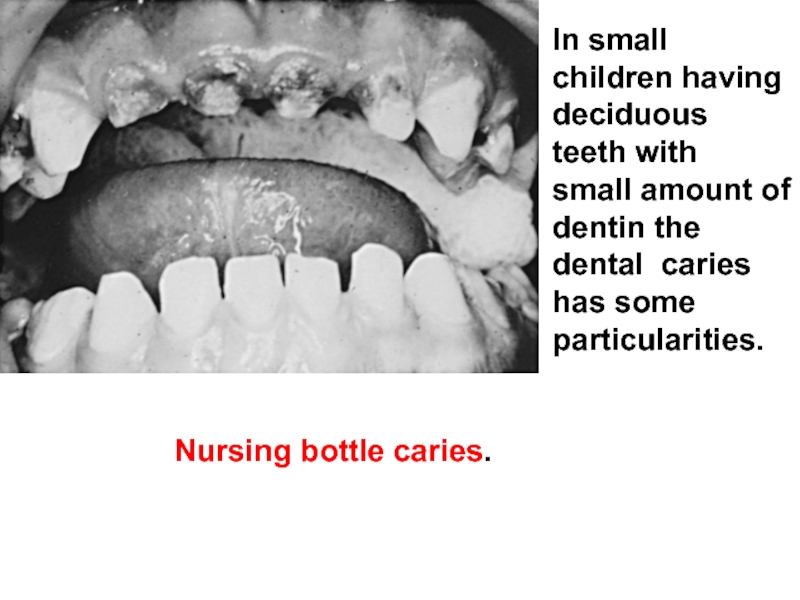
- 62. In small children having deciduous teeth with
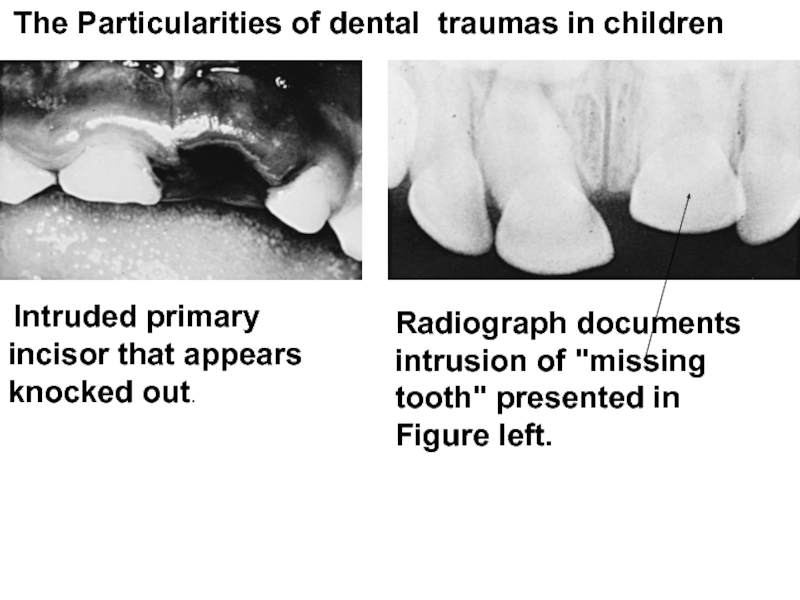
- 63. The Particularities of dental traumas in
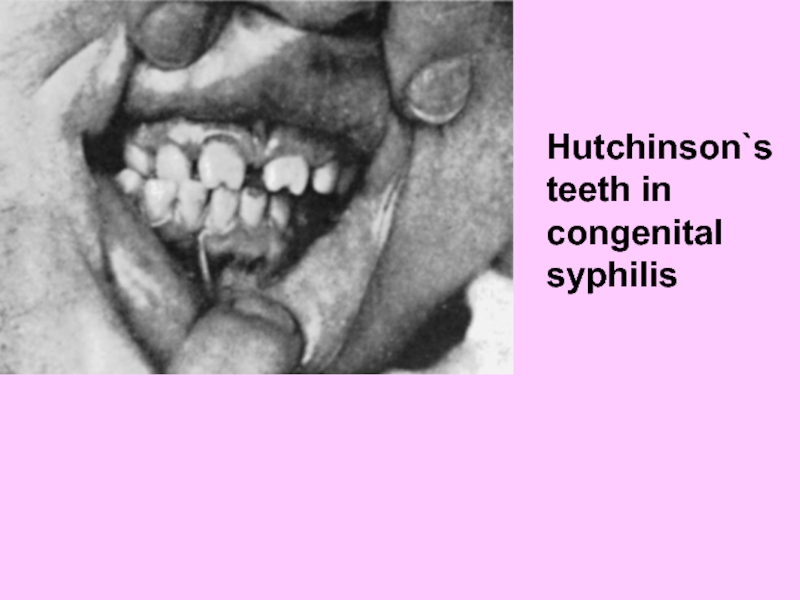
- 64. Hutchinson`s teeth in congenital syphilis
- 65. The features of muscles in children
- 66. Some features of muscles The hystomorfological studies
- 67. The skeleton muscles clinical investigation The complaints
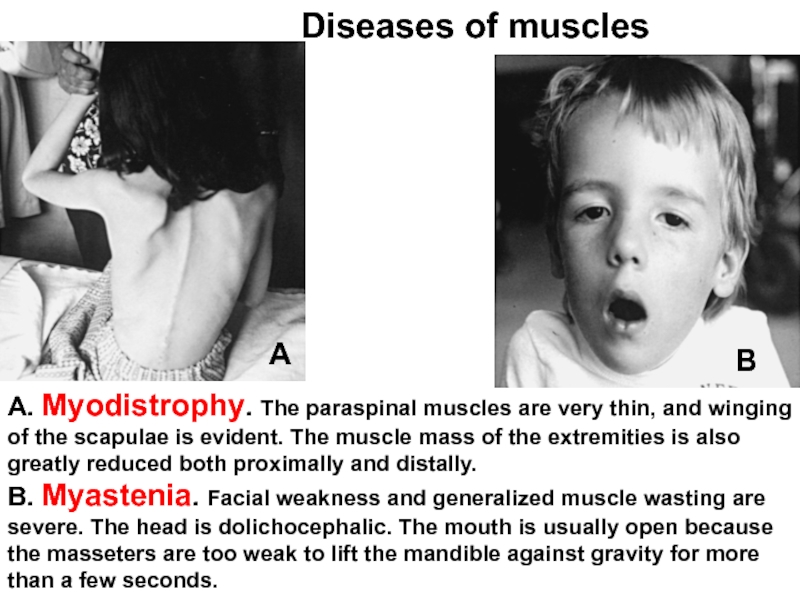
- 68. А. Myodistrophy. The paraspinal muscles are
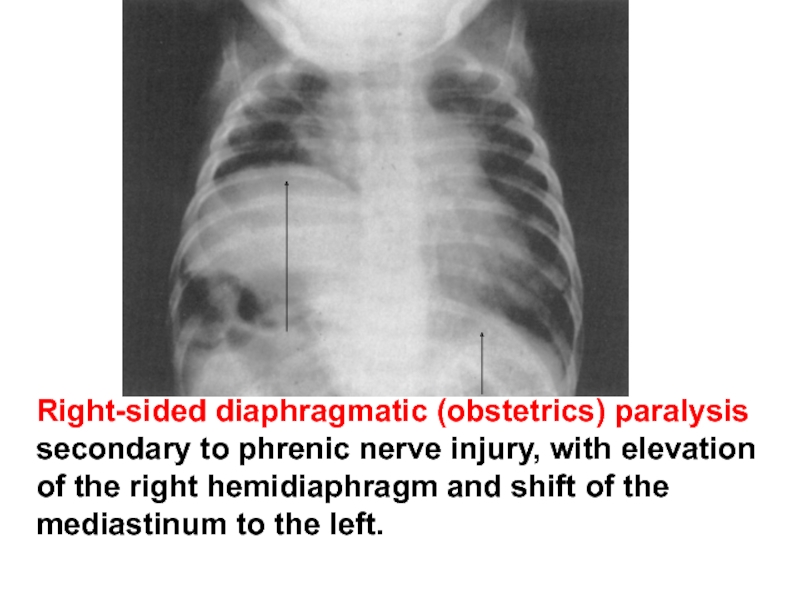
- 69. Right-sided diaphragmatic (obstetrics) paralysis secondary to phrenic
- 70. Thanks for your attention!
Слайд 1Background of the lecture
Anatomy of bones in childhood
When do the bones
Bones and teeth in Biological age evaluation.
4. The skeleton examination. The most important semiotics of bone diseases in children.
The skull
The Neck.
The chest
The spine.
The limbs and tubular bones.
