- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
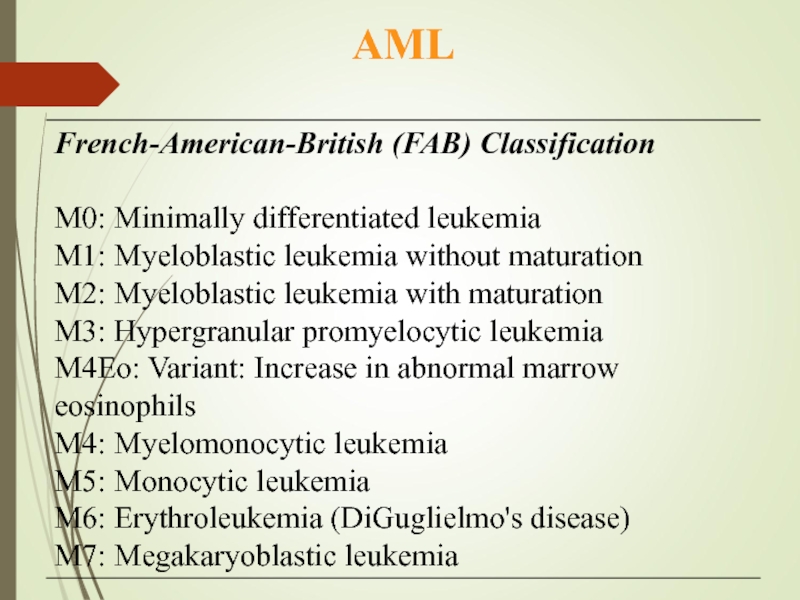
Acute leukemia презентация
Содержание
- 1. Acute leukemia
- 2. Leukemia Group of malignant disorders of the
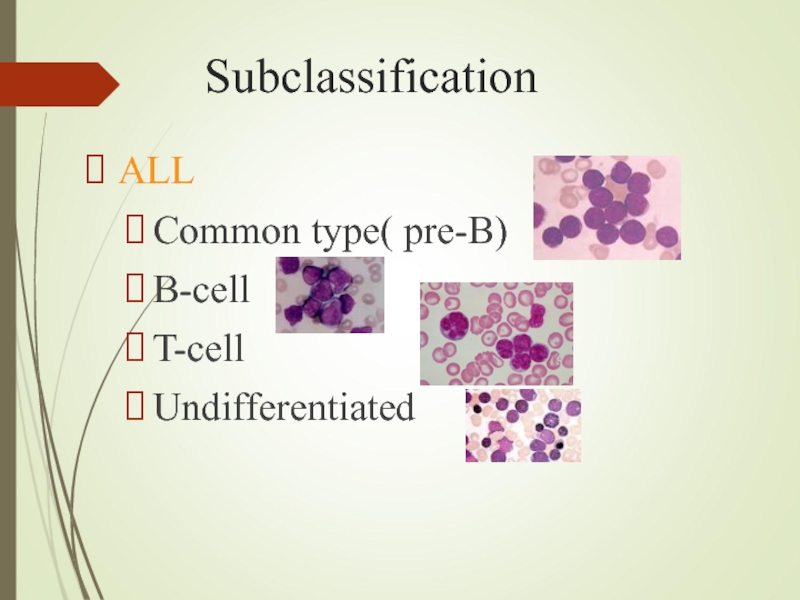
- 3. Subclassification ALL Common type( pre-B) B-cell T-cell Undifferentiated
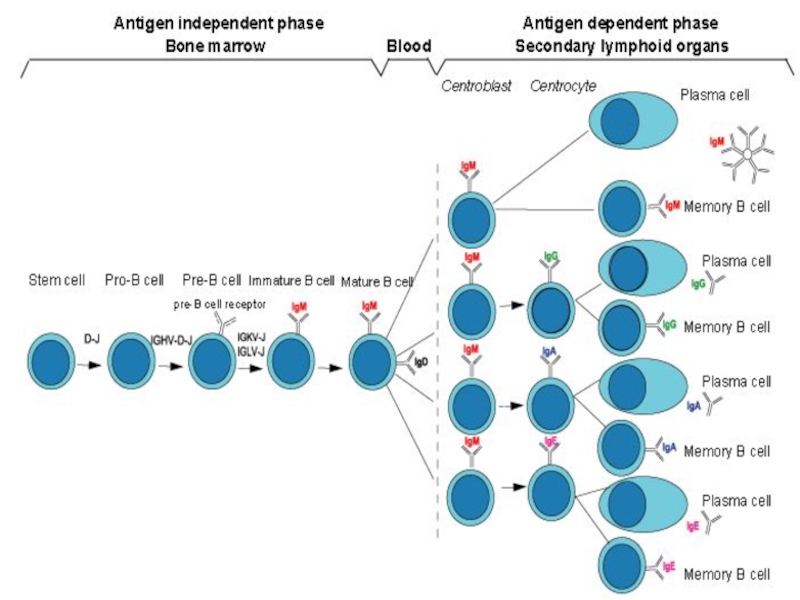
- 5. Myelomono
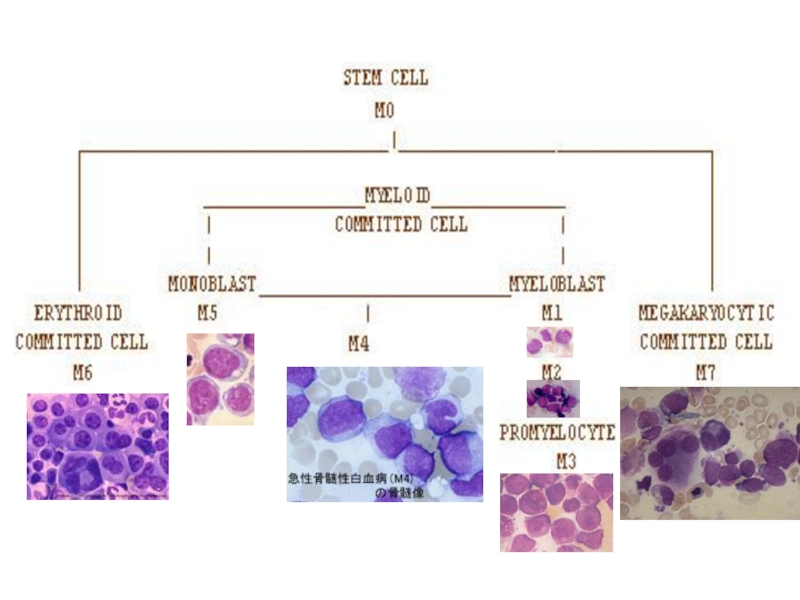
- 7. Acute Myeloid
