- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Collision Detection презентация
Содержание
- 1. Collision Detection
- 2. Essential Math for Games Collisions Up to
- 3. Essential Math for Games Computational Geometry Algorithms
- 4. Essential Math for Games Distance Testing Useful
- 5. Essential Math for Games Point-Point Distance Compute
- 6. Essential Math for Games Line-Point Distance Line
- 7. Essential Math for Games Line-Point Distance Final formula: If v isn't normalized:
- 8. Essential Math for Games Line-Line Distance From
- 9. Essential Math for Games Line-Line Distance Final
- 10. Essential Math for Games Segment-Segment Distance Determine
- 11. Essential Math for Games Bounding Objects Detecting
- 12. Essential Math for Games Bounding Sphere Tightest
- 13. Essential Math for Games Bounding Sphere (Cont’d)
- 14. Essential Math for Games Sphere-Sphere Collision Compute
- 15. Essential Math for Games Bounding Box
- 16. Essential Math for Games Axis-Aligned Bounding Box
- 17. Essential Math for Games Axis-Aligned Box-Box Collision
- 18. Essential Math for Games Object-Oriented Bounding Box
- 19. Essential Math for Games OBB Collision Idea:
- 20. Essential Math for Games OBB Collision To
- 21. Essential Math for Games Capsule Cylinder with
- 22. Essential Math for Games Capsule Compact Only
- 23. Essential Math for Games Capsule-Capsule Collision Key:
- 24. Essential Math for Games Caveat Math assumes
- 25. Essential Math for Games Which To Use?
- 26. Essential Math for Games Recap Sphere --
- 27. Essential Math for Games Collision Detection Naïve:
- 28. Essential Math for Games Broad Phase Obvious
- 29. Essential Math for Games Hierarchical Systems Can
- 30. Essential Math for Games Hierarchical Systems Can
- 31. Essential Math for Games Spatial Subdivision Break
- 32. Essential Math for Games Sweep and Prune
- 33. Essential Math for Games Spatial Subdivision Other
- 34. Essential Math for Games Temporal Coherence Objects
- 35. Essential Math for Games Narrow Phase Have
- 36. Essential Math for Games Contact Region Two
- 37. Essential Math for Games Contact Features Faceted
- 38. Essential Math for Games Contact Features For
- 39. Essential Math for Games Contact Points Can
- 40. Essential Math for Games Example: Spheres Difference
- 41. Essential Math for Games Example: Spheres Collision
- 42. Essential Math for Games Lin-Canny For convex
- 43. Essential Math for Games Lin-Canny Frame 0 Frame 1
- 44. Essential Math for Games GJK For Convex
- 45. Essential Math for Games GJK CSO Simplex Refinement
- 46. Essential Math for Games Missing Collision If
- 47. Essential Math for Games Missing Collision One
- 48. Essential Math for Games Missing Collision Another
- 49. Essential Math for Games Recap Collision detection
- 50. Essential Math for Games References Preparata, Franco
- 51. Essential Math for Games References Van den
Слайд 2Essential Math for Games
Collisions
Up to this point, objects just pass through
Two parts to handling collisions
Collision detection – uses computational geometry techniques (useful in other ways, too)
Collision response – modifying physical simulation
Слайд 3Essential Math for Games
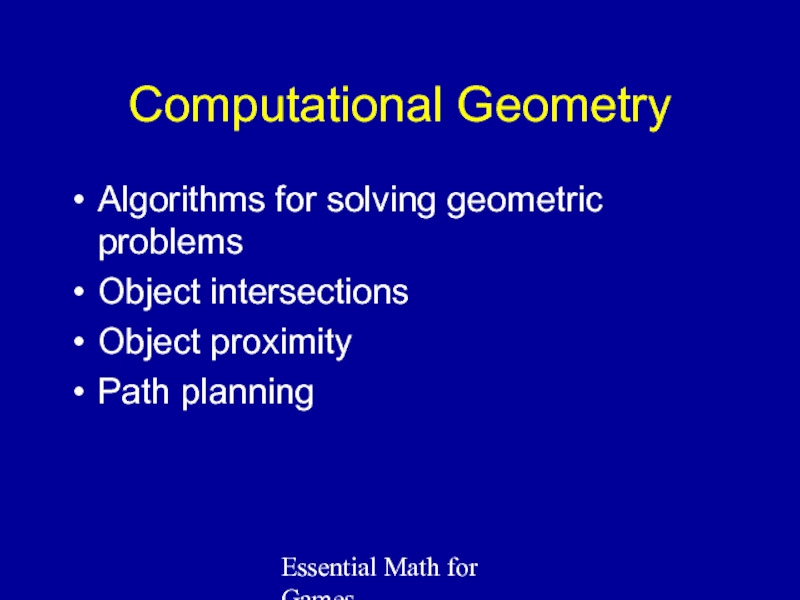
Computational Geometry
Algorithms for solving geometric problems
Object intersections
Object proximity
Path
Слайд 4Essential Math for Games
Distance Testing
Useful for computing intersection between simple objects
E.g.
