- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Intro to Geometric Modeling (GM) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Intro to Geometric Modeling (GM)
- 2. * Intro to Geometric Modeling (GM) The
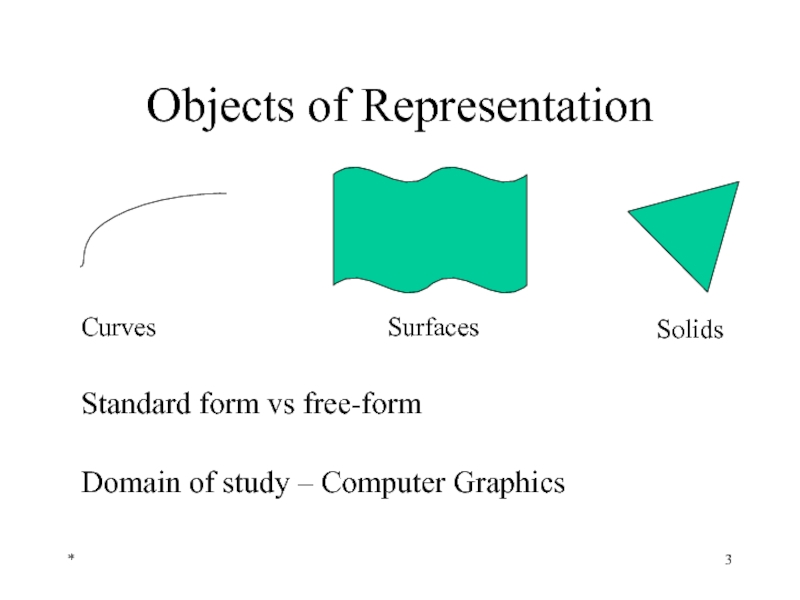
- 3. Objects of Representation * Standard form vs free-form Domain of study – Computer Graphics
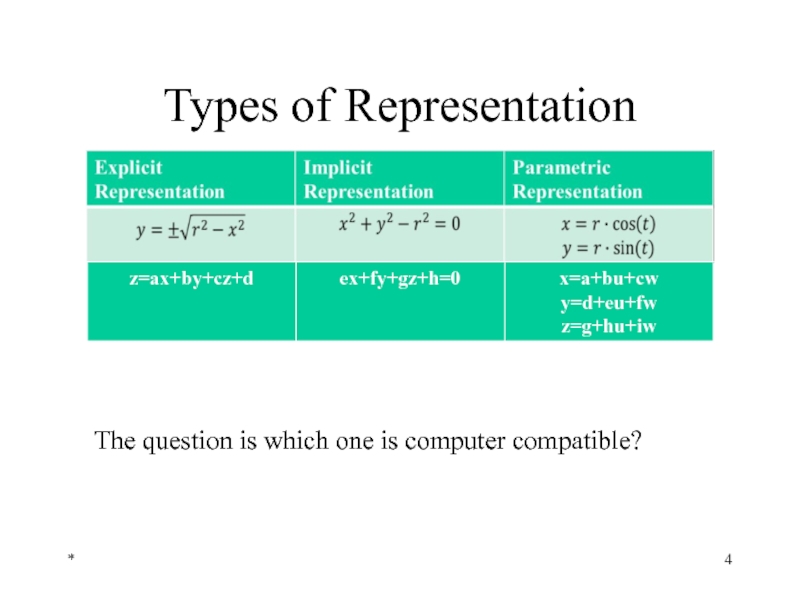
- 4. Types of Representation * The question is which one is computer compatible?