The symptoms of innate displastic/dislocative hip (DDH).
5. The teeth and teeth formula in children. The semiotics of teeth diseases.
6. The features of muscles in children
Слайд 2The Anatomical and physiological particularities of bone and muscular systems &
Слайд 3 The First kernel of the large bone ossification appears in
Слайд 4After birth the size of skeleton increases very intensively according the
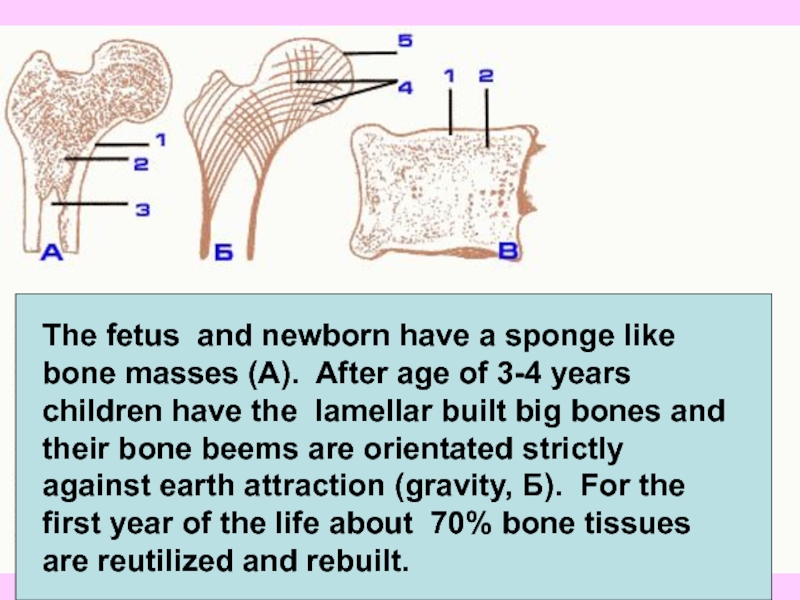
Слайд 5
The fetus and newborn have a sponge like bone masses (A).
Слайд 6 The regeneration and healing processes in child bones occur
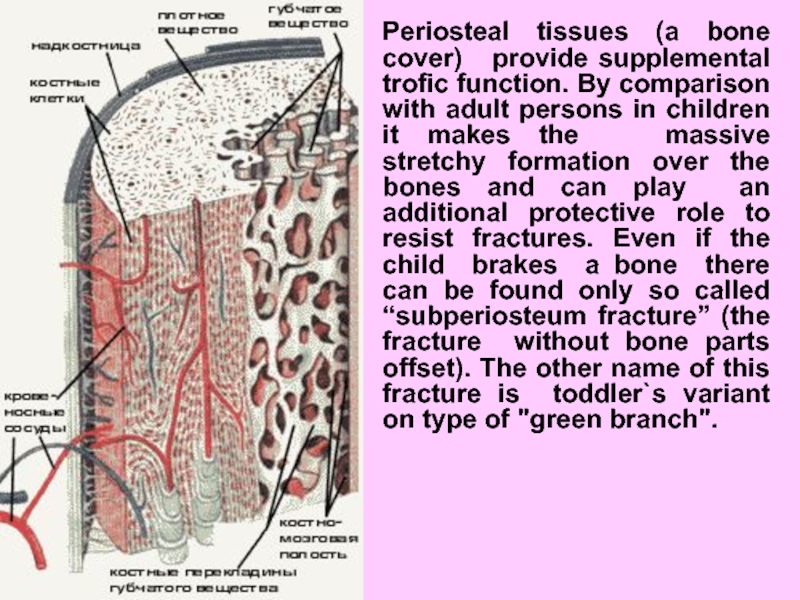
Слайд 7Periosteal tissues (a bone cover) provide supplemental trofic function. By
Слайд 9 3 parameters associated with bone tissue development and biochemicaly same
The Biological age can be evaluated on:
child growth (body length or height),
terms of bone ossification (ossification centers appearing),
terms of dentition (appearing of constant teeth).
