- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The Market Forces of Supply and Demand презентация
Содержание
- 1. The Market Forces of Supply and Demand
- 2. The Market Forces of Supply
- 3. Markets A market is
- 4. Markets Buyers determine demand. Sellers determine supply.
- 5. Market Type: A Competitive Market A
- 6. Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Products are
- 7. Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Monopoly One
- 8. Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Monopolistic Competition
- 9. Demand Quantity demanded is the amount
- 10. Law of Demand The law of demand
- 11. Demand Schedule The demand schedule is a
- 12. Demand Schedule
- 13. Determinants of Demand Market price Consumer income Prices of related goods Tastes Expectations
- 14. Demand Curve The demand curve is the downward-sloping line relating price to quantity demanded.
- 15. Demand Curve $3.00
- 16. Ceteris Paribus Ceteris paribus is
- 17. Market Demand Market demand refers to the
- 18. Determinants of Demand Market price Consumer income Prices of related goods Tastes Expectations
- 19. Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in
- 20. Changes in Quantity Demanded 0 D1 Price
- 21. Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in
- 22. Changes in Demand 0 D1 Price of
- 23. Consumer Income As income increases the demand
- 24. Consumer Income Normal Good $3.00
- 25. Consumer Income Inferior Good $3.00
- 26. Prices of Related Goods Substitutes & Complements
- 27. Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in
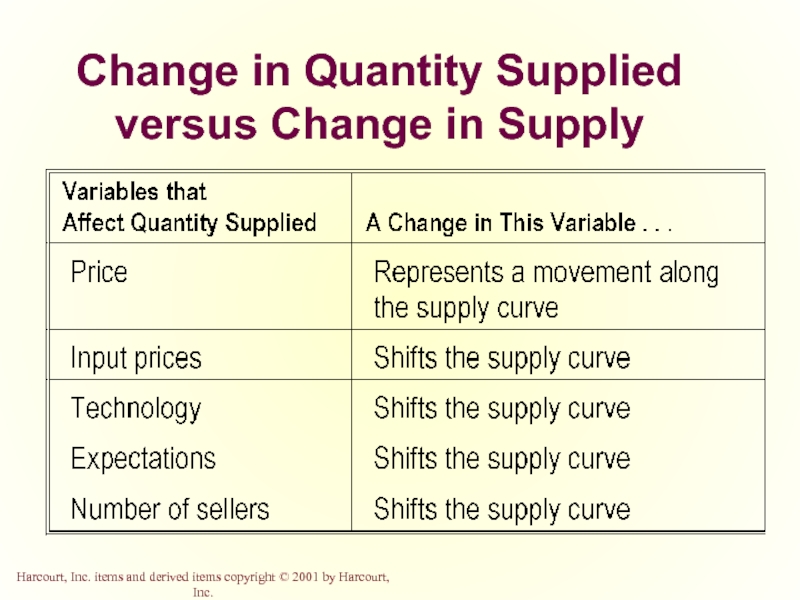
- 28. Supply Quantity supplied is the amount of
- 29. Law of Supply The law of supply
- 30. Determinants of Supply Market price Input prices Technology Expectations Number of producers
- 31. Supply Schedule The supply schedule is a
- 32. Supply Schedule
- 33. Supply Curve The supply curve
- 34. Supply Curve $3.00 2.50
- 35. Market Supply Market supply refers to the
- 36. Determinants of Supply Market price Input prices Technology Expectations Number of producers
- 37. Change in Quantity Supplied versus
- 38. Change in Quantity Supplied
- 39. Change in Quantity Supplied versus Change in
- 40. Change in Supply Price
- 41. Change in Quantity Supplied versus Change in Supply
- 42. Supply and Demand Together Equilibrium
- 43. Supply and Demand Together Demand
- 44. Price of Ice-Cream
- 45. Price of Ice-Cream
- 46. Surplus When the price is above the
- 47. Excess Demand Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Price
- 48. Shortage When the price is below the
- 49. Three Steps To Analyzing Changes
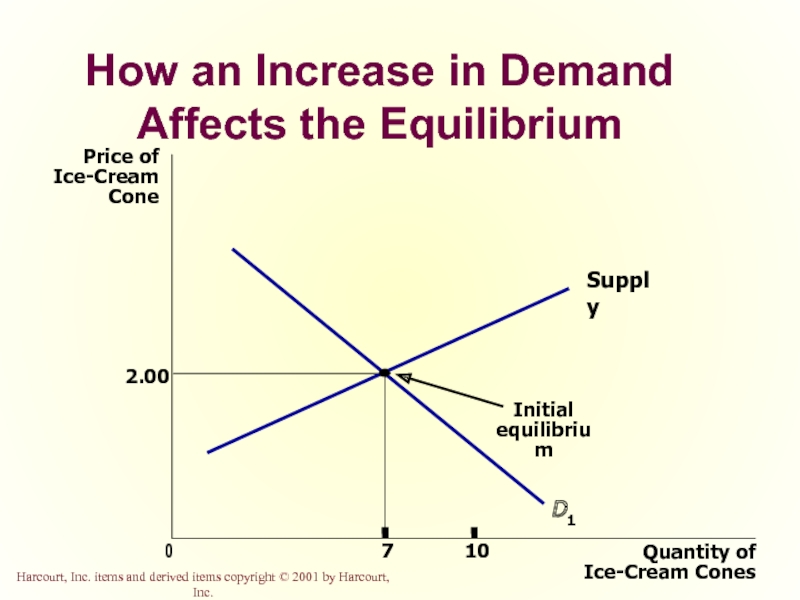
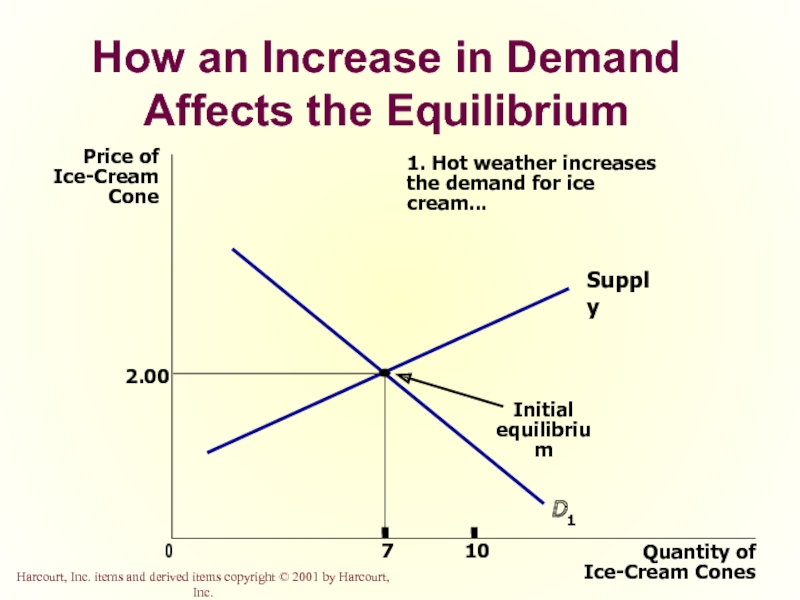
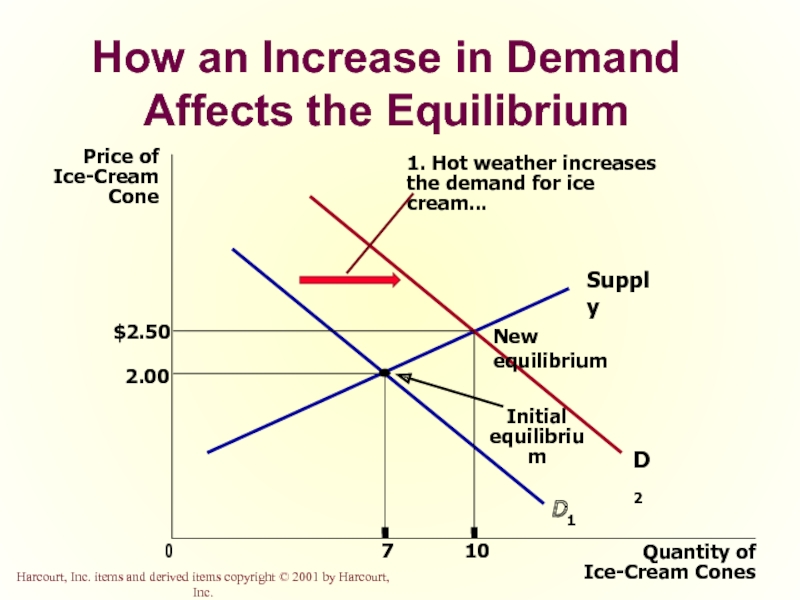
- 50. How an Increase in Demand Affects the
- 51. Shifts in Curves versus Movements along Curves
- 52. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the
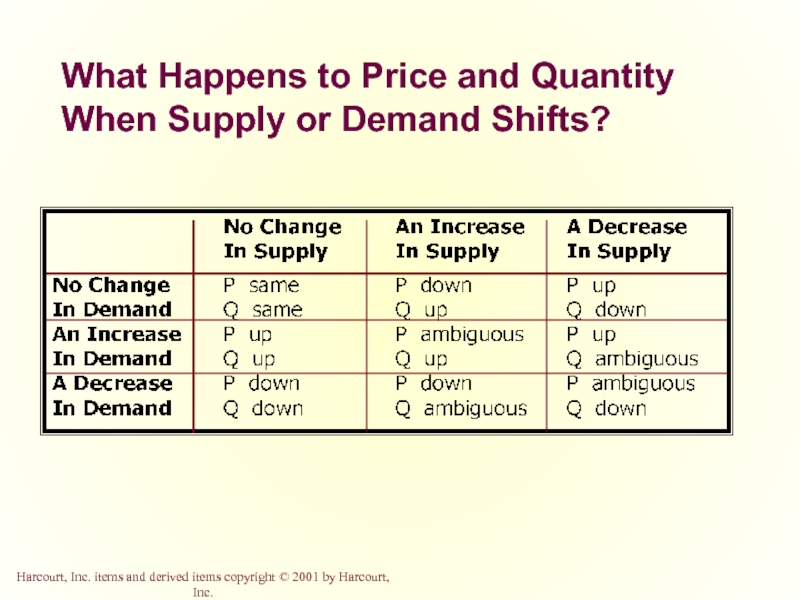
- 53. What Happens to Price and Quantity When Supply or Demand Shifts?
