ANATOMICAL & PHYSIOLOGICAL FEATURES
OF URINARY TRACT IN CHILDREN.
SEMIOTICS OF URINARY TRACT DISEASES.
RENAL FAILURE.
N.V. Kizima – M.D., associate professor
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Anatomical & physiological features of urinary tract in children. Semiotics of urinary tract diseases. Renal failure презентация
Содержание
- 1. Anatomical & physiological features of urinary tract in children. Semiotics of urinary tract diseases. Renal failure
- 2. Ureter Female or male urethra
- 3. Urination (passing out) organs of
- 4. THE URINARY SYSTEM EMBRYOGENESIS Ureter,
- 5. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY
- 6. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY
- 7. Duplication of the right collecting system with
- 8. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY
- 9. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS Congenital Bladder Outlet Obstruction
- 10. Vesicouretic reflux is a condition in which
- 11. Urination (passing out) organs of
- 12. Symptoms and syndromes of URINARY TRACTS
- 13. The clinical signs allowing to suspect
- 14. The clinical signs allowing to suspect
- 15. Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of
- 16. Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of
- 17. Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of urination
- 18. ISCHURIA (Urinary bladder retention) Partial urinary
- 19. microbial - inflammatory processes in urinary
- 20. Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
- 21. Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
- 22. Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
- 23. The presence of erythrocytes in
- 24. The instrumental and radiological signs of urinary
- 25. X-Ray (radiological) method INTRAVENOUS PYELOGRAPHY –
- 26. CYSTO(URETHRO)GRAPHY The X-ray contrast media substance is
- 27. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI):
- 28. The semiotics of common urine tract diseases
- 29. PYELONEPHRITIS – suppurative inflammation pelvis of
- 30. PYELONEPHRITIS Pain syndrome:
- 31. PYELONEPHRITIS – Urinary syndrome:
- 32. The calculi are formed in a
- 33. Urogenital tract tuberculosis. The tuberculosis (TB) of
- 34. KIDNEY (RENAL) FAILURE Renal failure or
- 35. ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI): basis of clinical
- 36. ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI): RENAL (INTRINSIC):
- 37. THE CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE (chronic kidney
- 38. THE CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
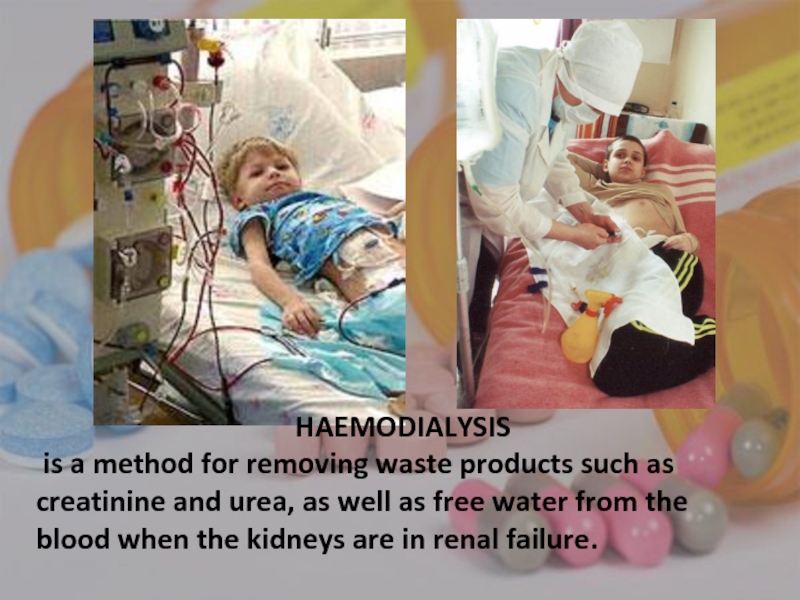
- 39. HAEMODIALYSIS is a method for removing
- 40. KIDNEY TRANSPLANTATION is the organ
Слайд 1 ZAPOROZHYE STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY PROPEDEUTICS OF PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT O.G. Ivanko – M.D. &
Слайд 3
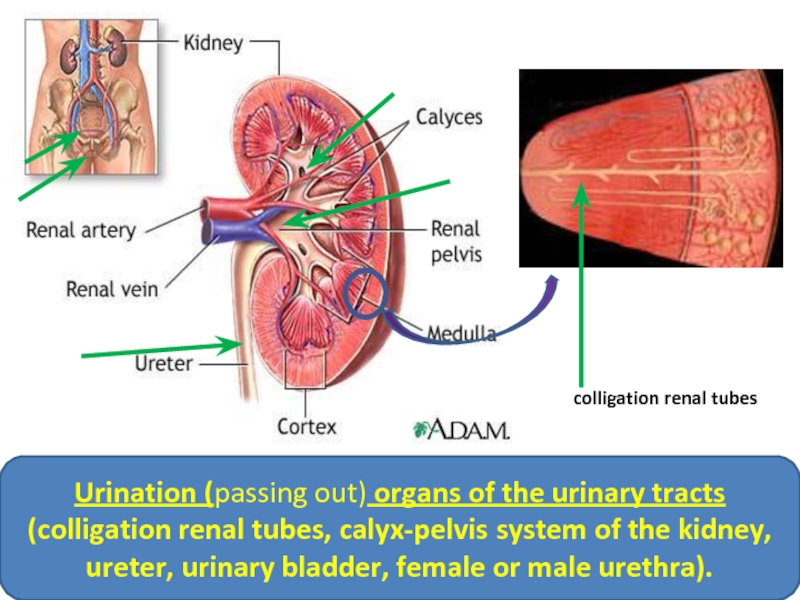
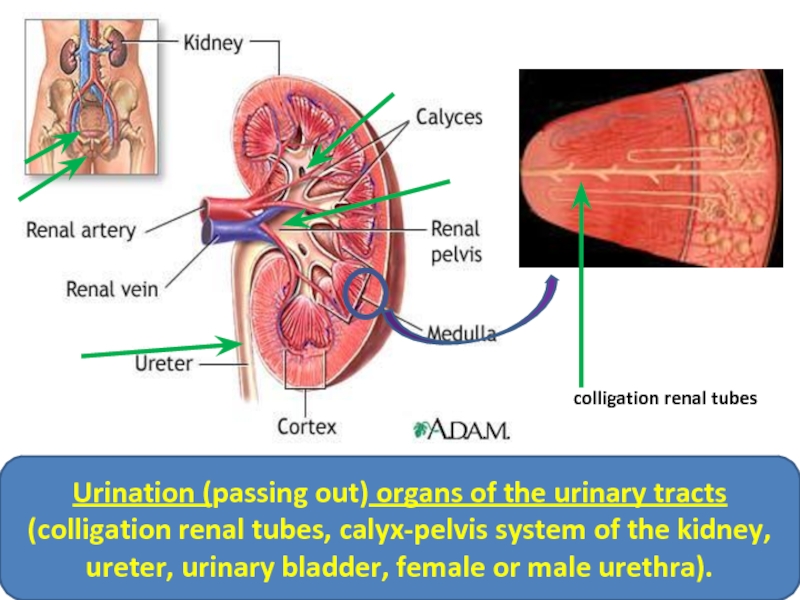
Urination (passing out) organs of the urinary tracts (colligation renal tubes,
colligation renal tubes
Слайд 4
THE URINARY SYSTEM EMBRYOGENESIS
Ureter, Renal pelvis, Major and minor calyces, Collecting
The urogenital sinus (also known as the persistent cloaca) is a part of the human body only present in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. The upper part of the urogenital sinus gives rise to the URINARY BLADDER.