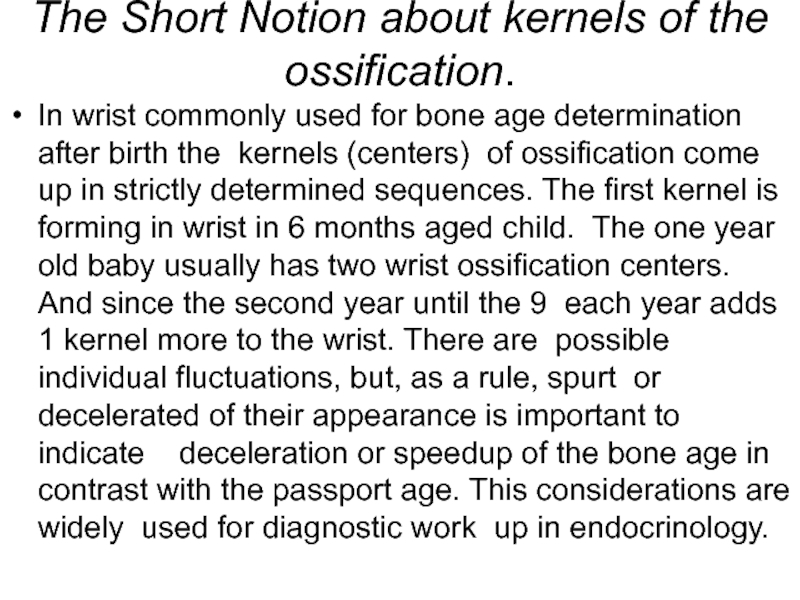
Слайд 10The Short Notion about kernels of the ossification.
In wrist commonly used
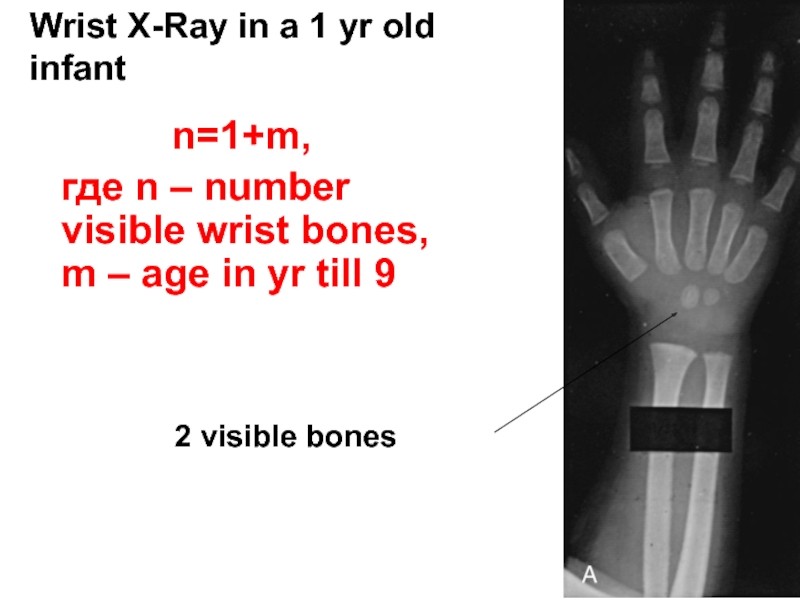
Слайд 11Wrist X-Ray in a 1 yr old infant
2 visible bones
где n – number visible wrist bones, m – age in yr till 9
Слайд 12 The bone, growth, teeth and passport age coincidence is indicative
Слайд 14Estimating the bone system the next clinical approaches are useful:
Complaints
Additional questioning
Objective methods:
visual inspection
palpation
bone percussion sometimes
Instrumental (mainly X-Ray) investigations.
Слайд 15 The most common complaint is the pain. Most often the
Слайд 16Complaints
"Pains of the growing" are typical bed time accidental and self
Слайд 17Complaints
The Flat foot Pains disturb some children commonly in shank and
Слайд 18Complaints
The most serious pain symptom which could be claimed by the
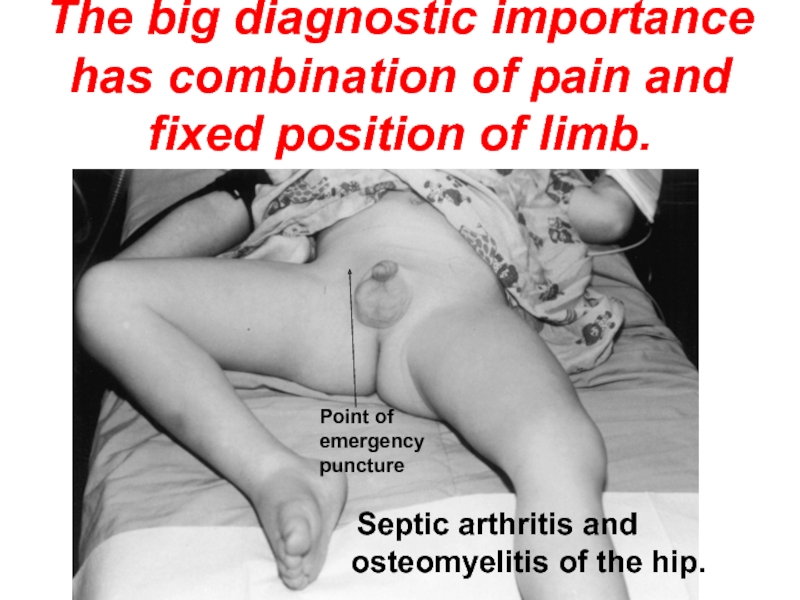
Слайд 19The big diagnostic importance has combination of pain and fixed position
Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis of the hip.
Point of emergency puncture
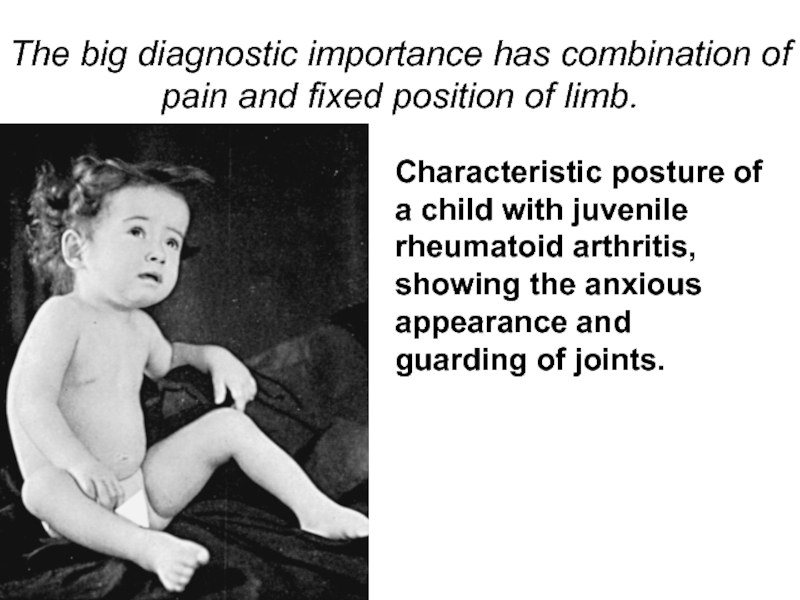
Слайд 20The big diagnostic importance has combination of pain and fixed position
Characteristic posture of a child with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, showing the anxious appearance and guarding of joints.