- 5. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency
- 6. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency
- 7. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency
- 8. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency
- 9. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency
- 10. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency
- 11. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency
- 12. Advantages of PR Get rid of dependency
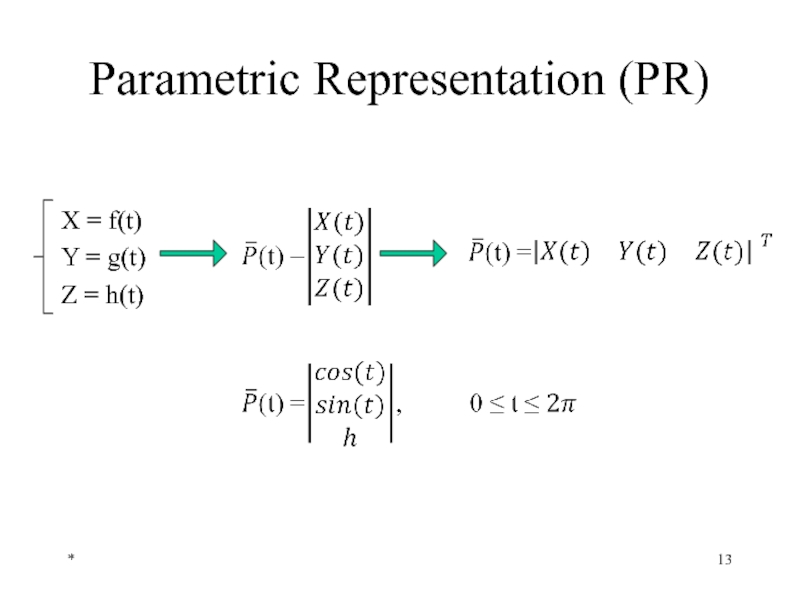
- 13. Parametric Representation (PR) X = f(t) Y
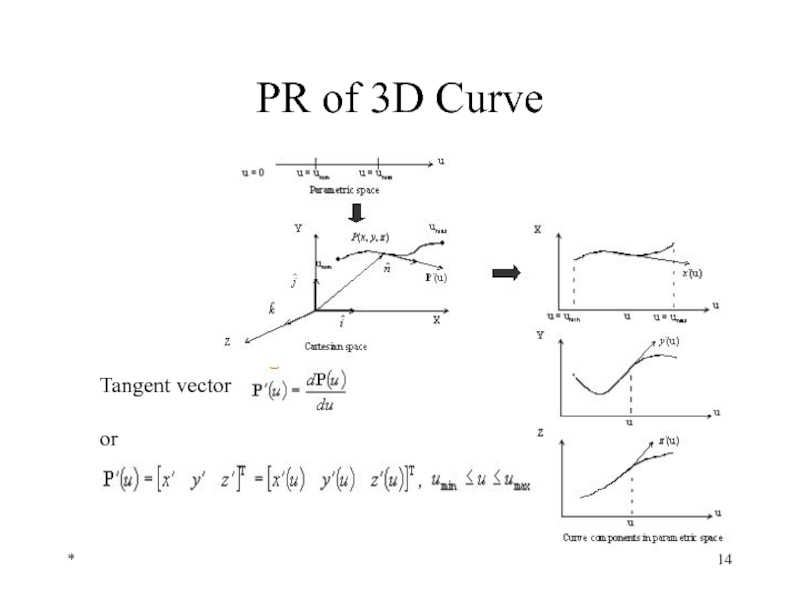
- 14. * PR of 3D Curve Tangent vector or
- 15. * PR of Analytic Curves Analytic curves
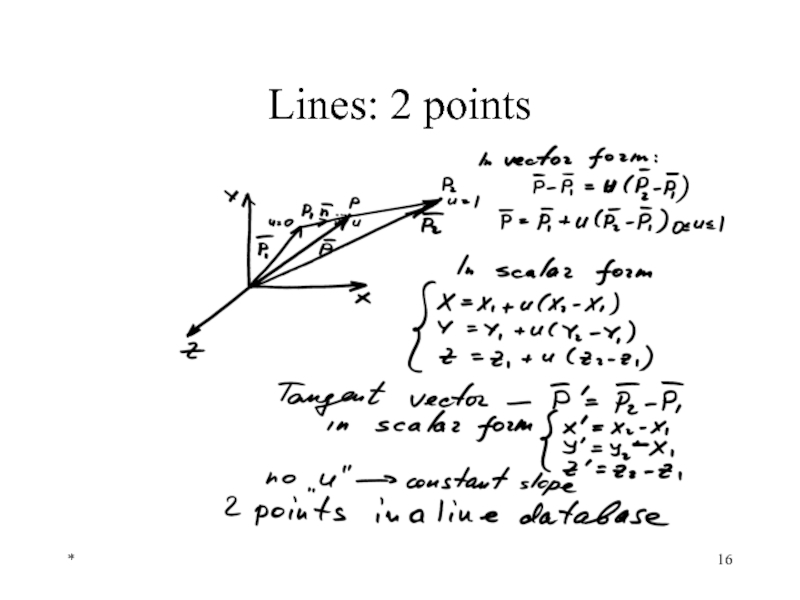
- 16. * Lines: 2 points
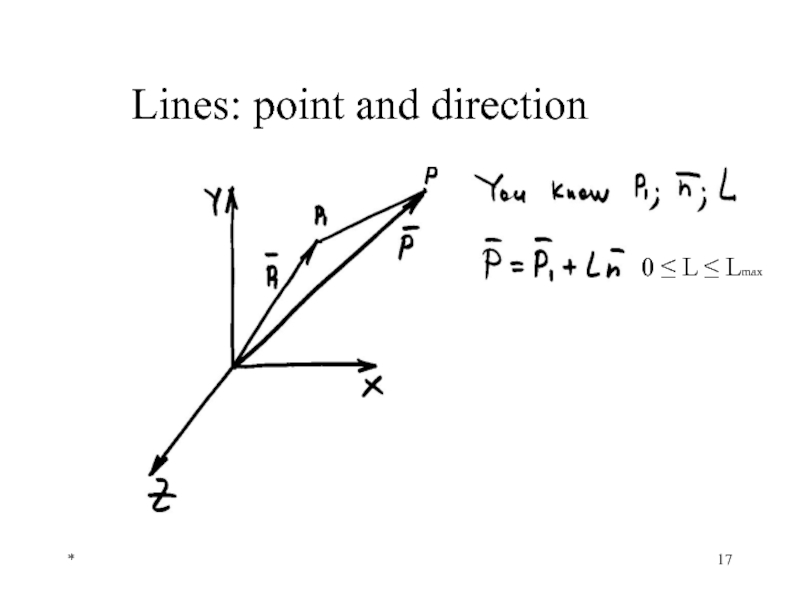
- 17. * Lines: point and direction n
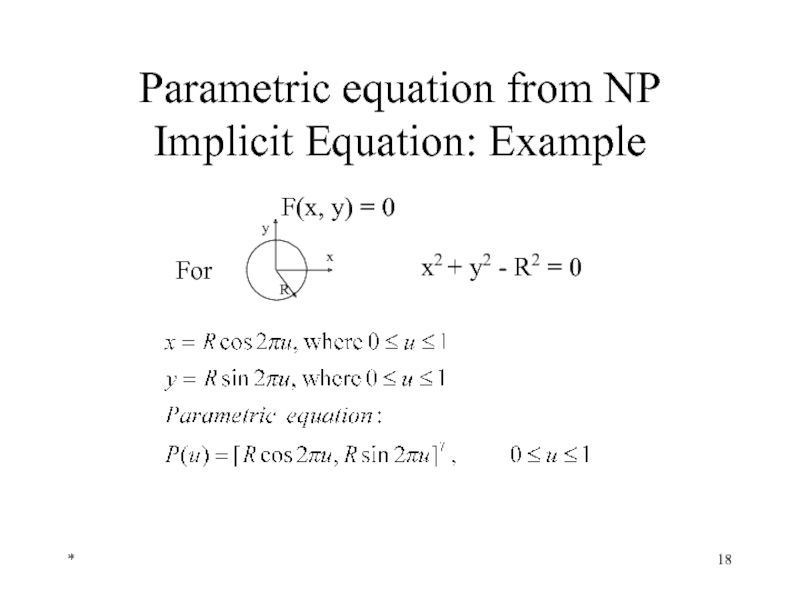
- 18. * Parametric equation from NP Implicit Equation:
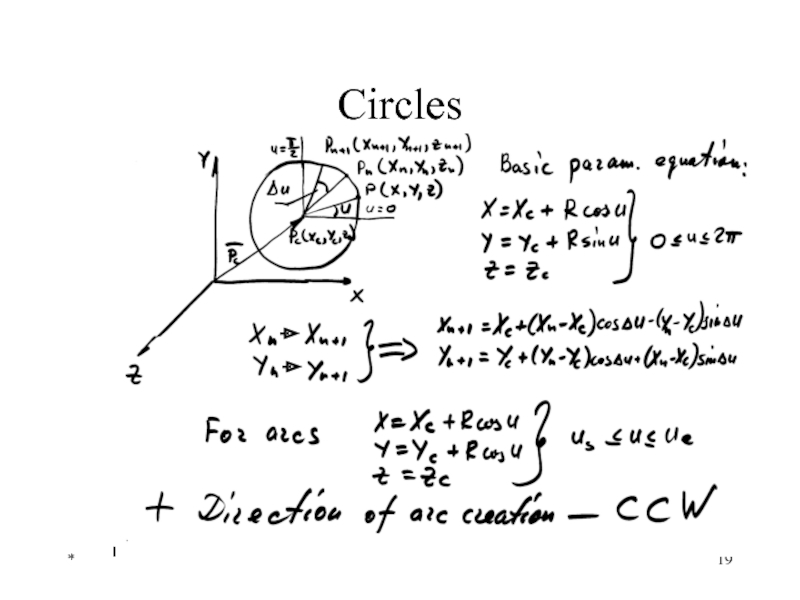
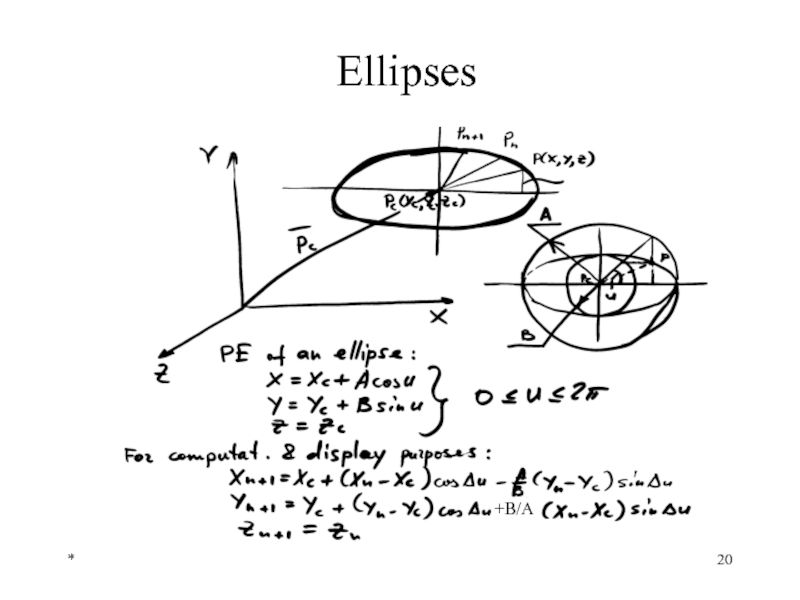
- 19. * Circles
- 20. * Ellipses +B/A
- 21. * Examples Find the equation and endpoints
Слайд 2*
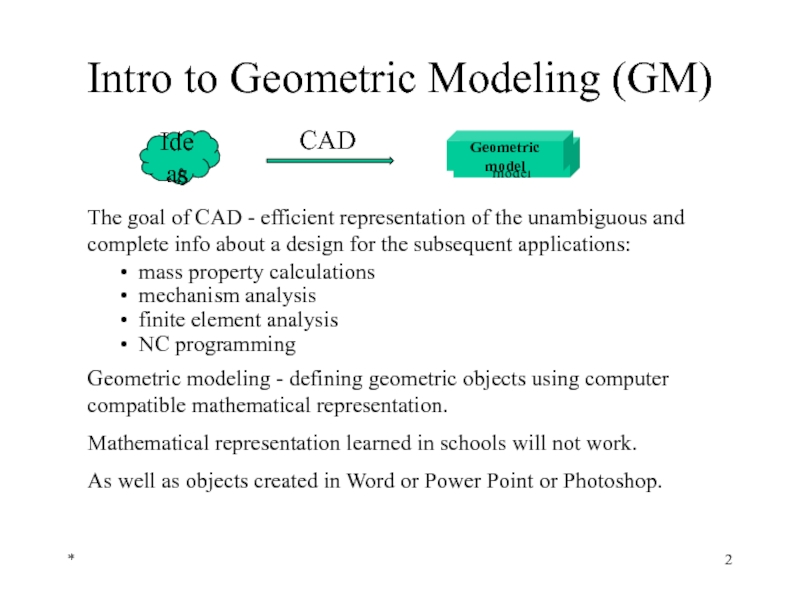
Intro to Geometric Modeling (GM)
The goal of CAD - efficient representation
mass property calculations
mechanism analysis
finite element analysis
NC programming
Geometric modeling - defining geometric objects using computer compatible mathematical representation.