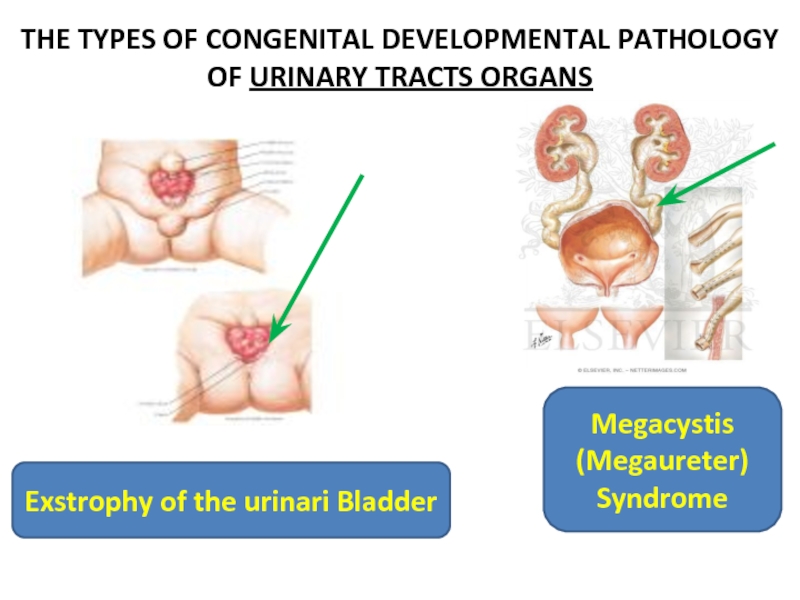
Слайд 5THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY
OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
Exstrophy of
Megacystis (Megaureter) Syndrome
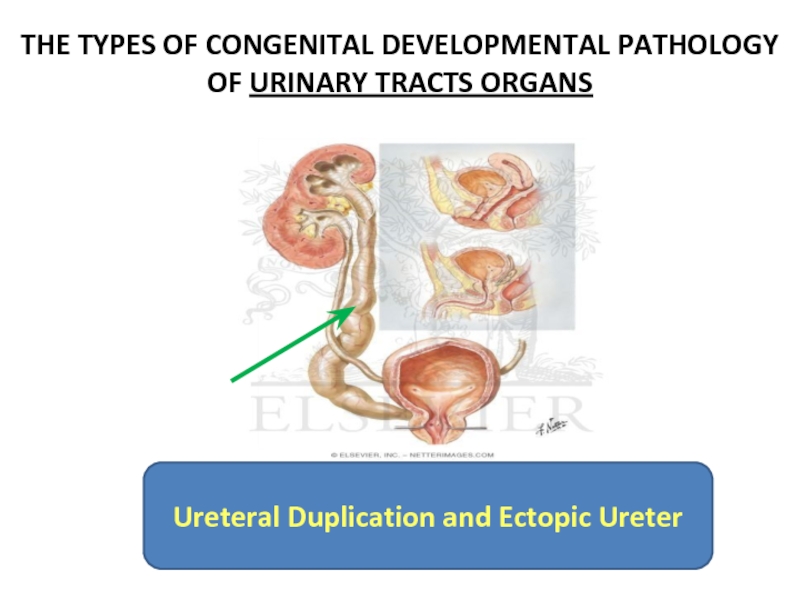
Слайд 6THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY
OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
Ureteral Duplication
Слайд 7Duplication of the right collecting system with ectopic ureter. Excretory urogram
THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
Слайд 8
THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY
OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
Duplication and
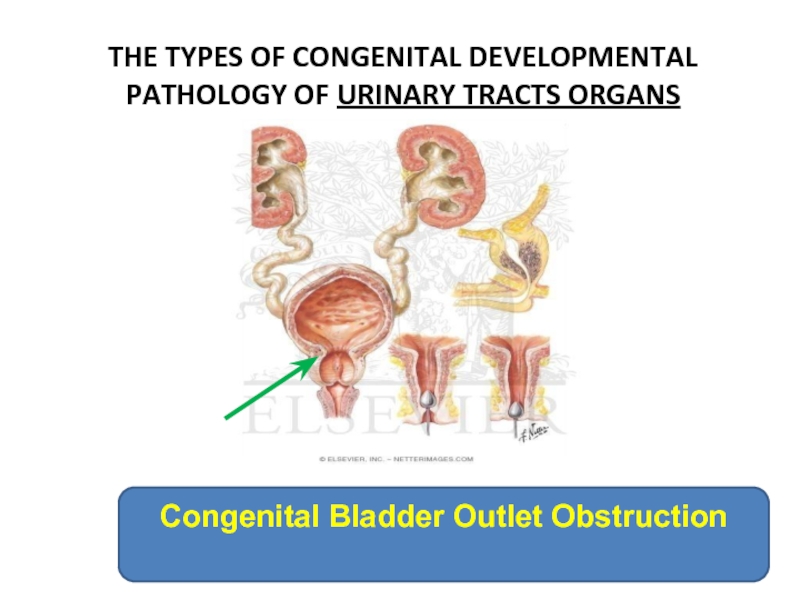
Слайд 9THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY OF URINARY TRACTS ORGANS
Congenital Bladder
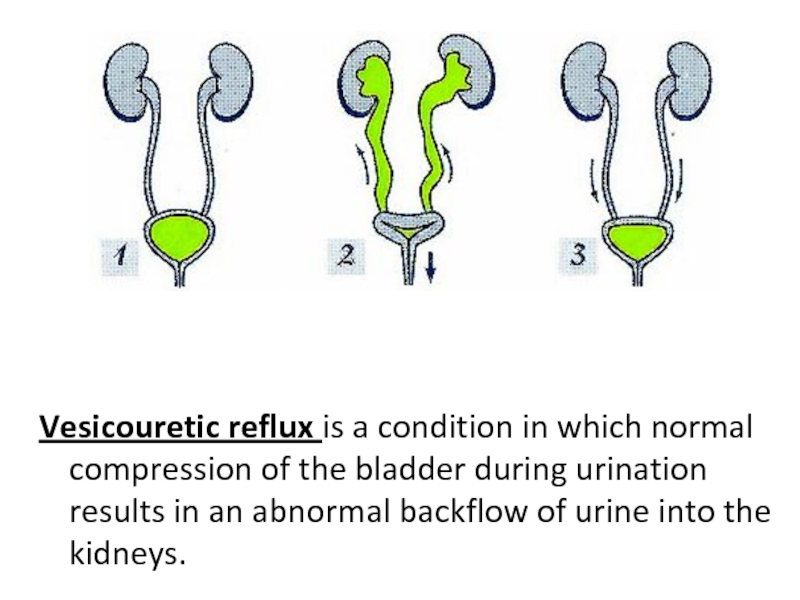
Слайд 10Vesicouretic reflux is a condition in which normal compression of the