- 54. Summary Economists use the model of supply
- 55. Summary According to the law of demand,
- 56. Summary The supply curve shows how the
- 57. Summary In addition to price, other determinants
- 58. Summary Supply and demand together determine the
- 60. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
- 61. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
- 62. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
- 63. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
- 64. How an Increase in Demand Affects the
- 65. How an Increase in Demand Affects the
- 66. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 67. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 68. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 69. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 70. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 71. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
Слайд 1
The Market Forces of Supply and Demand
Chapter 4
Copyright © 2001 by
Permissions Department, Harcourt College Publishers, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887-6777.
Слайд 2
The Market Forces of
Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are the
Supply and demand are the forces that make market economies work.
Modern microeconomics is about supply, demand, and market equilibrium.
Слайд 3
Markets
A market is a group of buyers and sellers of
The terms supply and demand refer to the behavior of people . . . as they interact with one another in markets.
Слайд 5Market Type:
A Competitive Market
A competitive market is a market. .
with many buyers and sellers.
that is not controlled by any one person.
in which a narrow range of prices are established that buyers and sellers act upon.
Слайд 6Competition:
Perfect and Otherwise
Products are the same
Numerous buyers and sellers so
Buyers and Sellers are price takers
Perfect Competition
Слайд 7Competition:
Perfect and Otherwise
Monopoly
One seller, and seller controls price
Oligopoly
Few sellers
Not always
Слайд 8Competition:
Perfect and Otherwise
Monopolistic Competition
Many sellers
Slightly differentiated products
Each seller may set
Слайд 9Demand
Quantity demanded
is the amount
of a good that buyers are
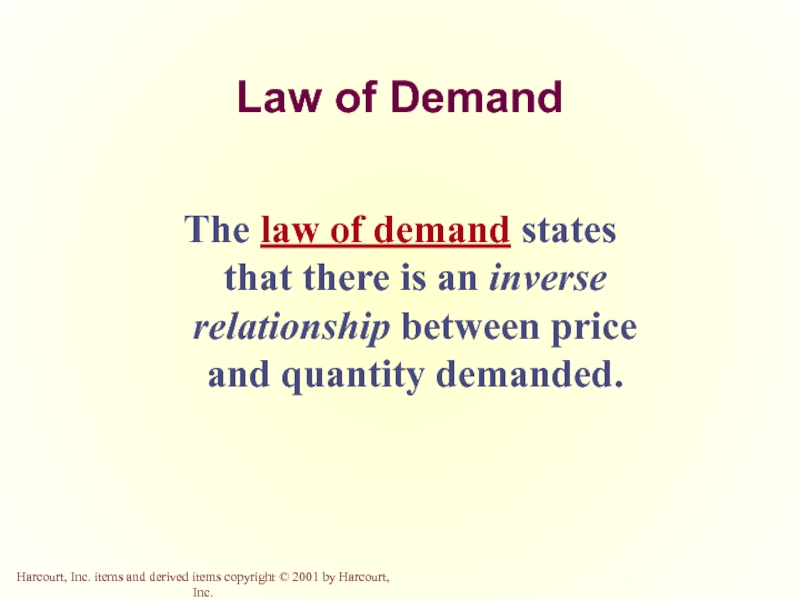
Слайд 10Law of Demand
The law of demand states that there is an
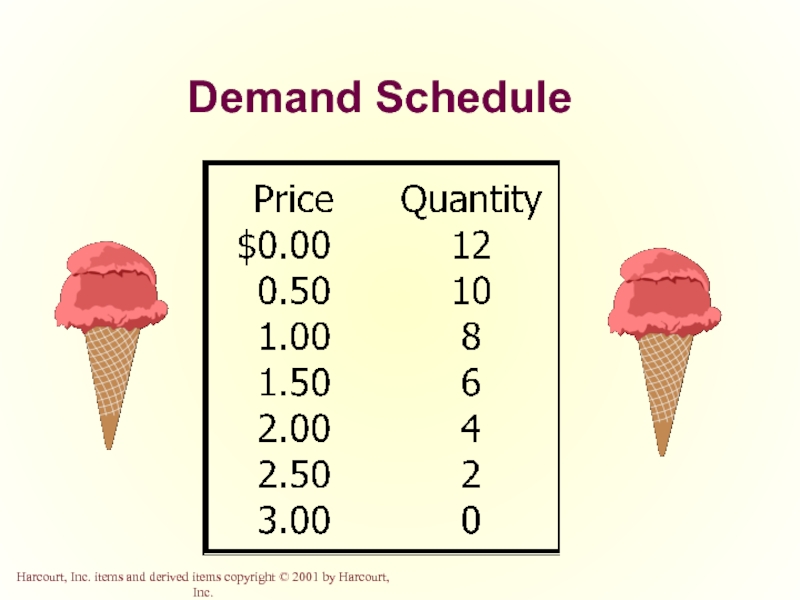
Слайд 11Demand Schedule
The demand schedule is a table
that shows the relationship
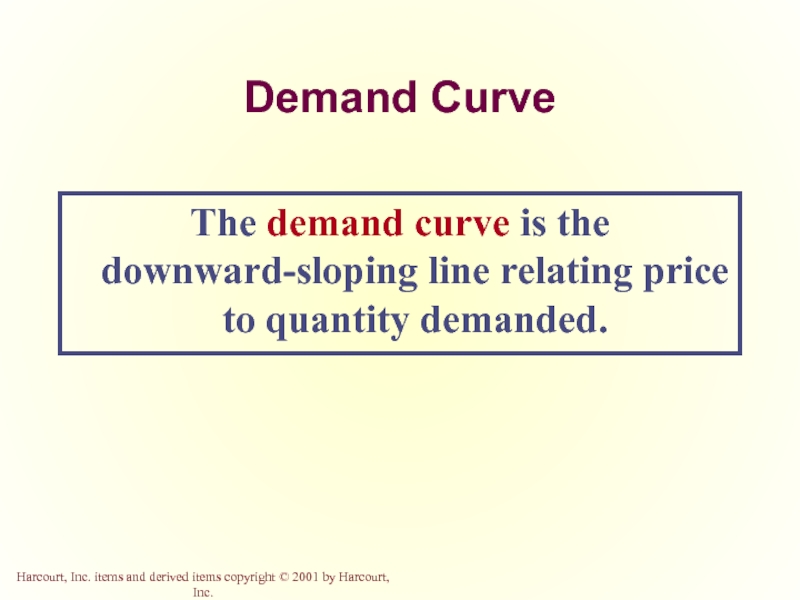
Слайд 14Demand Curve
The demand curve is the downward-sloping line relating price to
Слайд 15
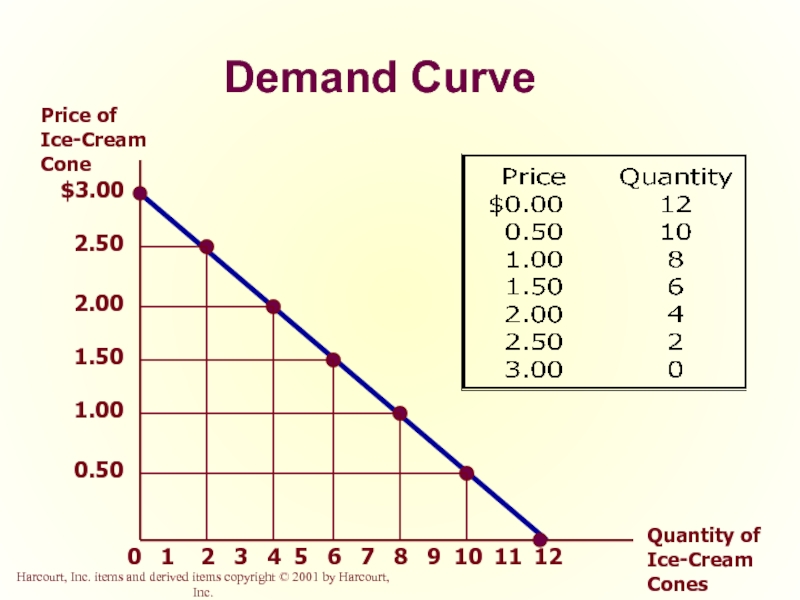
Demand Curve
$3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
11
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
0
Слайд 16
Ceteris Paribus
Ceteris paribus is a Latin phrase that means all variables
The demand curve slopes downward because, ceteris paribus, lower prices imply a greater quantity demanded!