Just cover a few examples
Слайд 5Essential Math for Games
Point-Point Distance
Compute length of vector between two points
Слайд 6Essential Math for Games
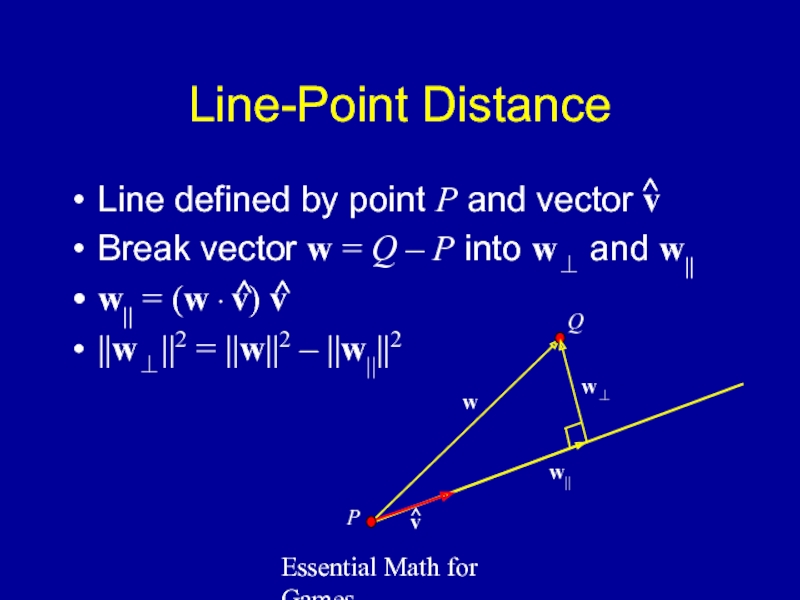
Line-Point Distance
Line defined by point P and vector
Break vector w = Q – P into w⊥ and w||
w|| = (w ∙ v) v
||w⊥||2 = ||w||2 – ||w||||2
^
^
^
v
Q
P
w
w||
w⊥
^
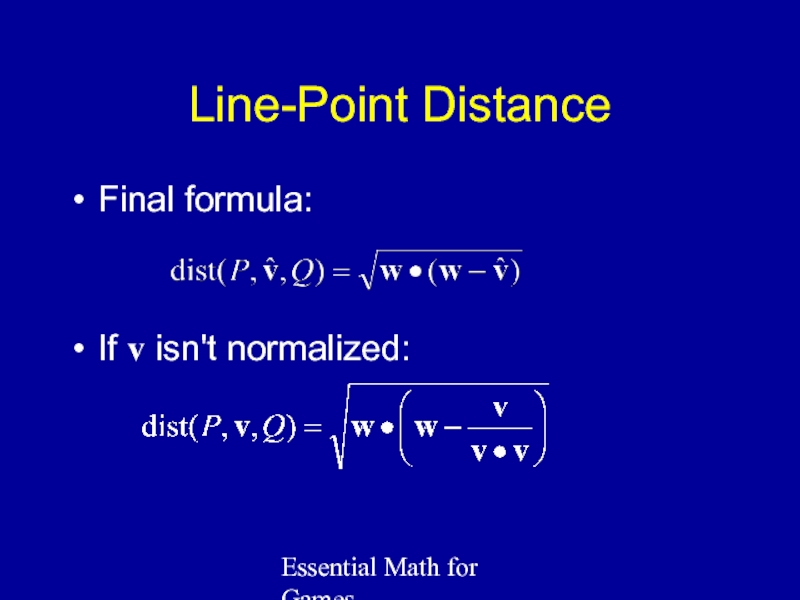
Слайд 8Essential Math for Games
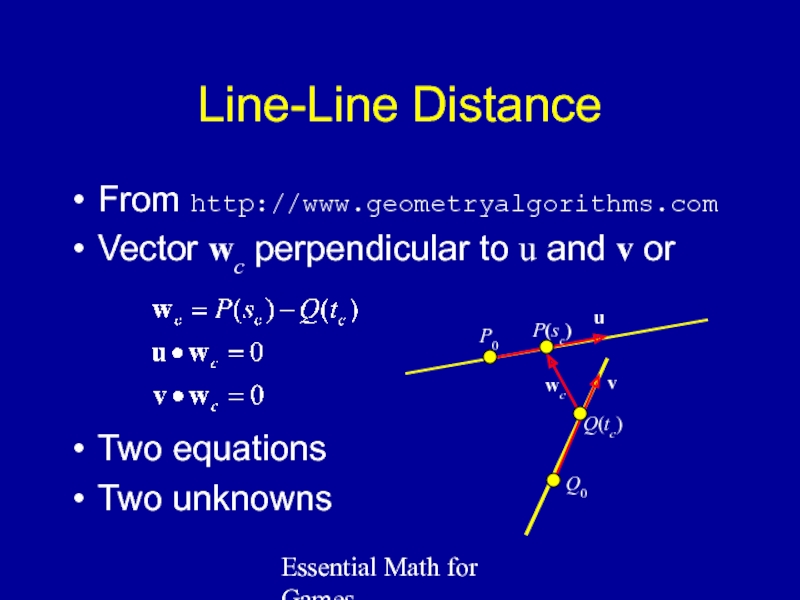
Line-Line Distance
From http://www.geometryalgorithms.com
Vector wc perpendicular to u and
Two equations
Two unknowns
P0
u
Q0
v
P(sc)
Q(tc)
wc
Слайд 10Essential Math for Games
Segment-Segment Distance
Determine closest point between lines
If lies on
Otherwise clamp against nearest endpoint and recompute
See references for details
Слайд 11Essential Math for Games
Bounding Objects
Detecting intersections with complex objects expensive
Provide simple
Use for collision, rendering, picking
Cover in increasing order of complexity
Слайд 12Essential Math for Games
Bounding Sphere
Tightest sphere that surrounds model
For each point,
Слайд 13Essential Math for Games
Bounding Sphere (Cont’d)
What to use for center?
Local origin
Centroid (average of all points)
Center of bounding box
Want a good fit to cull as much as possible
Linear programming gives smallest fit
Слайд 14Essential Math for Games
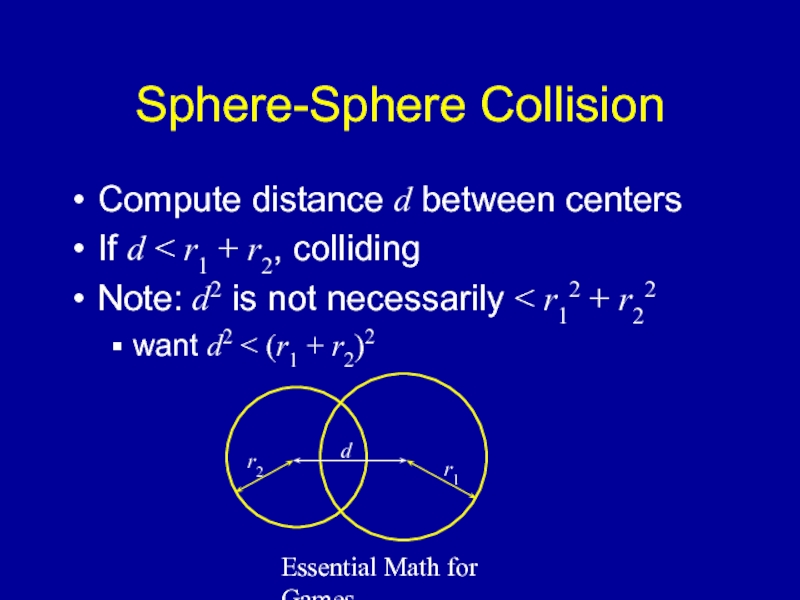
Sphere-Sphere Collision
Compute distance d between centers
If d
Note: d2 is not necessarily < r12 + r22
want d2 < (r1 + r2)2
d
r1
r2
Слайд 15Essential Math for Games
Bounding Box
Tightest box that surrounds model
Compare points to
If element less/greater, set element in min/max
(min x, min y)
(max x, max y)
Слайд 16Essential Math for Games
Axis-Aligned Bounding Box
Box edges aligned to world axes
Recalc
Collision checks are cheaper though
Слайд 17Essential Math for Games
Axis-Aligned Box-Box Collision