Слайд 11
Urination (passing out) organs of the urinary tracts (colligation renal tubes,
colligation renal tubes
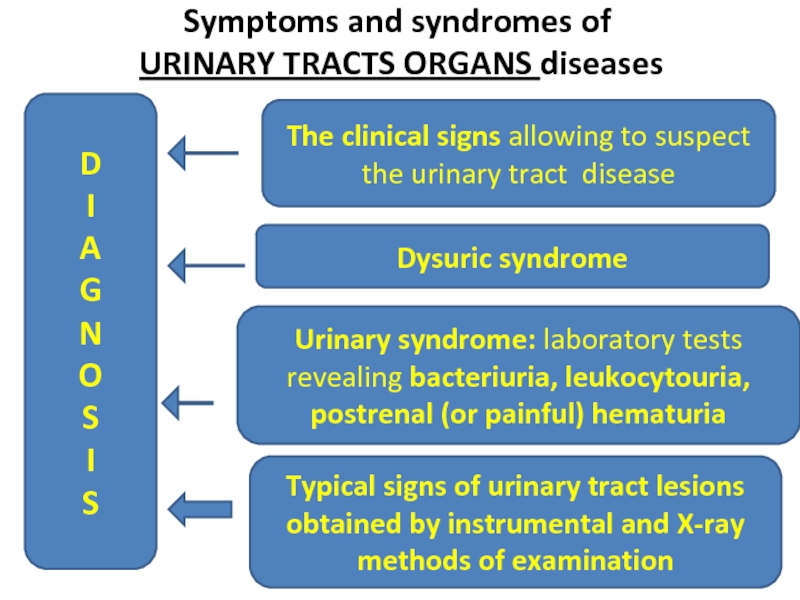
Слайд 12Symptoms and syndromes of
URINARY TRACTS ORGANS diseases
D
I
A
G
N
O
S
I
S
The clinical signs
Dysuric syndrome
Urinary syndrome: laboratory tests revealing bacteriuria, leukocytouria, postrenal (or painful) hematuria
Typical signs of urinary tract lesions obtained by instrumental and X-ray methods of examination
Слайд 13
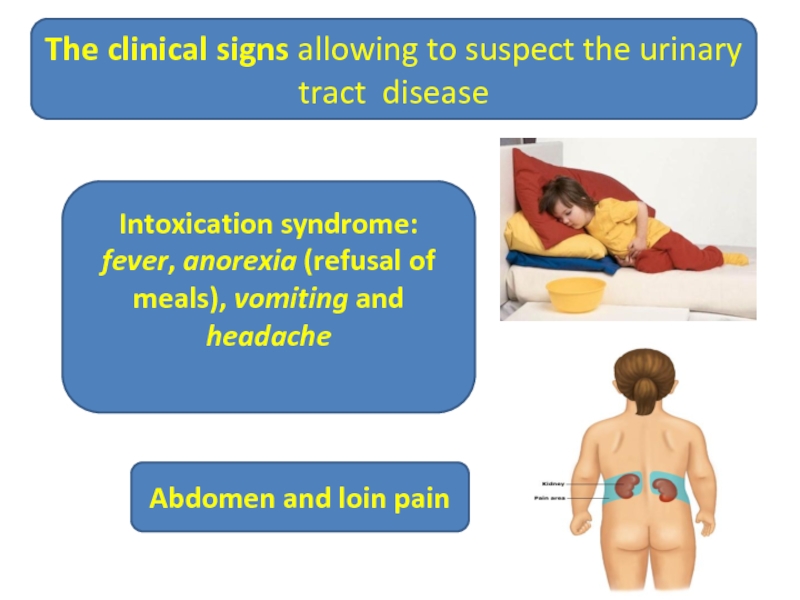
The clinical signs allowing to suspect the urinary tract disease
Abdomen and
Intoxication syndrome:
fever, anorexia (refusal of meals), vomiting and headache
Слайд 14
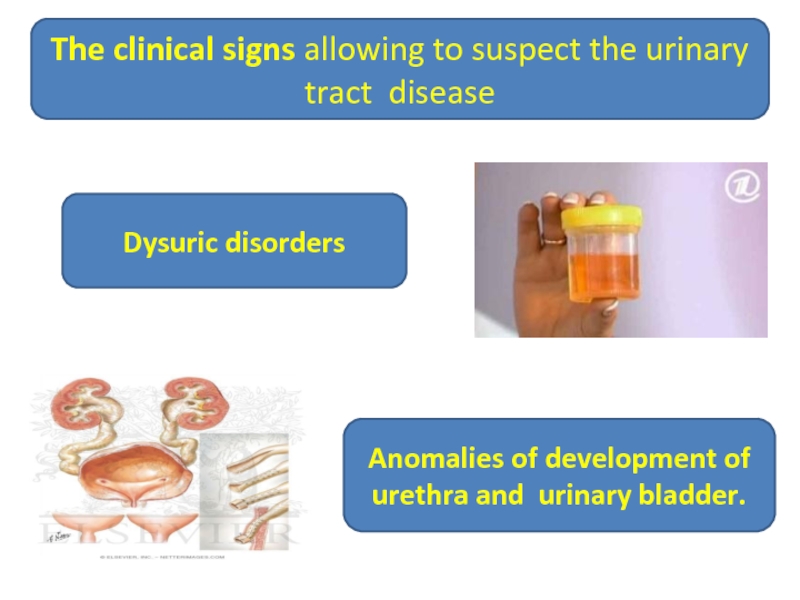
The clinical signs allowing to suspect the urinary tract disease
Dysuric disorders
Anomalies of development of urethra and urinary bladder.
Слайд 15
Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of urination act
Pollakiuria
is also frequent
Incontinence of urine
is disuric symptom and means incapacity to keep urine in bladder leading to undesirable urination without urinary bladder`s tenesmus.
Слайд 16
Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of urination act
Incontinence of urine
It
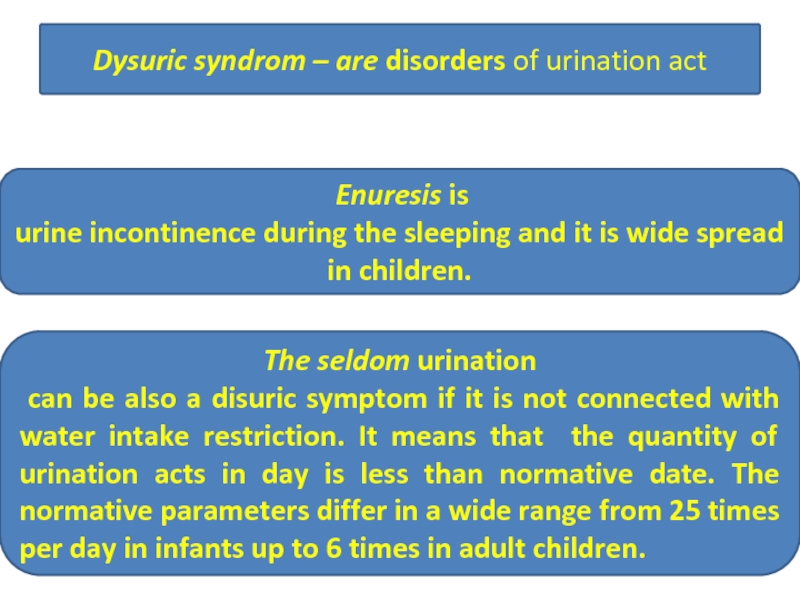
Слайд 17Dysuric syndrom – are disorders of urination act
Enuresis is
urine
The seldom urination
can be also a disuric symptom if it is not connected with water intake restriction. It means that the quantity of urination acts in day is less than normative date. The normative parameters differ in a wide range from 25 times per day in infants up to 6 times in adult children.
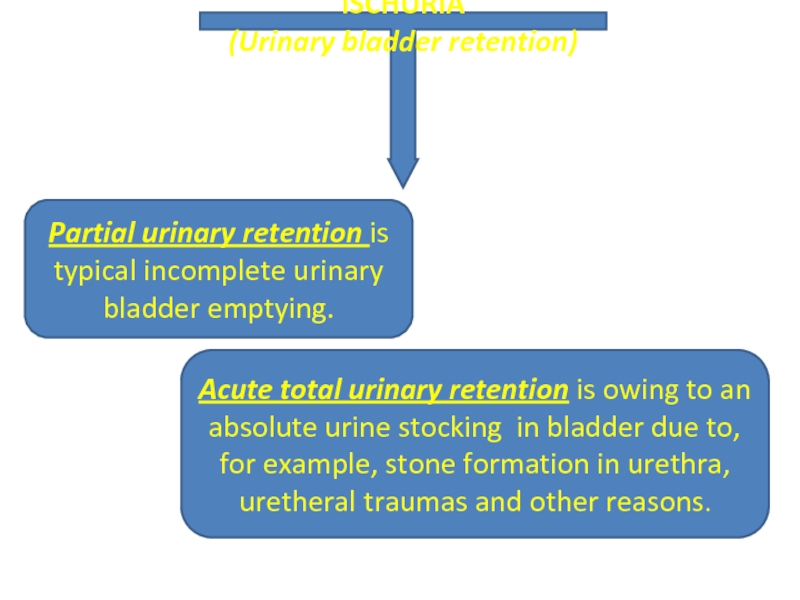
Слайд 18
ISCHURIA
(Urinary bladder retention)
Partial urinary retention is typical incomplete urinary bladder emptying.