Mathematical representation learned in schools will not work.
As well as objects created in Word or Power Point or Photoshop.
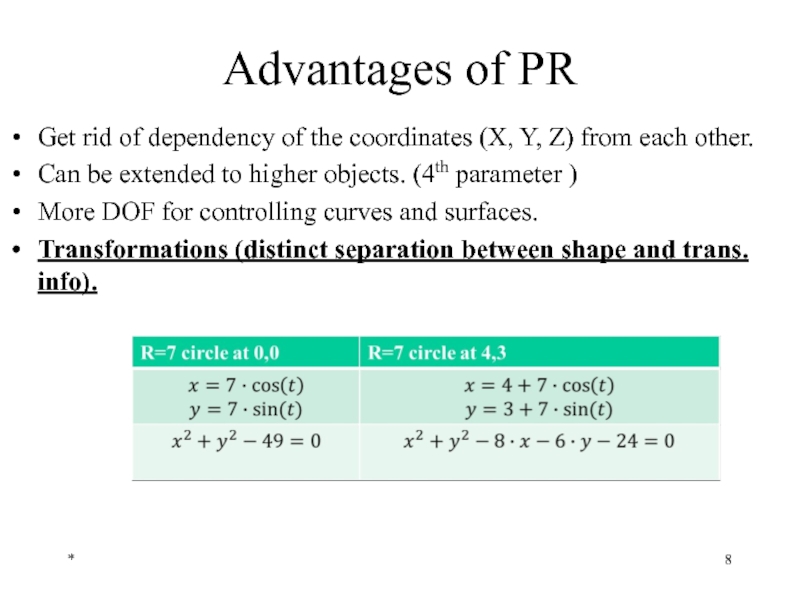
Слайд 6Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y,
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
*
Слайд 7Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y,
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
*
Слайд 8Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y,
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
*
Слайд 9Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y,
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
Vector – matrix multiplication (not good for you, good for comp).
*
Слайд 10Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y,
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
Vector – matrix multiplication (not good for you, good for comp.).
Bounded objects are represented with one-to one relationship.
*
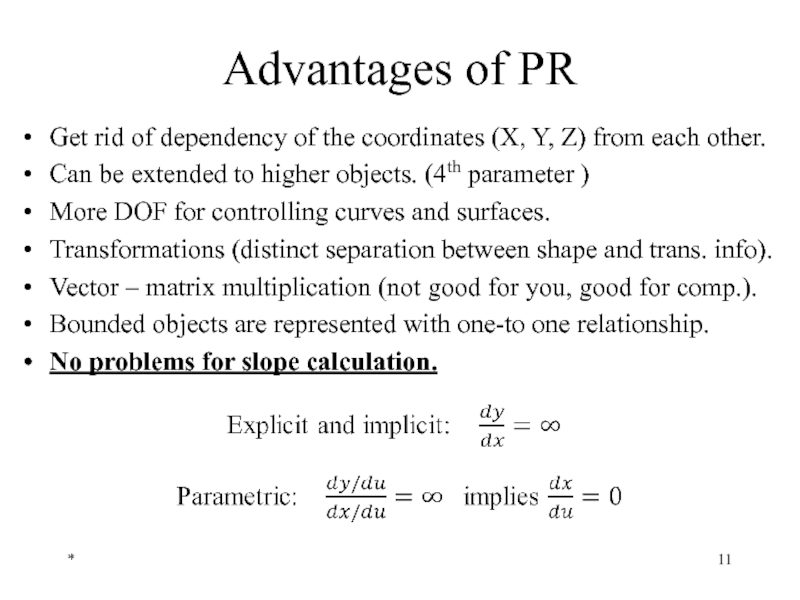
Слайд 11Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y,
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
Vector – matrix multiplication (not good for you, good for comp.).