- 8. Etiology Predisposing factors: Ionizing radiation exposure
- 9. Clinical features General :
- 10. Specific: M2 : Chloroma:-presents as a
- 12. Diagnosis Blood count :
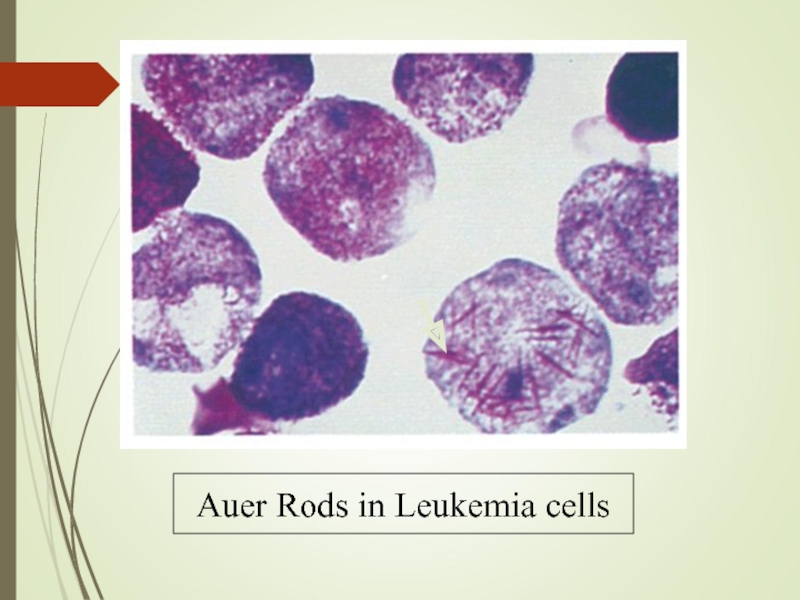
- 13. Auer Rods in Leukemia cells
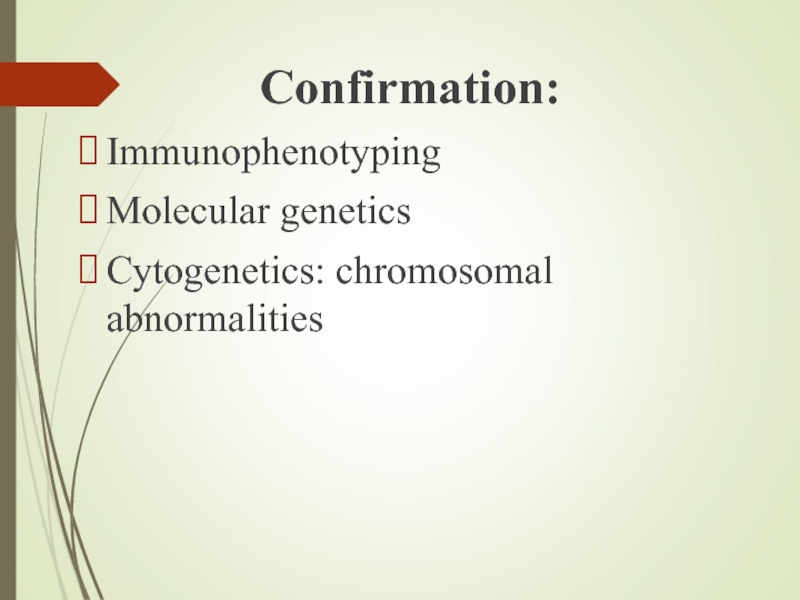
- 14. Confirmation: Immunophenotyping Molecular genetics Cytogenetics: chromosomal abnormalities
- 15. Other investigations: Coagulation screen, fibrinogen,
- 16. Management Supportive care Anemia
- 17. SPECIFIC THERAPHY: Chemotherapy : Induction: (4-6
- 18. (multiple cycles of intensive chemotherapy given over
- 20. Complete remission
- 22. Prognosis Median survival without treatment is 5
- 23. Poor prognostic factors Increasing age Male sex
- 24. Literature: 1. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN).
Слайд 1JSC “Astana Medical University”
Department of internal illnesses №1
Acute leukemia
Done by:
Checked by: Baidurin S.A.