Слайд 21Visual inspection & palpation
The Objective investigation of the skeleton is
Слайд 23In newborns and early infants the skull has more developed brain
There are a fontanels in points of bones joining on. Anterior fontanel is situated between frontal and temporal bones. Its normal size at birth is 2-3 sm referring to a measurement perpendicular to the bone edges. Its synostosis occurs in age between 4 to 18 mo. Posterior fontanel is found between temporal and occipital bones. It is locked in 75% of full term newborns. In rest of the children the posterior fontanel closes by the end of the first month of life.
Слайд 24During the difficult labor the skull bone edges are crawling one
The broadly opened and soft skull sutures are indicative for hydrocephalus. In opposite event the premature scull sutures lock happens and skull is getting small. The small head size reflects microcephalus as a reduction in volume of the whole brain skull. The circumfiarence of the child head are smaller than 5-th percentille size. Often children with microcephalus suffer from mental deficit disorders and spasticity.
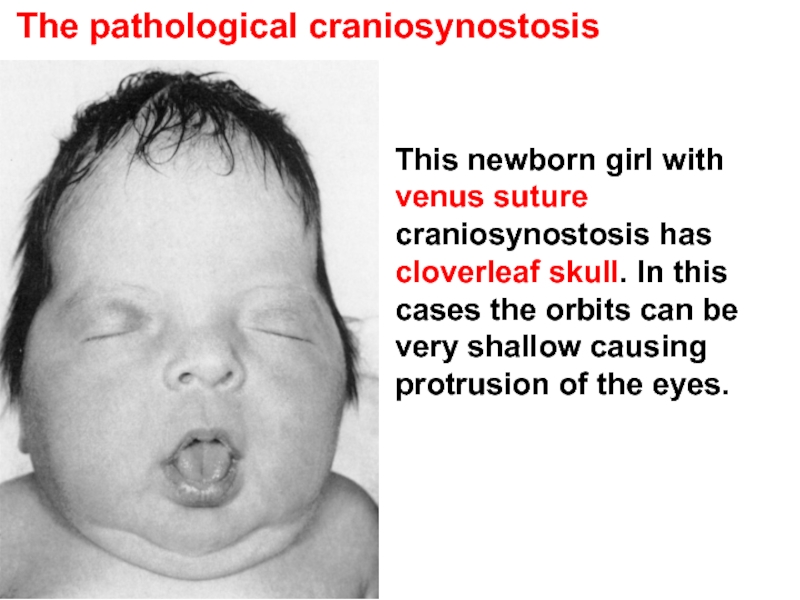
The pathological craniosynostosis is the disorder leading to skull growth partial limitation and various head deformations happen.
Слайд 25 The pathological craniosynostosis
This newborn girl with venus suture craniosynostosis has
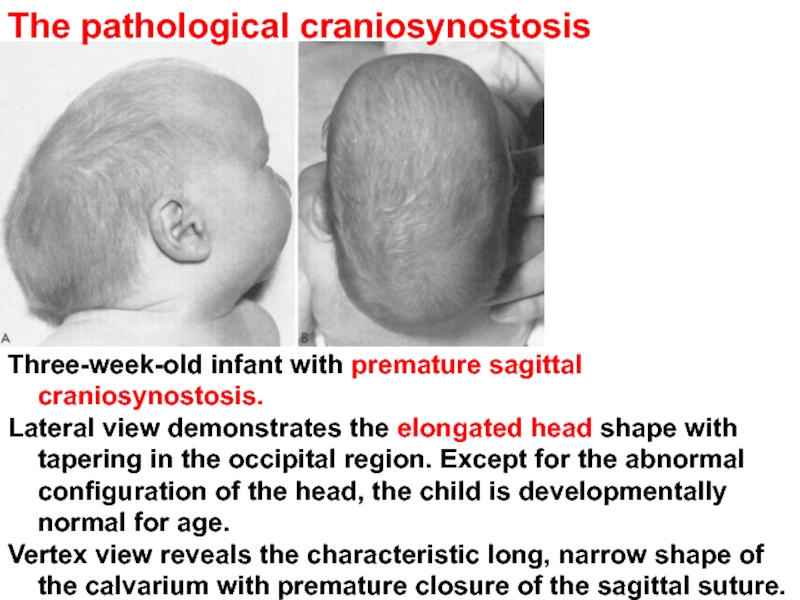
Слайд 26Three-week-old infant with premature sagittal craniosynostosis.
Lateral view demonstrates the elongated
Vertex view reveals the characteristic long, narrow shape of the calvarium with premature closure of the sagittal suture.
The pathological craniosynostosis
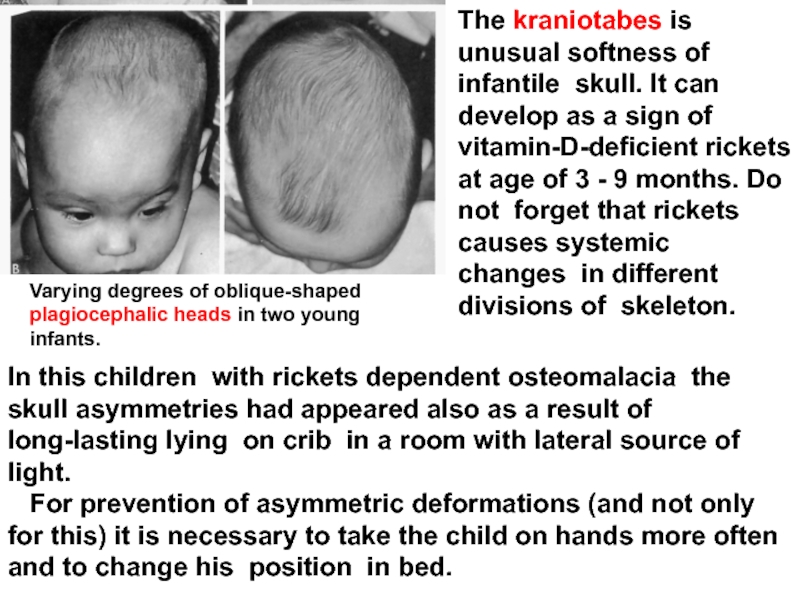
Слайд 27The kraniotabes is unusual softness of infantile skull. It can develop
In this children with rickets dependent osteomalacia the skull asymmetries had appeared also as a result of long-lasting lying on crib in a room with lateral source of light.