Bounded objects are represented with one-to one relationship.
No problems for slope calculation.
*
Слайд 12Advantages of PR
Get rid of dependency of the coordinates (X, Y,
Can be extended to higher objects. (4th parameter )
More DOF for controlling curves and surfaces.
Transformations (distinct separation between shape and trans. info).
Vector – matrix multiplication (not good for you, good for comp.).
Bounded objects are represented with one-to one relationship.
No problems for slope calculation.
Discretizing entities
*
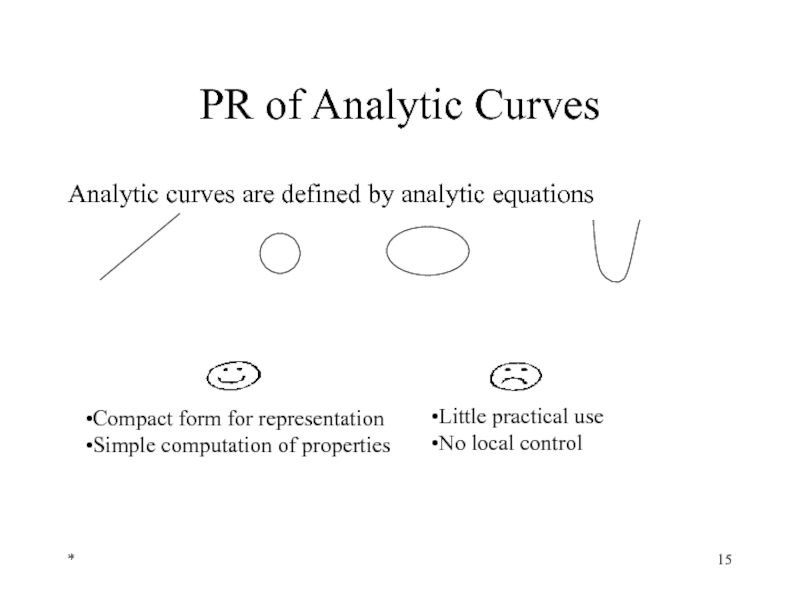
Слайд 15*
PR of Analytic Curves
Analytic curves are defined by analytic equations
Compact form
Simple computation of properties
Little practical use
No local control
Слайд 21*
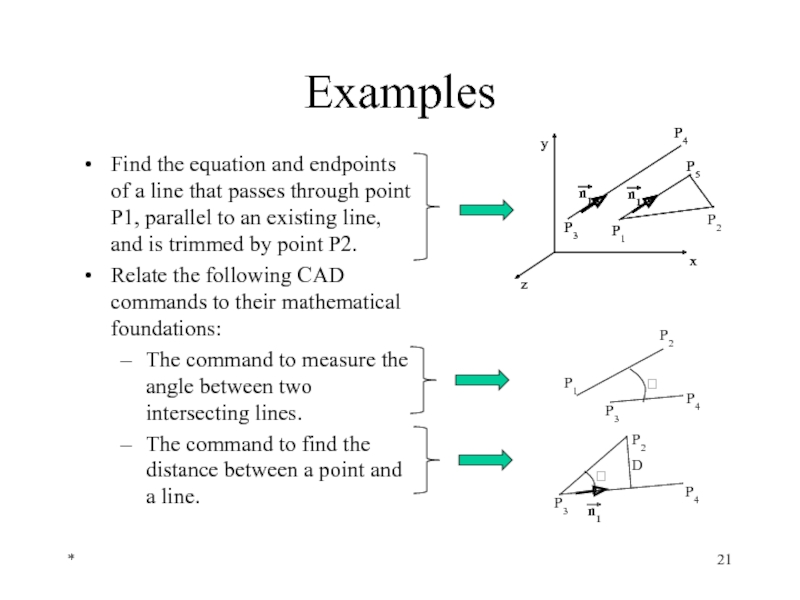
Examples
Find the equation and endpoints of a line that passes through
Relate the following CAD commands to their mathematical foundations:
The command to measure the angle between two intersecting lines.
The command to find the distance between a point and a line.
P2