Astana 2018
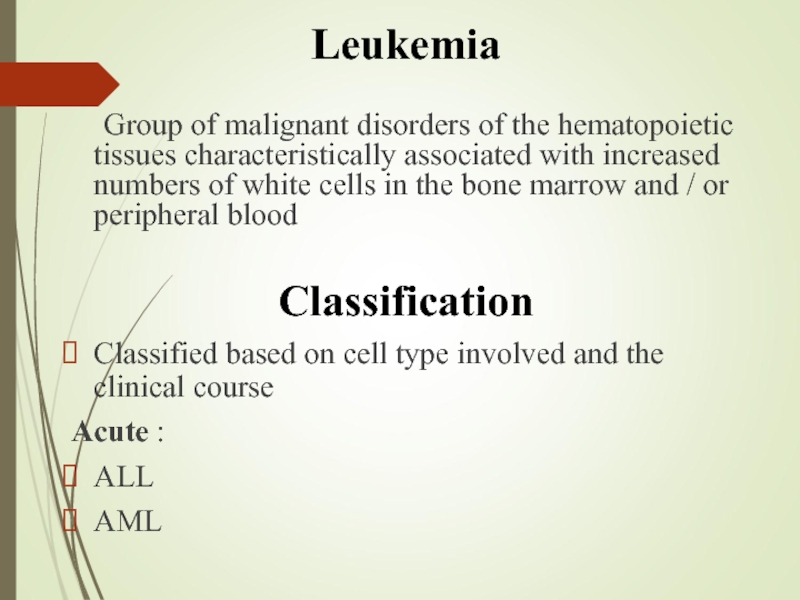
Слайд 2Leukemia
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with
Classification
Classified based on cell type involved and the clinical course
Acute :
ALL
AML
Слайд 7 Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Malignant transformation of a myeloid precursor cell ; usually occurs at a very early stage of myeloid development
Rare in childhood & incidence increases with age
Слайд 8Etiology
Predisposing factors:
Ionizing radiation exposure
Previous chemotherapy : alkylating agents
Occupational chemical exposure :
Genetic factors: Down’s Syndrome, Bloom’s, Fanconi’s Anemia
Viral infection ( HTLV-1)
Immunological : hypogammaglobulinemia
Acquired hematological condition -Secondary
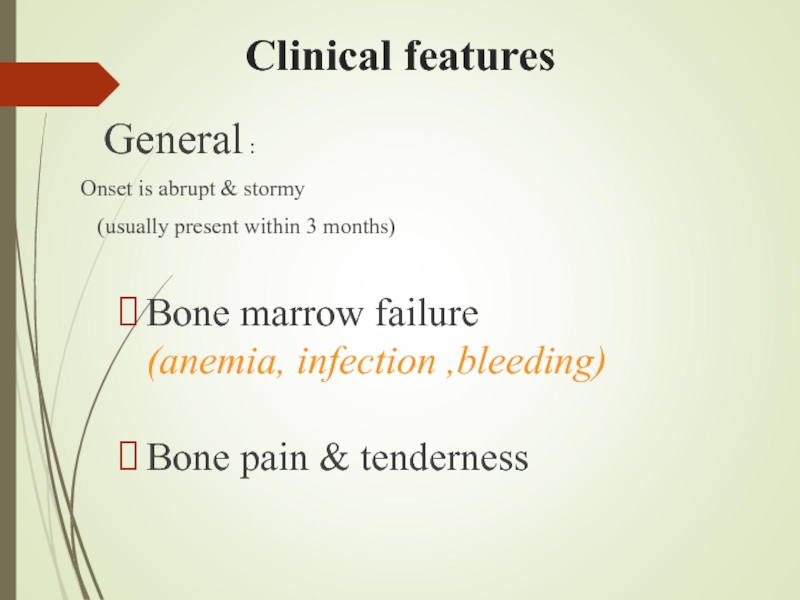
Слайд 9Clinical features
General :
Onset is abrupt & stormy
(usually present within 3 months)
Bone marrow failure (anemia, infection ,bleeding)
Bone pain & tenderness
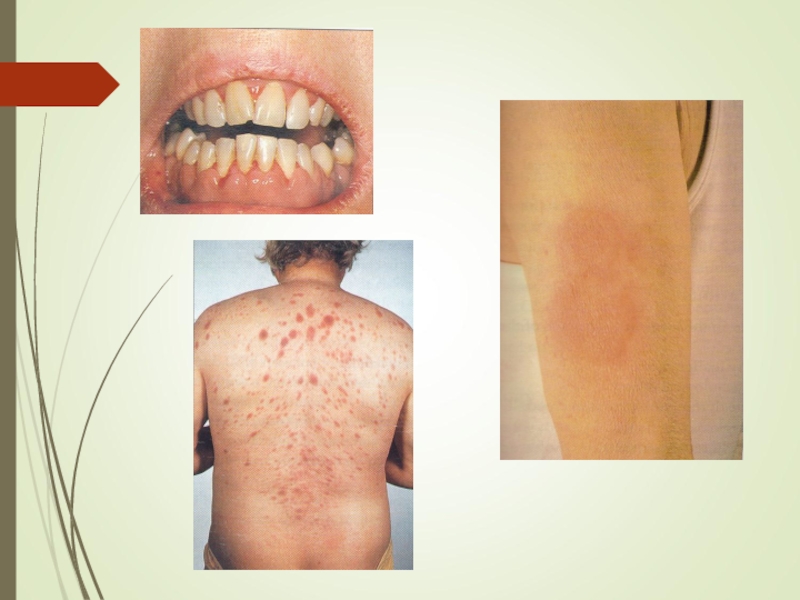
Слайд 10Specific:
M2 : Chloroma:-presents as a mass lesion ‘tumor of leukemic cells’
M3 : DIC