For prevention of asymmetric deformations (and not only for this) it is necessary to take the child on hands more often and to change his position in bed.
Varying degrees of oblique-shaped plagiocephalic heads in two young infants.
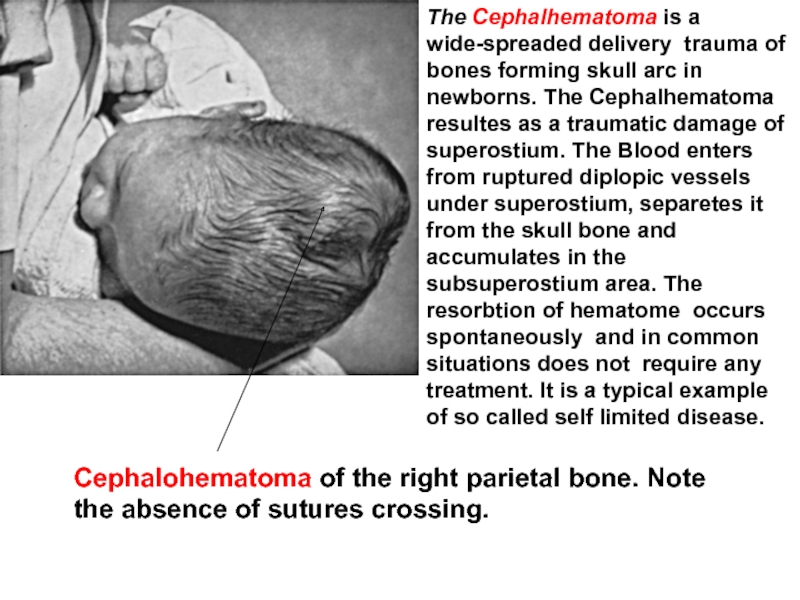
Слайд 28The Cephalhematoma is a wide-spreaded delivery trauma of bones forming skull
Cephalohematoma of the right parietal bone. Note the absence of sutures crossing.
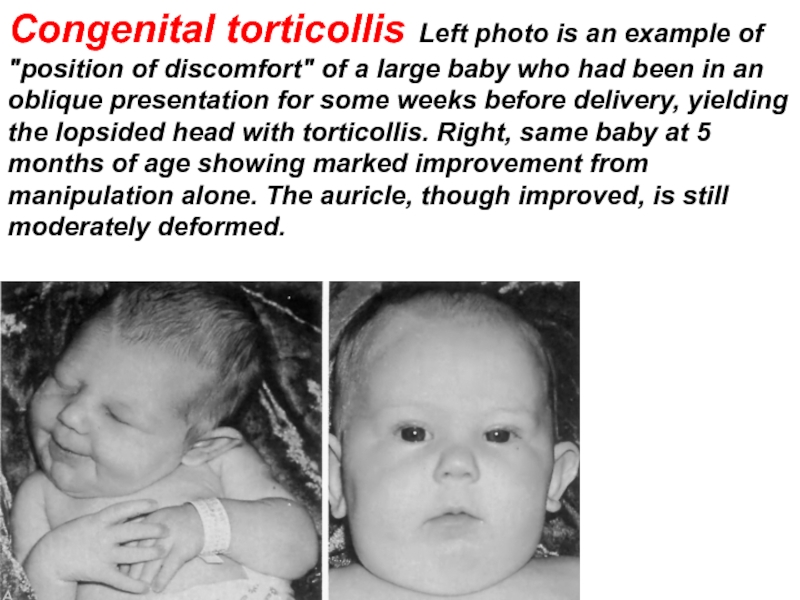
Слайд 30Congenital torticollis Left photo is an example of "position of discomfort"
Слайд 32In small children the thorax has rounded form and starts to
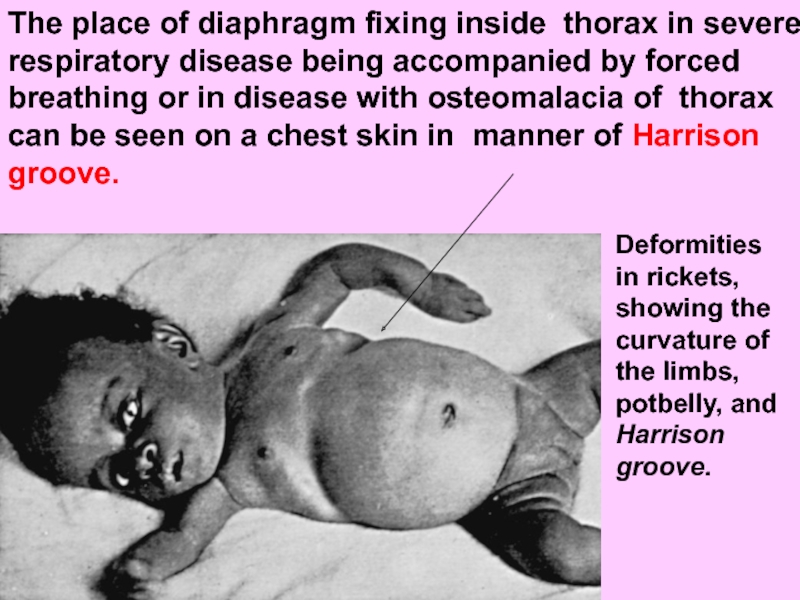
Слайд 33The place of diaphragm fixing inside thorax in severe respiratory disease
Deformities in rickets, showing the curvature of the limbs, potbelly, and Harrison groove.