Слайд 17Market Demand
Market demand refers to the sum of all individual demands
Graphically, individual demand curves are summed horizontally to obtain the market demand curve.
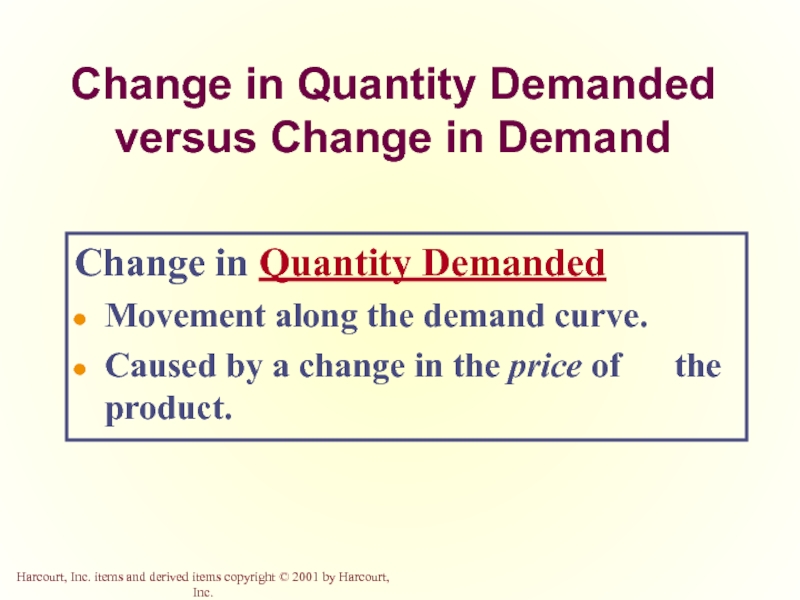
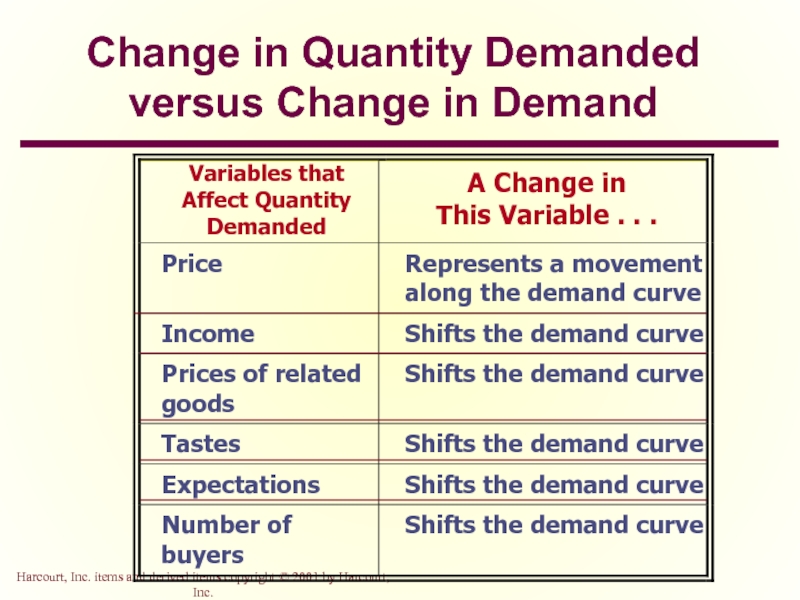
Слайд 19Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in Demand
Change in Quantity Demanded
Movement
Caused by a change in the price of the product.
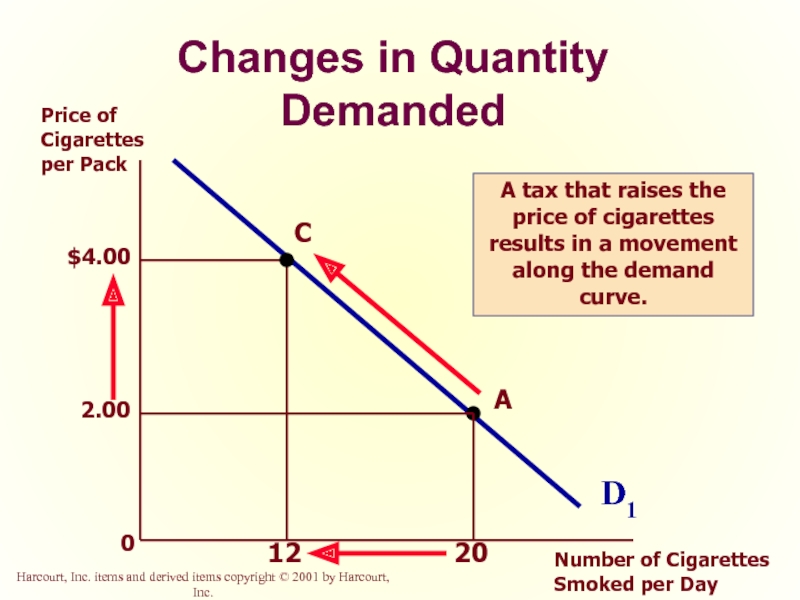
Слайд 20Changes in Quantity Demanded
0
D1
Price of Cigarettes per Pack
Number of Cigarettes Smoked
A tax that raises the price of cigarettes results in a movement along the demand curve.
A
20
2.00
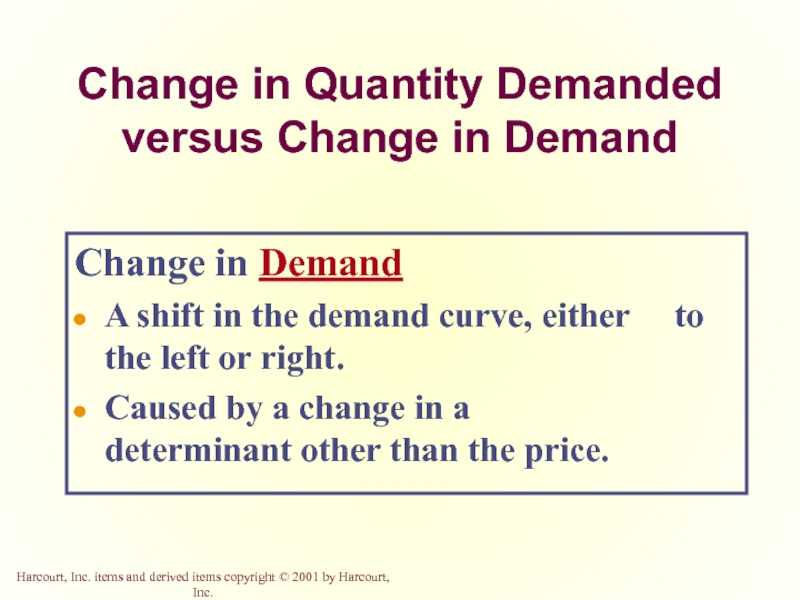
Слайд 21Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in Demand
Change in Demand
A shift
Caused by a change in a determinant other than the price.