Acute
Слайд 19
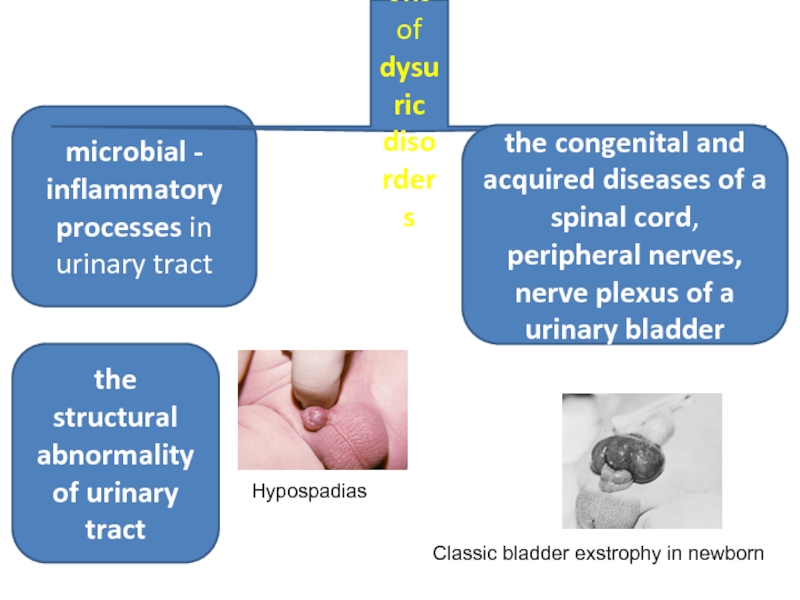
microbial - inflammatory processes in urinary tract
The reasons of dysuric disorders
the
the structural abnormality of urinary tract
Hypospadias
Classic bladder exstrophy in newborn
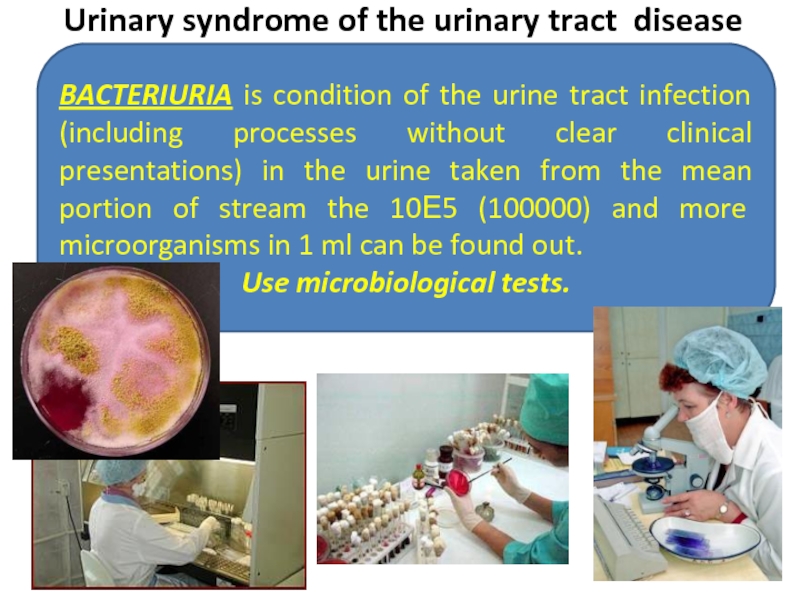
Слайд 20Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
BACTERIURIA is condition of the
Use microbiological tests.
Слайд 21Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
You can use microscopic test
Quantity urinalyses:
Addis`s test: The test is positive and leukocytouria is presented if more than 2 million (2000000 un.) leukocytes per day. Nechiporenko`s test : The test is positive and leukocytouria is presented if more than 2 thousand (2000 un.) leukocytes in 1 ml of urine.
The LEUKOCYTOURIA
is the presence of more than 5 leukocytes in visual field during the microscopic investigation of urine sediment.
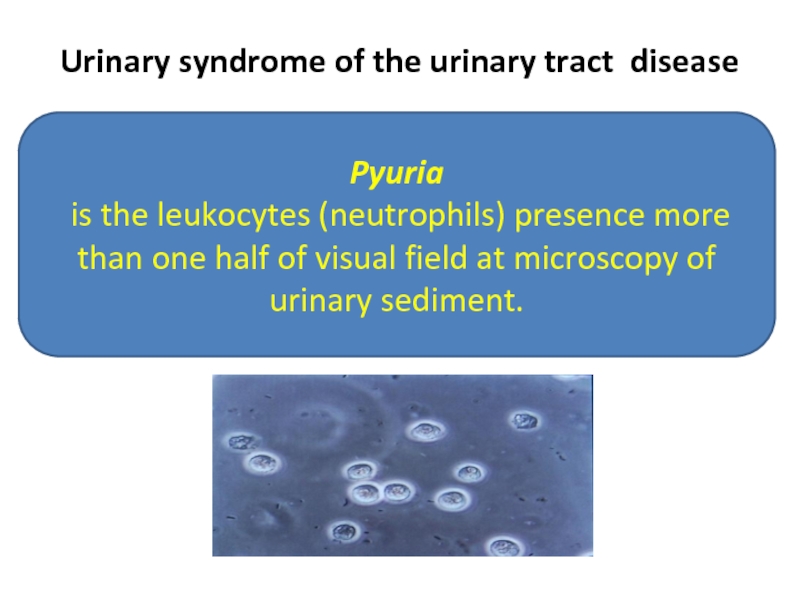
Слайд 22Urinary syndrome of the urinary tract disease
Pyuria
is the leukocytes (neutrophils)
Слайд 23
The presence of erythrocytes in urine directly from organs of urinary
POSTRENAL (PAINFUL) HEMATURIA.
Three measuring glass urine collect test:
the blood (erythrocytes) is presented in the beginning of urination (in the 1st measuring glass of urine) as result of urethra lesion
- the terminal (finishing) blood is presented in the end of urination act (in 3-th measuring glass) as result of urine bladder disease
- the proportional distribution of erythrocytes in all 3 portions (in measuring glasses) of urine as result of kidneys lesion either pelvis or ureter.
Слайд 24The instrumental and radiological signs of urinary tract examination.