Compare x values in min,max vertices
If
Otherwise check y and z directions
min1
max1
min2
max2
Слайд 18Essential Math for Games
Object-Oriented Bounding Box
Box edges aligned with local object
Much tighter, but collision calcs costly
Слайд 19Essential Math for Games
OBB Collision
Idea: determine if separating plane between boxes
Project box extent onto plane vector, test against projection btwn centers
c∙v
b∙v
a∙v
a
b
c
Слайд 20Essential Math for Games
OBB Collision
To ensure maximum extents, take dot product
Check against axes for both boxes, plus cross products of all axes
See Gottschalk for more details
Слайд 21Essential Math for Games
Capsule
Cylinder with hemispheres on ends
One way to compute
Calc
Use long axis for length
Next largest width for radius
Слайд 22Essential Math for Games
Capsule
Compact
Only store radius, endpoints of line segment
Oriented shape
Test path collision
Слайд 23Essential Math for Games
Capsule-Capsule Collision
Key: swept sphere axis is line segment
Compute distance between line segments
If less than r1 + r2, collide
Слайд 24Essential Math for Games
Caveat
Math assumes infinite precision
Floating point is not to
Precision worse farther from 0
Use epsilons
Careful of operation order
Re-use computed results
More on floating point on website
Слайд 25Essential Math for Games
Which To Use?
As many as necessary
Start with cheap
Sphere
Swept Sphere
Box
May not need them all
Слайд 26Essential Math for Games
Recap
Sphere -- cheap, not a good fit
AABB --
Swept Sphere -- oriented, cheaper than OBB but generally not as good a fit
OBB -- somewhat costly, but a better fit
Слайд 27Essential Math for Games
Collision Detection
Naïve: n2 checks!
Two part process
Broad phase
Cull out
Narrow phase
Determine penetration and contact points between pairs
Слайд 28Essential Math for Games
Broad Phase
Obvious steps
Only check each pair once
Flag object