M4/M5 : Infiltration of soft tissues, gum infiltration, skin deposits ,Meningeal involvement-headache, vomiting, eye symptoms
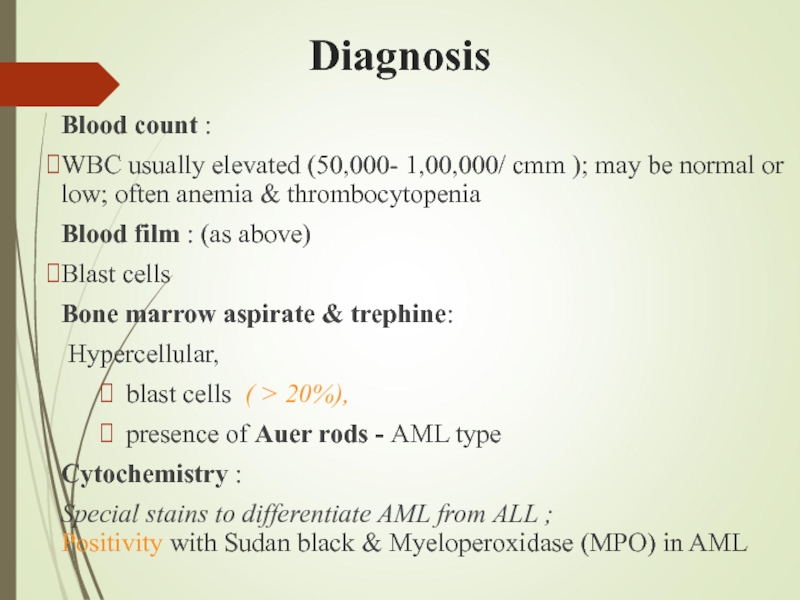
Слайд 12Diagnosis
Blood count :
WBC usually elevated (50,000- 1,00,000/ cmm ); may be normal or low; often anemia & thrombocytopenia
Blood film : (as above)
Blast cells
Bone marrow aspirate & trephine:
Hypercellular,
blast cells ( > 20%),
presence of Auer rods - AML type
Cytochemistry :
Special stains to differentiate AML from ALL ; Positivity with Sudan black & Myeloperoxidase (MPO) in AML
Слайд 15Other investigations:
Coagulation screen, fibrinogen,
RFT, LFT
LDH, Uric acid
Urine
CXR
ECG, ECHO
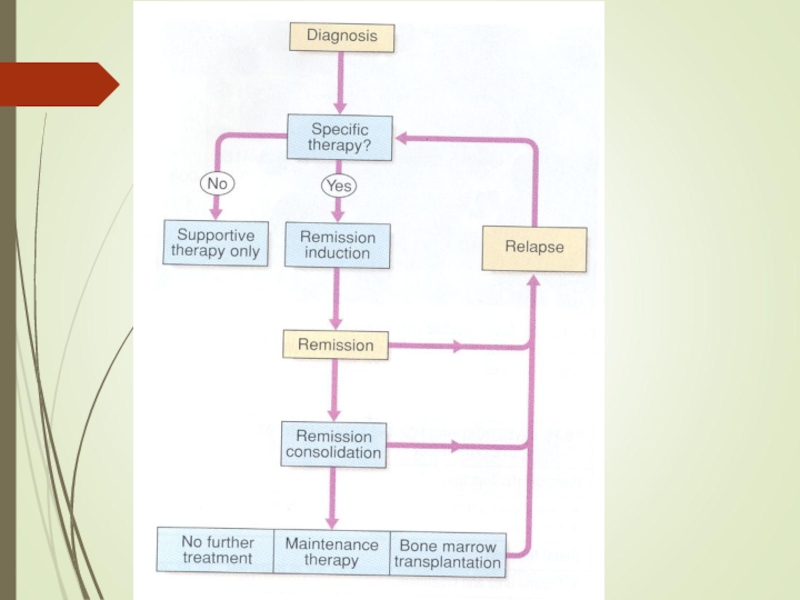
Слайд 16Management
Supportive care
Anemia – red cell transfusion
Thrombocytopenia – platelet
Infection – broad spectrum IV antibiotics
Hematopoietic growth factors: GM-CSF, G-CSF
Barrier nursing
Indwelling central venous catheter
Metabolic problems
Monitoring hepatic / renal / hematologic function
Fluid & electrolyte balance, nutrition hyperuricemia- hydration, Allopurinol
Psychological support
Слайд 17SPECIFIC THERAPHY:
Chemotherapy :
Induction: (4-6 wks)
vincristine, prednisone,