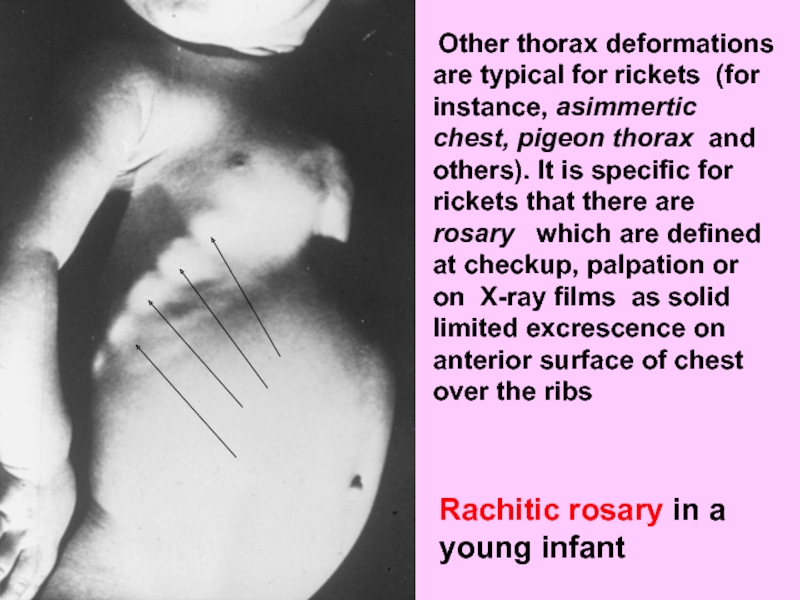
Слайд 34 Other thorax deformations are typical for rickets (for instance, asimmertic
Rachitic rosary in a young infant
Слайд 35Other thorax deformations
The insulated thorax deformations most often are
The big diagnostic importance in cases of advanced heart diseases with a cardiomegaly (big heart size) has a symptom of precordial bulge. The precordial bulge is formed on anterior thorax surface on area of the heart projection.
Слайд 37Spinal curves
In newborns the spine is direct with a small protuberance
After the child lies in prone position and begins to raise slightly the head upwards the cervical lordosis (onwards spinal arc) is forming. When the child starts to sit down the lumbar lordosis and to stand up the chest kyphosis will appear. The cases of the exaggerated lordosis and kyphosis (backwards spinal arc especially in thorax) are defined as hyperlordosis and hyperkiphosis and are to be treated.
Слайд 38 The spine deviations aside are never being physiological and are
One of the predisposing factors of scoliosis development is a phenomenon of functional human body asymmetry. By other words the left and right half of human body are seldom completely alike on size. Under monotonous load deforming spine the accustomed or functional scoliosis can appear.
That is way the parents and school teachers have to pay much attention on children bearing shaping. It means a pose correction at letter in school, advise do not carry briefcases etc. The bed in childhood has to have an enough hard better orthopedic mattress. All motor sports especially swimming as a rule promote the correct bearing shaping.
The pathological scoliosis appears as result of preceding diseases of bones and muscles.
Слайд 39
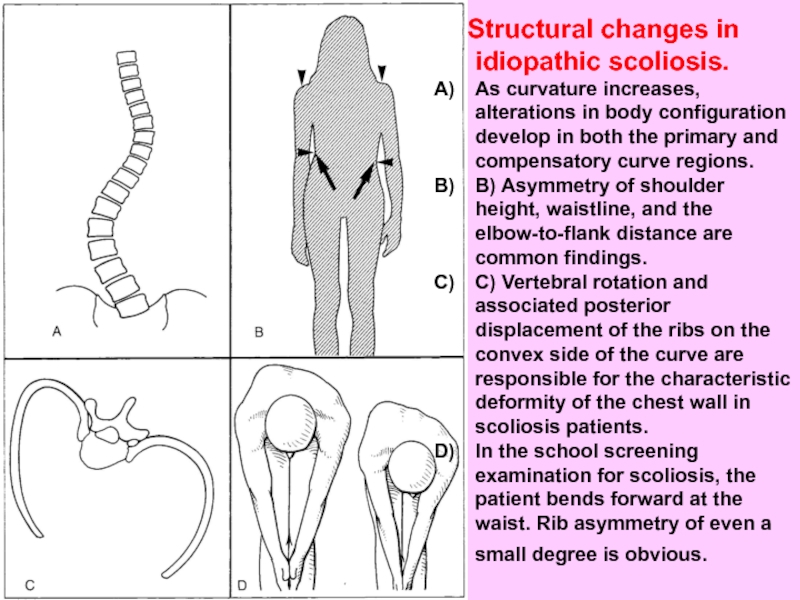
Structural changes in idiopathic scoliosis.
As curvature increases, alterations
B) Asymmetry of shoulder height, waistline, and the elbow-to-flank distance are common findings.
C) Vertebral rotation and associated posterior displacement of the ribs on the convex side of the curve are responsible for the characteristic deformity of the chest wall in scoliosis patients.
In the school screening examination for scoliosis, the patient bends forward at the waist. Rib asymmetry of even a small degree is obvious.
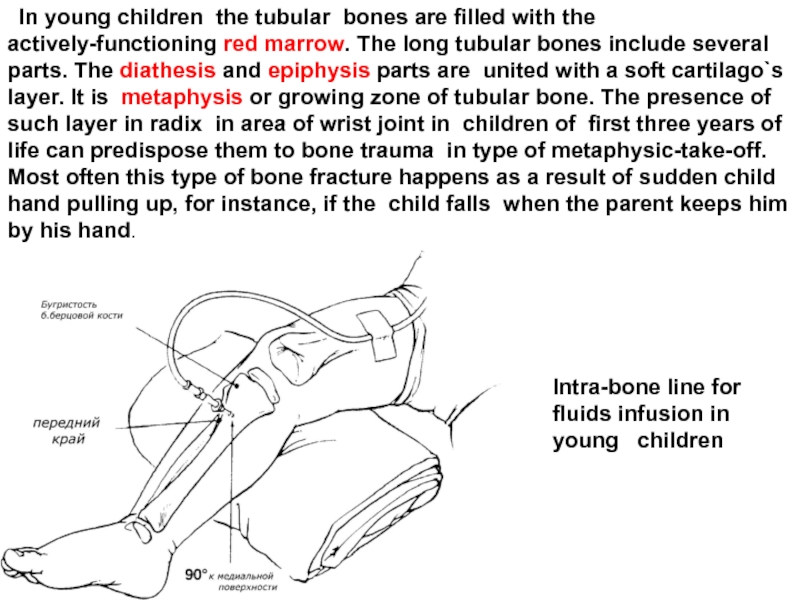
Слайд 41 In young children the tubular bones are filled with the
Intra-bone line for fluids infusion in young children
Слайд 42Limb` deformations
It is known that multiple symmetric deformations of upper and
However it must be kept in mind that in children younger 2 yr the first impression is that their legs are slightly varus – formed, and children aged 2-7 yr – valgus - formed.