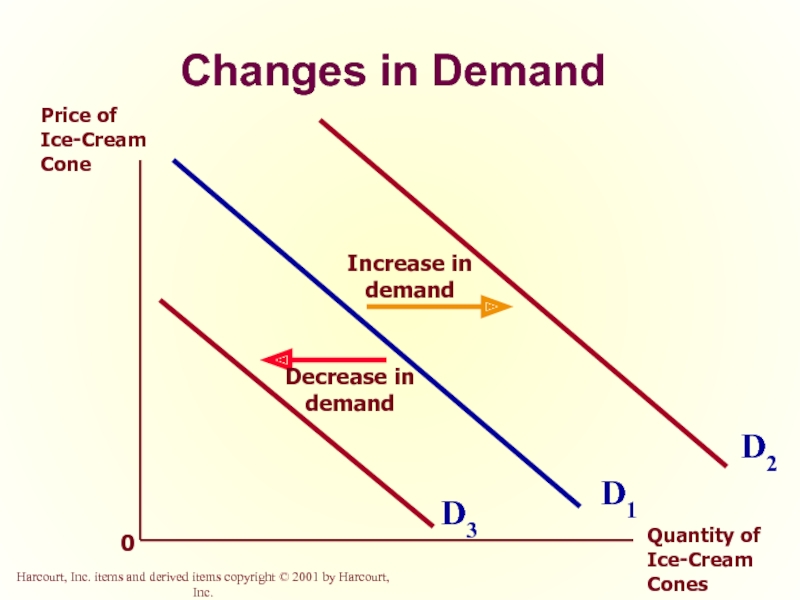
Слайд 22Changes in Demand
0
D1
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
D3
D2
Increase in demand
Decrease
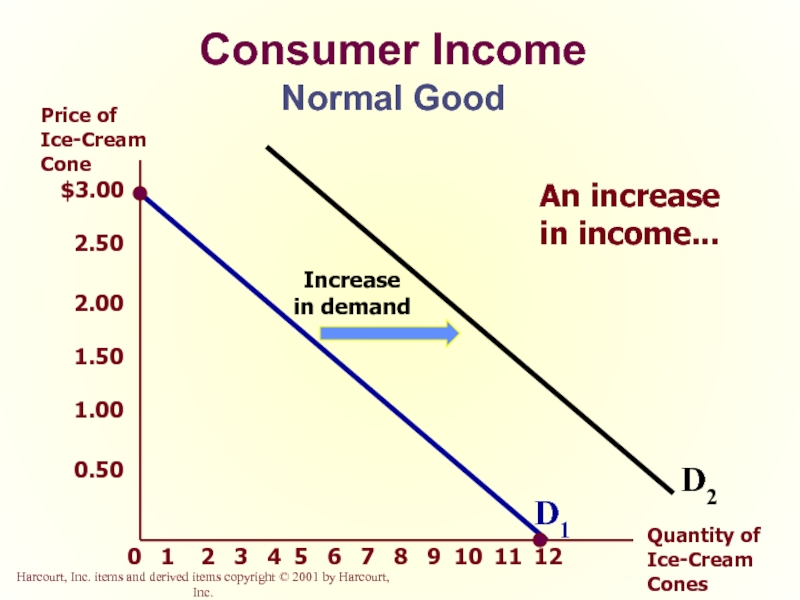
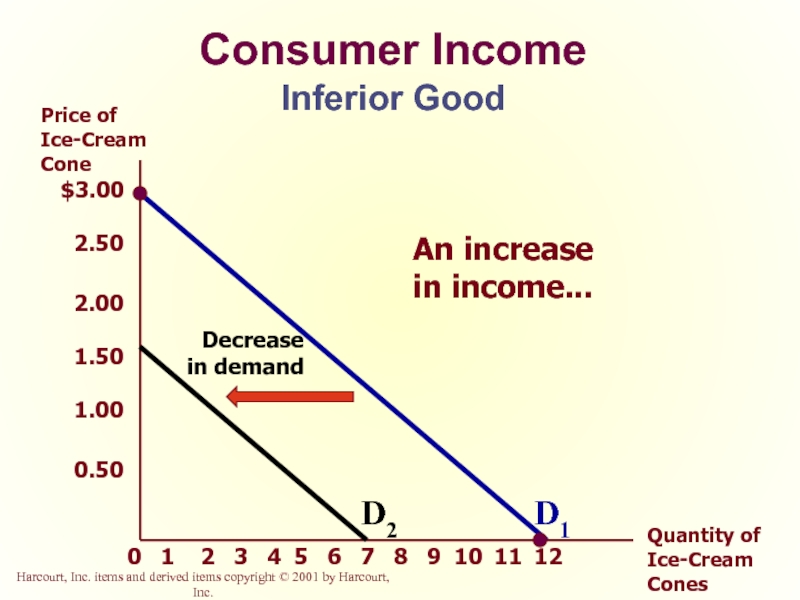
Слайд 23Consumer Income
As income increases the demand for a normal good will
As income increases the demand for an inferior good will decrease.
Слайд 24Consumer Income
Normal Good
$3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
11
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
0
Increase
in demand
An increase
D1
D2
Слайд 25Consumer Income
Inferior Good
$3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
11
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
0
Decrease
in demand
An increase
D1
D2
Слайд 26Prices of Related Goods
Substitutes & Complements
When a fall in the price
When a fall in the price of one good increases the demand for another good, the two goods are called complements.
Слайд 29Law of Supply
The law of supply states that there is a
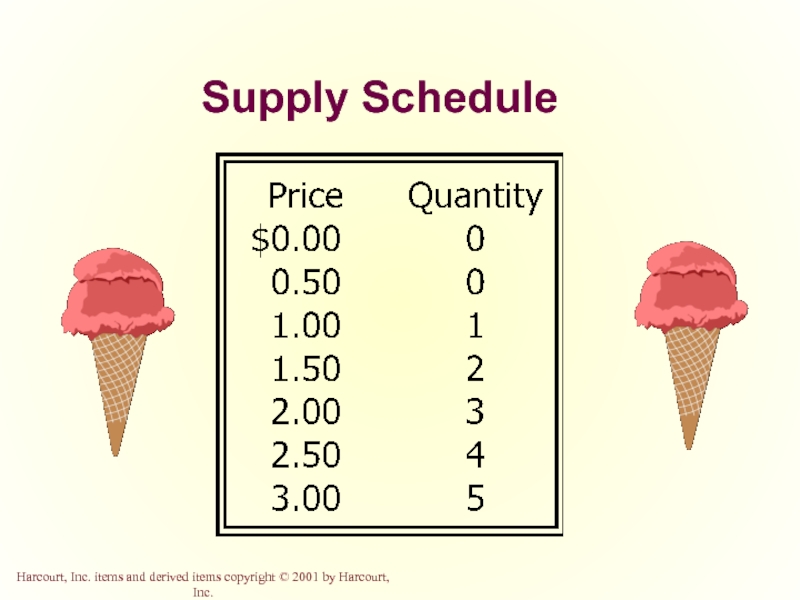
Слайд 31Supply Schedule
The supply schedule is a table that shows the relationship
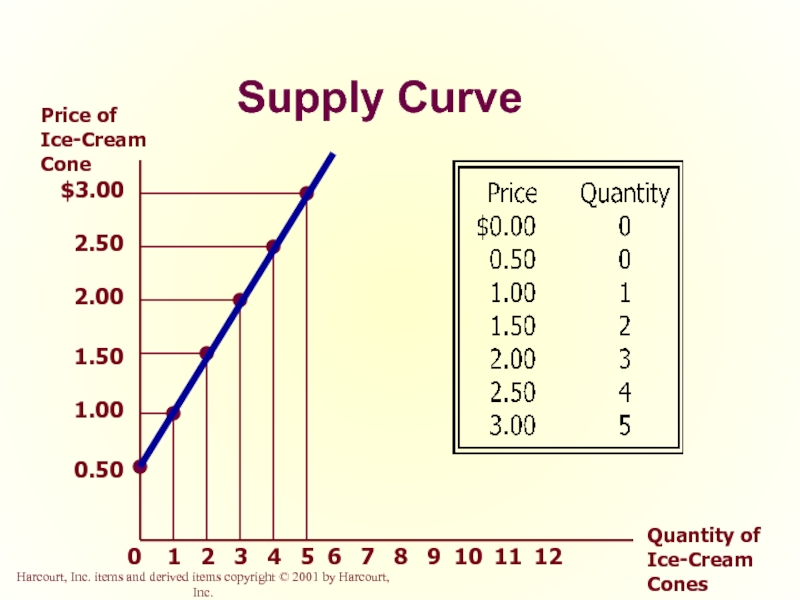
Слайд 33
Supply Curve
The supply curve is the upward-sloping line relating price to
Слайд 34
Supply Curve
$3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
11
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
0
Слайд 35Market Supply
Market supply refers to the sum of all individual supplies
Graphically, individual supply curves are summed horizontally to obtain the market supply curve.