Only check moving objects
Check against other moving and static
Check rough bounding object first
AABB or sphere
Слайд 29Essential Math for Games
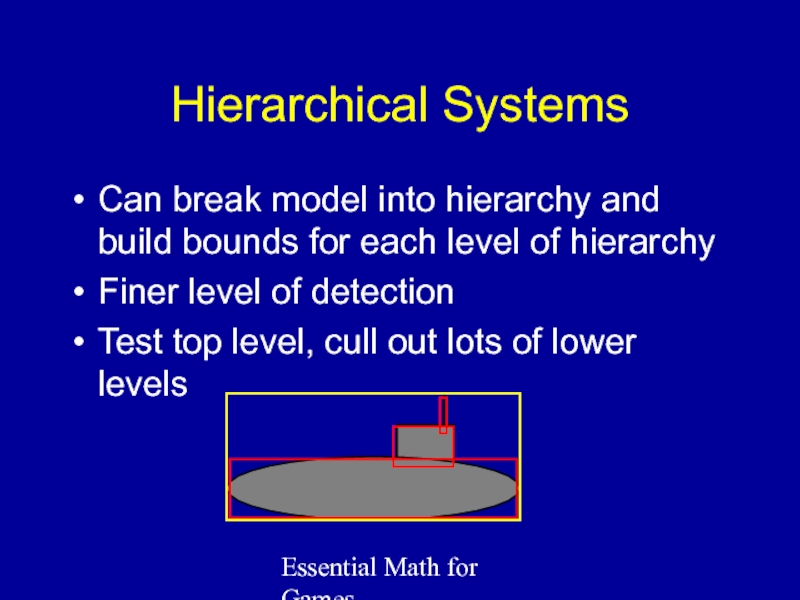
Hierarchical Systems
Can break model into hierarchy and build
Finer level of detection
Test top level, cull out lots of lower levels
Слайд 30Essential Math for Games
Hierarchical Systems
Can use scene graph to maintain bounding
Propagate transforms down to children
Propagate bound changes up to root
Слайд 31Essential Math for Games
Spatial Subdivision
Break world into separate areas
Only check your
Simplest: uniform
Slabs
Grid
Voxels
Слайд 32Essential Math for Games
Sweep and Prune
Store sorted x extents of objects
Sweep
As object min value comes up, make active, test against active objects
Can extend to more dimensions
Слайд 33Essential Math for Games
Spatial Subdivision
Other methods:
Quadtrees, octrees
BSP trees, kd-trees
Room-portal
Choice depends on
Слайд 34Essential Math for Games
Temporal Coherence
Objects nearby generally stay nearby
Check those first
Can
Слайд 35Essential Math for Games
Narrow Phase
Have culled object pairs
Need to find
Contact
Normal
Penetration (if any)
Слайд 36Essential Math for Games
Contact Region
Two objects interpenetrate, have one (or more)
A bit messy to deal with
Many try to avoid interpenetration
Слайд 37Essential Math for Games
Contact Features
Faceted objects collide at pair of contact
Only consider E-E and F-V pairs
Infinite possibilities for normals for others
Can generally convert to E-E and F-V
Ex: V-V, pick neighboring face for one
Слайд 38Essential Math for Games
Contact Features
For E-E:
Point is intersection of edges
Normal is
For F-V:
Point is vertex location
Normal is face normal
Слайд 39Essential Math for Games
Contact Points
Can have multiple contact points
Ex: two concave
Store as part of collision detection
Collate as part of collision resolution