ULTRASONOGRAPHY
It helps to
Слайд 25X-Ray (radiological) method
INTRAVENOUS PYELOGRAPHY – IVP:
The IVP should be
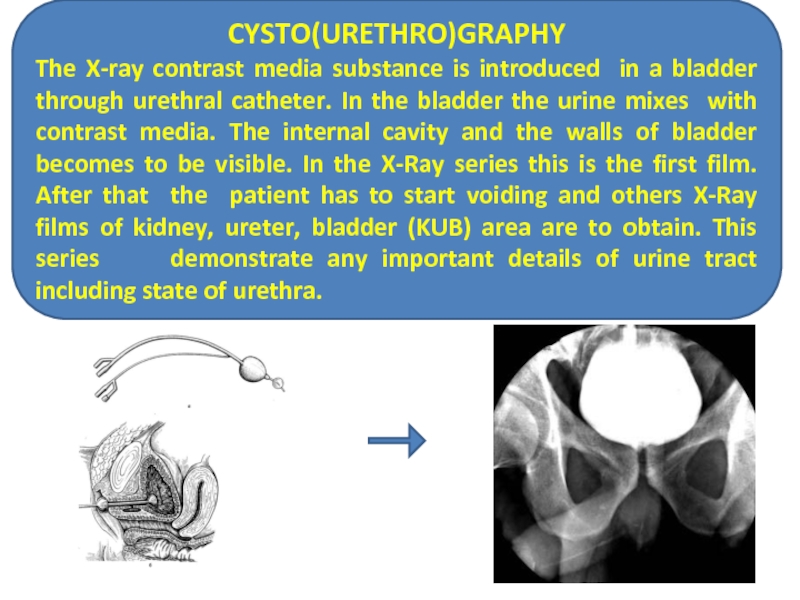
Слайд 26CYSTO(URETHRO)GRAPHY
The X-ray contrast media substance is introduced in a bladder through
Слайд 27
URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI):
85% - due to bacteria - gram negative
most common gram negative bacteria - E. coli , Proteus , Kliebsiella and enterobacter
two ways the bacteria can reach the kidney: through the blood stream - hematogenous infection - less common . Occurs in septicaemia , bacterial endocarditis and immunocompromised patients
can start in early childhood (in infants)
Слайд 28The semiotics of common urine tract diseases in children
CYSTITIS -
microbe
Pain in the inguinal region of the abdomen
- Dysuria: frequent, painful urination, urinary incontinence
- Bacteriuria,
Leukocyturia, pyuria
Terminal according to test of three measuring glass microhematuria
Слайд 29PYELONEPHRITIS – suppurative inflammation pelvis of kidneys, tubular system in medullar
PREDISPOSING FACTORS
urinary obstruction - either congenital or acquired
vesicoureteric reflux
diabetes mellitus - due to increased susceptiblity to infection
immunodepression and immunodeficiency
The pyelonephritis it is the complicated form of urine tract infection.
In pyelonephritis the microbes contaminate the pelvis of kidneys, tubular system in medullar substance of kidney.
Слайд 30
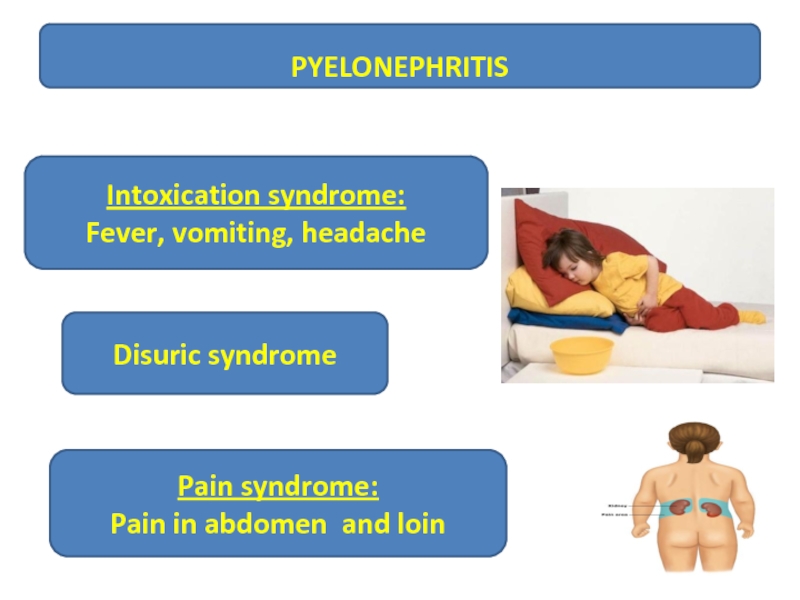
PYELONEPHRITIS
Pain syndrome:
Pain in abdomen and loin
Disuric syndrome
Intoxication syndrome:
Fever, vomiting,
Слайд 31
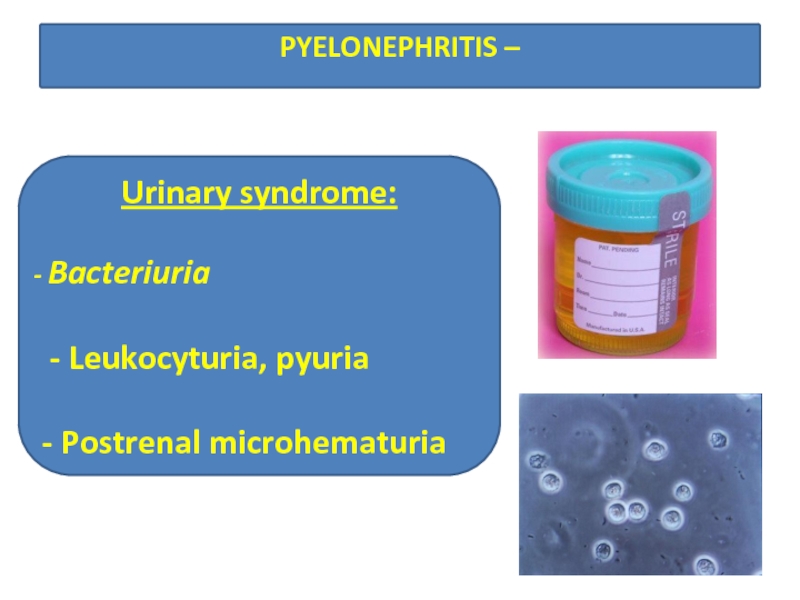
PYELONEPHRITIS –
Urinary syndrome:
Bacteriuria
- Leukocyturia, pyuria
- Postrenal microhematuria
Слайд 32
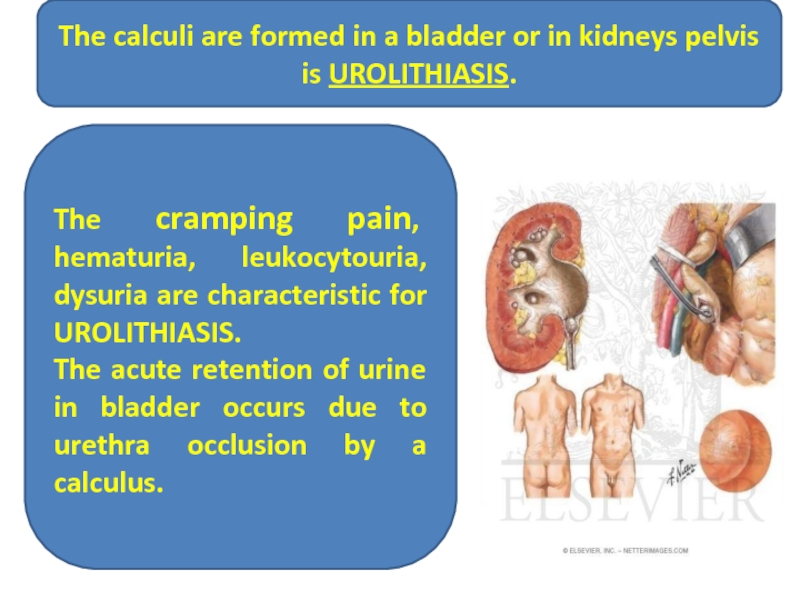
The calculi are formed in a bladder or in kidneys pelvis
The cramping pain, hematuria, leukocytouria, dysuria are characteristic for UROLITHIASIS.
The acute retention of urine in bladder occurs due to urethra occlusion by a calculus.
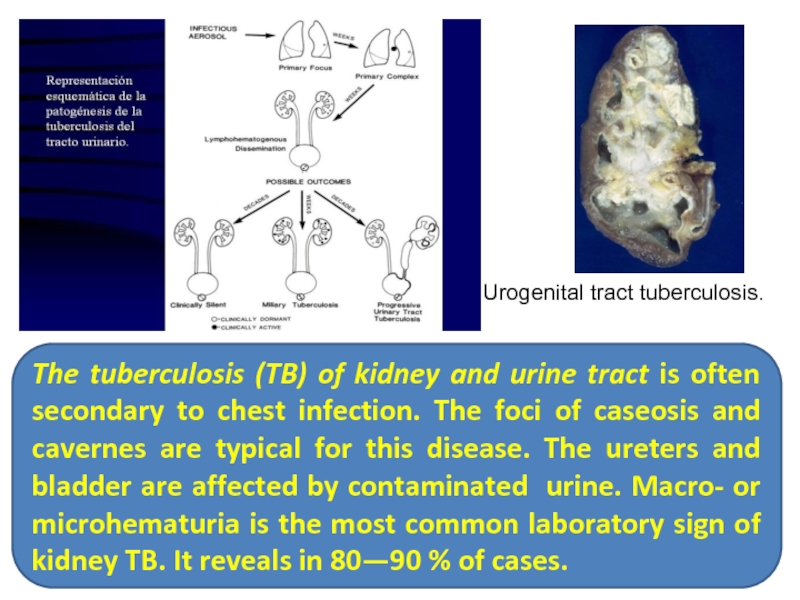
Слайд 33Urogenital tract tuberculosis.
The tuberculosis (TB) of kidney and urine tract is
Слайд 34
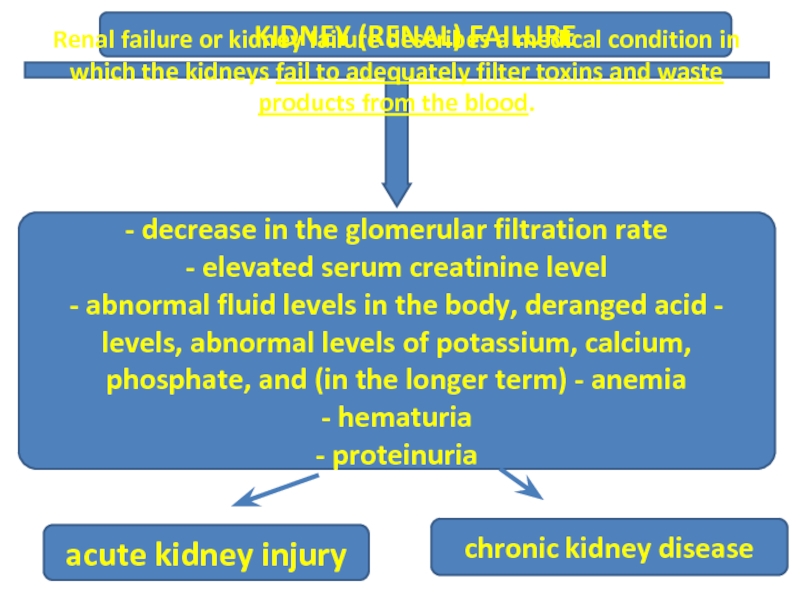
KIDNEY (RENAL) FAILURE
Renal failure or kidney failure describes a medical condition
acute kidney injury
chronic kidney disease
- decrease in the glomerular filtration rate
- elevated serum creatinine level
- abnormal fluid levels in the body, deranged acid - levels, abnormal levels of potassium, calcium, phosphate, and (in the longer term) - anemia
- hematuria
- proteinuria
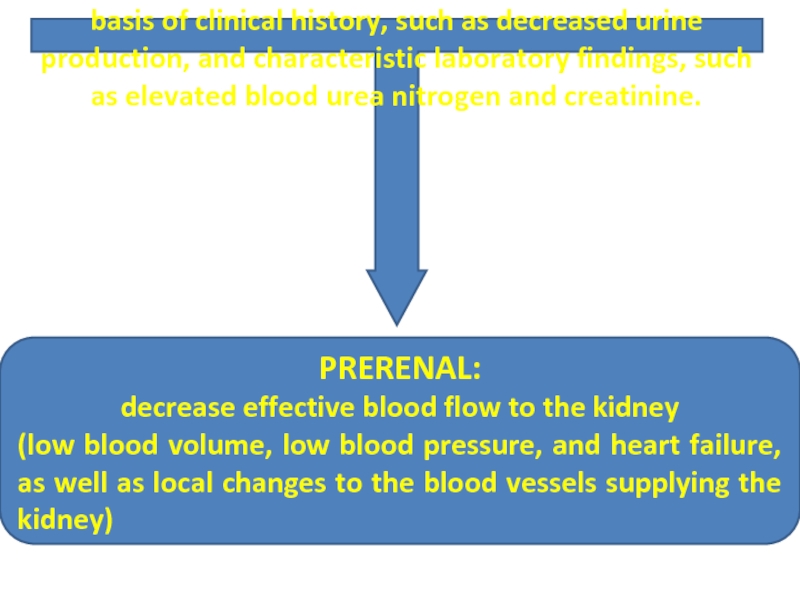
Слайд 35ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI):
basis of clinical history, such as decreased urine
PRERENAL:
decrease effective blood flow to the kidney
(low blood volume, low blood pressure, and heart failure, as well as local changes to the blood vessels supplying the kidney)
Слайд 36
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI):
RENAL (INTRINSIC): damage to the kidney itself .