anthracycline, (idarubicin or daunorubicin)
cyclophosphamide, and
Слайд 18(multiple cycles of intensive chemotherapy given over a 6 to 9
Consolidation:
Слайд 19 Maintenance phase: (18 to 24
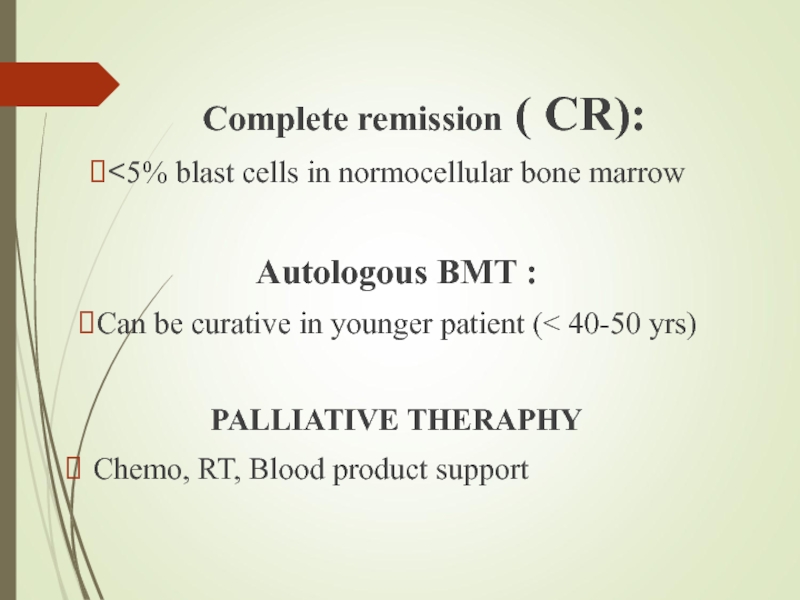
Слайд 20 Complete remission ( CR):
<5% blast cells in normocellular bone marrow
Autologous BMT :
Can be curative in younger patient (< 40-50 yrs)
PALLIATIVE THERAPHY
Chemo, RT, Blood product support
Слайд 22Prognosis
Median survival without treatment is 5 weeks
30% 5-yr survival in younger
Disease which relapses during treatment or soon after the end of treatment has a poor prognosis
Слайд 23Poor prognostic factors
Increasing age
Male sex
High WBC count at diagnosis
CNS involvement at
Cytogenetic abnormalities
Antecedent hematological abnormalities (eg. MDS)
No complete remission
Слайд 24Literature:
1. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). SIGN 50: a guideline developer’s
2. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. www.nccn.org.
3. Pui C.H., Evans W.E.Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;
4. Pui C.H., Evans W.E.Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;