Слайд 40Essential Math for Games
Example: Spheres
Difference between centers gives normal n (after
Penetration distance p is p = (r1+r2) - ||c2-c1||
c1
c2
Слайд 41Essential Math for Games
Example: Spheres
Collision point: average of penetration distance along
If touching, where normal crosses sphere
v = ½(c1 + r1n + c2 - r2n)
^
^
c1
c2
Слайд 42Essential Math for Games
Lin-Canny
For convex objects
Easy to understand, hard to implement
Closest
Track between frames
Modify by walking along object
Слайд 44Essential Math for Games
GJK
For Convex Objects
Hard to understand, easy to implement
Finds
Iteratively finds points by successive refinement of simplices
Слайд 46Essential Math for Games
Missing Collision
If time step is too large for
Слайд 47Essential Math for Games
Missing Collision
One solution: slice time interval
Simulate between slices
Same
Слайд 48Essential Math for Games
Missing Collision
Another solution: use swept volumes
If volumes collide,
With more work can determine time-of-impact (TOI), if any
Слайд 49Essential Math for Games
Recap
Collision detection complex
Combo of math and computing
Break into
Be careful of tunneling
Слайд 50Essential Math for Games
References
Preparata, Franco P. and Michael Ian Shamos, Computational
O’Rourke, Joseph, Computational Geometry in C, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1994.
Eberly, David H., 3D Game Engine Design, Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, 2001.
Gottschalk, Stephan, Ming Lin and Dinesh Manocha, “OBB-Tree: A Hierarchical Structure for Rapid Interference Detection,” SIGGRAPH ‘96.
Слайд 51Essential Math for Games
References
Van den Bergen, Gino, Collision Detection in Interactive
Eberly, David H., Game Physics, Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, 2003.
Ericson, Christer, Real-Time Collision Detection, Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, 2004.