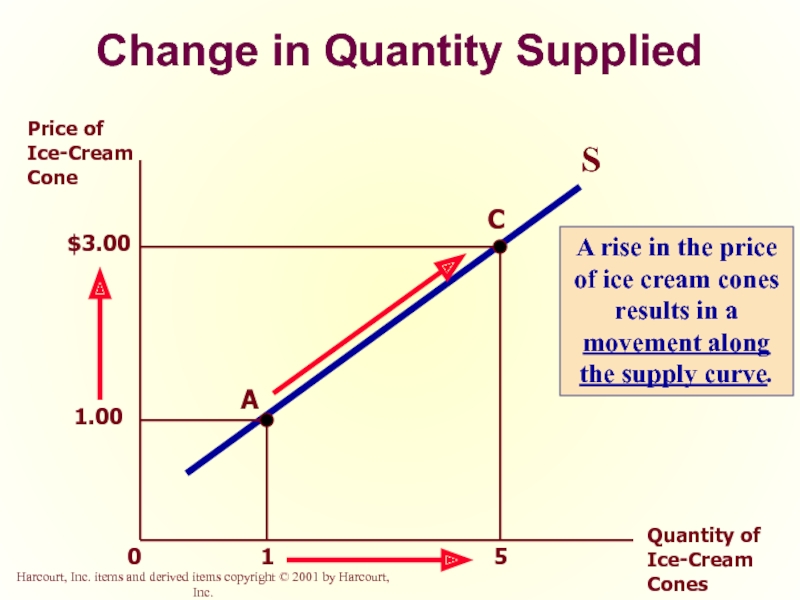
Слайд 37
Change in Quantity Supplied versus Change in Supply
Change in Quantity Supplied
Movement
Caused by a change in the market price of the product.
Слайд 38
Change in Quantity Supplied
1
5
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
0
S
A
C
A rise in the price of ice cream cones results in a movement along the supply curve.
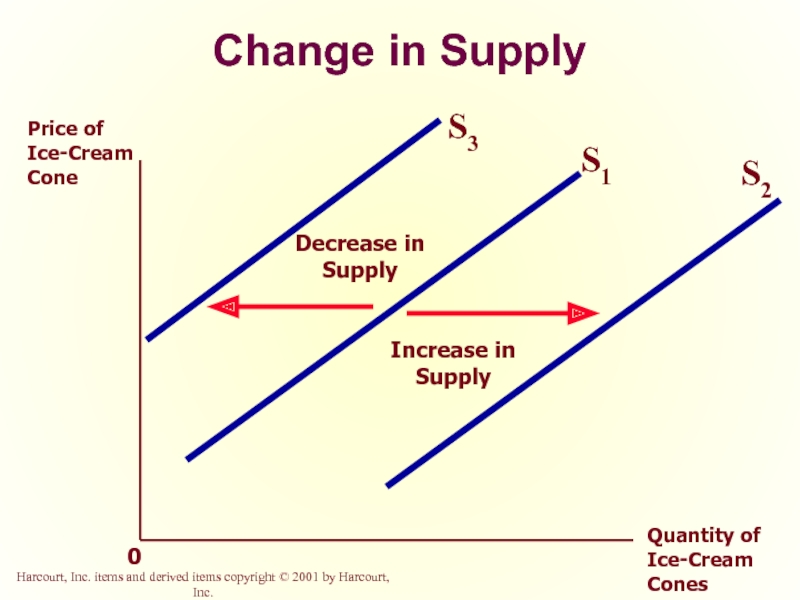
Слайд 39Change in Quantity Supplied versus Change in Supply
Change in Supply
A shift
Caused by a change in a determinant other than price.
Слайд 42
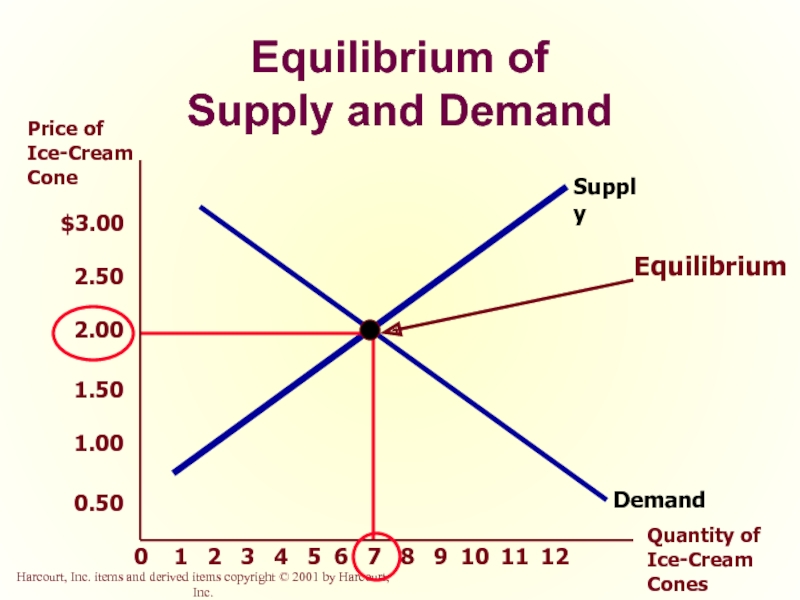
Supply and Demand Together
Equilibrium Price
The price that balances supply and demand.
Equilibrium Quantity
The quantity that balances supply and demand. On a graph it is the quantity at which the supply and demand curves intersect.