(to damage to the glomeruli, renal tubules, or interstitium. Common causes of each are glomerulonephritis, acute tubular necrosis (ATN), and acute interstitial nephritis (AIN)
POSTRENAL: consequence of urinary tract obstruction.
This may be related to benign kidney stones, obstructed urinary catheter, bladder stone, bladder, ureteral or renal malignancy. A renal ultrasound will demonstrate hydronephrosis if present.
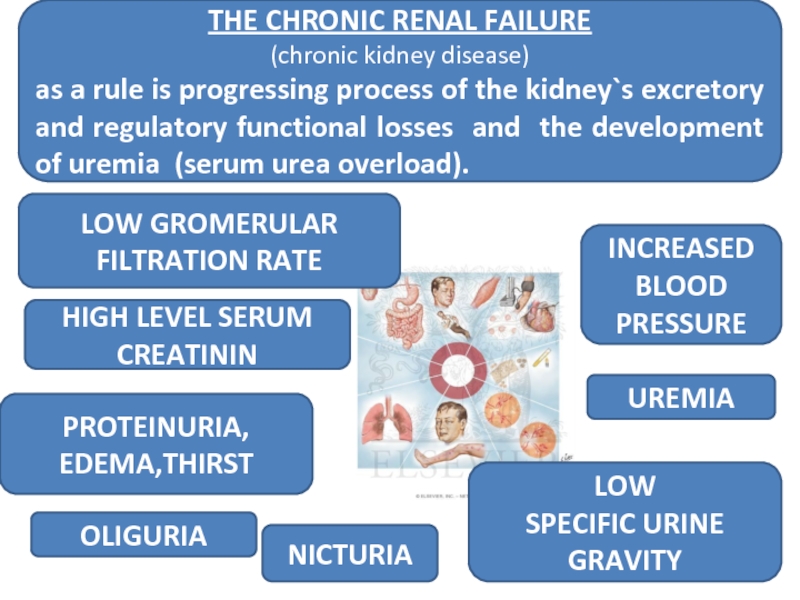
Слайд 37THE CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
(chronic kidney disease)
as a rule is progressing
NICTURIA
LOW
SPECIFIC URINE GRAVITY
HIGH LEVEL SERUM CREATININ
UREMIA
OLIGURIA
LOW GROMERULAR FILTRATION RATE
INCREASED BLOOD PRESSURE
PROTEINURIA, EDEMA,THIRST
Слайд 38
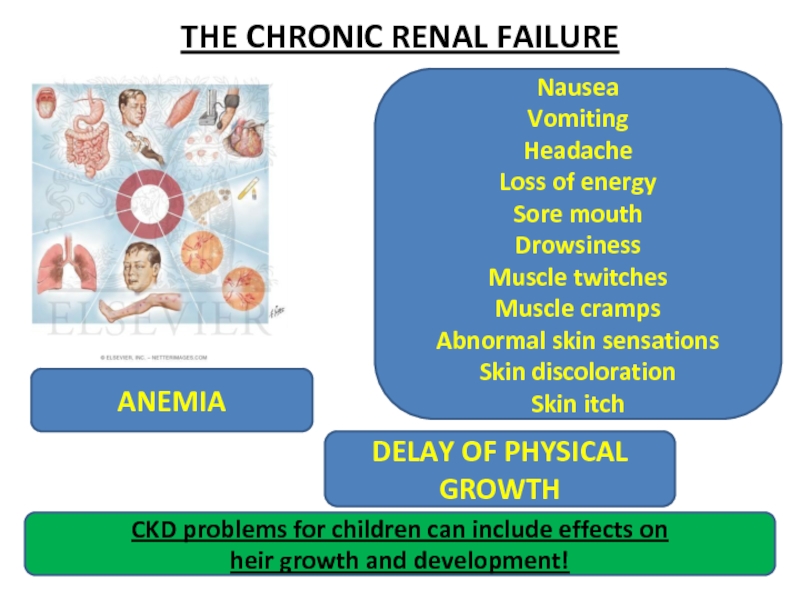
THE CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
CKD problems for children can include effects
heir growth and development!
Nausea
Vomiting
Headache
Loss of energy
Sore mouth
Drowsiness
Muscle twitches
Muscle cramps
Abnormal skin sensations
Skin discoloration
Skin itch
DELAY OF PHYSICAL GROWTH
ANEMIA