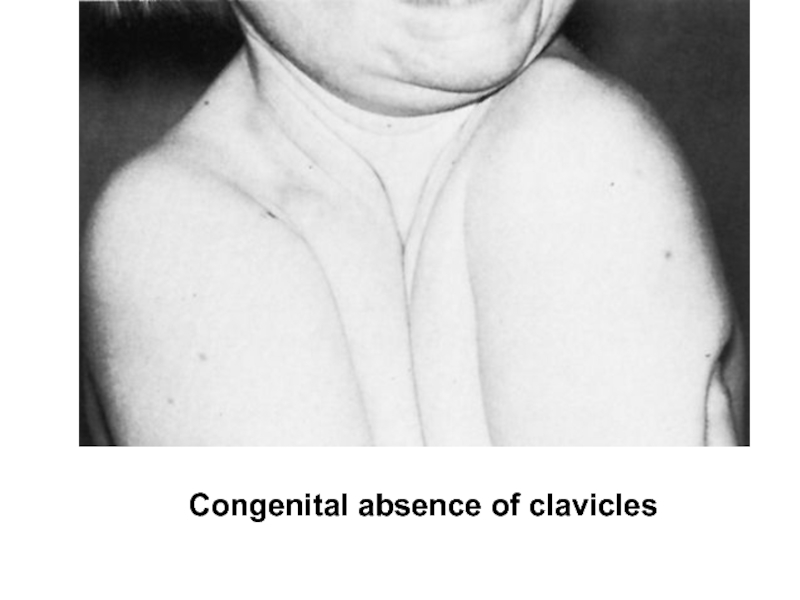
Слайд 43Skeleton` deformations
If the deformations of skeleton are conditioned by anatomical elements
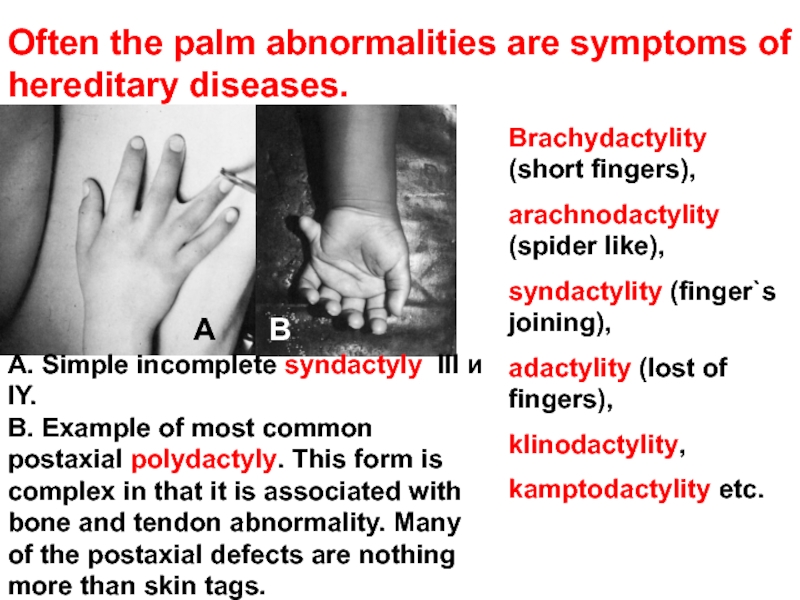
Слайд 45Often the palm abnormalities are symptoms of hereditary diseases.
Brachydactylity (short
arachnodactylity (spider like),
syndactylity (finger`s joining),
adactylity (lost of fingers),
klinodactylity,
kamptodactylity etc.
А. Simple incomplete syndactyly III и IY.
В. Example of most common postaxial polydactyly. This form is complex in that it is associated with bone and tendon abnormality. Many of the postaxial defects are nothing more than skin tags.
А
В
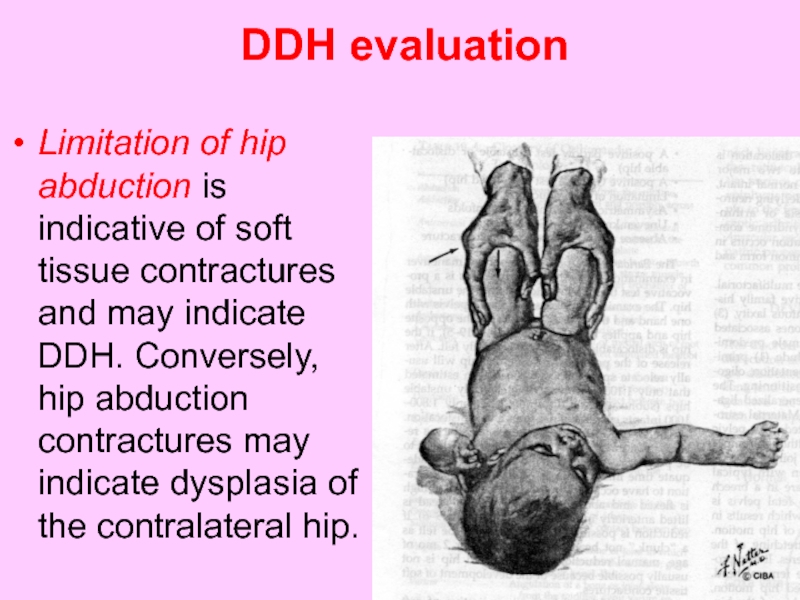
Слайд 48 DDH evaluation
Limitation of hip abduction is indicative of soft
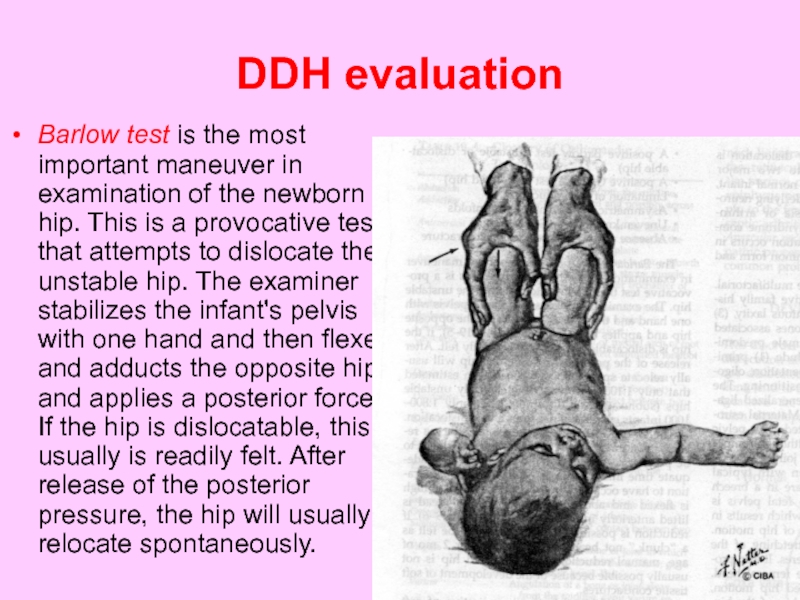
Слайд 49DDH evaluation
Barlow test is the most important maneuver in examination of
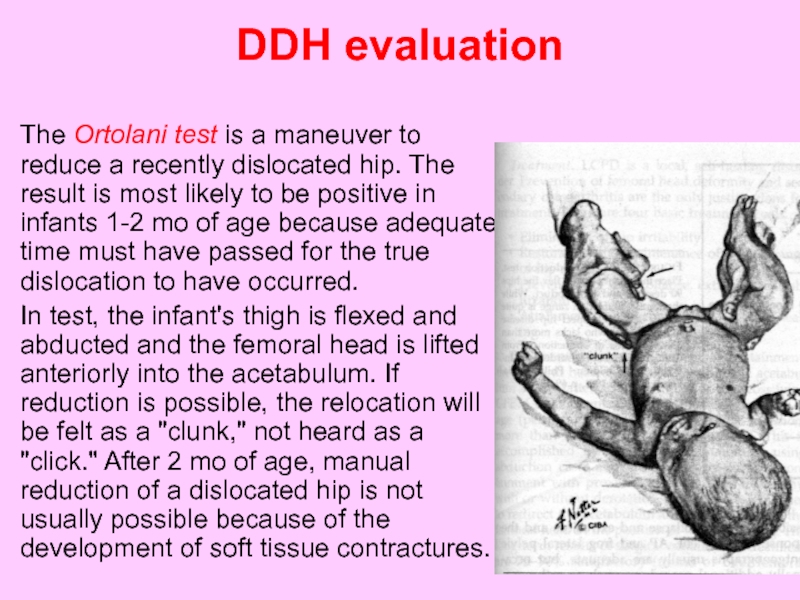
Слайд 50DDH evaluation
The Ortolani test is a maneuver to reduce a
In test, the infant's thigh is flexed and abducted and the femoral head is lifted anteriorly into the acetabulum. If reduction is possible, the relocation will be felt as a "clunk," not heard as a "click." After 2 mo of age, manual reduction of a dislocated hip is not usually possible because of the development of soft tissue contractures.
Слайд 51DDH evaluation
An asymmetric number of thigh skinfolds and apparent shortening
Слайд 52DDH evaluation
In older or walking children, complaints of limping, waddling
In this children the Trendelenburg`s sign becomes positive. Looking on the trunk from the back the pelvic movements upwards and downwards are seen when the child stands up on well or affected limb alternately.
Слайд 54 The teeth are a skin appurtenance because they are derived
Слайд 55 The appearing of baby teeth (or primary deciduous teeth) is
BA|AB
BA|AB
Слайд 56A 12 -15 mo old child as a rule has the
D BA|AB D
D BA|AB D
Слайд 57A 18 - 20 mo old child has the fangs (C)
DCBA|ABCD
DCBA|ABCD
A 22-24mo - second or posterior premolar teeth (E). So a 2 years old child as a rule has a full complement of baby teeth. They are 20:
EDCBA|ABCDE
EDCBA|ABCDE
Empirical formula for infantil teething is n = m – 4, where m – mo of age till 24, n – deciduous teeth quantity
Слайд 58Unlike infantile teeth a succedaneous (secondary) teeth have a bone alveolus
6EDCBA|ABCDE6
6EDCBA|ABCDE6
Слайд 59 The incisors are changing at age 7-9 years:
6EDC21|12CDE6
At age of 10-12 years in children the intensive secondary teething occurs. The succedaneous fangs (3) and premolars (4 and 5) change deciduous ones. The second molars (7) apeare. A little bit later the third molars (8) appear. This teeth are called “a teeth of wisdom". .
Слайд 60 What is the “difficult" teething?