Слайд 43
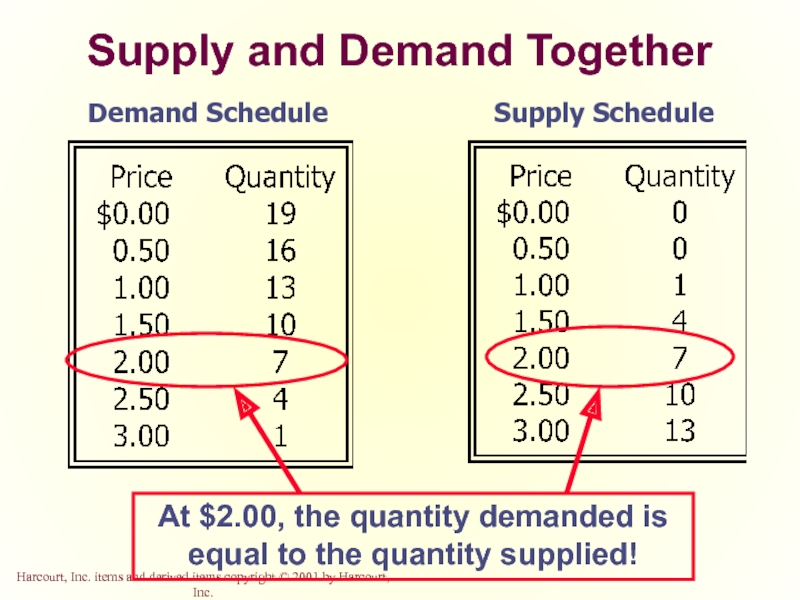
Supply and Demand Together
Demand Schedule
Supply Schedule
At $2.00, the quantity demanded is
Слайд 44
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
Equilibrium of
Supply and Demand
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
11
0
$3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
Слайд 45
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
11
0
$3.00
2.50
2.00
1.50
1.00
0.50
Supply
Demand
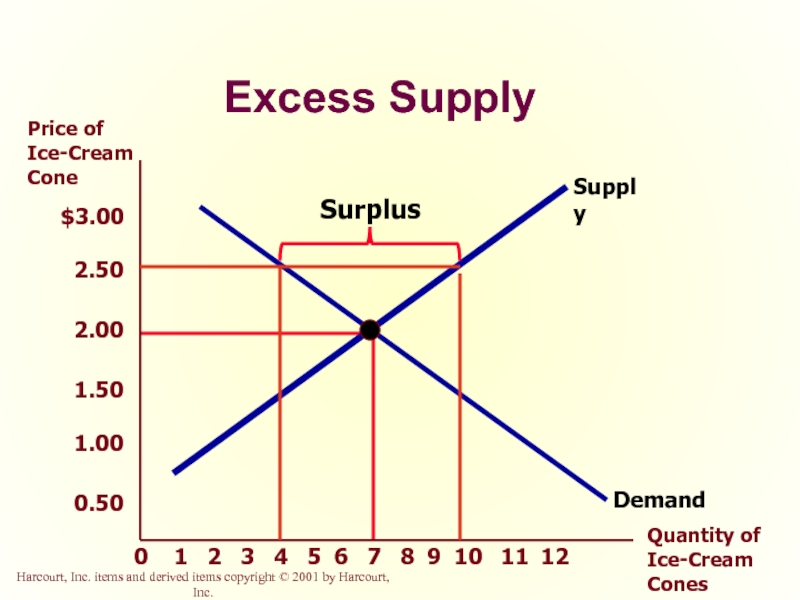
Surplus
Excess Supply
Слайд 46Surplus
When the price is above the equilibrium price, the quantity supplied
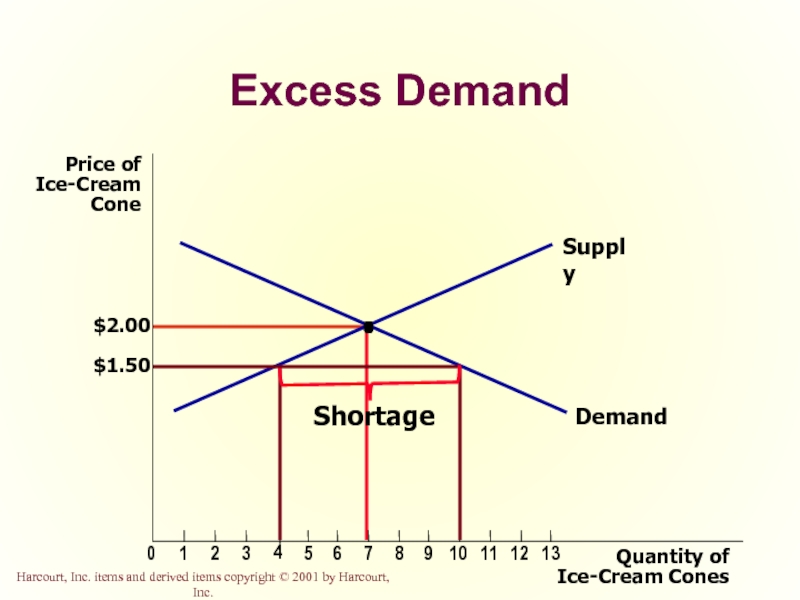
Слайд 47Excess Demand
Quantity of
Ice-Cream Cones
Price of
Ice-Cream
Cone
$2.00
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Supply
Demand
$1.50
Shortage
Слайд 48Shortage
When the price is below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded
Слайд 49
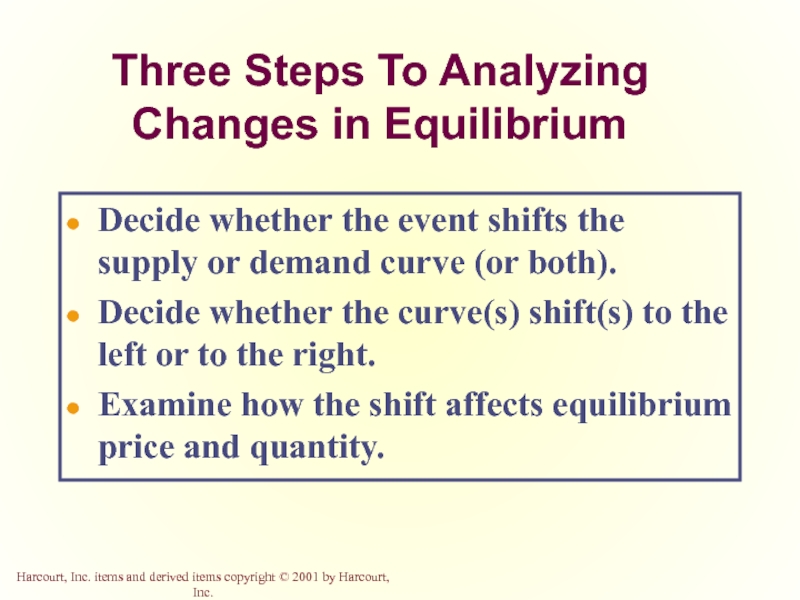
Three Steps To Analyzing Changes in Equilibrium
Decide whether the event shifts
Decide whether the curve(s) shift(s) to the left or to the right.
Examine how the shift affects equilibrium price and quantity.
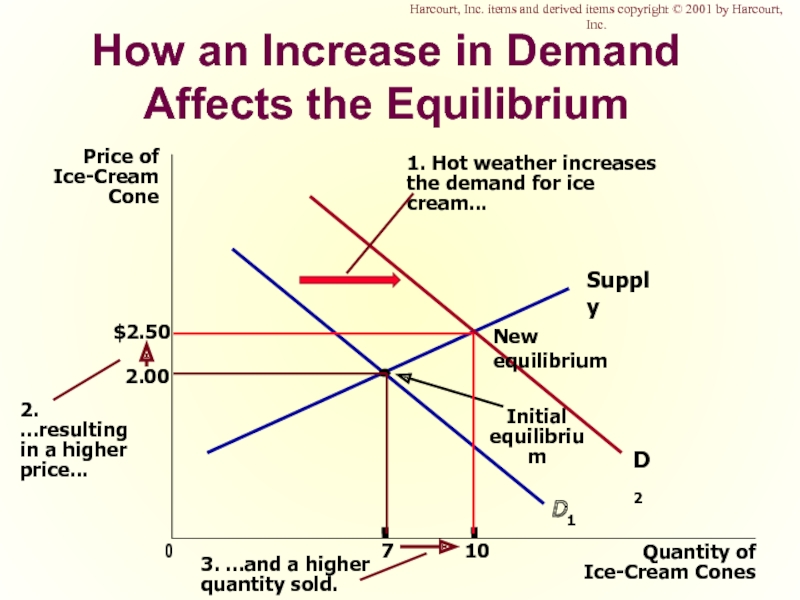
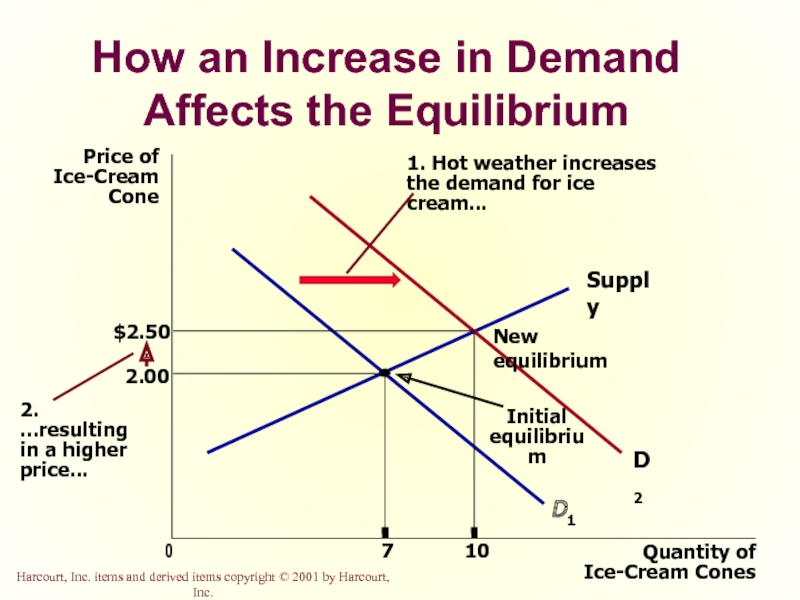
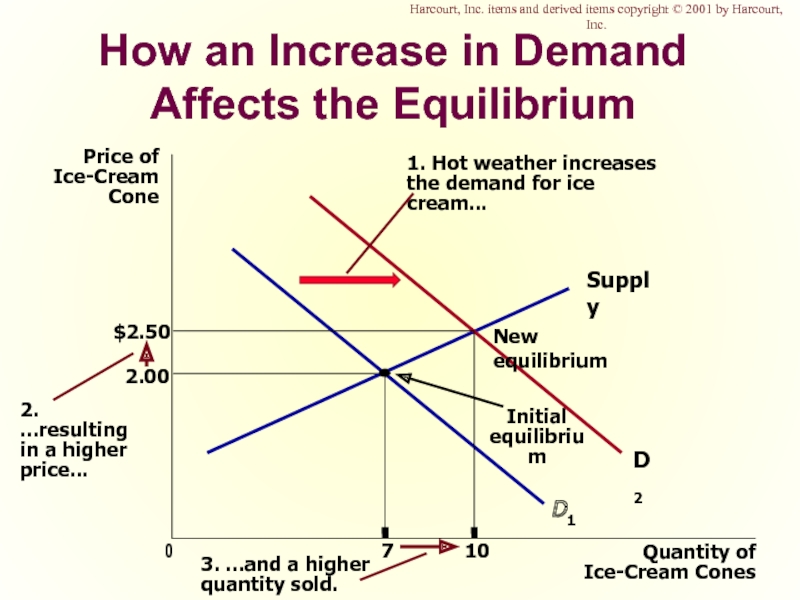
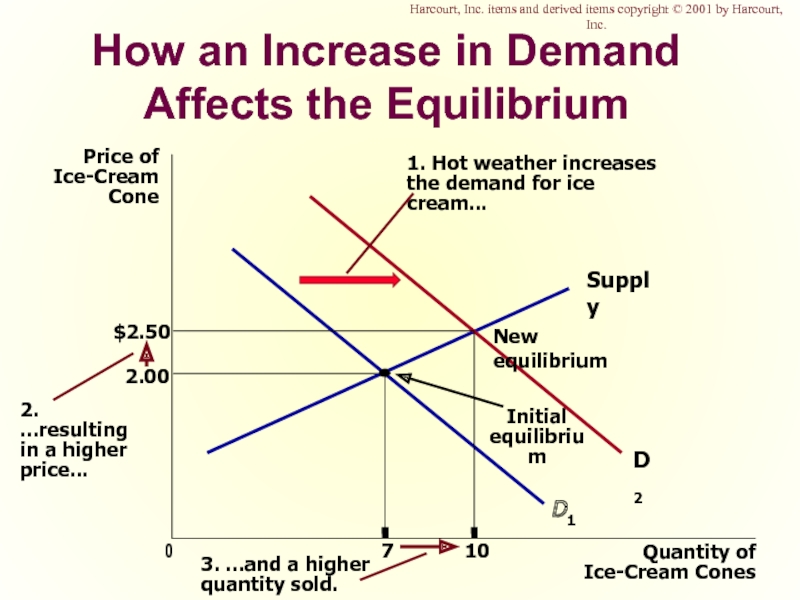
Слайд 50How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
Price of
Ice-Cream
Cone
2.00
0
7
Quantity of
Ice-Cream Cones
Supply
Initial
equilibrium
D1
1.
the demand for ice cream...
Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
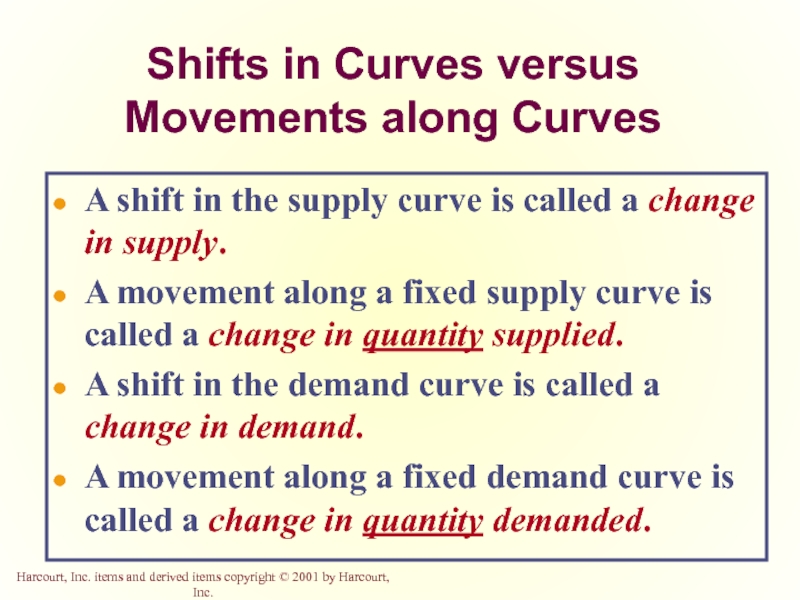
Слайд 51Shifts in Curves versus Movements along Curves
A shift in the supply
A movement along a fixed supply curve is called a change in quantity supplied.
A shift in the demand curve is called a change in demand.
A movement along a fixed demand curve is called a change in quantity demanded.
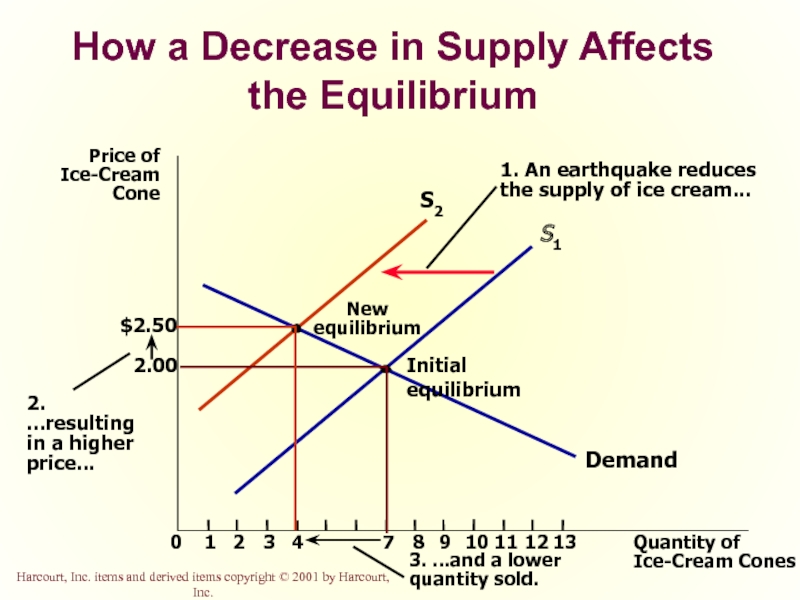
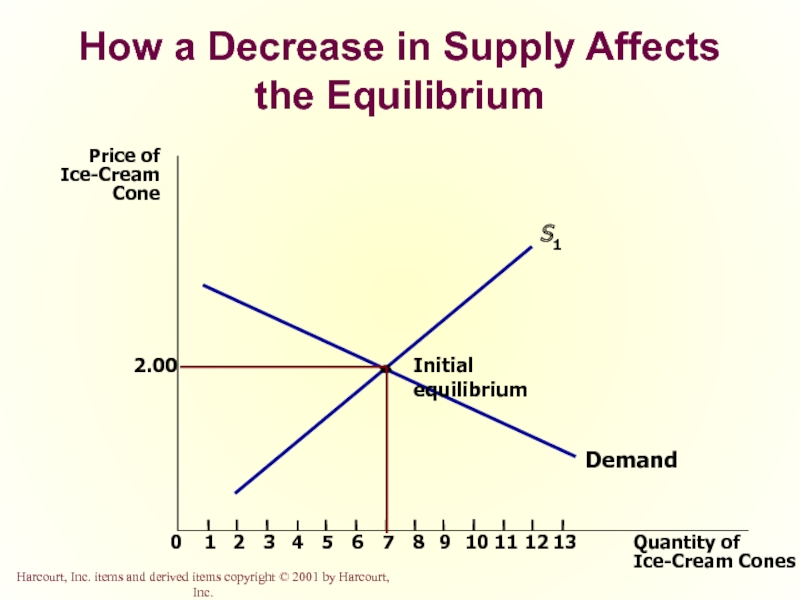
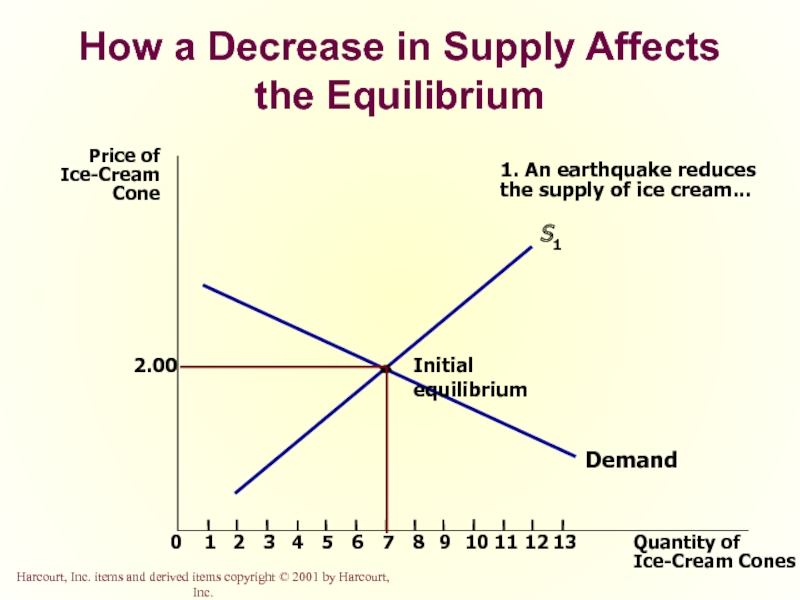
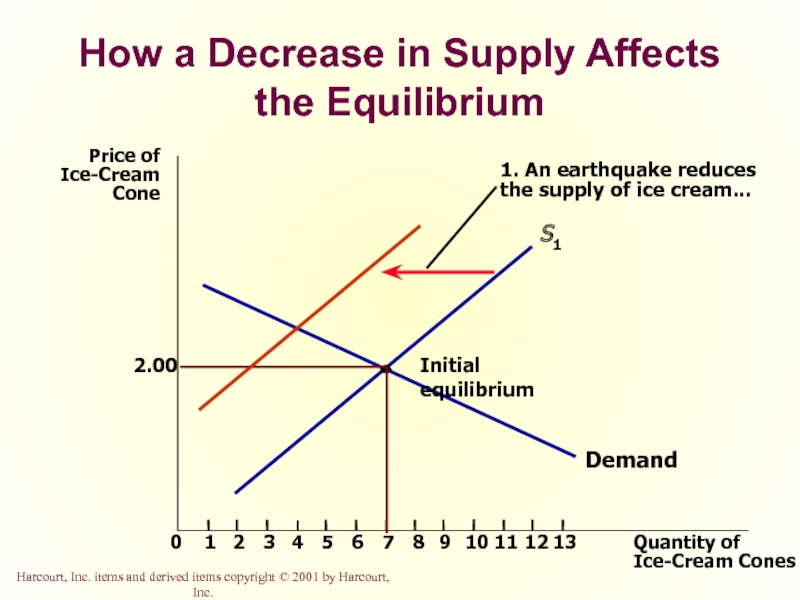
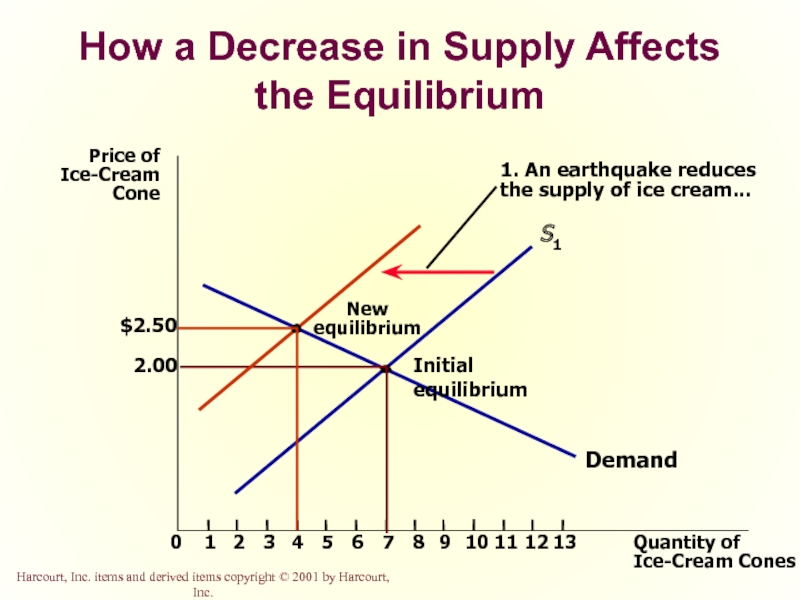
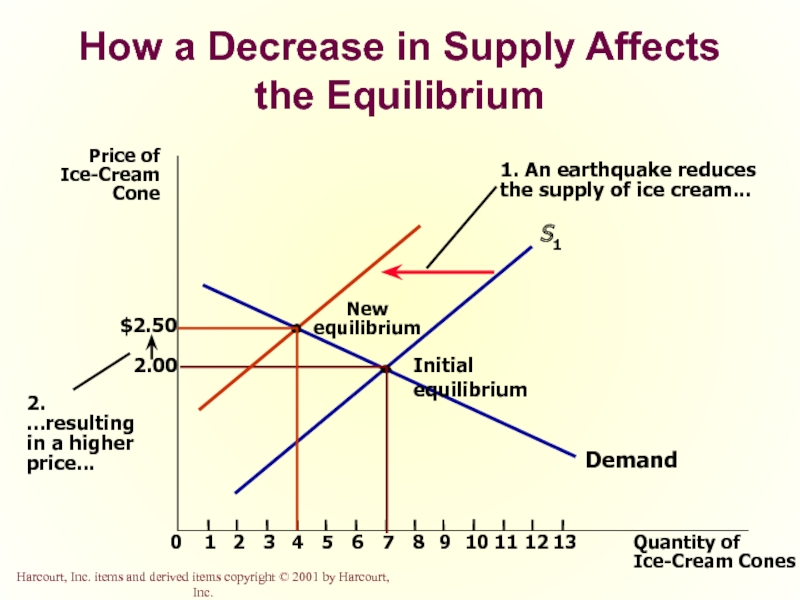
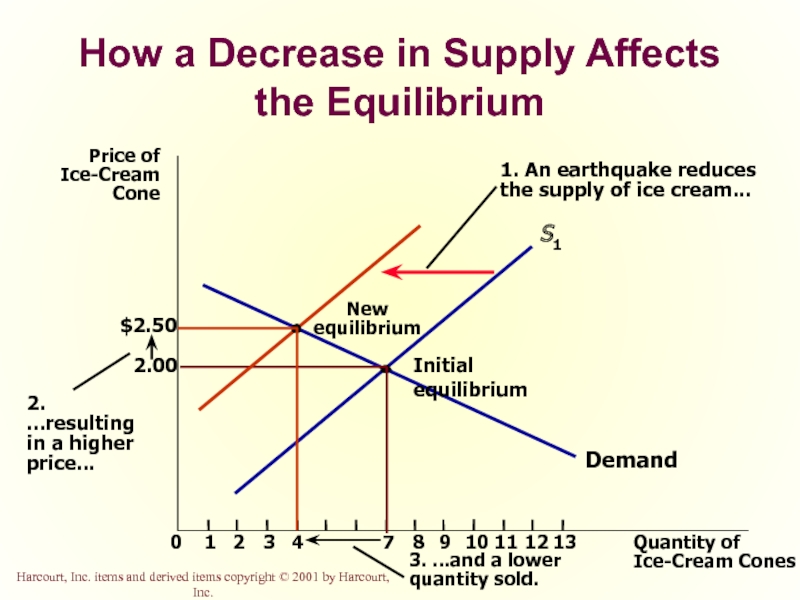
Слайд 52How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
Price of
Ice-Cream
Cone
2.00
0
1
2
3
4
7
8
9
11
12
Quantity of
Ice-Cream Cones
13
Demand
Initial
S1
10
1. An earthquake reduces
the supply of ice cream...
New
equilibrium
Слайд 54Summary
Economists use the model of supply and demand to analyze competitive
The demand curve shows how the quantity of a good depends upon the price.
Слайд 55Summary
According to the law of demand, as the price of a
In addition to price, other determinants of quantity demanded include income, tastes, expectations, and the prices of complements and substitutes.
Слайд 56Summary
The supply curve shows how the quantity of a good supplied
According to the law of supply, as the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied rises.
Слайд 57Summary
In addition to price, other determinants of quantity supplied include input
Market equilibrium is determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves.
Слайд 58Summary
Supply and demand together determine the prices of the economy’s goods
In market economies, prices are the signals that guide the allocation of resources.