Pain, itching, hypersalivation.
Head cold.
Fever.
Diarrhea.
Always a physician has to pay attention to complicated dentition which a parents as a rule involve with term "difficult but harmless teething”.
Слайд 61The caries and toothache in children.
The caries is a destruction of
Thereby if the painful tooth is damaged by caries the toothache is always the pulpitis sign. The pulpitis is characteristic for extensive or wide-spread dental caries often accompanied with bacteremia and its septic complications.
Basic dental anatomy: 1 - enamel; 2 - dentin; 3 - gingival margin; 4 - pulp; 5 - cementum; 6 - periodontal ligament; 7 - alveolar bone;
8 - neurovascular bundle.
Слайд 62In small children having deciduous teeth with small amount of dentin
Nursing bottle caries.
Слайд 63 The Particularities of dental traumas in children
Intruded primary
Radiograph documents intrusion of "missing tooth" presented in Figure left.
Слайд 66Some features of muscles
The hystomorfological studies of muscular tissues in young
The children skeleton muscles comparatively with such adults contain less myosin and actine contractive proteins and more water. As a result the children muscles are very stretchable and are not prone to ruptures.
The strength of muscular contractions is lesser then in adults.
It is considered that intensive blood flow in children muscles promote quick elimination of acidity forming during muscular load. This fact explains the high physiological muscular activity in children which can feel the true muscular joy moving. In any event it is prohibited to limit children in their motor activity.
Common muscular mass begins to increase only in teens - from 22 - 25% from body weight in pre-pubertal children up to 45% in male-teenagers aged 15 years. The muscular mass increasing occurs by account of each myocyte size increasing. The represented facts undoubtedly witness that so called "body building" and other athletics are for children younger 13 meaningless and even harmful.
Слайд 67The skeleton muscles clinical investigation
The complaints most often concern such subjective
The spontaneous pain is characteristic for myalgia. For children it is very typical the muscular pains related with fever. The mechanism of their origin is not clear yet.
The muscle groups clinical survey usually combines with their palpations. During this procedure it is necessary to reveal the muscular atrophies, hypertrophies, contracturas and tenderness.
Слайд 68
А. Myodistrophy. The paraspinal muscles are very thin, and winging of
В. Myastenia. Facial weakness and generalized muscle wasting are severe. The head is dolichocephalic. The mouth is usually open because the masseters are too weak to lift the mandible against gravity for more than a few seconds.
Diseases of muscles
А
В